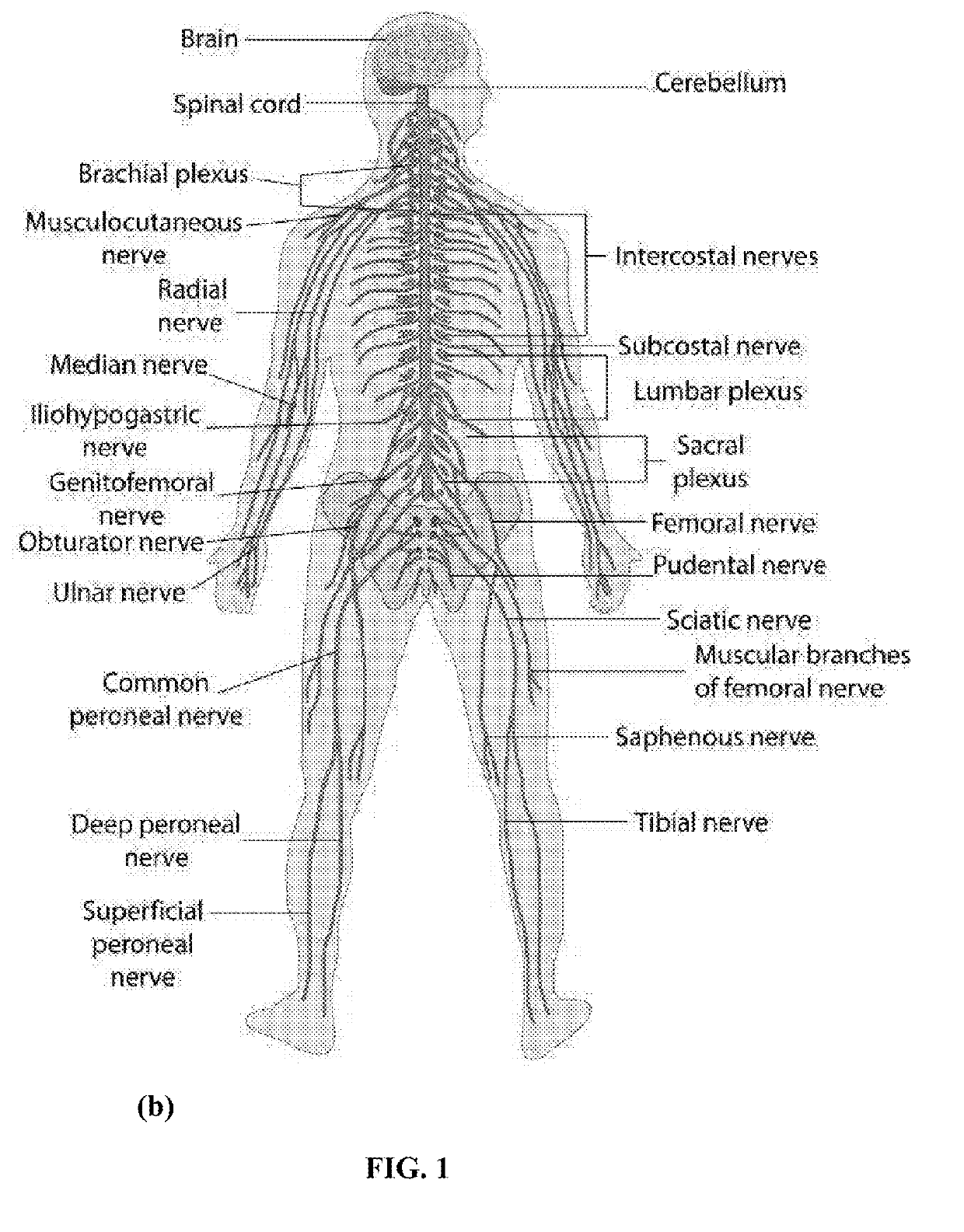
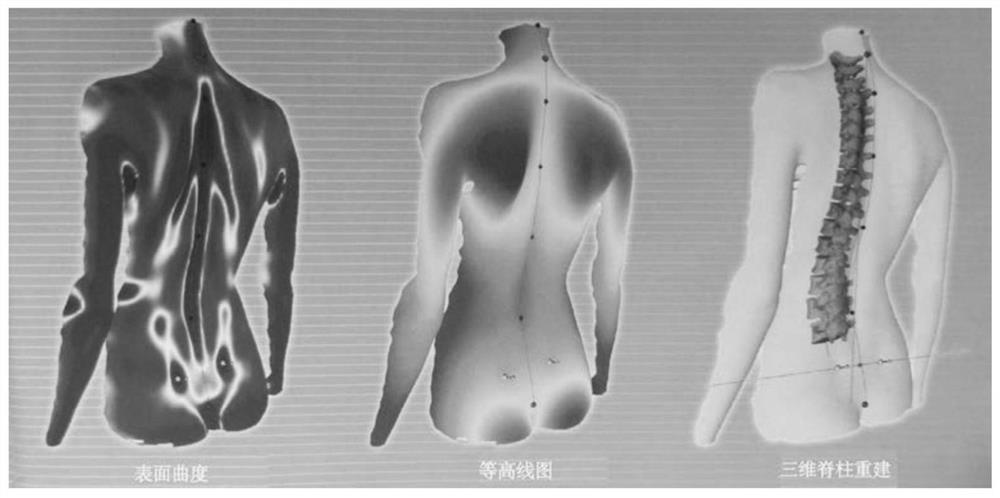
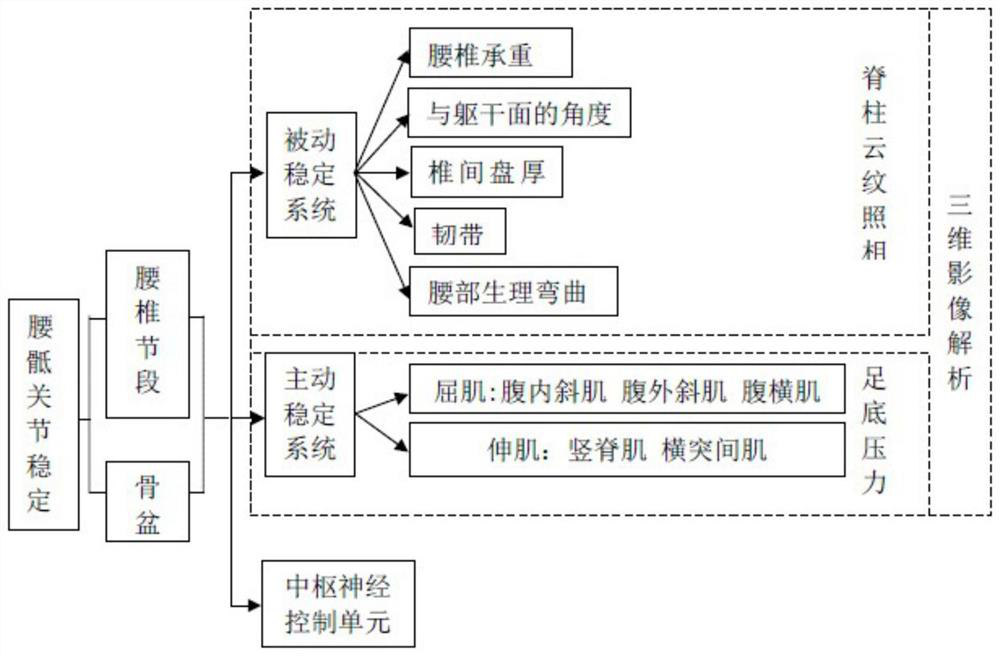
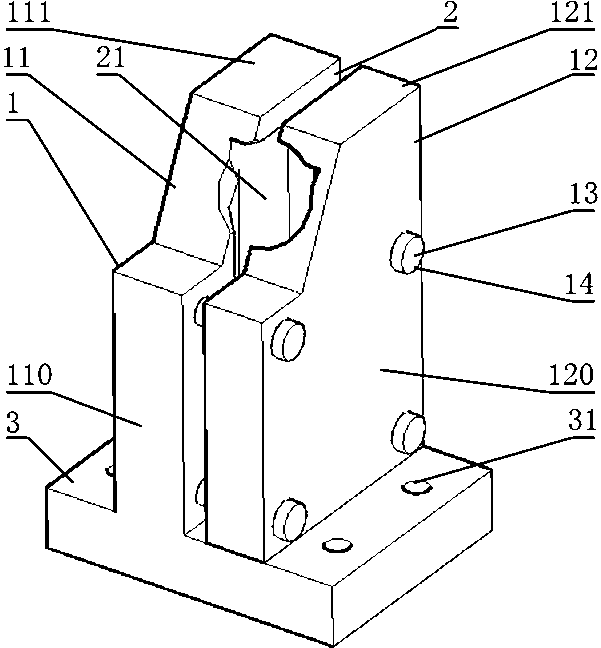
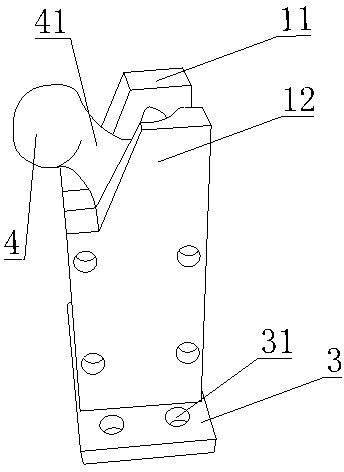
Patents
Literature
78 results about "Biomechanical testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
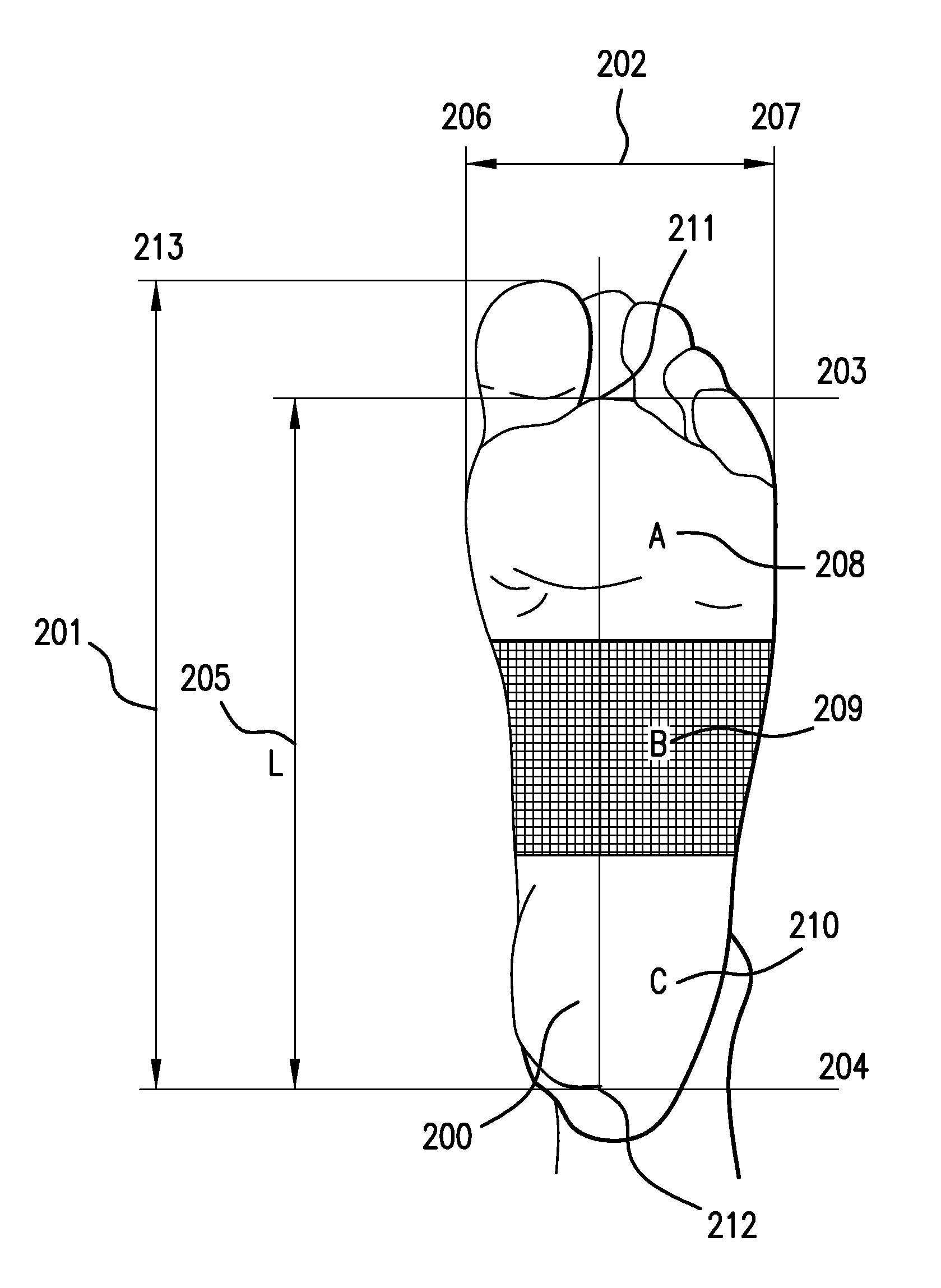
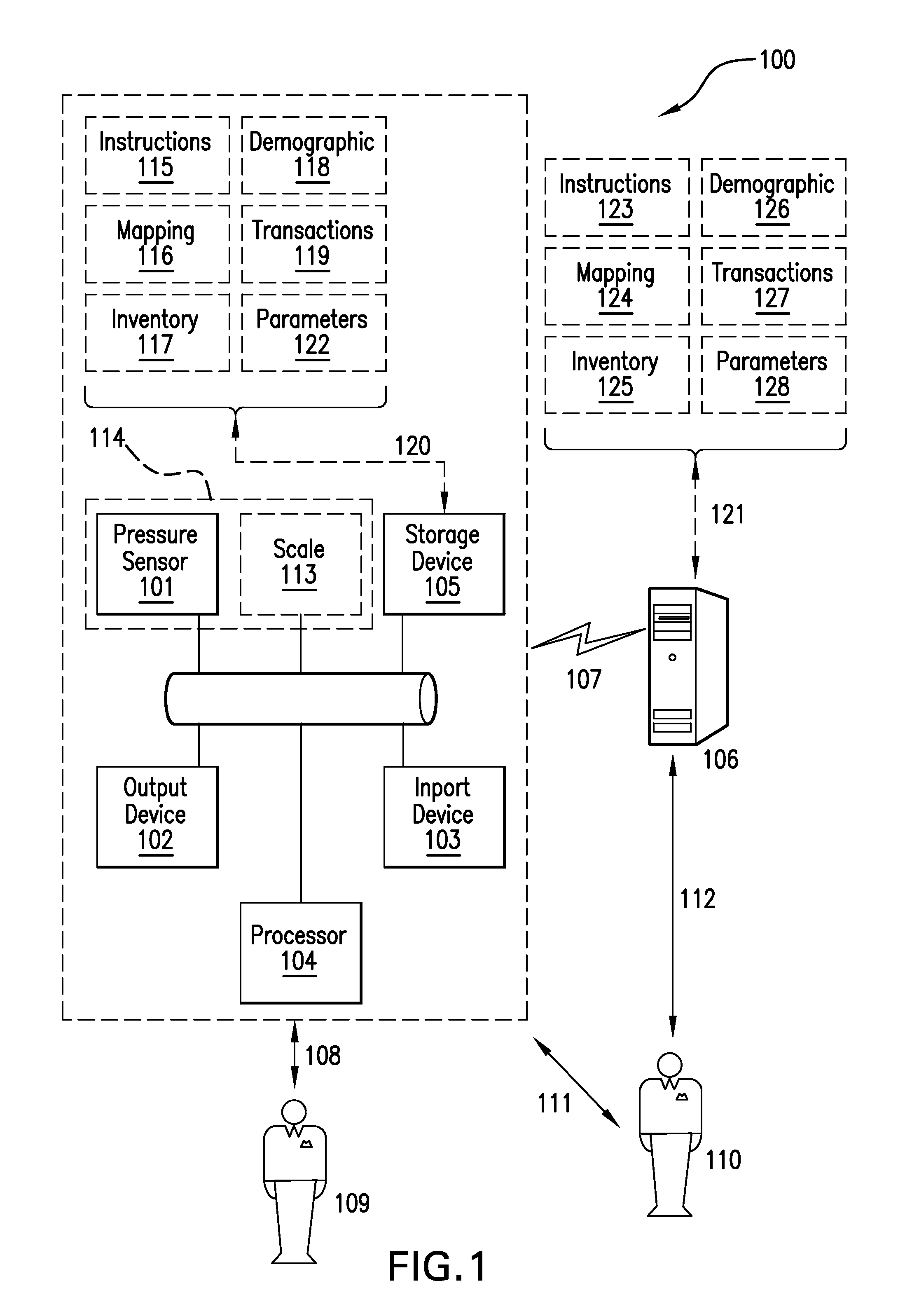
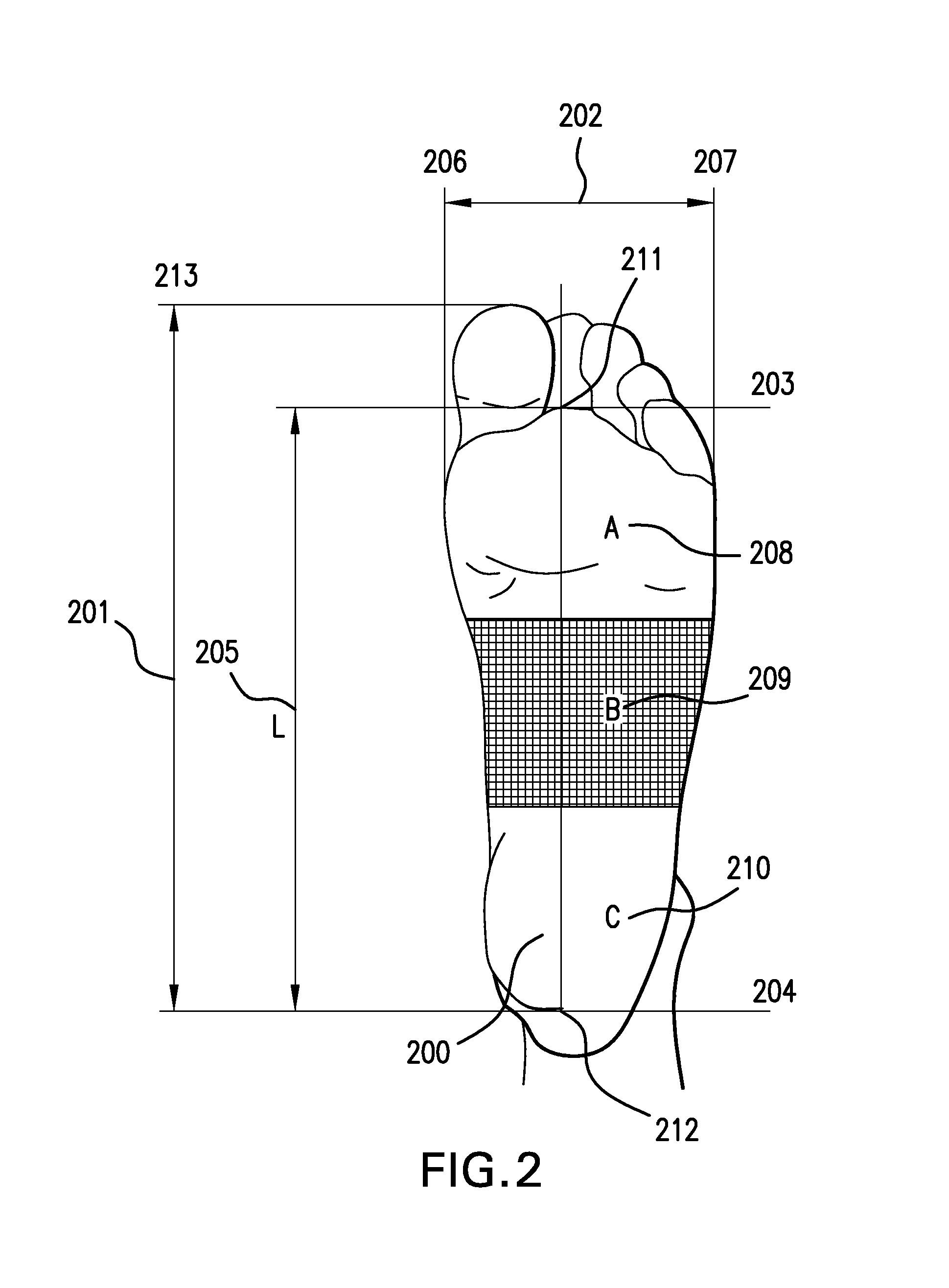
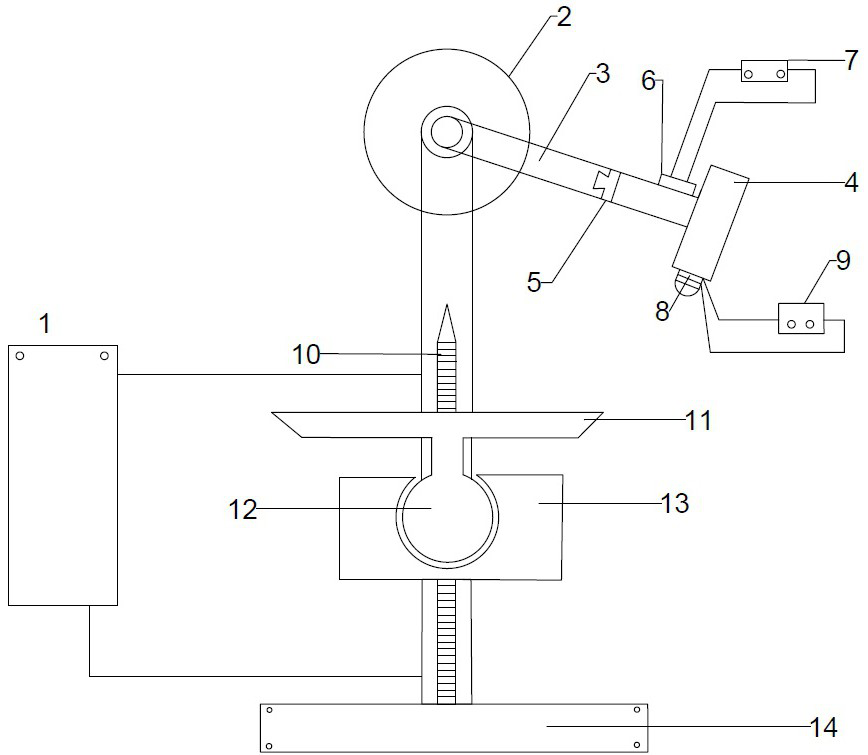
Footcare product dispensing kiosk
InactiveUS20120198949A1Foot measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringProduct base
A kiosk apparatus that may select for a person a recommended footcare product based on pressure measurements collected from pressures sensors or calculated biomechanical data estimates. Pressure measurements and calculated biomechanical data estimates may be used to determine if a foot is unshod on the pressure sensor and also group a person into a classified subgroup. The pressure measurement and calculated biomechanical data estimates may also be used to select a recommended footcare product.
Owner:MSD CONSUMER CARE INC
Smart joint care
ActiveUS20160030281A1Effective painEffective edema reliefDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesBiomechanicsEngineering
A system that applies vibration to a desired region of a human body comprising a plurality of vibratory stimulators installed in a flexible material; a programmable control unit (PCU) connected to each said vibratory stimulator a plurality of sensors to collect biofeedback data; a set of programs for the operation of the PCU; a biomechanical database stored in a computer and being populated by the biomechanical data collected by the sensors after application of each said predefined pattern of vibration; and an algorithm to analyze and rank said patterns of vibration according to a ranking factor, wherein a user can choose a pattern of vibration that has a higher ranking factor.
Owner:SHAFIELOO IMAN
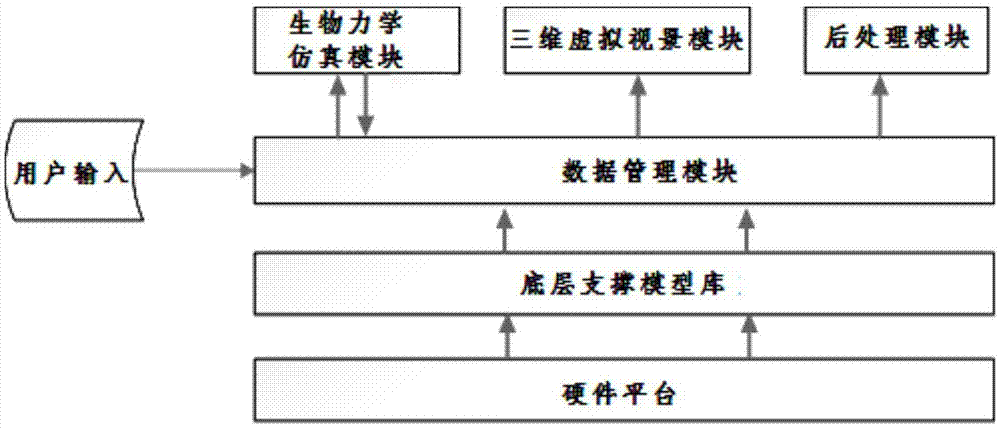
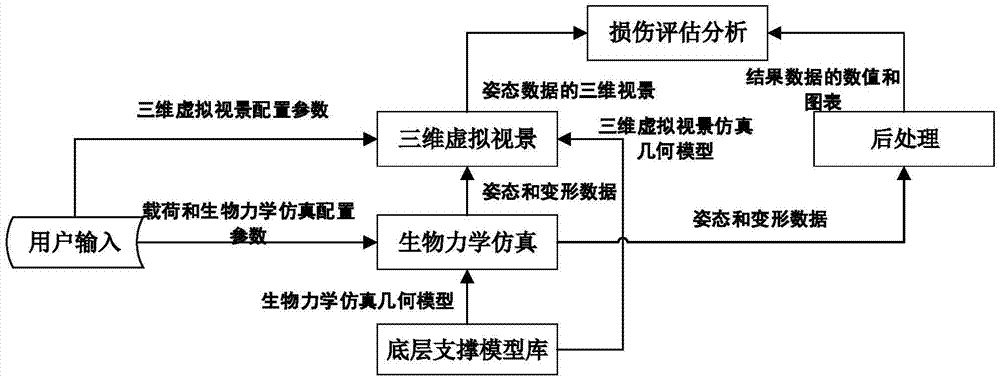
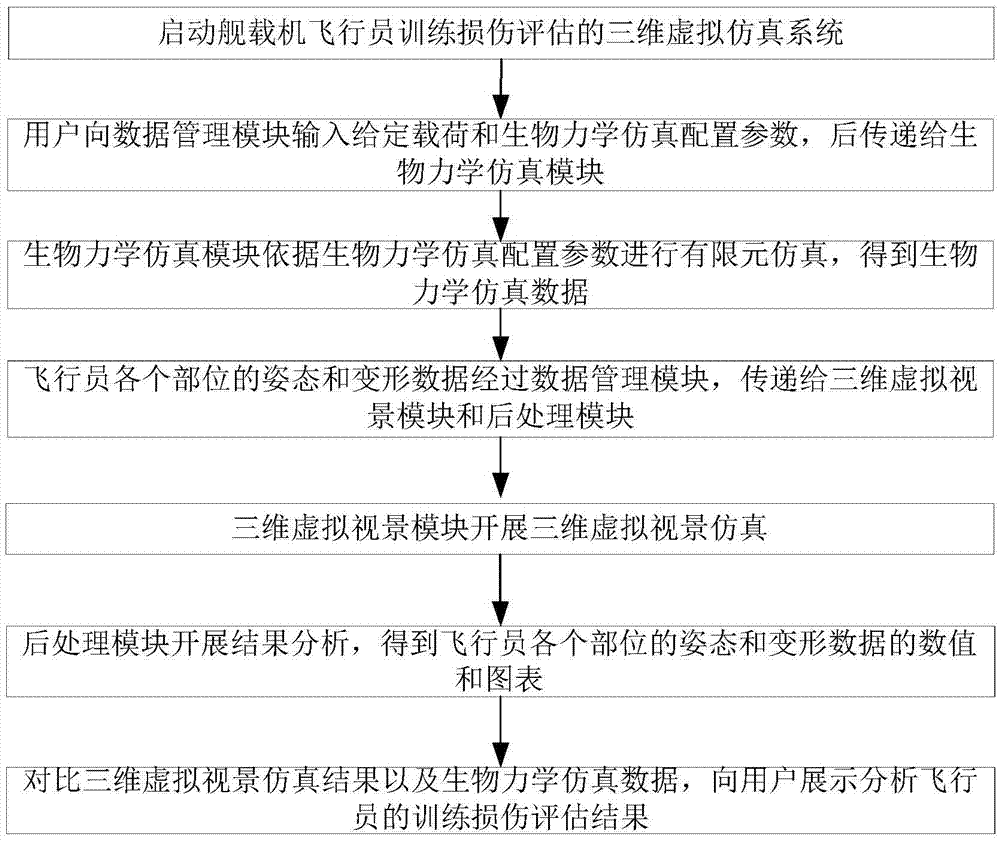
Three dimensional virtual simulation system and simulation method for shipboard aircraft pilot training injury assessment
ActiveCN105448159ASolve the repeatabilityAddress riskCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsBiomechanicsComputer module
The invention discloses a three dimensional virtual simulation system and simulation method for shipboard aircraft pilot training injury assessment. The three dimensional virtual simulation system comprises a hardware platform, a bottom layer support model base, a data management module, a bio-mechanical simulation module, a three dimensional virtual scene view module and a post processing module. The three dimensional virtual simulation method comprises: the data management module receives the data and configuration parameters input by a user, and transmits configuration parameter management to the bio-mechanical simulation module and the three dimensional virtual scene view module; the obtained bio-mechanical simulation data is transmitted to the post processing module and the three dimensional virtual scene view module respectively; three dimensional virtual scene view simulation is carried out and the result is stored; and by means of comprehensive comparison between the three dimensional virtual scene view simulation data and the bio-mechanical simulation data, the training injury assessment result for pilots are displayed and analyzed to the user. The three dimensional virtual simulation system and simulation method for shipboard aircraft pilot training injury assessment solve the defects of nonrepeatability and high risk of a traditional experimental study, and have the advantages of being high in efficiency, having repeatability and being low in cost.
Owner:PLA NAVY GENERAL HOSIPTAL +2
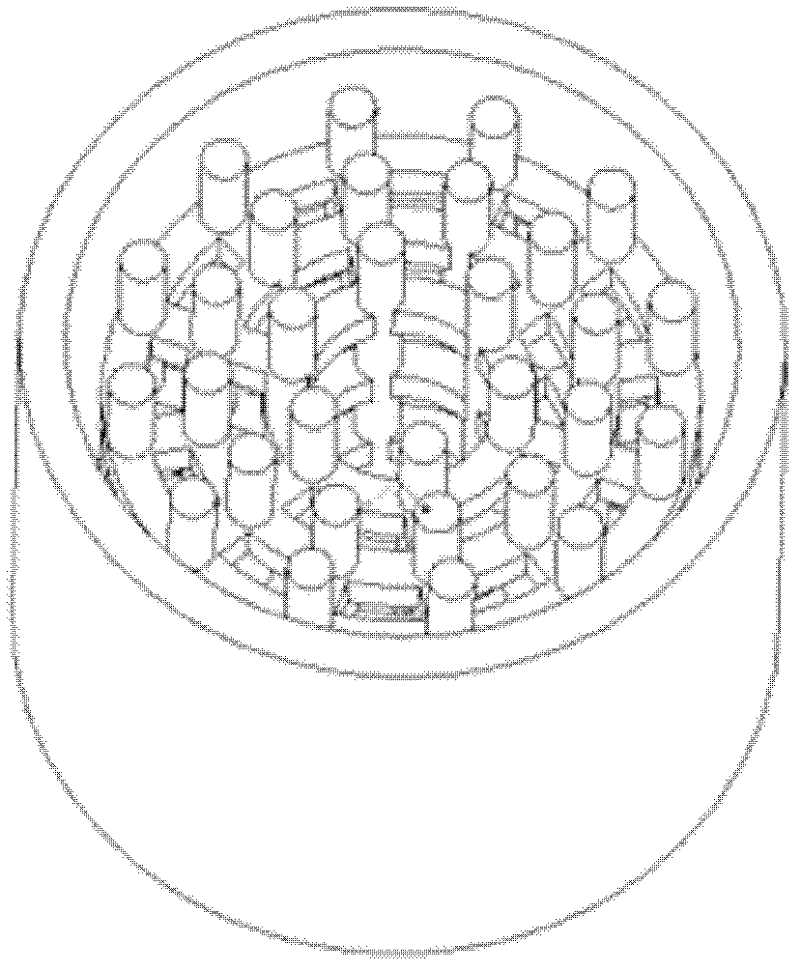
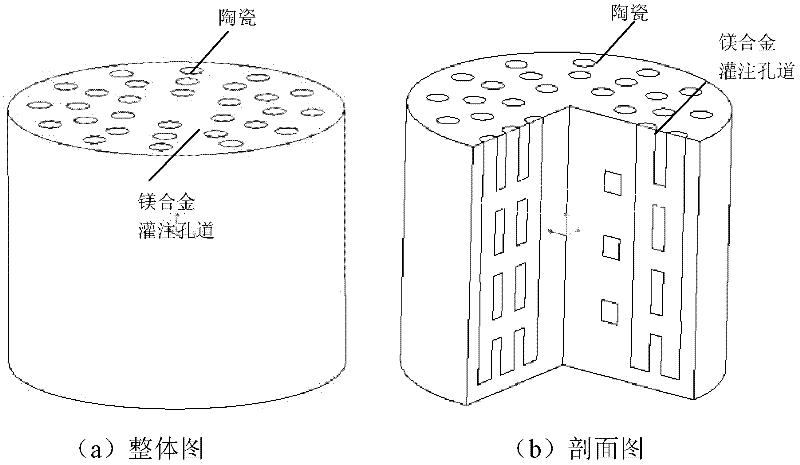
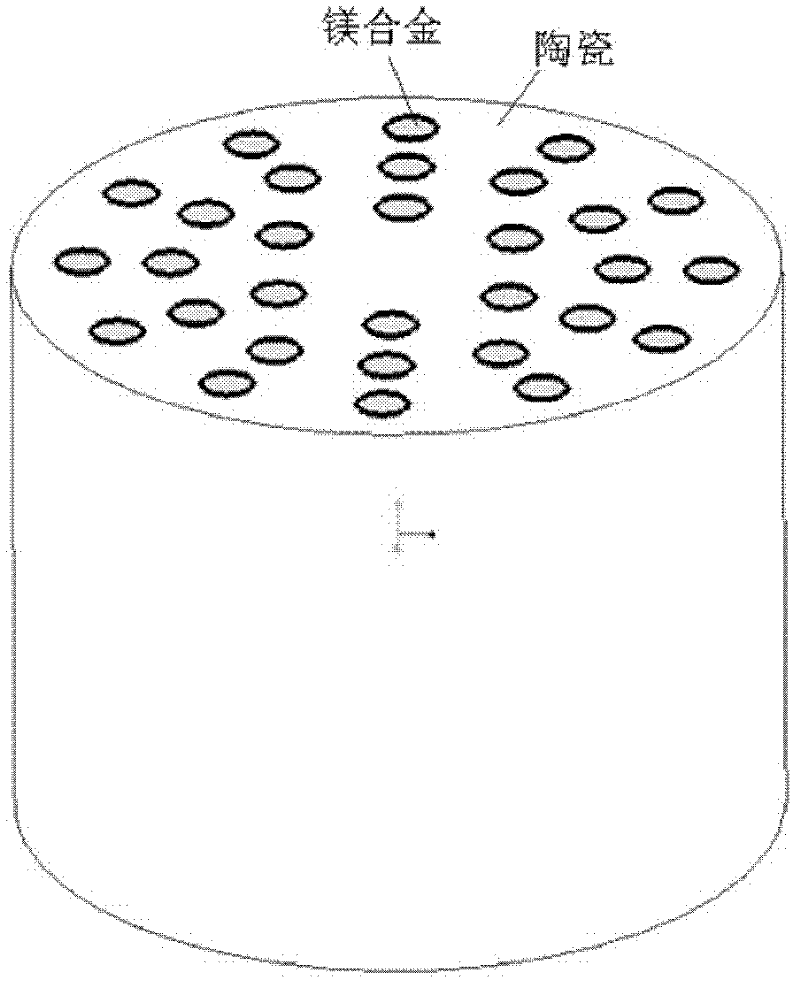
Magnesium alloy/biological ceramic bone bracket based on photocuring and gel casting and forming method of bone bracket
InactiveCN102335460AImprove early mechanical propertiesMeet growthBone implantBiomechanicsGel casting
The invention discloses a magnesium alloy / biological ceramic bone bracket based on photocuring and gel casting and a forming method of the bone bracket. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing computer-aided design (CAD) models of the bracket and a bracket negative model through shape correlation and microstructure simulation by using reverse engineering and CAD according to the structures of different bone defect parts and the analysis results of biomechanics; making a resin bracket negative model by a photocuring technology; filling ceramic slurry into the bracket negative model by a gel casting process, curing and sintering at a high temperature to make a biological activity ceramic framework with mutually-communicated porous pipelines; and casting molten magnesium alloy into the porous pipelines of the biological activity ceramic framework by a vacuum suction casting method, cooling for solidification, and thus obtaining the magnesium alloy / biological ceramic simulation composite structure bone bracket. The internal microstructure of the made bracket consists of the mutually-communicated pipelines, the magnesium alloy is filled in the pipelines to increase the early mechanical property of the composite bracket, and the pipelines filled with the magnesium alloy become mutually-communicated pore passages as the magnesium alloy is corroded and degraded, so that the requirements of organization growth, nutrition and metabolism are met.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
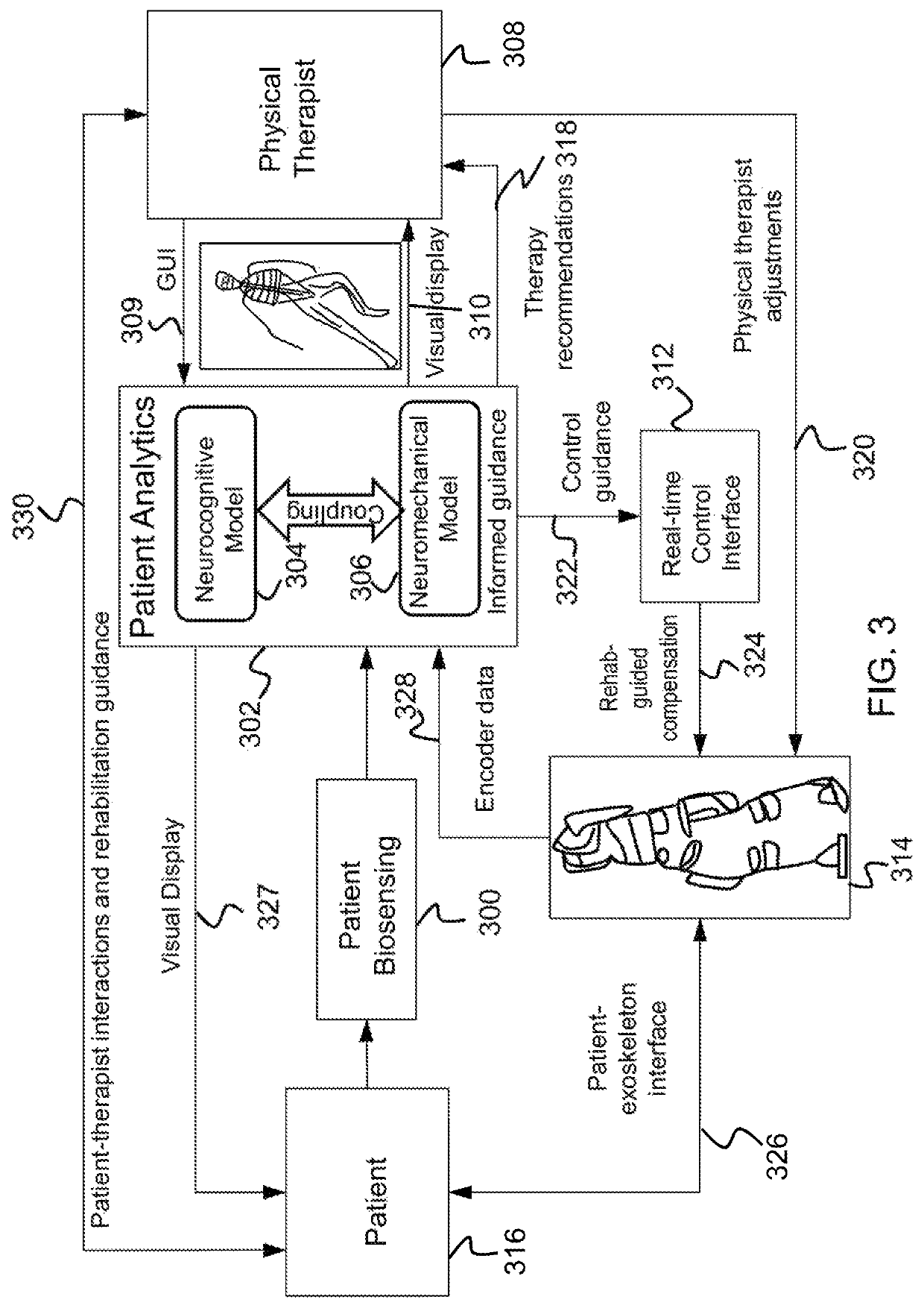
Integrated platform to monitor and analyze individual progress in physical and cognitive tasks
Described is a system for online characterization of biomechanical and cognitive factors relevant to physical rehabilitation and training efforts. A biosensing subsystem senses biomechanical states of a user based on the output of sensors and generates a set of biomechanical data. The set of biomechanical data is transmitted in real-time to an analytics subsystem. The set of biomechanical data is analyzed by the analytics subsystem, and control guidance is sent through a real-time control interface to adjust the user's motions. In one aspect control guidance is sent to a robotic exoskeleton worn by the user to adjust the user's motions.
Owner:HRL LAB
Biomechanical monitoring apparatus
InactiveUS20090043230A1Effective warningExpensive to maintainPerson identificationInertial sensorsMovement activityBiomechanics
The present invention relates to a biomechanical monitoring apparatus (1) which includes a mounting means adapted to allow the apparatus to be worn by a user and a motion a detection means (2) adapted to detect the motion of a user when the apparatus is worn. The apparatus also includes an accumulation means (4) adapted to indicate the extent of motion activity completed by a user since a specific time. The invention also relates to a method of using such apparatus where the extent of motion activity completed is compared against at least one movement activity threshold level to potentially activate an alarm indicator when such thresholds are exceeded.
Owner:MOVEMENT METRICS
Real-time and accurate soft tissue deformation prediction
For soft tissue deformation prediction, a biomechanical or other tissue-related physics model is used to find an instantaneous state of the soft tissue. A machine-learned artificial neural network isapplied to predict the position of volumetric elements (e.g., mesh node) from the instantaneous state. Since the machine-learned artificial neural network may predict quickly (e.g., in a second or less), the soft tissue position at different times or a further time given the instantaneous state is provided in real-time without the minutes of physics model computation. For example, a real-time, biomechanical solver is provided, allowing interaction with the soft tissue model, while still getting accurate results. The accuracy allows for generating images of a soft tissue with greater accuracy and / or the benefit of user interaction in real-time.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
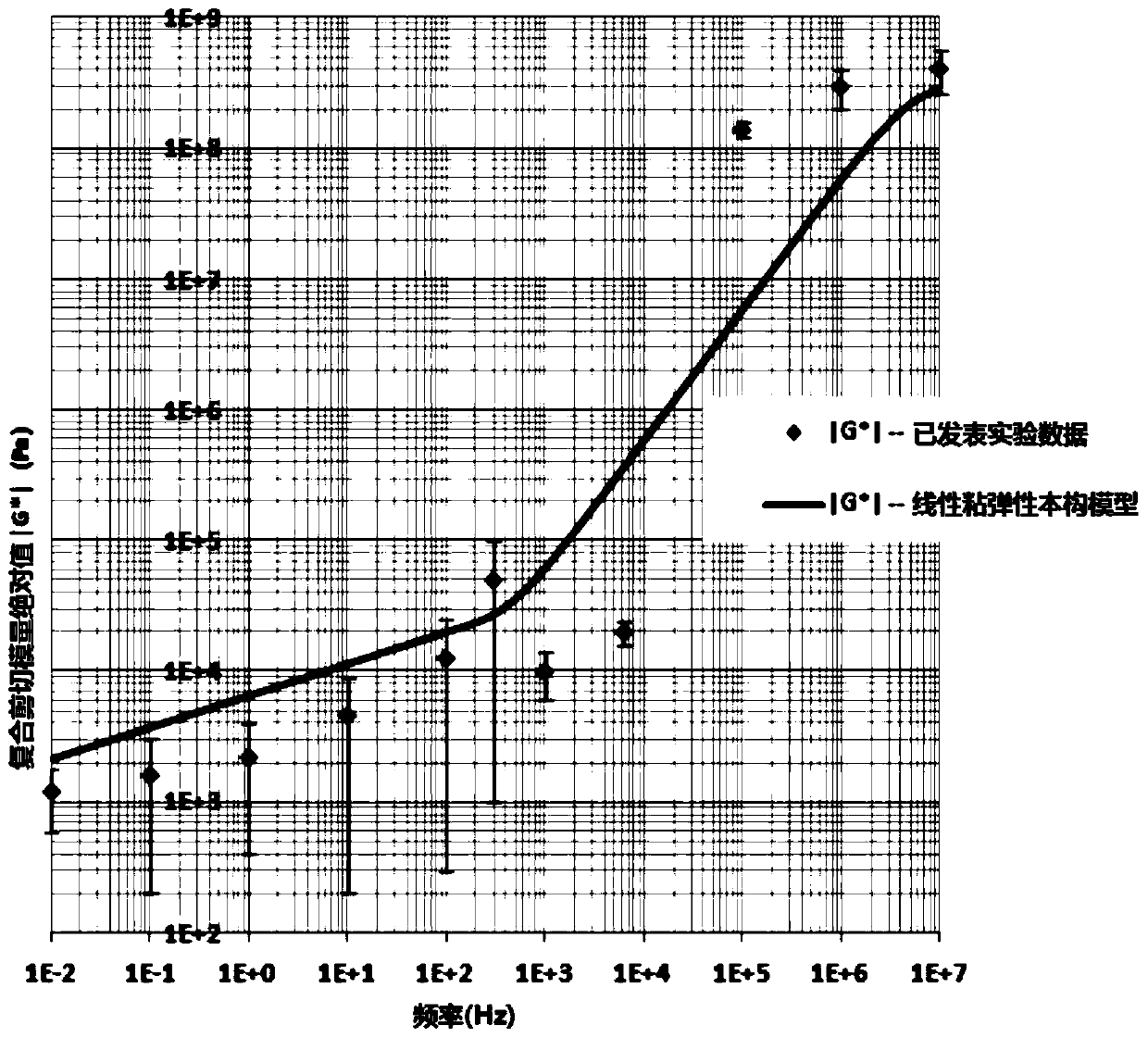
Measuring method and measuring platform for biomechanical performance parameters of in vitro corneas
InactiveCN103674829ARealize measurementUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisPhysicsConstitutive equation
The invention relates to a measuring method and a measuring platform for biomechanical performance parameters of in vitro corneas. The measuring method comprises the following steps: 1, fixing a cornea sample and spraying powder; 2, continuously exerting pressure to deform the cornea sample and recording a pressure value; 3, recording the variations of intervals of powder particles; 4, computing the three-dimensional deformation in each area of the surface of the cornea sample; 5, computing the biomechanical performance parameters through a general constitutive equation. The measuring platform comprises a mounting platform, wherein a cornea fixing device is mounted on the mounting platform and provided with an inner chamber; a clamping end for clamping the cornea sample is arranged at one end of the inner chamber; the other end of the inner chamber is connected with a pressure unit; shooting equipment is arranged at the front end of the cornea fixing device; the pressure unit is connected with a pressure sensor; pressure on the cornea sample is monitored by the pressure unit and the pressure sensor, and deformation of the cornea sample is recorded by the shooting equipment, so that the measurement of regional differences of constitutive parameters of corneas is realized so as to provide references for diagnosis and treatment of related cornea diseases.
Owner:THE EYE HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV +1
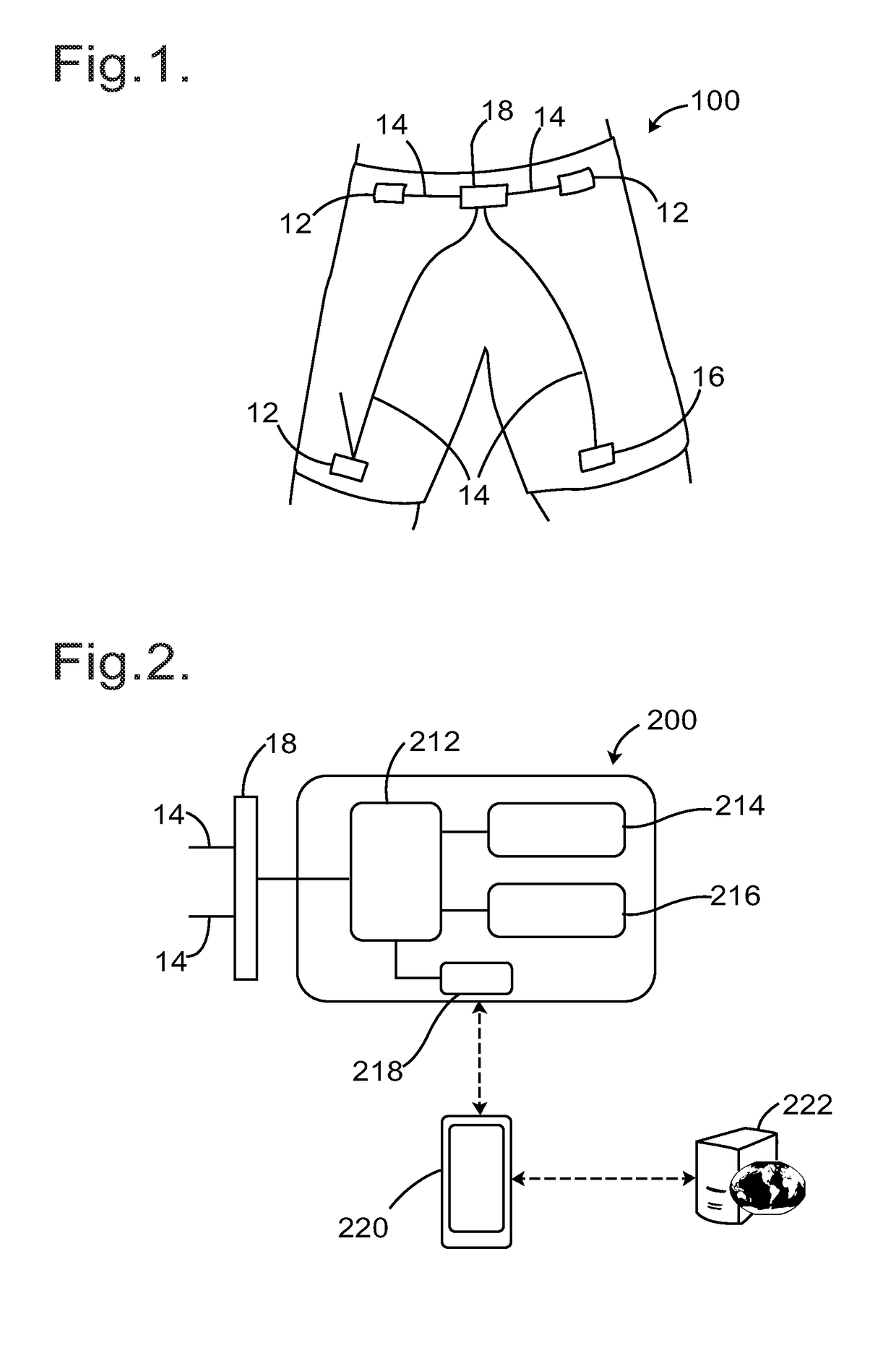
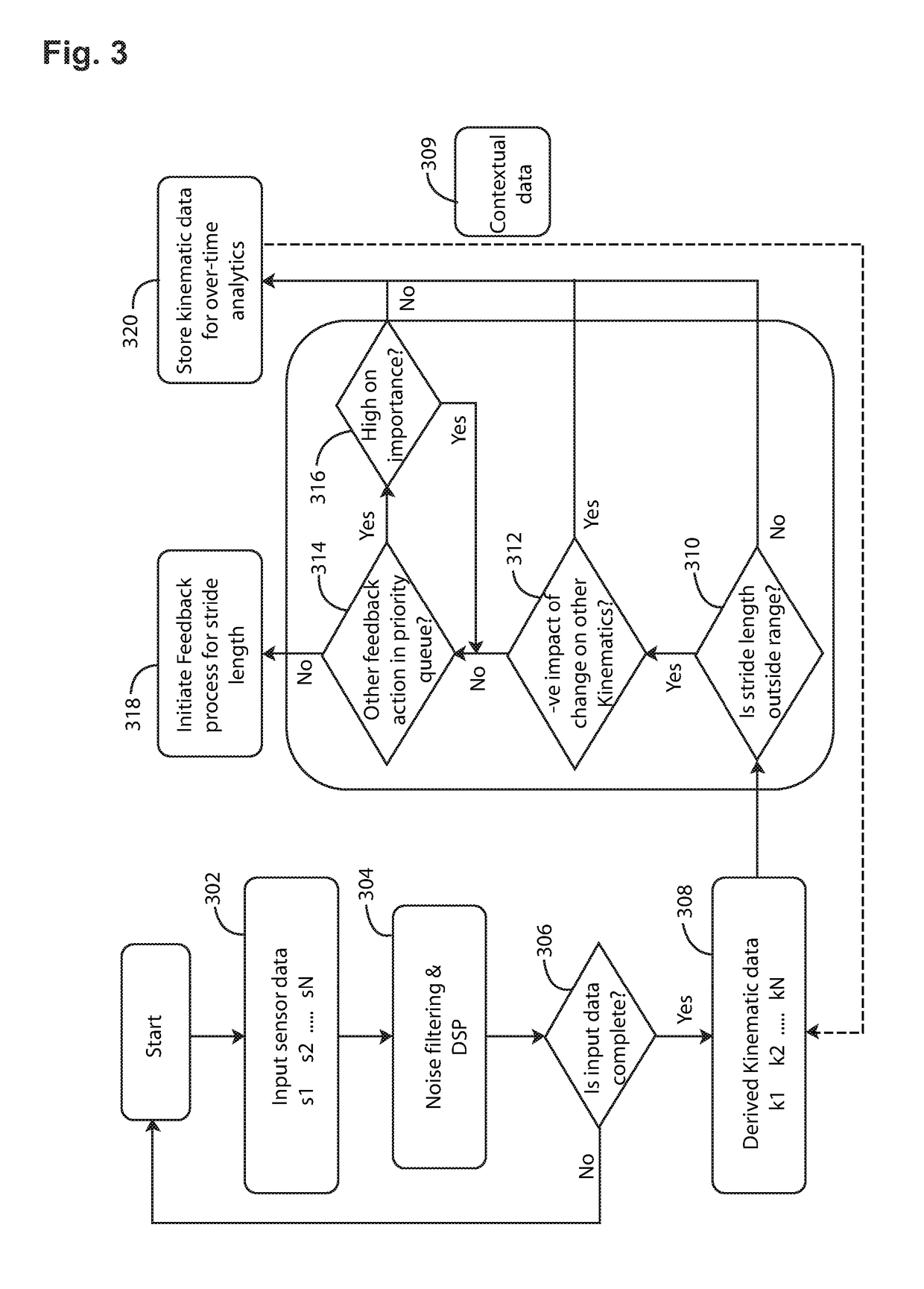
System and Method for Monitoring the Running Technique of a User
PendingUS20180279916A1Improve performanceReduce the possibilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiomechanical modelProcessing element
A system and method for monitoring the running technique of a user undertaking a physical activity is described. The system comprises: a garment worn by the user incorporating a sensor for the detection of a parameter relating to the movement of the pelvis of the user; a processing unit configured to receive information about the parameter from the sensor, to compare the parameter with an aspect of a biomechanical model, and to determine if a feedback response is required; and means for providing the feedback response to the user. The method comprises the steps of: measuring a parameter relating to the movement of the pelvis of the individual; comparing the parameter with a biomechanical model to determine whether a feedback response is required and providing a feedback response if required.
Owner:MAS INNOVATION
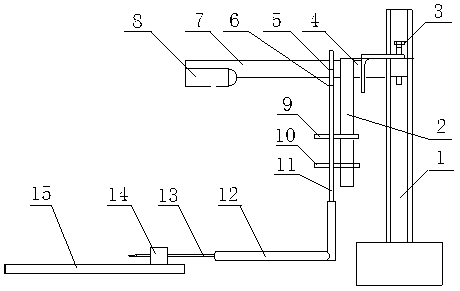
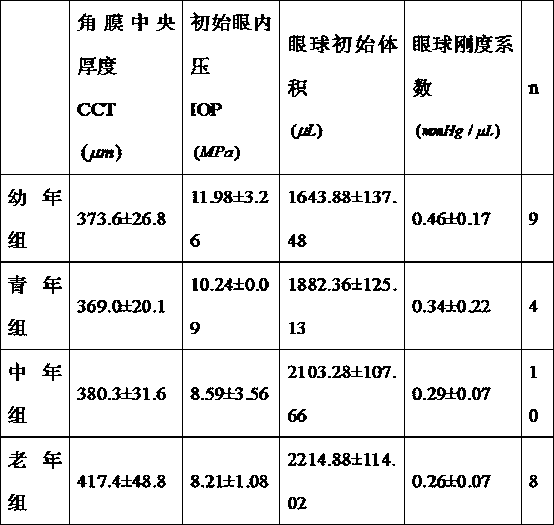
Device for measuring overall mechanical characteristics of eyeball of living animal and method of device
InactiveCN103284685AImproving the ability to detect the impact of biomechanical propertiesAccurate measurementEye diagnosticsDiseaseOPHTHALMOLOGICALS
The invention relates to a device for measuring overall mechanical characteristics of an eyeball of a living animal, and a method of the device. The device is characterized in that a movable camera and a glass tube are fixed on a lifting support; the end of the glass tube is communicated with a hose and an infusion syringe; and a stop valve and a horizontal operating platform for injecting to the eyeball of the living animal are arranged on the infusion syringe. The method comprises the steps of communicating internal and external testing devices of the eyeball in a puncture injection manner for the eyeball of the experimental animal according to a communicator principle, and calculating to obtain the overall biomechanical characteristics of the eyeball, such as rigidity and elastic modulus by changing a liquid level of the external testing device. With the adoption of the device and the method, accurate measurement of a biomechanical characteristic carrier of the eyeball of the experimental animal is realized, the detectability of influence of ocular diseases and drugs on the biomechanical characteristics of the eyeball, and theoretical data is provided for selecting LASK (Laser Assisted In-situ Keratomi) operation parameters.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Artificial intelligence assistance to change biomechanical loading
PendingUS20200078638A1Reduce the risk of injuryMinimizes probabilityPhysical therapies and activitiesInput/output for user-computer interactionPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSimulation
A system configured to generate a motion adjustment instruction for a user performing an action is provided. The system comprises: a target module configured to obtain a target biomechanical load distribution for the user, a sensor arrangement configured to monitor the motion of the user so as to obtain monitored motion data, a monitoring module configured to calculate a monitored biomechanical load distribution for the user in accordance with the monitored motion data, an adjustment module configured to calculate a target adjustment to the motion of the user that corresponds to a reduction of a deviation of the monitored biomechanical load distribution from the target biomechanical load distribution, and an instruction module configured to generate a motion adjustment instruction in accordance with the target adjustment.
Owner:ATO GEAR HLDG BV
Device and method for measuring skin soft tissue biomechanic parameters
ActiveCN108760489AAccurate and effective measurementRealize standard cuttingPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesHuman skinTissue biomechanics
The invention discloses a device and a method for measuring skin soft tissue biomechanic parameters. The device is characterized in that a set of biomechanic parameter measuring device for skin soft tissue is designed, and a skin soft tissue biomechanic parameter measuring method based on the measuring device is established. The measuring device is capable of achieving regular cutting of skin softtissue and ensuring that a skin sample does not slide or machine damage is avoided in a testing process; by adopting the measuring method, regulation of biomechanic parameter testing on human skin soft tissue can be achieved, and effectiveness and accuracy of skin soft tissue biomechanic parameter measurement can be ensured.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for real-time measurement of parameters of mechanical stress state and biomechanical properties of soft biological tissue
ActiveUS20130289365A1Avoid mechanical damageSimultaneous measurementDiagnostics using vibrationsDiagnostics using pressureSelf-oscillationBiomechanics
A device and a method for simultaneous recording, in real time, parameters characterising the mechanical tension, elasticity, dynamical stiffness, creepability and mechanical stress of soft biological tissue are provided. By means of the myometer, a constant external pre-pressure is created, independently of the device's position, between the tissue and the testing end of the device. Next, the tissue is subjected to a short-term external dynamic influence. A mechanical change in the shape of the tissue and its mechanical response are registered as a graph of the tissue's oscillations. For calculating the parameters, a time span on the graph is used which involves an oscillation period from the beginning to the end of the effect on the tissue plus its subsequent first 1.5 self-oscillation period. This enables recording and data-processing to be carried out simultaneously as well as statistically significant estimates to be made in real time.
Owner:MYOTON
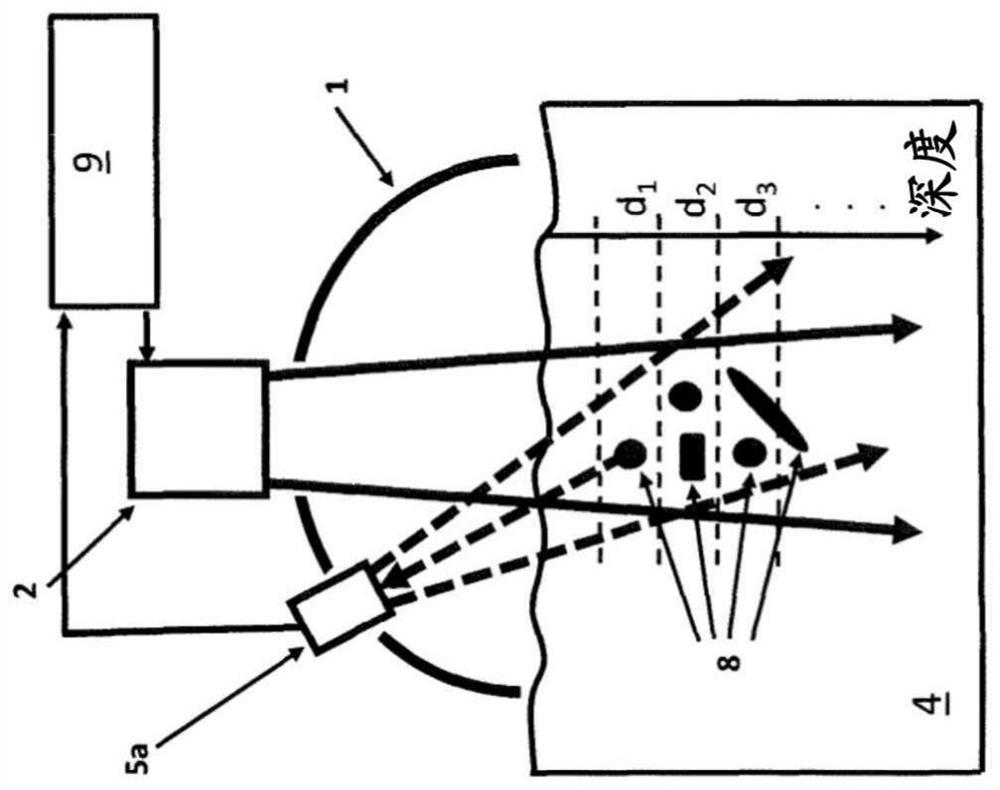
Diagnostic for in situ deformation and strain measurements applicable to traumatic internal injury investigation and prevention
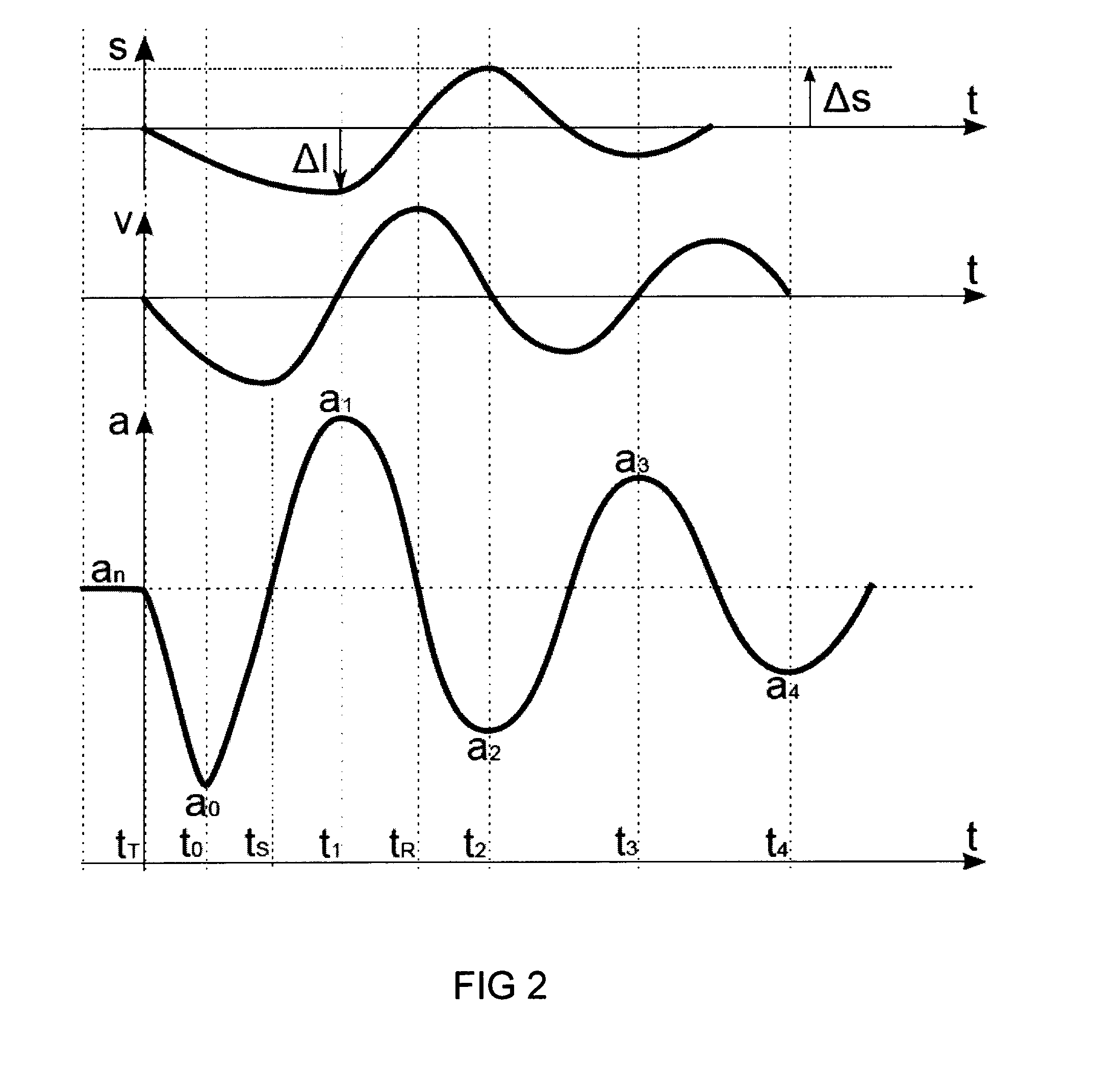
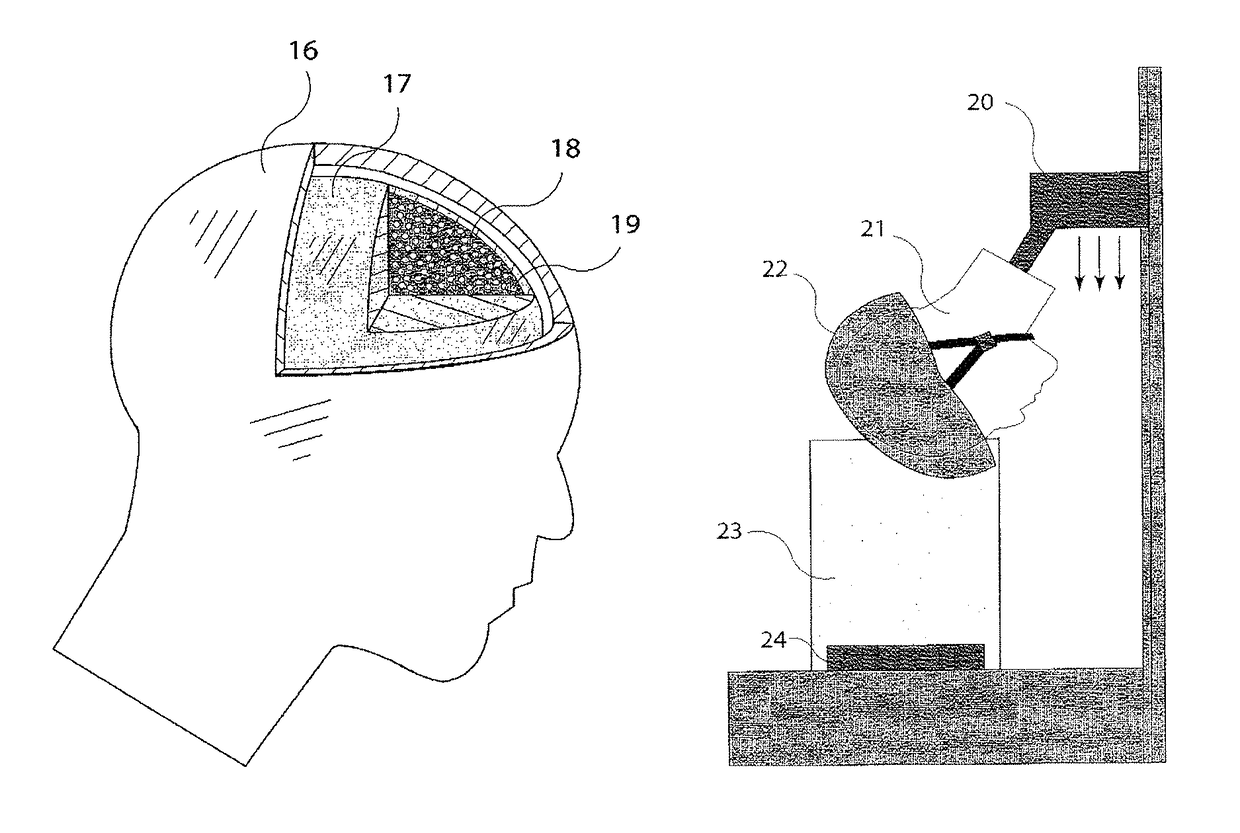
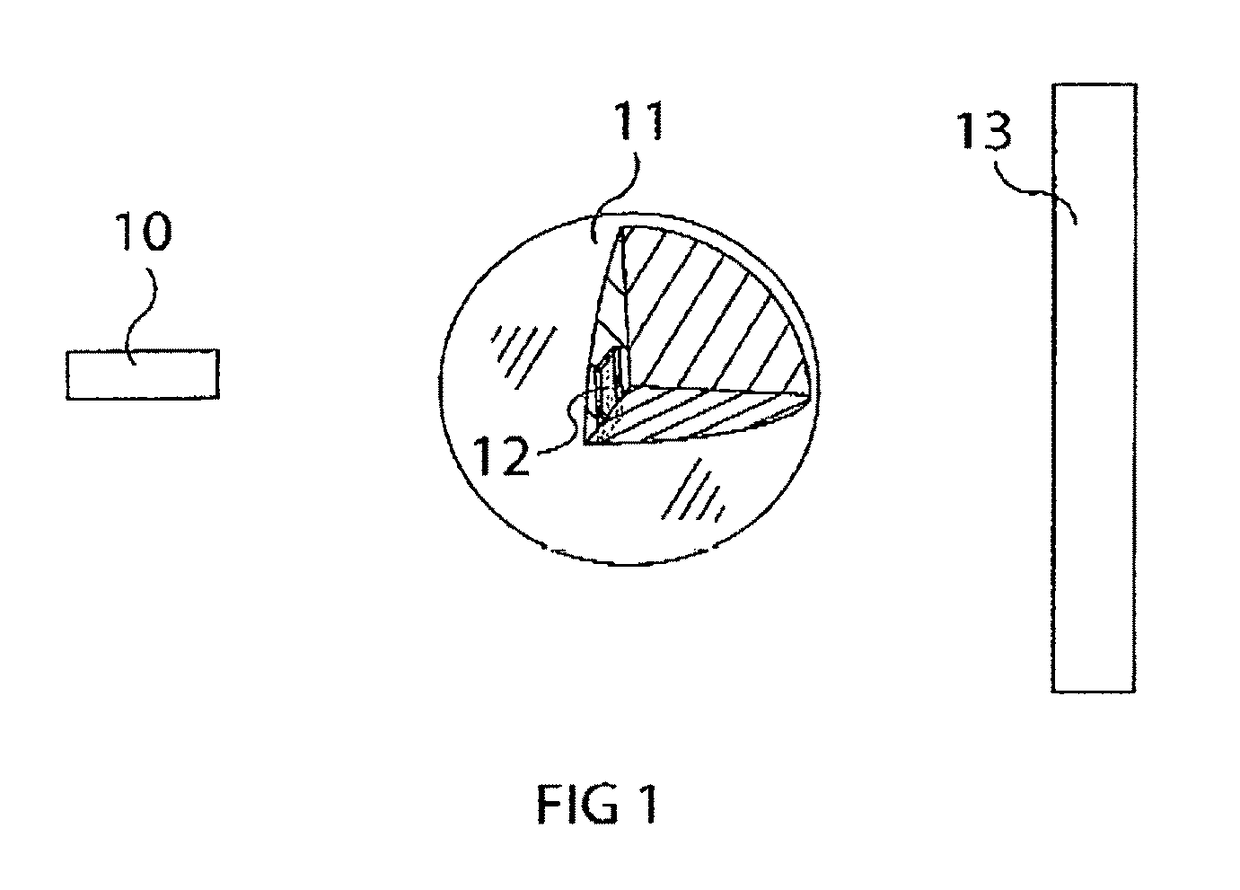
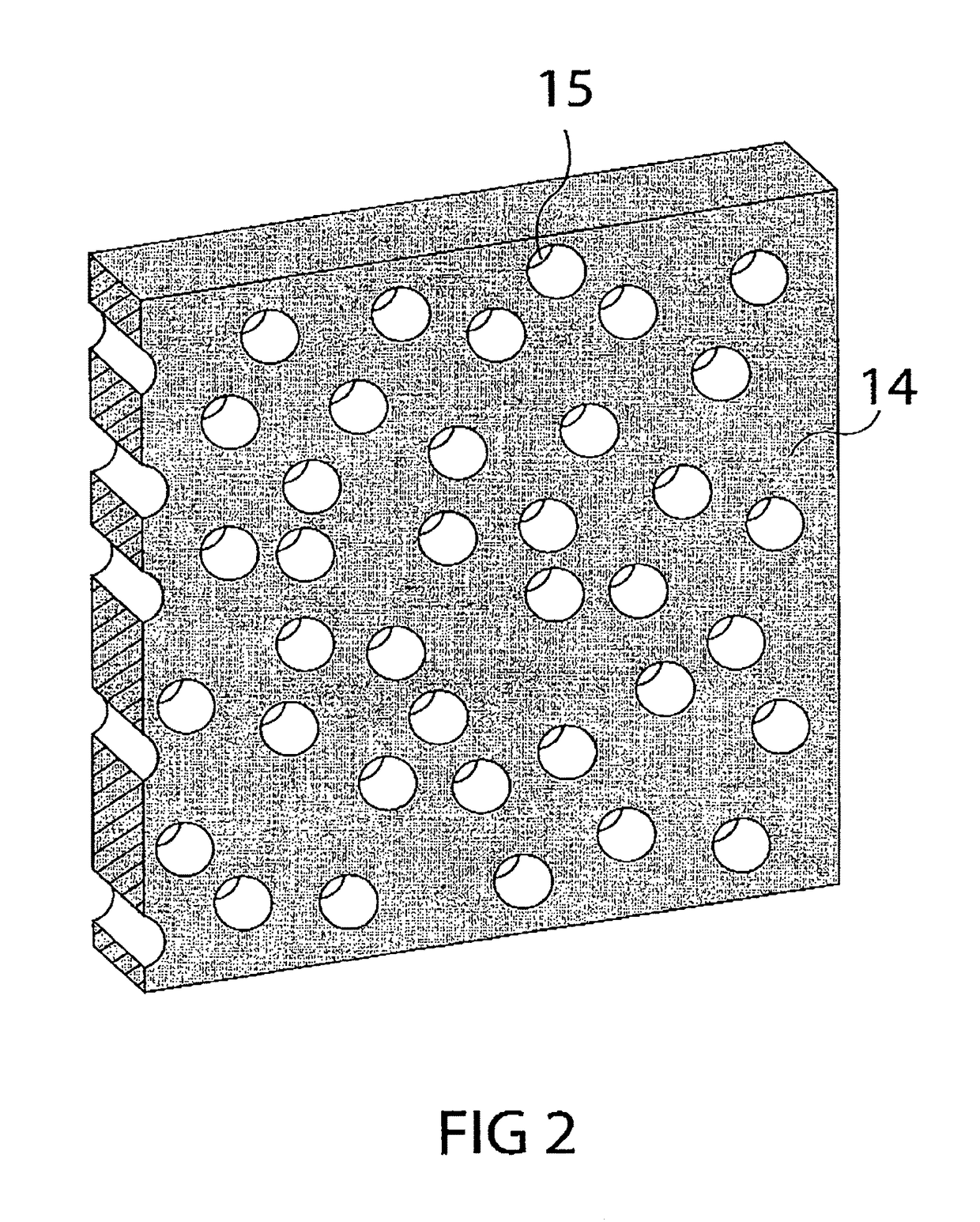
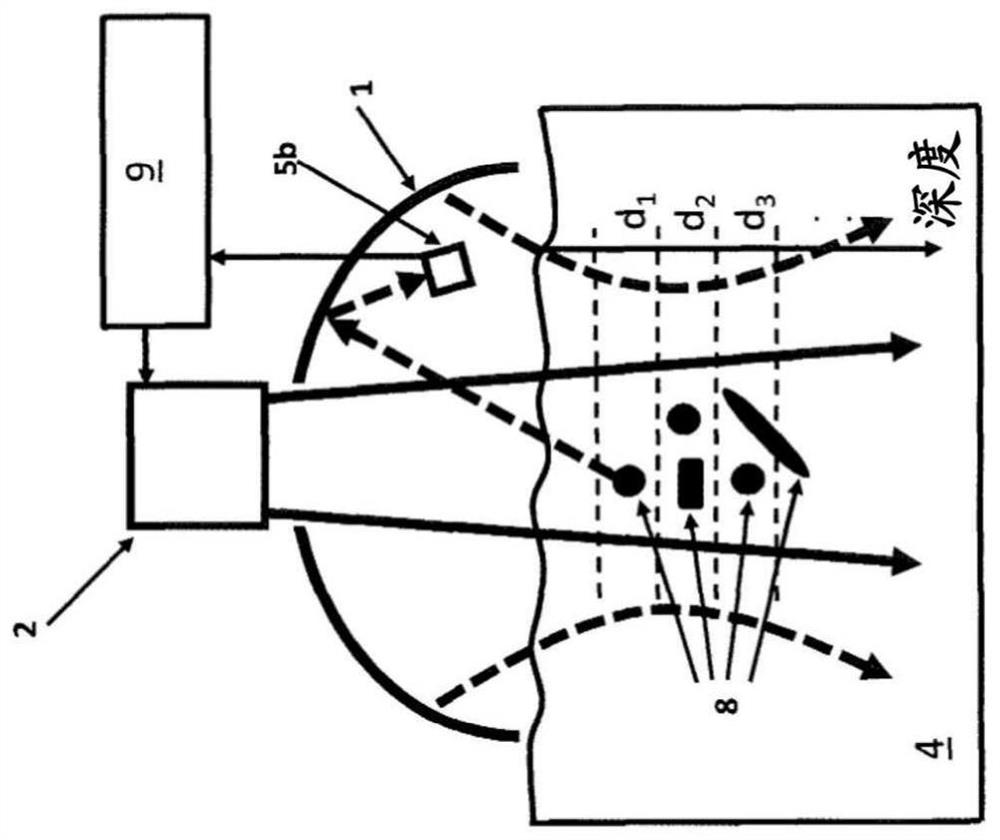
ActiveUS9826954B2Improve reliabilityImprove certification standardMedical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringBiomechanicsX-ray
A diagnostic gage (12) that can be implemented into a tissue-simulating headform (17) or other anthropomorphic surrogate test device (11) as a means of determining the internal strain within the test surrogate. One embodiment of the gage consists of a matrix or substrate embedded with x-ray contrast agents (14) and a series of holes within the substrate (15) that provide contrasting markers in an x-ray image and a means of closely coupling the gage to the test specimen. The relative motion of these contrasting markers can be monitored using x-ray fluoroscopy equipment (e.g., source (10) and detector (13)). This gage provides a means of determining the internal strain within a headform surrogate model for the purpose of evaluating the performance of helmets in terms of reducing the occurrence of concussion among other biomechanical injuries from trauma.
Owner:PETEL OREN E
Simulation of physiological functions for monitoring and evaluation of bodily strength and flexibility
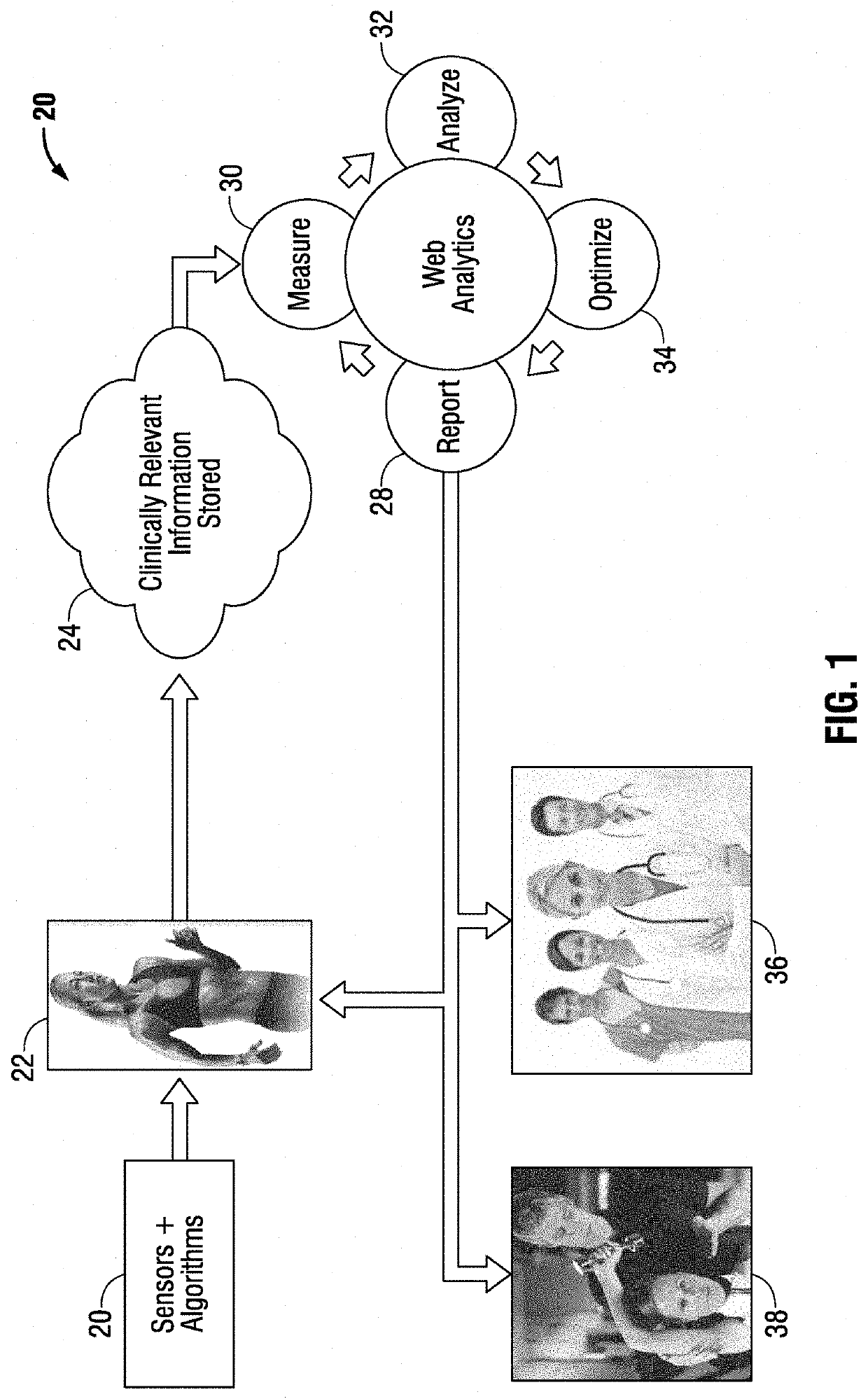
The simulation of physiological functions for monitoring and evaluation of bodily strength and flexibility includes a method and system for automated biomechanical analysis for simulated bodily joint movements. In one use, the simulation supports anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury prevention and recovery. The disclosure includes processing an automated and simulated biometric analysis algorithm on a computer processor and recording measurements relating to a plurality of physical therapy tests. The disclosure tracks the movement of joints on the subject's body from the subject's trunk downward to the subject's toes and calculates the results of the physical therapy tests for analyzing angles, movement quality, and related interrelationships amongst said joints. The method and system further derive and provide reports of comparisons of results with normative values and associate indicators for the comparisons to the potential of the subject to experience biomechanical conditions of injury or development.
Owner:L & C ORTHOPEDICS LLC
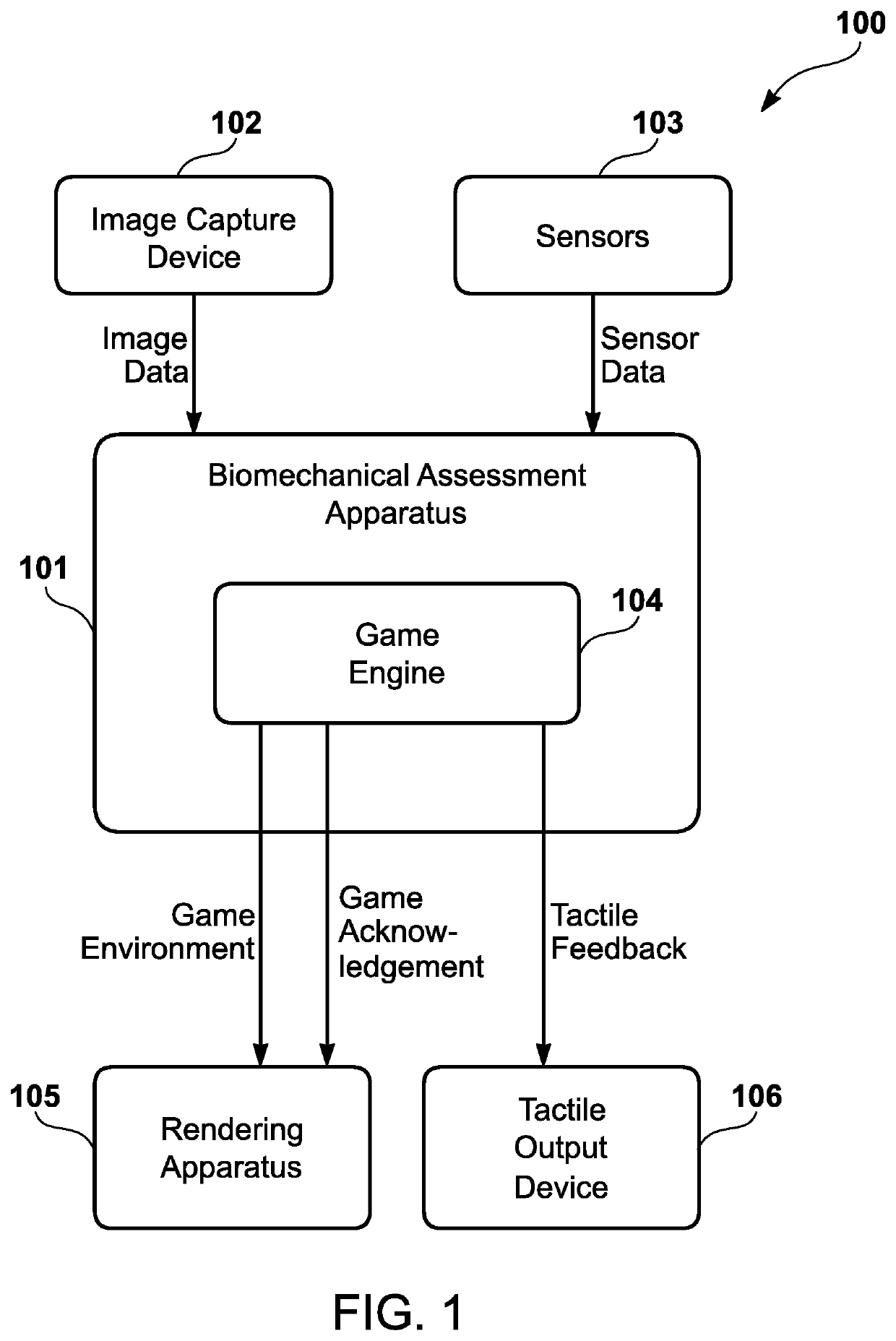
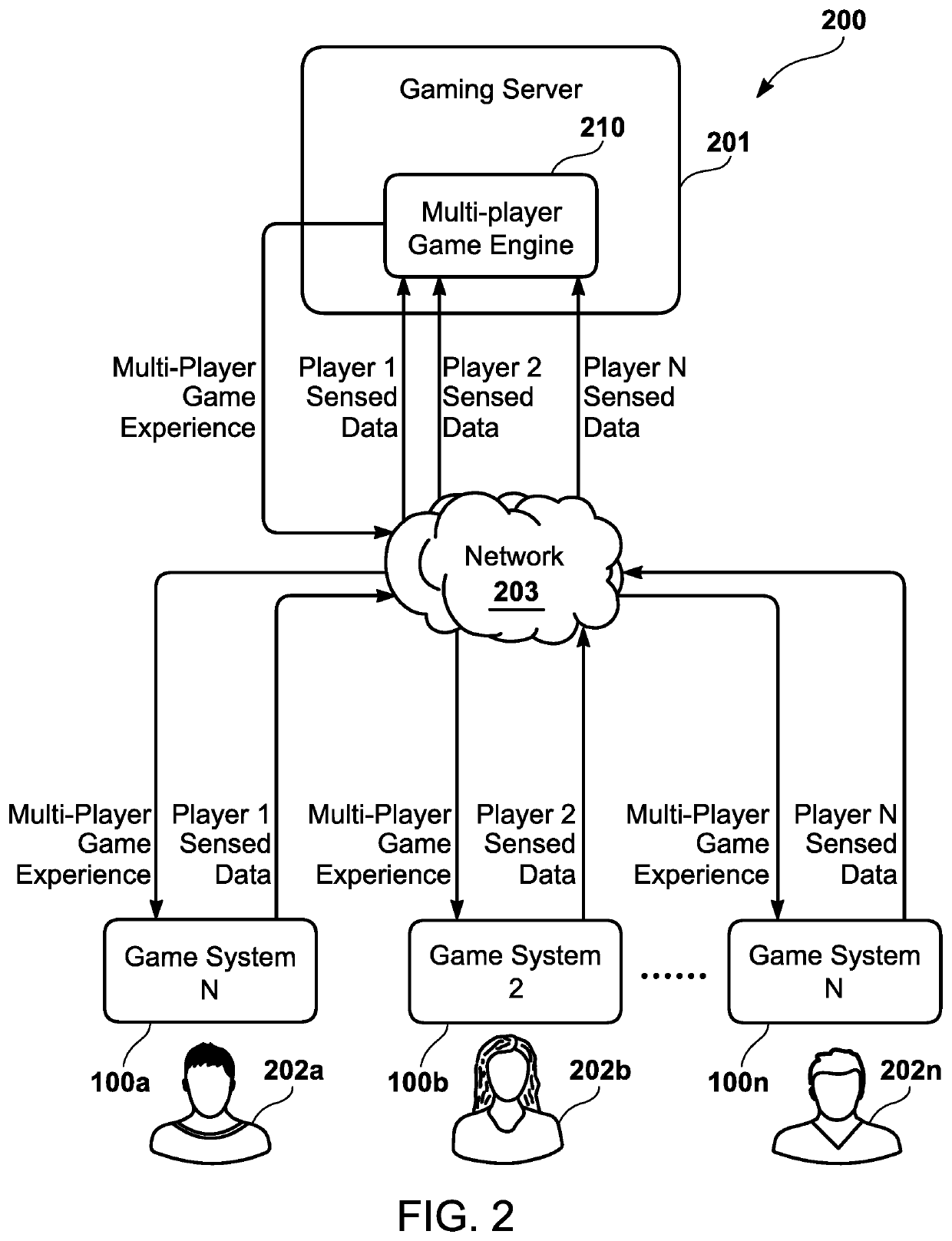
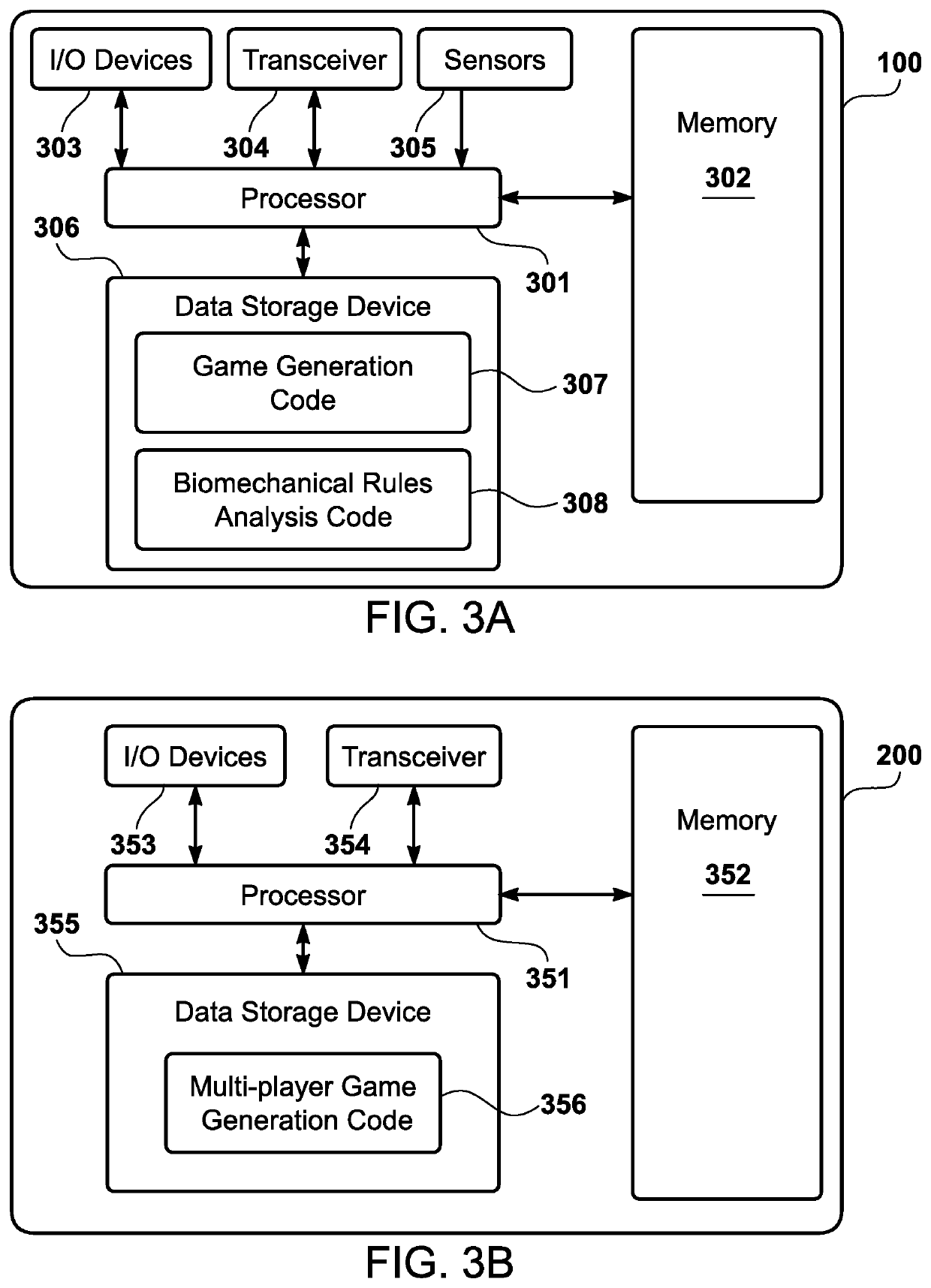
Gaming system for sports-based biomechanical feedback
A gaming system has one or more biomechanical detection units that detect one or more user biomechanical movements of a real-world user. Furthermore, the gaming system has a processor that is programmed to invoke a game engine to generate a virtual game environment. The game engine also determines a real-world athlete having one or more characteristic biomechanical movements. Furthermore, the game engine generates a virtual avatar corresponding to the real-world user. The game engine also presents one or more virtual stimuli in the virtual game environment to the real-world user. Additionally, the game engine determines if the one or more user biomechanical movements in reaction to the one or more virtual stimuli correspond to the one or more characteristic biomechanical movements within a predetermined tolerance threshold, and generate a virtual game acknowledgement based upon the determination that the predetermined tolerance threshold is met.
Owner:QUANTUM ATHLETE TECH LLC
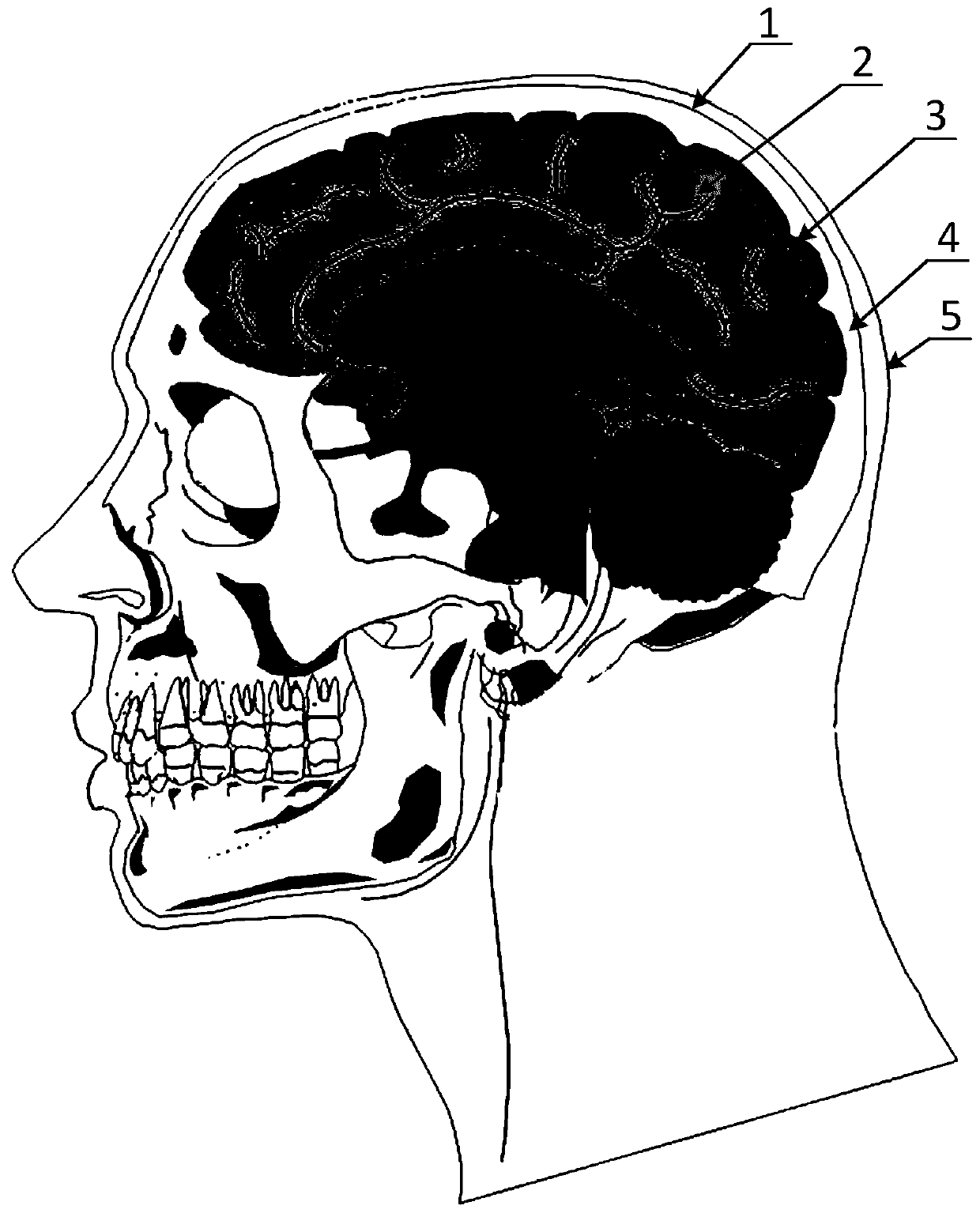
Dynamic test system based on high-simulation physical head model and protection evaluation method
ActiveCN111351627ATruly reflect the dynamic response characteristicsSolve the problem that the relative tangential displacement is difficult to measure accuratelyCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsAnatomical structuresPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention provides a dynamic test system based on a high-simulation physical head model and a protection evaluation method. The high-simulation physical head model is established completely basedon a head anatomical structure and mechanical properties of biological tissues of each part of the head anatomical structure, so that the occurrence process of two common injuries, namely brain tissuecontusion and subarachnoid hemorrhage, can be truly represented; a skull and brain tissue relative tangential displacement measurement system, an intracranial pressure dynamic test system, a skull strain dynamic test system, a skull acceleration dynamic test system and a head overall acceleration test system are established, and six biomechanical injury indexes for evaluating the degree of craniocerebral injury can be obtained; the damage state corresponding to the head model without wearing the protective equipment is taken as a reference; based on the six mechanical damage indexes and the severity of brain tissue contusion and rupture and subarachnoid hemorrhage, mechanical damage evaluation and physiological damage evaluation are conducted on the biological protection efficiency of thehead protection equipment, and therefore comprehensive evaluation of the protection equipment is achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
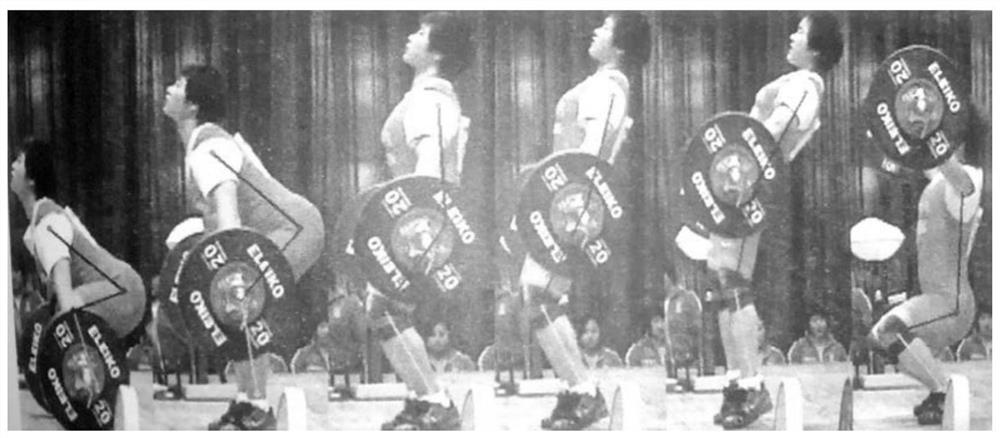
Female weightlifting athlete lumbosacral joint biomechanical analysis method based on numerical simulation
PendingCN112489762AGuaranteed universal applicabilityGuaranteed accuracyMedical simulationPhysical therapies and activitiesAnatomical structuresSpinal column
The invention relates to a female weightlifting athlete lumbosacral joint biomechanical analysis method based on numerical simulation; the method comprises the steps: selecting a plurality of female weightlifting athletes as to-be-tested athletes, and screening a target athlete according to spine form data; monitoring in the whole weightlifting process of the target athlete, and establishing a weightlifting action model; conducting static spine CT scanning on the target athlete, and establishing a finite element model of the lumbosacral joint according to a scanning result, finally performingnumerical simulation analysis to generate an analysis result. Modeling and numerical simulation analysis are specially carried out on lumbosacral joints of female weightlifting athletes to obtain stress change conditions of anatomical structures such as joints, muscles and soft tissues in the weightlifting movement process, so that structural optimization is carried out on weightlifting actions ofthe female weightlifting athletes, the competitive ability is improved, movement injuries are avoided, the safety of the female weightlifting athletes is improved, and guidance opinions are providedfor exercise rehabilitation.
Owner:宋雅伟
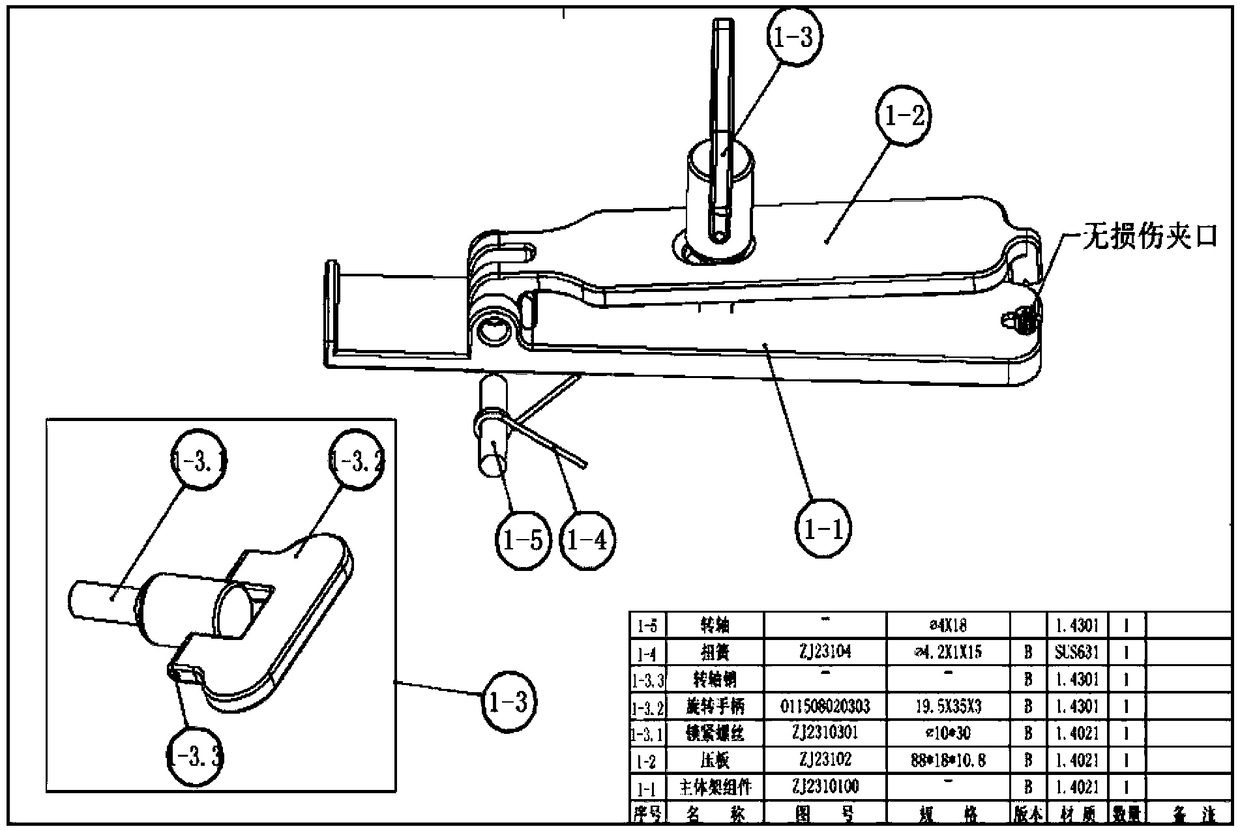
Specimen fixation apparatus of femur neck test instrument
InactiveCN103323330AAvoid breakingPrevent displacement and deformationStrength propertiesEngineeringFemoral neck
The invention discloses a specimen fixation apparatus of a femur neck test instrument. The apparatus comprises a body, wherein the body is mainly formed by a fixation member and a movement member, the movement member is closes to the fixation part or separates from the fixation part in a fixed range, and the fixation member surface opposite to the movement member forms a clamping part for clamping a specimen. The apparatus has the following beneficial effects that: the middle-upper segment specimen of the femur can be effectively fixed during a femur neck biomechanical test, and corpus femoris fracture or the whole deformation shift of the femur specimen under the femur specimen tuberositas can be avoided.
Owner:夏胜利
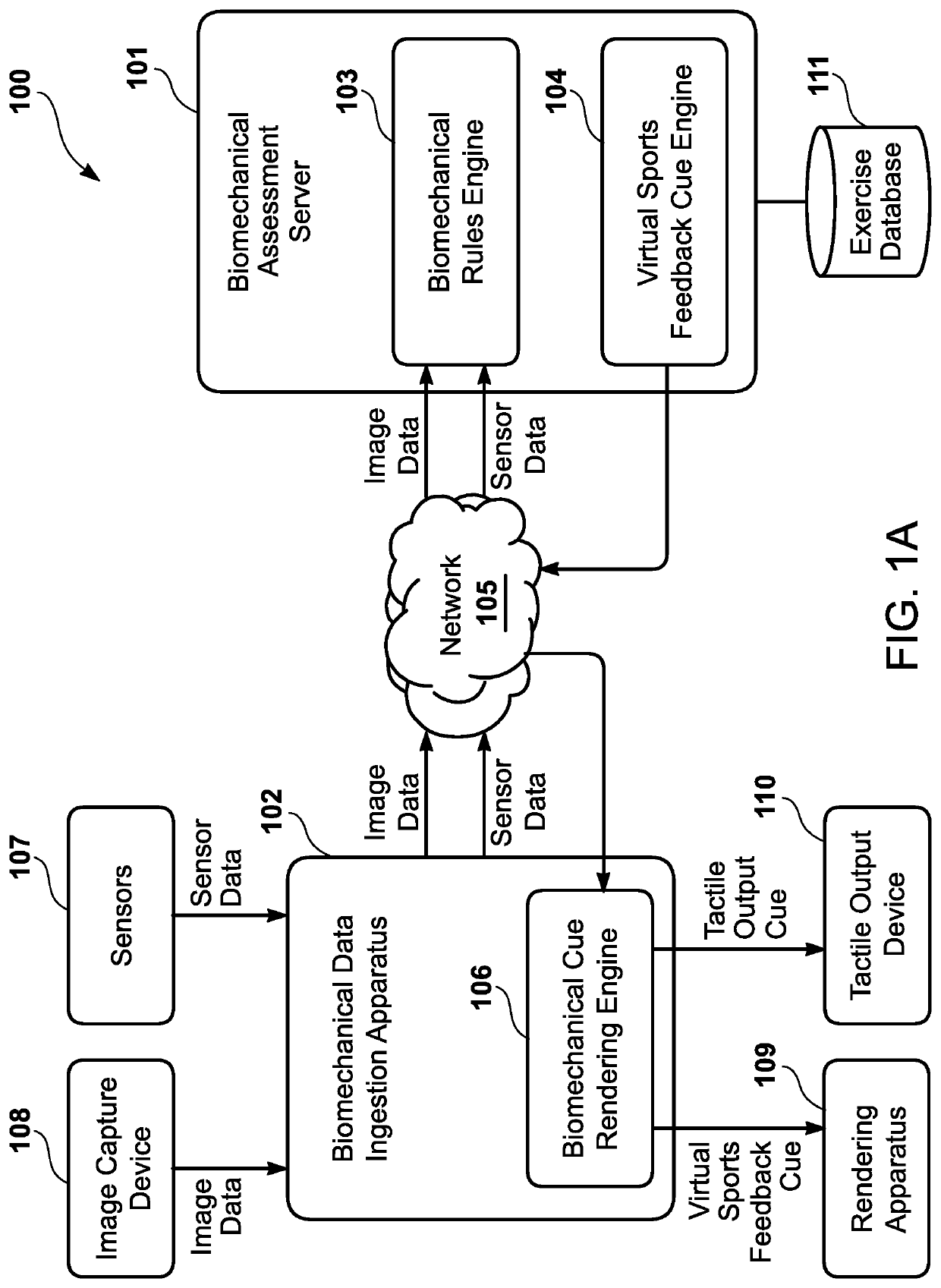
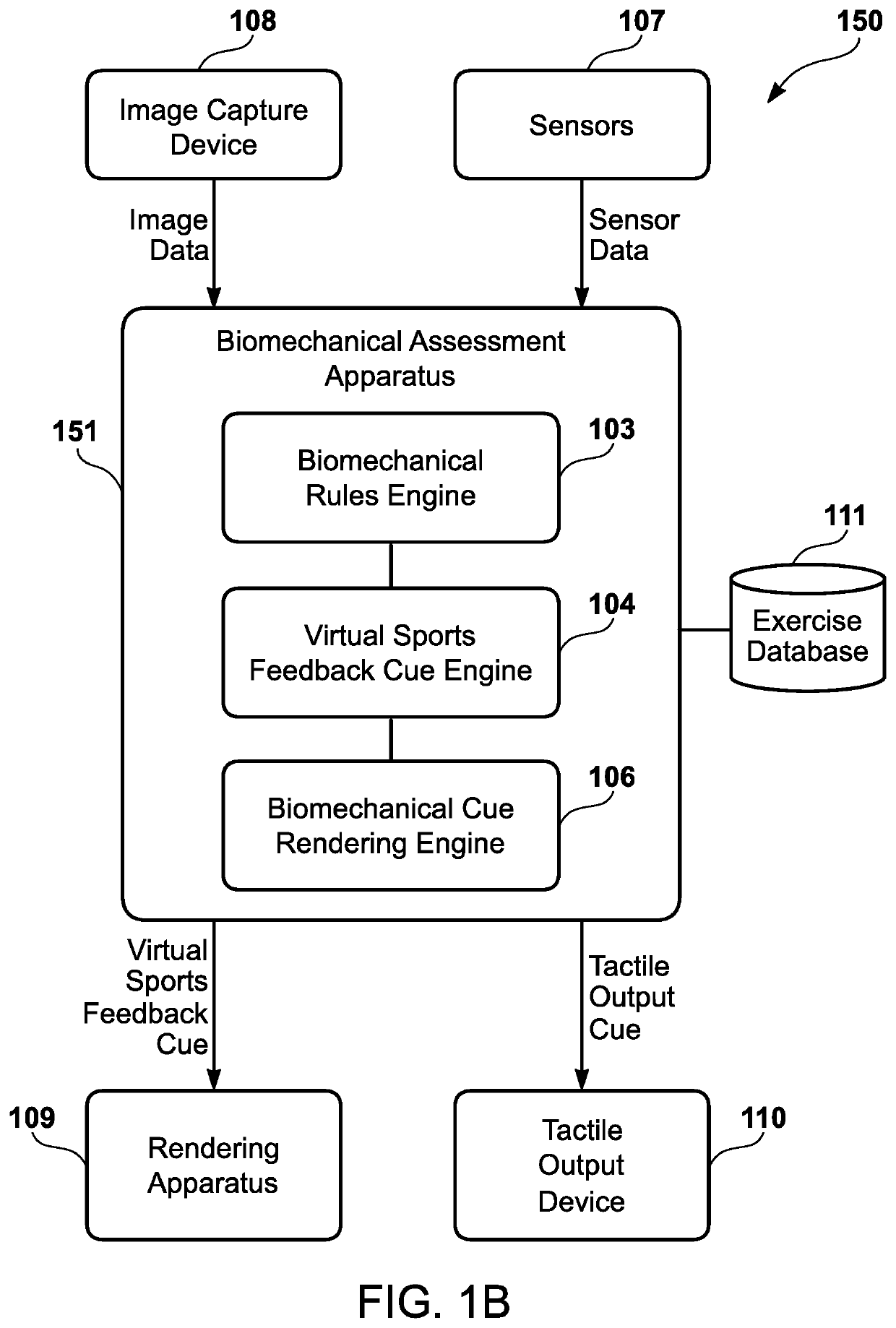
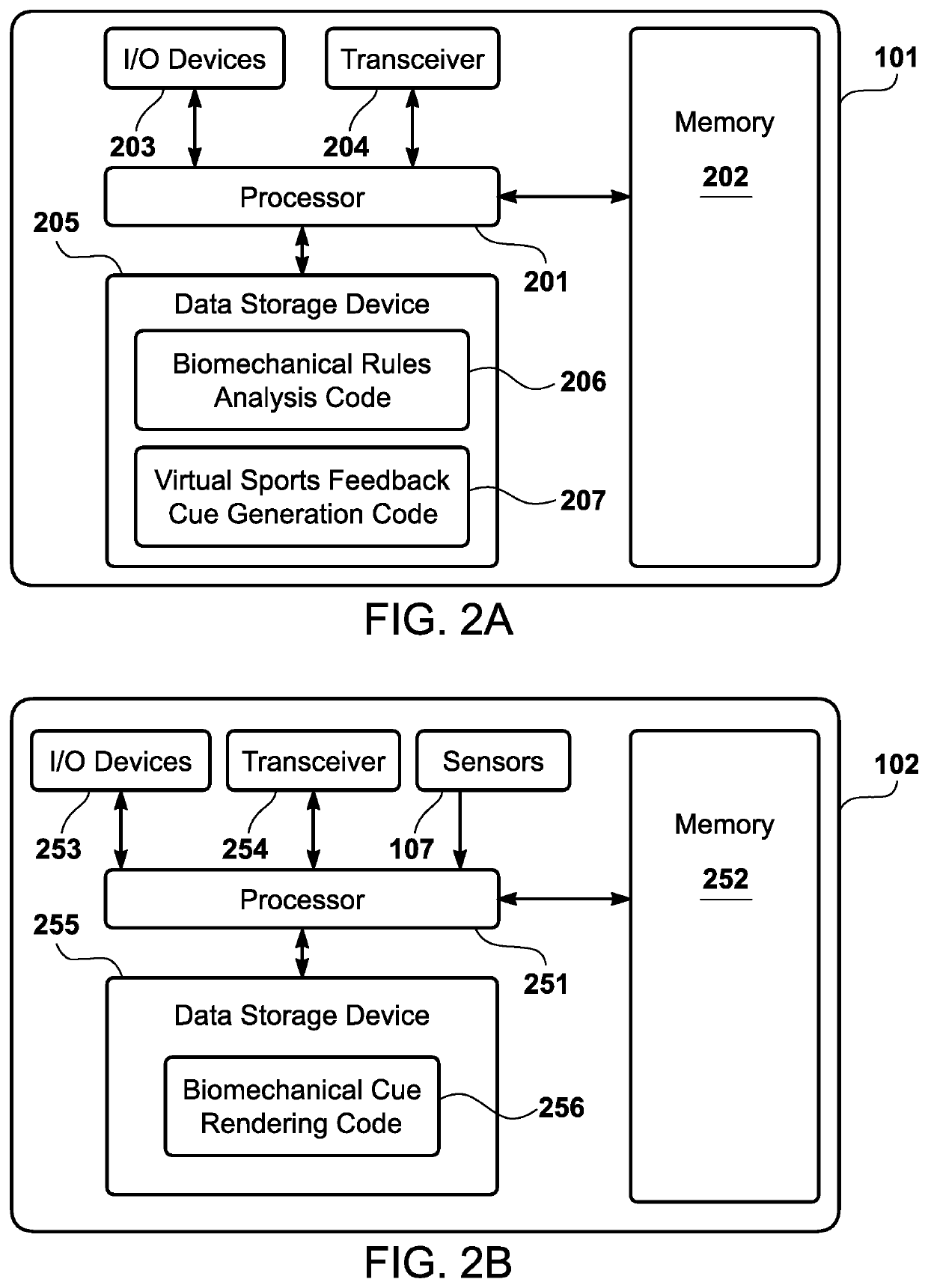
Interactive visualization system for biomechanical assessment
ActiveUS20210154529A1Input/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementVirtual locomotionData ingestion
An interactive visualization system has a receiver that receives image data corresponding to one or more biomechanical movements of a user. Further, the interactive visualization system has a processor that performs a biomechanical analysis, via a biomechanical rules engine, of the image data to determine that the one or more biomechanical movements of the user lack compliance with one or more biomechanical rules. The processor generates a virtual sports feedback cue to be rendered, in at least substantially real-time, via a virtual sports performance expert during performance of the one or more biomechanical movements of the user. Finally, the interactive visualization system has a transmitter that transmits the virtual sports feedback cue to the biomechanical data ingestion apparatus so that a rendering apparatus renders the virtual sports performance expert performing the virtual sports feedback cue in a manner visible to the user during the one or more biomechanical movements.
Owner:QUANTUM ATHLETE TECH LLC
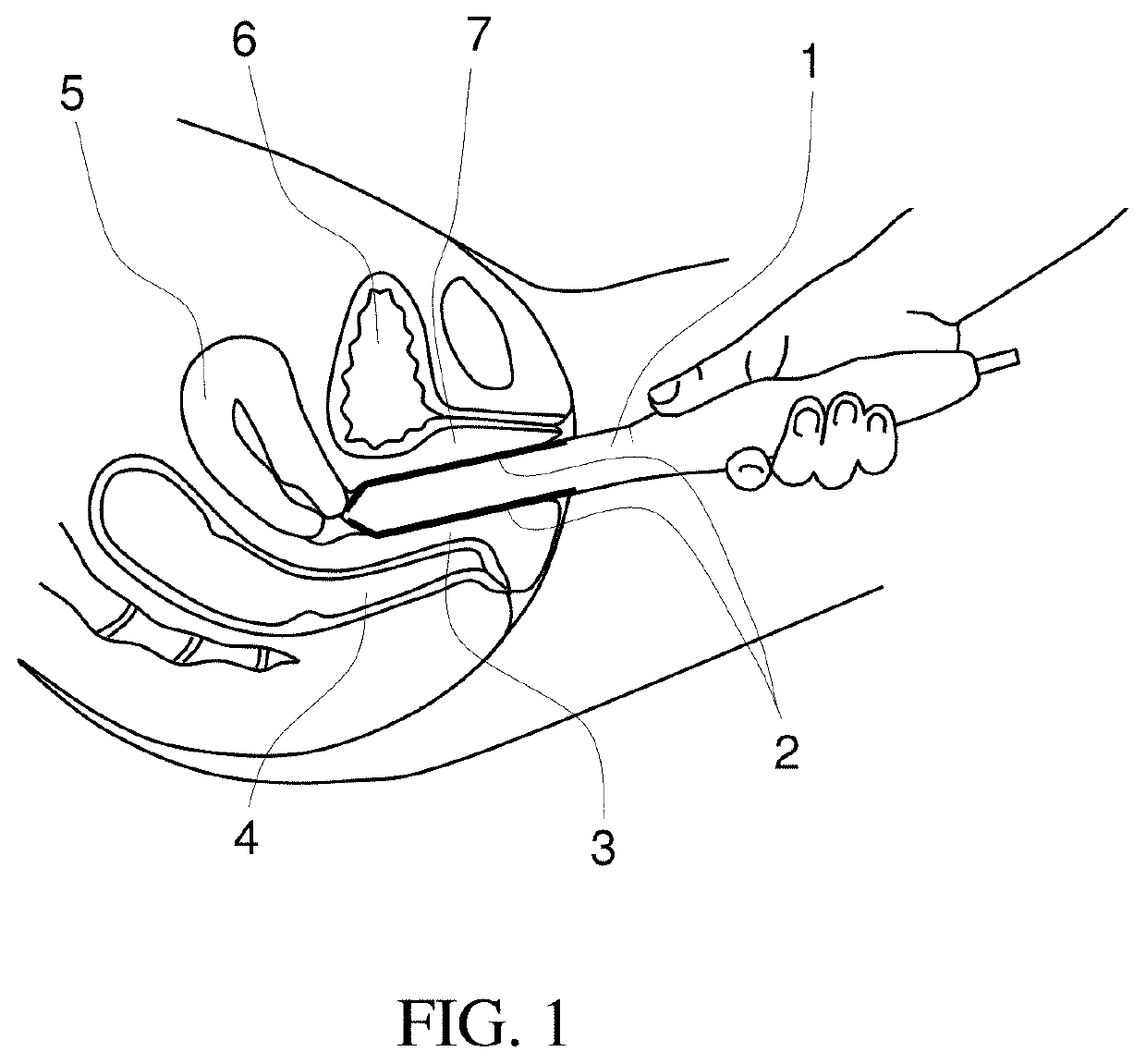
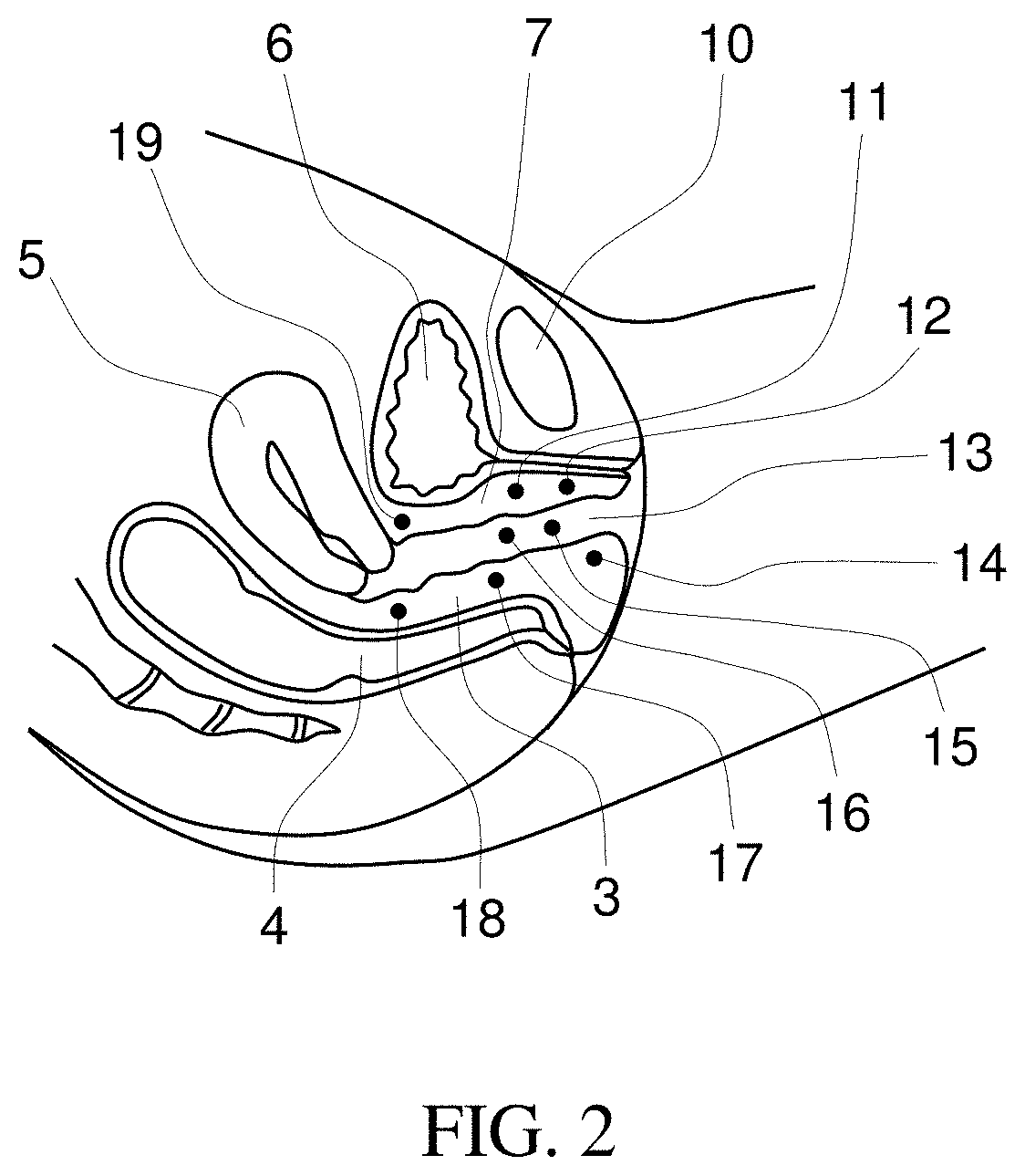
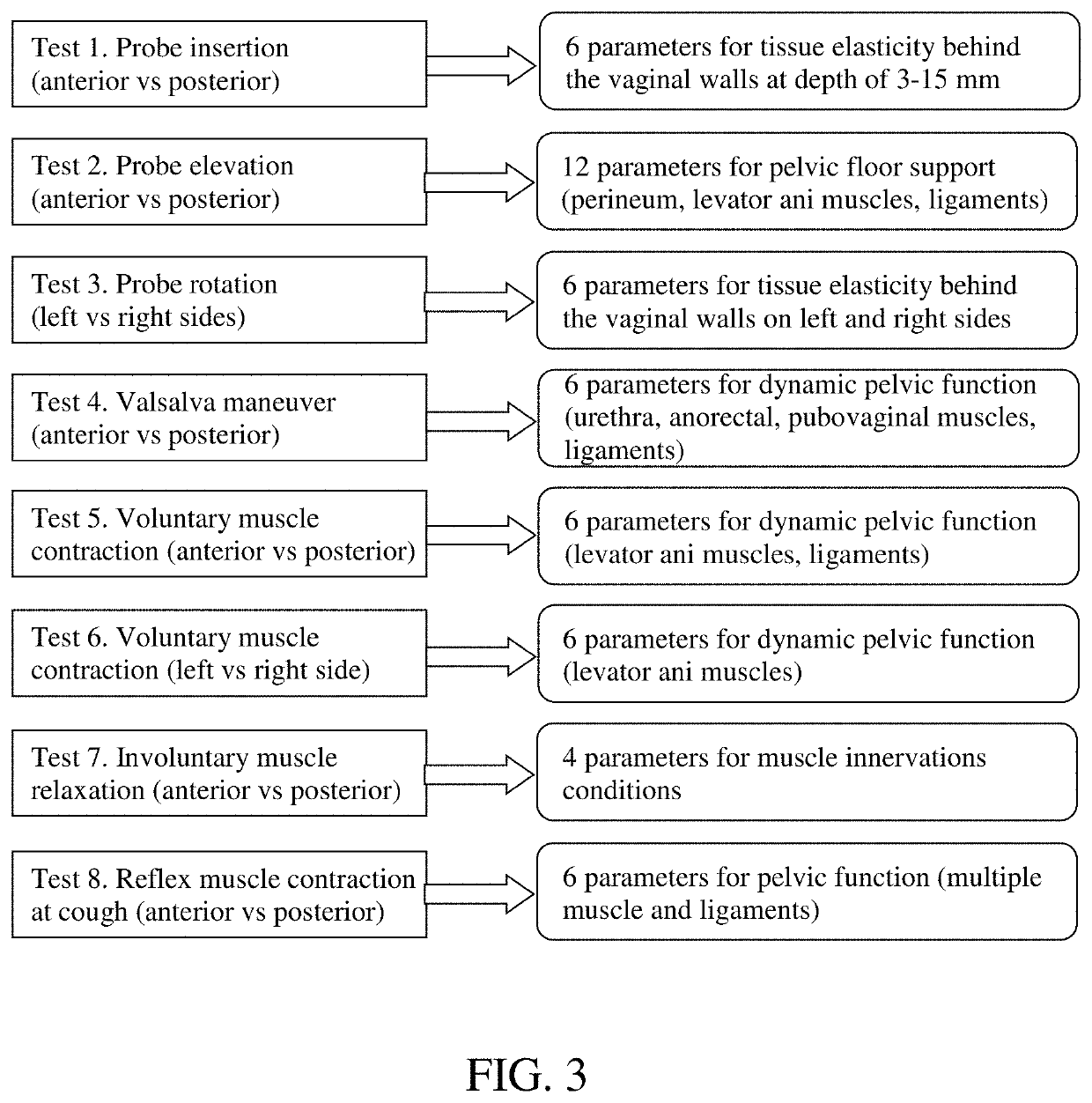
Methods for biomechanical mapping of the female pelvic floor
InactiveUS20200037950A1Overcomes drawbackNovel methodUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterPelvic regionDisease
Owner:ADVANCED TACTILE IMAGING
Clamp for assisting mechanical arm-universal sensor testing system in realizing knee joint biomechanical test
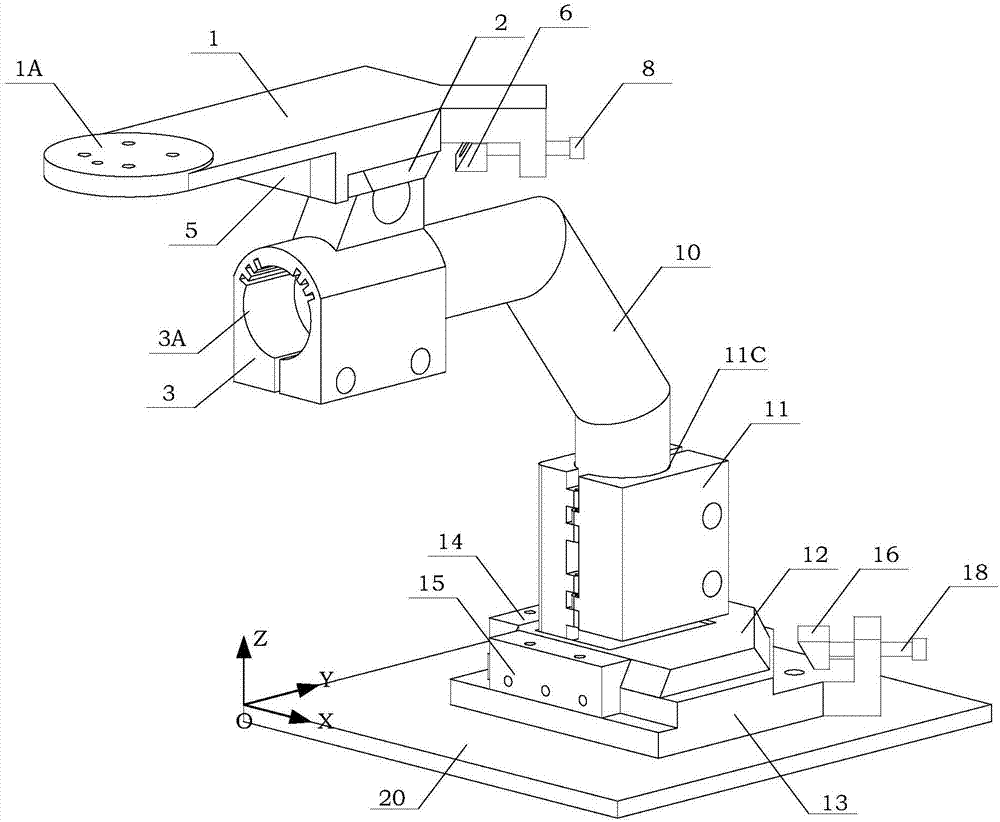
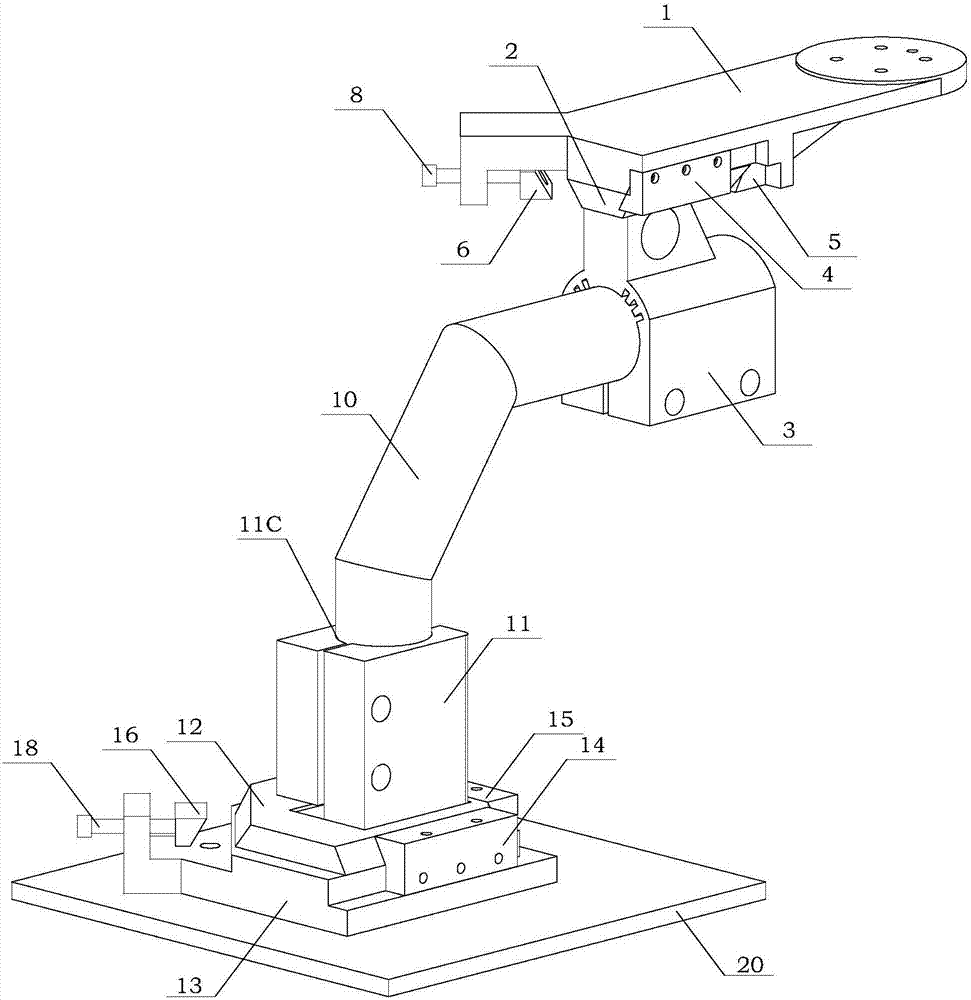
ActiveCN107300502ASolve the position accuracy problemGuaranteed unityStrength propertiesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationDiaphysis
The invention discloses a clamp for assisting a mechanical arm-universal sensor testing system in realizing a knee joint biomechanical test. The clamp consists of a tibia shaft fixing mechanism and a femur shaft fixing mechanism; and a knee joint specimen is connected between the tibia shaft fixing mechanism and the femur shaft fixing mechanism. An upper bottom plate (2) is arranged between a supporting (1) and an upper clamping piece (3), and a knee joint tibia is fixed by the upper clamping piece (3). A lower bottom plate (12) is arranged between a lower clamping piece (11) and a lower base (13), and a knee joint femur is fixed by the lower clamping piece (11). A top block is pushed by a squeezing screw, so that the upper bottom plate (2) and the lower bottom plate (12) are pushed, an oblique movement sliding groove panel on the side of each bottom plate and an oblique movement sliding groove panel of a wedge block are superposed to form right-angle intersected inclined grooves to be occluded, the problem about the measuring position precision during repeated mounting and dismounting of the knee joint specimen is solved, and biomechanical tests of the knee joint specimen under different states are completed.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
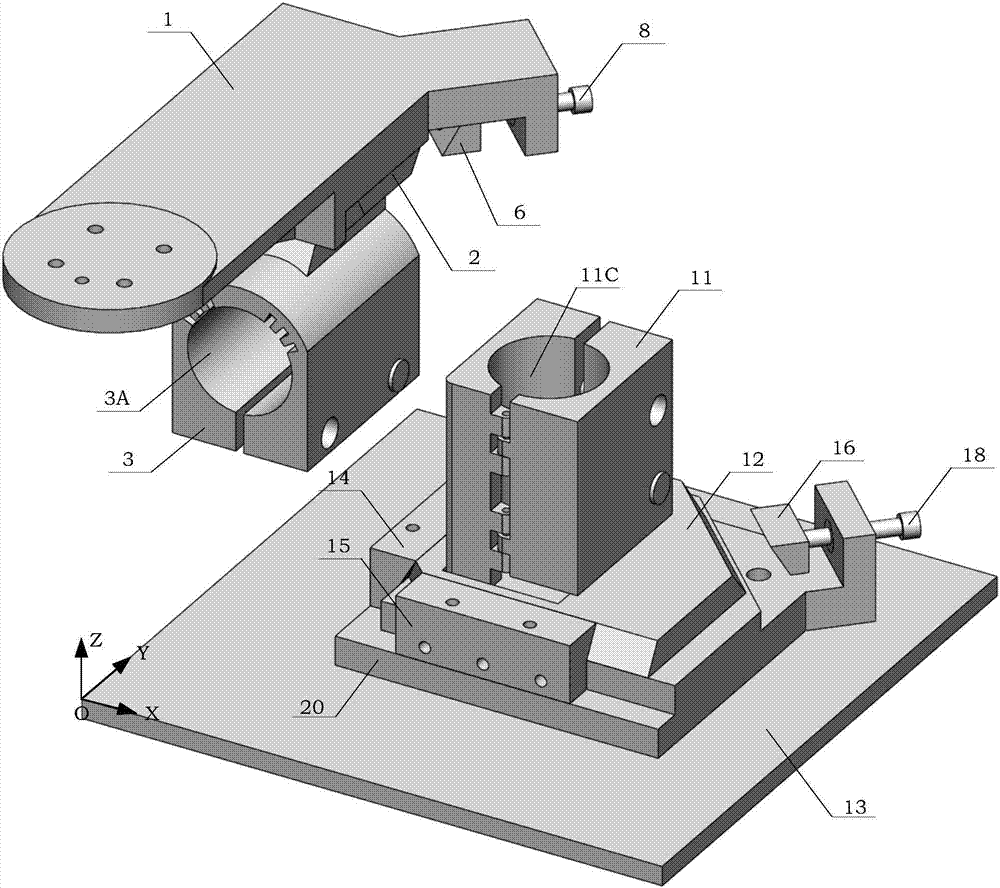
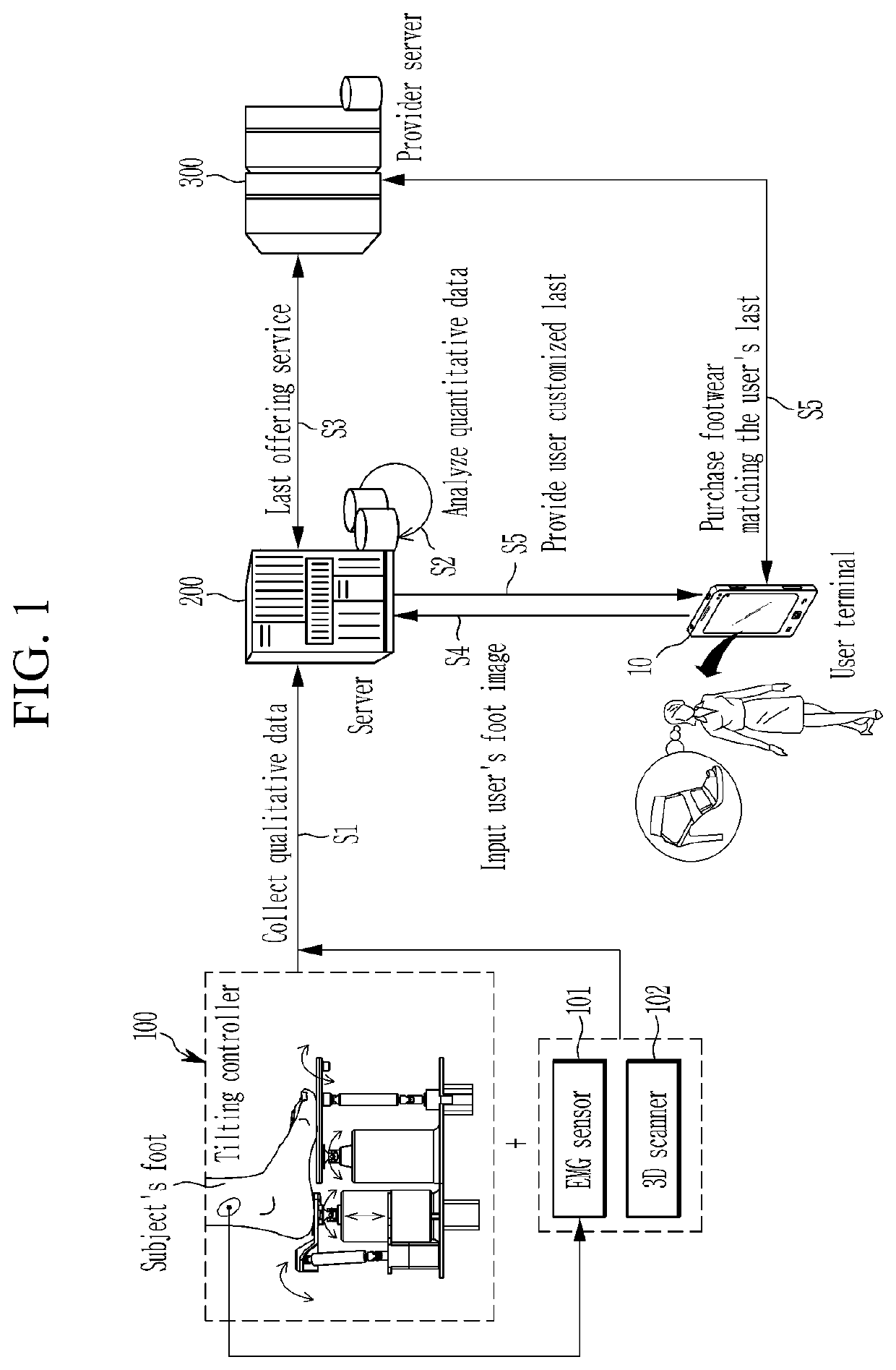
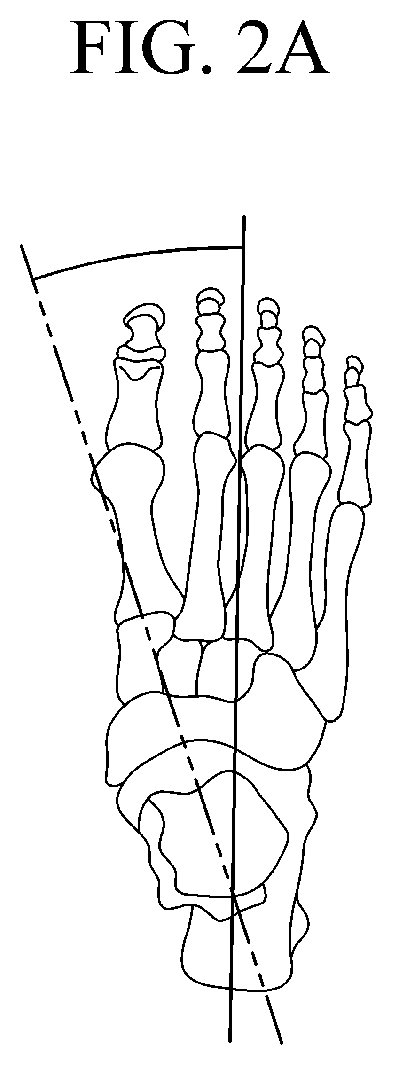
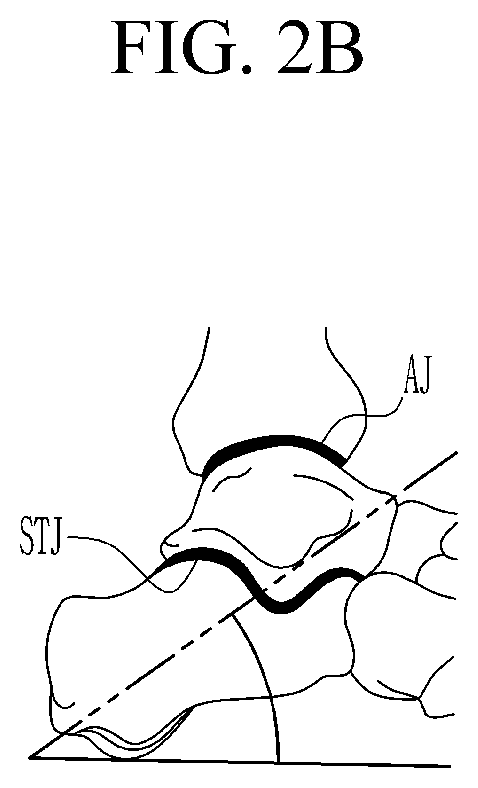
System for providing user-customized last and method therefor
PendingUS20200275742A1Improve comfortReduce exchangeFoot measurement devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Owner:KIM IL SOO
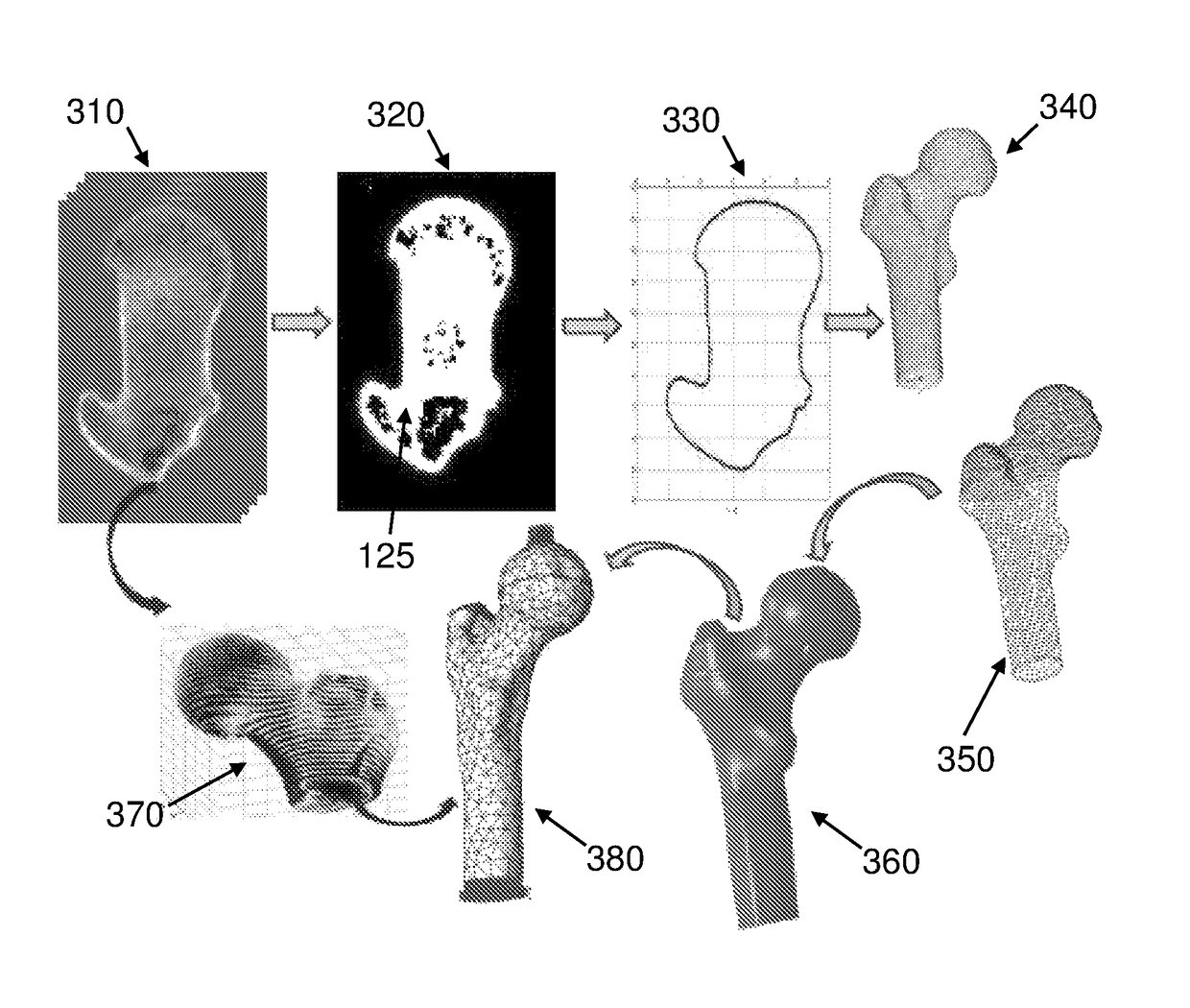
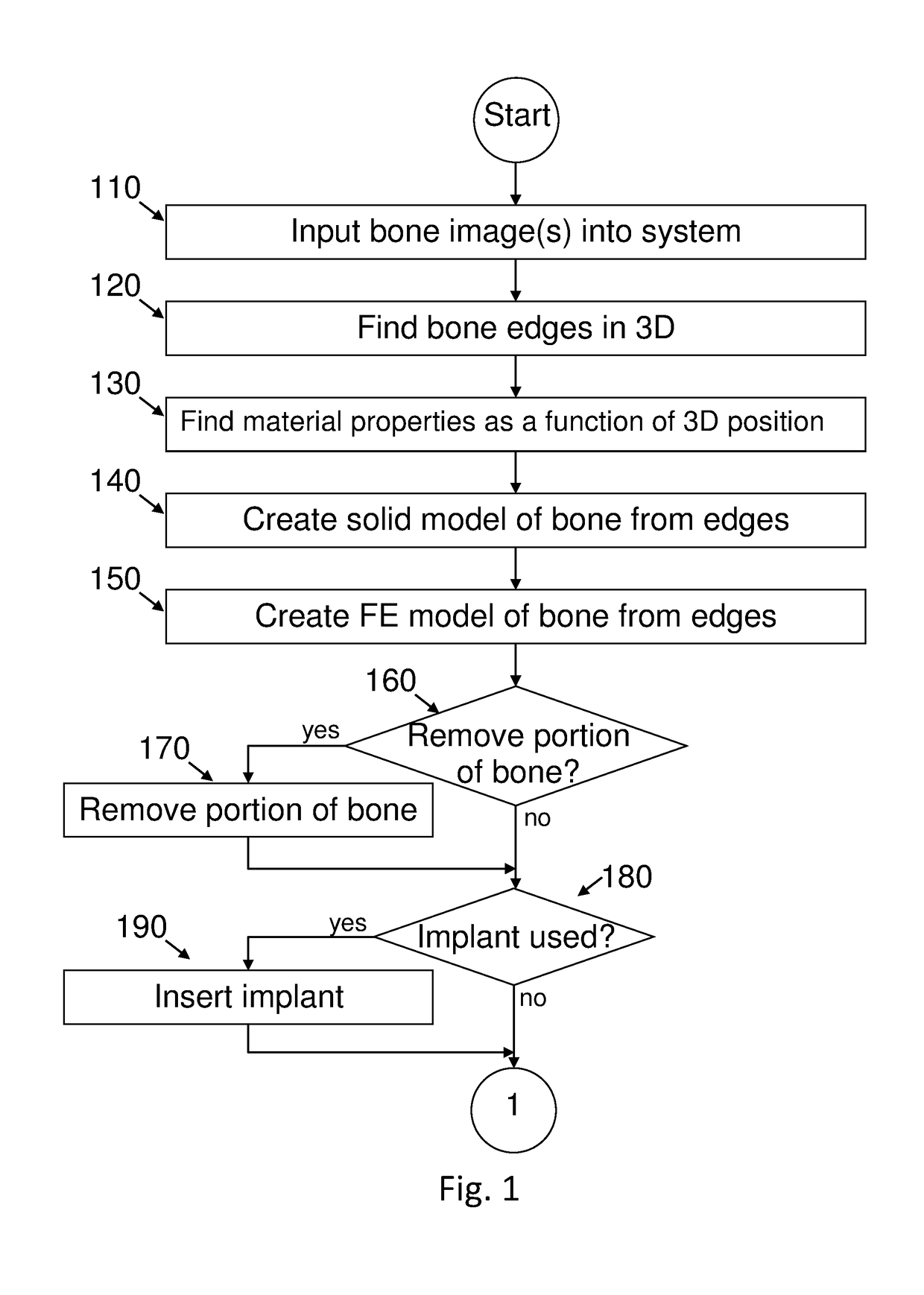
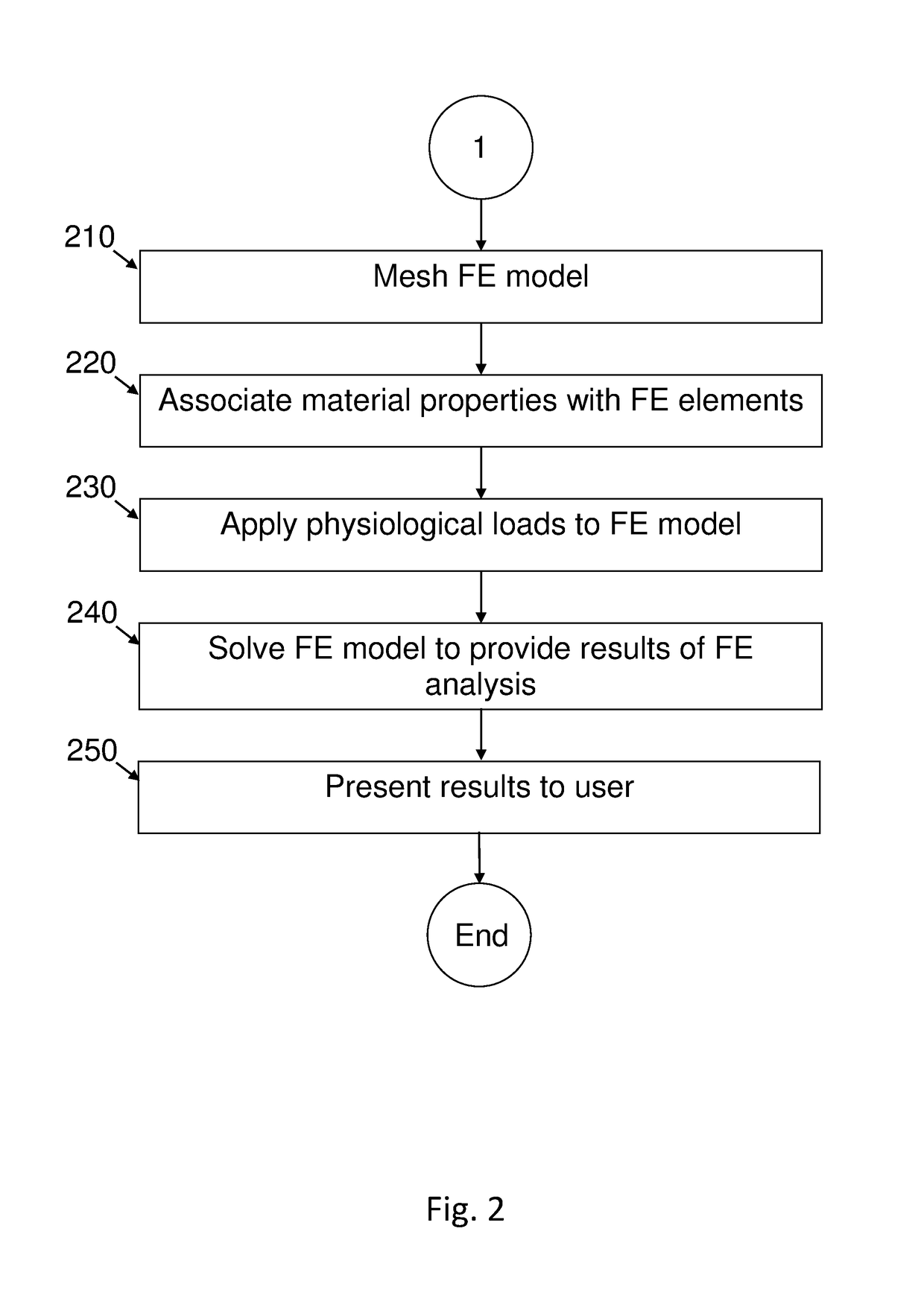
Automated patient-specific method for biomechanical analysis of bone
ActiveUS9937011B2Reduce in quantityFlat surfaceDetails involving 3D image dataCharacter and pattern recognitionMedicineHand held
A computer-implemented method for providing FEA analysis of at least a portion of at least one bone in a patient, the method comprising steps of: providing at least one image of at least a portion of a bone; selecting at least a portion of the bone; automatically performing an FE analysis of the selected portion of the bone; and displaying at least one result of the FE analysis. Bone selection and display of the bone, the selected portion thereof, and the results of the FE analysis occur via a hand-held device, with processing and data storage performed remotely.
Owner:PERSIMIO LTD
Soft tissue modeling method based on position constraint and nonlinear spring
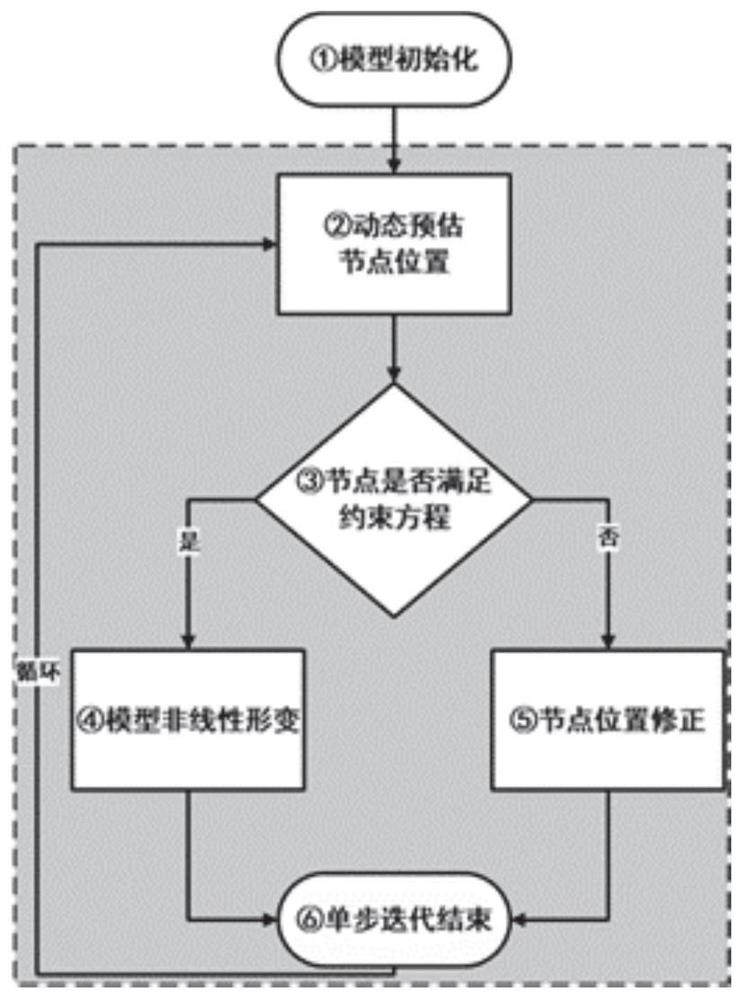
ActiveCN113409443AEffective feedback of biomechanical propertiesMake up for the shortcomings of instabilitySustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationDeformation effectEngineering
The invention discloses a soft tissue modeling method based on position constraint and a nonlinear spring. The method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a soft tissue model formed by tetrahedron units formed by the nonlinear spring and a virtual body spring; (2) simulating the deformation behavior of the soft tissue model; (3) estimating the approximate position of each node, judging whether the state of a node constraint equation is changed or not, wherein constraints comprise spring length and curvature constraints; if the initial state of the equation is changed, correcting the node to a correct position within a reasonable range; if the initial state of the equation is not changed, indicating that the nonlinear spring and the virtual body spring simulate the deformation effect of the soft tissue; and (4) ending the single-step iteration of deformation calculation, and entering the next cycle. The non-linear spring system and the virtual body spring are adopted to simulate the biomechanical characteristics of the soft tissue, a new constraint equation is adopted to limit node displacement so as to enhance the stability of the model, and the defects that a traditional mass spring model is poor in accuracy and unstable are overcome.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
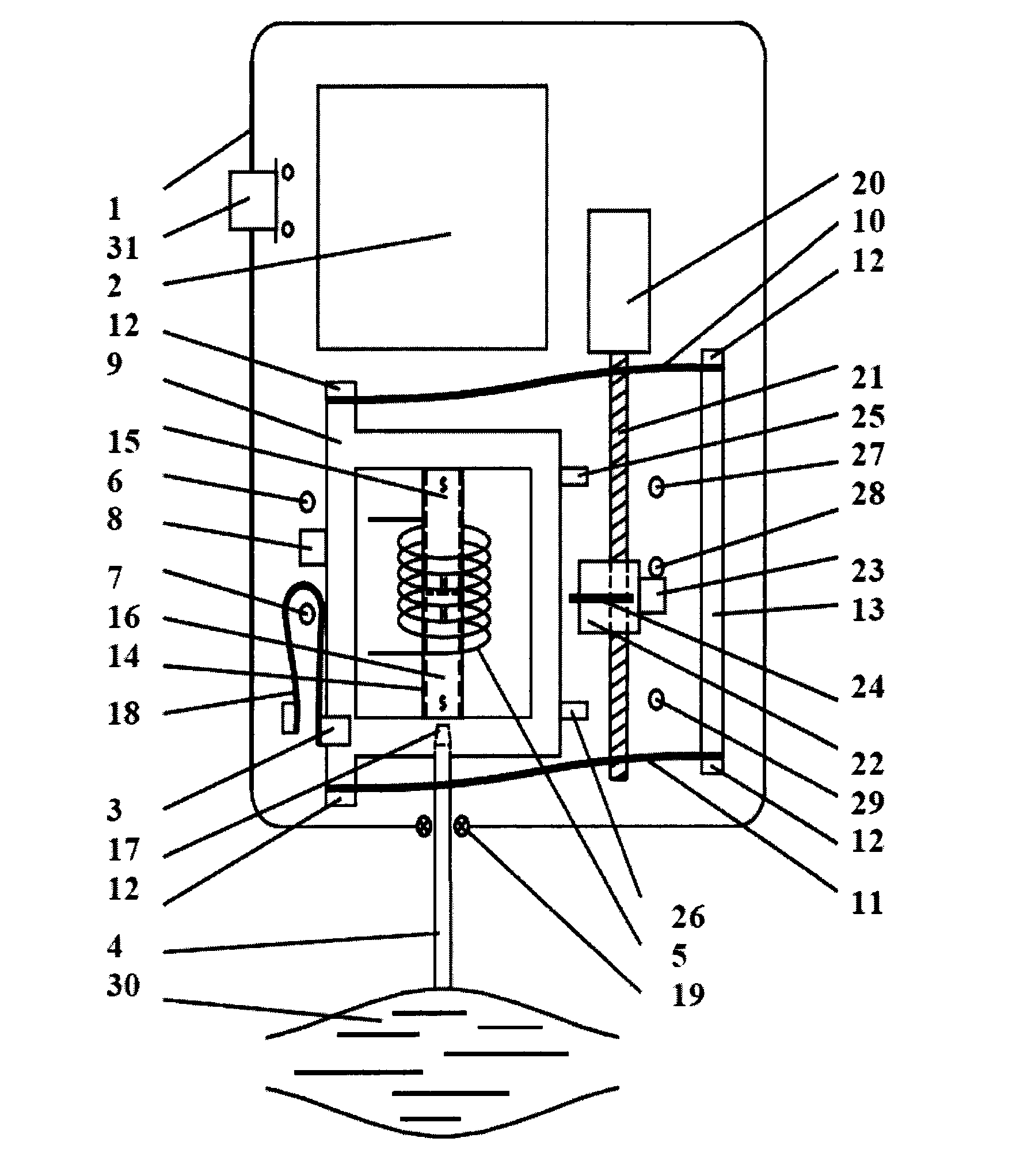
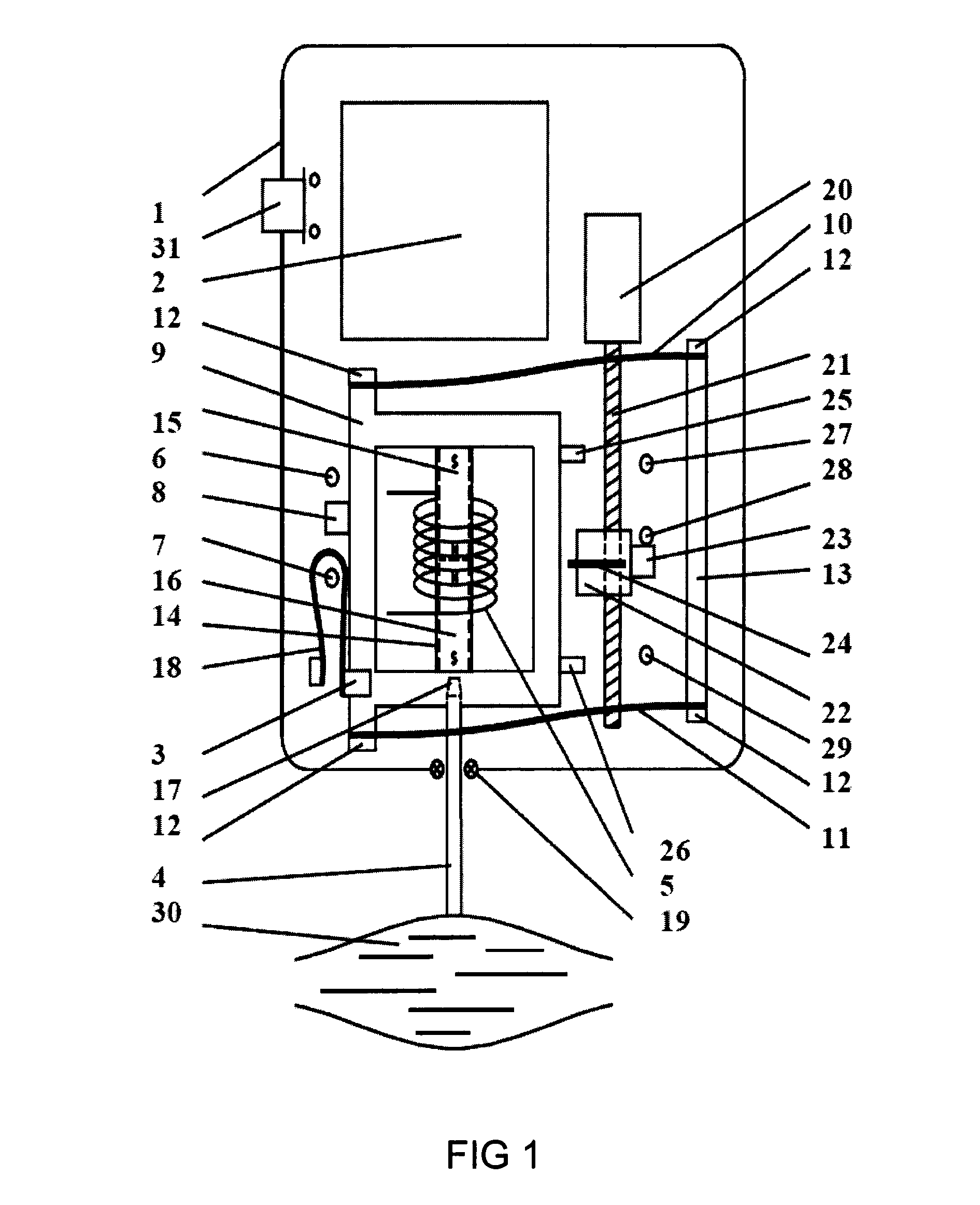
System and method for non-invasive measurement of soft biological tissue
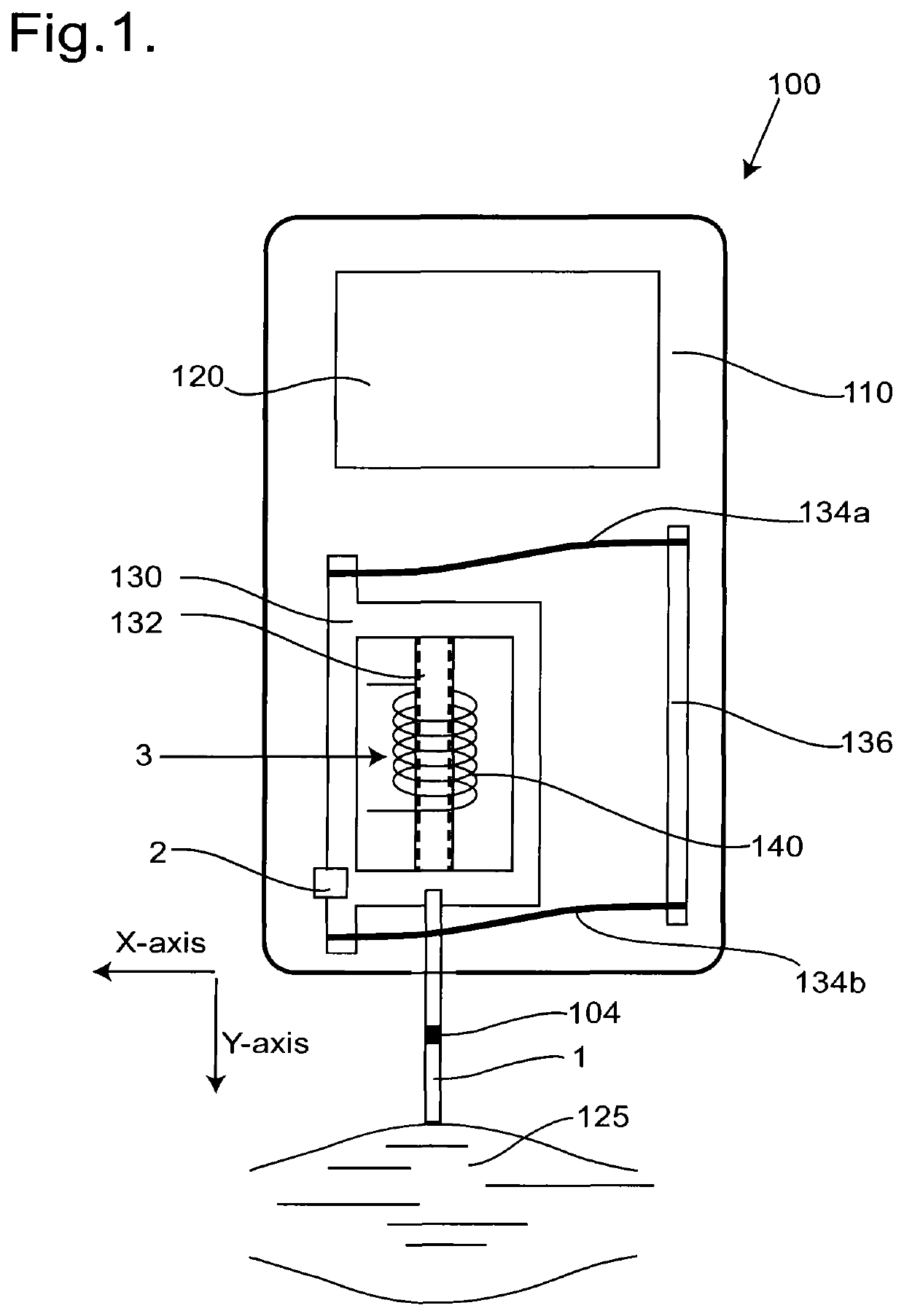
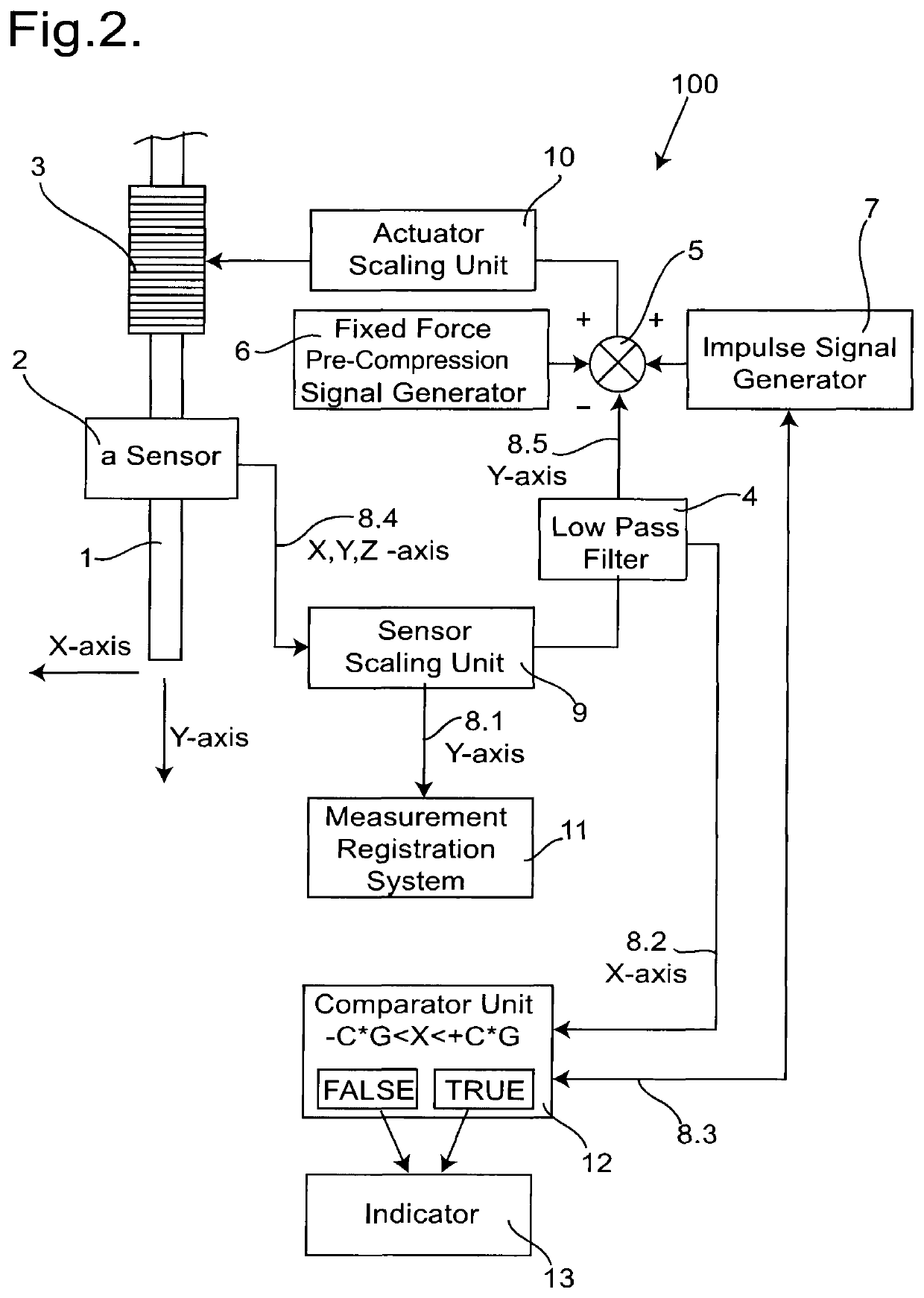
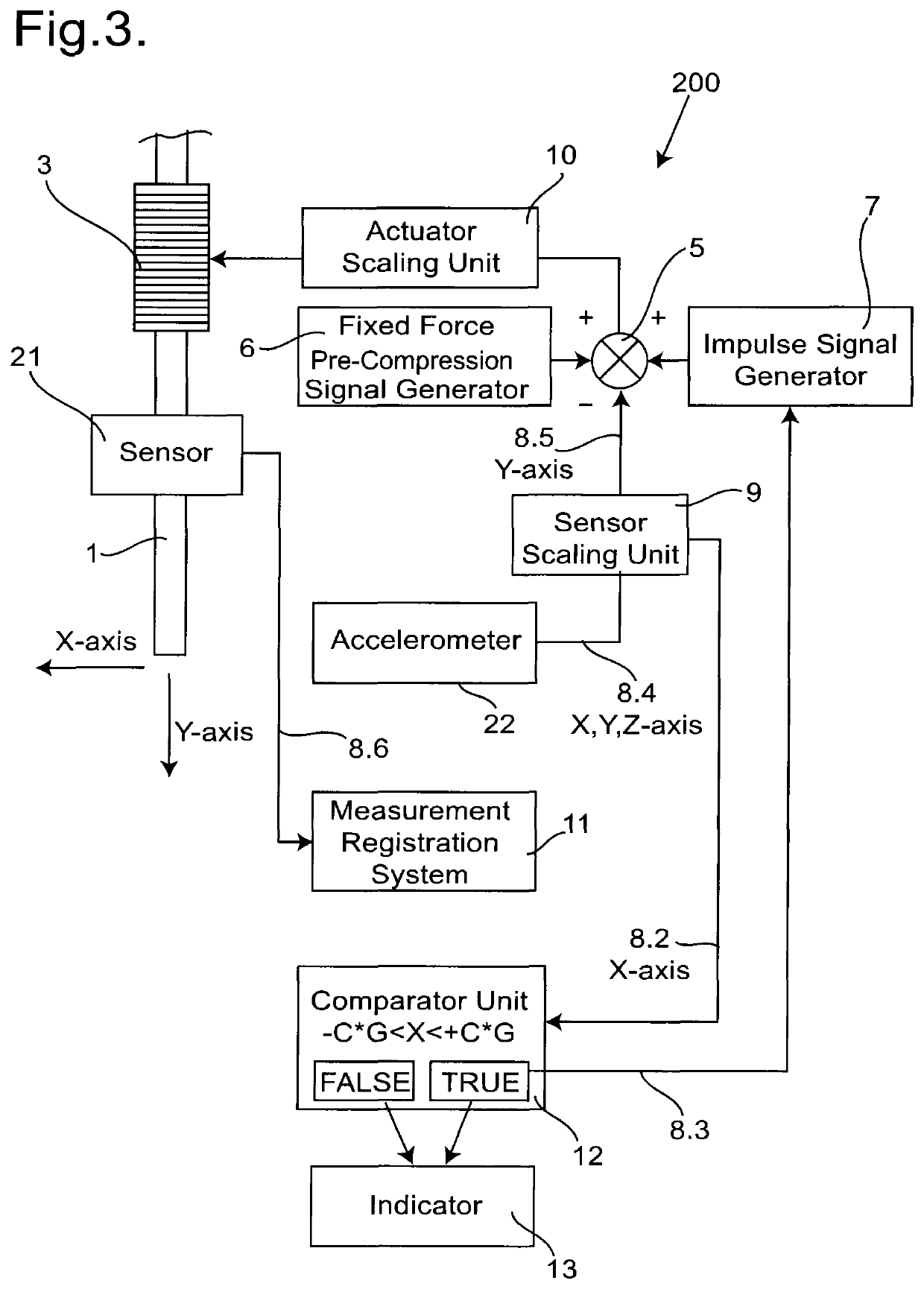
A system and method for the non-invasive measurement of tone, state of tension, biomechanical or viscoelastic properties of soft biological tissues includes a testing-end, an actuator arranged to apply a force to the testing-end, and a sensor to sense movement of the testing-end. A signal generating circuit supplies a control signal to the actuator so the biological tissues are subjected by the testing-end to a load, including means to adjust the signal provided by the signal generating circuit in accordance with the component of weight acting through the testing-end onto the biological tissue so that the load to which the biological tissue is subjected is constant. An impulse signal generating circuit supplies an impulse signal to the actuator so the biological tissue is subjected by the testing-end to a mechanical deformation. In use the soft biological tissue is subjected first to the constant load, and then to the impulse signal; and the consequent movement of the biological tissue is then registered.
Owner:MYOTON
Bionic bone sample for terahertz in-situ impact testing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108548732ASimplify the fine structurePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansNatural boneBiological materials
The invention relates to a bionic bone sample for terahertz in-situ impact testing and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of biomechanical testing. The bionic bone sample consisting of bionic skins, muscles and bones is constructed with a outside-to-inside topological structure. The bionic bones with porous gradient characteristics are prepared; the bionic muscle with similar mechanical properties to the natural biological muscles is attached to the outer layer of the bionic bone, and the outer layer of the muscle is wrapped with artificial skin, so as to prepare the bionicbone sample simulating a whole biological limb structure. Membrane pressure sensors are embedded in various components of the bionic bone sample, thus implementing all-directional, multi-level and stereoscopic detection on the values of the impact force on the various components of the bionic bone sample. The bionic bone sample can replace the natural bone for impact performance experiments and can integrate a variety of new detection methods, so that an effective tool is provided for biomaterial impact performance testing, and a new study means is provided for the study on the impact failuremechanism of biomimetic material instruments including bionic limbs, implanted bionic bones and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Multifunctional skull and maxillofacial bone impact mechanics experiment device
InactiveCN112116855AAccurate and comprehensive experimental conditionsCosmonautic condition simulationsEducational modelsGonial angleSkull bone
The invention belongs to the field of biomechanics, and particularly relates to an experimental device for performing multi-type, angle and force collision on human skull and maxillofacial bone. The experimental device comprises a pendulum impact device, a replaceable rammer, an impact force and acceleration measuring system and a multi-angle height adjusting model mounting platform. The inventionaims to realize an impact test of human skull and maxillofacial bone under different conditions. According to the experimental device, a scale spherical hinge and a height adjusting chute are additionally arranged on the model mounting platform, so that multidirectional accurate adjustment of a model is realized; the detachable rammer is adopted, so that the collision conditions of different sizes, shapes and materials are realized; and an impact force sensor and an acceleration sensor are additionally arranged, so that the acceleration and the impact force are obtained in an experiment. Theexperimental device provides more accurate and comprehensive experimental conditions for researching the damage form, tolerance limit, function damage degree and protective measures of the human skulland maxillofacial bone. Meanwhile, an experimental system can be applied to more fields not limited to biomechanics.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Sensor for tissue measurements
PendingCN111836572AEnhanced Sensing CapabilitiesAcoustic sensorsCatheterAnatomyBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to a sensor for non-invasive optoacoustic measurements of biomechanical and / or morphological features of skin and / or other tissue.
Owner:TECH UNIV MUNCHEN
Knee joint force loading and biomechanical characteristics detection experimental platform
ActiveCN108766169BImplement servo controlQuick and easy muscle loading methodEducational modelsTotal knee replacement surgeryArticularis genus
The invention provides an experimental platform for knee joint force loading and biomechanical detection. The experimental platform is mainly composed of seven parts including a frame unit, a femoralpose adjustment unit, a femoral reactivity and ligament strain measurement and force loading unit, a knee joint flexion driving unit, a tibia pose driven unit, a tibia internal and external rotationmeasurement unit, and a patella pose detection unit. The device compares the biomechanical characteristics of the in-vitro knee joint under different surgical techniques by detecting the biomechanicalcharacteristics of the knee joint after surgeries such as total knee replacement, anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, and posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOMOTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com