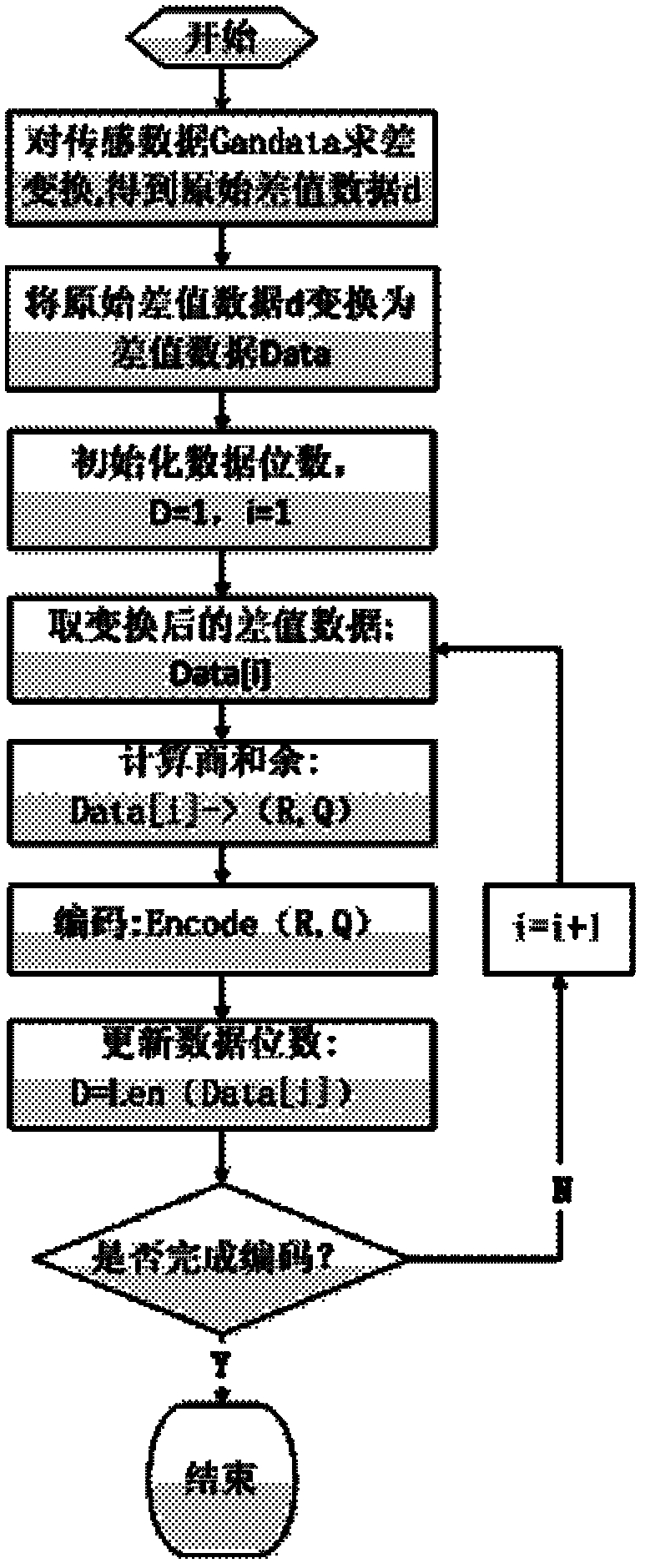
Context-adaptive quotient and remainder encoding method used for sensing data of wireless sensing nodes
A technology of wireless sensor nodes and sensing data, which is applied in the field of data compression, and can solve the problems of loss of original data accuracy, failure of lossy compression algorithm, discarding, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
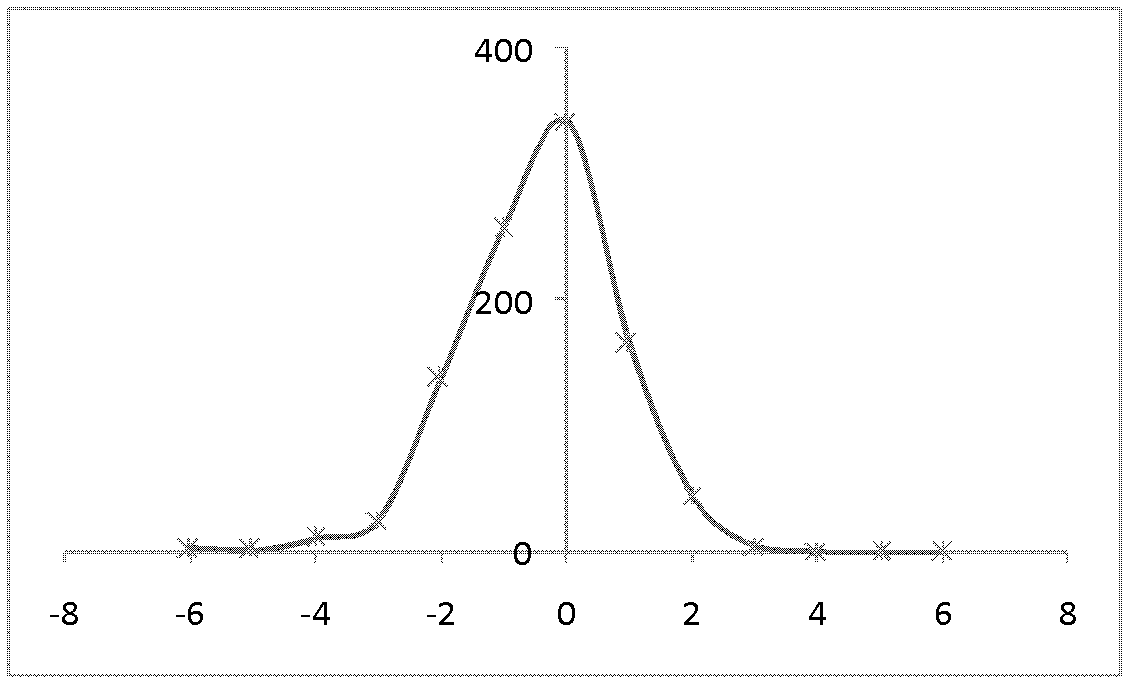
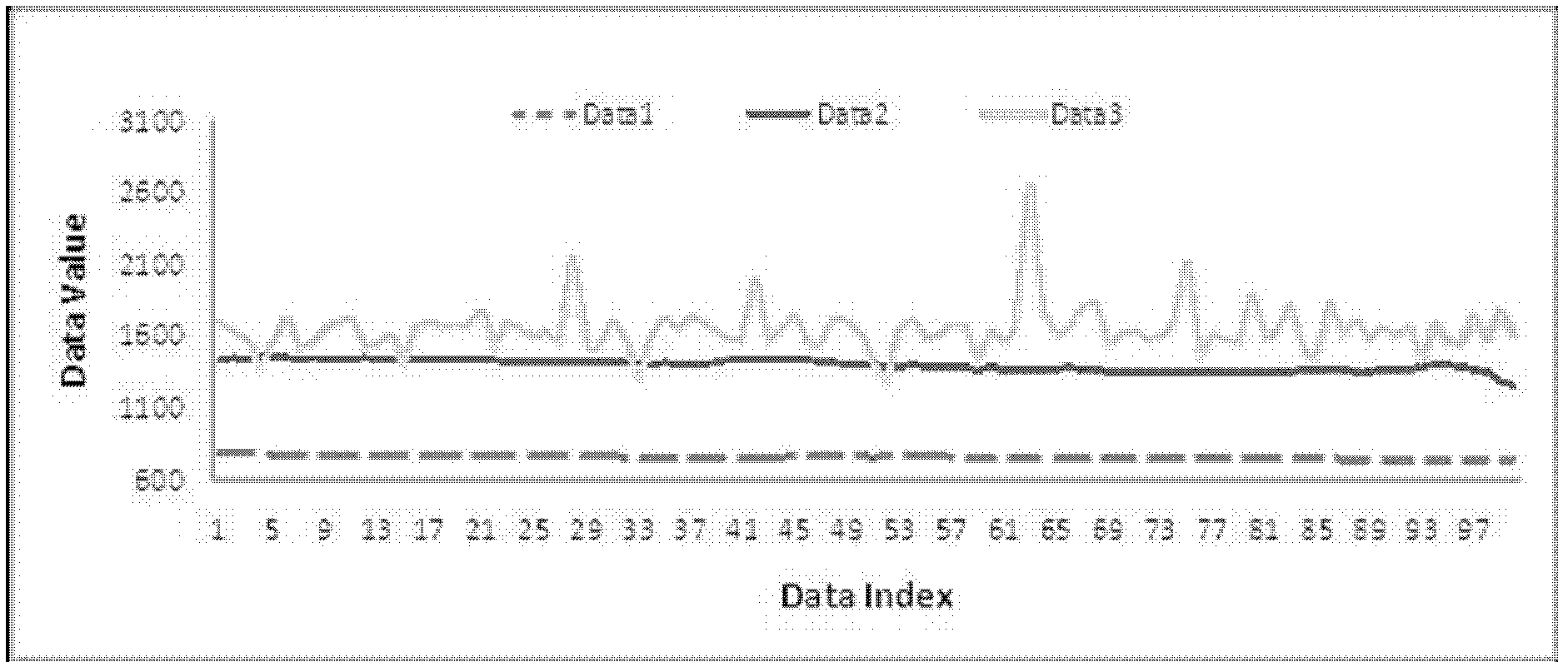
[0032] The invention divides the sensing data of the wireless sensor nodes into two types: slowly changing data and non-slowly changing data. Among them, the slow-varying data refers to the data whose standard deviation of the difference sequence of the sensor node perception data is less than or equal to 3, and the fluctuation degree of the slowly-varying data is small; Variable data, non-slowly variable data fluctuate greatly.
[0033] The analysis of the probability distribution characteristics of sensor node perception data is as follows:
[0034] The data to be collected by sensor nodes is a function that changes with time. For each specific moment, due to the influence of factors such as various interferences and node acquisition accuracy, there is a slight error between the actually collected data and the real value. Obviously, the data collected by the sensor d i and the real collected volume m i have d i =m i +ε i , ε i ~N(0,σ i 2 ), where ε i is the error, σ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com