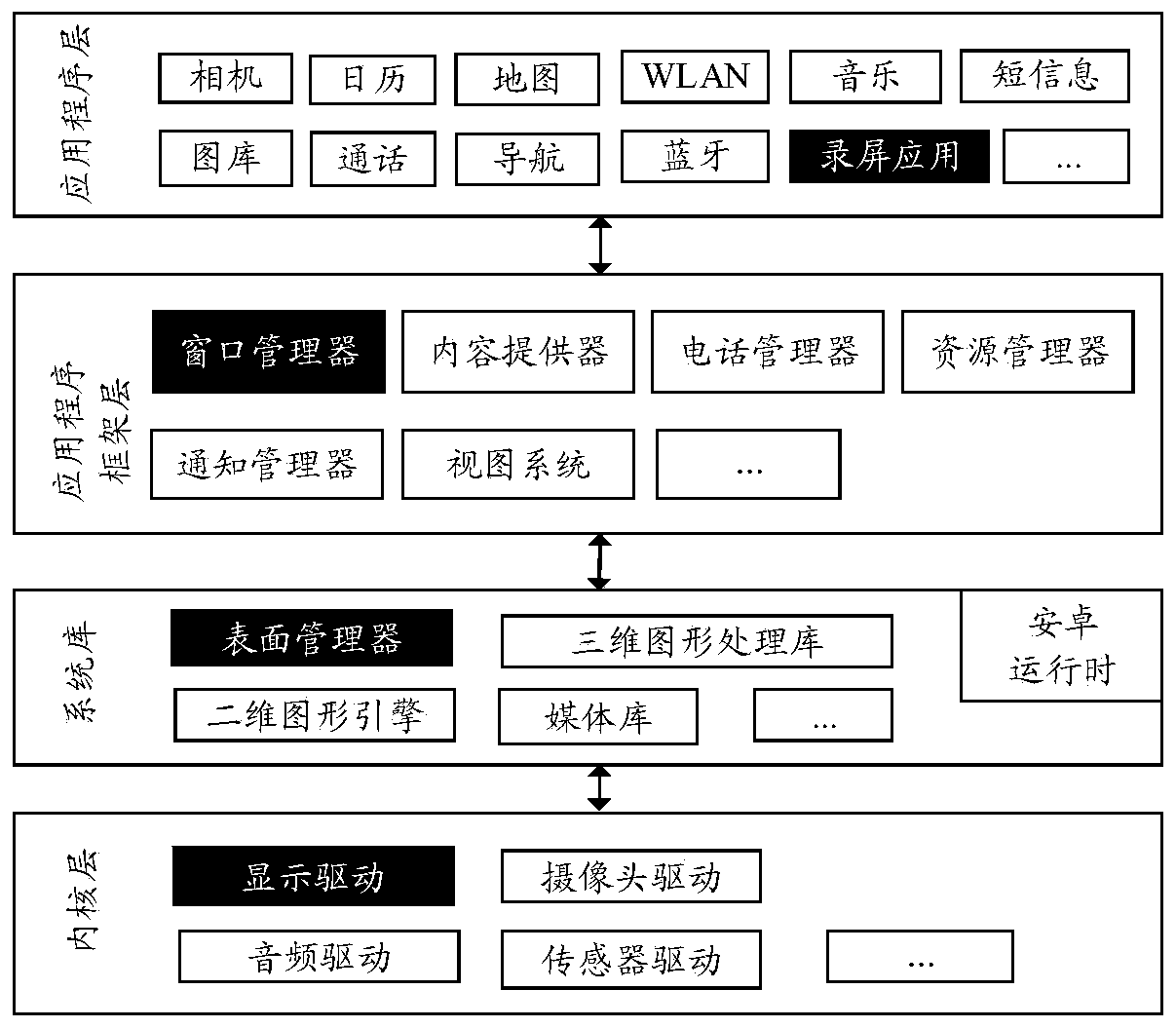
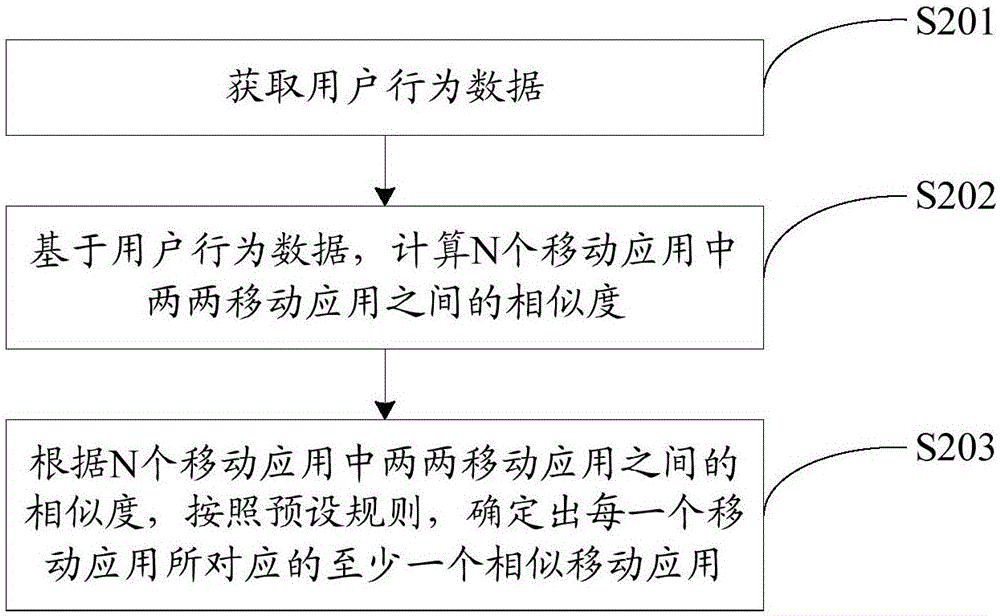
Patents
Literature
140 results about "N application" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
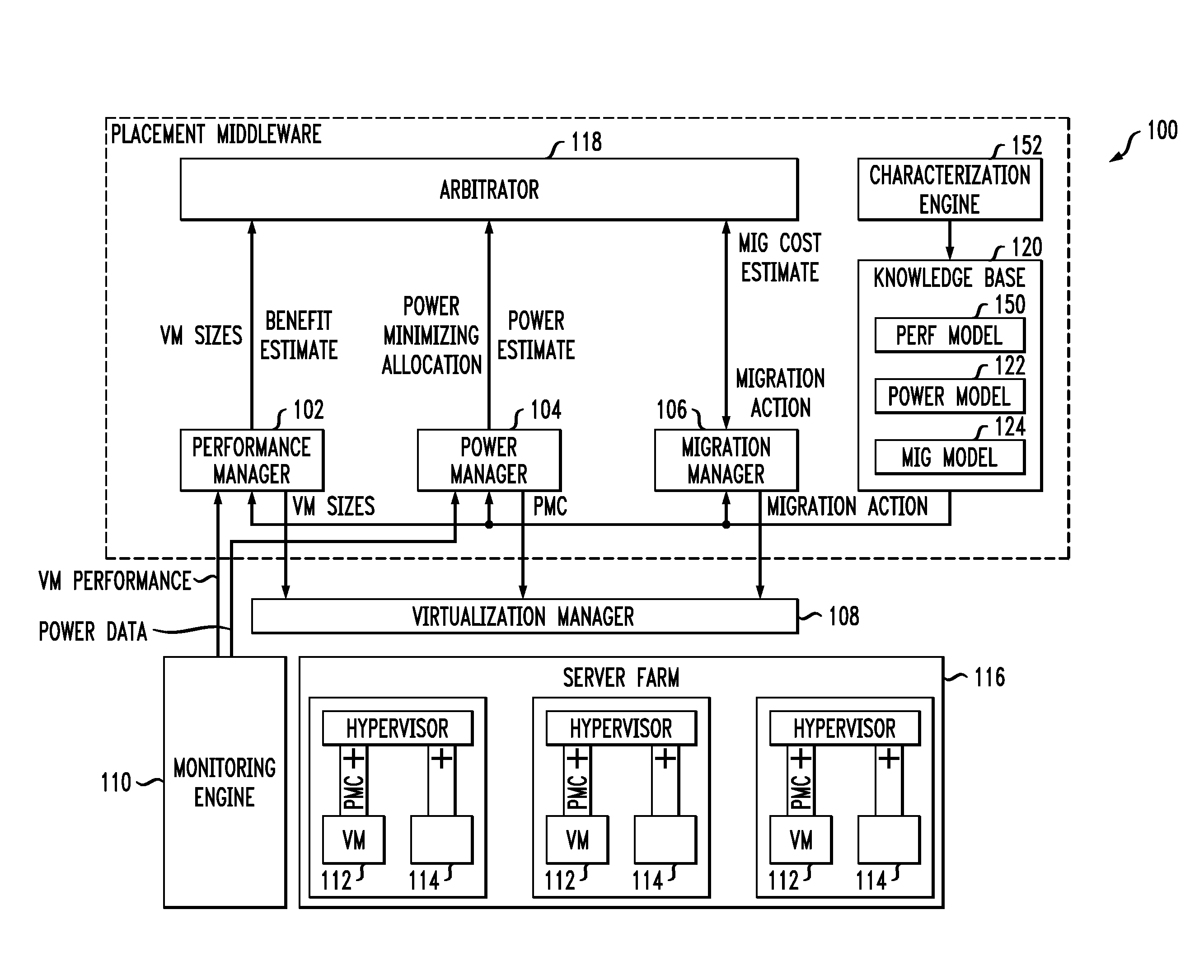
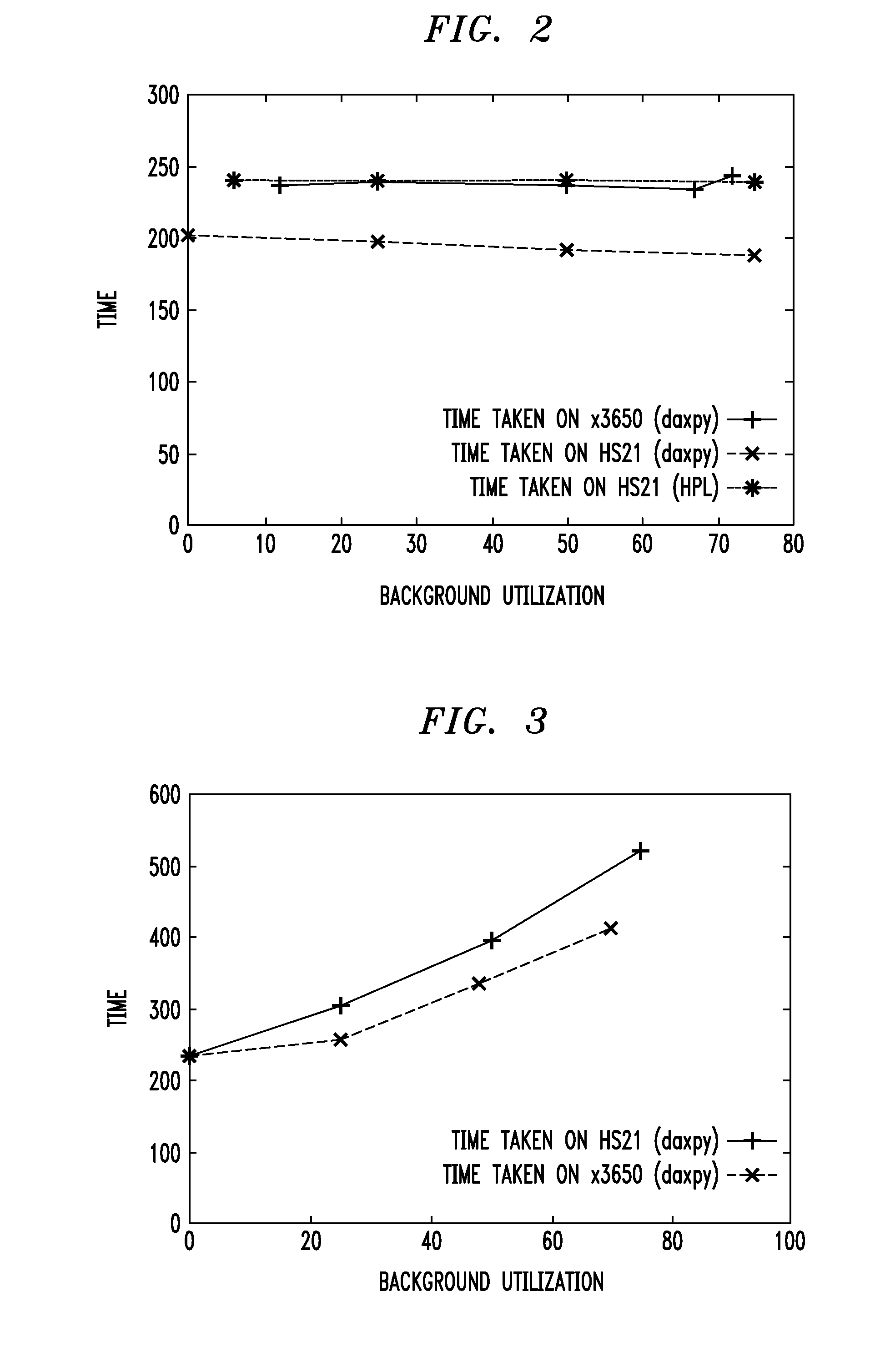
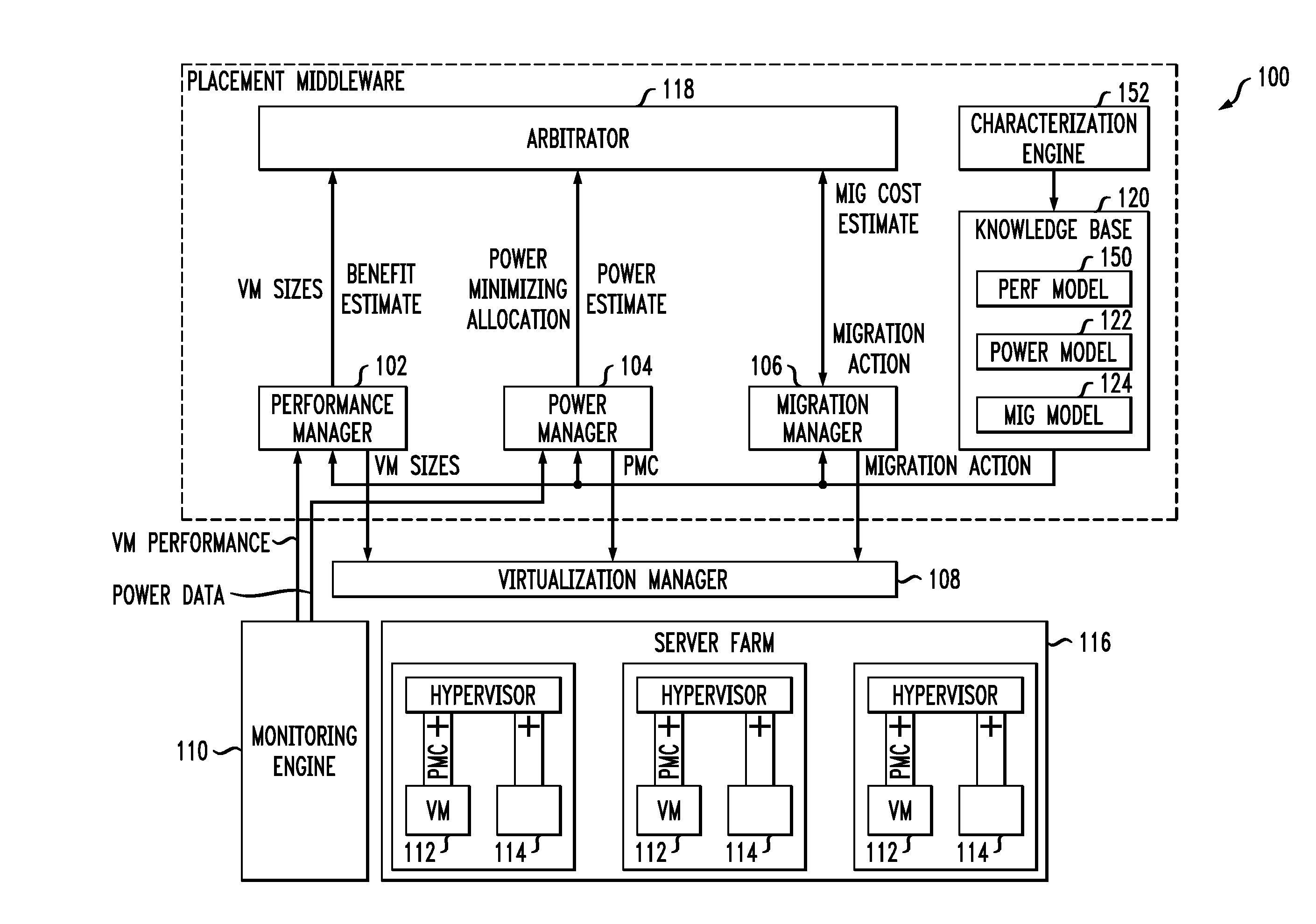
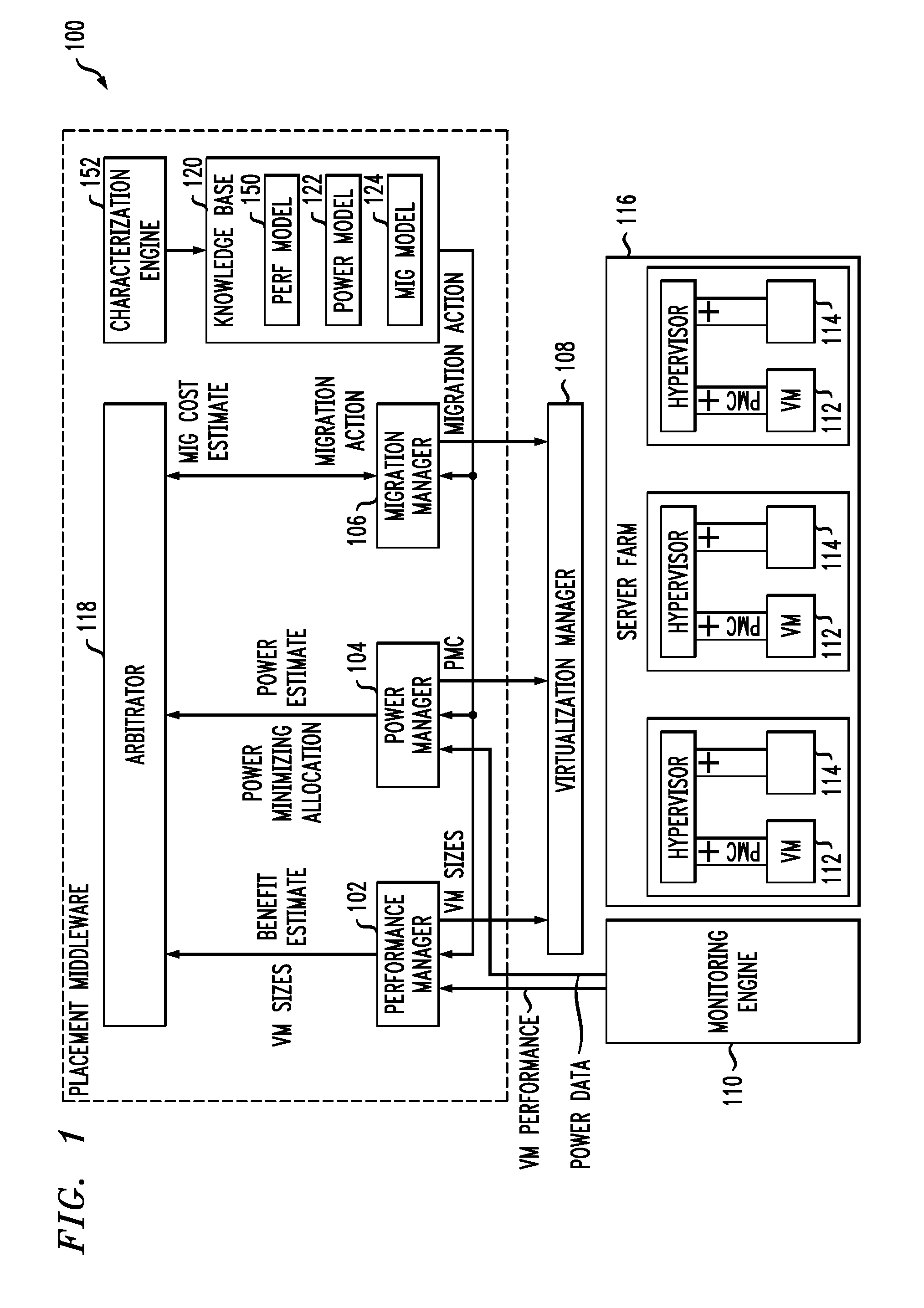
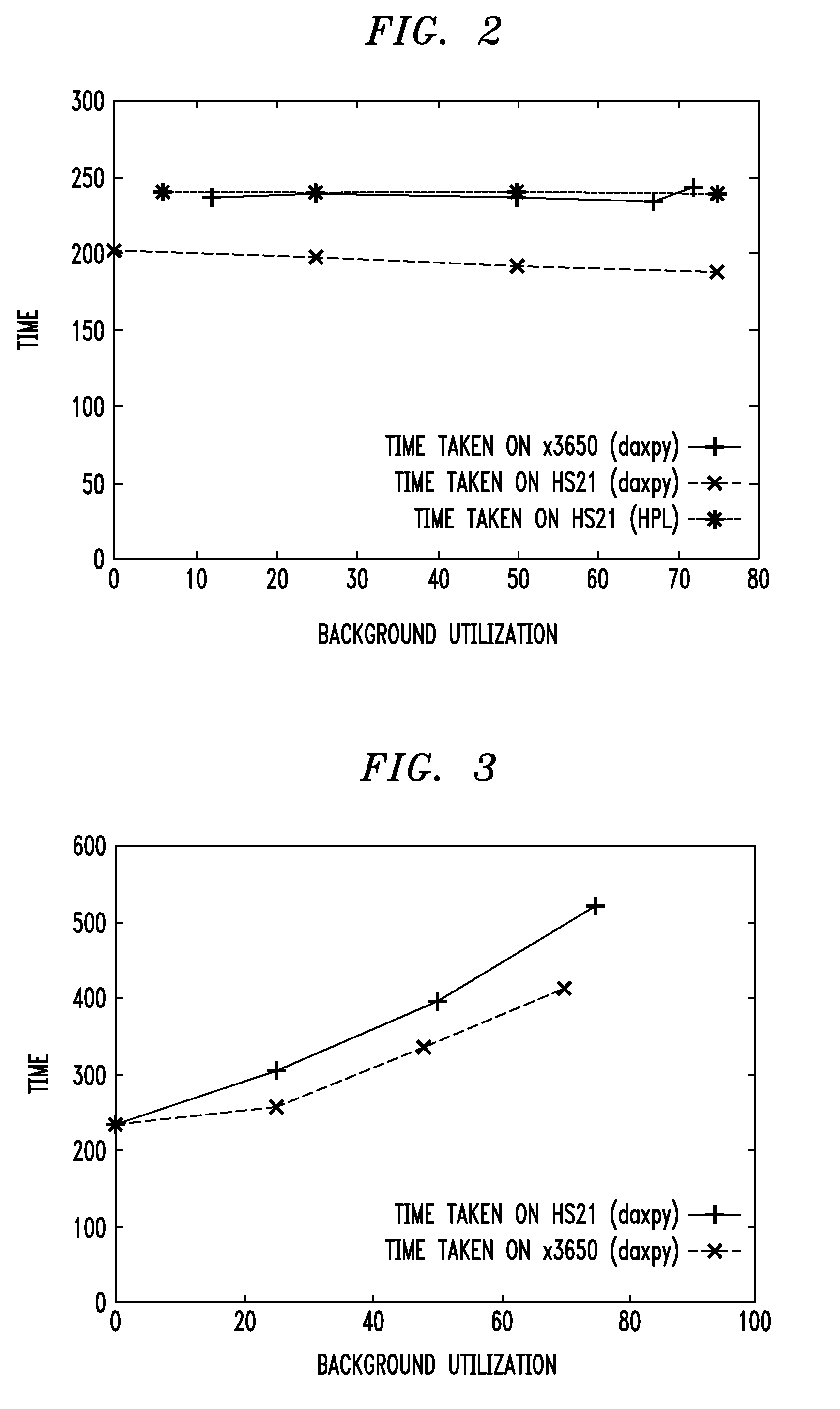
Techniques for placing applications in heterogeneous virtualized systems while minimizing power and migration cost
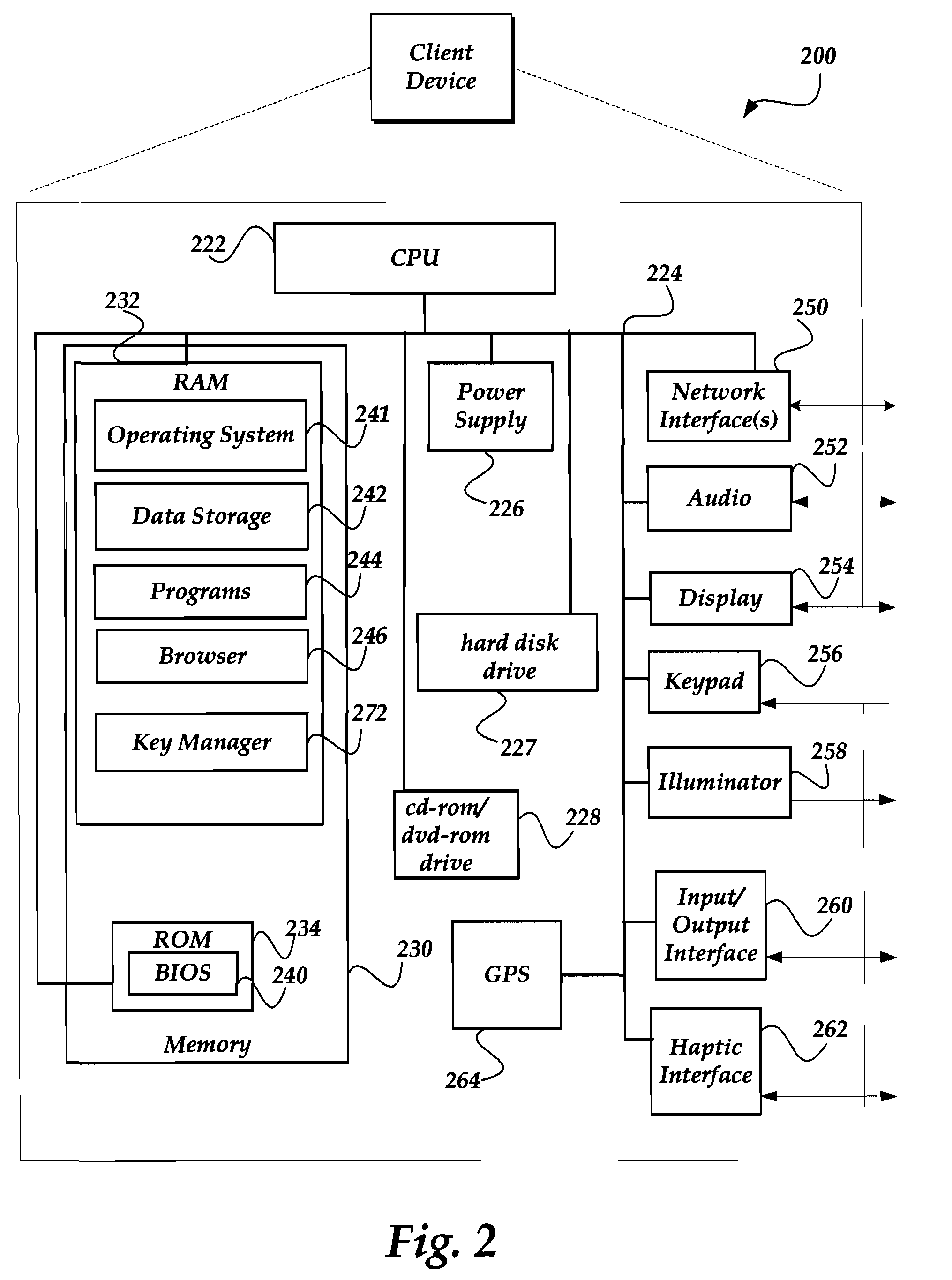
ActiveUS20100180275A1Minimizing migrationMinimize powerVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingVirtualizationN application
N applications are placed on M virtualized servers having power management capability. A time horizon is divided into a plurality of time windows, and, for each given one of the windows, a placement of the N applications is computed, taking into account power cost, migration cost, and performance benefit. The migration cost refers to cost to migrate from a first virtualized server to a second virtualized server for the given one of the windows. The N applications are placed onto the M virtualized servers, for each of the plurality of time windows, in accordance with the placement computed in the computing step for each of the windows. In an alternative aspect, power cost and performance benefit, but not migration cost, are taken into account; there are a plurality of virtual machines; and the computing step includes, for each of the windows, determining a target utilization for each of the servers based on a power model for each given one of the servers; picking a given one of the servers with a least power increase per unit increase in capacity, until capacity has been allocated to fit all the virtual machines; and employing a first fit decreasing bin packing technique to compute placement of the applications on the virtualized servers.
Owner:IBM CORP
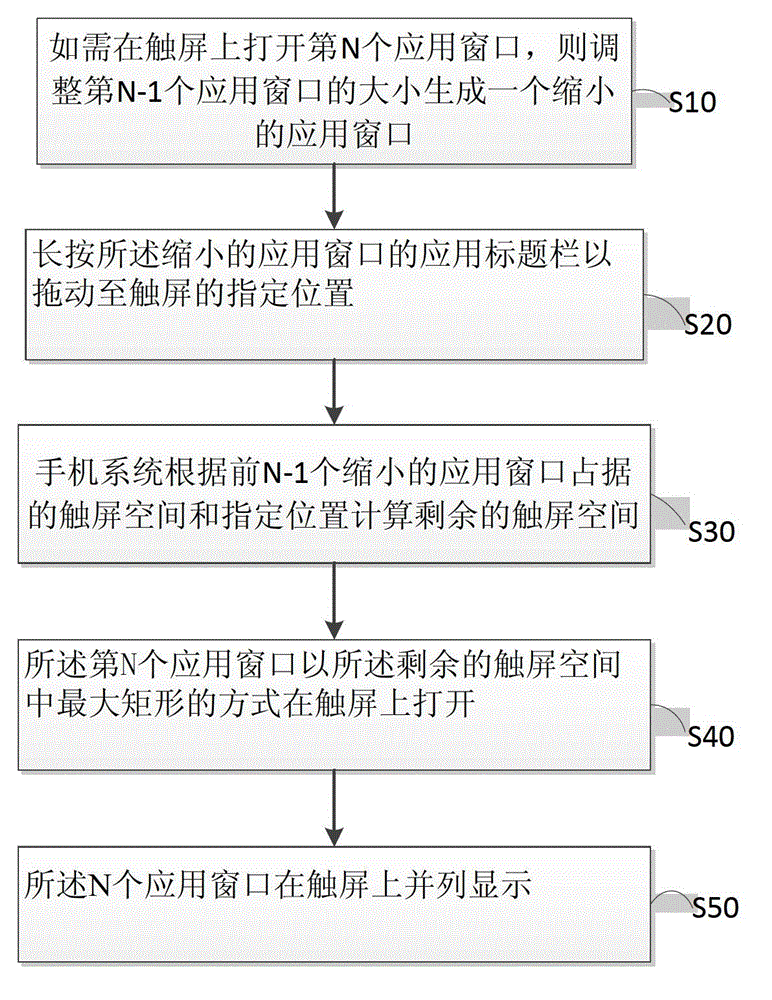
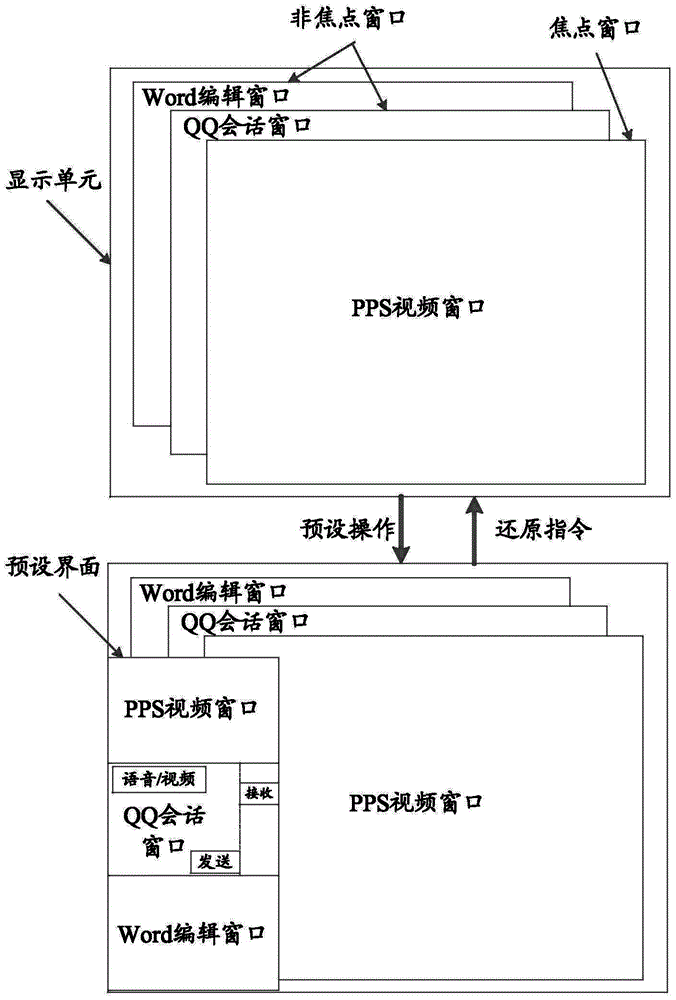
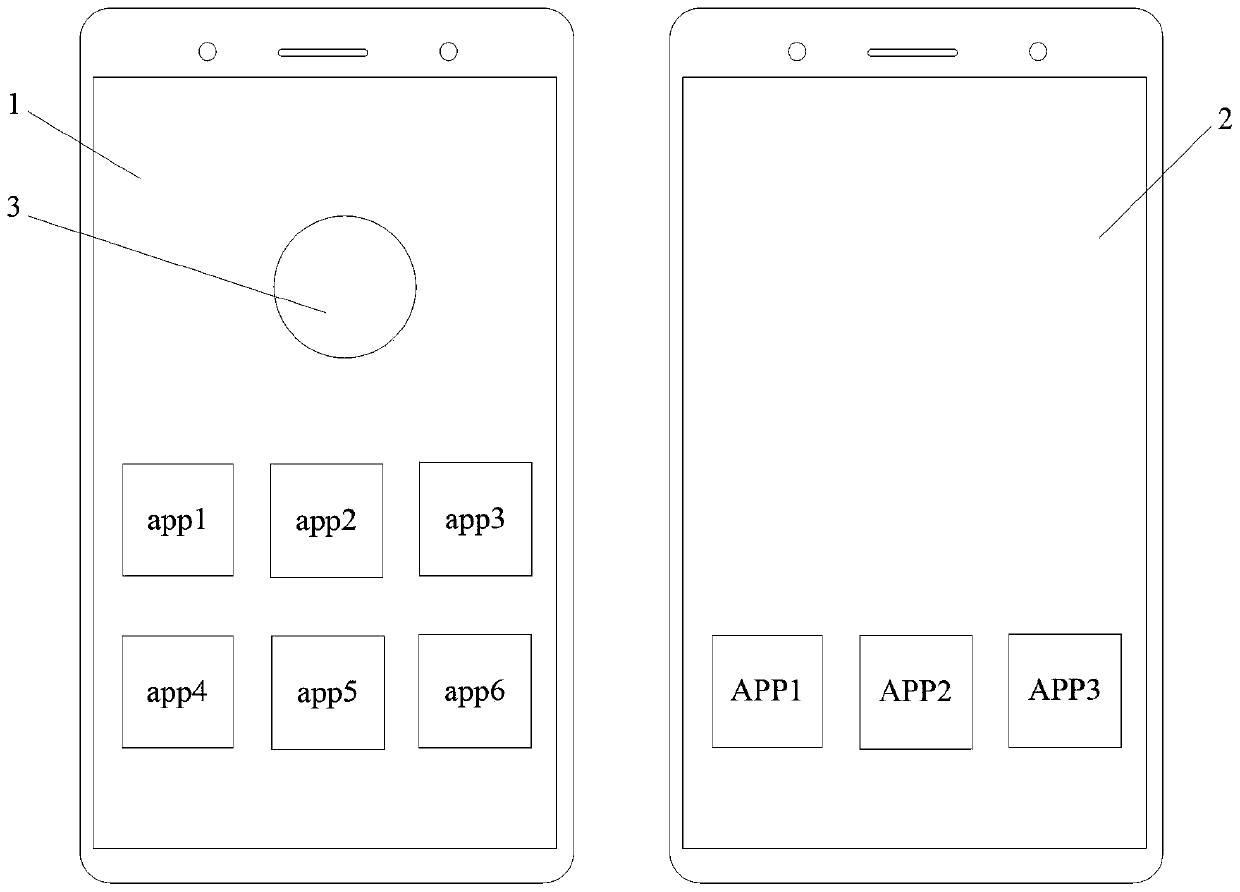
Method and device of multi-window displaying of smart phone
ActiveCN103067569AEnables switching-free operationImprove experienceSubstation equipmentInput/output processes for data processingN applicationComputer engineering
The invention discloses a method and a device of multi-window displaying of a smart phone. The method of multi-window displaying of the smart phone comprises steps as below: if the Nth application window needs to be opened on a touch screen, the size of the N-1th application window is adjusted to generate a contractible application window (S10). The application title bar of the contractible application window is pressed for a long time to drag the application title bar to a designated position (S20) of the touch screen. The remaining space (S30) of the touch screen is automatically calculated according to the occupied space of the touch screen of all the N-1 contractible application windows. The Nth application window is opened as the biggest rectangle of the remaining space of the touch screen. All the N application windows are displayed (S50) in parallel on the touch screen. Due to the method of multi-window displaying of the smart phone, no switching operations of multi-screen and multi-task windows are achieved, procedures of exiting and opening an application repeatedly are avoided, and efficiency is improved, and user experience is improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
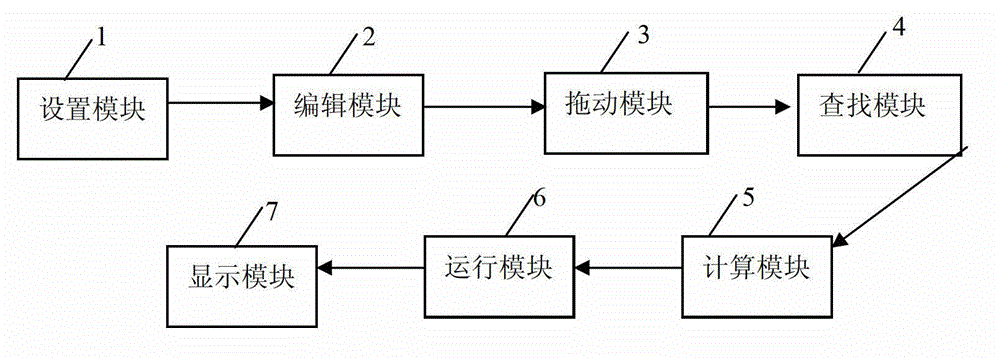
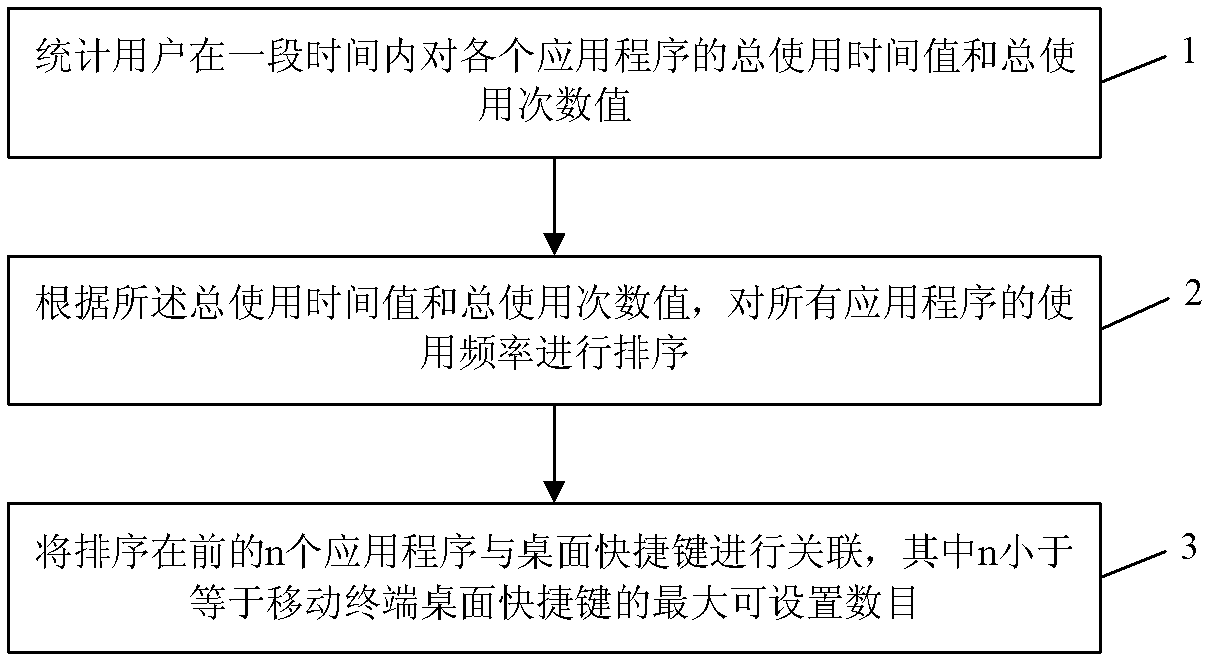
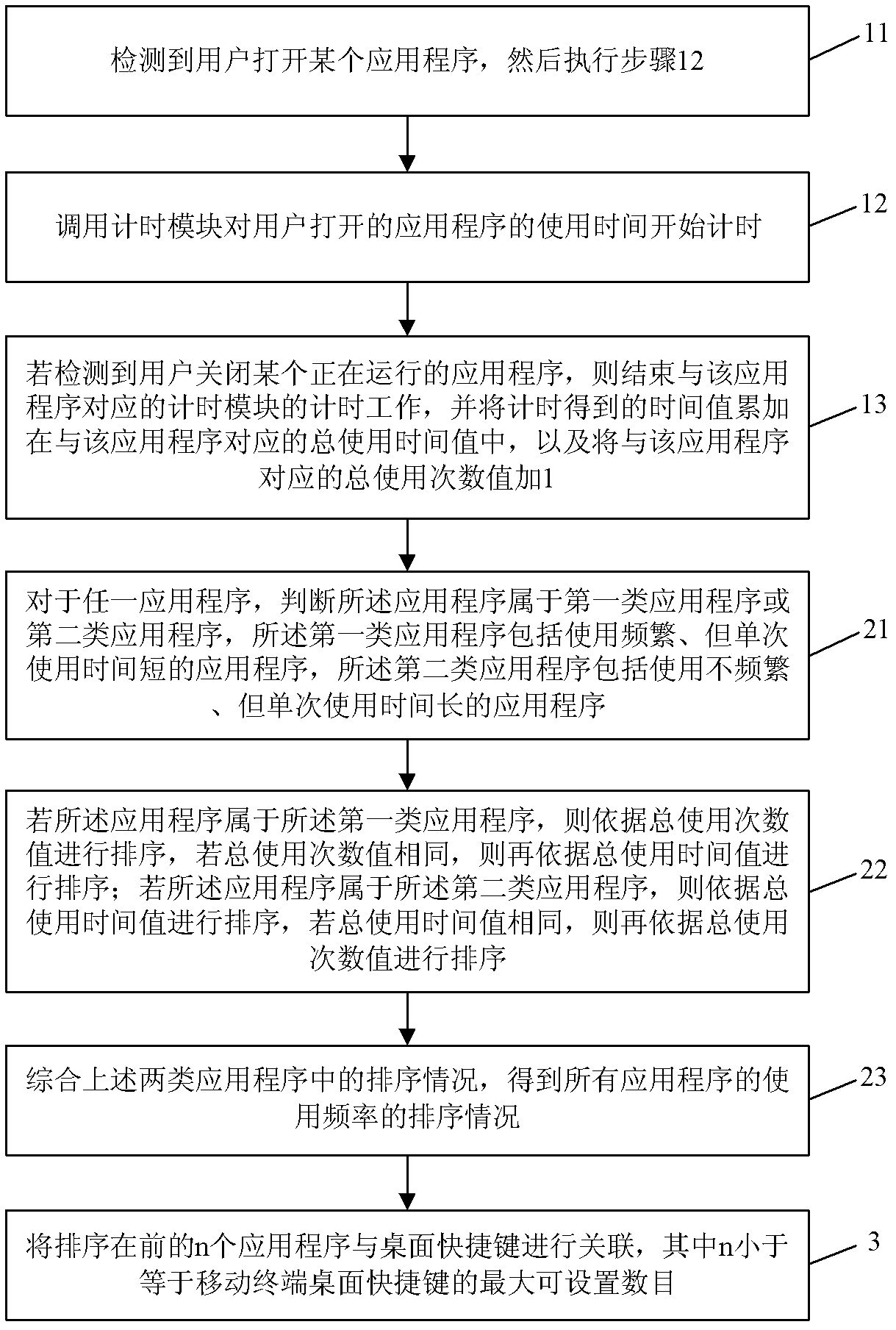
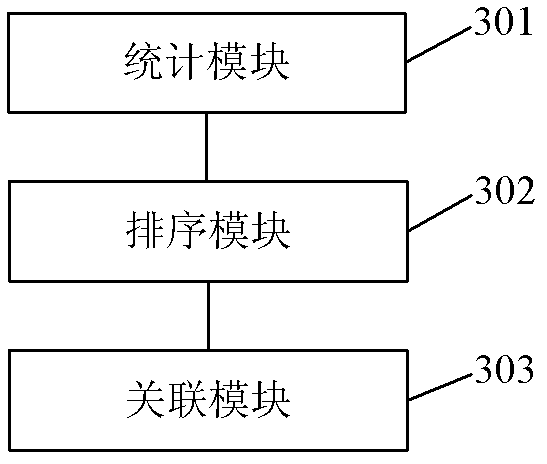
Method and device for automatically setting desktop shortcut keys on mobile terminal
InactiveCN102147732AStatistical usage frequencyImprove experienceSpecific program execution arrangementsN applicationKeyboard shortcut
The invention discloses a method and a device for automatically setting desktop shortcut keys on a mobile terminal. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, counting a total using time value and a total used time value of a user on each application program within a period of time; 2, sequencing using frequencies of all application programs according to the total using time value and the total used time value; and 3, associating the sequenced leading n application programs with the desktop shortcut keys, wherein n is less than or equal to a maximum settable number of the desktop shortcut keys on the mobile terminal. By the invention, the using frequencies of the user on the application programs in the mobile terminal can be counted in real time, and the application programs with high using frequencies are automatically set into the desktop shortcut keys, so that the user does not need to manually select and set the desktop shortcut keys according to the requirements; and a user experience is enhanced.
Owner:SHENZHEN WUJU SCI TECH
Selective muting of applications
Methods, computer program products, and electronic devices are provided for managing sound in a plurality of computer-executed applications. One method includes: operating a sound manager function to provide a user with an option to selectively mute up to n−1 applications of n applications, where n>1; and in response to the user choosing to selectively mute up to n−1 applications, the sound manager function selectively muting the up to n−1 applications. Another method includes providing a user with an option to selectively mute up to n−1 applications of n applications, where n>1. In response to the user choosing to selectively mute up to n−1 applications, at least one action is performed in response to requests to play sounds by the selectively muted applications so that the sounds are muted with respect to a sound device.
Owner:TWITTER INC
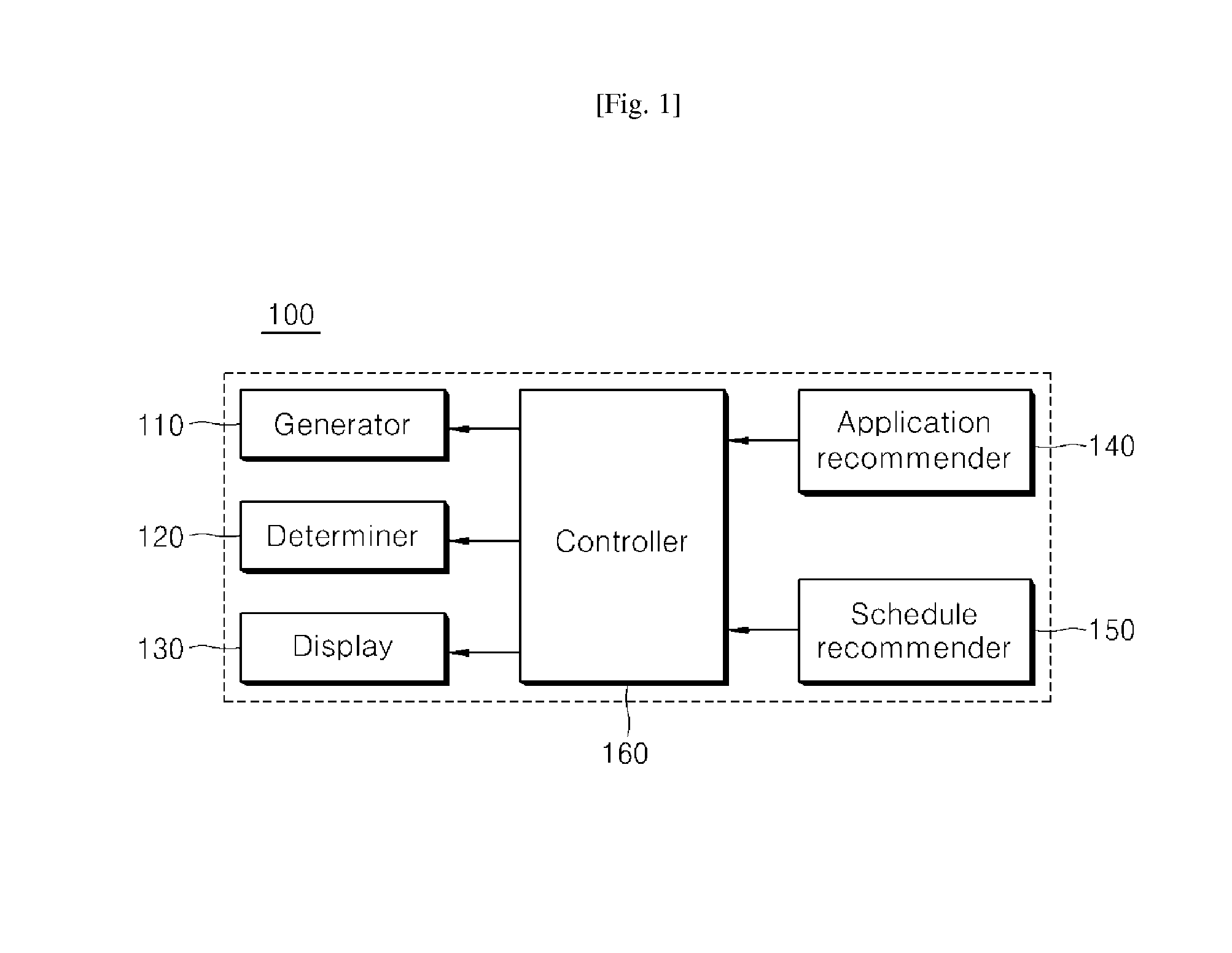
Apparatus and method for user-centered icon layout on main screen
InactiveUS20130311946A1Improve convenienceImprove accessibilitySubstation equipmentDigital output to display deviceN applicationDisplay device
Disclosed herein is an apparatus for user-centered icon layout on a main screen. The apparatus includes a generator which analyzes a usage pattern of a user terminal according to applications and generates lifestyle information based on a user preference of the applications, a determiner which determines order of priority with regard to the applications according to usage frequency and duration for each of the applications installed in the user terminal based on the lifestyle information, and a display which selects N applications (where, N is a natural number) based on the determined order of priority with regard to the applications, loads icons respectively corresponding to the N selected applications from a memory, and displays the icons on the main screen of the user terminal.
Owner:KWON O HYEONG
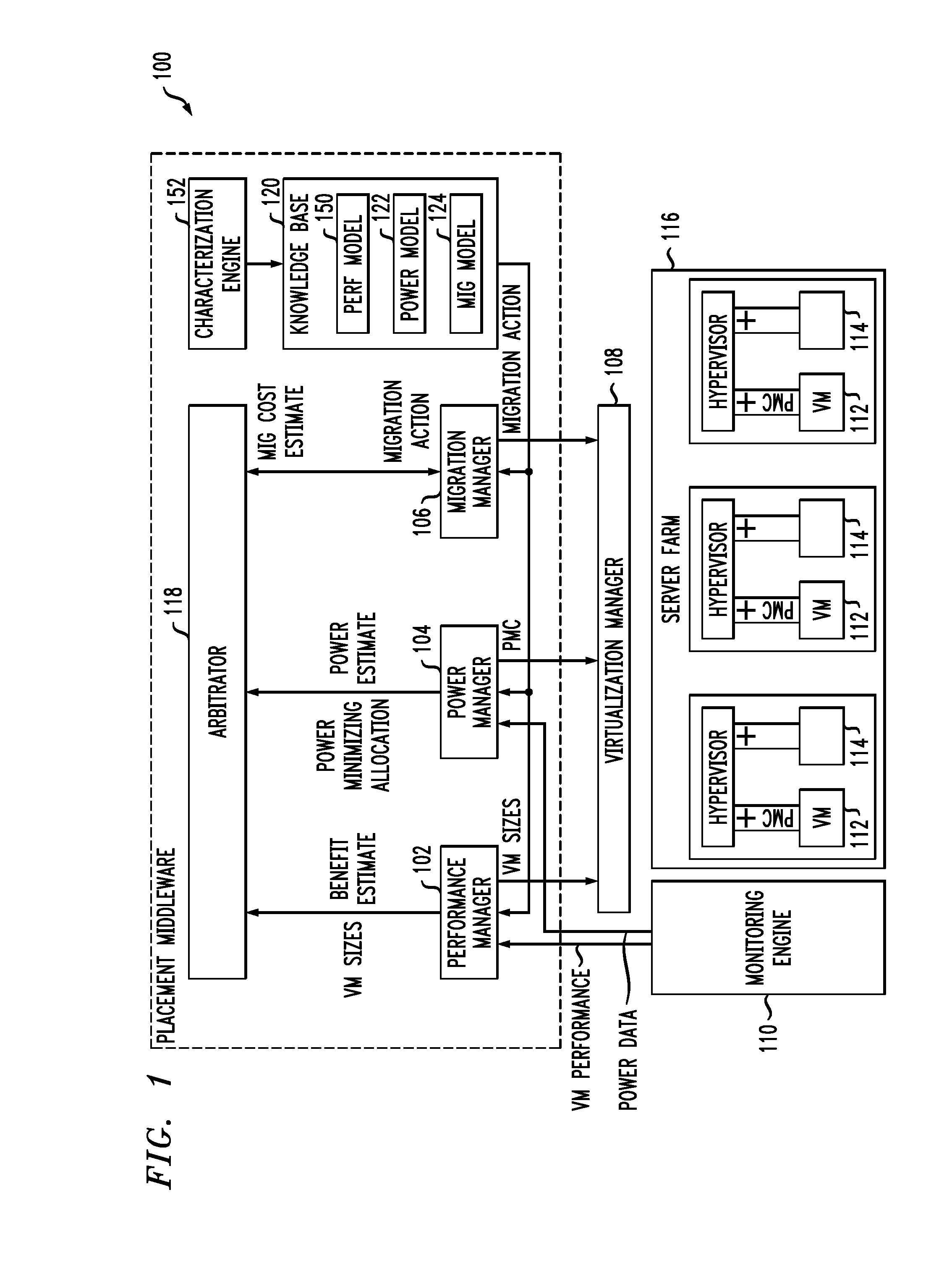
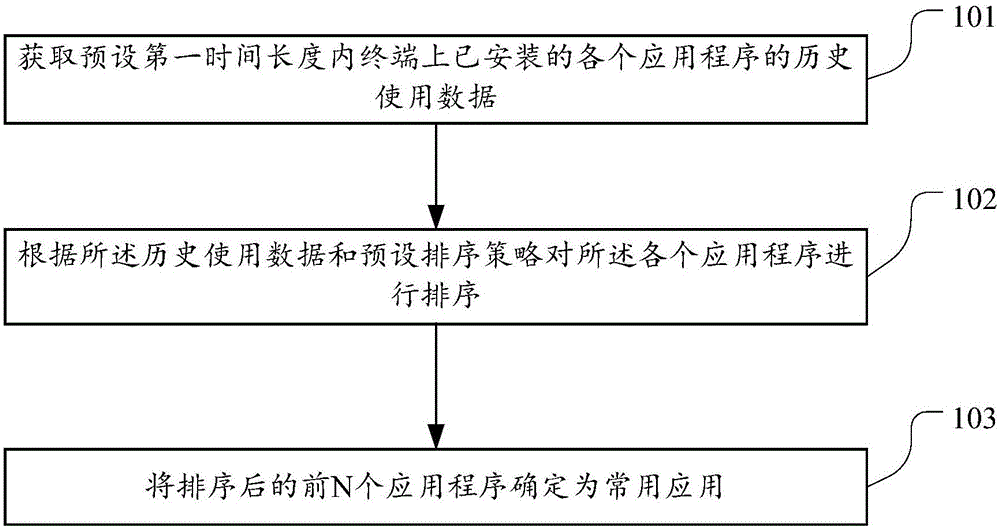
Techniques for placing applications in heterogeneous virtualized systems while minimizing power and migration cost
ActiveUS8214829B2Minimizing migrationMinimize powerVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingVirtualizationTime range
N applications are placed on M virtualized servers having power management capability. A time horizon is divided into a plurality of time windows, and, for each given one of the windows, a placement of the N applications is computed, taking into account power cost, migration cost, and performance benefit. The migration cost refers to cost to migrate from a first virtualized server to a second virtualized server for the given one of the windows. The N applications are placed onto the M virtualized servers, for each of the plurality of time windows, in accordance with the placement computed in the computing step for each of the windows. In an alternative aspect, power cost and performance benefit, but not migration cost, are taken into account; there are a plurality of virtual machines; and the computing step includes, for each of the windows, determining a target utilization for each of the servers based on a power model for each given one of the servers; picking a given one of the servers with a least power increase per unit increase in capacity, until capacity has been allocated to fit all the virtual machines; and employing a first fit decreasing bin packing technique to compute placement of the applications on the virtualized servers.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
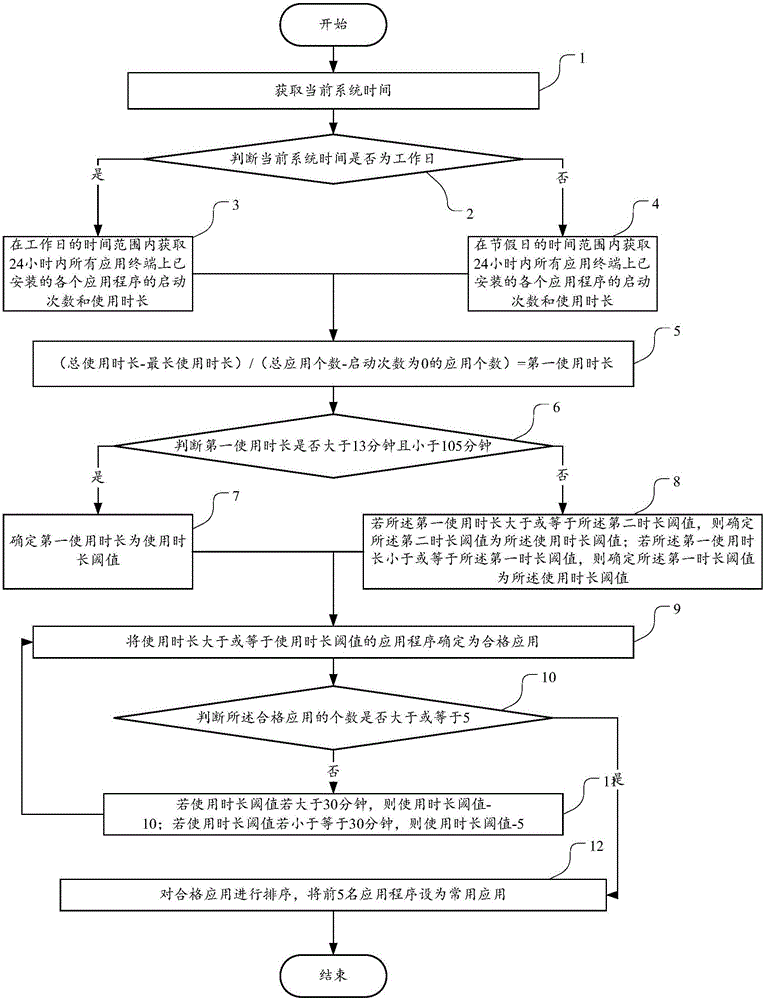
Application program management method and device
ActiveCN106445664AImplement automatic settingsAvoid closingProgram initiation/switchingUser needsProgram management
The embodiment of the invention discloses an application program management method and aims at solving the problem that a user needs to manually add or delete applications in a commonly used application list. The application program management method comprises the steps that historical usage data of application programs installed on a terminal is obtained in a first preset time length; the application programs are sorted according to the historical usage data and a preset sorting strategy; previous N application programs after sorting are determined as commonly used application, wherein N is a preset positive integer. The embodiment of the invention further provides an application program management device.
Owner:SHENZHEN BOWAY ELECTRONICS
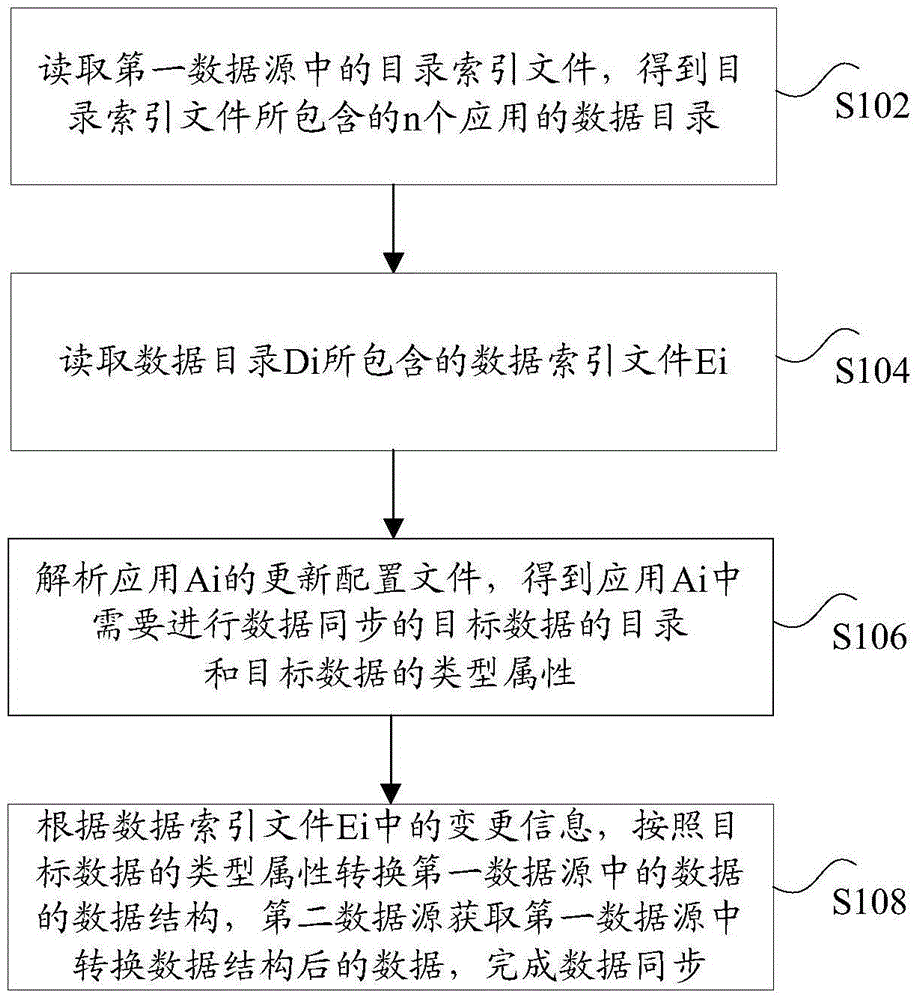
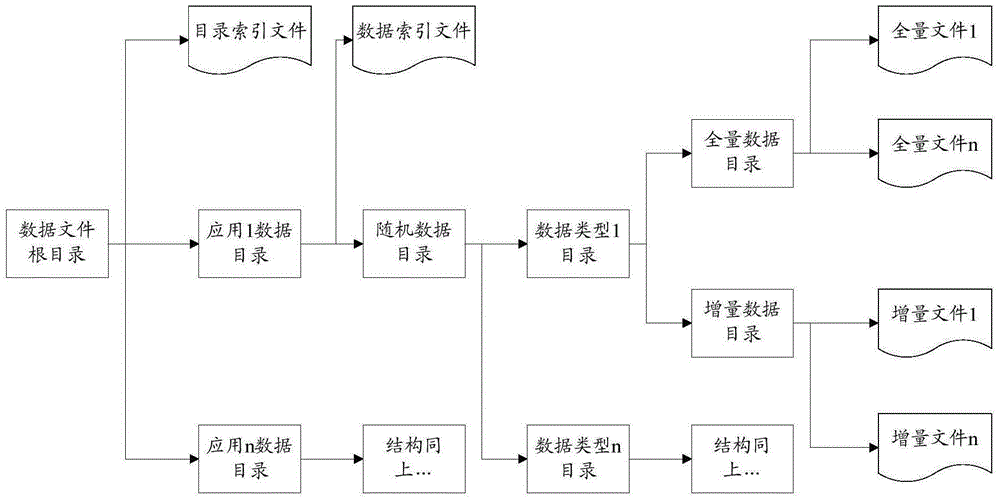
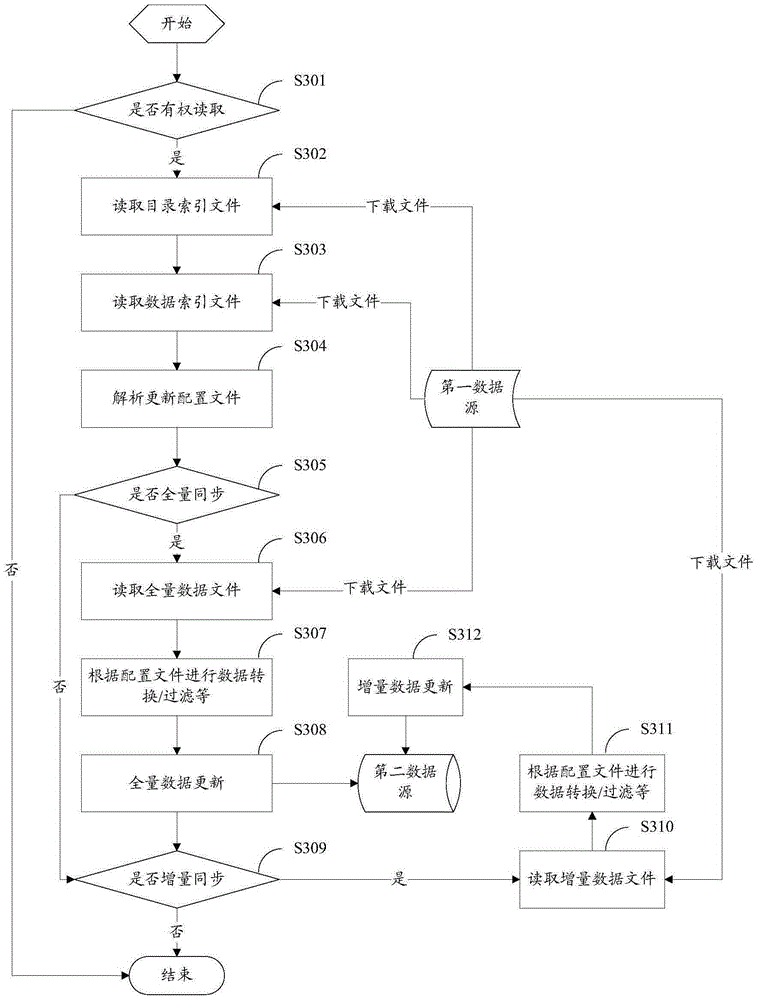
Data synchronization method and device
ActiveCN106469158AFast read and writeOrderly read and writeSpecial data processing applicationsData synchronizationN application
The invention discloses a data synchronization method and device. The method comprises the steps of reading a catalogue index file in a first data source, thereby obtaining data catalogues of n applications contained in the catalogue index file; reading a data index file Ei contained in the data catalogue Di; resolving an update configuration file of the application Ai, thereby obtaining catalogues of target data and a type attribute of the target data in the application Ai, wherein the target data is the data on which data synchronization needs to be carried out; and converting a data structure of the data in the first data source according to the change information in the data index file Ei and the type attribute of the target data, wherein a second data source obtains the data after the data structure is converted in the first data source, thereby finishing data synchronization. According to the method and the device, the technical problem that in the prior art, the synchronization performance of the data between different databases is relatively low due to the fact that a user cannot screen the data needing to be synchronized according to the demand of the user is solved.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION SYST TECH
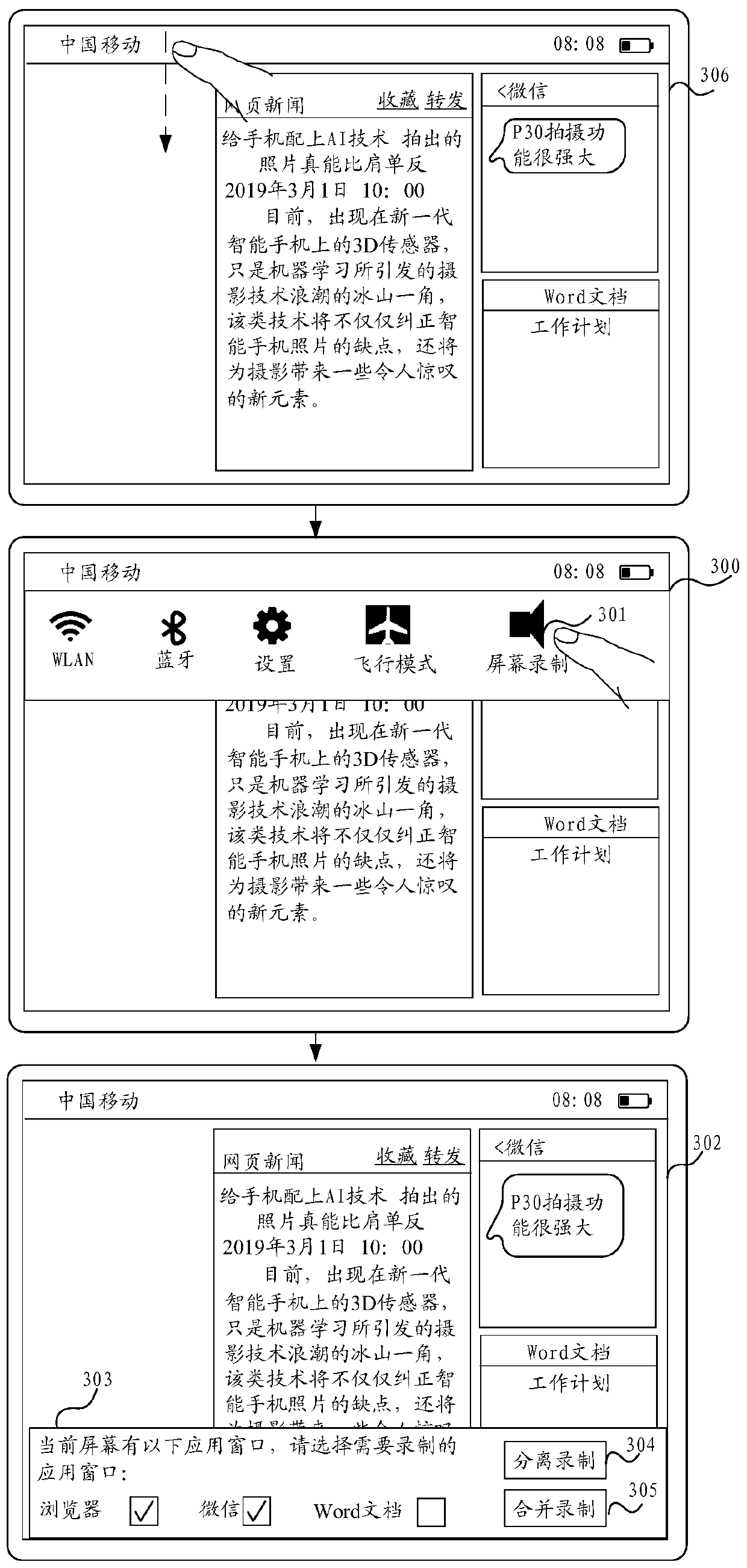
Screen recording method and electronic equipment
ActiveCN110417991AIncrease the proportionMeet diverse needsSubstation equipmentComputer hardwareN application
The invention discloses a screen recording method and electronic equipment, relates to the technical field of communication, and aims at performing screen recording on one or more application windowsin a current screen, improving the proportion of effective contents in a screen recording file and meeting diversified requirements. The method comprises: enabling the terminal to display a first interface comprising N application windows; detecting an operation of starting a screen recording function, and displaying a second interface comprising N controls; detecting one or more operations for the N controls, and determining M application windows as recording objects; when the terminal detects recording starting operation, enabling the terminal to start to record the contents of the M application windows; when the terminal detects an operation of adjusting one application window in the M application windows, enabling the terminal to change the size or position of the application window inthe screen; when the terminal detects the operation of stopping recording, enabling the terminal to generate a video file comprising the contents of M application windows, or generate M video files,wherein each video file comprises the content of one application window in the M application windows.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
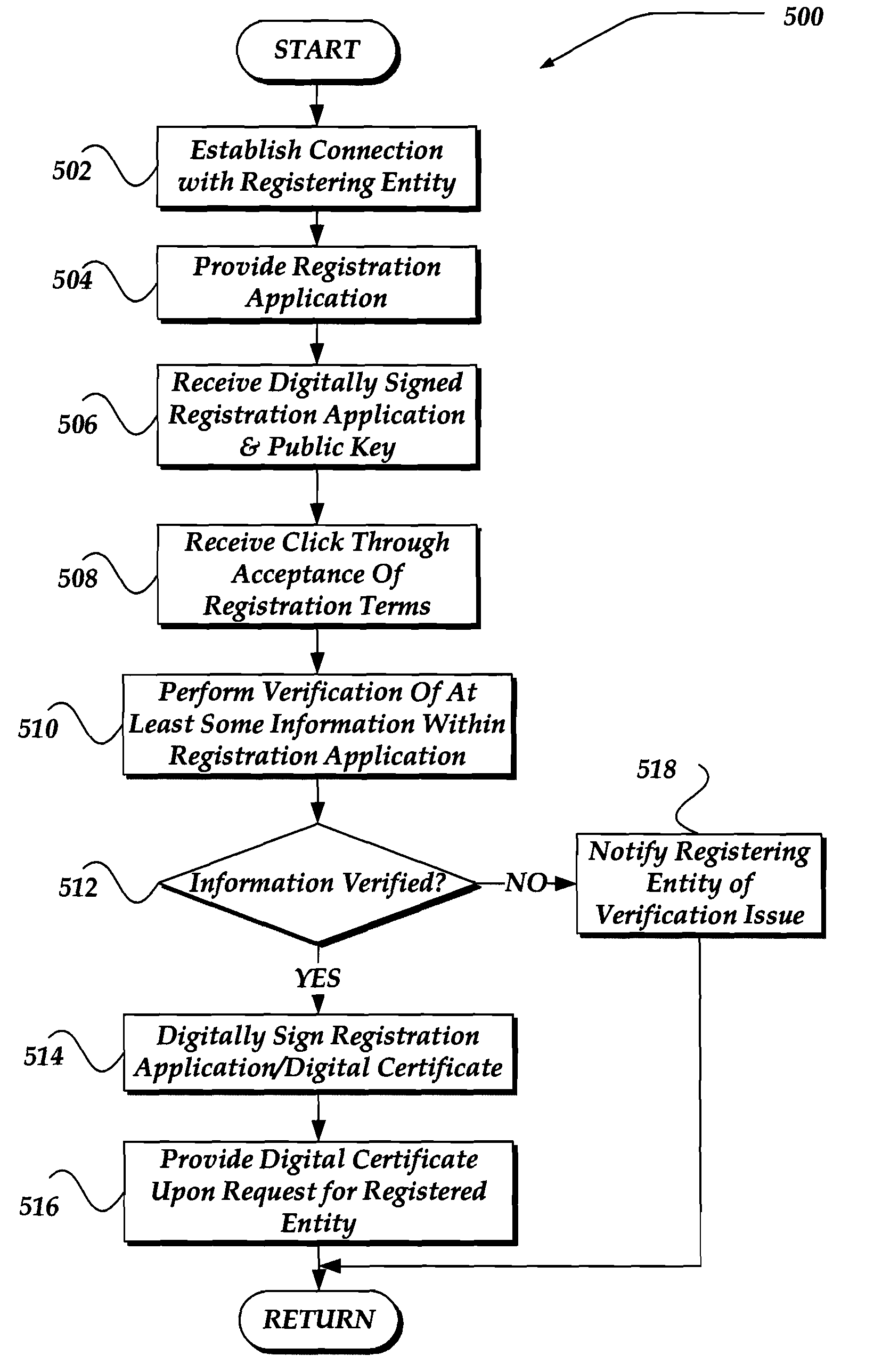
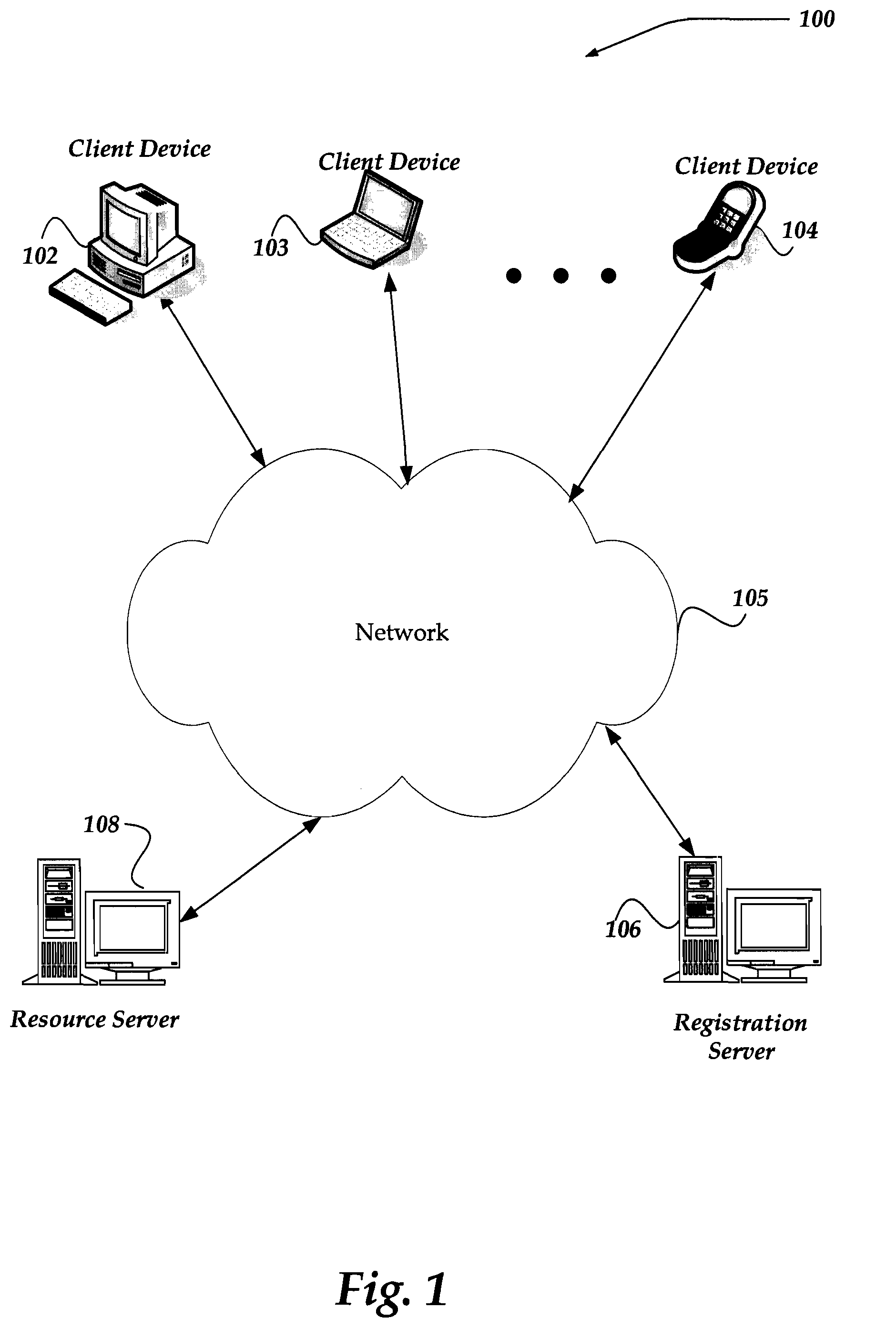
Pre-binding and tight binding of an on-line identity to a digital signature
ActiveUS8321677B2Multiple keys/algorithms usageUser identity/authority verificationRegistration authorityN application
A method, apparatus, and system are directed towards generating a public / private key pair prior to registration. The generation of the public / private key pair is performed by the entity to which the key pair is to be associated. The entity may then complete n application. The entity may then employ the generated public / private key pair to digitally sign the application. In one embodiment, the public key is provided with the application to a registration authority. Upon request, the public key and at least some of the application information may be provided to requester for use in identification, authentication, integrity, and / or non-repudiation of the registered entity. In another embodiment, the registration authority or other entity may verify the identity of the registering entity using the application. In one embodiment, the registration authority may select to digitally sign the application to indicate that the information has been verified.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Selective muting of applications
ActiveUS7706903B2Manually-operated gain controlSpecial data processing applicationsN applicationFunctional selectivity
Methods, computer program products, and electronic devices are provided for managing sound in a plurality of computer-executed applications. One method includes: operating a sound manager function to provide a user with an option to selectively mute up to n-1 applications of n applications, where n>1; and in response to the user choosing to selectively mute up to n-1 applications, the sound manager function selectively muting the up to n-1 applications. Another method includes providing a user with an option to selectively mute up to n-1 applications of n applications, where n>1. In response to the user choosing to selectively mute up to n-1 applications, at least one action is performed in response to requests to play sounds by the selectively muted applications so that the sounds are muted with respect to a sound device.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Audio playing methods and mobile terminals
ActiveCN109525707ACompatible with audio playback requirementsSubstation equipmentN applicationAudio frequency
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Control method and electronic device
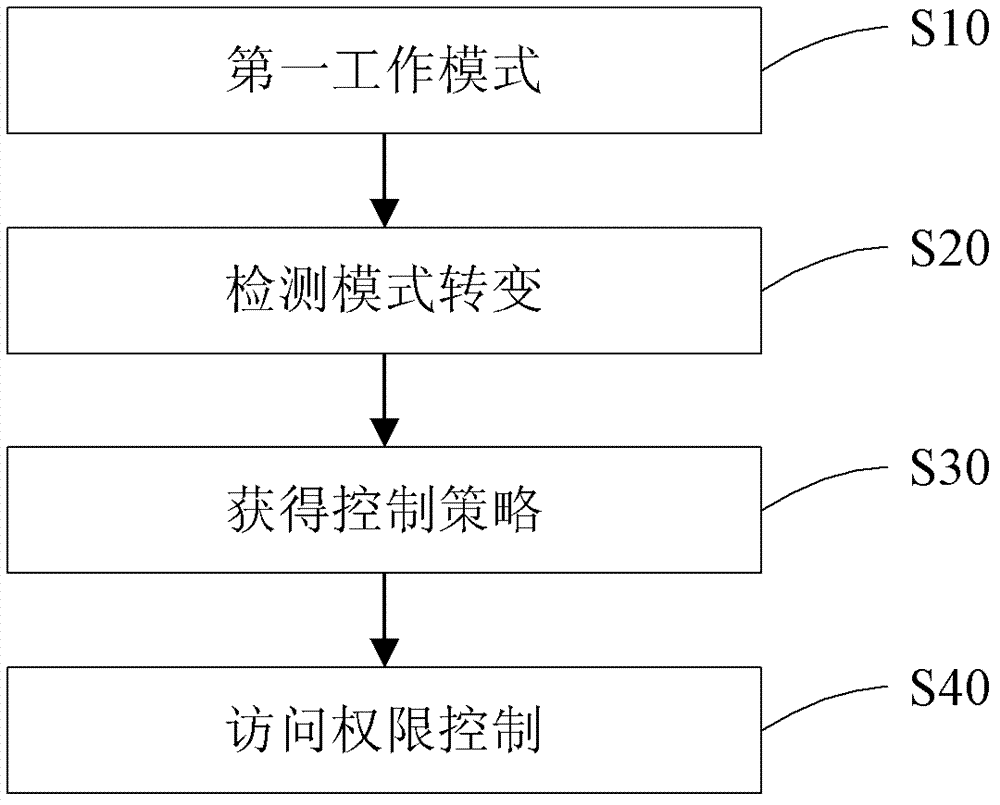
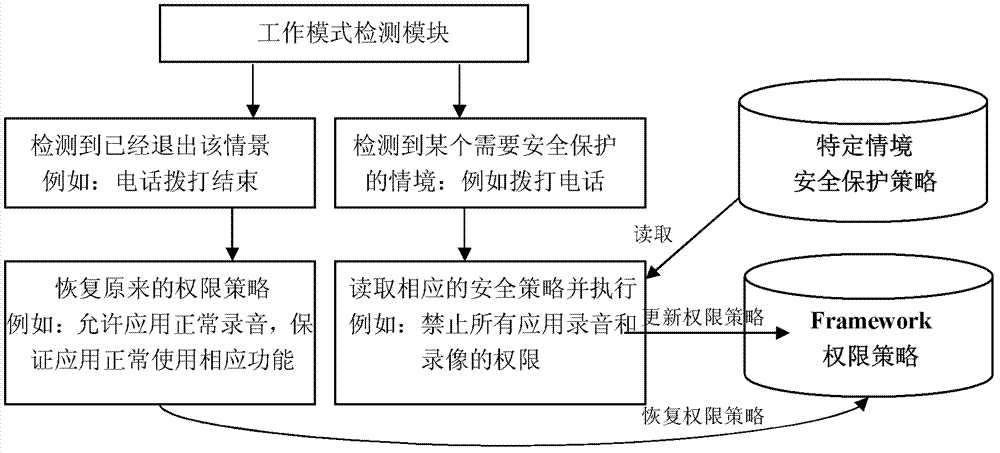
ActiveCN103246834AImprove convenienceImprove securityDigital data authenticationWork patternN application
Provided are a control method and an electronic device. The control method is applied to the electronic device with P applications and access resources of the applications. The method includes that when the electronic device is in a first work mode, M applications in the P applications have access right to a first resource; whether the electronic device enters a second work mode from the first work mode is detected; when the electronic device enters the second work mode, a control strategy is obtained, and N applications in the P applications have the access right to the first resource under the second work mode, wherein the M applications are not totally same as the N applications; and the electronic device is controlled so as to guarantee that only the N applications under the second work mode have the access right to the first resource. By means of the control method and the electronic device, the control strategy can be started automatically when the work modes are switched so as to change access right of applications to a specific resource, and the safety of a whole system is improved while use convenience of users is improved.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
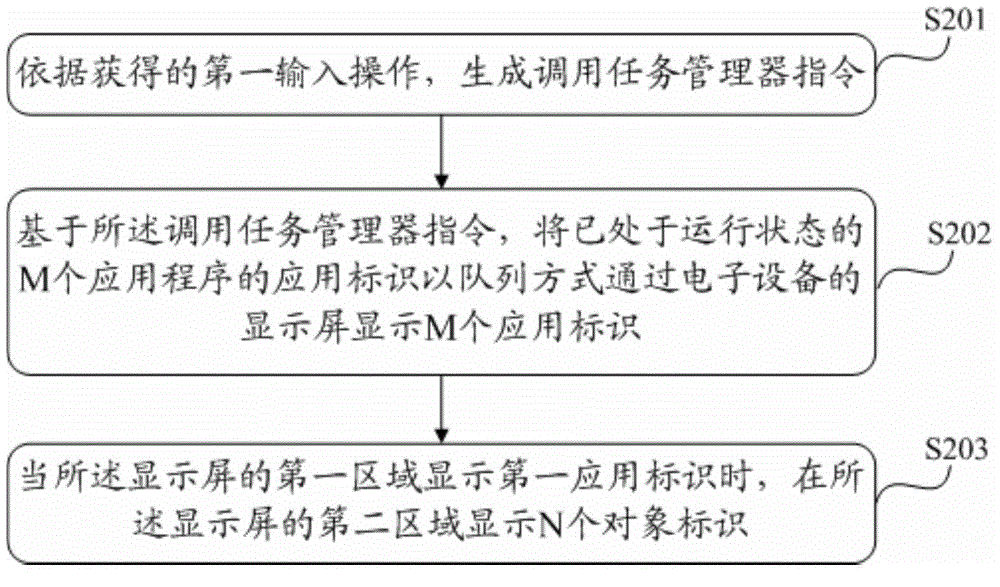
Information processing method and electronic device
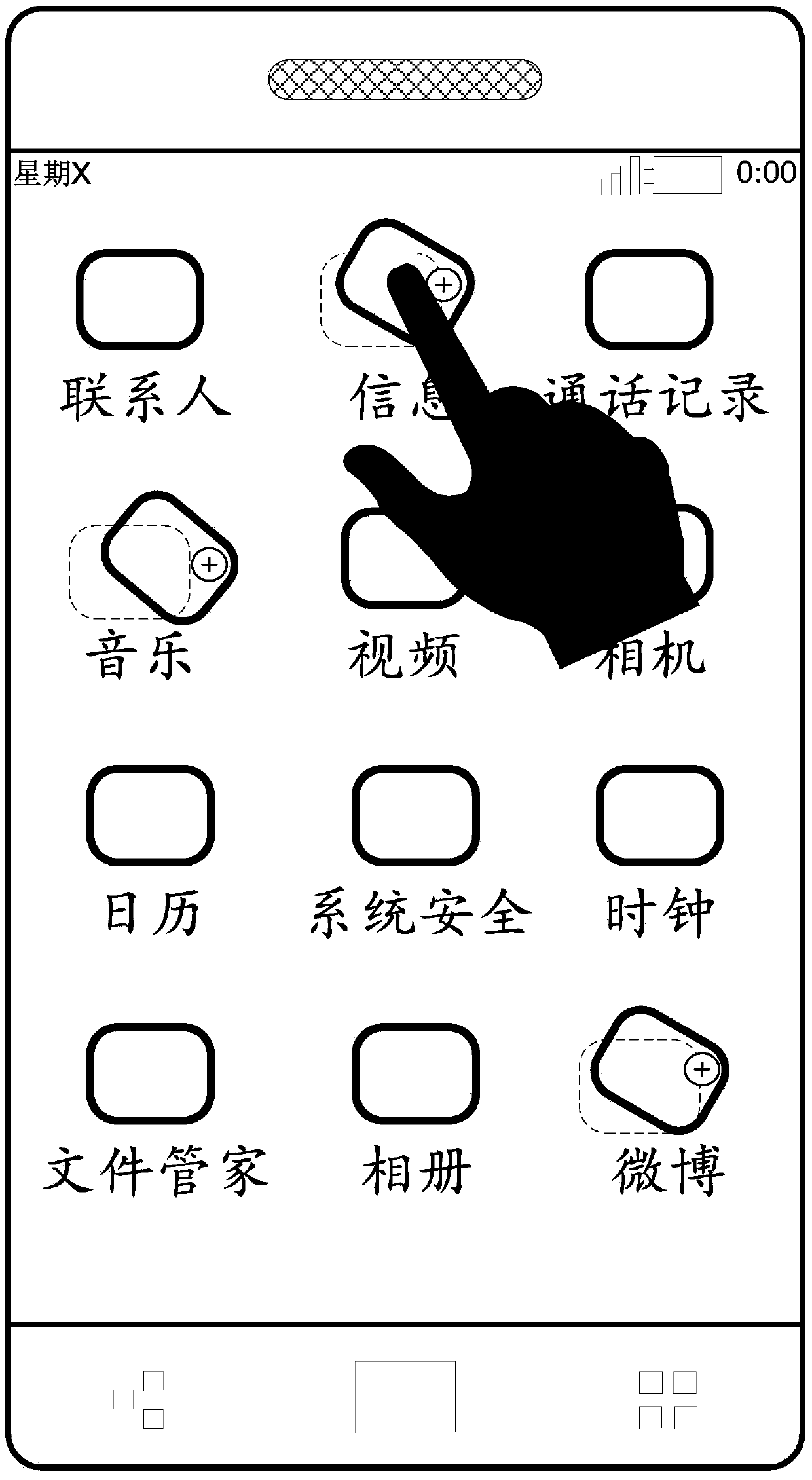
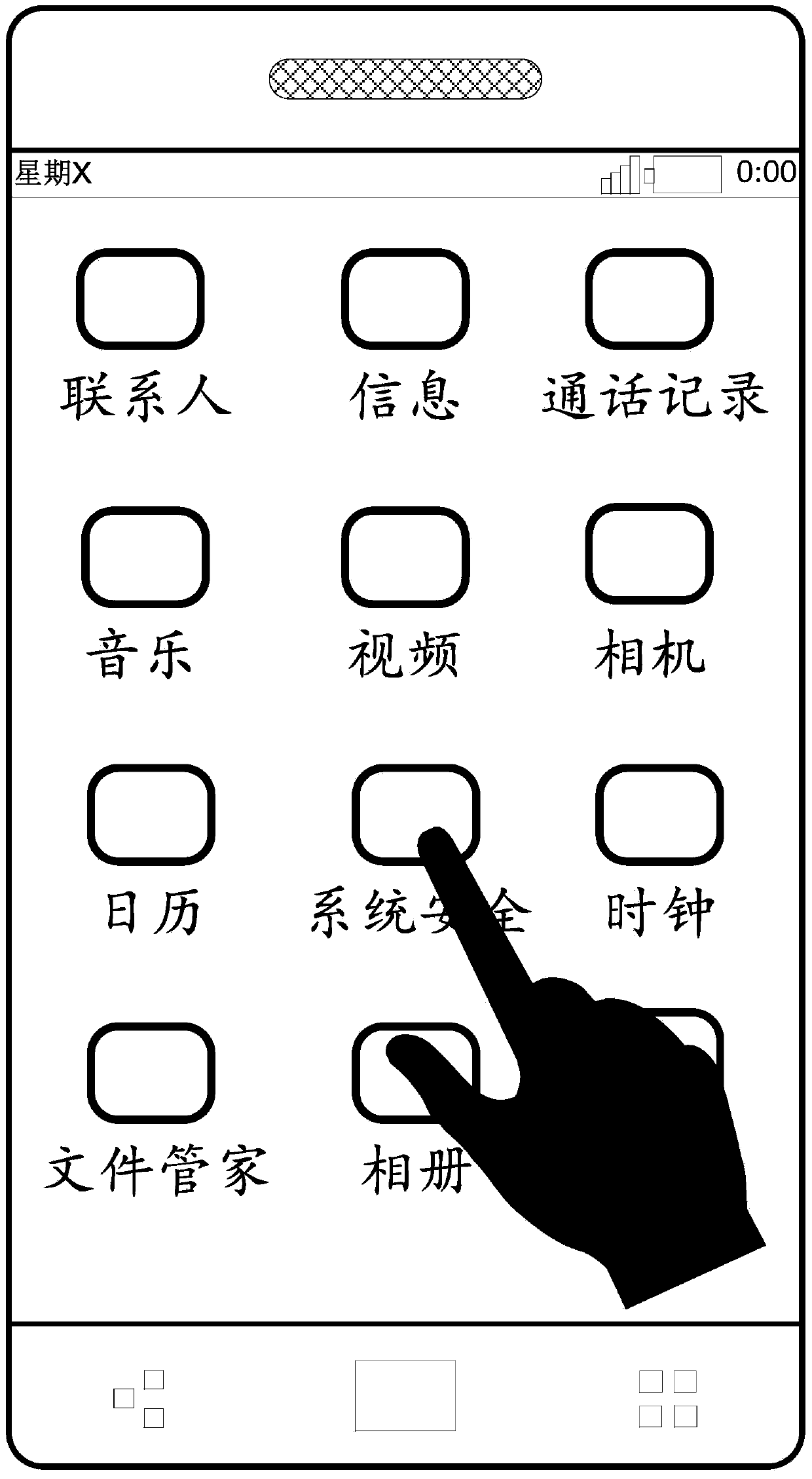
ActiveCN104142794AImprove convenienceEasy to operateInput/output processes for data processingInformation processingGraphics
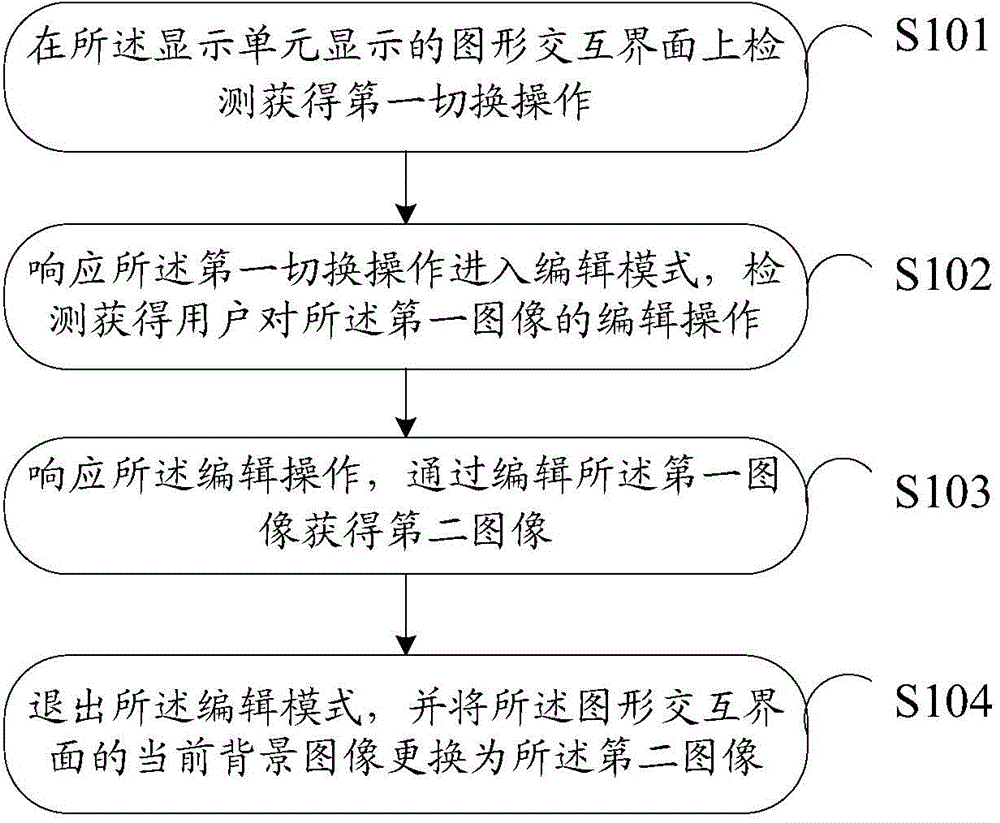
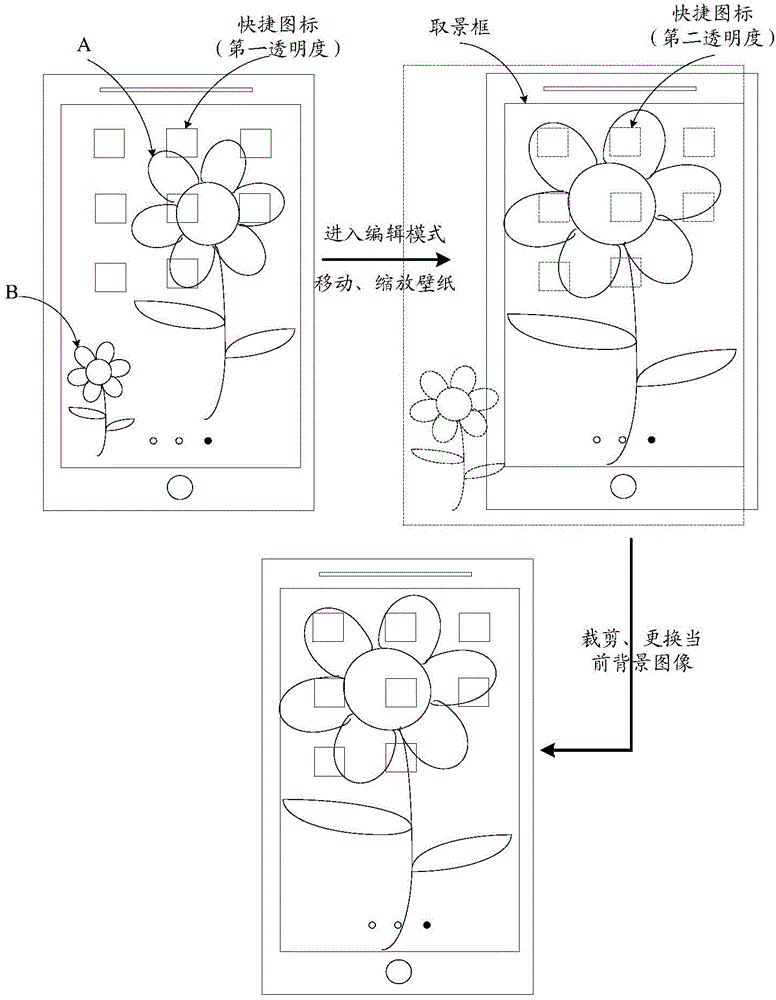
The invention discloses an information processing method and an electronic device. The information processing method is applied to the electronic device. The electronic device comprises a display unit. The information processing method comprises the steps of carrying out detection on a graphic interaction interface of the display unit to obtain a first switching operation, wherein a current background image of the graphic interaction interface is a first image, the graphic interaction interface comprises N shortcut icons of N application programs, and the N is a positive integer; entering an editing mode responding to the first switching operation, and carrying out detection to obtain an editing operation of a user on the first image; responding to the editing operations and obtaining a second image by editing the first image; exiting from the editing mode, changing the current background image of the graphic interaction interface into the second image. According to the technical scheme, the technical problem that in the prior art, operations for editing desktop wallpaper cannot be conveniently performed, and the wallpaper can be edited more conveniently and faster.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
Method for processing information and electronic device
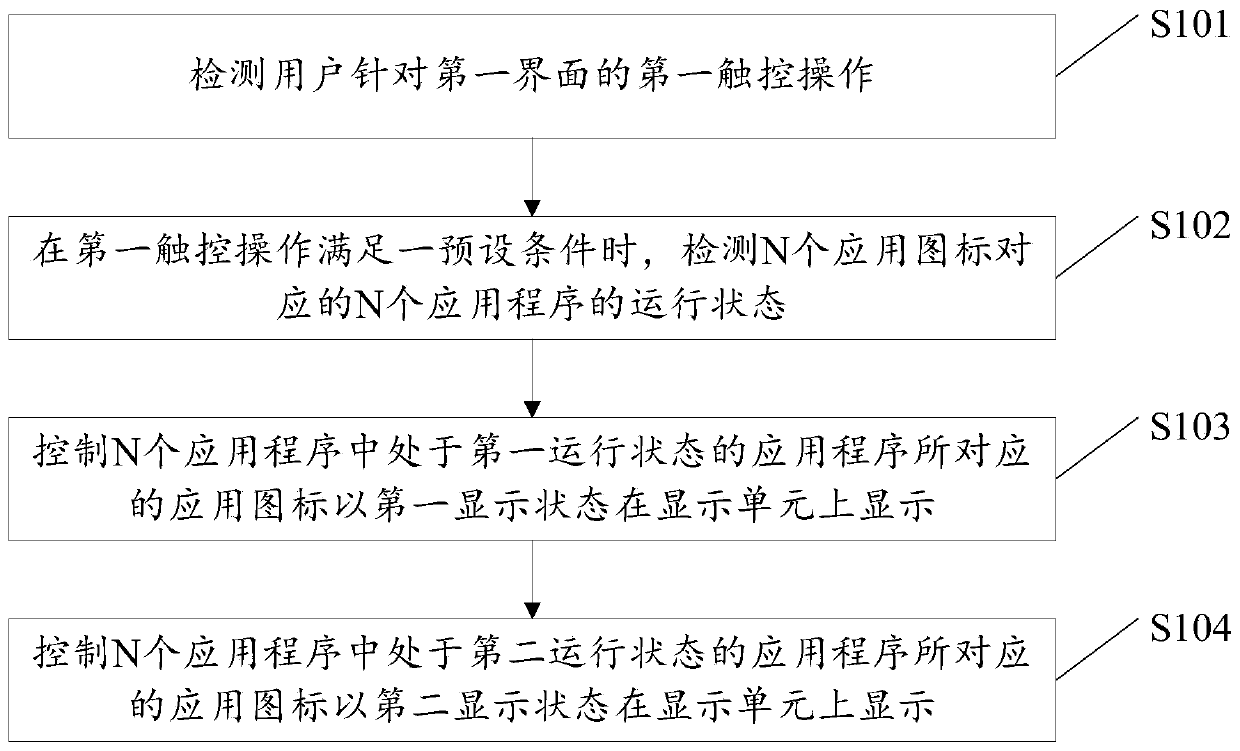
InactiveCN104182123AEliminates technical issues that are very complex to operateInput/output processes for data processingN applicationApplication software
An embodiment of the invention provides a method for processing information and an electronic device. The method for processing the information is applied to the electronic device. A first interface with N application icons can be displayed by a display unit of the electronic device. The method includes detecting first touch operation of users on the first interface; detecting running states of the N application programs corresponding to the N application icons when the first touch operation meets a preset condition; displaying the certain first application icons in first display states on the display unit; displaying certain second application icons in second display states on the display unit under the control. The running states at least include first running states and second running states. The certain first application icons correspond to the certain first application programs among the N application programs, and the certain first application programs among the N application programs are in the first running states. The certain second application icons correspond to the certain second application programs among the N application programs, and the certain second application programs among the N application programs are in the second running states. The method and the electronic device have the advantage that technical problem of excessive complexity in operation required for displaying application programs in running states in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
Networking method and terminal
ActiveCN104427586ARelieve pressureImprove experienceAssess restrictionComputer hardwareN application
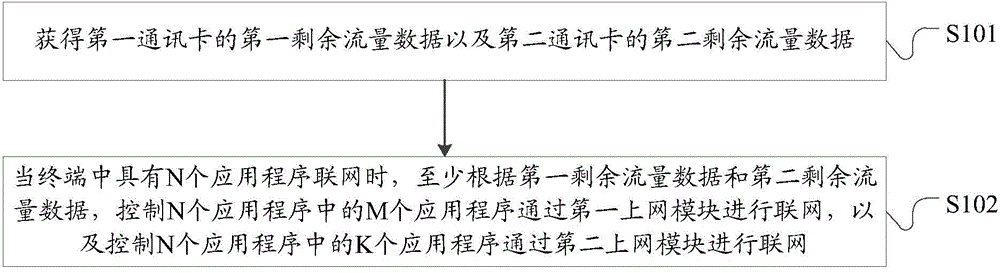
The application discloses a networking method and a terminal. The terminal comprises a first internet access module and a second internet access module, as well as a first communication card and a second communication card, wherein the first internet access module provides internet access support for the first communication card, and the second internet access module provides the internet access support for the second communication card. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining first remaining traffic data of the first communication card and second remaining traffic data of the second communication card; and when N application programs exist in the terminal for networking, controlling M application programs in the N application programs to perform networking through the first internet access module and controlling K application programs in the N application programs to perform networking through the second internet access module at least according to the first remaining traffic data and the second remaining traffic data, wherein M and K are integers which are not less than 1, and the sum of M and K is not more than N.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
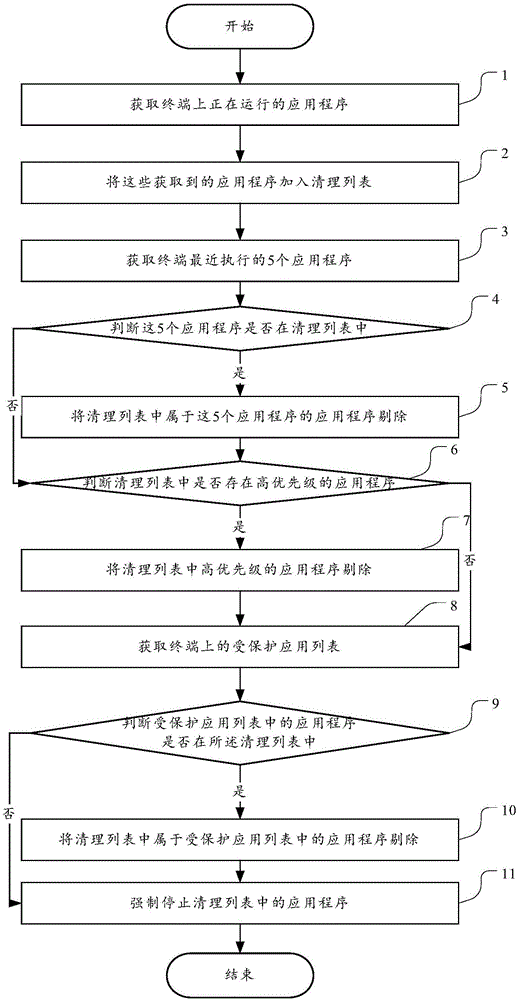
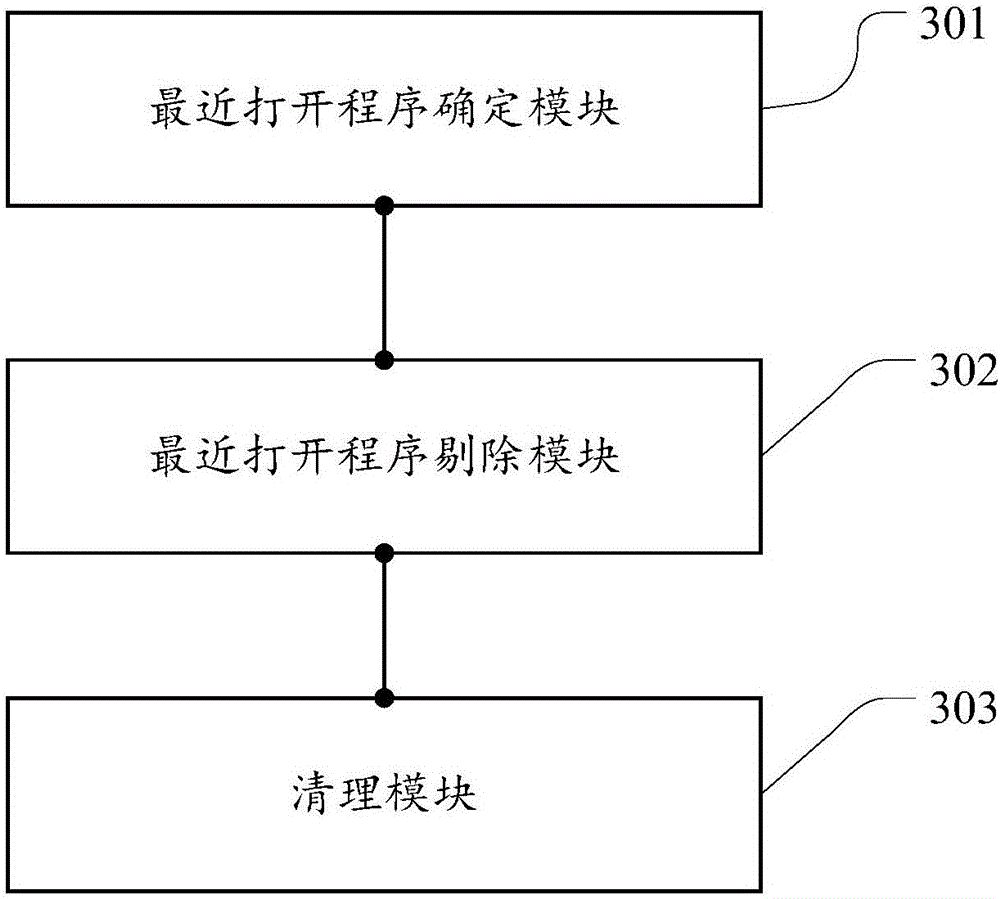
Clearing method and device for applications
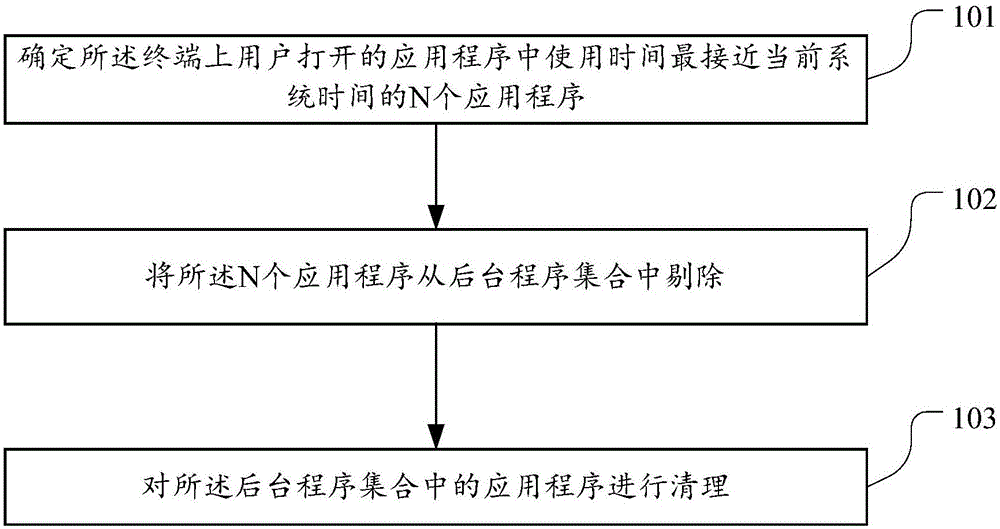
The embodiment of the invention discloses a clearing method for applications. The clearing method is used for solving the problems that when background applications are cleared, all the background applications are directly switched off, and the background applications needed by a user are easily cleared away. The method includes the steps that N applications with the use time closest to current system time in the applications switched on by the user on a terminal are determined, wherein N is a preset positive integer; the N applications are removed from a background application set, wherein the background application set comprises all applications, running on the background, of the terminal; the applications in the background application set are cleared. The embodiment of the invention further provides a clearing device for the applications.
Owner:SHENZHEN BOWAY ELECTRONICS
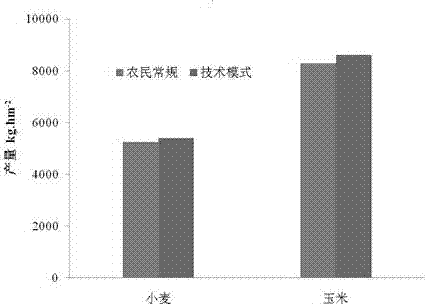
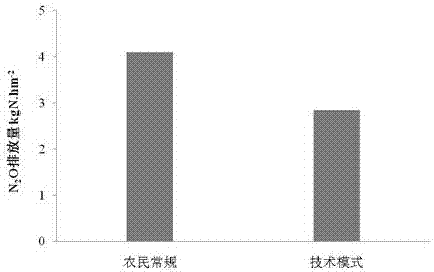
Winter wheat-summer corn rotation one-time fertilizing emission reduction method
InactiveCN107047006AAvoid many disadvantages caused by unreasonable phenomenaLabor savingFertilising methodsPlant cultivationControlled releaseN application
The invention provides a winter wheat-summer corn rotation one-time fertilizing emission reduction method, and belongs to the technical field of farm fertilizing. The method considers the nutriment demand and allocation of two crops in one year. An organic fertilizer and a slow controlled-releasing nitrogenous fertilizer are mixed to be applied to winter wheat during N application of the winter wheat; and the fertilizing manner includes: smashing all the corn straw, returning the smashed straw to soil, performing rotary tillage, and applying the mixed fertilizer to the soil once. A slow controlled-releasing nitrogenous fertilizer provides N elements to summer corn, and is applied to the soil once with corn sowing on the primes of applying the sufficient organic fertilizer to the winter wheat. The times of field fertilizing is 2, labor forces can be greatly saved, soil disturbance is reduced, the emission of N2O is reduced, the use amount of the nitrogenous fertilizer is reduced by 14-25%, the yield of the two crops is increased by 400-500 kg / hm<2>, the average income is increased by 1400-1600 yuan / hm<2>, the fertilizer utilization rate is improved by 25-35%, labors can be saved by 30-45, and the emission of N2O is lowered by 25-35%.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
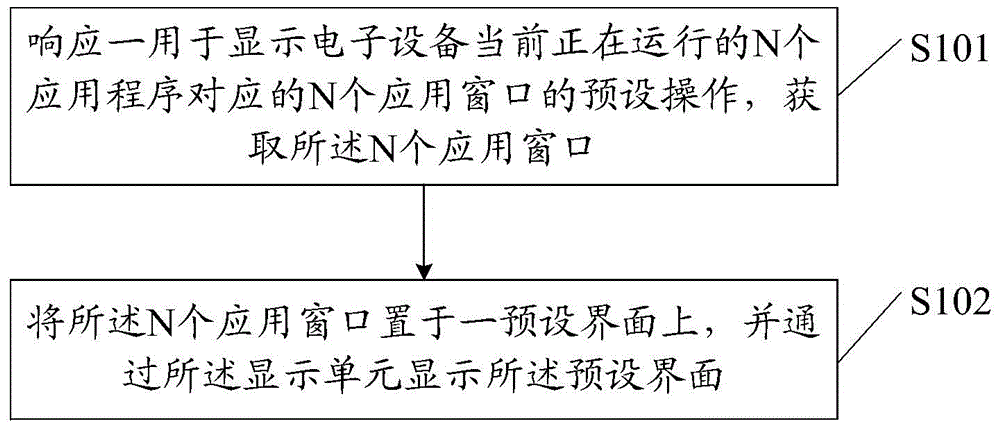
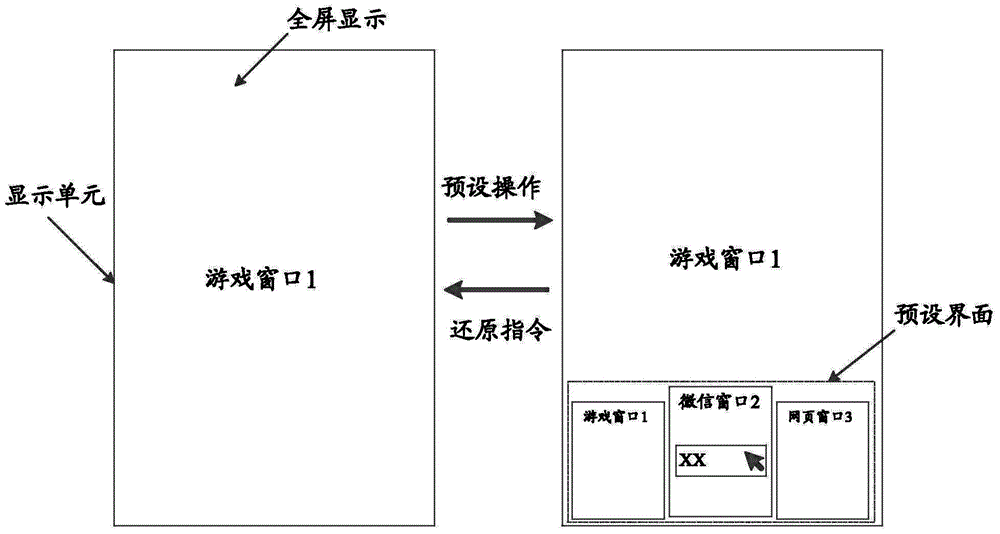
Information processing method and electronic equipment
ActiveCN104063128AAvoid switching operationsSolve technical problems with inconvenient operationInput/output processes for data processingInformation processingN application
The invention discloses an information processing method and electronic equipment. The method is applied to the electronic equipment comprising a display unit, and comprises the following steps that a preset operation used for displaying N application windows corresponding to N application programs running in the current time in the electronic equipment is responded, the N application windows are obtained, the first application window in the N application windows is the window which is operated by a user at the current time and is completely displayed by the display unit, at least one second application window in the N application windows is not completely displayed on the display unit, and the N is an integer being greater than or equal to 2; the N application windows are arranged on a preset interface, and in addition, the preset interface is displayed, wherein on the preset interface, all application windows of the N application windows are not mutually overlapped, and in addition, the user is allowed to operate the application control on any one application window in the N application windows. Through the technical scheme, the technical problem of operation inconvenience of background application programs when a plurality of application programs run in the prior art is solved.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
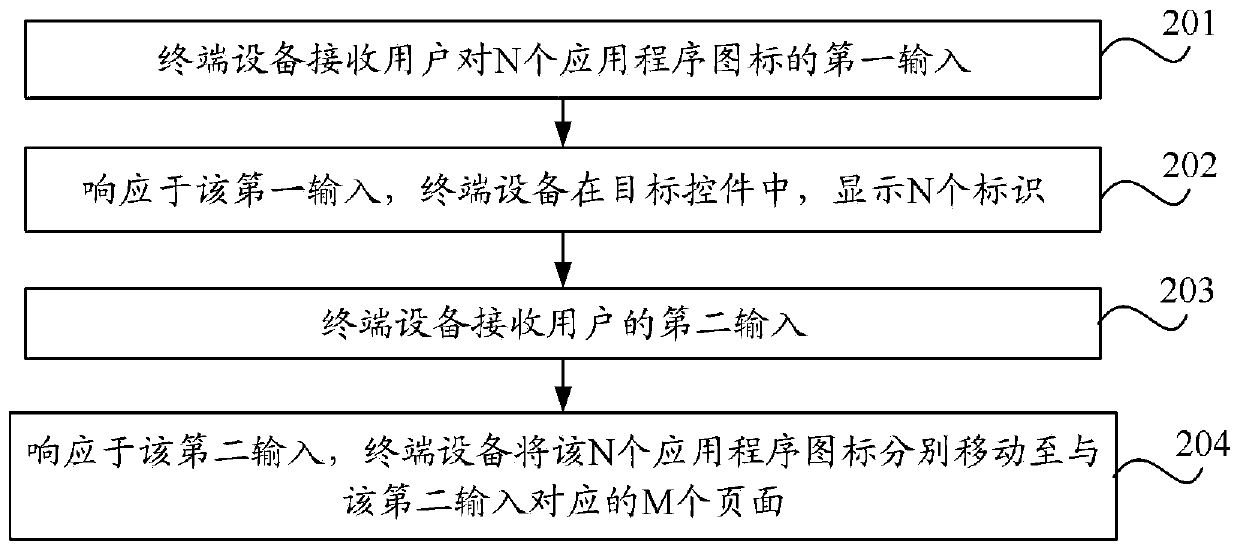
An application icon moving method and terminal equipment
InactiveCN109814772AMove quicklySolve the lack of a single-sided screenInput/output processes for data processingTarget controlN application
The embodiment of the invention discloses an application icon moving method and terminal equipment, relates to the technical field of communication, and is used for solving the problem that in the prior art, a universal application icon moving method for single-side screen and double-side screen terminal equipment does not exist. The method comprises the following steps: receiving first input of Napplication icons by a user; in response to the first input, displaying N identifiers in a target control, wherein each identifier is used for indicating different application icons in the N application icons; receiving a second input of the user; in response to the second input, respectively moving the N application icons to M pages corresponding to the second input; wherein M and N are both positive integers, and M is smaller than or equal to N.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
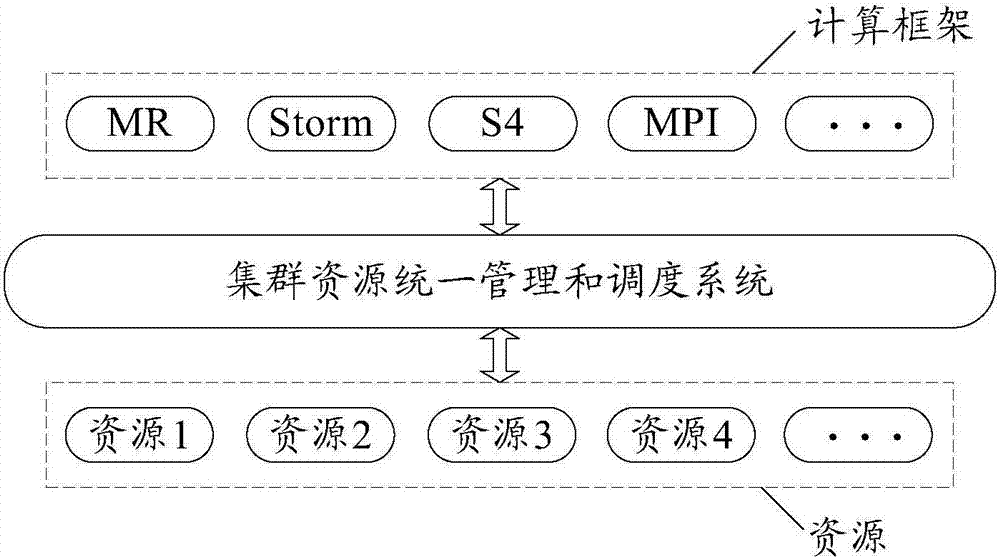
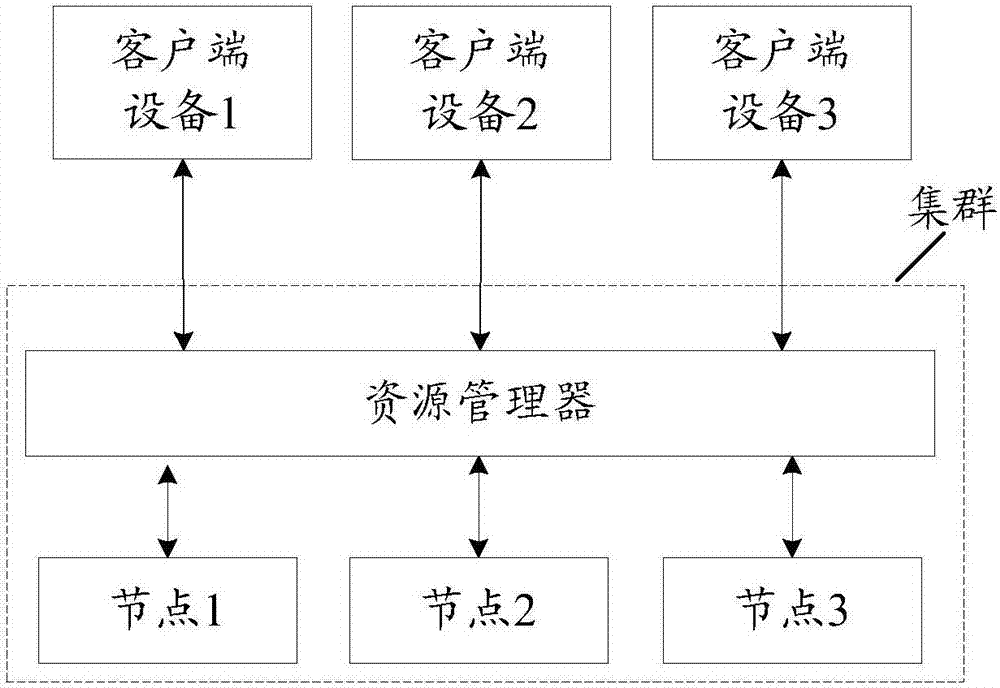
Resource scheduling method and device
ActiveCN107291546AReasonable schedulingAvoid wastingResource allocationN applicationResource management
The embodiment of the invention discloses a resource scheduling method and device, and relates to the technical field of the resource management. The resource scheduling method and device are used for improving the use ratio of the cluster resource. The method is applied to a resource manager, the resource manager is used for managing and scheduling the cluster resource; the cluster comprises multiple nodes, R application programs adapted to a computing framework supported by the cluster are run on multiple nodes, and R is positive integer. The method comprises the following steps: the resource manager receives a resource request of each of R application programs; the resource manager acquires the historic feature information; the historic feature information comprises at least one of the first historic feature information and the second historic feature information; the resource manager schedules the resource for N application programs according to the first historic feature information and a first scheduling strategy; or the resource manager schedules the resource for at least one application program in R application programs according to the second historic feature information and a second scheduling strategy.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
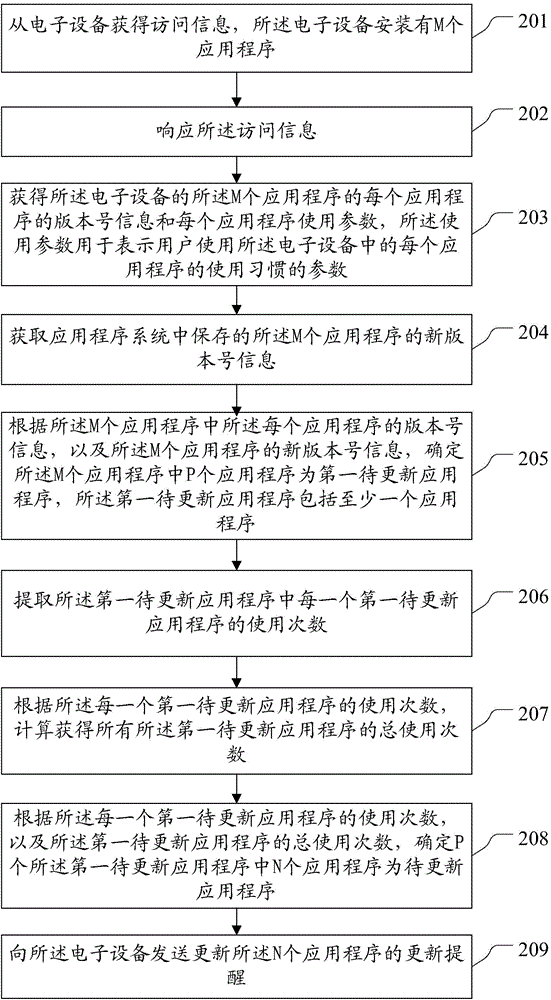
Method and device for noticing update of applications
InactiveCN104423985AReduce power consumptionPower supply for data processingProgram loading/initiatingN applicationApplication software
The invention discloses a method and a device for noticing update of applications, relating to the technical field of computers, being capable of reducing the power consumption of an application system. The method provided by the embodiment of the invention includes the steps of: obtaining visit information from an electronic device, wherein M applications are installed in the electronic device; responding to the visit information; obtaining the vision number information of each one of the M applications of the electronic device and the usage parameter of each application, wherein each usage parameter is the parameter for expressing the habits of a user for using the corresponding application in the electronic device; determining the N applications in the M applications to be the applications to be updated; sending update notifications for updating the N applications to the electronic device. The method and device for noticing the update of the applications provided by the embodiment of the invention is applicable to noticing the updating of the applications.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
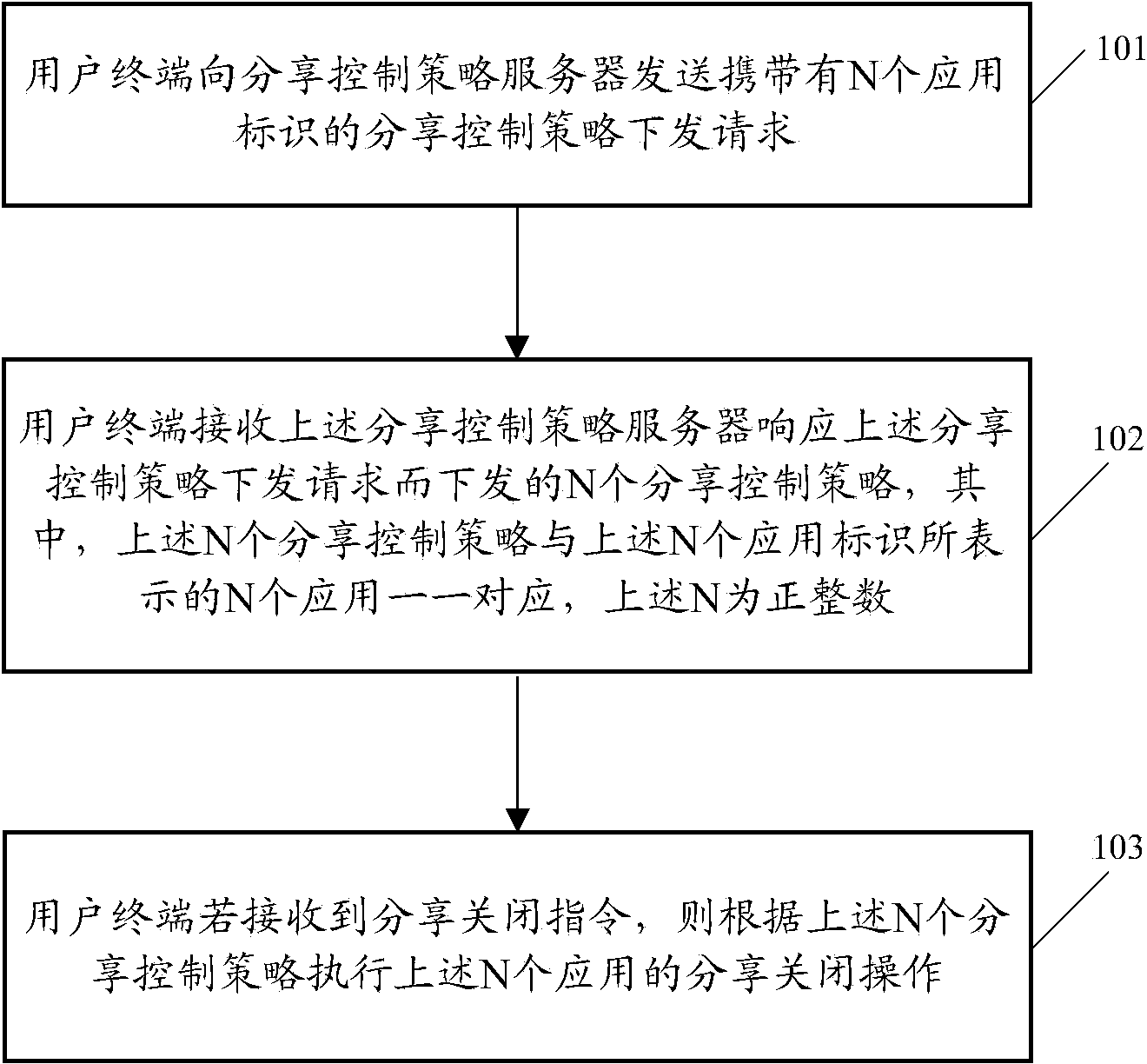
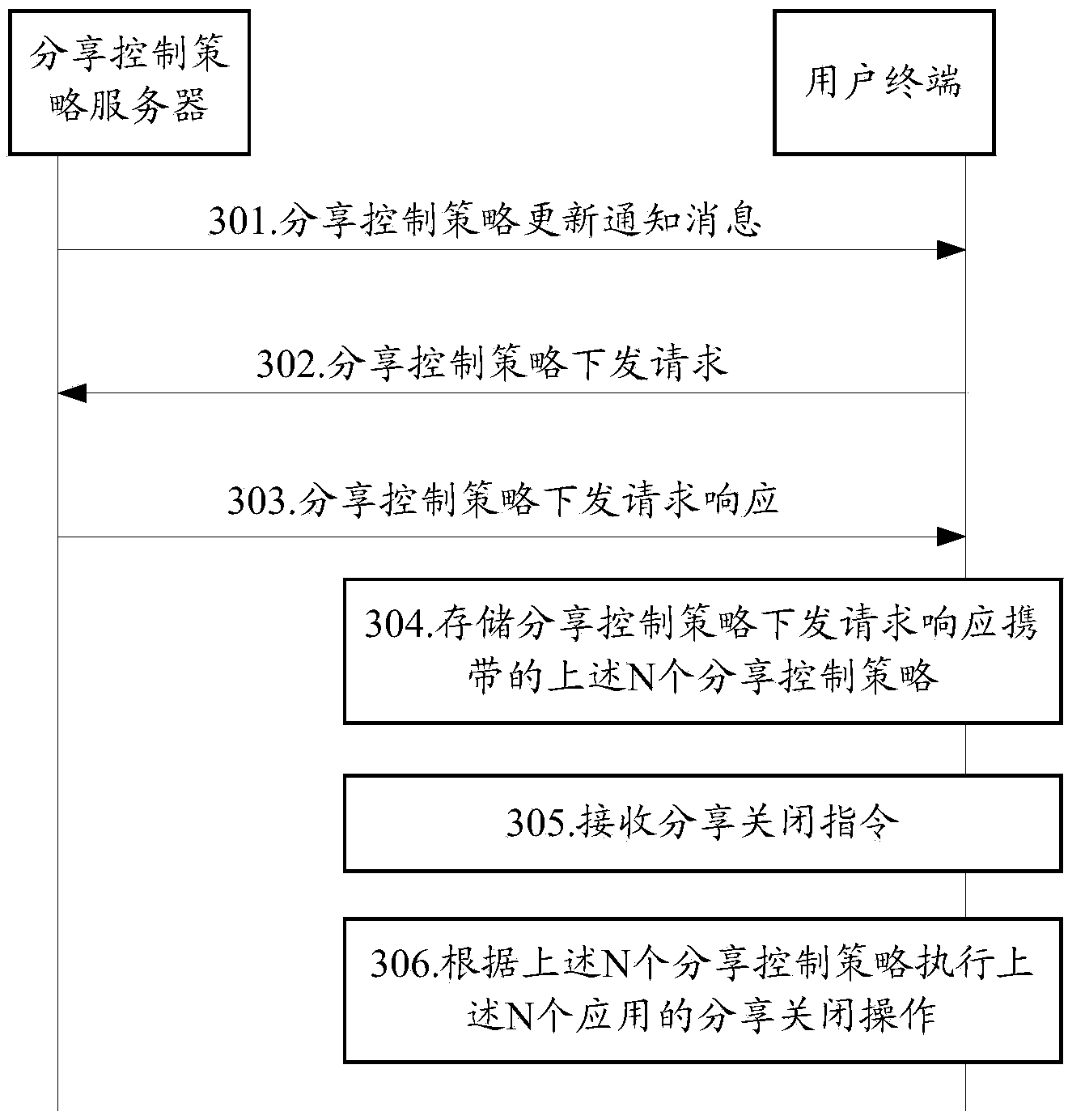
Sharing control method and related equipment and communication system
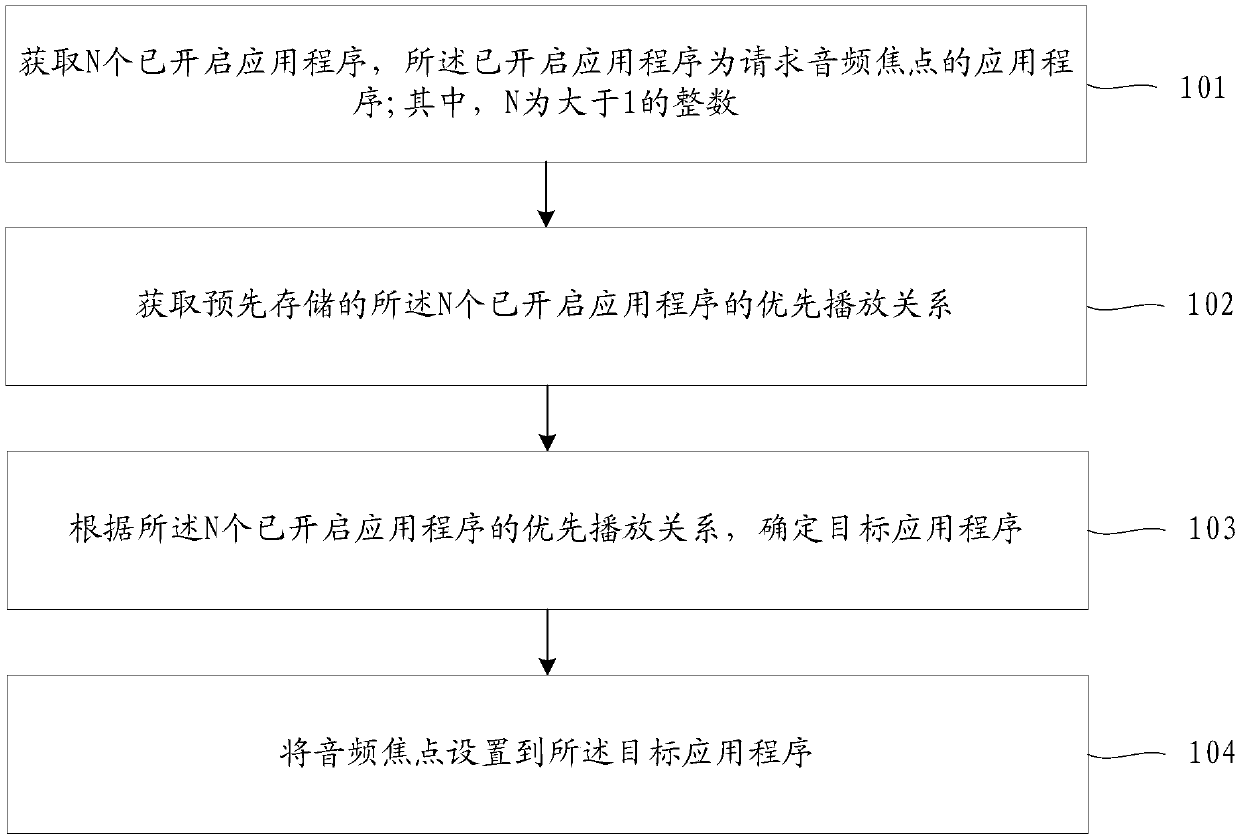
ActiveCN103532945AFlexible and convenient sharing control featuresIncrease flexibilityTransmissionCommunications systemN application
The embodiment of the invention discloses a sharing control method and related equipment and a communication system. The sharing control method can comprise the following steps: sending a sharing control strategy issuing request carrying N application identifiers to a sharing control strategy server by a user terminal; receiving N sharing control strategies which are issued by the sharing control strategy server in response to the sharing control strategy issuing request, wherein the N sharing control strategies are in one-to-one correspondence with N applications which are represented by the N application identifiers, and N is a positive integer; if a sharing closing command is received, executing the sharing closing operation of the N applications according to the N sharing control strategies. The scheme of the embodiment is favorable to improvement on sharing control flexibility and convenience.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
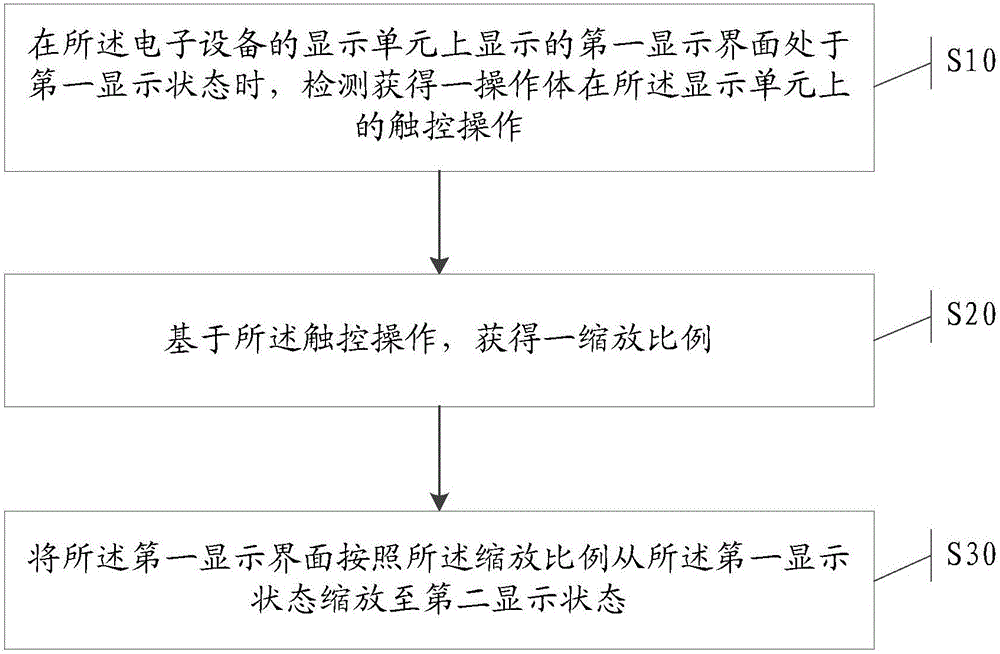
Information processing method and electronic equipment
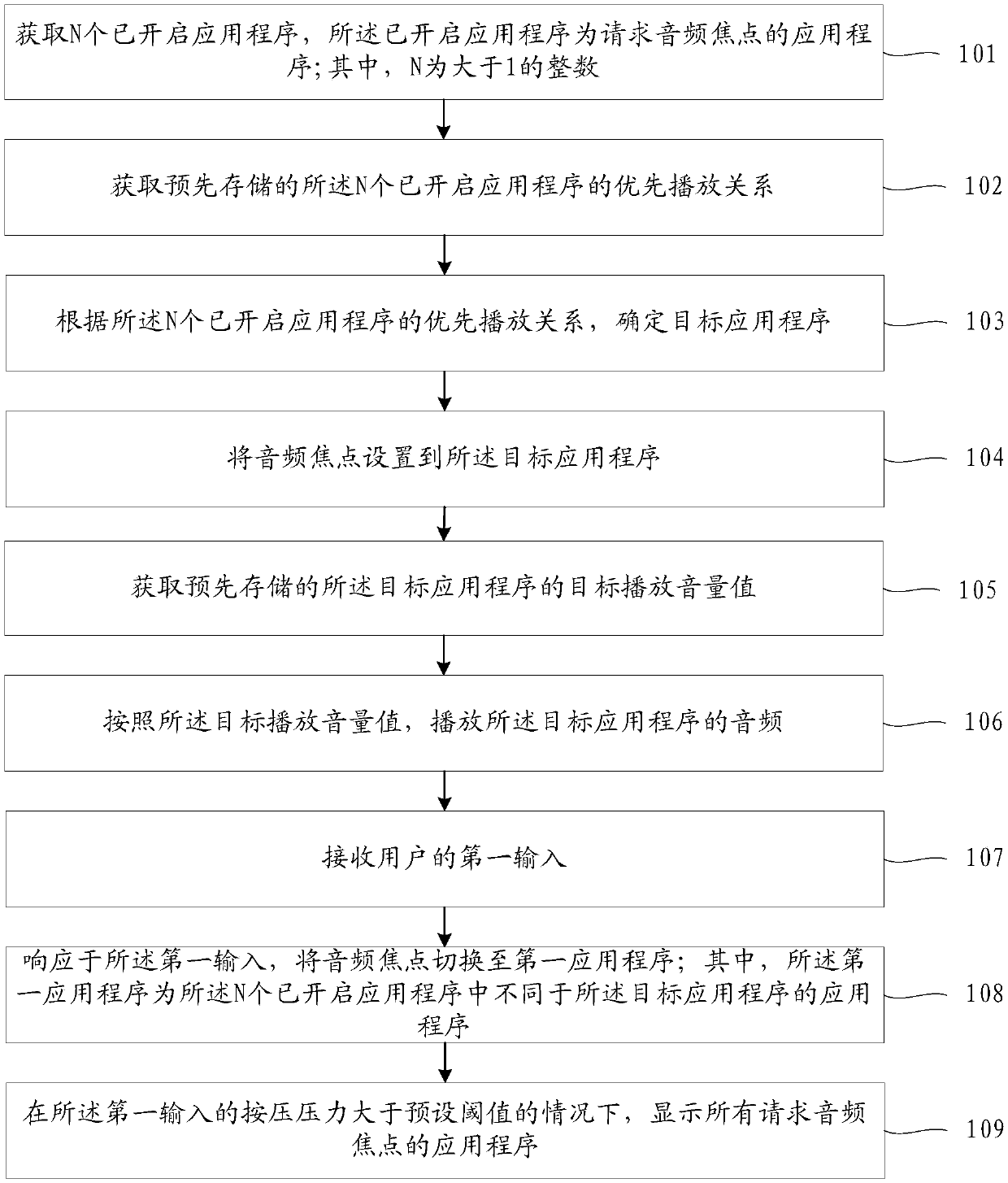
ActiveCN104991696AQuick searchEliminate inconvenient technical issuesInput/output processes for data processingInformation processingN application
The invention provides an information processing method and a kind of electronic equipment. The method comprises that when a first display interface displayed by a display unit of the electronic equipment stays at a first display state, a touch operation of an operator on the display unit is detected and acquired, wherein when the first display interface stays at the first display state, N icons of N application programs are displayed on the display unit, and N is a positive integer; based on the touch operation, a scaling is obtained; according to the scaling, the first display interface is scaled from the first display state to a second display state; and when the first display interface stays at the second display state, M icons are displayed on the display unit, and M is a positive integer which is not equal to N.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
Terminal equipment and switching method of application programs of terminal equipment
InactiveCN104424025AImprove search efficiencyImprove operational efficiencyProgram initiation/switchingN applicationTerminal equipment
The invention discloses terminal equipment and a switching method of application programs of the terminal equipment. The method comprises the following steps that: the terminal equipment receives an instruction for activating a switching interface; the switching interface is popped up; all tags of all application programs / specific application programs currently in an operation state and / or tags of application programs / specific application programs which are opened in the preset time and are currently closed are obtained; a corresponding round-robin queue is built; instruction identifiers corresponding to continuously N applications / tags in the round-robin queue are displayed on the popped-up switching interface; and the terminal equipment receives the operation of any instruction identifier displayed on the switching interface and executes the switching or closing action corresponding to the operation. When the terminal equipment and the switching method are applied, the switching of the application programs can be efficiently performed.
Owner:BEIJING SAMSUNG TELECOM R&D CENT +2
Application control method and mobile terminal
ActiveCN104978132AImprove convenienceImprove accuracyInput/output processes for data processingKey pressingN application
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Display method and electronic device
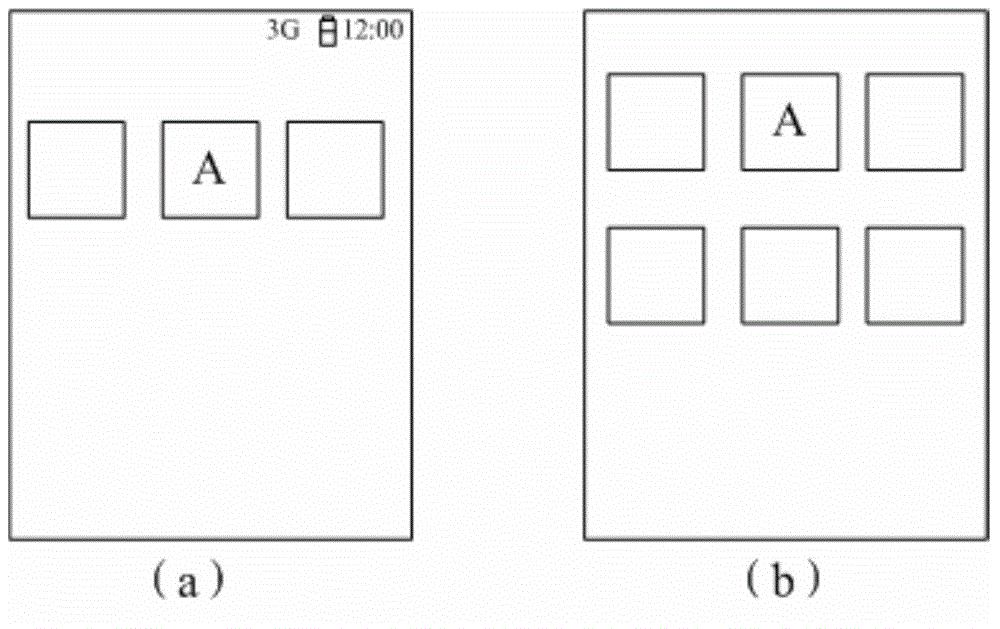
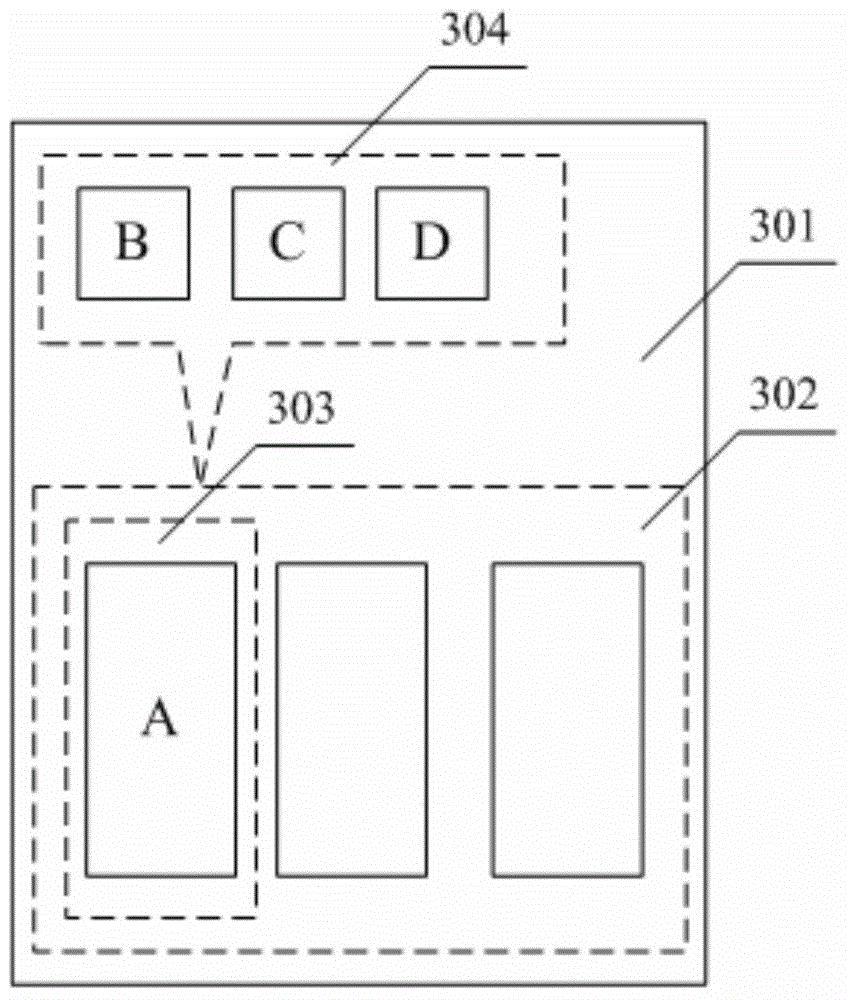
ActiveCN105094556AEasy to operateImprove experienceExecution for user interfacesInput/output processes for data processingN applicationApplication software
The invention provides a display method, comprising based on a task calling manager instruction generated by first input operation, displaying corresponding number of application IDs of a plurality of application programs which are in an operating state in a queue manner through the display screen of an electronic device; when a first region of the display screen of an electronic device displays a first application ID, a second region of the display screen displaying N object IDs, the N object ID being corresponding to the N application programs in a one-to-one manner, the N application programs having incidence relation with the first application program corresponding to the first application ID, a corresponding page of a task manager displaying a plurality of application programs operating at present in the electronic device, each application program being capable of associating with a plurality of application programs, and operating based on selection in the corresponding page of the task manager, when an application program in an operating state is selected, directly displaying the applications associated with the application program, so as to provide convenience for a user to select an associated application program to operate.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
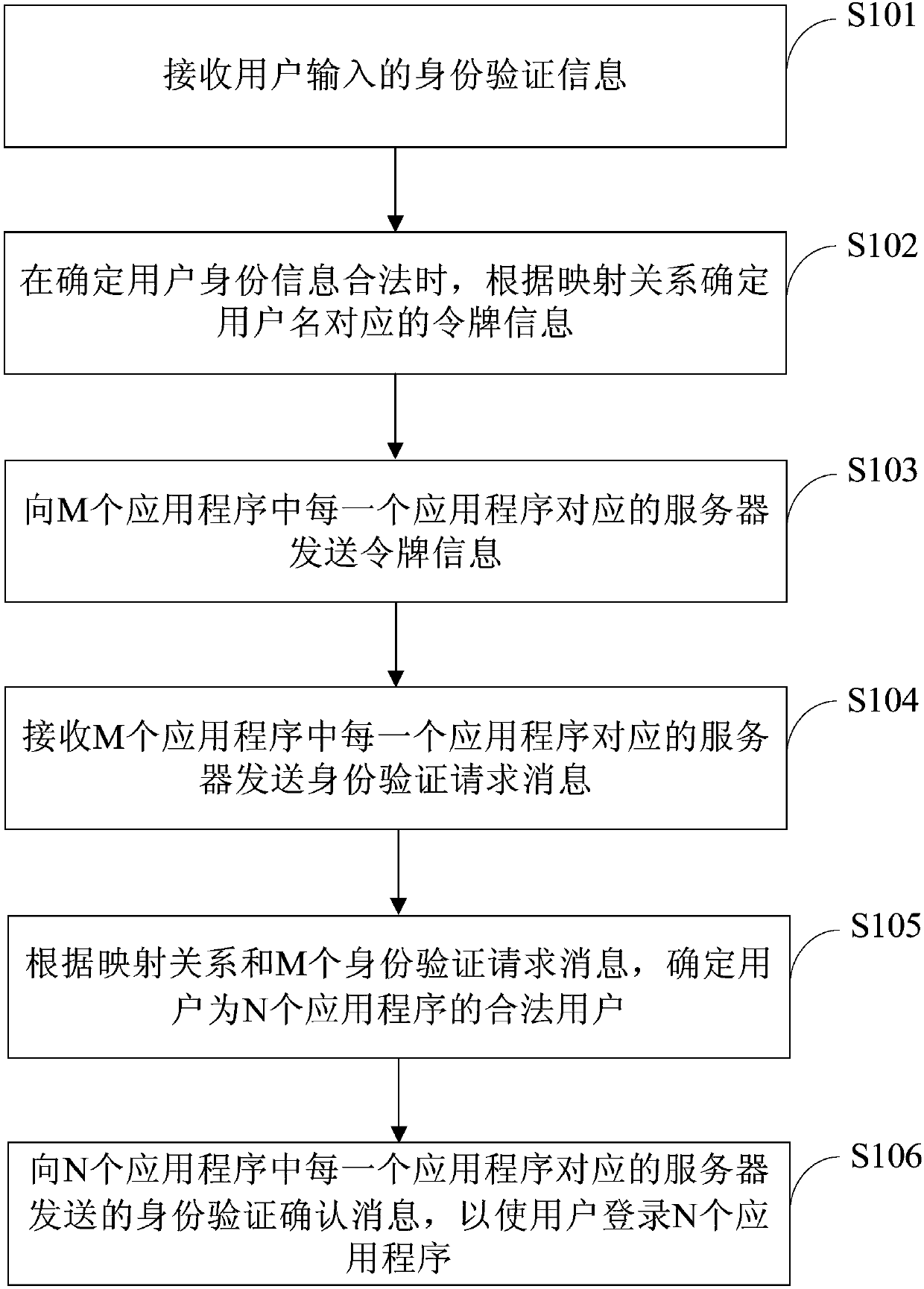
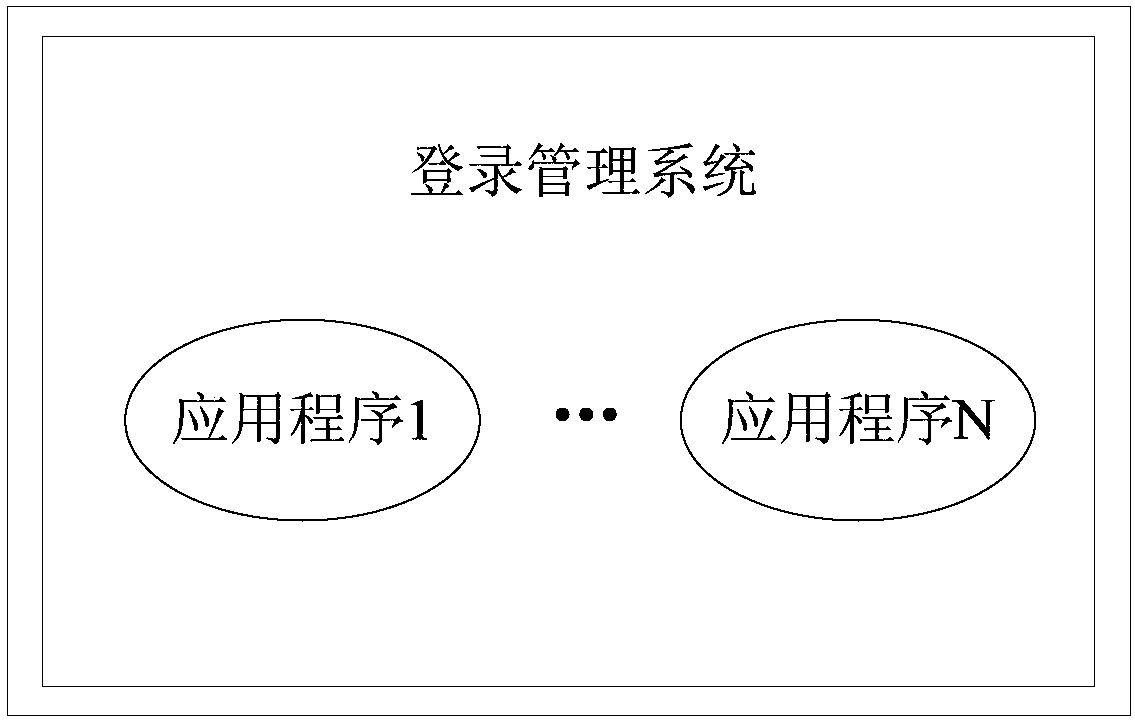
Application login method and device, medium, and electronic equipment
The embodiment of the invention provides an application login method and device, a medium, and electronic equipment. The application login method is applied to a login management system. The login management system is used for managing M applications, and the M applications are applications which are independent from one another. The method comprises the following steps: receiving identity authentication information input by a user; when it is determined that identity information of the user is valid, receiving an identity authentication request message sent by a server corresponding to each of the M applications; and sending an identity authentication confirmation message to the server corresponding to each of N applications according to the M identity authentication request messages, sothat the user can log in to the N applications. The application login method and device, the medium and the electronic equipment provided by the embodiment of the invention have the advantage that theuser can simultaneously log in to the multiple applications in a more efficient manner.
Owner:TAIKANG LIFE INSURANCE CO LTD
Clustering method and device for application
InactiveCN106776906AReduce search timeImprove experienceWeb data indexingCharacter and pattern recognitionN applicationData mining
Owner:NUBIA TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
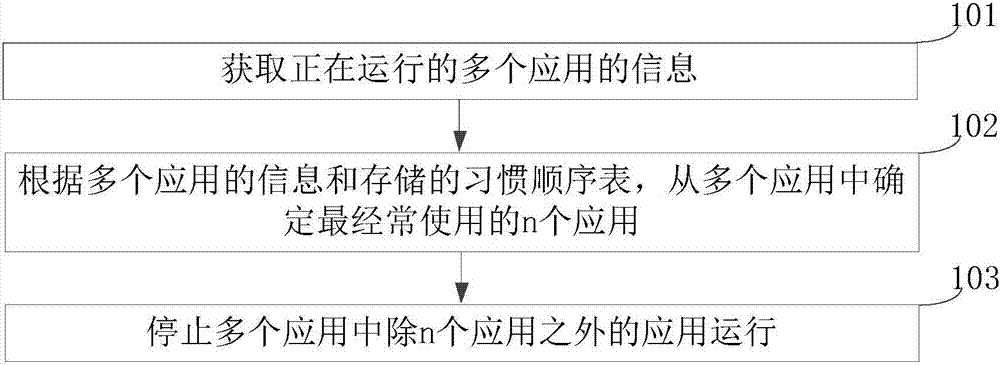
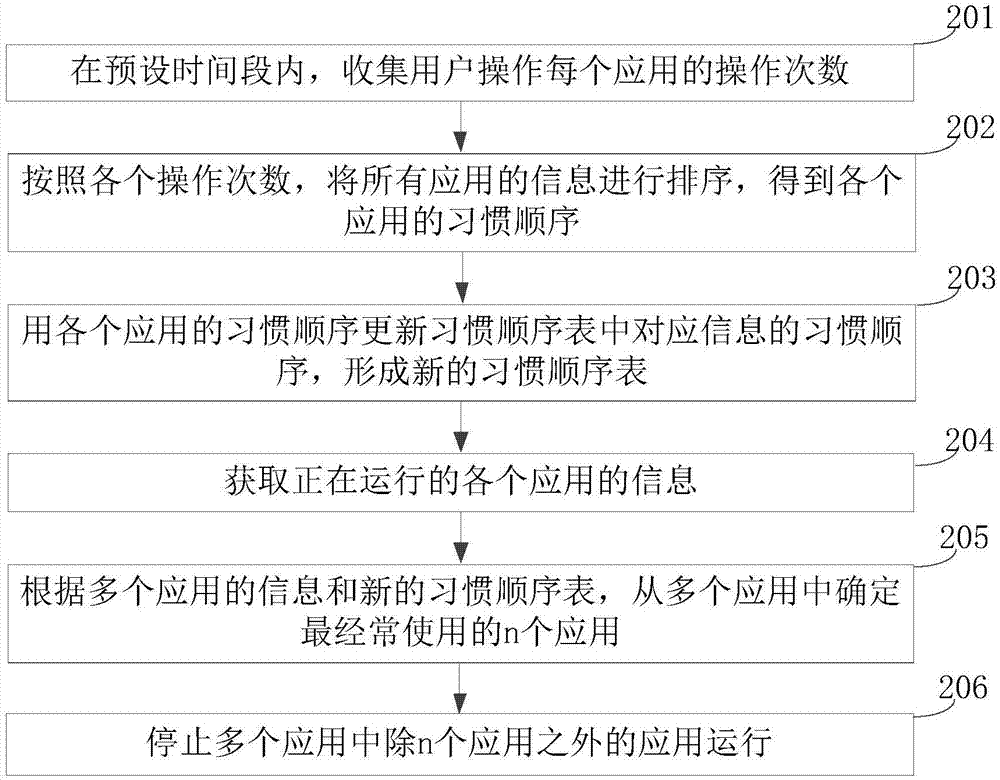
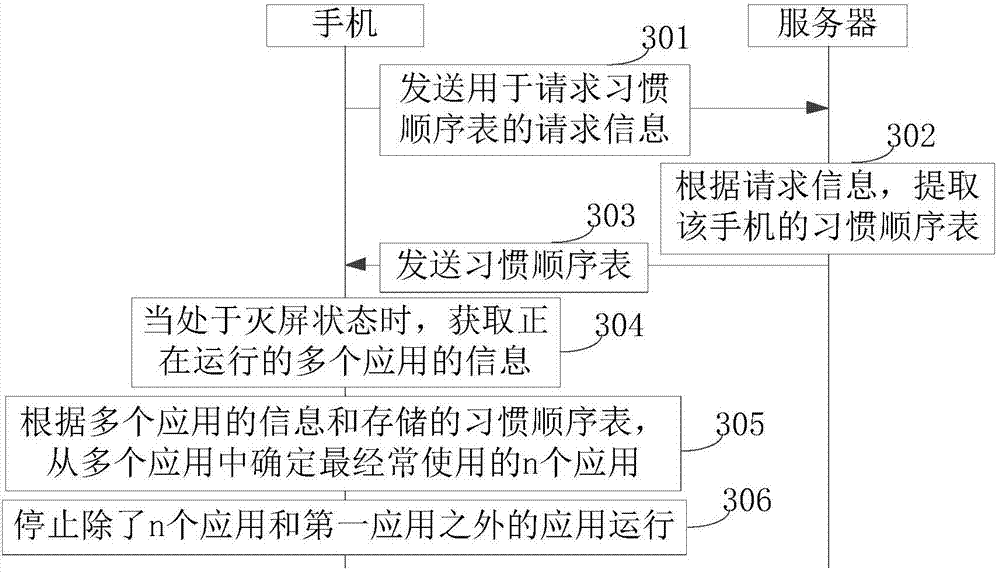
Application cleaning method and device
PendingCN106919448AImprove experienceReduce memory utilizationProgram initiation/switchingN applicationCleaning methods
The disclosure relates to an application cleaning method and device. The method comprises following steps: obtaining information of multiple applications which are running; according to the information of the multiple application and a stored habit sequence list, determining n applications which are most frequently used from the applications; the habit sequence list comprises information of all applications according to the use frequency of the applications; the n is a positive integer; stopping the operating of applications apart from the n application. According to the technical scheme, when multiple applications are running, the n applications having the highest use frequency are retained and other applications are stopped; therefore, the kept n applications are the most likely to be used by a user; accordingly, the memory utilization rate is reduced and the applications possibly to be used are not stopped, which increases user experience.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com