Botanical pesticide for effectively controlling Dioryctria splendidella Herrich-Schaeffer, preparation thereof and application thereof
A botanical pesticide and pine borer technology, which is applied in the directions of botanical equipment and methods, applications, plant growth regulators, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to estimate economic losses and serious damage, and achieves reduction of economic costs and environmental pollution. , reduce the possible effects of resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
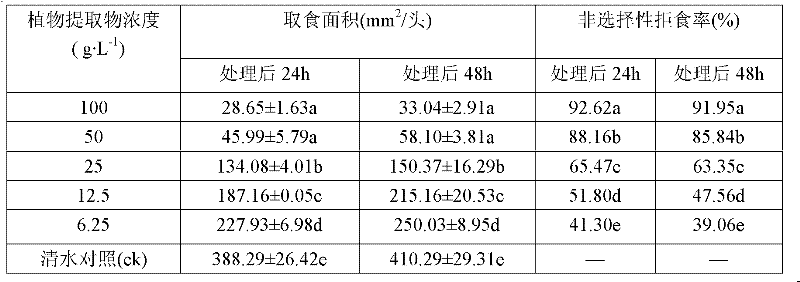
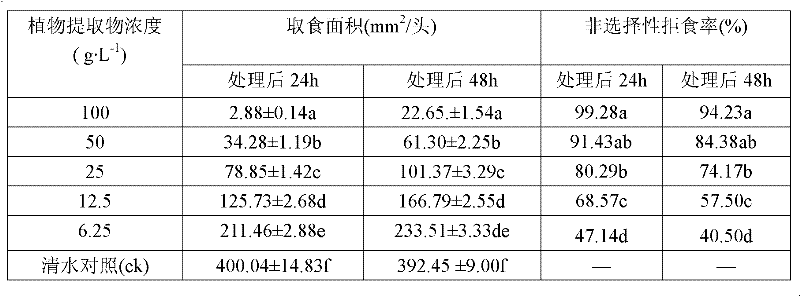
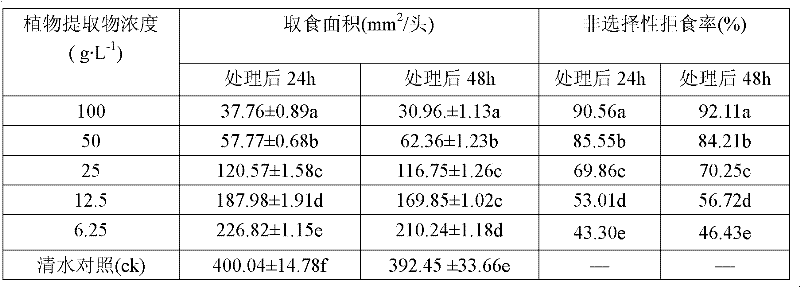
[0024] Determination of antifeeding effects of three plant extracts on pine borer larvae, the main pest of Pine massoniana
[0025] Use the non-selective loose tip method. First the test stock solution is diluted with 60% ethanol into five concentration gradient test solutions of 100, 50, 25, 12.5, and 6.25 g / L. Pick healthy larvae with the same individual size and age and put them into a 9 cm culture dish moistened with filter paper, and starve one head per dish for 6 hours. Select fresh, uniformly thick and thin branches of Pinus massoniana tips with a diameter of about 7 mm, cut them into 20 mm long wood segments, soak them in different concentrations of test solutions for 10 seconds, take them out, and let them dry naturally. 10 test insects were treated at each concentration, and each treatment was repeated 5 times. After the treatment, they were reared in the insect culture room. The ingested area of the wood section was measured 24 hours and 48 hours after the treatm...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Inhibitory effects of three plant extracts on the growth of Pine shoot borer, the main pest of Pine massoniana
[0036] Use the method of dipping the loose tip. Select fresh, uniform thickness and diameter of 7 mm Pinus massoniana shoots, cut them into 20 mm long wood sections, soak them in different concentrations of test solutions for 10 seconds, take them out, dry them naturally, and place the treated pine shoots in In a 9cm petri dish, pick healthy larvae with the same size and age as starvation for 6 hours, insert one into each dish, and weigh its weight before inserting. 10 test insects were treated at each concentration, and each treatment was repeated 5 times, and water treatment was used as a control. Weigh its body weight once at 24h and 48h after the treatment, discard the dead insects and remaining pine tip sections after 48h, and replace the fresh pine tip sections that have not been treated with the test solution for the test insects to feed on, replace o...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Contact killing effect of three plant extracts on Pine shoot borer, the main pest of Pine massoniana
[0048] Use the worm method. Immerse the healthy test insects with the same individual size and insect age in the test solution of different concentrations for 5 seconds, then take them out, absorb the excess liquid with filter paper, and raise them in the insect culture room normally. Treat 10 test insects at each concentration, and repeat 3 times for each treatment. Water was used as a blank control, and commercially available thiacloprid was used as a positive control. After 24 hours of treatment, the death of the test insects was investigated, and the total number of insects and the number of dead insects were recorded. The results are shown in Table 7, Table 8 and Table 9.
[0049] Mortality rate (%) = number of dead insects / total number of insects × 100%;
[0050] Corrected mortality rate (%)=(treatment mortality rate-control mortality rate) / (1-control mortalit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com