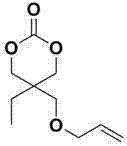
Structure, synthesis and use of 2-ethyle-2-allyloxymethyl-1,3-propylene carbonate
A technology of propylene glycol carbonate and allyloxymethyl, which is applied in the field of biomedical polymers, can solve the problems of residual protective group, low yield, affecting the application of polymers, etc., and achieves the effects of high application value and simple preparation method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
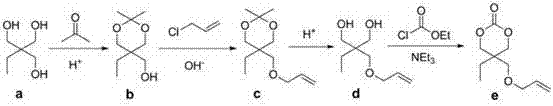
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Compound of Example 1 b : 2,2-Dimethyl-5-ethyl-5-hydroxymethyl-[1,3]-dioxane
[0021] Add trimethylolpropane to a 500 mL three-necked round bottom flask equipped with a condenser and a mechanical stirrer a (67.09g, 0.5mol) and acetone 400mL. After the trimethylolpropane was completely dissolved, 0.5 g of p-toluenesulfonic acid was added to the system, followed by stirring and reacting at room temperature for 16 hours. Then 1 g of potassium carbonate was added, and after stirring at room temperature for 1 hour, excess acetone was recovered by rotary evaporation. The resulting mixture was distilled under reduced pressure at 5mmHg / 110-112°C to obtain the ketal compound b A total of 68g, yield 78%. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , 300MHz), δ: 0.8 (t, C H 3 CH 2 , 3H), 1.25 (q, CH 3 C H 2 ,2H), 1.39 (s, CCH 3 , 3H), 1.43 (s, CCH 3 , 3H), 1.72 (br, OH, 1H), 3.66 (s, C H 2 O, 2H), 3.67 (s, C H 2 O, 2H), 3.76 (d,C H 2 OH,2H).
Embodiment 2
[0022] Compound of Example 2 c : 2,2-Dimethyl-5-ethyl-5-allyloxy-[1,3]-dioxane
[0023] In a 500mL three-necked round bottom flask equipped with a condenser, a constant pressure dropping funnel and a mechanical stirrer, add the ketal compound in sequence b (61g, 0.35mol), tetrabutylammonium bisulfate (11.9g, 0.035mol) and 300ml of 50wt% NaOH solution. The reaction solution was cooled to 0°C, and allyl chloride (107.1 g, 1.14 mol) was slowly added dropwise to the stirring reaction mixture. Thereafter, the reaction solution was heated to 40° C., stirred for 18 hours, and cooled to room temperature after the reaction. Subsequently, 300 mL of dichloromethane was added, allowed to stand, and the organic phase was separated and washed three times with distilled water, and dried over magnesium sulfate. Then, the desiccant was filtered off, dichloromethane and excess allyl chloride were recovered by rotary evaporation, and the residue obtained was subjected to vacuum distillati...
Embodiment 3
[0024]Example 3 compound d : 2-Ethyl-2-allyloxymethyl-1,3-propanediol
[0025] In a 500mL three-neck round bottom flask equipped with a condenser and a mechanical stirrer, the compounds were added sequentially c (64.3g, 0.3mol), methanol 200mL and 1mol / L hydrochloric acid 200mL, heated up to 40°C, and stirred for 24 hours. After the reaction, the reaction solution was concentrated by rotary evaporation, and the residue was dissolved in 100 mL of ether, washed with distilled water until neutral, and dried over magnesium sulfate. The resulting solution was spin-dried and distilled under reduced pressure at 10mmHg / 130-131°C to obtain the diol compound d A total of 48.9g, yield 93.6%. 1 H NMR (CDCl 3 , 300 MHz), δ:0.85 (t, C H 3 CH 2 , 3H) , 1.33 (q, CH 3 C H 2 , 2H), 2.53 (br, OH, 2H), 3.46 (s, C H 2 O, 2H), 3.62 (d, C H 2 OH, 2H), 3.74 (d, C H 2 OH, 2H), 3.98 (d, C H 2 CH=CH 2 , 2H), 5.24 (m, CH=C H 2 , 2H), 5.89 (m, H C=CH 2 , 1H).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com