Adjustment of a mixed reality display for inter-pupillary distance alignment
A technology of mixed reality and interpupillary distance, applied in the direction of instruments, image enhancement, user interface execution, etc., can solve problems such as eye fatigue or headaches, and difficult integration of users
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
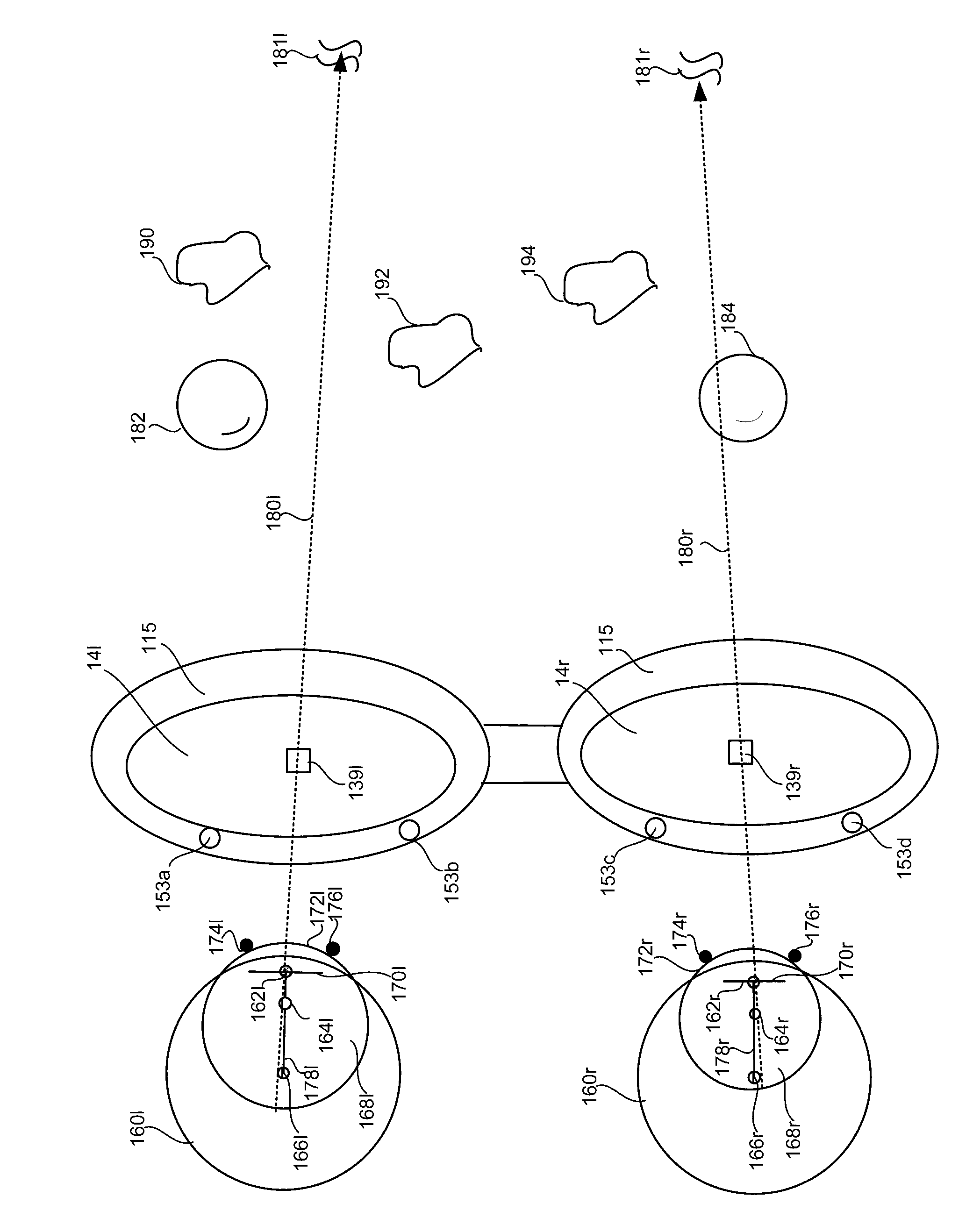
[0052] Interpupillary distance (IPD) generally refers to the horizontal distance between a user's pupils. IPDs may also include vertical or height dimensions. Additionally, many people have IPD that is asymmetrical relative to their nose. For example, the left eye is closer to the nose than the right eye.
[0053] The see-through, near-eye mixed reality display includes display optics for each eye with an optical axis positioned to be see-through by the respective eye. The display device is aligned with the user's IPD (asymmetric or symmetric) when the optical axis of each display optical system is aligned with the corresponding pupil. If each pupil is not aligned with the optical axis within a criterion, the corresponding display optics are adjusted via the display adjustment mechanism until the alignment satisfies a criterion. An example of a criterion is a distance, eg 1 mm. When the pupils are satisfactorily aligned with the optical axis, the distance between the optic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com