Single-task and multi-core scheduling method based on critical path and task duplication
A critical path, task replication technology, applied in multi-programming devices, program startup/switching, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that the processor core cannot perform effective scheduling, cannot adjust the scheduling sequence, and shorten the product completion time. Reduce inter-core communication, reduce overall time, reduce the effect of communication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
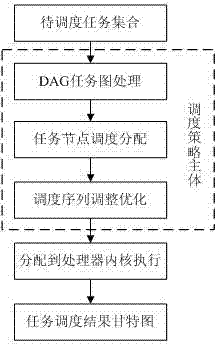
[0051] A kind of single-task multi-core scheduling method based on critical path and task duplication, it is characterized in that: the method mainly comprises the steps: DAG task diagram processing module adopts the method for task duplication, the fork node in DAG task diagram is copied to its successor The task node forms a join structure task graph, and further converts the join graph into a product processing tree; the task node scheduling and allocation module introduces the critical path idea in comprehensive scheduling, searches for the critical path of the product processing tree, and prioritizes the nodes on the critical path, Try to advance the execution time of nodes on the critical path; the scheduling sequence adjustment optimization module adopts the method of merging the scheduling sequences with the largest similarity, and merges the scheduling sequences so that the number of scheduling sequences is not greater than the number of processor cores, so as to achiev...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The above-mentioned single-task multi-core scheduling method based on critical path and task replication, the specific implementation steps of the scheduling method are as follows:
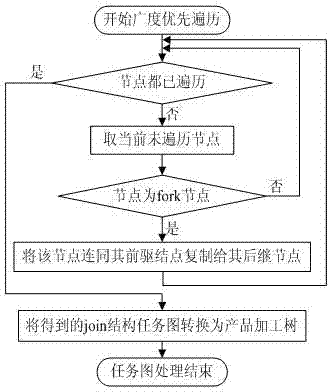
[0054] Step 1: traverse the DAG task graph, and copy the fork node in the task graph to its successor task node to form a task graph containing only join nodes;
[0055] Step 2: Convert the join task graph into a corresponding product processing tree;
[0056] Step 3: Calculate the path length from the root node to each leaf node in the product processing tree, find the longest path, and use it as the key path, if the path lengths are the same, find the path that contains the most nodes, and use it as the key path;
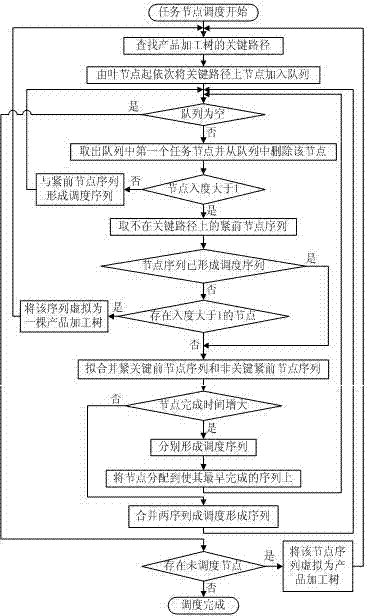
[0057] Step 4: Add the critical path to the queue sequentially from the first node;
[0058] Step 5: Determine whether the queue is empty, if it is not empty, continue to execute downwards, otherwise jump to step 14;
[0059] Step 6: Take the first task node in the queue, jud...
Embodiment 3
[0076] In the above single-task multi-core scheduling method based on critical path and task replication, the length of the path from the root node to each leaf node is the sum of the processing time of each process on the path and the communication time between nodes.
[0077] In the above single-task multi-core scheduling method based on critical path and task replication, the task node scheduling assignment module introduces the critical path strategy in comprehensive scheduling, and adopts the early scheduling strategy of the immediately preceding node group to schedule nodes on the critical path.
[0078] In the above-mentioned single-task multi-core scheduling method based on critical path and task replication, the scheduling sequence adjustment optimization module adopts the strategy of merging the maximum similarity, and adjusts the number of scheduling sequences according to the number of processor cores.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com