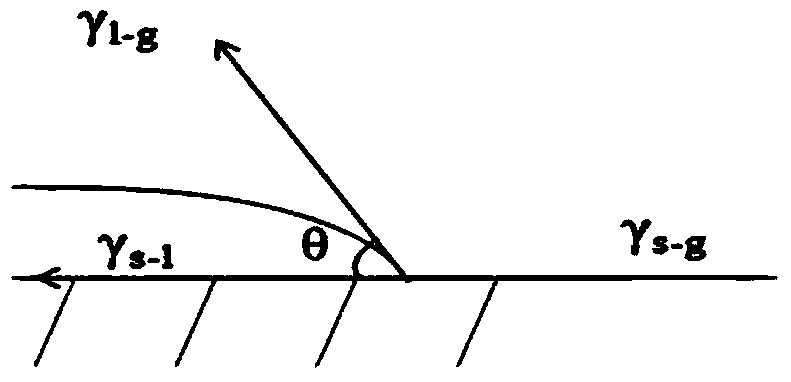
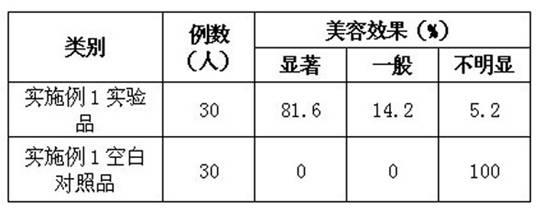
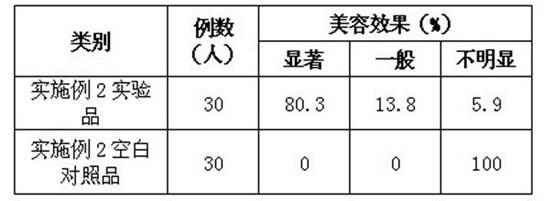
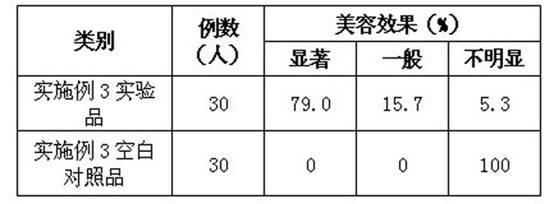
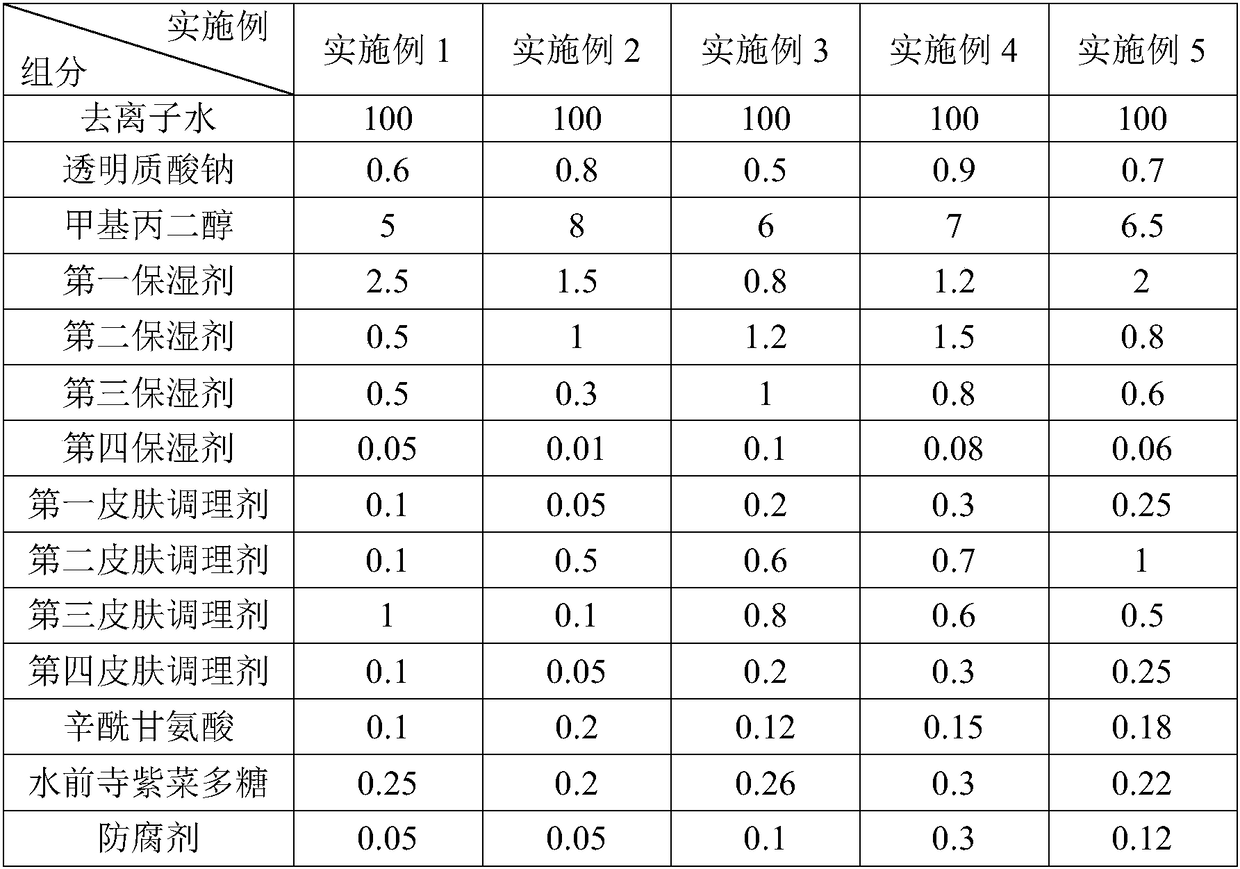
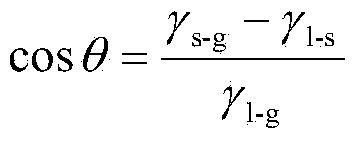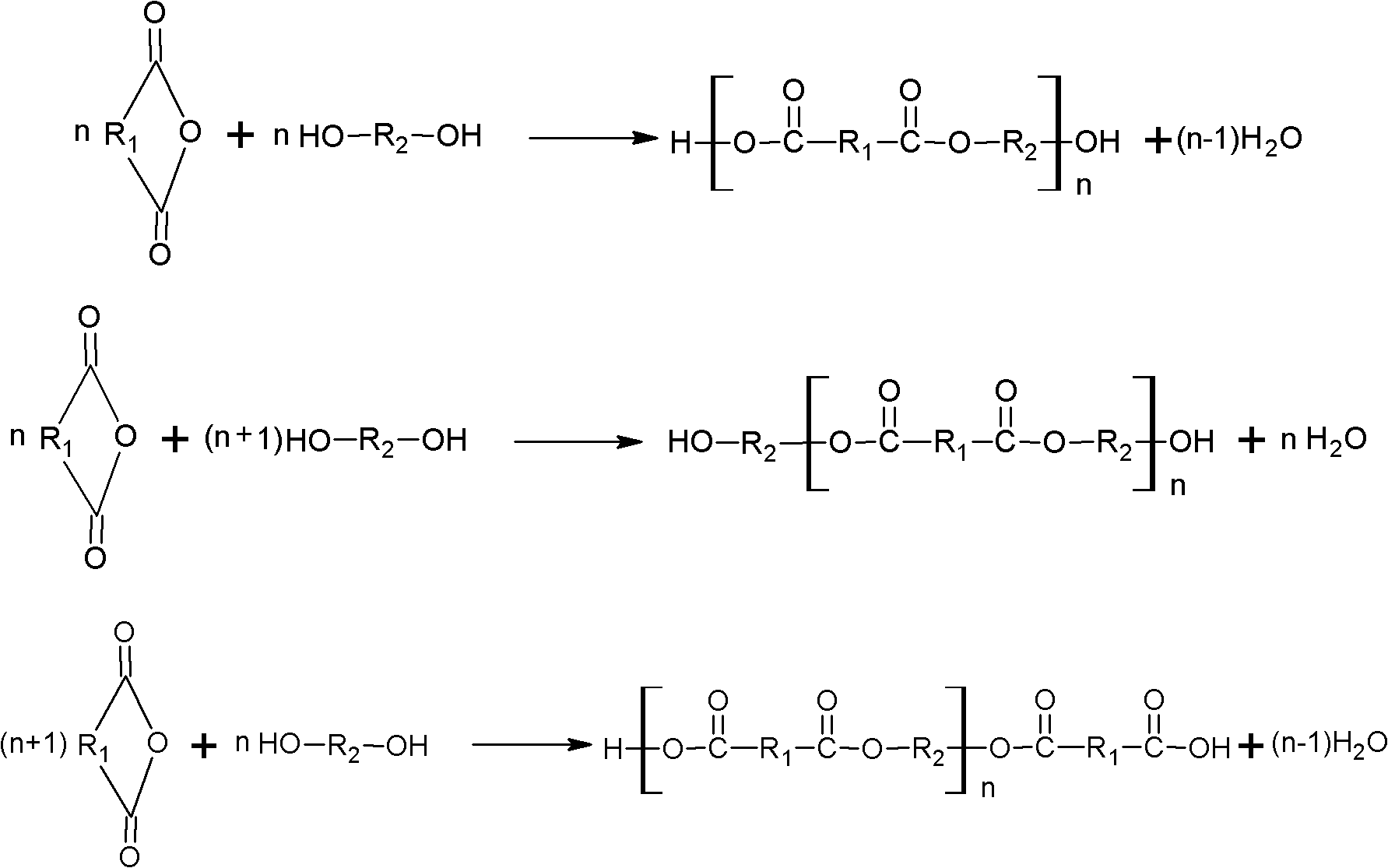Patents
Literature
281 results about "METHYLPROPANEDIOL" patented technology
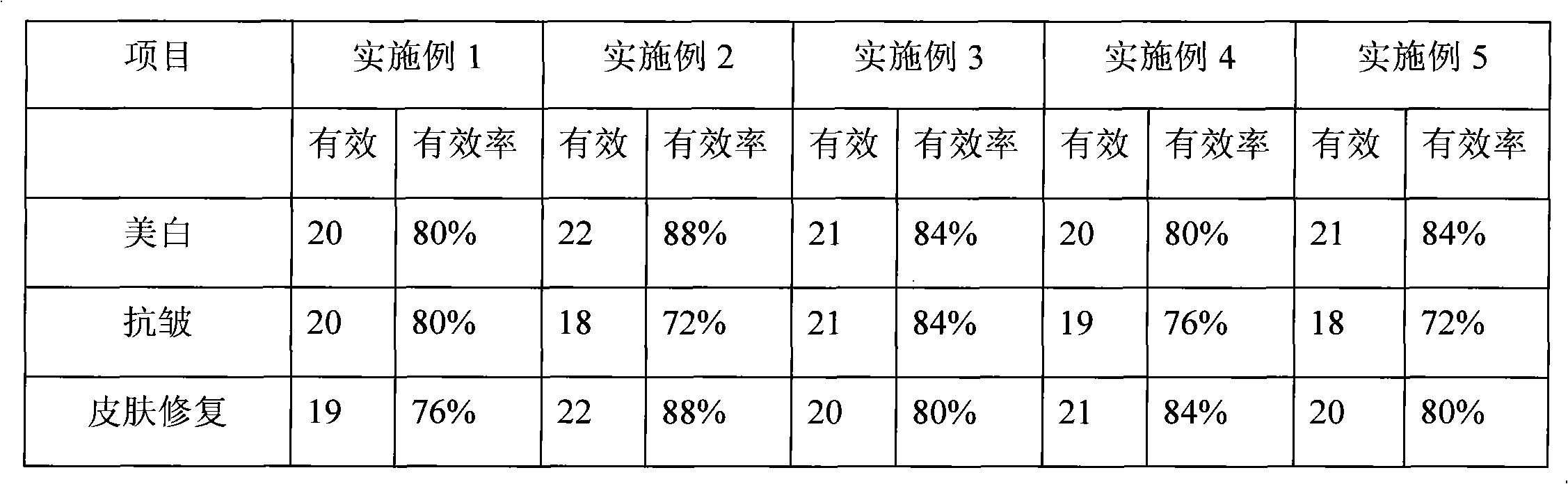
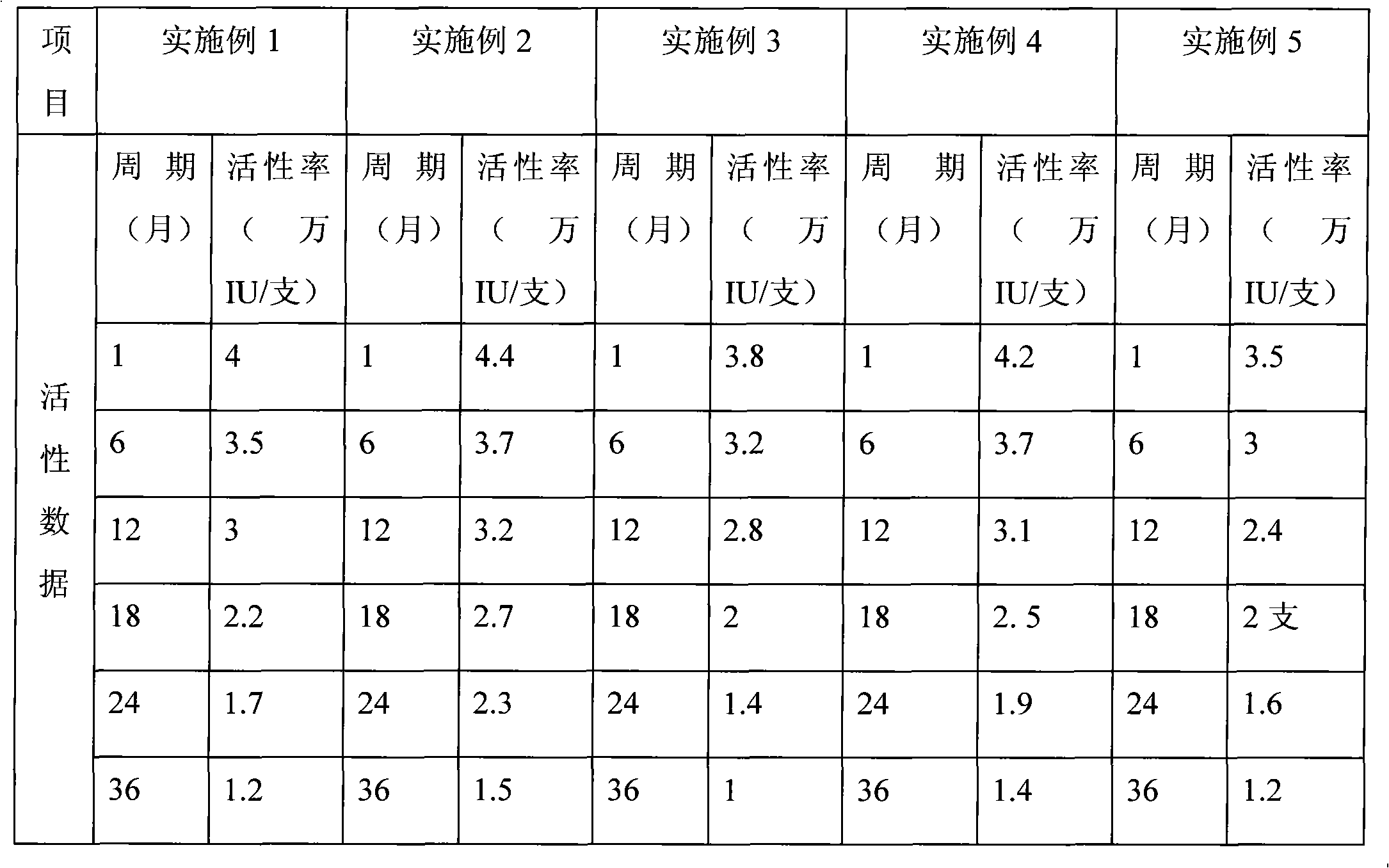
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Whitening cosmetic product, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101816620AGood whitening effectFor long-term storageCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsVitamin CSide effect
The invention discloses a whitening cosmetic product, a preparation method and application thereof. The whitening cosmetic product comprises the components in percentage by mass: 0.00001to 0.001 percent of recombined human angiogenin, 0.00001 to 0.001 percent of metallothionein, 0.00001 to 0.001 percent of human epidermal growth factor, 0.00001to 0.001 percent of IL-1RA, 0.1 to 0.5 percent of superoxide dismutase, 0.1 to 0.5 percent of low molecular liquaemin, 1 to 5 percent of arbutin, 5 to 25 percent of stabilizer, 0.02 to 0.3 percent of hyaluronic acid, 0.5 to 5 percent of methylpropanediol, 0.5 to 3.5 percent of lactobacillus / mung bean fermentation liquid, 0.5 to 5 percent of dissolved protease, 0.5 to 8 percent of vitamin C sodium phosphate, 0.3 to 0.7 percent of 1,2-hexanediol or 1,2-capryl glycol, 1 percent to 5 percent of oat Beta-glucan, 1 to 5 percent of soy isoflavone and the balance of water. The whitening cosmetic product can be preserved for a long time, has no side effect on skin and is suitable for long term use.
Owner:广州泰润合投资有限公司
Matrix with skin barrier repairing and anti-aging effects and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106265348AImprove and repair the skin barrierImprove anti-aging effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSequence signalHydrolysis
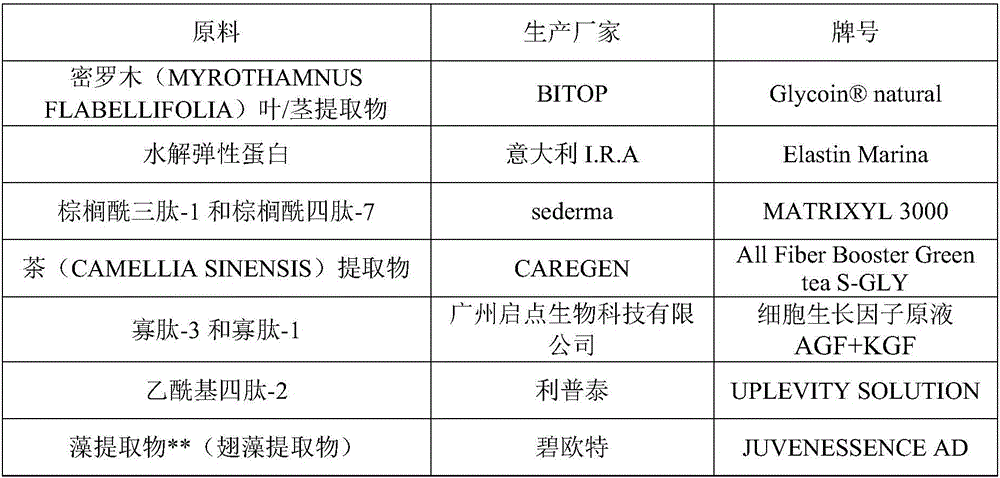
The invention belongs to the technical field of cosmetics, and particularly discloses a matrix with skin barrier repairing and anti-aging effects. The matrix is prepared from, by mass, 3-4% of 1,2-pentanediol, 10-15% of methyl propanediol, 1-2% of sodium hyaluronate, 3-5% of myrothamnus flabellifolia leaf / stem extracts, 10-15% of hydrolysis elastic protein, 10-20% of an anti-aging agent containing 100-200 ppm palmitoyl oligopeptide, 5-10% of tea extracts, 0.2-0.5% of a cell growth factor stock solution, 3-5% of an anti-aging agent containing 45-55 ppm neurotransmitter inhibition signal peptides, 5-10% of algae extracts and the balance water. According to the skin protection matrix, the skin barrier repairing and anti-aging effects are remarkable, the effect can be seen in a short period, and the skin barrier can be repaired when a user uses the matrix for a long time, so that wrinkles are reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG MARUBI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Micromolecular donkey-hide gelatin essence anti-aging facial mask
InactiveCN108785241AStable moisturizingFade fine linesCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWrinkle skinChondrus crispus extract
The invention relates to a micromolecular donkey-hide gelatin essence anti-aging facial mask, which contains the following components: glycerin, methylpropanediol, glyceryl polyether-26, 1,2-hexanediol, p-hydroxyacetophenone, butanediol, PEG-60 hydrogenated castor oil, panthenol, xanthan gum, allantoin, carbomer, glycerin polyacrylate, tromethamine, sodium hyaluronate, EDTA disodium, glycerin acrylate / acrylic copolymer, phenoxyethanol, propylene glycol, proplis extract, a PVM / MA copolymer, dipotassium glycyrrhizinate, essence, silk amino acids, beta-glucan, BAMBUSA VULGARIS WATER bambusa vulgaris water, hydrolyzed collagen, rice extract, glycine ussuriensis seed extract, sesame seed extract, chondrus crispus extract, ethylhexylglycerin, polysorbates-20, potassium chloride, locust bean gum,dipotassium phosphate, sodium citrate, hydrolyzed hyaluronic acid, glucose, calcium lactate, glucomannan, sodium acetylated hyaluronate and acetyl hexapeptide-8. The micromolecular donkey-hide gelatin essence anti-aging facial mask has the efficacies of supplementing skin nutrition, moisturizing, removing wrinkles and resisting senility.
Owner:SHAN DONG DONG E E JIAO
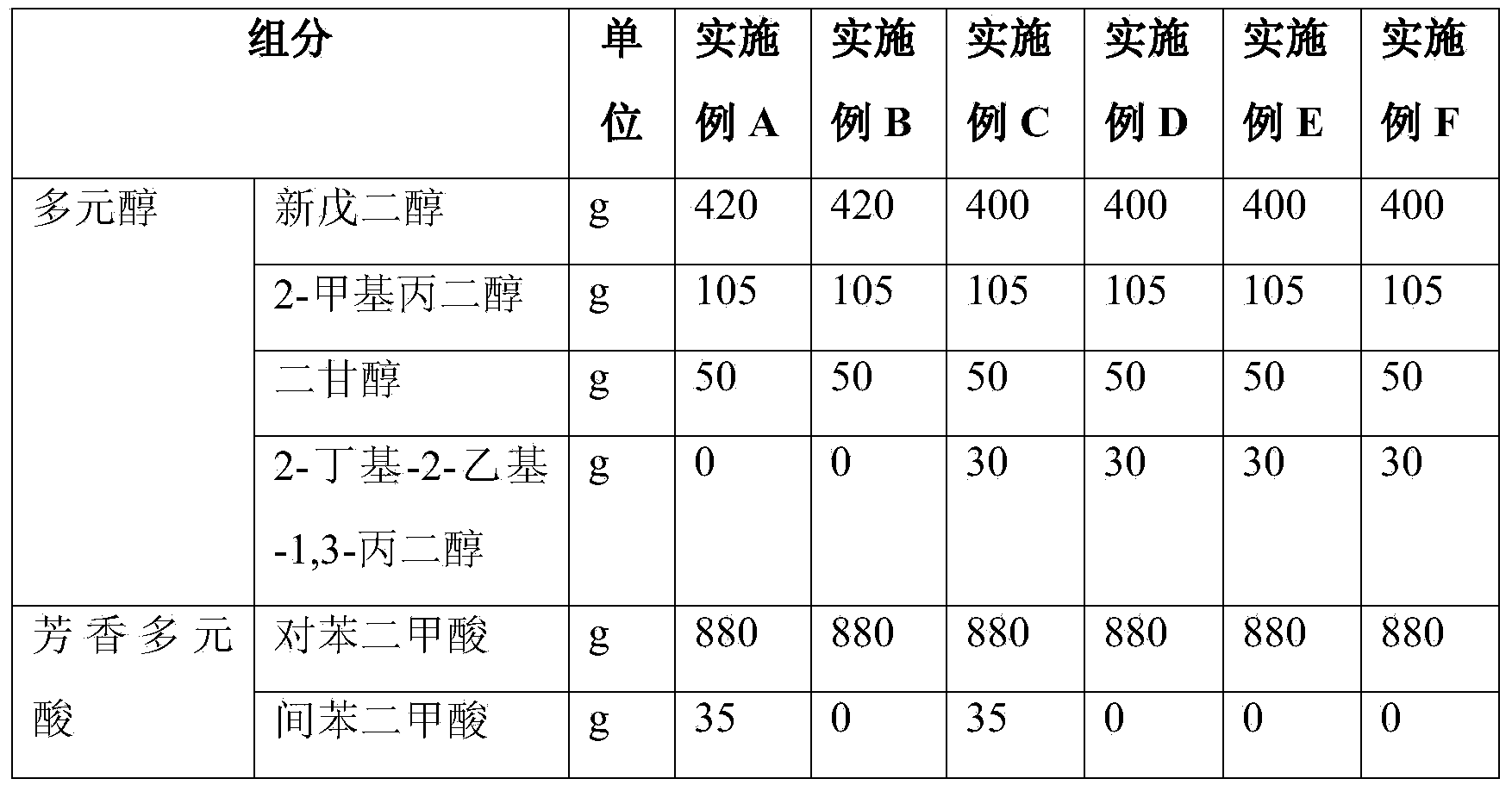
Polyester resin for epoxy-cured powder coating with high glossiness and high leveling property and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103642014AControl surface tensionControl Melt ViscosityPowdery paintsEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxy1,3-Propanediol
The invention relates to a polyester resin for an epoxy-cured powder coating with high glossiness and high leveling property and a preparation method thereof. The polyester resin has relatively high glass-transition temperature. The technical scheme is as follows: the polyester resin for the epoxy-cured powder coating with high glossiness and high leveling property orderly comprises the following components: neopentyl glycol, 2-methylpropanediol, diglycol, 2-butyl-2-ethyl-1, 3-propylene glycol, terephthalic acid, isophthalic acid, sebacic acid and trimellitic anhydride. The preparation method of the polyester resin for the epoxy-cured powder coating with high glossiness and high leveling property comprises the following steps: 1) adding a proportioning amount of polyhydric alcohol to a reaction kettle, heating at normal temperature, and then feeding a proportioning amount of polyatomic acid and esterification catalyst; 2) carrying out thermal reaction until the water yield of the esterified water can be up to 95% or more of theoretical water yield; 3) adding trimellitic anhydride and isophthalic acid, and carrying out thermal reaction; 4) gradually vacuumizing, and reacting; 5) discharging.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHUANHUA TIANSONG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Polyester coil coating, process of coating a coil, and coated coil
A coil coating composition producing a coil coating with excellent properties at a lower peak metal temperature includes (a) a first, branched polyester with an hydroxyl number of at least about 80 mg KOH / g, (b) a second, essentially linear polyester with an hydroxyl number of at least about 44 mg KOH / g, and (c) a crosslinking agent. The branched polyester is prepared by condensation of a polyol component consisting essentially of a flexibilizing diol, a branched diol, and, optionally, a polyol having at least three hydroxyl groups and a polyacid component consisting essentially of one or more aromatic or cycloaliphatic dicarboxylic acids and polymerizable anhydrides and esters thereof and, optionally, a polyacid having at least three carboxylic acid groups or poymerizable anhydrides or esters thereof, wherein at least one of the polyol having at least three hydroxyl groups and the polyacid having at least three carboxyl groups or an anhydride or methyl ester thereof is included. The essentially linear polyester is prepared by condensation of a polyol component consisting essentially of a flexibilizing diol and a branched diol and a polyacid component consisting essentially of one or more aromatic or cycloaliphatic dicarboxylic acids and polymerizable anhydrides and esters thereof. The branched diols of the first and second polyesters are independently selected from the group consisting of 2-methyl-1,3-propanediol, 2,2,4-trimethyl-1,3-pentanediol, 2-ethyl-2-butyl-1,3-propanediol, propylene glycol, neopentyl glycol, and combinations thereof.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
High-quality collagen mask
InactiveCN106913510ARaw materials are non-toxicPermeableCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSide effectIrritation
The invention discloses a high-quality collagen mask. The high-quality collagen mask is prepared from, by weight, water, glycerin, dipropylene glycol, methylpropanediol, SC glucan, super repair peptide, carnosine, fucogel-1, milk skin conditioner, dipotassium glycyrrhizinate, hydrolyzed collagen, allantoin, preservative, citric acid, methylparaben, sodium hyaluronate, EDTA disodium, PEG-hydrogenated castor oil and essence. The adopted raw materials are free of toxicity, irritation or side effect. The high-quality collagen mask has higher permeability, trophism, repairability, moisture retention property and compatibility and better whitening and wrinkle removing functions than masks available in the market at present, and can improve skin elasticity, shrink pores, remove facial wrinkles, improve dark and oily skin, deeply permeate into skin to provide nutrients and water for skin constantly, and repair aged and damaged cells, so as to realize a long-term skin nourishing effect.
Owner:HEFEI KADIER COSMETIC CO LTD
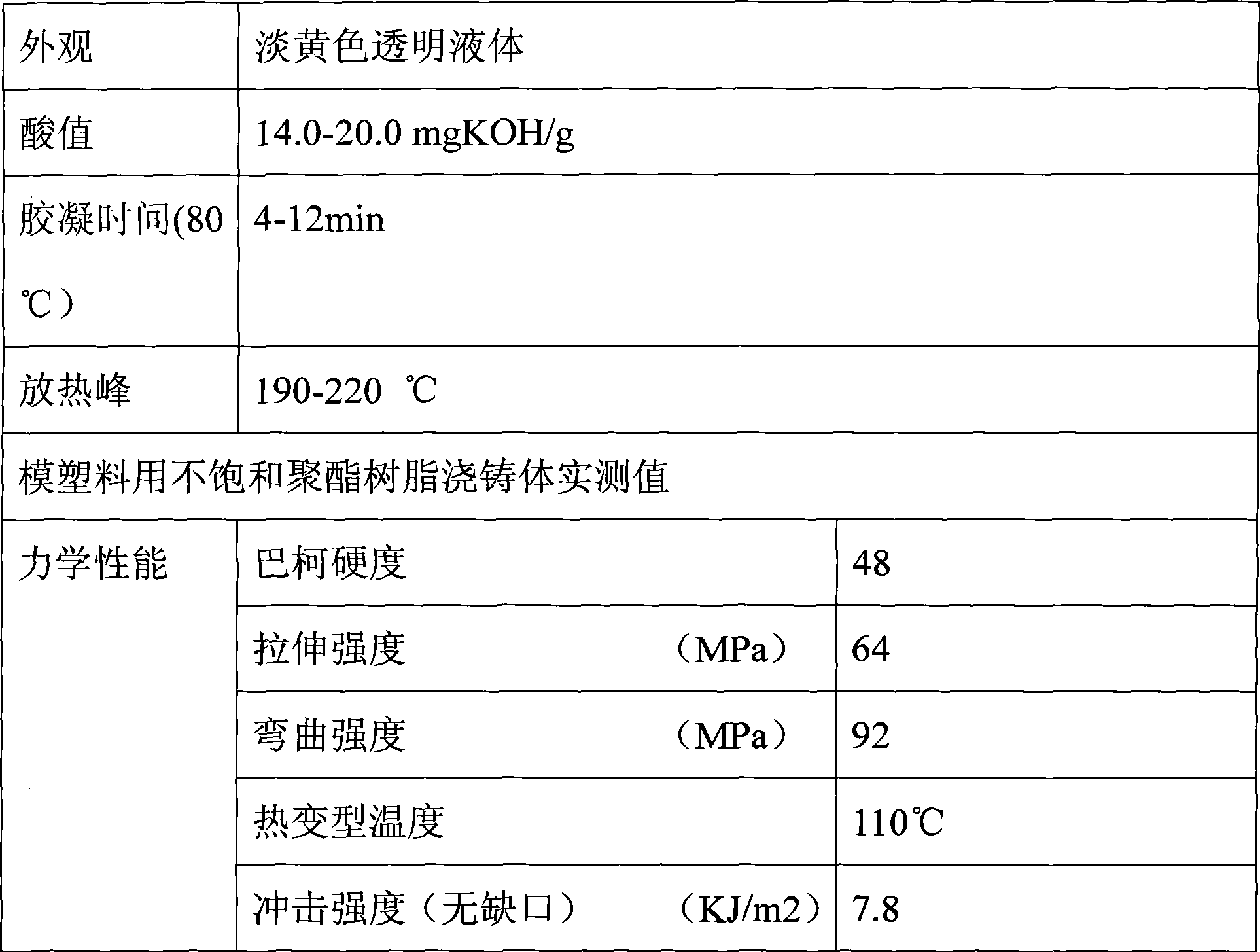
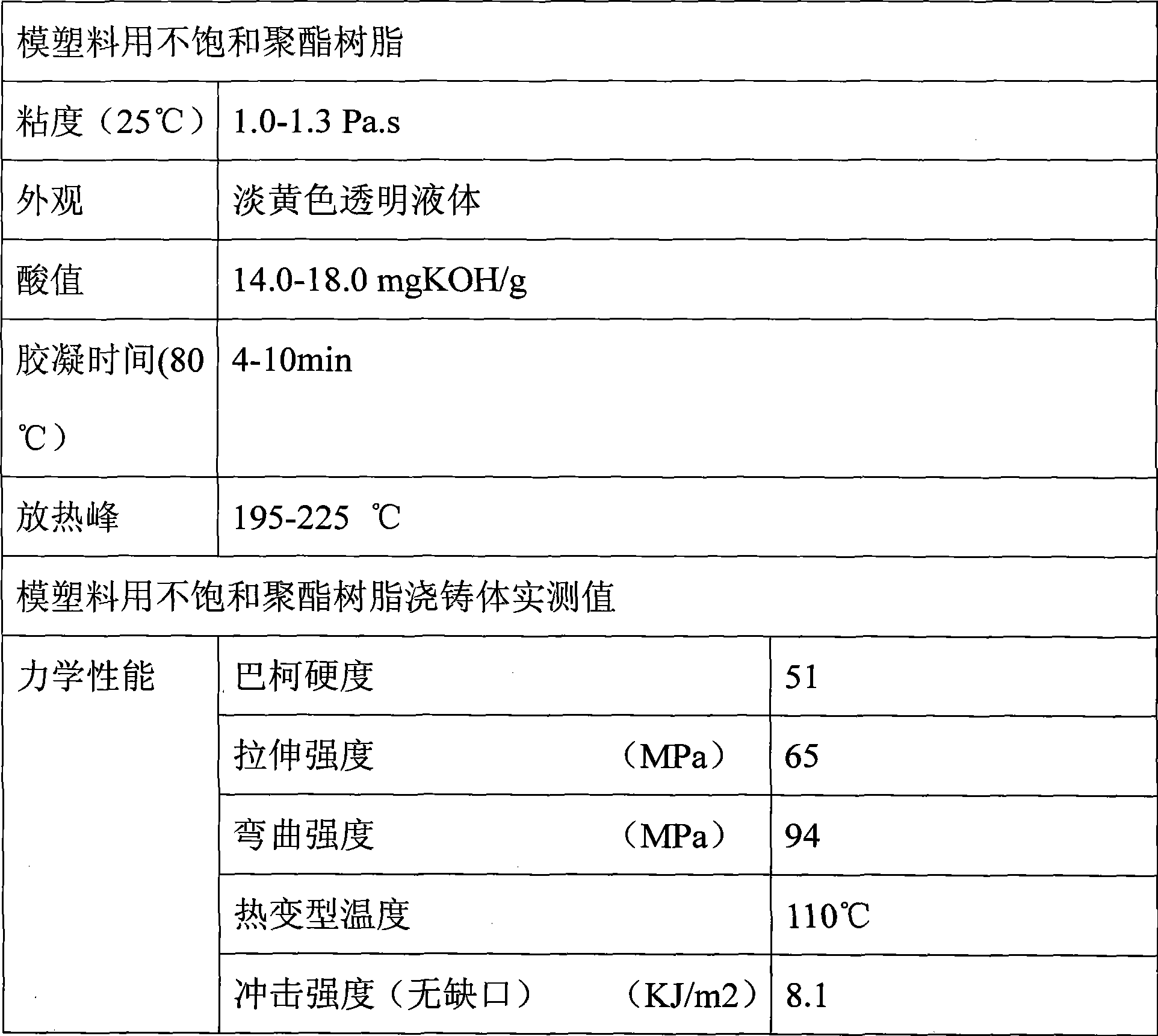
Unsaturated polyester resin for die pressing and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102174182AHigh surface finishHigh heat distortion temperatureSurface finishThermal deformation
The invention discloses unsaturated polyester resin for die pressing and a preparation method thereof. The resin mainly comprises the following raw materials in part by weight: 120 to 150 parts of phthalic anhydride, 290 to 350 parts of propylene glycol, 440 to 470 parts of maleic anhydride, 70 to 100 parts of dipropylene glycol, 40 to 50 parts of methylpropanediol, 70 to 85 parts of neopentyl glycol and 420 to 470 parts of styrene. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that: the thermal deformation temperature of the resin is higher than 113 DEG C, the surface finishment of a sheet molding compound / bulk molding compound (SMC / BMC) product taking the product as a substrate can meet the requirement of a class A surface, and the resin is particularly suitable for manufacturing an electric appliance switch, an automobile reflecting lamp, a bumper and the like.
Owner:宜兴市兴合树脂有限公司
Broad-spectrum antibacterial cosmetic antiseptic and application thereof
InactiveCN102920612AImprove compatibilityLess irritatingCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsIrritationPhenethyl alcohol
The invention discloses a broad-spectrum antibacterial cosmetic antiseptic comprising the components of, by mass: 8-12% of caprylhydroxamic acid, 38-45% of phenethyl alcohol, and 46-54% of methylpropanediol. The antiseptic provided by the invention has the advantages that: (1) the antiseptic has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, and can effectively inhibit Gram-negative and positive bacteria, yeasts and molds; (2) the antiseptic does not contain traditional antiseptic and bactericide, and is a cosmetic-use complex system completely satisfying a concept of no antiseptic addition; and the antiseptic has low irritation and high safety; and (3) the antiseptic has good compatibility with most of cosmetic raw materials; and the antibacterial capability of the antiseptic is not affected by surfactant, proteins and Chinese herbal medicine additives in cosmetics.
Owner:SPEC CHEM IND INC
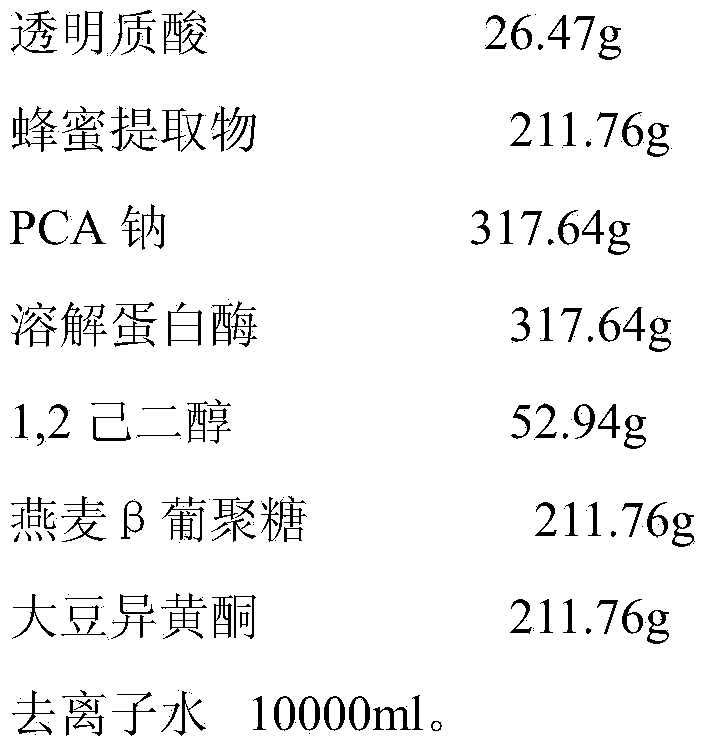
Antimicrobial peptide freeze-dried preparation for treating colpitis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104043098AStrong anti-inflammatory, anti-itch and anti-bacterialProtect physical and mental healthOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsProtozoaCancer cell
The invention provides a freeze-dried preparation for treating colpitis. The preparation includes an antimicrobial peptide freeze-dried powder and an antibacterial peptide basic liquid. The antibacterial peptide freeze-dried powder comprises the following components according to the total mass percentage: 0.1%-8% of an antibacterial peptide human beta defensin, 0.01%-0.2% of a low molecular weight heparin sodium and 1%-15% of a stabilizing agent; the antibacterial peptide basic liquid comprises the following components according to the total mass percentage: 0.01%-0.4% of hyaluronic acid, 0.5%-4% of menthoxypropanediol, 0.5%-5% of a honey extract, 0.5%-5% of PCA sodium, 0.5%-5% of dissolved protease, 0.3%-0.7% of 1,2 hexanediol, 1.5%-6% of oat beta dextran, 1%-5% soybean isoflavone, and the balance of deionized water or water for injection. The antimicrobial peptide freeze-dried preparation provided by the invention has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, and strong killing effect on bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa and cancer cells, and even can enhance immunity, accelerate wound healing process; in addition, the preparation has obvious curative effect, and no rebound or side effect.
Owner:广州舒泰生物技术有限公司
Skin care composition with sunscreen repair effect and application and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109662928AFree from hardeningElegant silky feelingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBetaineYeast Proteins
The invention relates to a skin care composition with sunscreen repair effect and an application and a preparation method thereof. The composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0.1-3 pbw plant sensitizer; 0.01 to 1.0 pbw of codogen; 0.1 to 1.0 pbw of hydrolyzed yeast protein; 0.01 to 0.5 pbw of green algae extract; 0.01 to 0.1 pbw of hamamelis extract; 0.01 to 0.1 pbw of tremella polysaccharide; 0.1 to 1.0 pbw of oat glucan; 0.1 to 1.0 pbw of allantoin; 0.01 to 1.0 pbw of compound ceramide; 0.01 to 1.0 pbw of sunflower unsaponifiable matter; 1.0-10.0 pbw of glycerol; 1.0-10.0 pbw of methyl propylene glycol; 0.01-1.0 pbw of sodium hyaluronate; 0.1-10.0 pbw of betaine and 0.1-1.0 pbw of panthenol. According to the skin care composition with sunscreen repair effect and the application and the preparation method thereof, the synergistic effect among the components is fully exerted by utilizing different medicinal mechanisms of the components, so that the obtained composition can enhance the cell self-repairing function, promote the division and growth of skin cells, resist ultraviolet damage and repair the skin barrier function.
Owner:葆姿生物科技(成都)有限公司
Anti-allergic restoring facial mask
InactiveCN107496309ARestore physical functionImprove the immunityCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticSide effectIrritation
The invention discloses an anti-allergic restoring facial mask which comprises the following components: water, dipropylene glycol, glycerin, methyl propanediol, SC-glucan, Shuminjia, an olea europaea fruit extract, a milk skin conditioner, allantoin, sodium hyaluronate, biosaccharide gum-1, PEG-40 hydrogenated castor oil, disodium EDTA, a GPL preservative, methylparaben and essences. The raw materials used in the invention have mild nature, no irritation, no toxic and side effects, and significant effects of relieving sensitivity, diminishing inflammation and sterilizing, astringing and restoring skin, activating skin cells, enhancing skin resistance and restoring physiological functions of the skin, can rapidly relieve swelling and pain caused by skin allergy, astringe and restore sensitive and damaged cells, deeply penetrate the skin, continuously replenish nutrients and moisture of the skin, lock water and keep moisture for long term, play a nourishing role while supplementing water, and achieve a long-term skin beautifying effect.
Owner:HEFEI KADIER COSMETIC CO LTD
Stabilized atorvastatin
InactiveUS20070190138A1Amount being removedReduce the amount requiredBiocideGranular deliveryOral medicationMETHYLPROPANEDIOL
A stable pharmaceutical composition for oral administration comprising atorvastatin and an amount of a pharmaceutically acceptable organic alkalizing compound capable of establishing a microenvironment for atorvastatin having a pH of at least about 5, for example 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol (trometamol).
Owner:VELOXIS PHARMA
Repair essence
InactiveCN107496344AGood moisturizing effectPromote generationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPreservativeGlycerol
The invention discloses repair essence. The repair essence is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 40 to 45 percent of distilled water, 15 to 25 percent of methylpropanediol, 10 to 20 percent of lubrajel oil, 5 to 15 percent of glycerol, 3 to 7 percent of mushroom glucan, 2 to 4 percent of snail extract, 1 to 2 percent of portulaca oleracea extract, 2 to 3 percent of conotoxin, 0.1 to 0.2 percent of sodium hyaluronate, 0.1 to 0.2 percent of GPL preservative, 0.1 to 0.15 percent of disodium EDTA, 0.1 to 0.15 percent of allantoin and 0.1 to 0.15 percent of methylparaben, wherein the sum of all the components is 100 percent. The invention provides the repair essence which has better moisturizing and wetting effects and the efficacy of powerfully repairing the skin, resisting oxidation and resisting aging.
Owner:HEFEI KADIER COSMETIC CO LTD
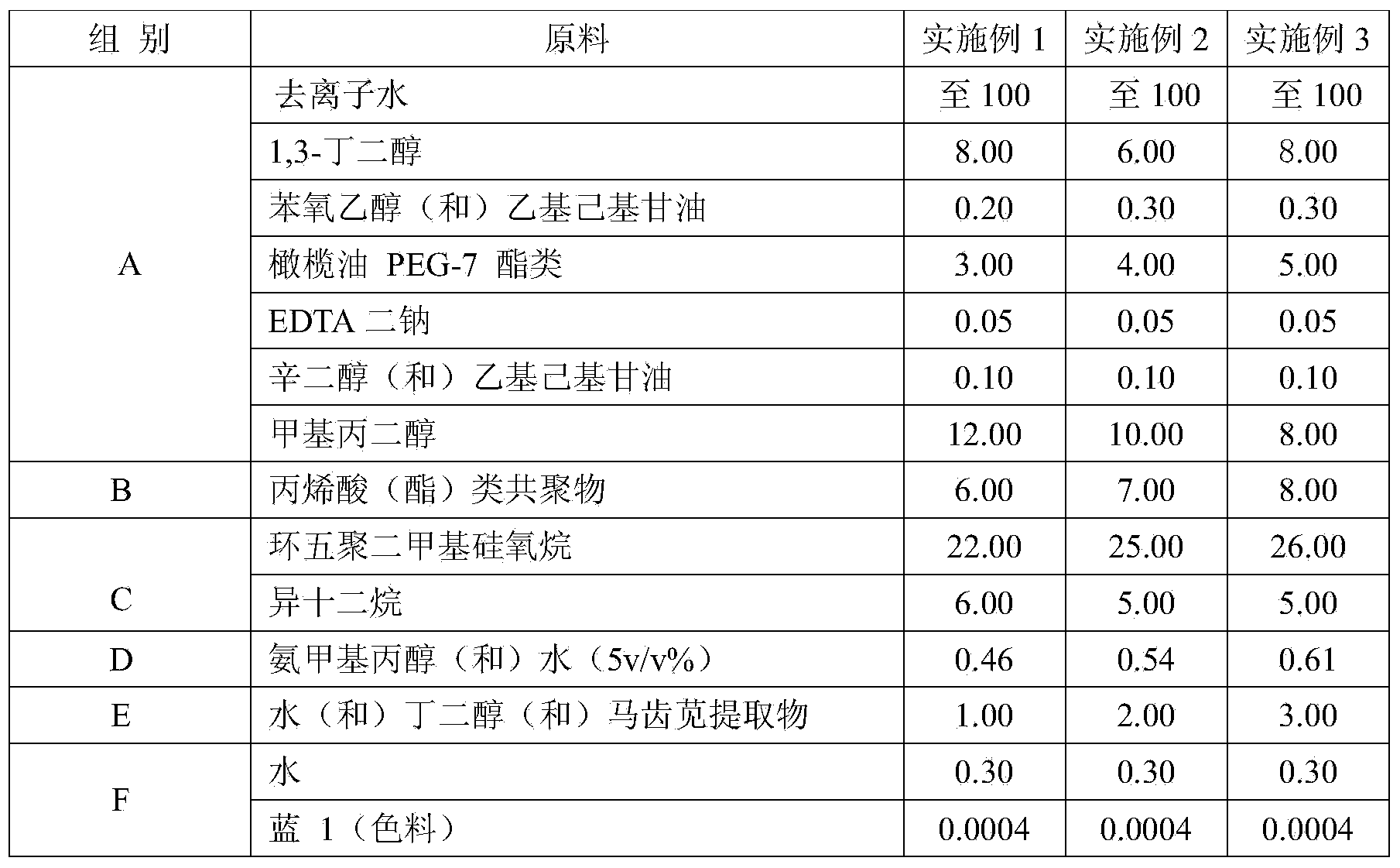
Mild eye and lip cleansing gel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104367516ARemove makeupLightweight and dewy lookCosmetic preparationsMake-upEthylene diaminePurslane extract
The invention provides mild eye and lip cleansing gel. The eye and lip cleansing gel comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 22-26 percent of cyclopentasiloxane, 6-8 percent of 1,3-butanediol, 0.2-0.3 percent of phenoxyethanol / ethylhexylglycerin, 5-6 percent of isododecane, 0.46-0.61 percent of aminomethyl propanol / water mixture, 0.05 percent of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) disodium, 6-8 percent of acrylic acid (ester) copolymer, 0.1 percent of octylene glycol / ethylhexylglycerin, 0.0004 percent of pigment, 8-12 percent of methylpropanediol, 1-3 percent of purslane extracts / water / butanediol mixture, 3-5 percent of olive oil PEG-7 ester and the balance of water. The mild eye and lip cleansing gel is attractive and moisturizing in appearance, mild in chemical characteristic and free of greasy feeling, and has a refreshing and comfortable feeling; moreover, various kinds of make-up products can be completely cleansed.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SHEENCOLOR COSMETICS CO LTD
Method for preparing relaxing and face-cleansing cosmetics and application
ActiveCN102379838ACosmetic preparationsAntipyreticRecombinant Human Keratinocyte Growth FactorVitamin C
The invention relates to a method for preparing relaxing and face-cleansing cosmetics and application. The cosmetics comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.00001 to 0.001 percent of recombinant human keratinocyte growth factors, 0.00001 to 0.001 percent of recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, 0.1 to 0.5 percent of low-molecular sodium heparin, 5 to 25 percent of stabilizer, 0.02 to 0.3 percent of hyaluronic acid, 0.5 to 8 percent of vitamin C sodium phosphate, 0.5 to 5 percent of methyl propanediol, 0.3 to 0.7 percent of 1,2 hexanediol, 0.5 to 3.5 percent of lactobacillus / mung bean fermentation liquor, 0.5 to 5 percent of dissolved protease and the balance of water. The relaxing and face-cleansing cosmetics are applied to sensitive skin, can be stored for a long time, and is suitable for long-term use.
Owner:广州泰润合投资有限公司
Stock solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109394653AHas penetrationPromote absorptionCosmetic preparationsAntipyreticAphanothece sacrumCAPRYLOYL GLYCINE
The invention discloses a stock solution and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of skin care products. The stock solution comprises, by weight, 0.5-0.9 part of sodium hyaluronate, 5-8 parts of methylpropanediol, 0.8-2.5 parts of first moisturizing agent, 0.5-1.5 parts of second moisturizing agent, 0.3-1.0 part of third moisturizing agent, 0.01-0.1 part of fourth moisturizing agent, 0.05-0.3 part of first skin conditioning agent, 0.1-1.0 part of second skin conditioning agent, 0.1-1.0 part of third skin conditioning agent, 0.05-0.3 part of fourth skin conditioningagent, 0.1-0.2 part of capryloyl glycine, 0.2-0.3 part of aphanothece sacrum polysaccharide, 0.05-0.3 part of preservative and 100 parts of deionized water. The stock solution has the advantages of gentleness in moisturizing and moisture preserving, no stimulation to skin and capability of restoring damaged skin.
Owner:HANGZHOU FACECARE COSMETICS
Caulis dendrobii multi-effect stock solution and production method thereof
InactiveCN107049896AImprove allergies, acne, oily shine and other problemsImprove immunityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsHydrolysateGlycerol
The invention discloses a caulis dendrobii multi-effect stock solution and a production method thereof and belongs to the field of cosmetics. The caulis dendrobii multi-effect stock solution is prepared from the following raw materials: caulis dendrobii extract, glycosyl trehalose, ceramide, sodium hyaluronate, butylene glycol, glycerol, 1,2-pentanediol, phenoxyethanol, hydrogenated starch hydrolysate, methylpropanediol, seaweed extract, opuntia streptacantha stem extract, cucumber extract, alchemilla japonica leaf extract, lecithin and water; the caulis dendrobii multi-effect stock solution is prepared by mixing all the raw materials. According to the caulis dendrobii multi-effect stock solution, any harmful chemical additive is not added so that the caulis dendrobii multi-effect stock solution has no toxin, harms or side effect, has multiple functions and good effects and is especially suitable for repairing various skin problems caused by the fact that a user stays up late.
Owner:GUANGXI RONGXIAN COUNTY TIANSHUN DENDROBIUM CO LTD
Anti-yellowing unsaturated polyester resin and synthetic method thereof
ActiveCN105482087AImprove anti-yellowing effectHigh heat distortion temperatureAntioxidantCis-Butenedioic Acid
The invention provides anti-yellowing unsaturated polyester resin, comprising the following components in percentage by weight: 13-20% of adipic acid, 23-28% of maleic anhydride, 30-33% of dihydric alcohol, 0.04-0.05% of an antioxidant, 0.01% of an inhibitor, 23-24% of styrene, 4% of metacrylic acid methyl ester, 0.04% of paraffin, 0.01% of copper naphthenate and 0.1% of a light stabilizer, wherein the dihydric alcohol is a mixture of neopentyl glycol, glycol and propylene glycol, or a mixture of neopentyl glycol, methyl propylene glycol and propylene glycol. The unsaturated polyester resin provided by the invention has very good yellowing resistance and weather resistance.
Owner:广东百汇达新材料有限公司
Epoxy cured high-flexibility polyester resin used for powdery paint and a preparing method thereof
ActiveCN106634476AGood flexibilityImprove athletic abilityPowdery paintsEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyWater discharge
The invention relates to epoxy cured high-flexibility polyester resin used for powdery paint and a preparing method thereof. The provided polyester resin has a characteristic of high flexibility. The provided method has characteristics of simple and concise steps. According to a technical scheme, the polyester resin includes neopentyl glycol, 2-methyl propanediol, and the like. The method includes steps of 1) adding the neopentyl glycol, the 2-methyl propanediol and 3-methyl-1,5-pentanediol into a reaction kettle, raising the temperature, then adding terephthalic acid, adipic acid and a catalyst and raising the temperature under stirring; 2) generating esterification water and evaporating the water to remove the water, controlling and regulating the temperature raising rate, reacting under a maintained temperature, and finishing temperature maintaining when the amount of the esterification water is 95% or above of the theoretical water discharge amount; 3) adding triphenyl phosphite, gradually vacuumizing and reacting continuously; 4) adding trimellitic anhydride and reacting under a maintained temperature; and 5) adding an antioxidant and a curing promoter, reacting under stirring and discharging a material.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHUANHUA TIANSONG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Metal paint and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102993791AHigh hardnessScratch resistantCoatingsPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsGlycidyl methacrylateMeth-
The invention discloses a metal paint, which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 180 to 190 parts of dodecenylsuccinic acid, 130 to 135 parts of propylene glycol, 210 to 215 parts of glycidyl methacrylate, 360 to 365 parts of 2-ethyl hexyl acrylate, 430 to 435 parts of methylpropanediol, 105 to 108 parts of phenolic resin, 85 to 90 parts of styrene, 100 to 110 parts of ethylenediamine, 300 to 310 parts of titanium dioxide, 20 to 30 parts of modified diatomite, 7 to 8 parts of formic acid, 100 to 105 parts of water, and 14 to 16 parts of sodium hydroxyethyl sulfonate. The raw materials are mixed, dispersed at a high speed, and grinded into nano-grade metal paint. The coating formed by the metal paint has the advantages of high hardness, scratch prevention, strong attachment, salt mist resistance, saline water resistance, acid and alkali resistance, water and oil resistance, recycling on oil paint film surface, paint film hurt prevention, super-strong paint film flexibility and the like. The service life of a conventional paint film can be between 5 and 8 years.
Owner:怀远县巨龙机械制造有限公司
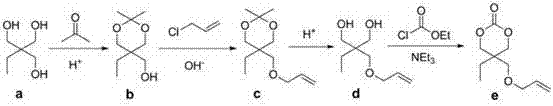
Structure, synthesis and use of 2-ethyle-2-allyloxymethyl-1,3-propylene carbonate
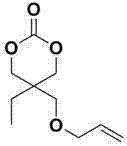
InactiveCN104744426ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getEasy to prepareOrganic chemistryPolymer scienceSide chain
The invention discloses a structure, use and synthesis method of 2-ethyle-2-allyloxymethyl-1,3-propylene carbonate monomer. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: with trimethylolpropane as raw material, firstly protecting two hydroxyls, and allyl etherizing the other hydroxyls, de-protecting to obtain glycol precursor, cyclizing to obtain a carbonate monomer containing double-bond lateral groups. The polymer prepared from the monomer can realize the physical, chemical and biological performance modification for the polycarbonate through a series of reactions such as hydrogenation, addition, cycloaddition, epoxidation and cross-linking reaction of the lateral group double bonds so as to obtain the functionalized polycarbonate to meet different requirements of biomedicine applications.
Owner:CHANGZHOU HIGH TECH RES INST OF NANJING UNIV
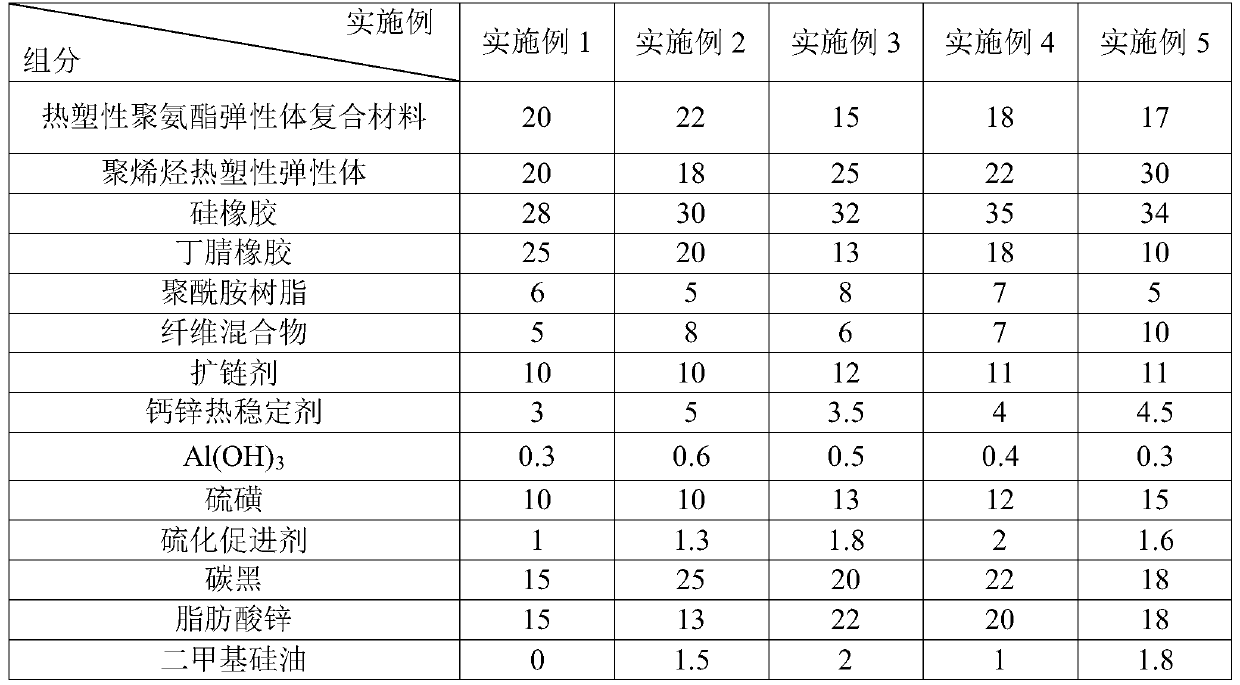
Elastic insulation sole material and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses an elastic insulation sole material and a preparation process thereof. The elastic insulation sole material is prepared from 15 to 22 parts of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer composites, 18 to 30 parts of thermoplastic polyolefin elastomers, 28 to 35 parts of silicon rubber, 10 to 25 parts of nitrile rubber, 5 to 8 parts of polyamide resin, 5 to 10 parts of fiber mixtures, 10 to 12 parts of chain expanders, 3 to 5 parts of calcium-zinc thermal stabilizers, 0.3 to 0.6 part of Al(OH)3, 10 to 15 parts of sulphur, 1 to 2 parts of vulcanization accelerators, 15 to 25 parts of carbon black and 13 to 22 parts of zinc fatty acid, wherein the chain expanding agents are one kind of materials from methylpropanediol, DMTDA and TDMA-02; the fiber mixture comprises at leasttwo kinds of materials in nylon fiber, aramid fiber and bamboo charcoal fiber. The elastic insulation sole has the advantages that the elasticity is good; the wear-resistant performance is good.
Owner:WENZHOU XIAOLIN SHOES MATERIALS
Water-borne acrylic primer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105001727AAvoid erosionQuality improvementAnti-corrosive paintsEpoxy resin coatingsOrganic solventWeather resistance
The invention discloses water-borne acrylic primer and a preparation method thereof. The water-borne acrylic primer comprises, by weight, the following components of 25-35 parts of modified acrylic resin, 15-25 parts of amino resin, 2-8 parts of titanium dioxide, 3-9 parts of 2-methyl-1,3-propanediol, 5-15 parts of filler, 2-7 parts of a pH regulator, 4-12 parts of a defoaming agent, 4-10 parts of a dispersing agent and 20-30 parts of deionized water. The prepared water-borne acrylic primer can effectively prevent finishing coat from being eroded by wall body soluble substances, and the quality of the finishing coat is improved. No organic solvent is contained, no solvent evaporates during solidification, and the anti yellowing effect and the weather resistance are good. The preparation method of the water-borne acrylic primer has the advantages that the technology is simple, no special post-processing is needed, the cost is low, and the preparation method of the water-borne acrylic primer is suitable for requirements of industrial production.
Owner:黎司华
Preparation containing diol
InactiveUS20050058679A1Improve propertiesReduce viscosityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPolyolAntioxidant
The invention is a cosmetic or dermatological formulation comprising a) at least one polyol in a concentration of from 0.1 to 20% by weight, based on the total weight of the formulation, and b) at least one diol selected from the group consisting of 2-methyl-1,3-propanediol, pentanediol, and hexanediol, in a concentration of from 0.1 to 25% by weight, based on the total weight of the formulation. The invention also includes formulations further comprising at least one antioxidant, and formulations further comprising at least one UV filter. The invention also includes a method of moisturizing skin comprising applying the formulation to the skin. The invention further includes a method for reducing the tacky sensation, a method for reducing the viscosity, and a method for increasing the stability of a polyol-containing formulation comprising adding a diol selected from the group consisting of 2-methyl-1,3-propanediol, pentanediol, and hexanediol.
Owner:BEIERSDORF AG
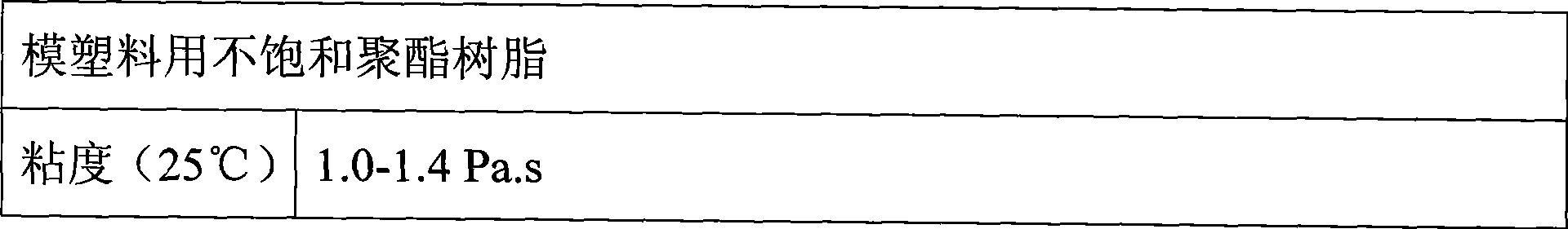
Unsaturated polyester resin for moulding compound and preparation thereof
The invention relates to unsaturated polyester resins and provides an unsaturated polyester resin used for molding compounds. The resin is prepared by dissolving the polymer of propanediol, glycol, dipropylene glycol, phthalandione and maleic anhydride in styrene. The invention has the advantages that: (1) the dipropylene glycol and methyl propanediol are adopted for synthesizing the unsaturated polyester resin to lead the resin to have favorable water resistance and flexibility, besides, the product of the resin has good moisture resistant capacity and excellent mechanical property; (2) when the resin is matched with proper low profile agent for use, the product can reach zero shrinkage, with the precision of size ensured; and (3) the phthalandione can be used for shortening reaction time and reducing energy consumption.
Owner:CHANGZHOU HUARUN COMPOSITE MATERIALS +1
Modified polyester chip for manufacturing high-elasticity polyester fiber and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107216448AImprove ductilityIncrease elasticityMonocomponent polyesters artificial filamentMETHYLPROPANEDIOLDiol
The present invention relates to a kind of modified polyester chip for making high elastic polyester fiber, which is characterized in that it is directly esterified into an esterified product after adding methyl propylene glycol in the slurry prepared by dibasic acid, dibasic alcohol and additives , the esterified product is then subjected to liquid phase polycondensation in a prepolymerization tank and a final polymerization tank, and after liquid phase polycondensation, it is cooled and sliced to obtain modified polyester chips with an intrinsic viscosity of 0.5-1.2dl / g for the production of high-elastic polyester fibers Finished product, wherein the molar ratio of methylpropanediol to diol is 1:4~1:99. The present invention also designs the preparation method of the modified polyester chip for producing high elastic polyester fiber. The invention has the advantage that the short and long polyester filaments produced by melt spinning have good dyeability, spinnability and elasticity.
Owner:CHINA RESOURCES PACKAGING MATERIALS CO LTD +1
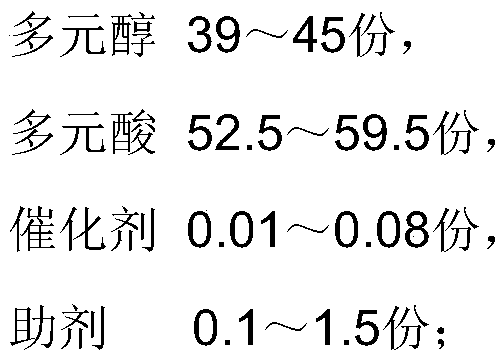
Polyester resin for low-temperature cured high-leveling powder coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111072939AHigh glossImprove impact performancePowdery paintsPolyester coatingsPolymer sciencePtru catalyst
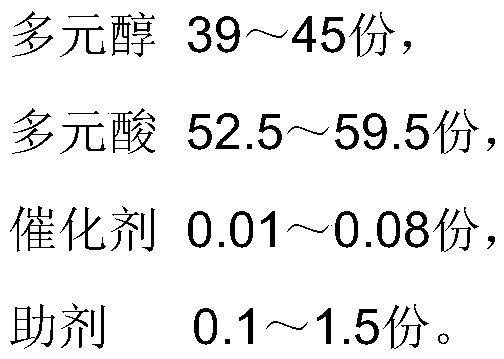
The invention discloses polyester resin for low-temperature curing high-leveling powder coating and a preparation method of the polyester resin. The polyester resin is prepared from the following rawmaterials in parts by weight: 39 to 45 parts of polyhydric alcohol, 52.5 to 59.5 parts of polyacid, 0.01 to 0.08 part of a catalyst and 0.1 to 1.5 parts of an auxiliary agent, wherein the polyhydric alcohol is at least one of neopentyl glycol, 2-butyl-2-ethyl-1,3-propylene glycol, 2-methyl propylene glycol and diethylene glycol, and the polyacid includes polyacid for esterification and polyacid for acidification. The polyester resin prepared by the invention not only has good gloss and impact performance after low-temperature curing, but also has a flat and smooth surface, and the leveling grade can reach 8 or above.
Owner:JIANGSU RAP RESIN TECH CO LTD
Carboxymethyl starch sizing agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103866620AGood low temperature stabilityHigh strengthWater-repelling agents additionNon-macromolecular organic additionCarboxymethyl starchPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a carboxymethyl starch sizing agent and a preparation method thereof. The carboxymethyl starch sizing agent is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 9-11 parts of carboxymethyl starch, 4-5 parts of polyethylene glycol, 3-6 parts of gelatin, 7-8 parts of methylpropanediol, 2-4 parts of potassium carbonate, 6-8 parts of castor oil phosphate, and 185-190 parts of deionized water. The preparation method of the carboxymethyl starch sizing agent comprises the following steps: mixing, agitating, shearing and cooling. The prepared carboxymethyl starch sizing agent has good low-temperature stability, and the surface strength of paper can be obviously improved.
Owner:SUZHOU HENGKANG NEW MATERIALS
Skin care product composition with high-efficiency moisturizing effect and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108158850AThe formula is reasonableImprove permeabilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCuticleAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses skin care product composition with a high-efficiency moisturizing effect. The skin care product composition is prepared from the following ingredients of glyceryl polyether-26,methyl propanediol, an amino acid wetting agent, sodium hyaluronate and hydrolyzed hyaluronic acid. The skin care product composition disclosed by the invention has the advantages of reasonable formula match, gentleness, no stimulation, good skin permeability, ability in quickly permeating into skin tissues, ability in replenishing water for skin cuticle cells, deep-layer water replenishing effect, ability in improving skin microcirculation, ability in increasing skin moisture, effect of slowing down skin moisture loss and effect of replenishing water for the skin in a long-acting mode.
Owner:国妆汉美(广州)化妆品有限公司
Repairing anti-aging mask containing coenzyme Q10 and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110433097AMoisturizes and moisturizesResist damageCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWrinkle skinArginine
The invention discloses a repairing anti-aging mask containing coenzyme Q10 and a preparation method thereof. The repair anti-aging mask specifically includes: A-phase raw materials comprising 0.02-0.1% of EDTA-Na2, 0.1-0.3% of p-hydroxyacetophenone, 0.1-0.3% of allantoin, 0.2-0.5% of jojoba wax PEG-120 ester, and 1-3% of glycerin; B-phase raw materials comprising 6-8% of methylpropanediol, 0.02-0.2% of sodium hyaluronate, 0.08-0.2% of carbomer, and 0.05-0.15% of xanthan gum; a C-phase raw material comprising0.08 to 0.22% of arginine; D-phase raw materials comprising 0.1 to 0.5% of euglena gracilis polysaccharide / hydrolyzed collagen, 0.2 to 2% of beta-glucan, 0.1-0.5% of hydroxyethylpiperazine ethane sulfonic acid, 2.01-6.05% of a plant extract, 0.5-2% of a PEG / PPG-17 / 6 copolymer, 0.5-3% of bio-saccharide gum-1, and 0.3-0.8% of lipids. The anti-aging mask provided by the present invention can deeply replenish water, removes facial skin wrinkles and upper and lower eye bags, makes the skin firm, lightens dark spots, improves the skin's antioxidant ability, cannot cause skin allergies and other problems, and achieves repairing and anti-aging effects.
Owner:帅发(厦门)投资有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com