Systems and methods for improving motor function with assisted exercise
A technology of motor function and exercise, applied in sports accessories, passive exercise equipment, physical therapy, etc., can solve the problems of small drug effect and weakening the ability of patients to exercise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
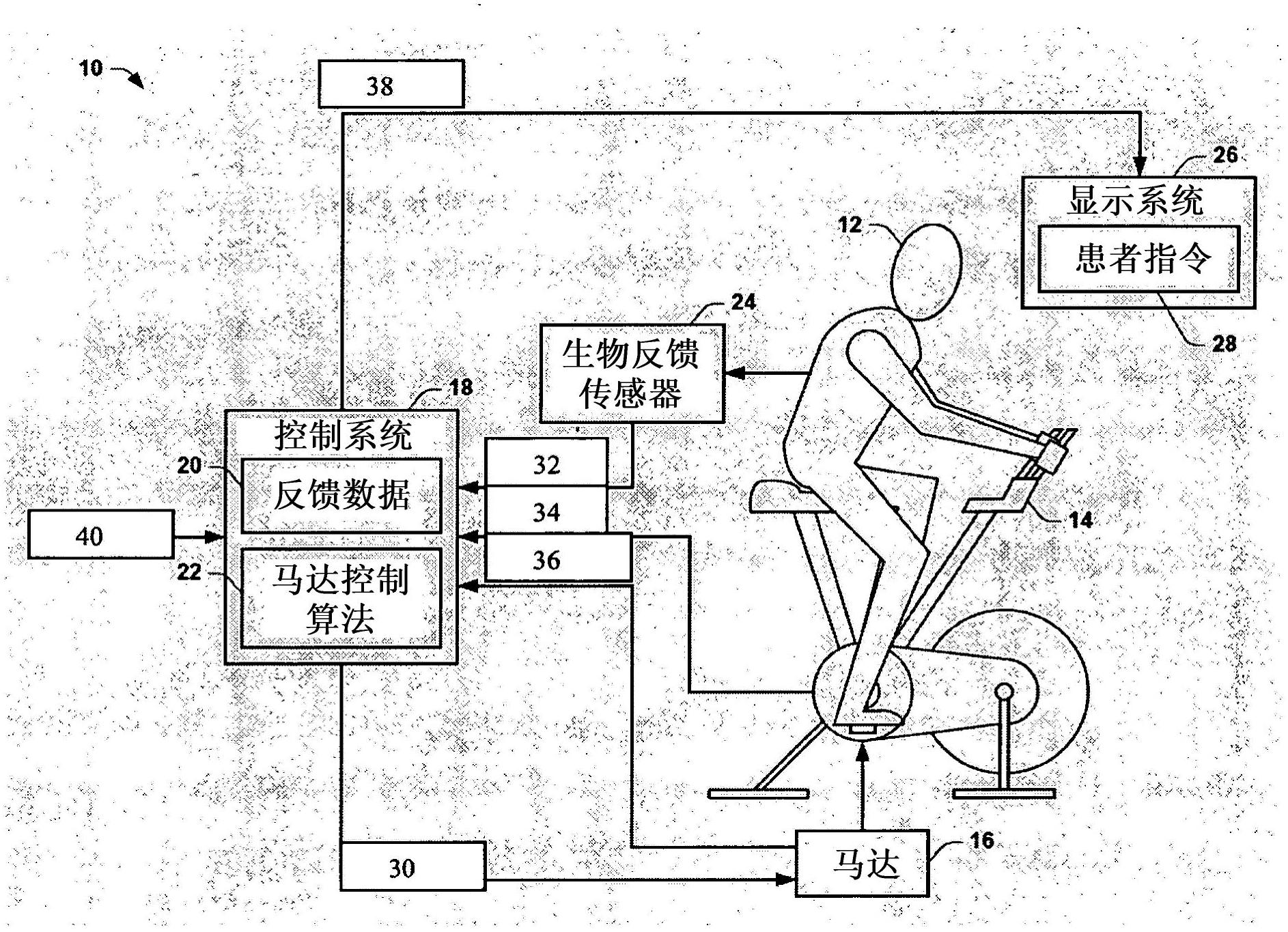
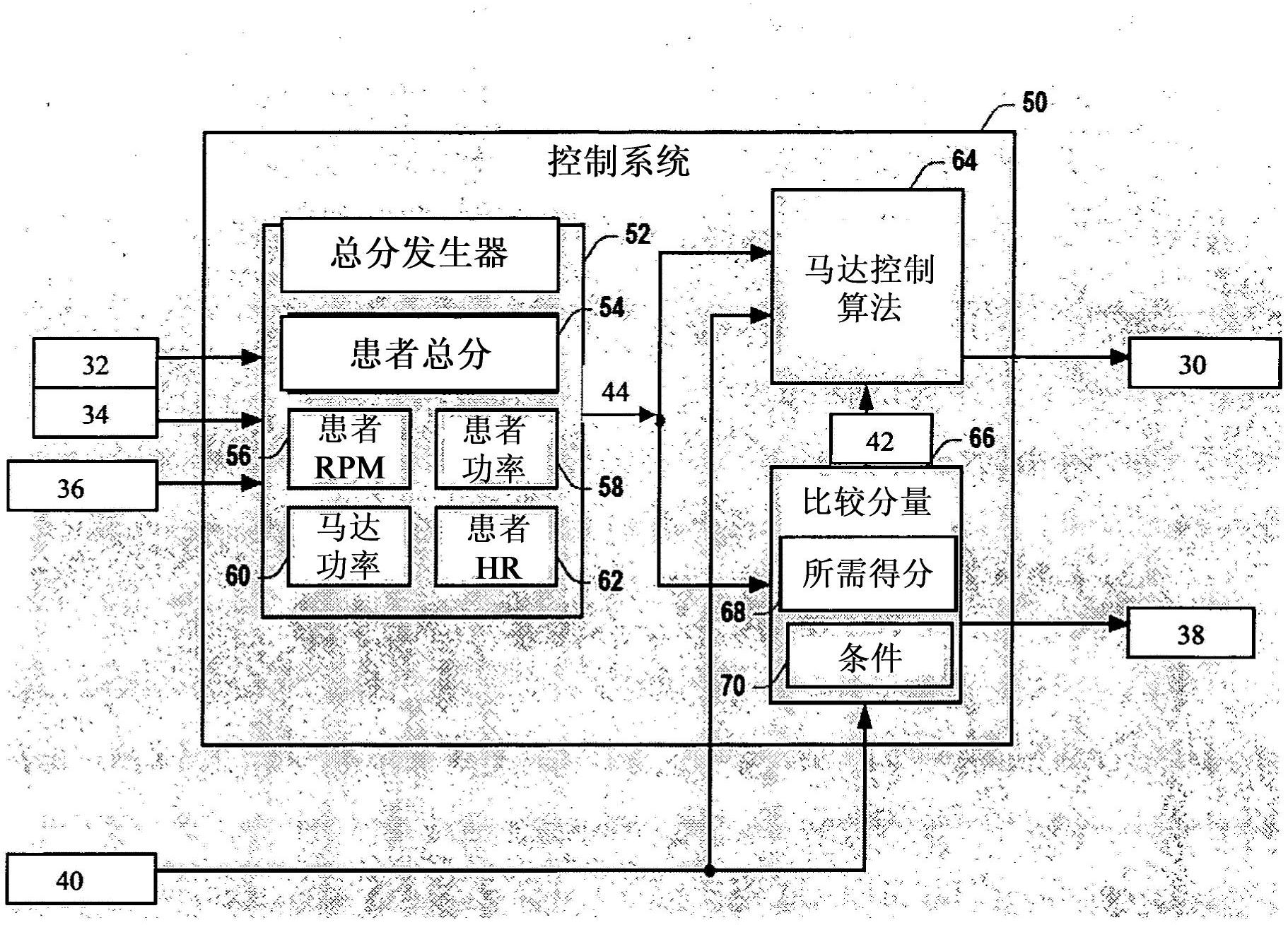
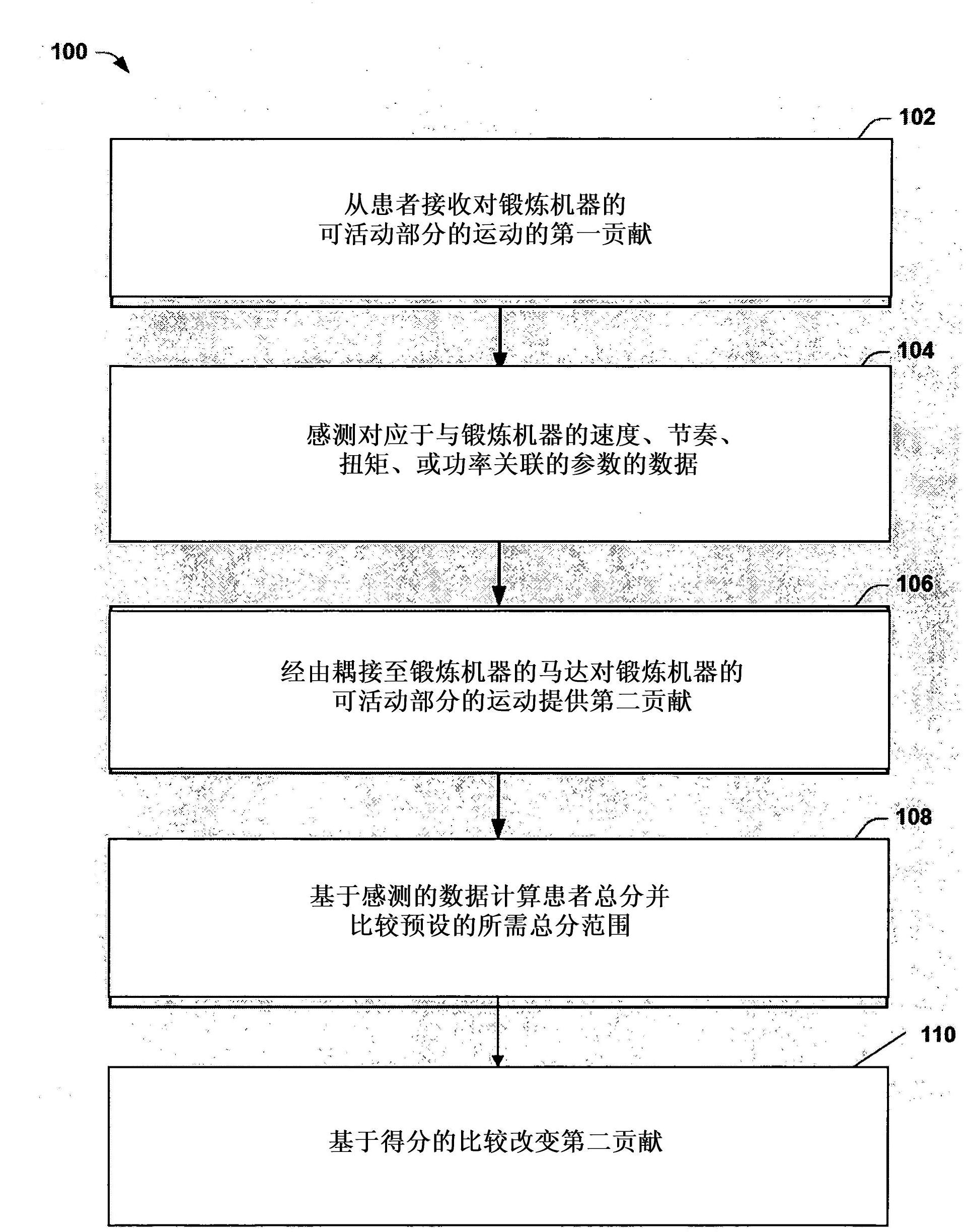
[0080] Ten patients (8 men and 2 women; age 61.2±6.0 years, Table 1) with idiopathic PD were randomly assigned to complete an 8-week forced exercise (FE) or voluntary (VE) intervention. After the 8-week intervention, patients were instructed to return to their pre-enrollment activity levels; compliance with this requirement was tracked for patient return instructions. Patients in the FE group exercised on a stationary cascaded bicycle with the training machine ( Figure 4 a), however the VE group (Schoberer Rad Me βtechnik (SRM)) was exercised on a stationary single bicycle. The work performed by the patient and the trainer on the cascade bicycle was measured independently with 2 commercially available power meters (SRM PowerMeter; Jülich, Germany).
[0081] Table 1
[0082] group statistics a
[0083]
[0084] Abbreviations: bpm, heartbeat per minute; EOT, end of training; EOT+4, 4 weeks after EOT; kJ, kilojoules; PD, Parkinson's disease; rpm, revolutions per minute; U...
Embodiment 2
[0112] Using an MRI protocol including whole-brain MPGR anatomical images, diffuse tensor muscle imaging, and functional MRI (fMRI), the effects of vigorous compulsive exercise on brain activation patterns were investigated in six patients with mild to moderate PD. For all scanning sessions, patients were "off" anti-Parkinsonian medications. Patients were scanned under two conditions, no exercise and after forced exercise. The order of these scans was randomized among the six patients and the scans were separated by 5-7 days. Over two days, patients reported to the laboratory at approximately 9 am and completed UPDRS and biomechanical testing, and completed a familiarization test with a motor task to be performed within the scanner. On forced exercise days, patients performed 40 minutes of forced exercise (same as demonstrated in Example 1) and were clinically assessed with UPDRS, blinded assessment. After completing these activities, the patient rested and was offered a sna...
Embodiment 3
[0120] In a situation similar to that described in Example 2, mean fMRI data from ten patients in three different groups (drug off, on drug, and off drug and underwent forced exercise) were obtained at Figure 9 shown in . This fMRI data demonstrates activation of supplementary motor areas of the cortex (top image) and basal ganglia (bottom image) after forced exercise.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com