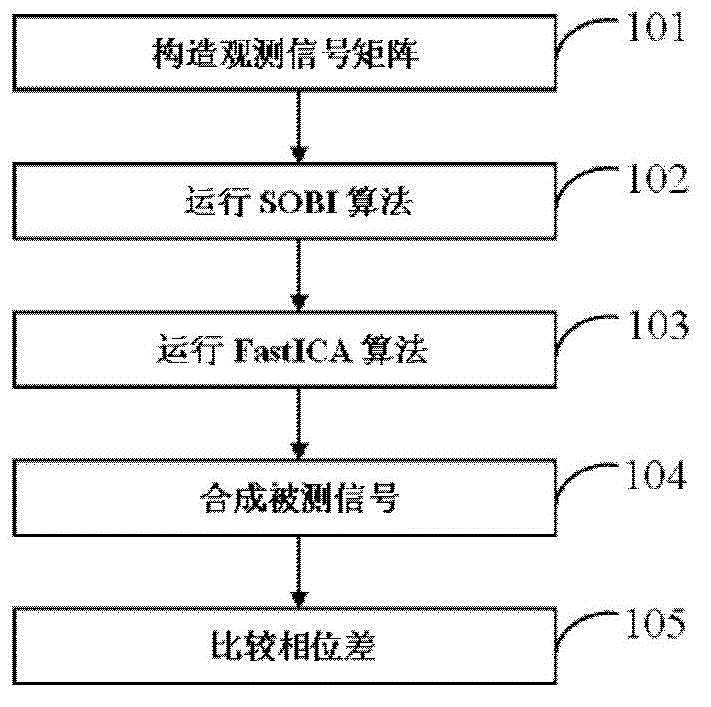
Measurement method for phase difference among same-frequency signals based on SOBI (Second Order Blind Identification) and FastICA (fast Independent Component Analysis)
A technology of same-frequency signal and measurement method, which is applied in the field of signal processing, can solve problems such as difficult to eliminate harmonic interference, difficult to meet measurement requirements, and slow measurement speed, so as to avoid zero drift, fast calculation speed and wide application range Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
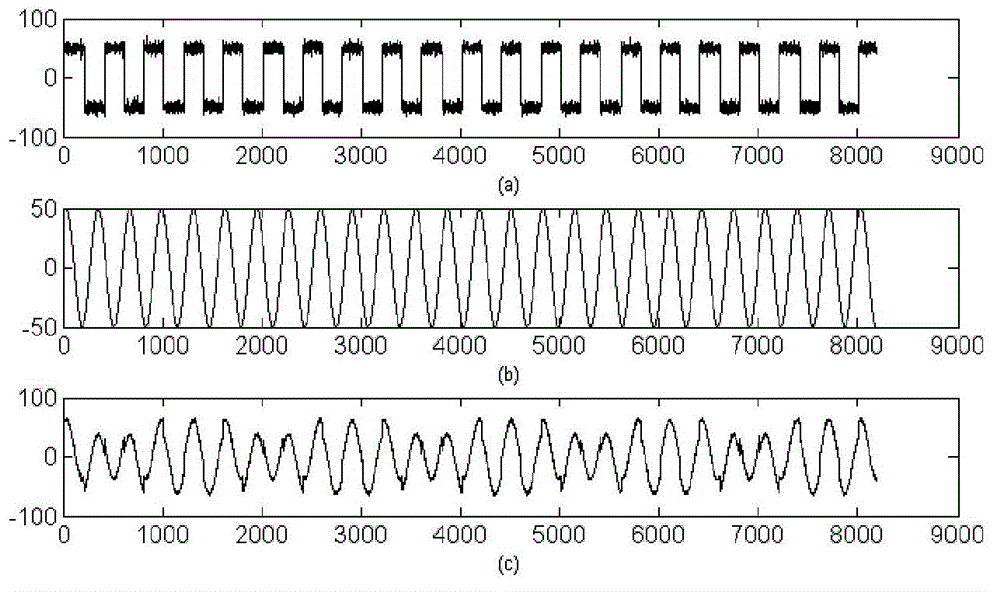
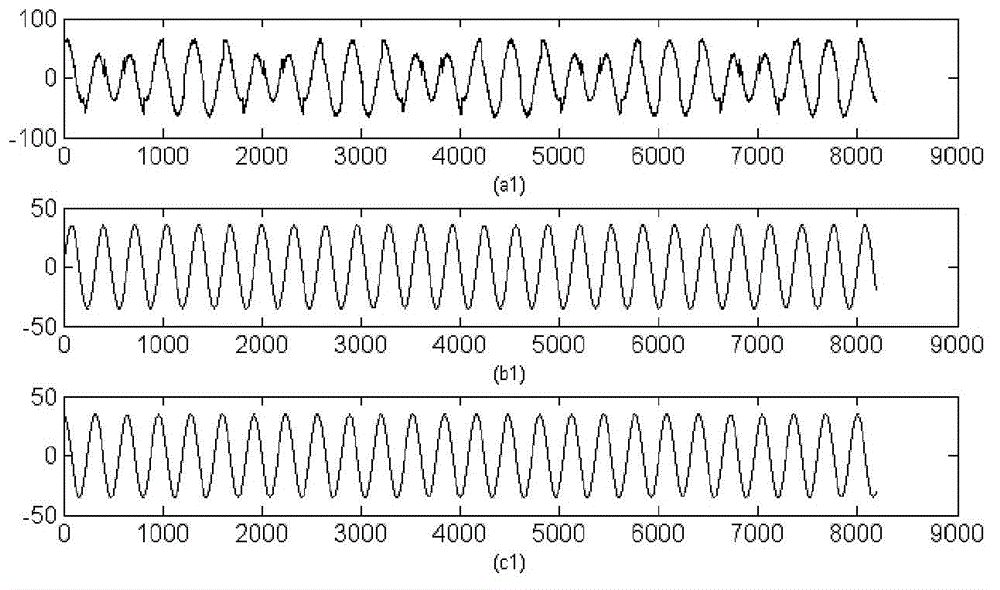
[0052] In order to verify the measurement effect of the same-frequency signal phase difference measurement method based on SOBI and FastICA provided by the present invention, a phase difference measurement experiment was carried out on the sinusoidal signal interfered with by noise and the standard sinusoidal signal. Experimental samples such as figure 2 As shown, where (a) is the noise signal, (b) is the standard signal, (c) is the measured signal, which is a linear mixture of (a) and (b), the signal-to-noise ratio is 6.07dB, and the sample length is 8K , the sampling interval is 50 μ s, and the experiment adopts the same-frequency signal phase difference measurement method based on SOBI and FastICA provided by the present invention to compare the phase difference of signals (b) and (c), and this measurement result can be regarded as the result of the method of the present invention Measurement error.
[0053] According to the measurement method provided by the present inve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com