Device and method for direction dependent spatial noise reduction
A space and equipment technology, applied in the field of direction-dependent spatial noise reduction, which can solve problems such as inappropriate hearing aid configuration and sensitivity to the geometry of microphone arrays
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
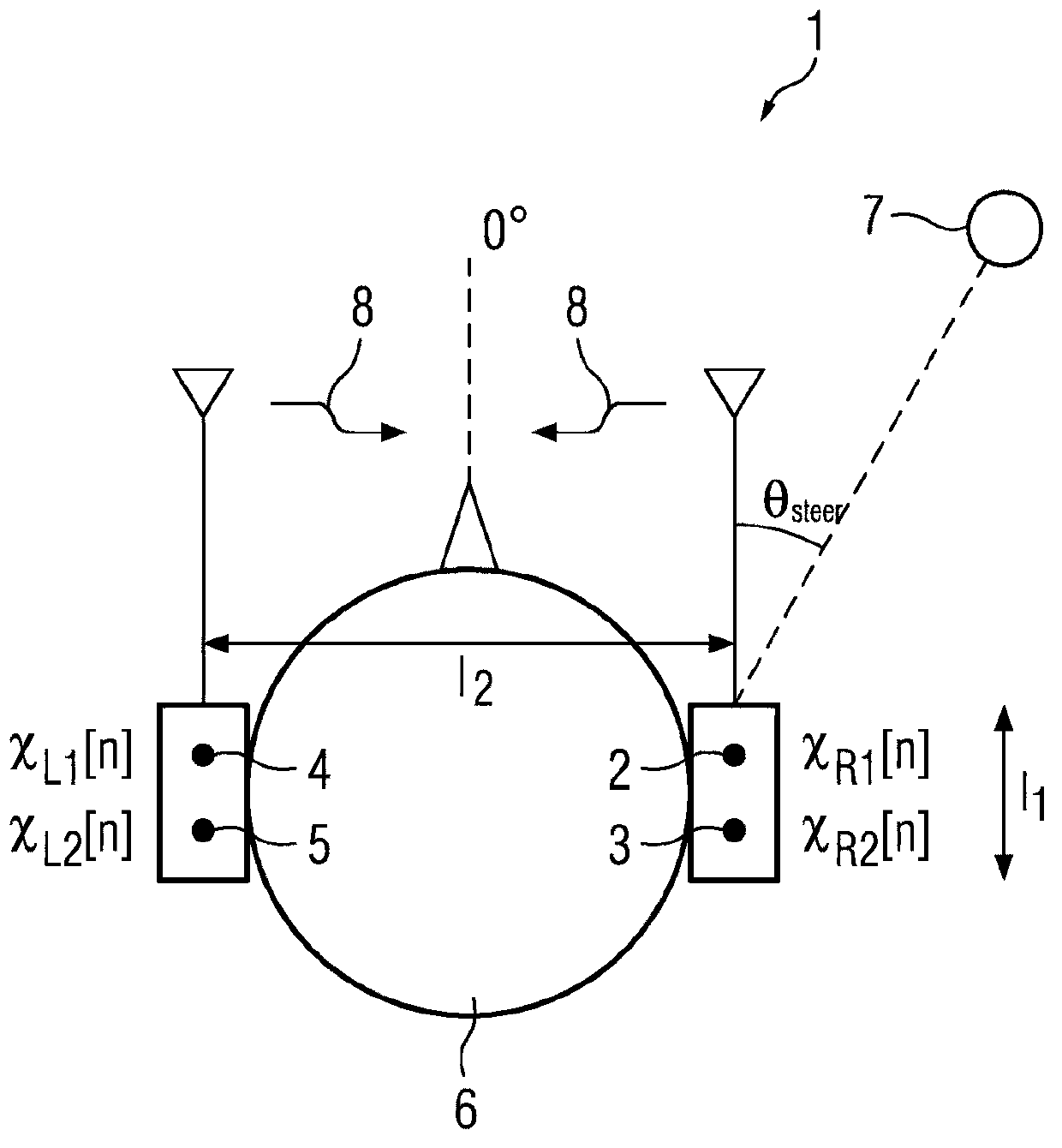
[0032] Embodiments of the invention discussed below provide apparatus and methods for direction-dependent spatial noise reduction, which can be implemented in, for example, figure 1 The binaural hearing aids shown are used in configuration 1. Configuration 1 comprises: a right hearing aid comprising a first pair of monaural microphones 2,3; and a left hearing aid comprising a second pair of monaural microphones 4,5. The left and right hearing aids are installed in the left and right ears of the user 6, respectively. The monaural microphone in each hearing aid is measured at a distance l 1 separated, due to size constraints, the distance l 1 For example, it may be approximately equal to 10 mm. The distance between the left and right hearing aids is l 2 Separate and connected by a two-way audio link 8, typically a wireless link. To minimize power consumption, only one microphone signal can be passed from one hearing aid to the other. In this example, the front microphones ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com