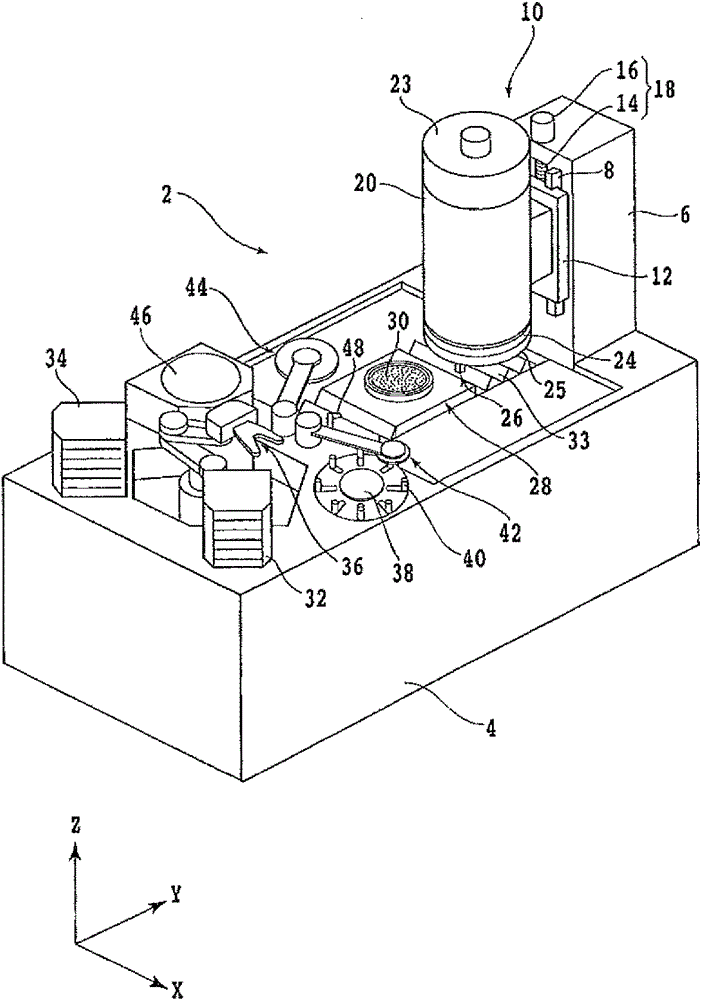
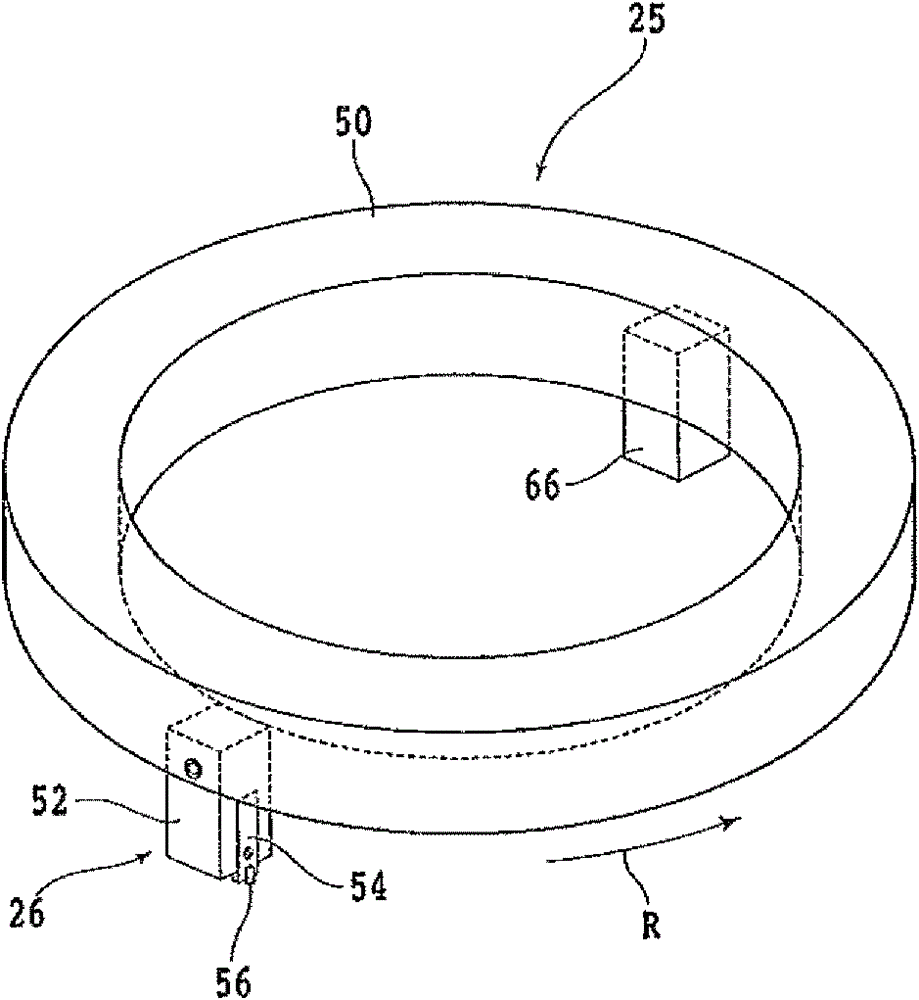
Processing method of optical device wafer
A processing method and technology of optical devices, applied in the fields of semiconductor devices, metal processing equipment, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of electrode short circuit, quality degradation, squeezing, etc., to eliminate squeezing, ductility suppression, elimination The effect of electrodes short-circuiting each other
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
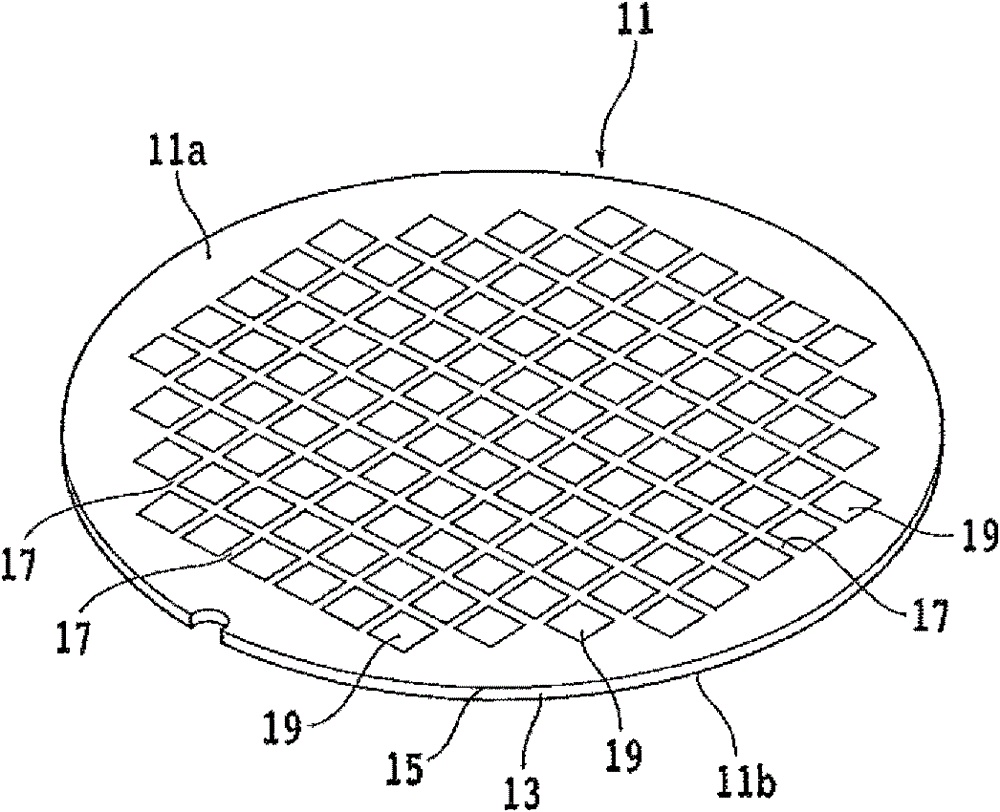
[0033] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. refer to figure 1 , shows a front side perspective view of an optical device wafer. The optical device wafer 11 is formed by laminating an epitaxial layer (light emitting layer) 15 such as gallium nitride (GaN) on a sapphire substrate 13 . The optical device wafer 11 has: a surface 11 a formed by laminating light emitting layers 15 ; and a back surface 11 b exposed from the sapphire substrate 13 .
[0034] In the light-emitting layer 15 , a plurality of optical devices 19 such as LEDs are divided and formed by dividing lines (segments) 17 formed in a grid pattern. The optical device wafer 11 to be processed in the present invention is formed by covering the surface 11 a with a translucent molding resin (not shown).
[0035] That is, if Figure 8 As shown in the partially enlarged cross-sectional view of (A), the light emitting layer 15 includes: an n-type se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com