Method for accurately positioning electronic tag
A technology of precise positioning and electronic labeling, applied in positioning, radio wave measurement systems, measurement devices, etc., can solve problems such as less research, and achieve the effect of simple operation principle, small amount of calculation, and excellent real-time performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
[0021] An electronic tag precise positioning algorithm, the specific steps are:
[0022] 1. Establish the antenna array of the RF signal detector in three-dimensional space
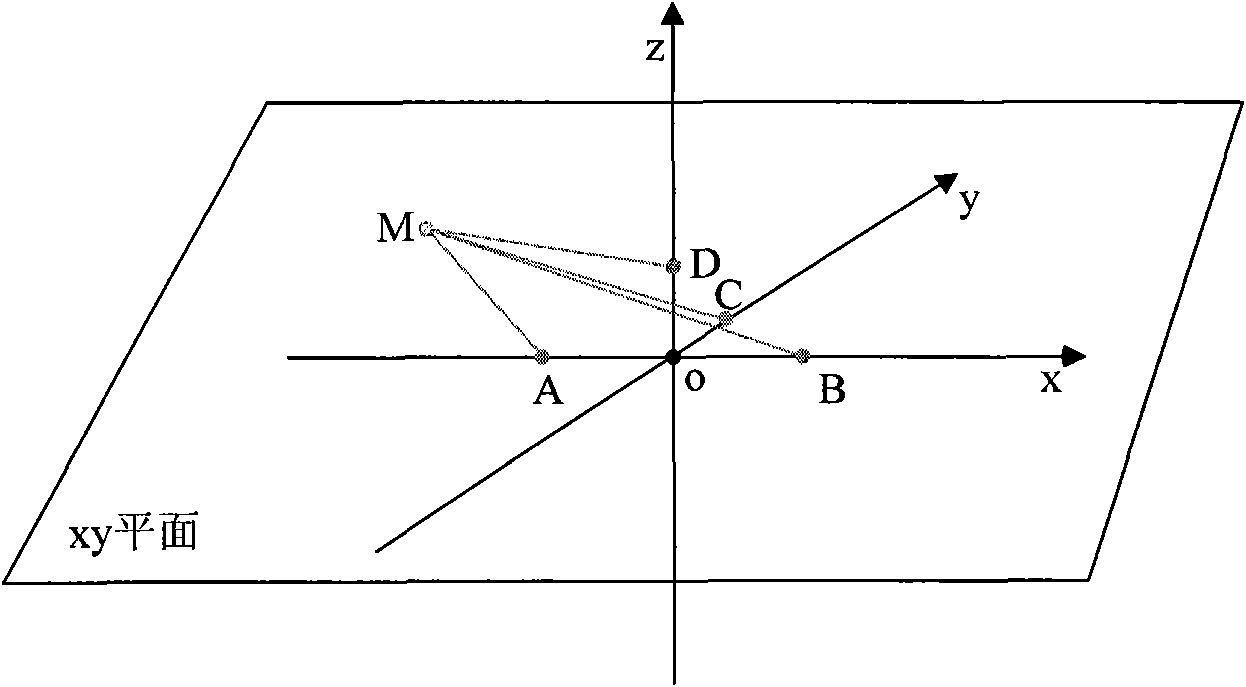
[0023] Such as figure 1 As shown, in three-dimensional space, it is assumed that there is a passive electronic tag at any point M. There is a radio frequency signal detector within the effective detection range. The antenna of the instrument is an array antenna, and the tops of each antenna are arranged according to the four points A, B, C, and D in Figure 1, where AO=OB=mλ, OC=nλ, OD=kλ, λ is the radio frequency wavelength and AO, OB, OC, and OD are fixed values, and point M is the location of the hypothetical electronic tag.
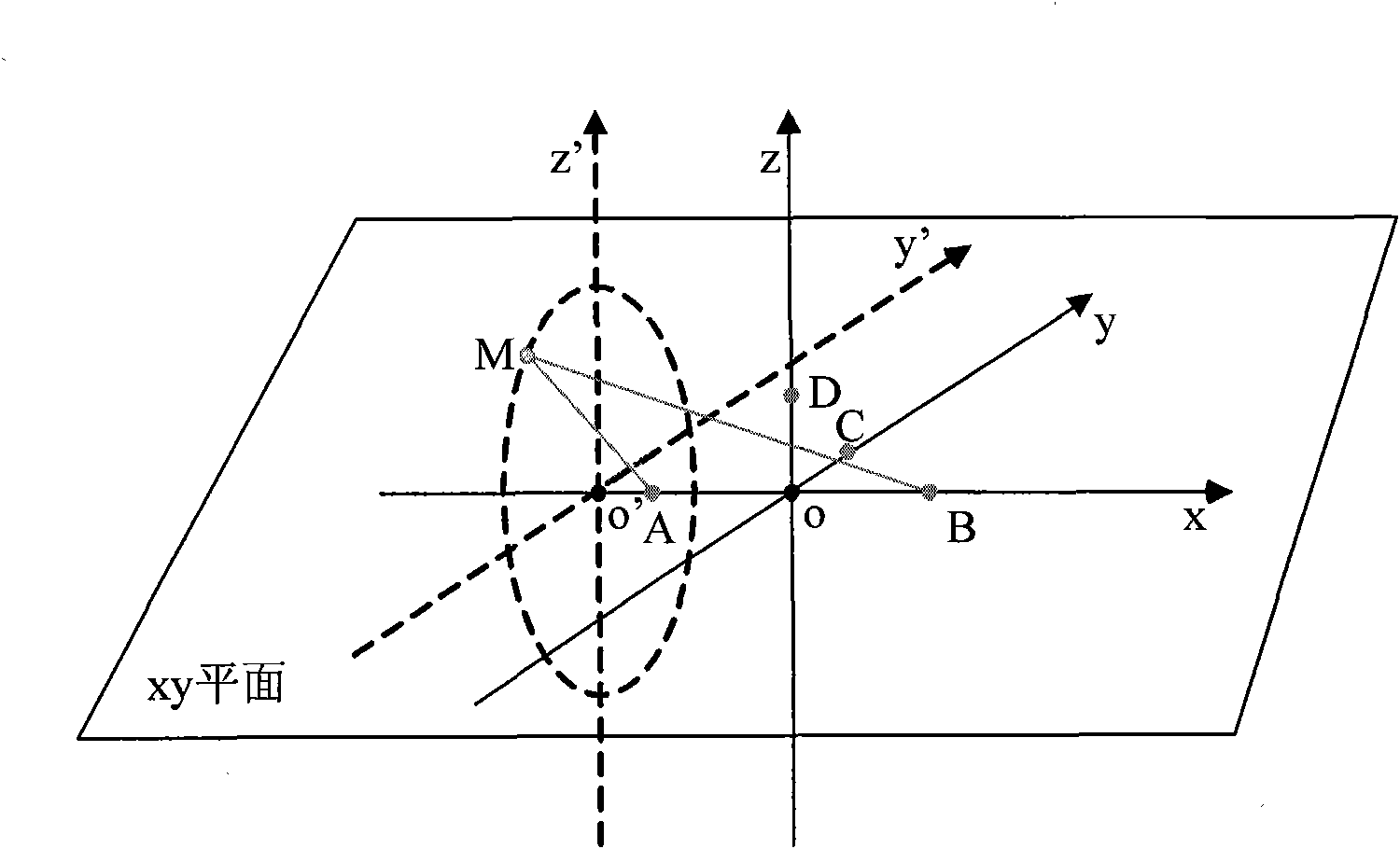
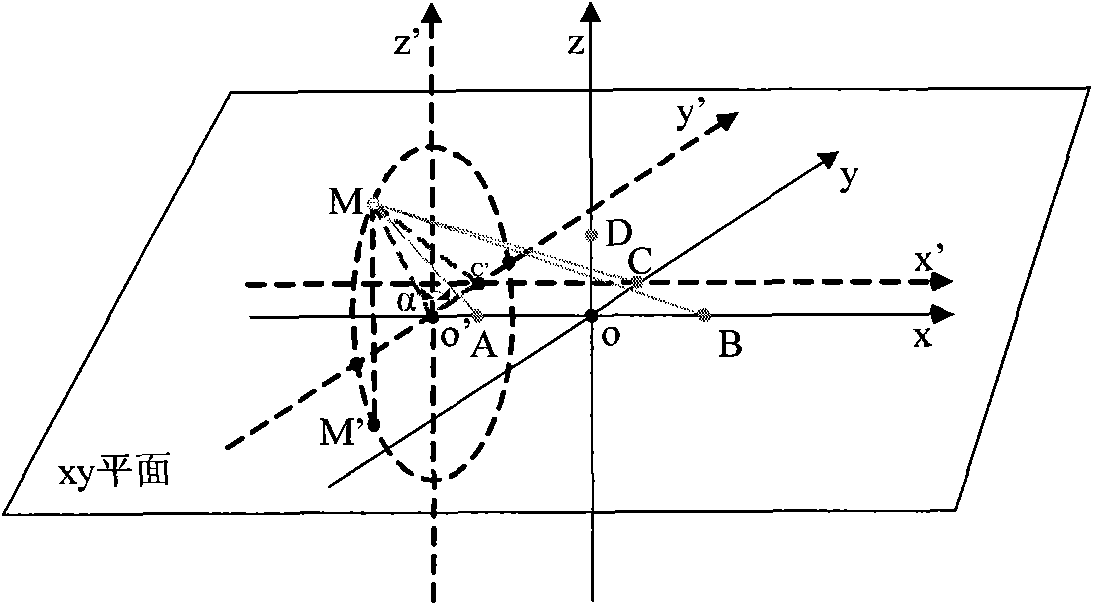
[0024] 2. Locate the three-dimensional space to the two-dimensional plane, and determine the M value range
[0025] RF signal detector at t ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com