Node-similarity-based network community division method in network
A network community and similarity technology, applied in the field of network community division based on node similarity, can solve the problems of not meeting the ideal requirements of users, not comprehensively utilizing node information, and inaccurate network community structure division.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
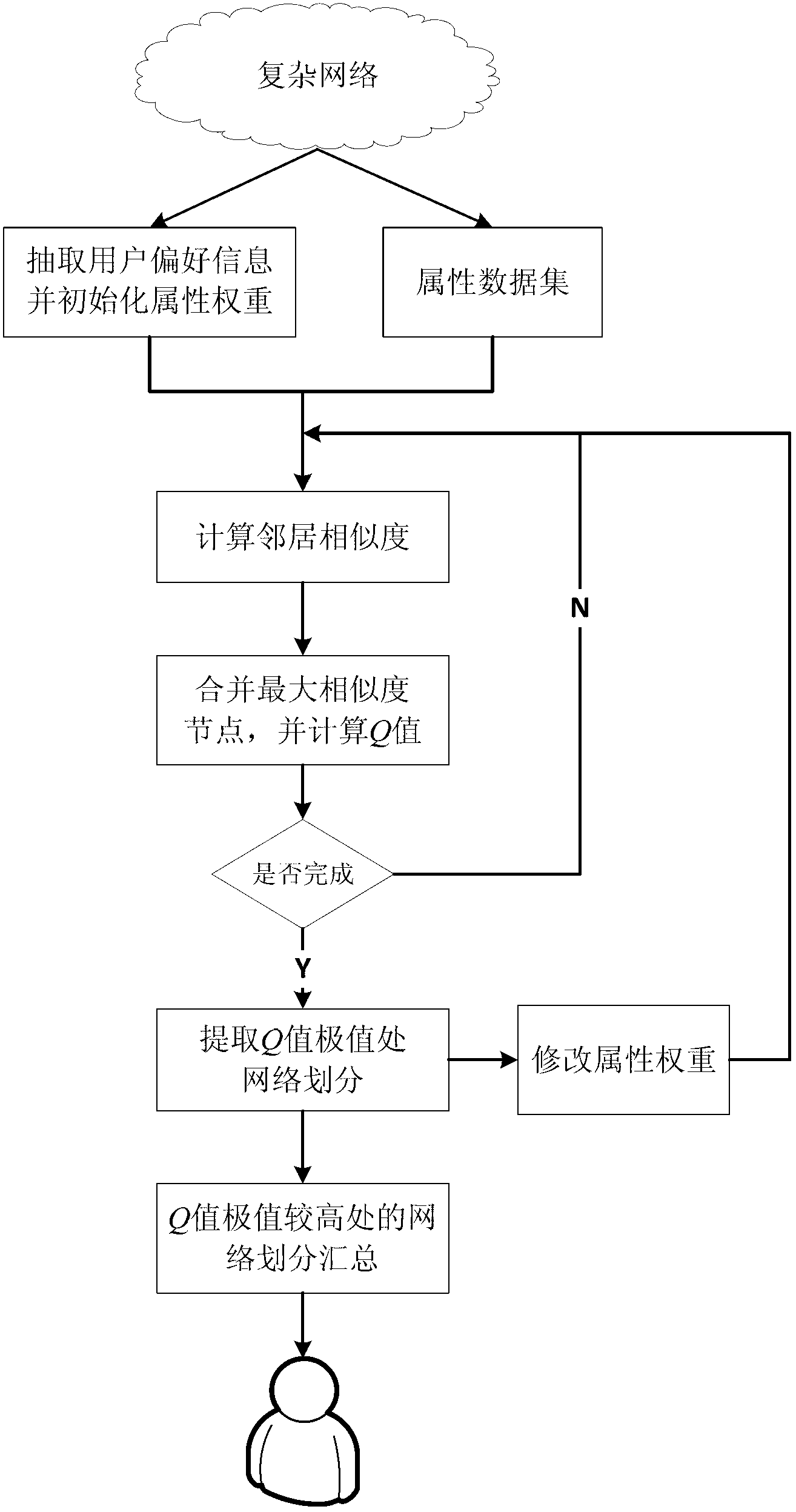
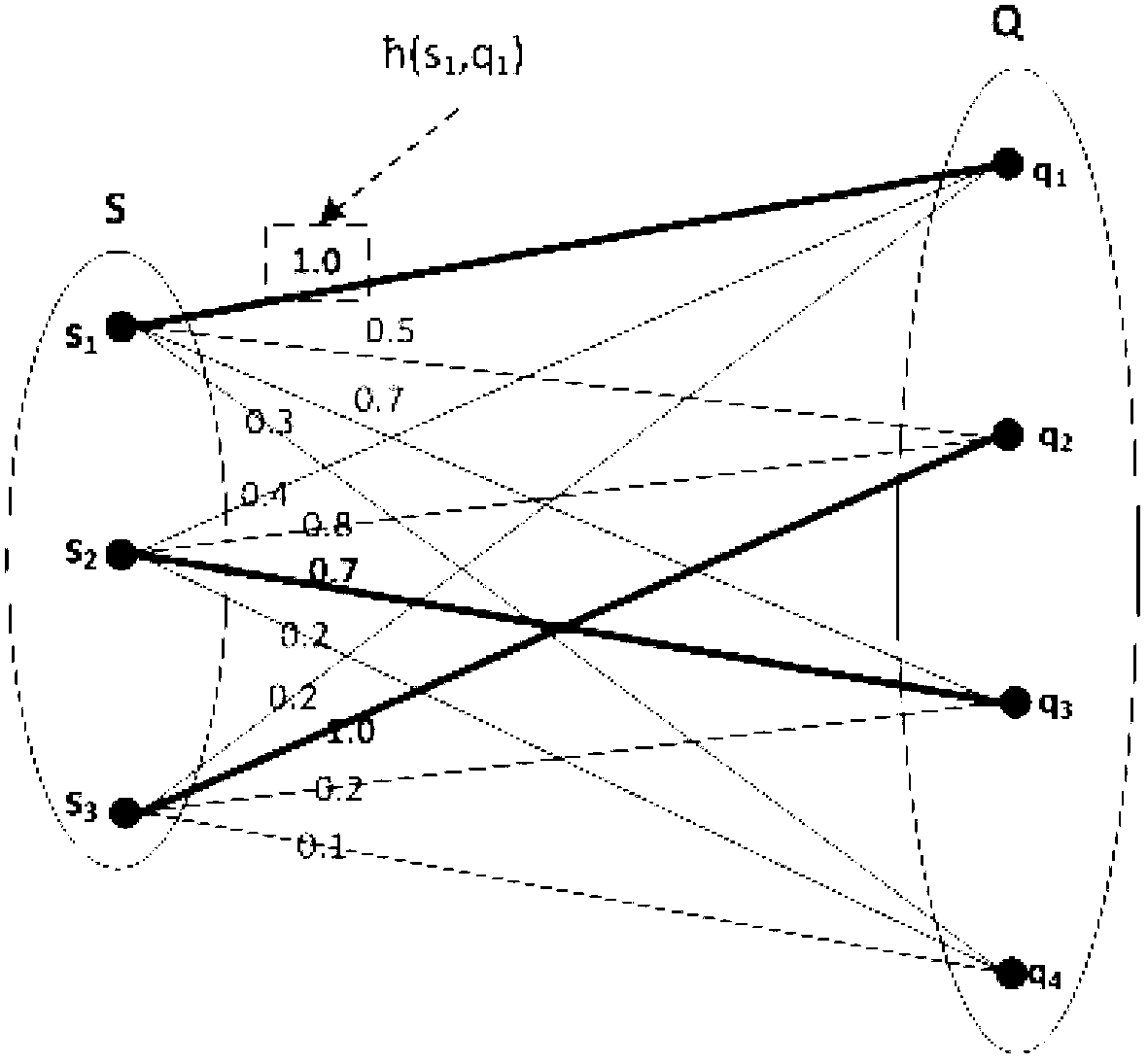
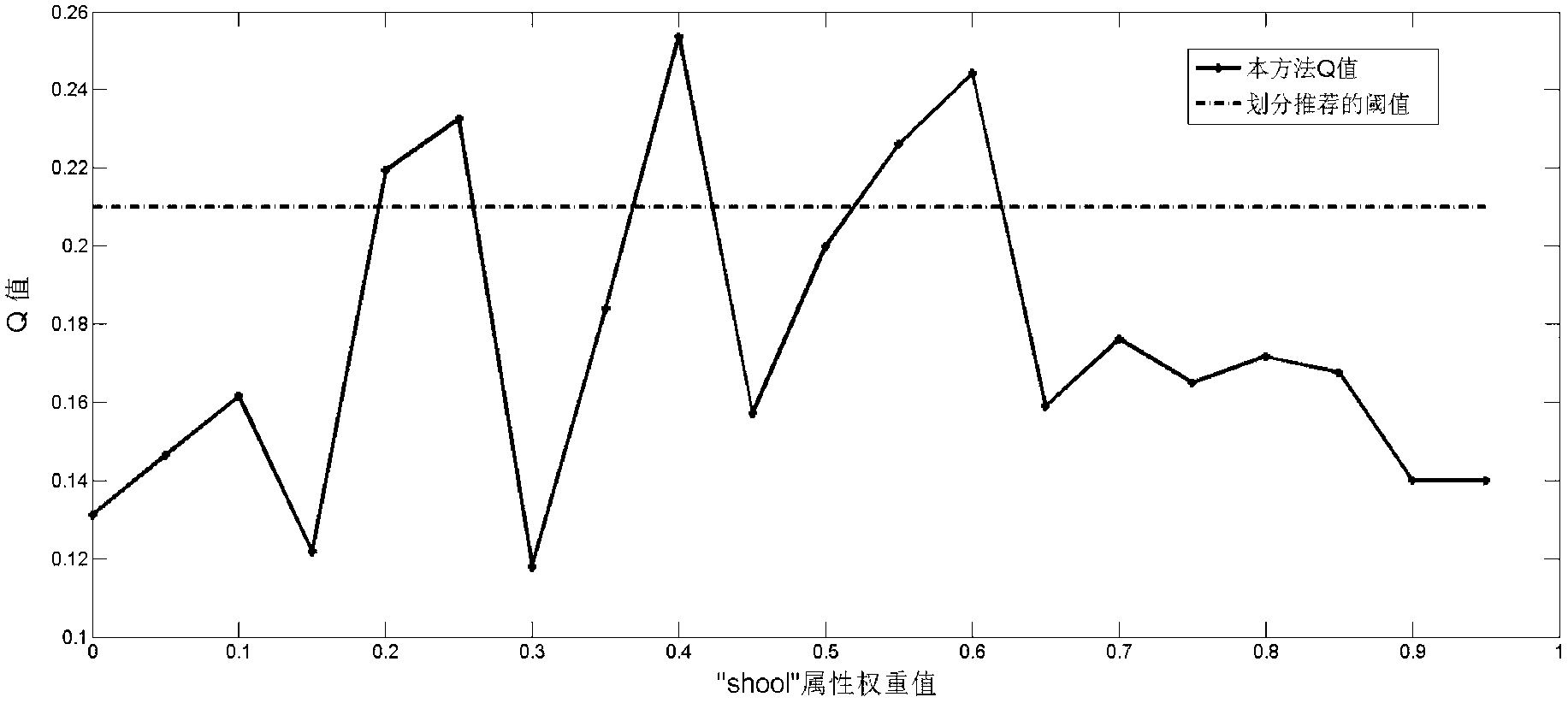
[0063] In this embodiment, a scientist cooperation network is built by counting the relevant data of the computer department teachers in a certain university. The nodes in the network represent the teachers of the computer department of the school, and the links between the scientists represent that the two have one or more cooperatively published papers. The data comes from the DBLP database. Assuming that the user expects the algorithm to take into account the attributes of the scientist’s school and research direction into the network community division, Table 1 shows the selected node attributes and network link attributes, where Schools and Interests are node attributes, and Schools is used to record scientists Relevant school information, such as the school during the doctoral degree, the recent exchange visit school, etc. If there are more than one, only the four most influential schools will be recorded. Interests is used to record the research direction or research int...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com