Method for distributing wireless sensor nodes for nuclear pollution detection
A wireless sensor and nuclear detection technology, applied in the field of nuclear pollution detection, can solve problems such as low work efficiency, long working hours, and time-consuming, and achieve the effect of improving work efficiency, improving work efficiency, and avoiding path duplication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
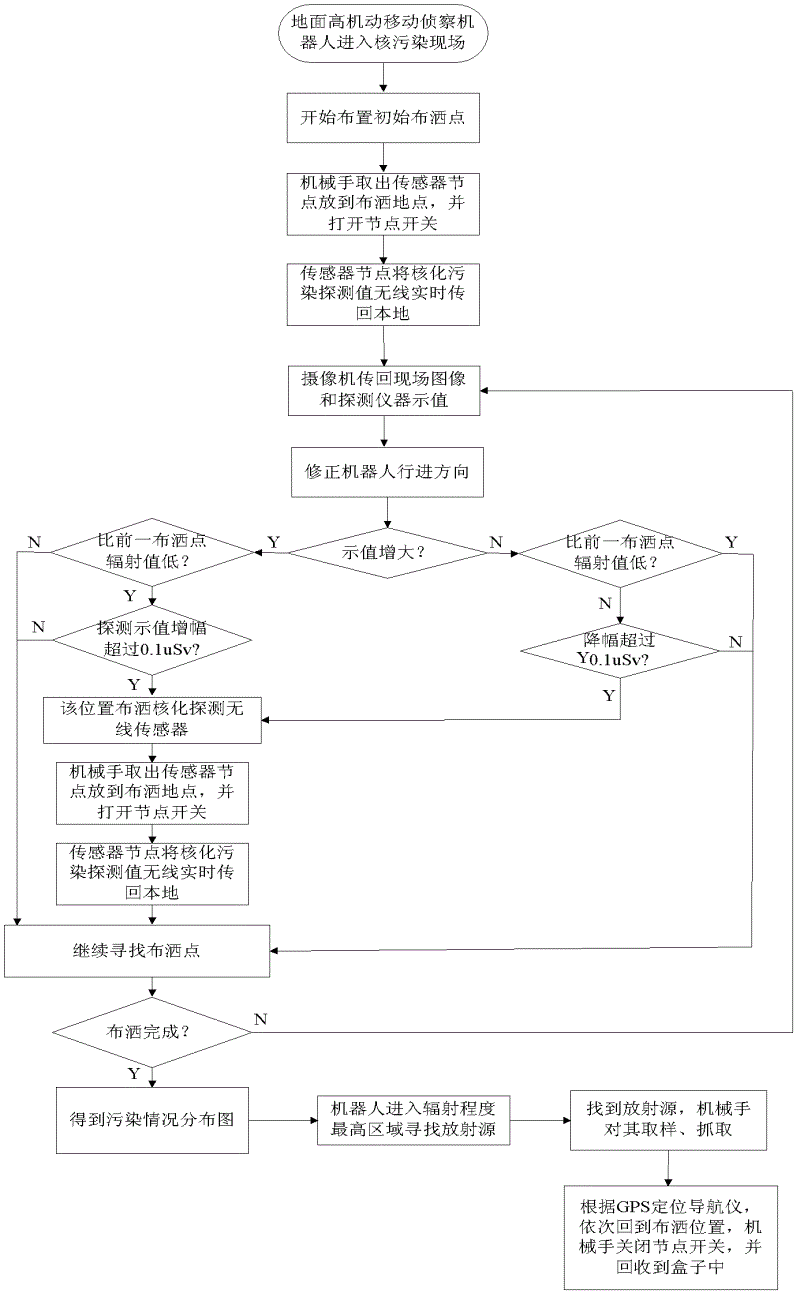
[0019] The method for distributing nuclear pollution detection wireless sensor nodes of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
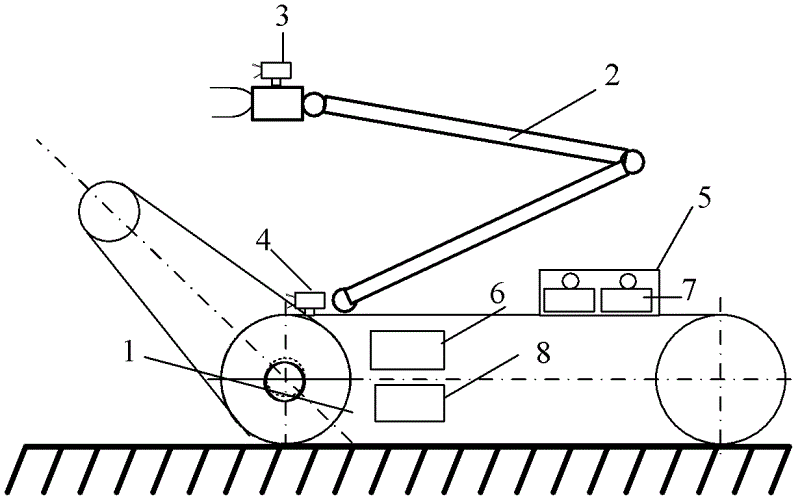
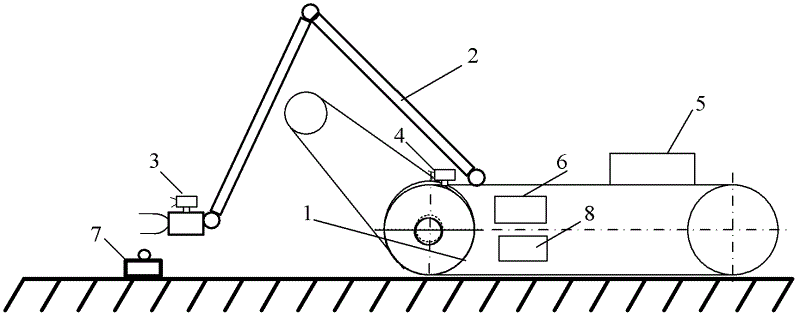
[0020] like figure 1 As shown, a manipulator 2, a first camera 3, a second camera 4, a nuclear detector 8 and a GPS positioning navigator 6 are installed on the ground high-mobility mobile reconnaissance robot 1, and a nuclear detection wireless sensor node 7 and a box 5 are carried. The detector 8 and the GPS positioning navigator 6 are installed in the robot 1, the manipulator 2 is installed on the front end of the mobile reconnaissance robot 1, the first camera 3 is installed on the end of the manipulator, the second camera 4 is installed on the head of the mobile reconnaissance robot, and the nuclear detection wireless sensor There is a key-type power switch on the node 7, and the nuclear detection wireless sensor node 7 is stored in the box 5.
[0021] like...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com