Two-dimensional heat curing porous medium model for microscopic oil displacement and manufacturing method for model
A technology of porous media and production methods, which is applied in the field of petroleum micro-mechanism research, and can solve problems such as low degree of visualization, high technical requirements, and difficult fluid collection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0025] First of all, yes figure 1 The core shown is pre-treated. The natural core obtained by coring is cut to a thickness of about 1 cm and a bottom diameter of about 3 cm. Encapsulate and protect the core, that is, use turpentine to fully dissolve the rosin, soak the core in the rosin solution, heat the core to fully saturate the core with rosin, and leave it to cool down. As a result, the rosin is saturated in the core pores in a solid form. Played a protective role for the core hole.
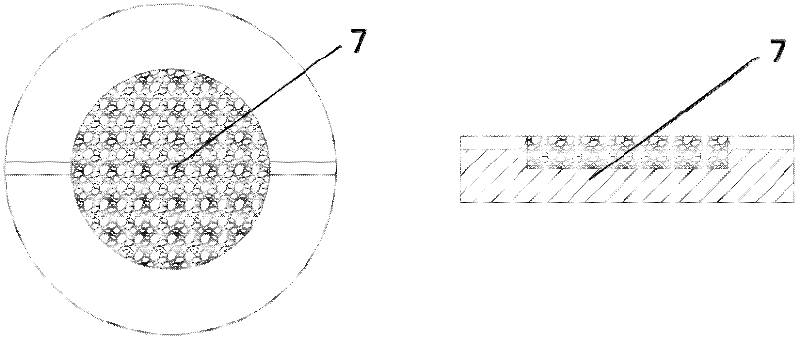
[0026] Secondly, use the processed core to make the master 7. The thermosetting resin and curing agent are prepared in a weight ratio of 20:1 to 5:1, and the preferred weight ratio is 10:1. The thermosetting resin is epoxy resin, which can also be other resins in the field. The curing agent is The curing agent material known in the art preferably uses triethanolamine. After the thermosetting resin and the curing agent are prepared, they are cast around the core saturated with rosin, and set ...
example 2
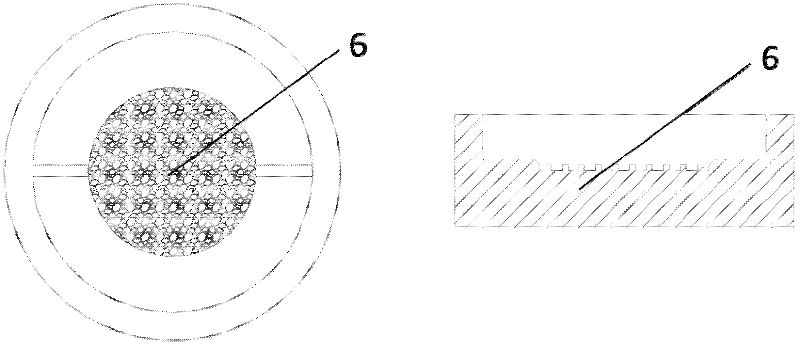
[0032] Another method is used in the core pretreatment step. The natural core obtained by coring is cut to a thickness of about 1 cm and a bottom diameter of about 3 cm. Encapsulate and protect the core: wrap the core block with a commonly used heat-resistant film, and vacuum-encapsulate the core block in the film with a vacuum packaging machine, and the other film is close to the side wall of the core. The thermosetting resin and curing agent are prepared in a weight ratio of 20:1 to 5:1, and the preferred weight ratio is 10:1. The thermosetting resin is epoxy resin, and the curing agent is a known curing agent material in the art. Use triethanolamine. After the thermosetting resin and curing agent are formulated, they are cast around the core, and set in a thermostat at a temperature of 50-80°C for 6-10 hours to make the resin solidify and form around the core. After the resin is cured, cut the entire block transversely, take the block containing the main core surface, grin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com