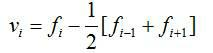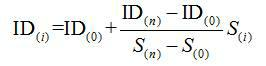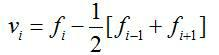Quick fine tuning method for ballastless track of high-speed rail based on track deviation
A ballastless track and deviation technology, applied in track, track laying, track maintenance, etc., can solve the problems of long-wave irregularity correction ability, high construction cost, low operation efficiency, etc., to optimize track smoothness, measurement and solution The effect of high calculation efficiency and accurate detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Track smoothness data is associated with high-speed rail ballastless track slabs, as attached figure 1 As shown, the list of sleeper numbers is established according to the line data and imported into the track inspection instrument. After the system is initialized, the ID number of the current track slab is input; then the track inspection instrument is implemented to collect track smoothness data and automatically record the mileage; after the data collection is completed, enter the end point Track plate ID number, recalculate the track plate ID corresponding to each mileage, as shown in formula 5.
[0042] In this embodiment, when dealing with the track smoothness data recorded by the track tester and the track slab of the high-speed rail ballastless track, the track smoothness recorded by the track tester can be automatically recorded by using the high-speed rail ballastless track line data and the track tester marking function. The data is associated with the ID n...
Embodiment 2
[0046] To calculate the adjustment amount, firstly, the target value of the track smoothness state is obtained according to the line data, and the ride comfort data is to be imported into the iteration matrix (as shown in Equation 3), and the coordinate deviation under the inertial coordinates of the track is calculated.
[0047] The calculation process is attached figure 2 shown and illustrated with Gauss-Seidel iterations,
[0048]
[0049] in, f i (k) Department mileage location i Department k The coordinates under the inertial coordinates of the iteration. The iterative calculation converges to f i * . Substituting the result into formula 4, the mileage position can be obtained i The reference value of the adjustment amount at .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com