bias circuit
A bias circuit, bias current technology, applied in electrical components, amplifiers with semiconductor devices/discharge tubes, improving amplifiers to reduce temperature/power supply voltage changes, etc., to achieve the effect of suppressing temperature dependence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described based on the drawings.
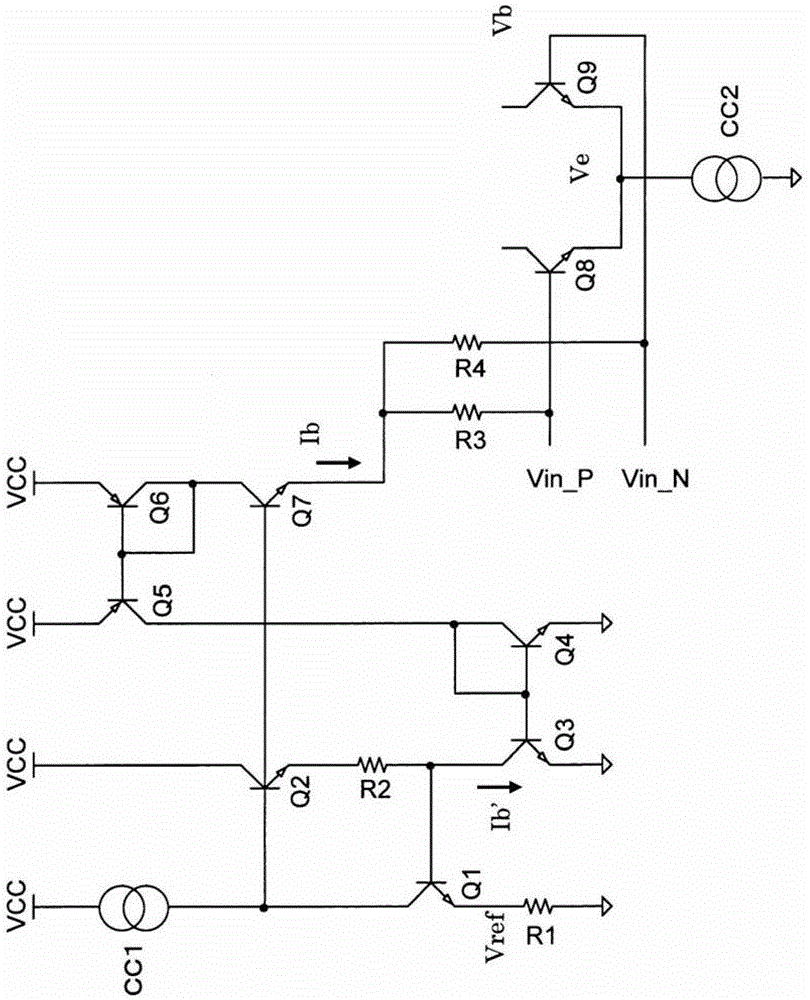
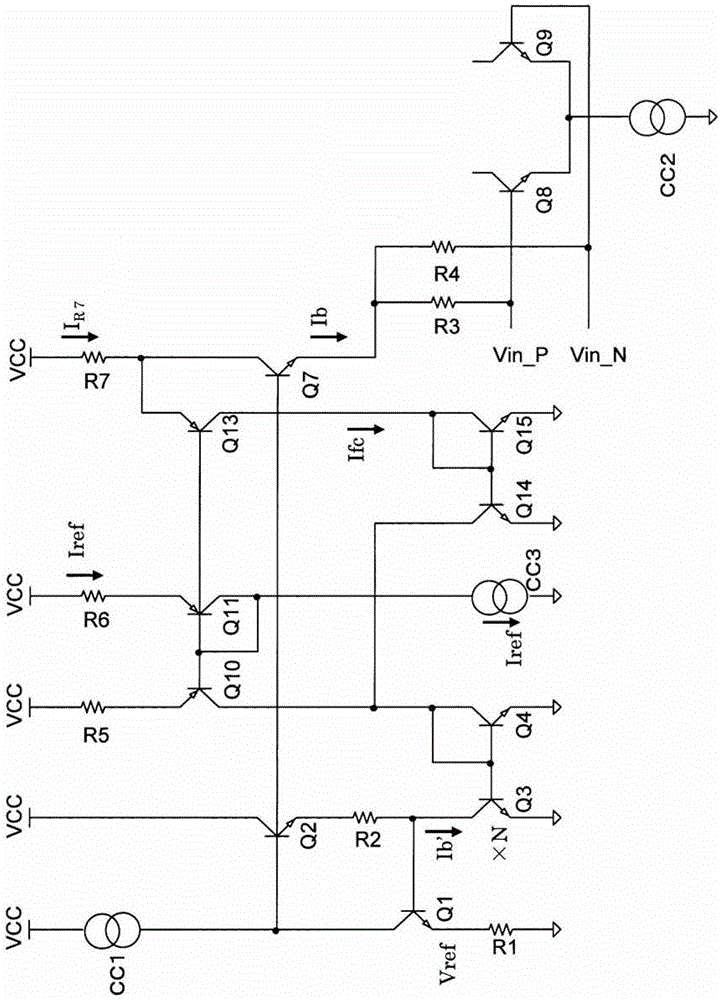
[0020] figure 1 The circuit configuration including the bias circuit according to the embodiment is shown.
[0021] The emitters of the NPN differential transistors Q8 and Q9 are connected in common, and the emitters are connected to the ground via the constant current circuit CC2. Here, the emitter voltages of the differential transistors Q8 and Q9 are set to Ve. The differential transistors Q8 and Q9 are part of the differential amplifier, and provide a pair of complementary signals, namely the signal Vin_P and the signal Vin_N to the bases of the differential transistors Q8 and Q9. Furthermore, bias currents are supplied to the bases of the transistors Q8 and Q9 via resistors R3 and R4, respectively.
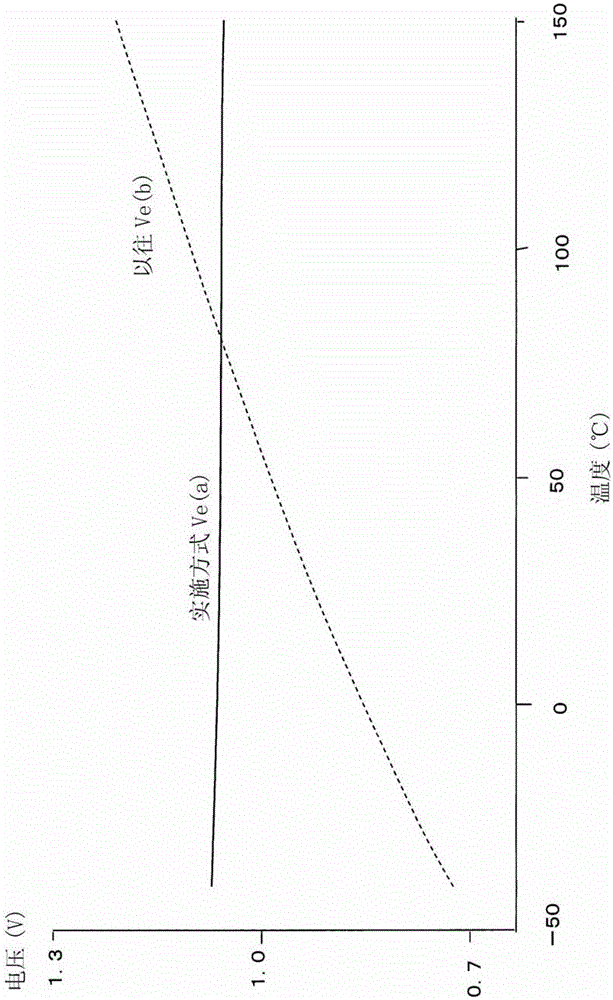
[0022] The current value Ib, which is the sum of the currents flowing through the resistors R3 and R4, is the base current (bias current) of the differential transistors Q8 and Q9 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com