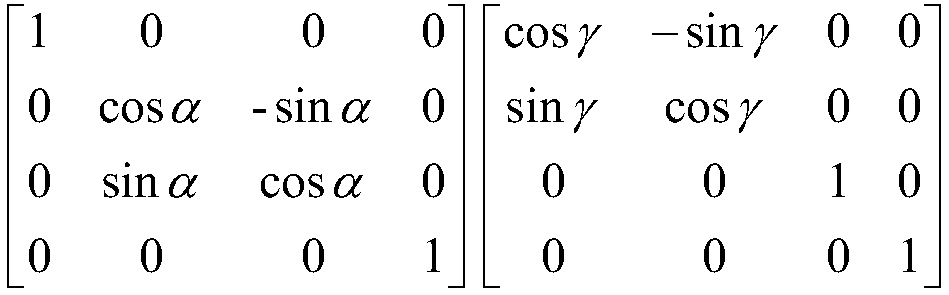Patents
Literature
90 results about "Process graph" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In graph theory a process-graph or P-graph is a directed bipartite graph used in workflow modeling. The vertices of the graph are of two types, operation (O) and material (M). The two vertex types form two disjunctive sets. The edges of the graph link the O and M vertices. An edge from an operation vertex (O) connects to a material vertex (M) if M is the output of O, such as a 'document' (material) that is output by a 'write-up' (operation). An edge from M to O indicates that M is an element of the input set of O, e.g. a document may be part of the input to a 'review' operation.
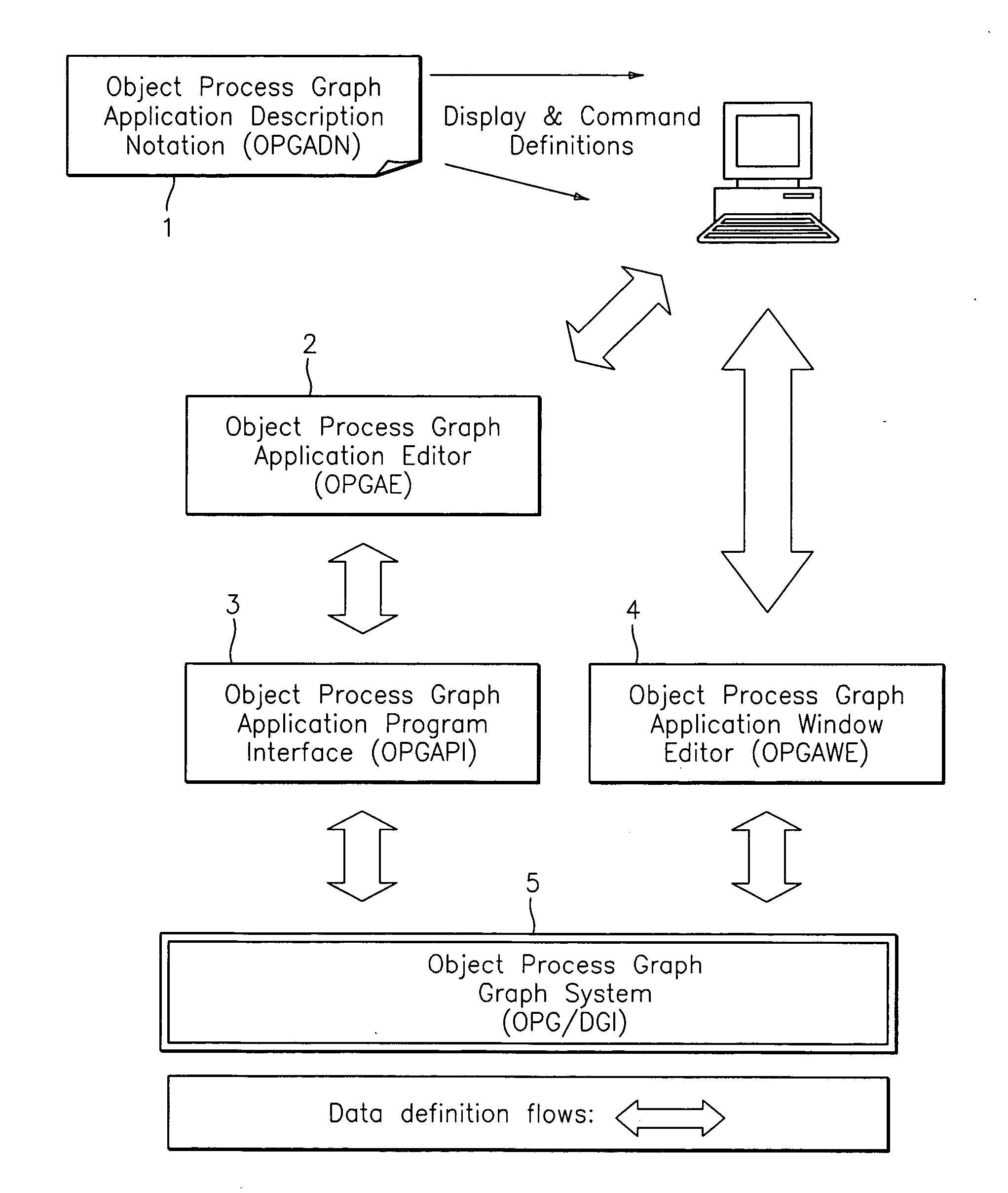
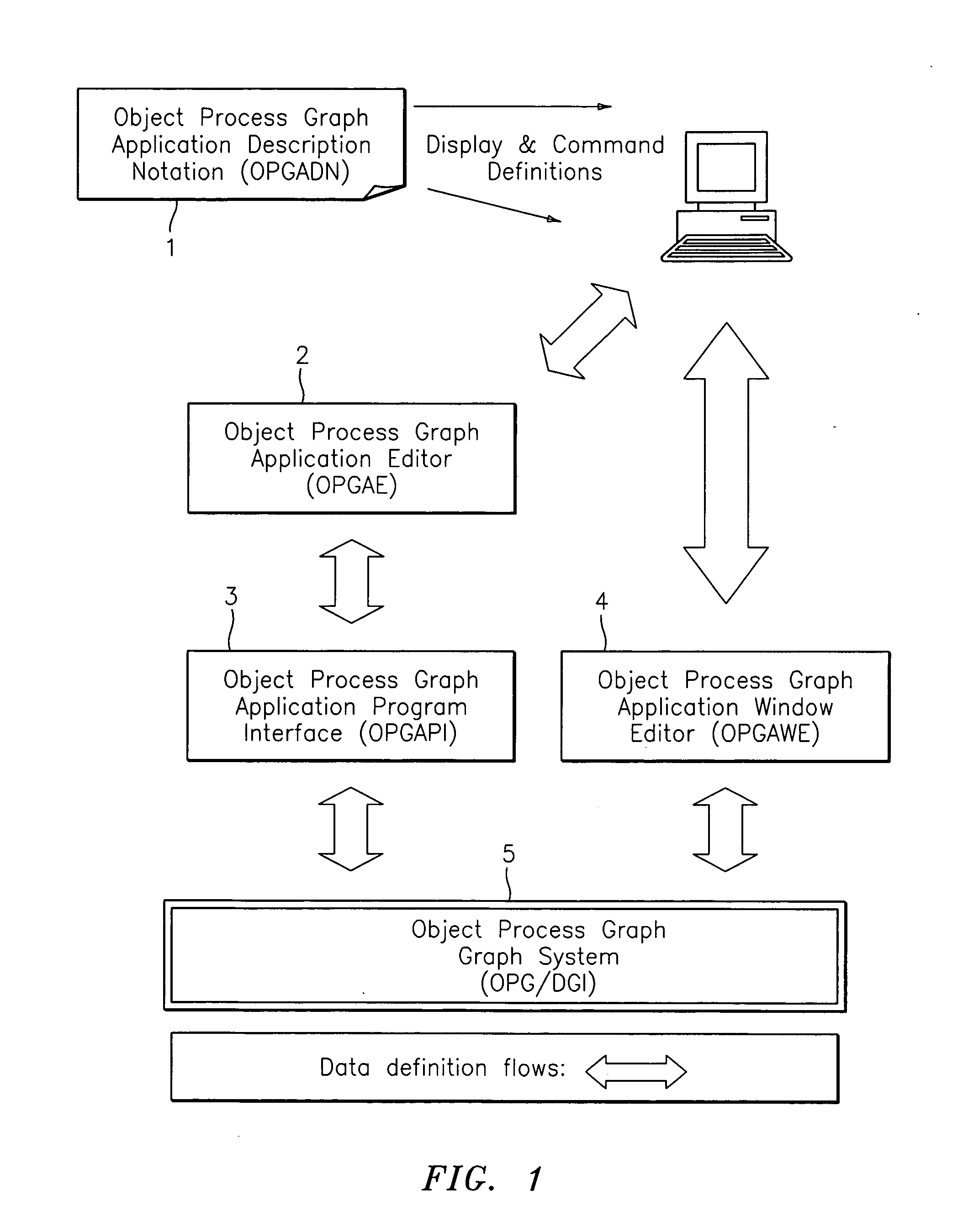
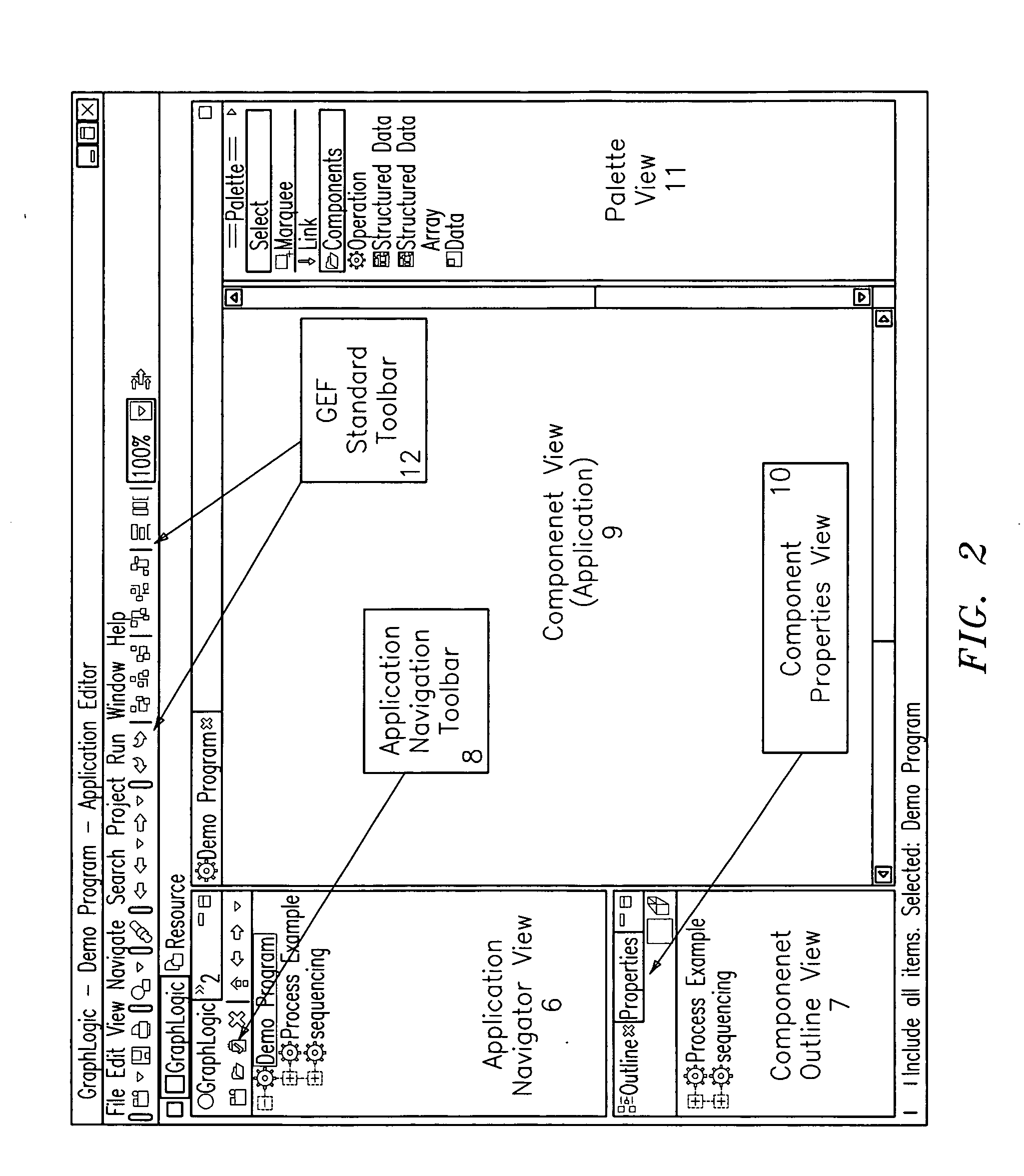
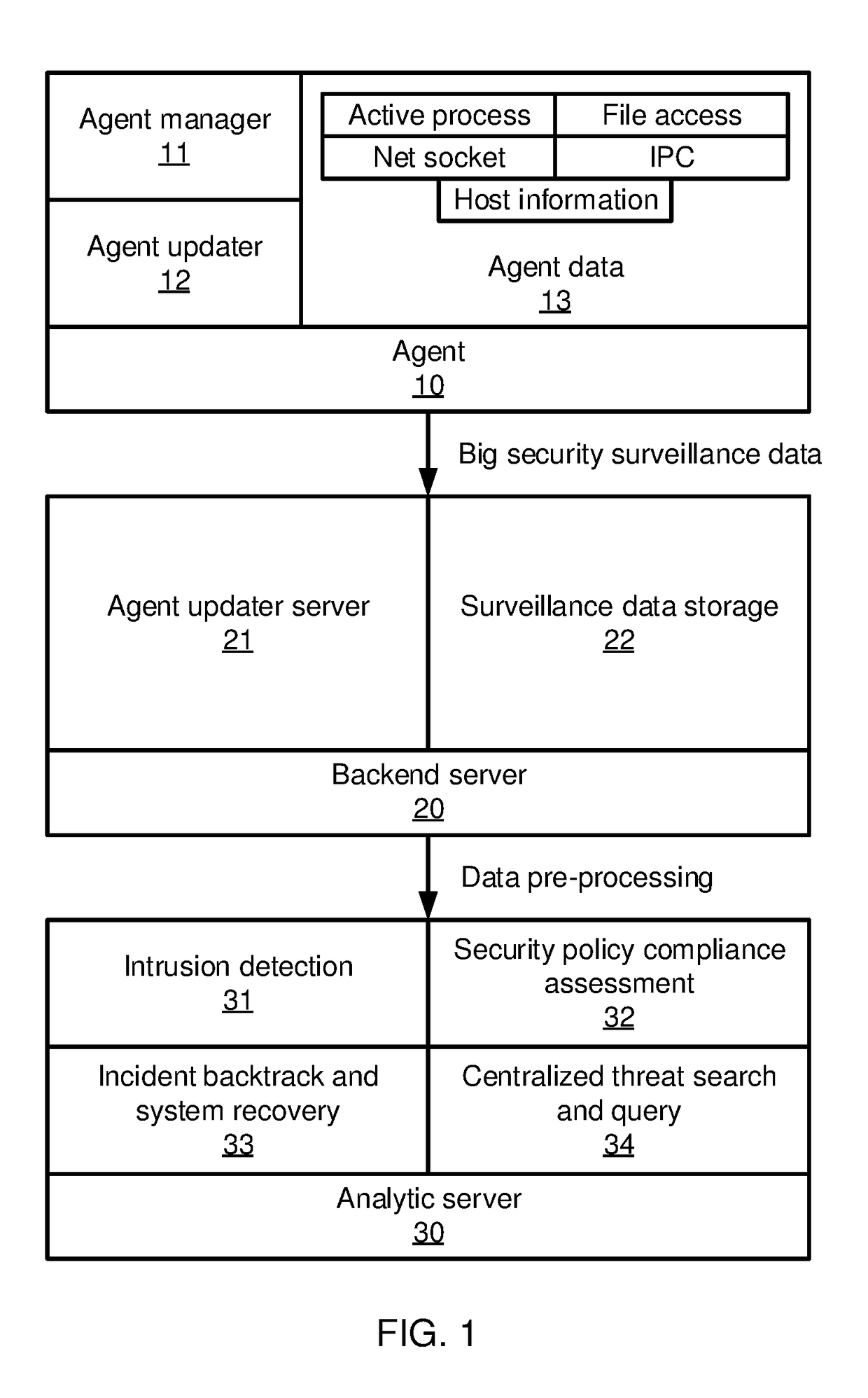
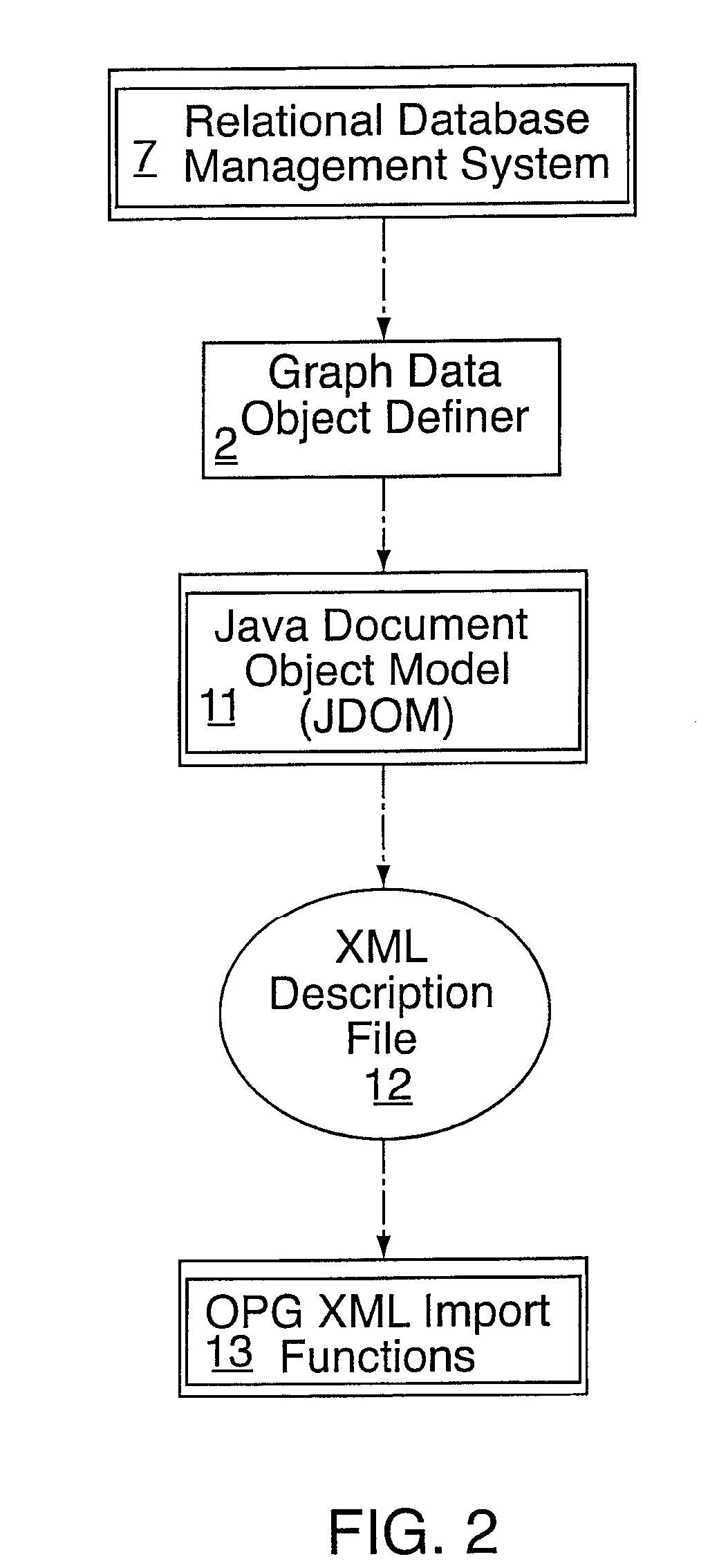
Object process graph application controller-viewer
InactiveUS20060059461A1Low costReduce riskSoftware designVisual/graphical programmingApplication softwareUser interface
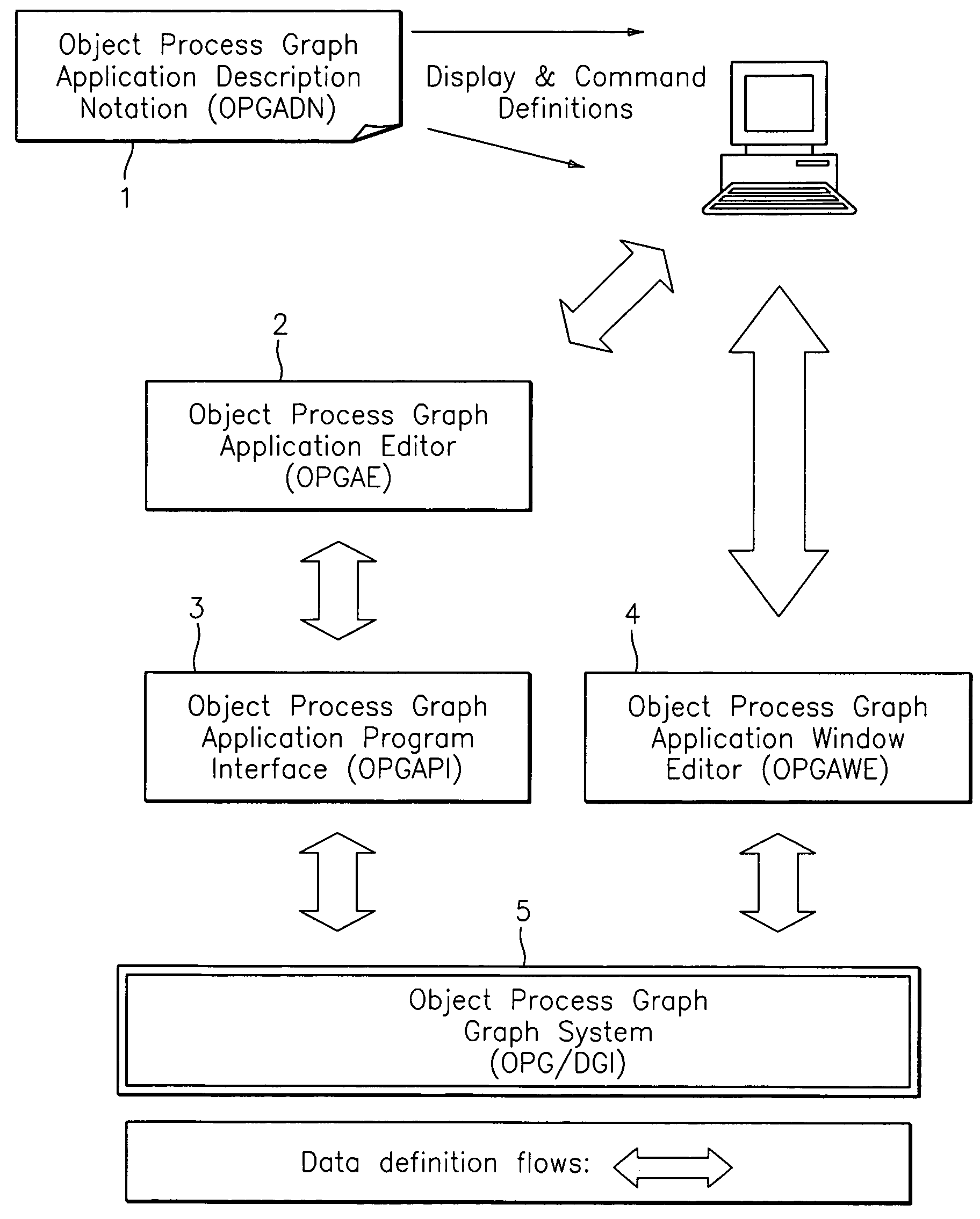
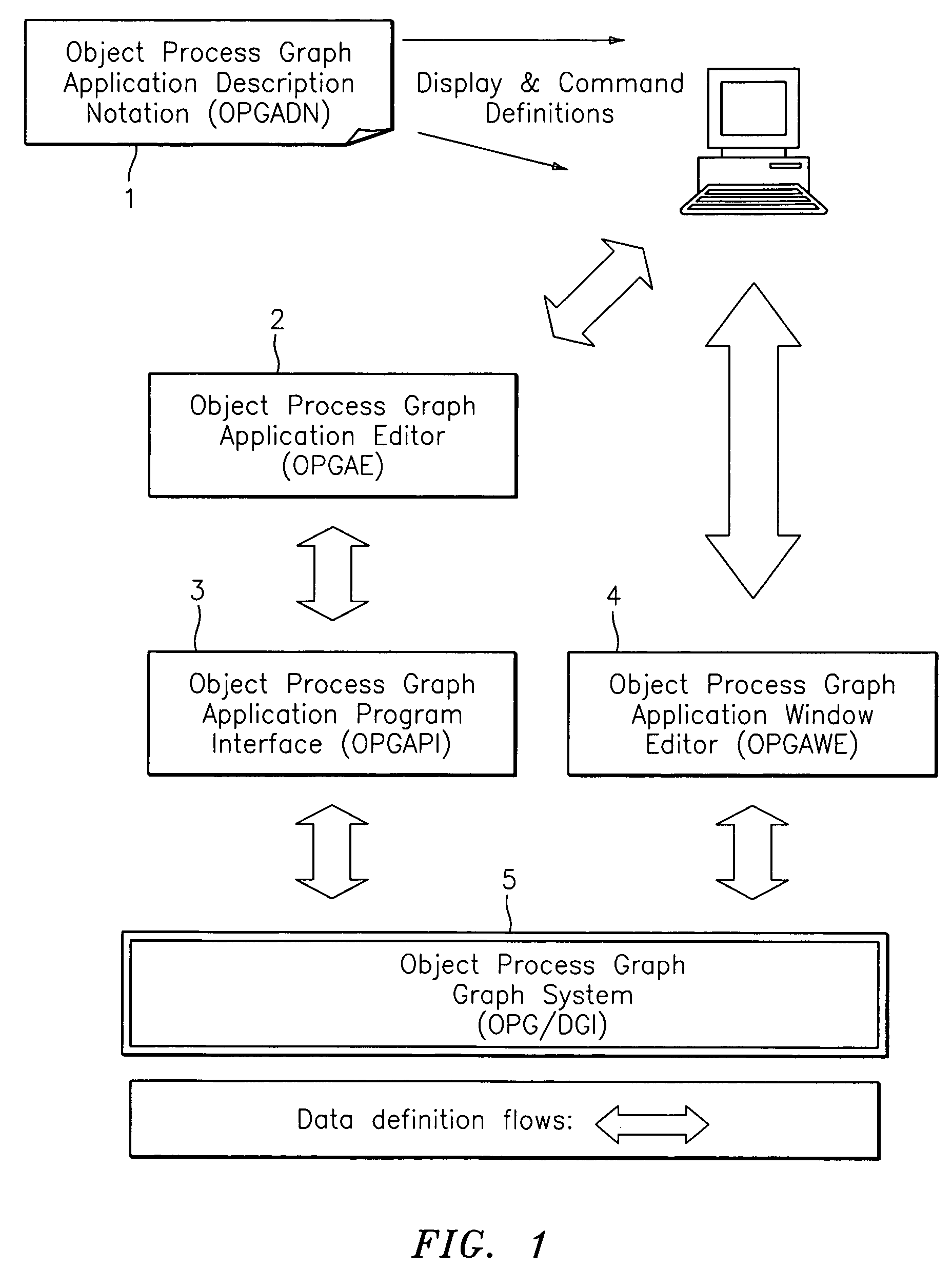
An object process graph (OPG) application development system. The system includes an OPG application program interface (API), an OPG application editor, an OPG application window editor, and an OPG application notation. The OPG API provides access to functions of an OPG system. The OPG application editor facilitates the creating and editing of the OPG applications via the OPG API. The OPG application window editor facilitates the editing of OPG application user interface windows while an OPG application is running. The OPG application notation includes a plurality of key words and associated definitions for describing and defining OPG applications.
Owner:GRAPHLOGIC INC
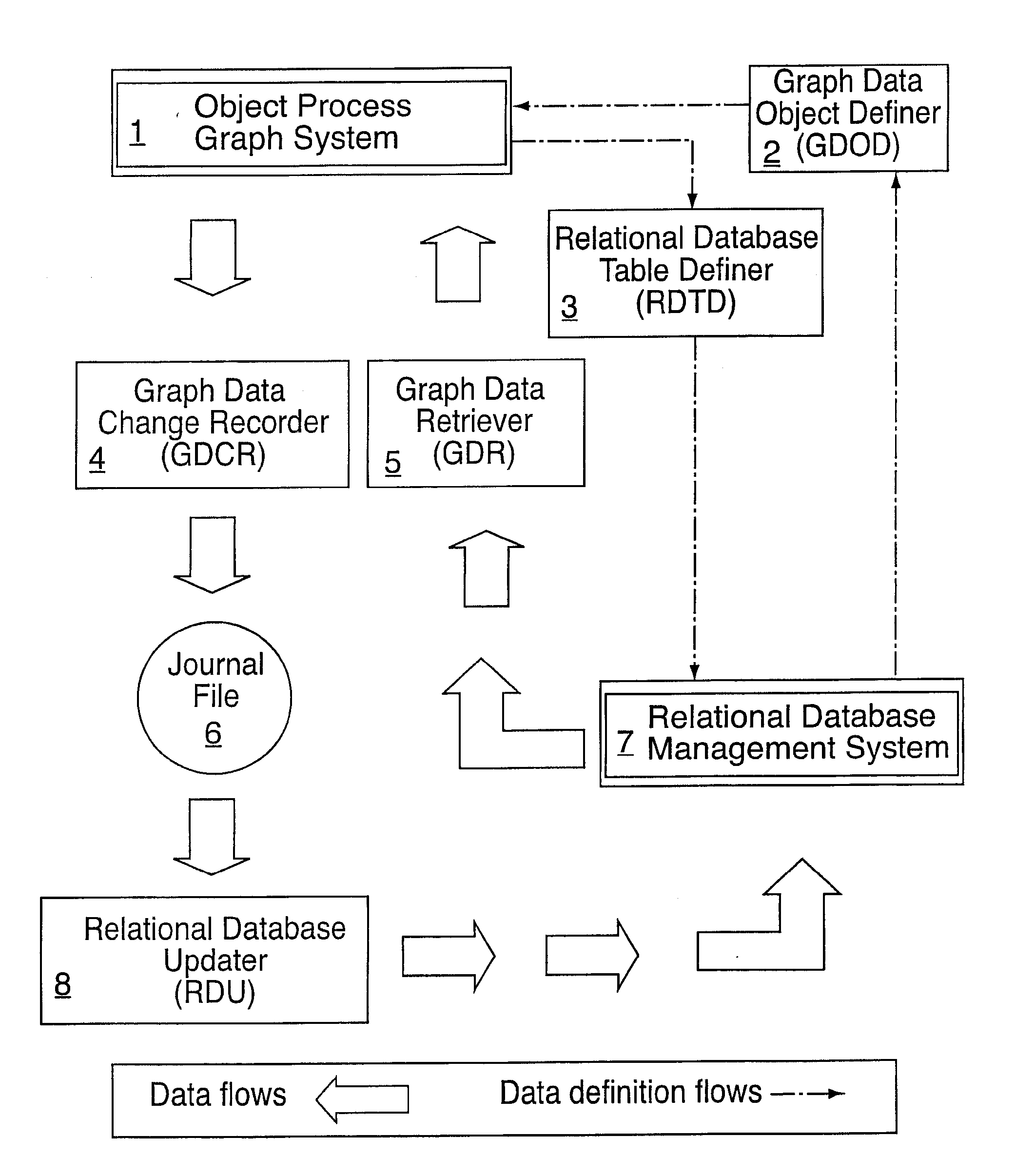
Object process graph relational database interface
InactiveUS20060004851A1Rich basic functionsCreate quicklyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDatabase interfaceRelational database
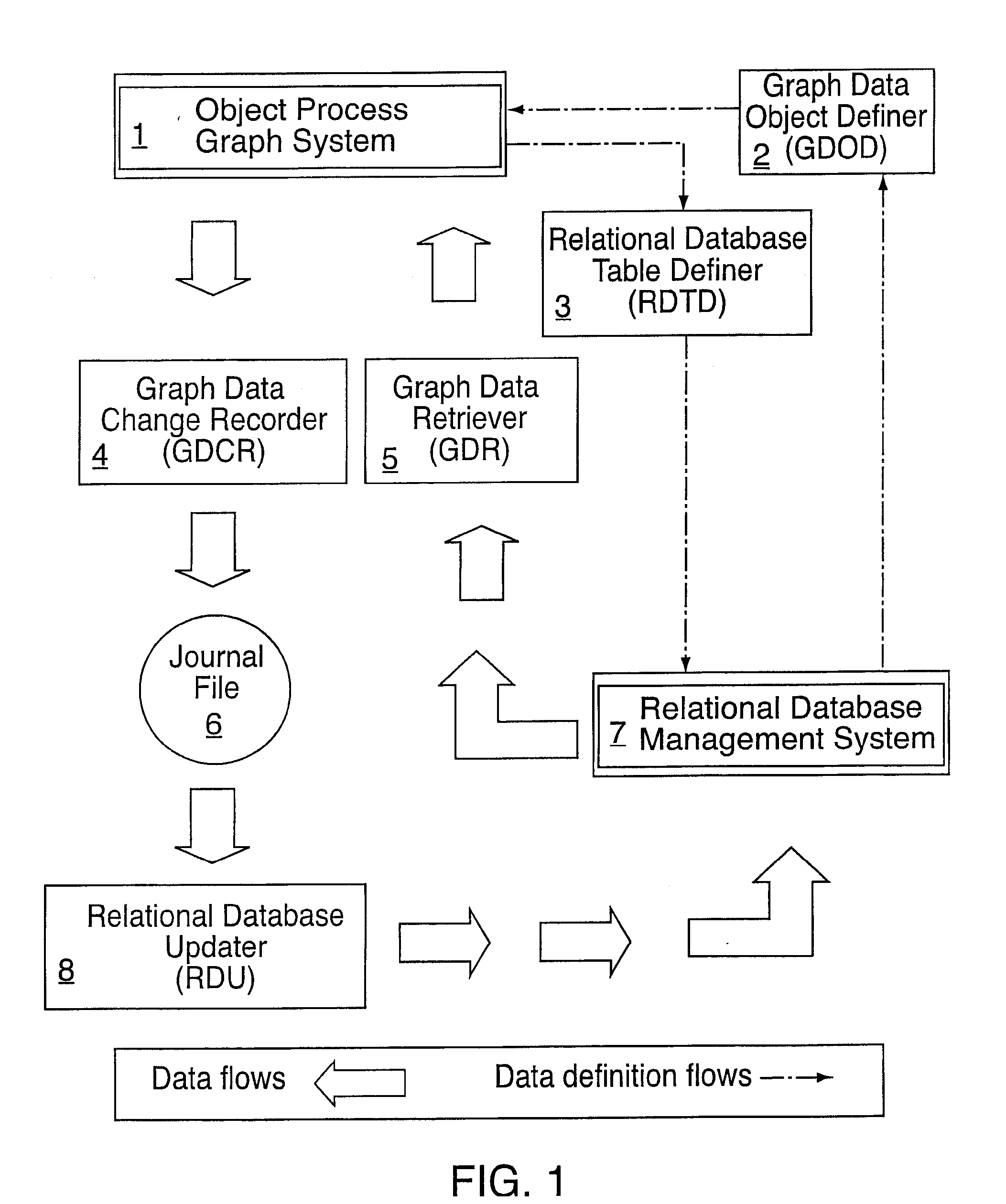
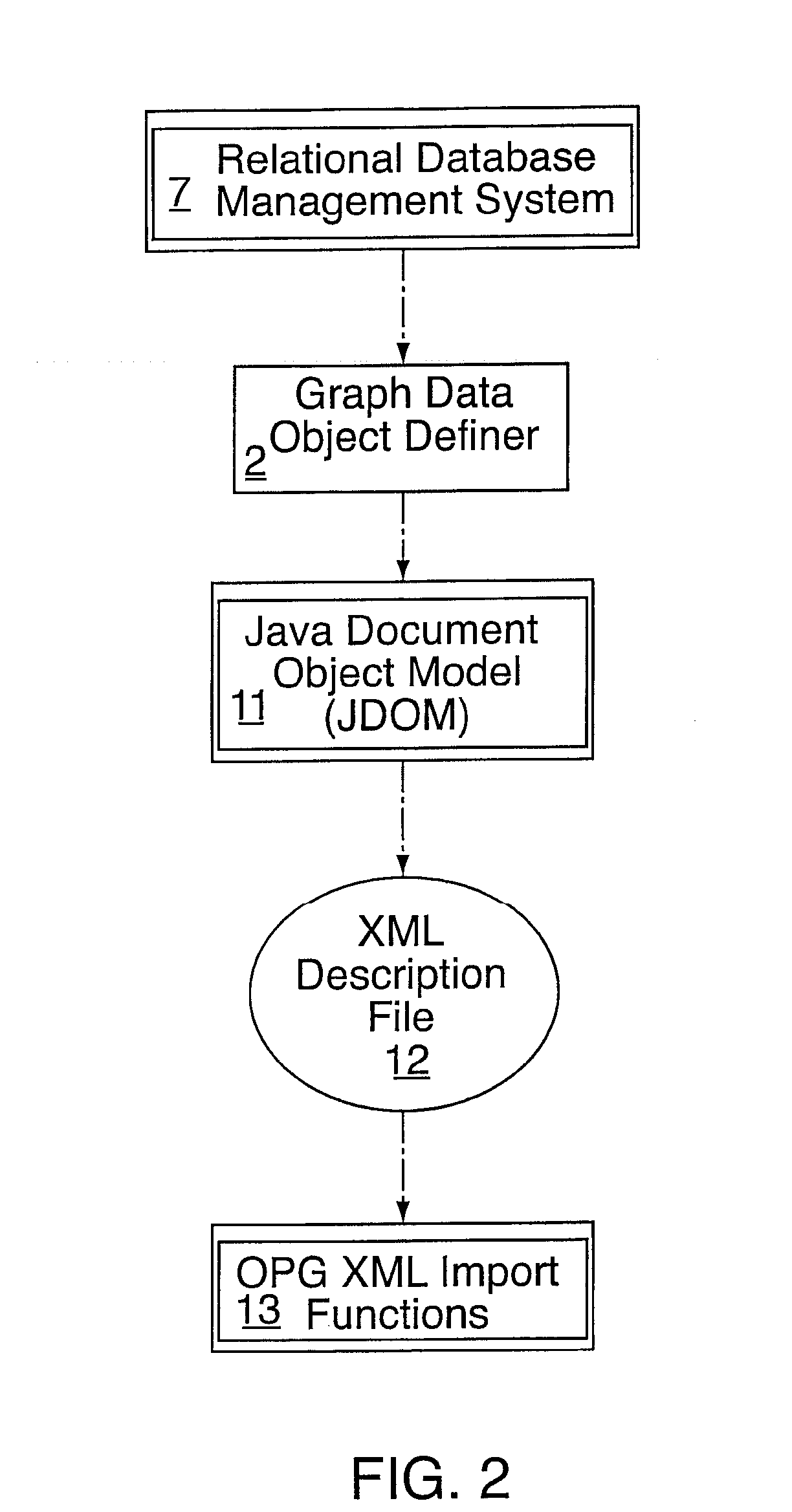
A computer software system is provided, namely An Object Process Graph Relational Database Interface (OPGRDI) system. The OPGRDI defines and updates relational database tables based on an OPG and stores and retrieves data in the tables as an OPG-defined application is run. The OPGRDI also defines and updates OPG persistent data object elements based on relational database table schemas. The OPGRDI functions can be enabled by users who want to store and retrieve application information in a relational database system, such as Oracle, Sybase, SQL Server, etc. The OPGRDI alters relational database tables as a user changes the structure of OPG-defined application.
Owner:GRAPHLOGIC INC
Object process graph system
InactiveUS20050273773A1Low costReduce riskData processing applicationsVisual/graphical programmingGraphicsSoftware system
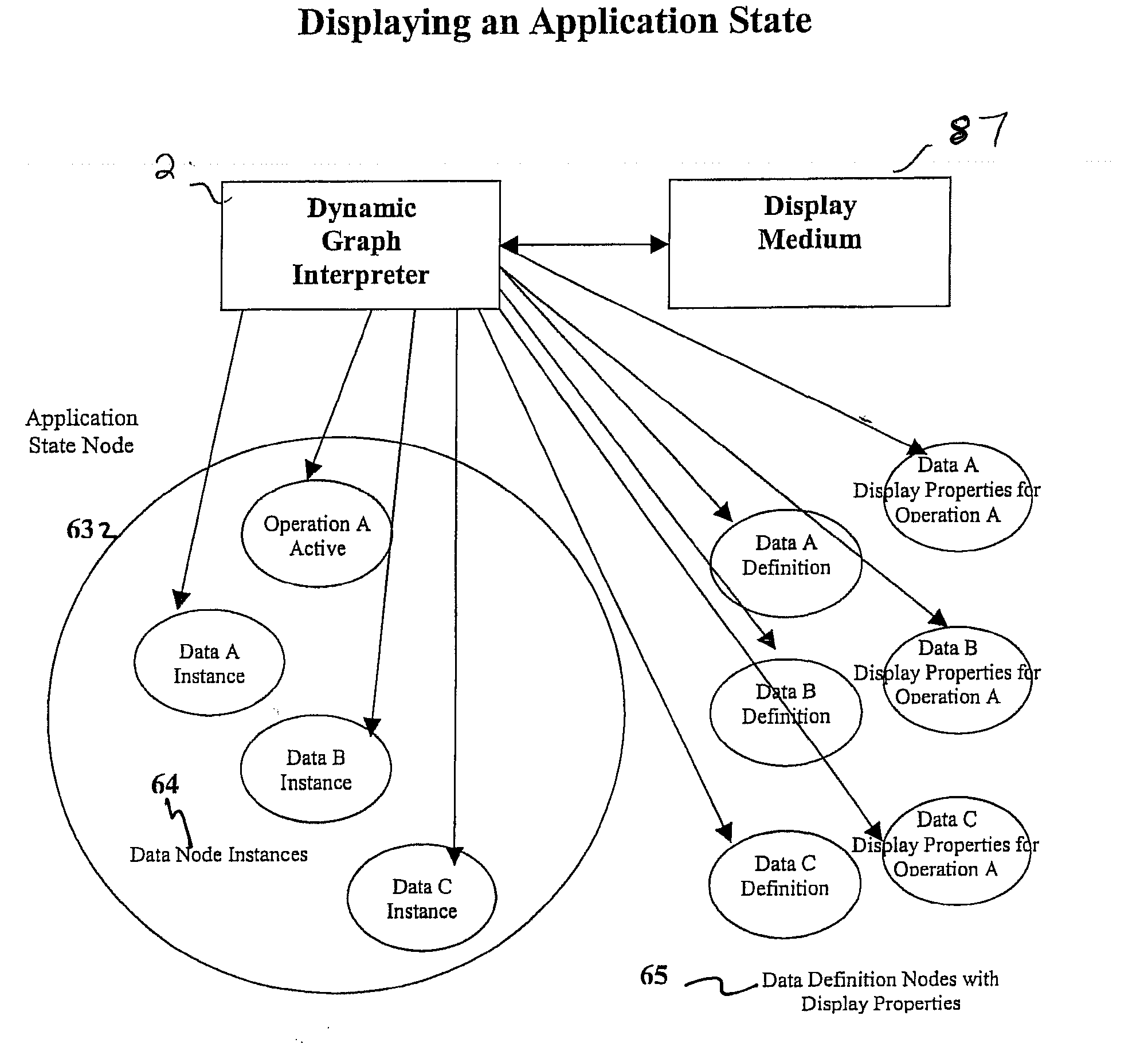
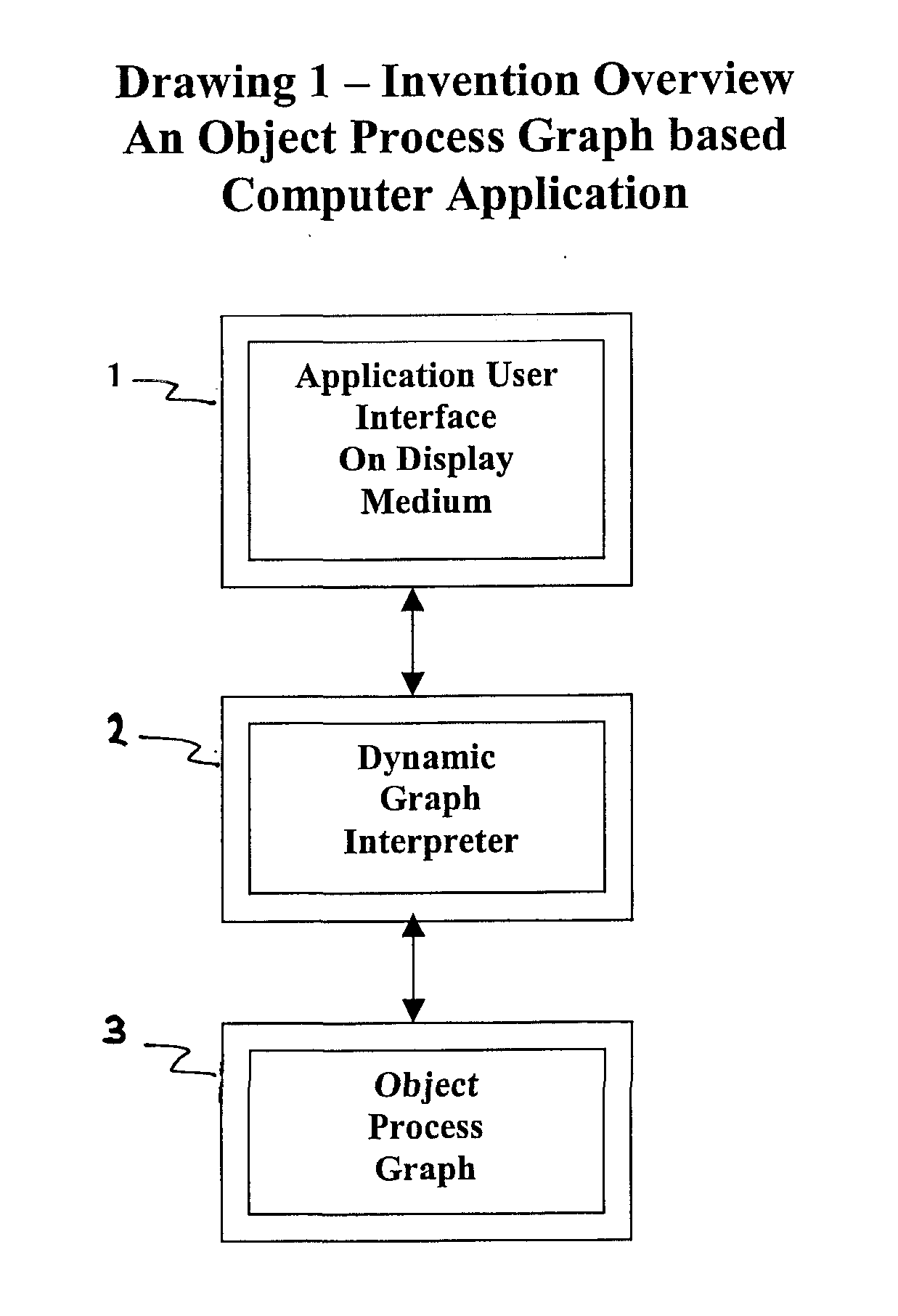
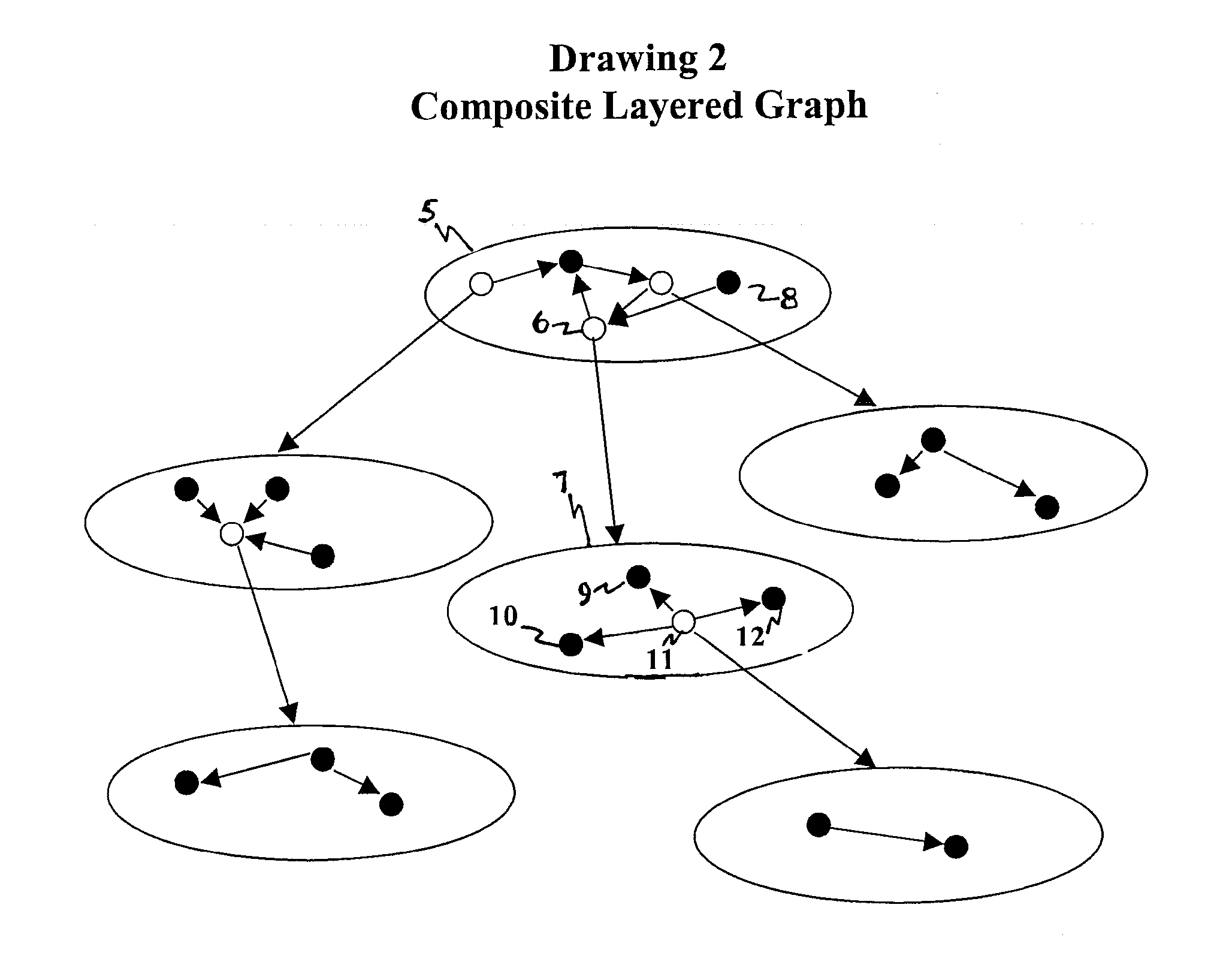
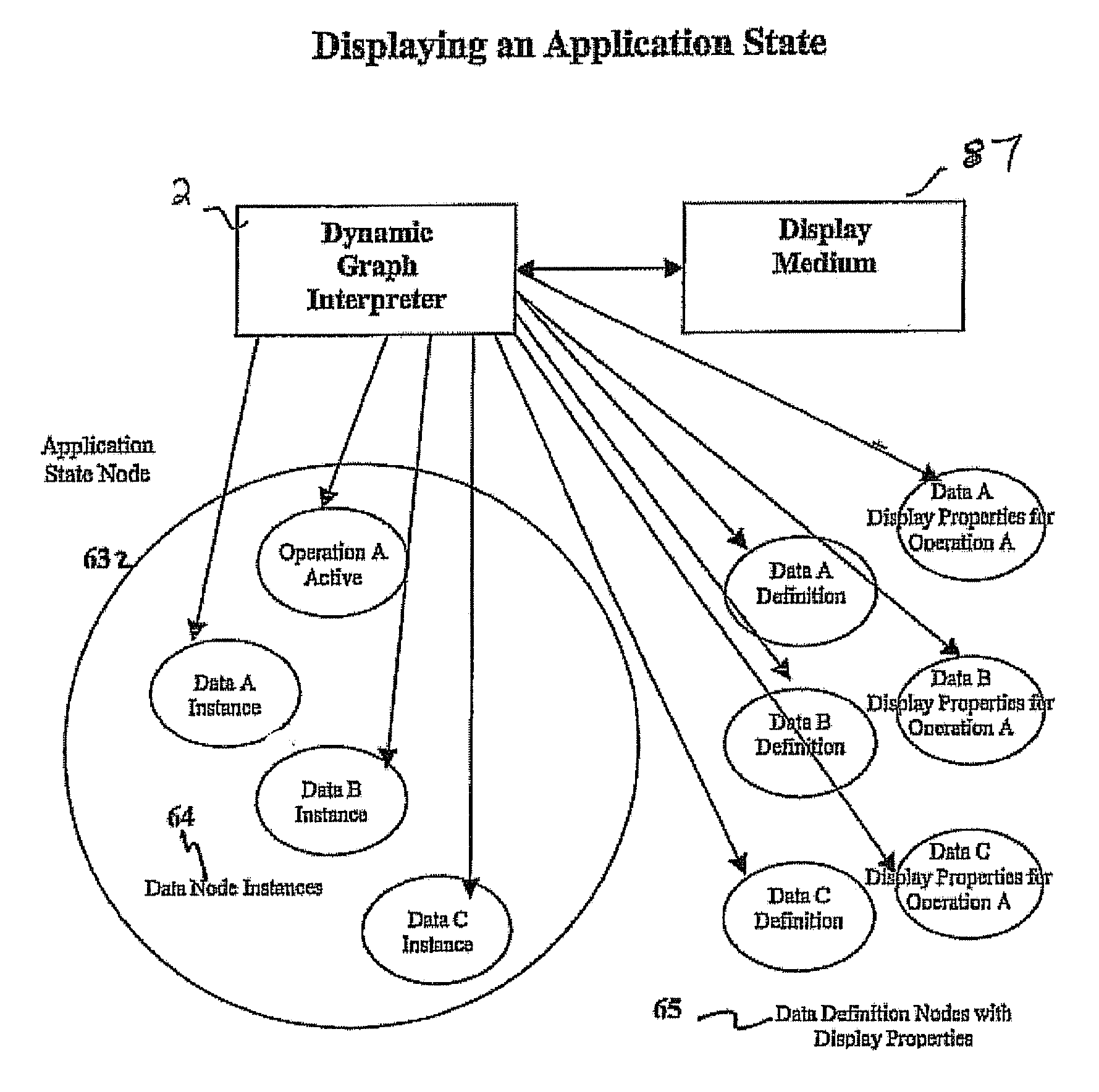
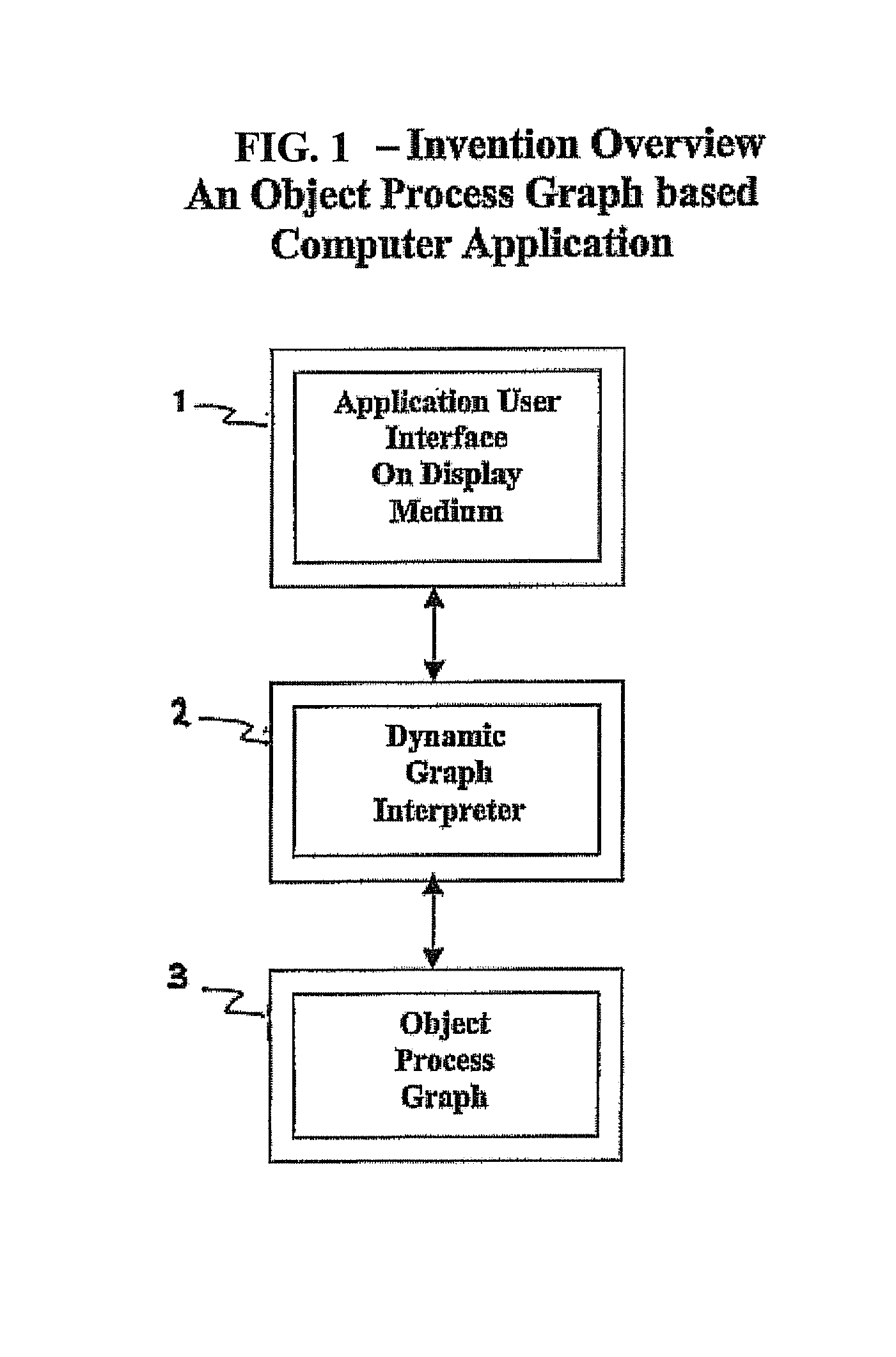
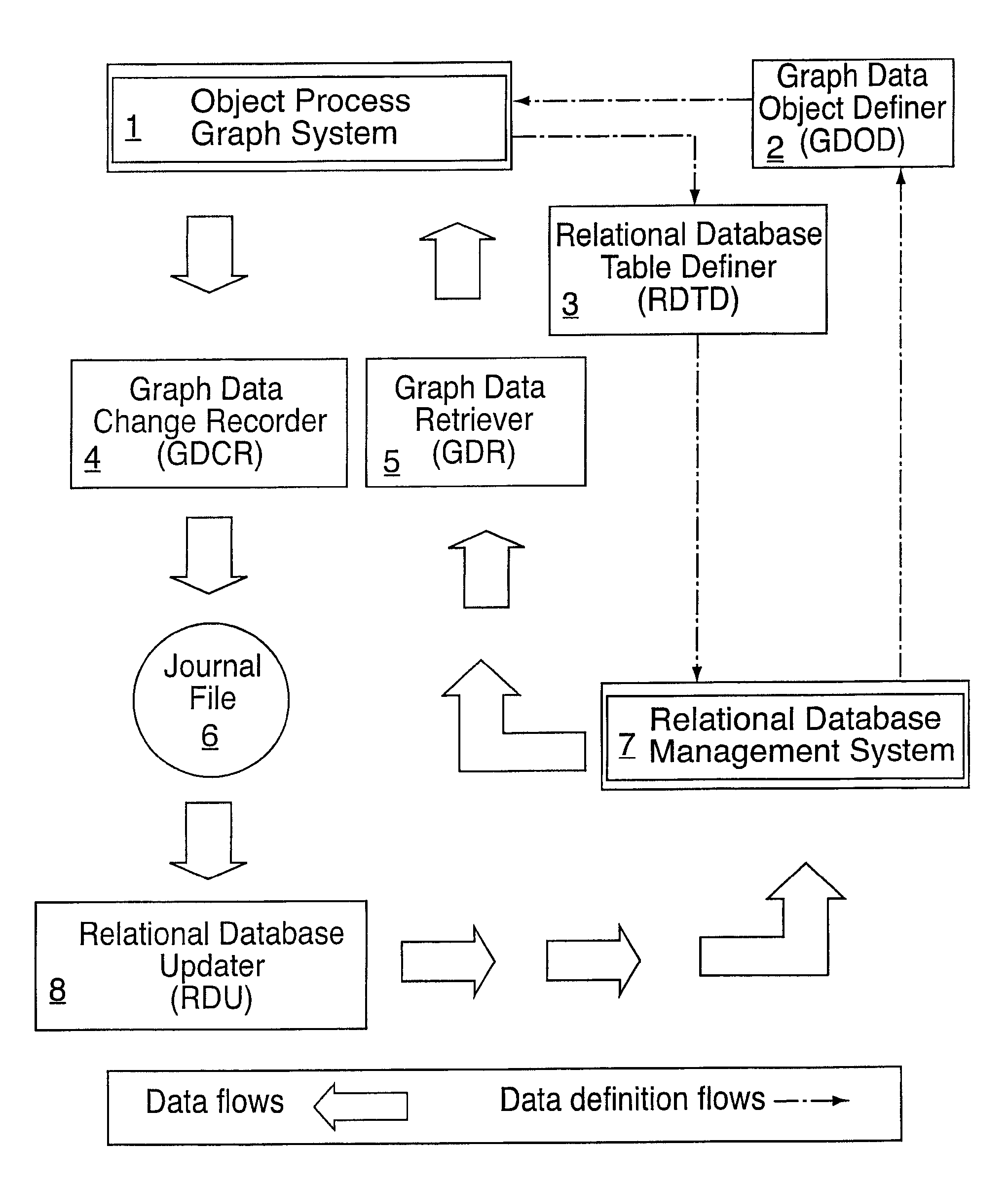
A software system is provided including an Object Process Graph for defining applications and a Dynamic Graph Interpreter that interprets Object Process Graphs. An Object Process Graph defines all of an application's manipulations and processing steps and all of the application's data. An Object Process Graph is dynamic, making it possible to change any aspect of an application's data entry, processing or information display at any time. When an Object Process Graph is interpreted, it functions to accept data, process the data and produce information output. Modifications made to an Object Process Graph while it is being interpreted take affect immediately and can be saved. Object Process Graphs and Dynamic Graph Interpreters can be deployed on single user workstation computers or on distributed processing environments where central servers store Object Process Graphs and run Dynamic Graph Interpreters, and workstation computers access the servers via the intranet or local intranets.
Owner:GRAPHLOGIC INC
Object process graph application controller-viewer
InactiveUS7536676B2Low costReduce riskSoftware designVisual/graphical programmingApplication softwareUser interface
An object process graph (OPG) application development system. The system includes an OPG application program interface (API), an OPG application editor, an OPG application window editor, and an OPG application notation. The OPG API provides access to functions of an OPG system. The OPG application editor facilitates the creating and editing of the OPG applications via the OPG API. The OPG application window editor facilitates the editing of OPG application user interface windows while an OPG application is running. The OPG application notation includes a plurality of key words and associated definitions for describing and defining OPG applications.
Owner:GRAPHLOGIC INC
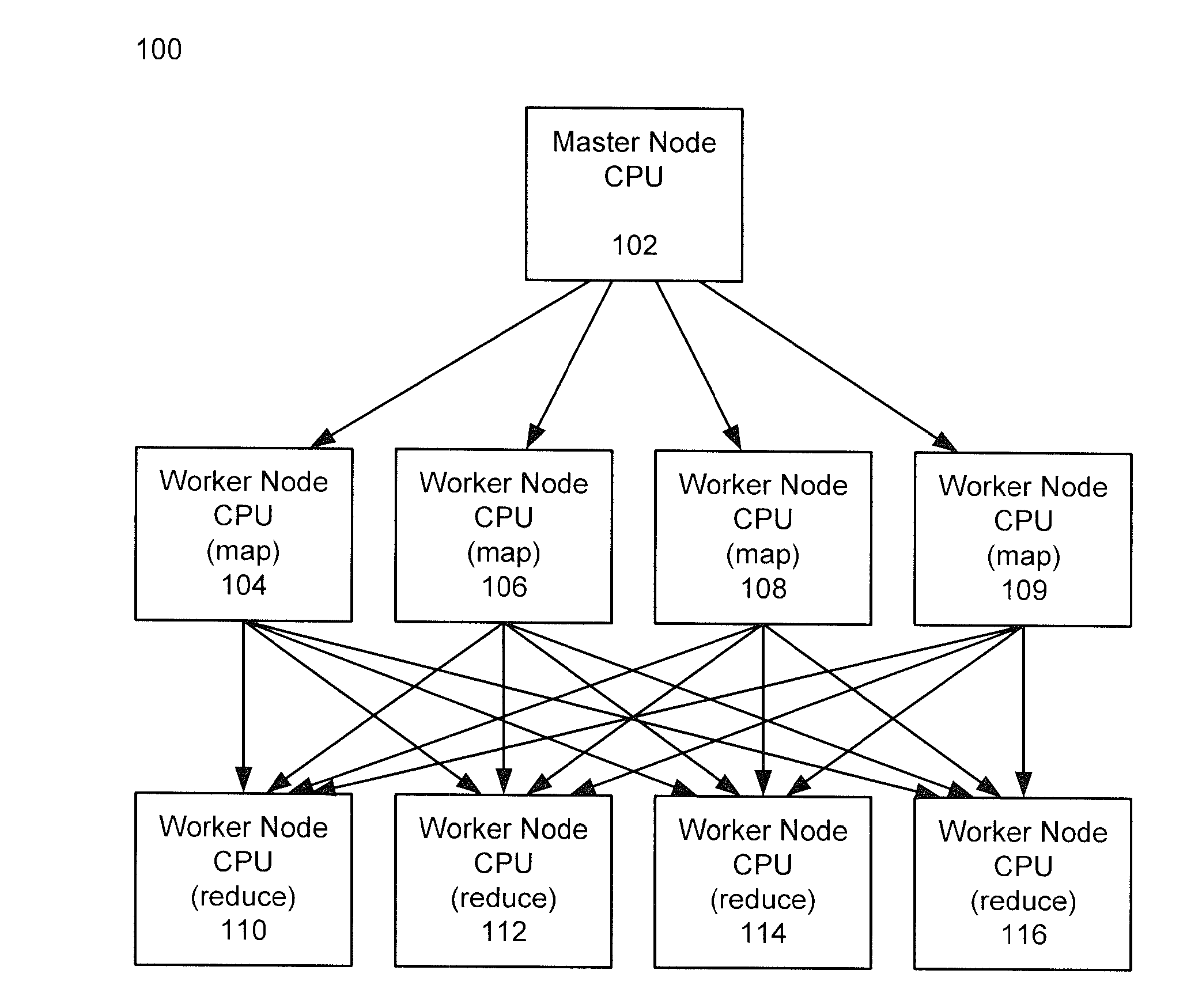
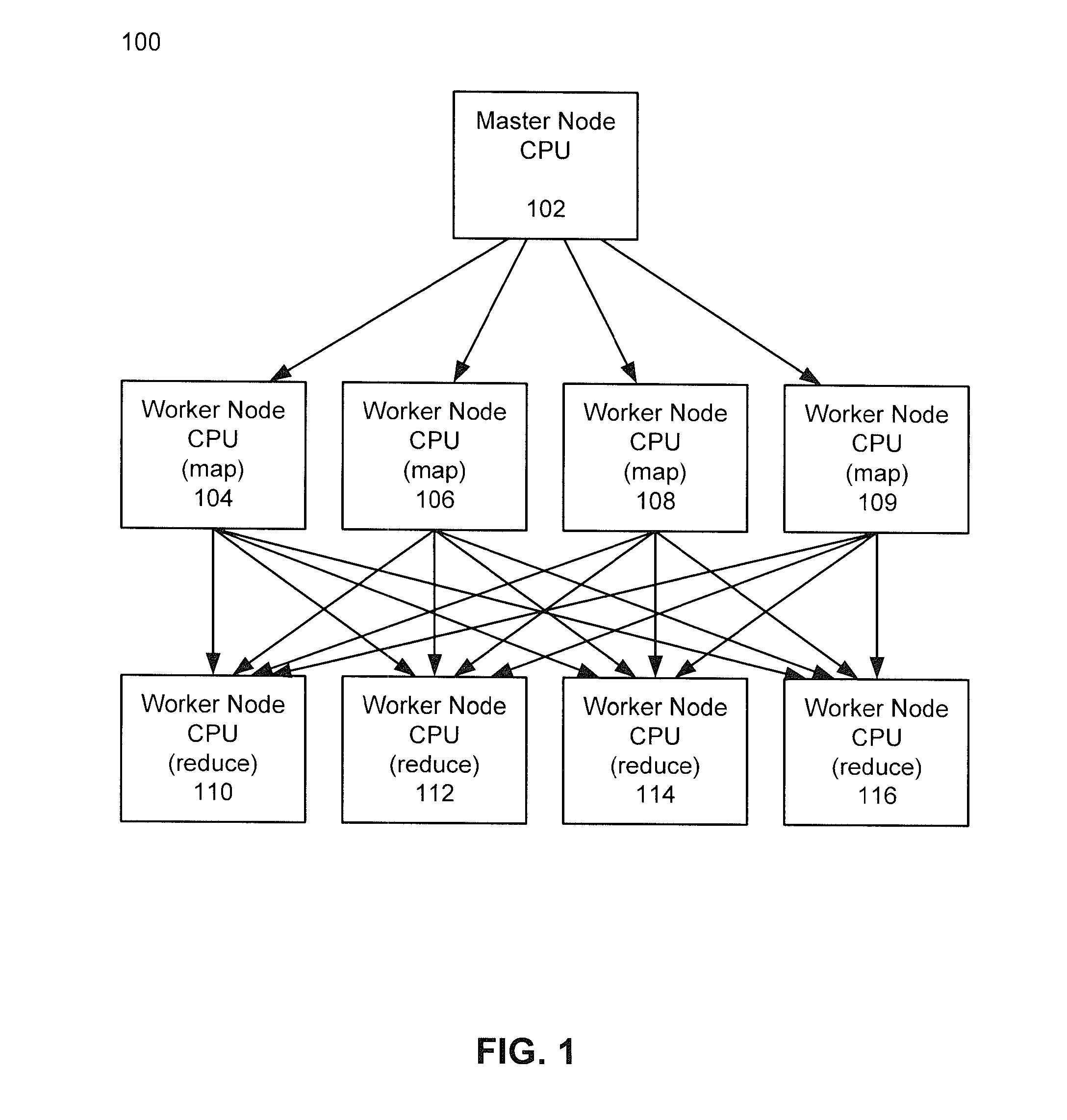
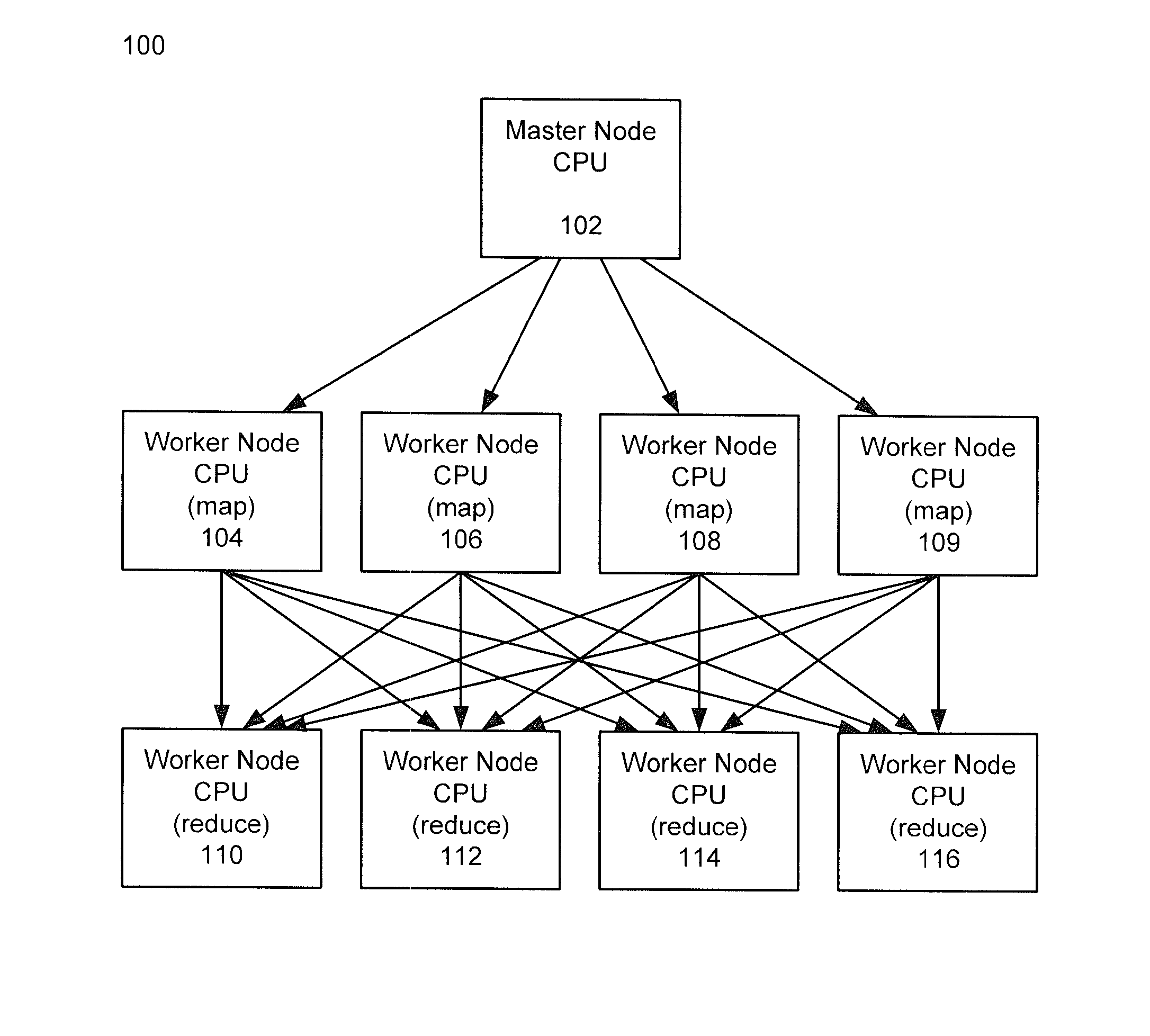
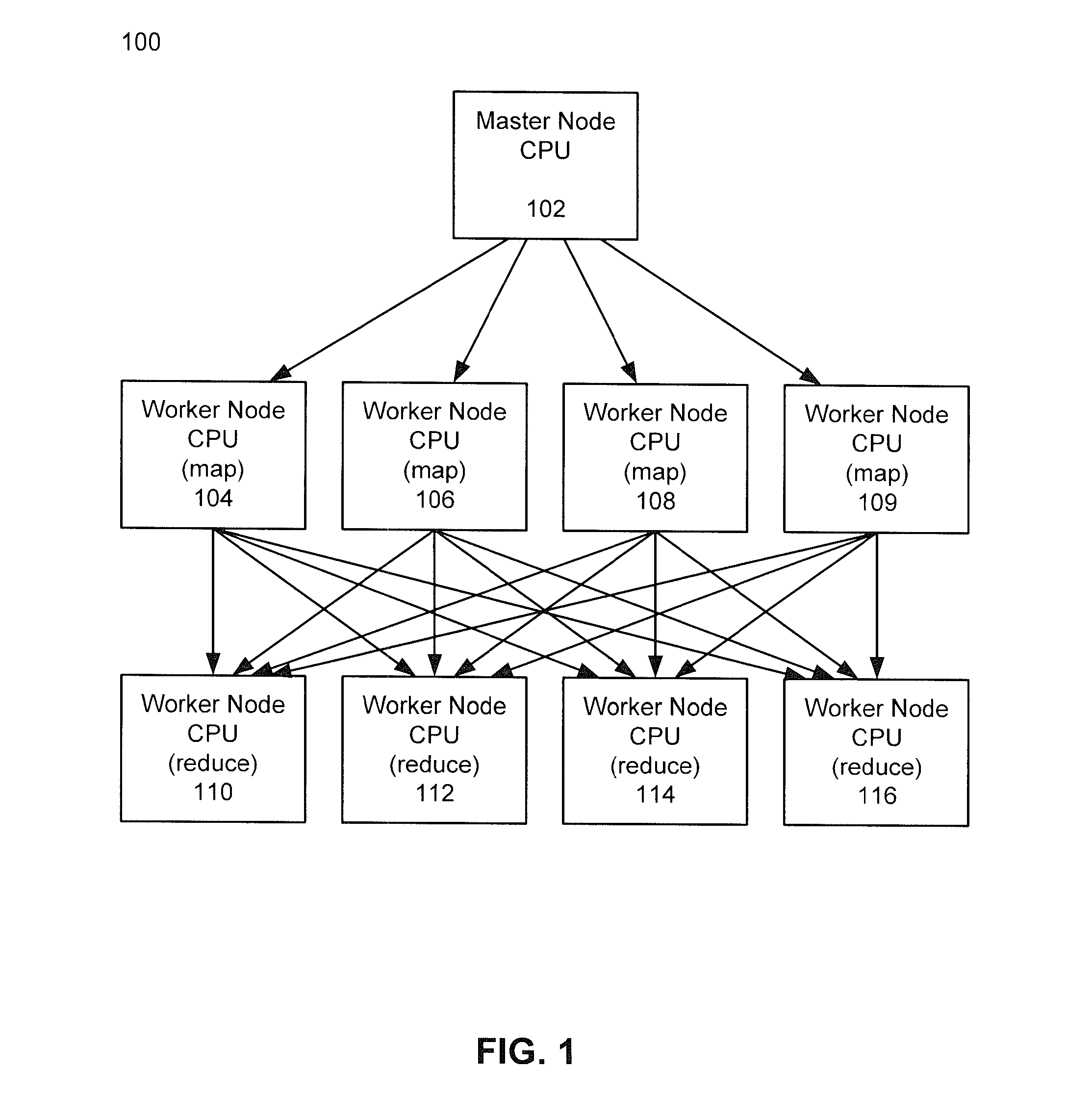
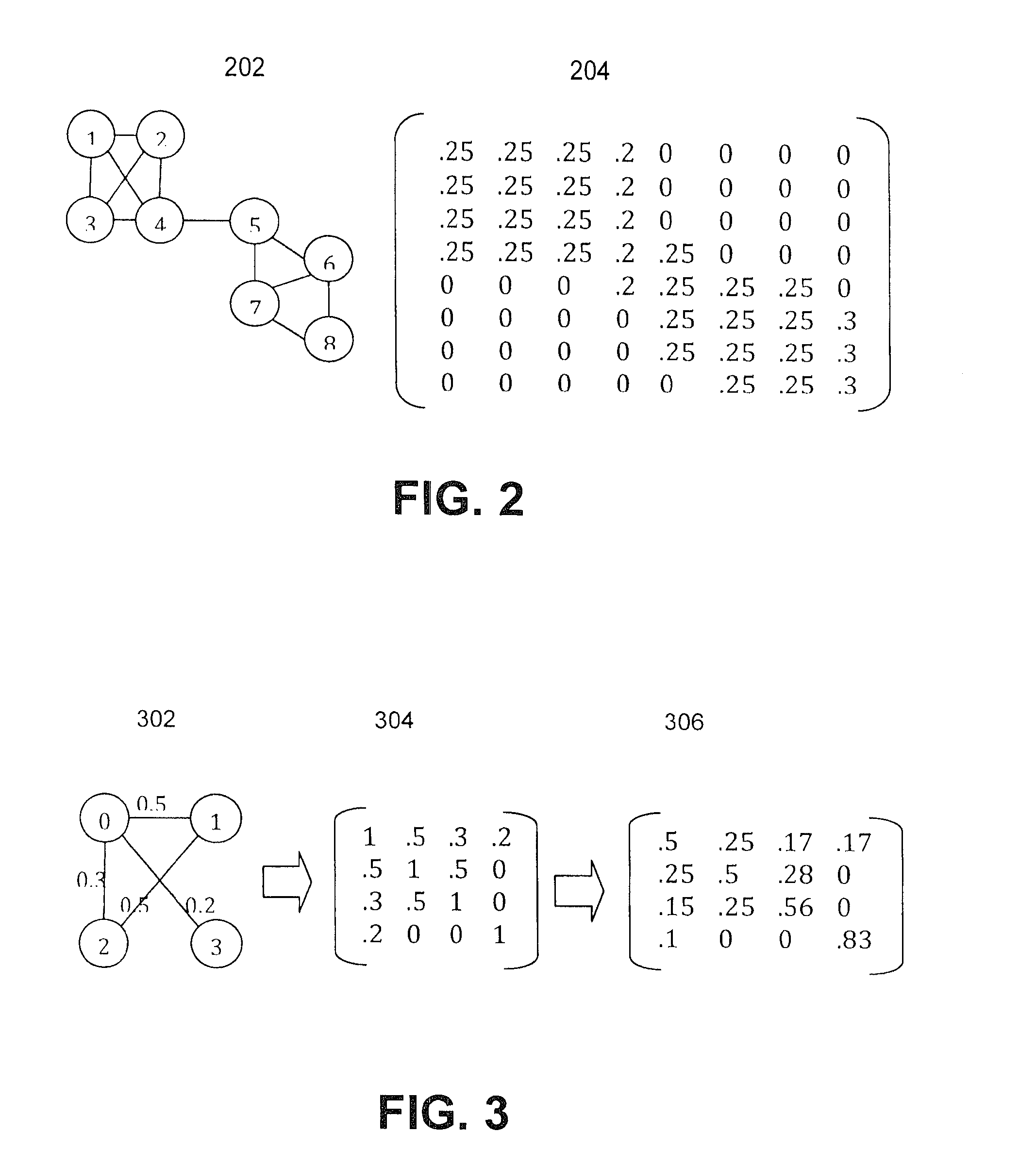
Methods and systems for using map-reduce for large-scale analysis of graph-based data
ActiveUS20130024412A1Improve memory usageEasy to implementKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsCluster algorithmMarkov clustering
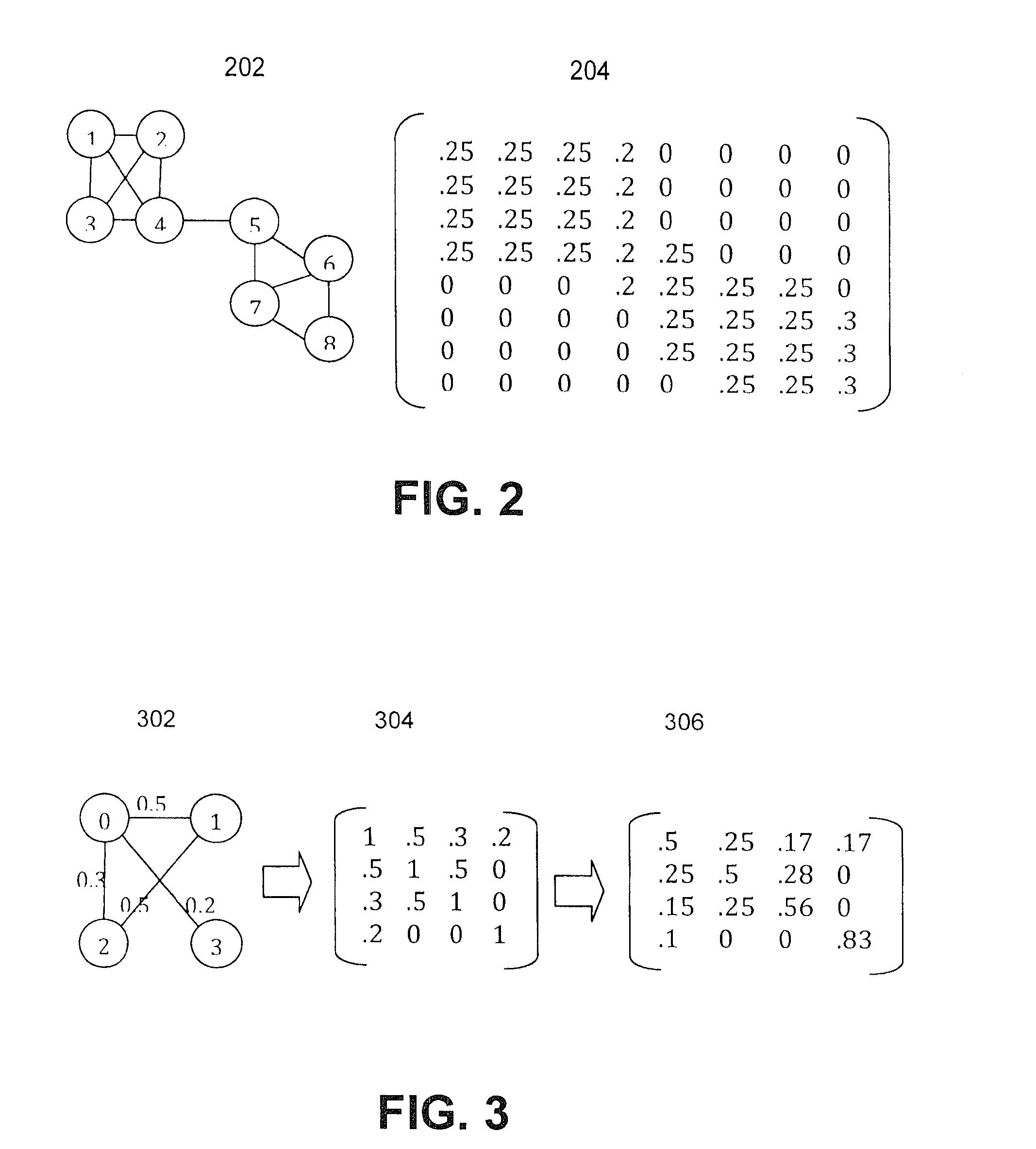
Embodiments are described for a method for processing graph data by executing a Markov Clustering algorithm (MCL) to find clusters of vertices of the graph data, organizing the graph data by column by calculating a probability percentage for each column of a similarity matrix of the graph data to produce column data, generating a probability matrix of states of the column data, performing an expansion of the probability matrix by computing a power of the matrix using a Map-Reduce model executed in a processor-based computing device; and organizing the probability matrix into a set of sub-matrices to find the least amount of data needed for the Map-Reduce model given that two lines of data in the matrix are required to compute a single value for the power of the matrix. One of at least two strategies may be used to computing the power of the matrix (matrix square, M2) based on simplicity of execution or improved memory usage.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
Graph data processing method and graph data calculation task distribution method
ActiveCN108683738AImprove publishing efficiencyImprove processing efficiencyEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesProgram controlNode clusteringDistribution method
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Object process graph system
InactiveUS7316001B2Low costReduce riskData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSoftware systemComputer access
A software system is provided including an Object Process Graph for defining applications and a Dynamic Graph Interpreter that interprets Object Process Graphs. An Object Process Graph defines all of an application's manipulations and processing steps and all of the application's data. An Object Process Graph is dynamic, making it possible to change any aspect of an application's data entry, processing or information display at any time. When an Object Process Graph is interpreted, it functions to accept data, process the data and produce information output. Modifications made to an Object Process Graph while it is being interpreted take affect immediately and can be saved. Object Process Graphs and Dynamic Graph Interpreters can be deployed on single user workstation computers or on distributed processing environments where central servers store Object Process Graphs and run Dynamic Graph Interpreters, and workstation computers access the servers via the intranet or local intranets.
Owner:GRAPHLOGIC INC
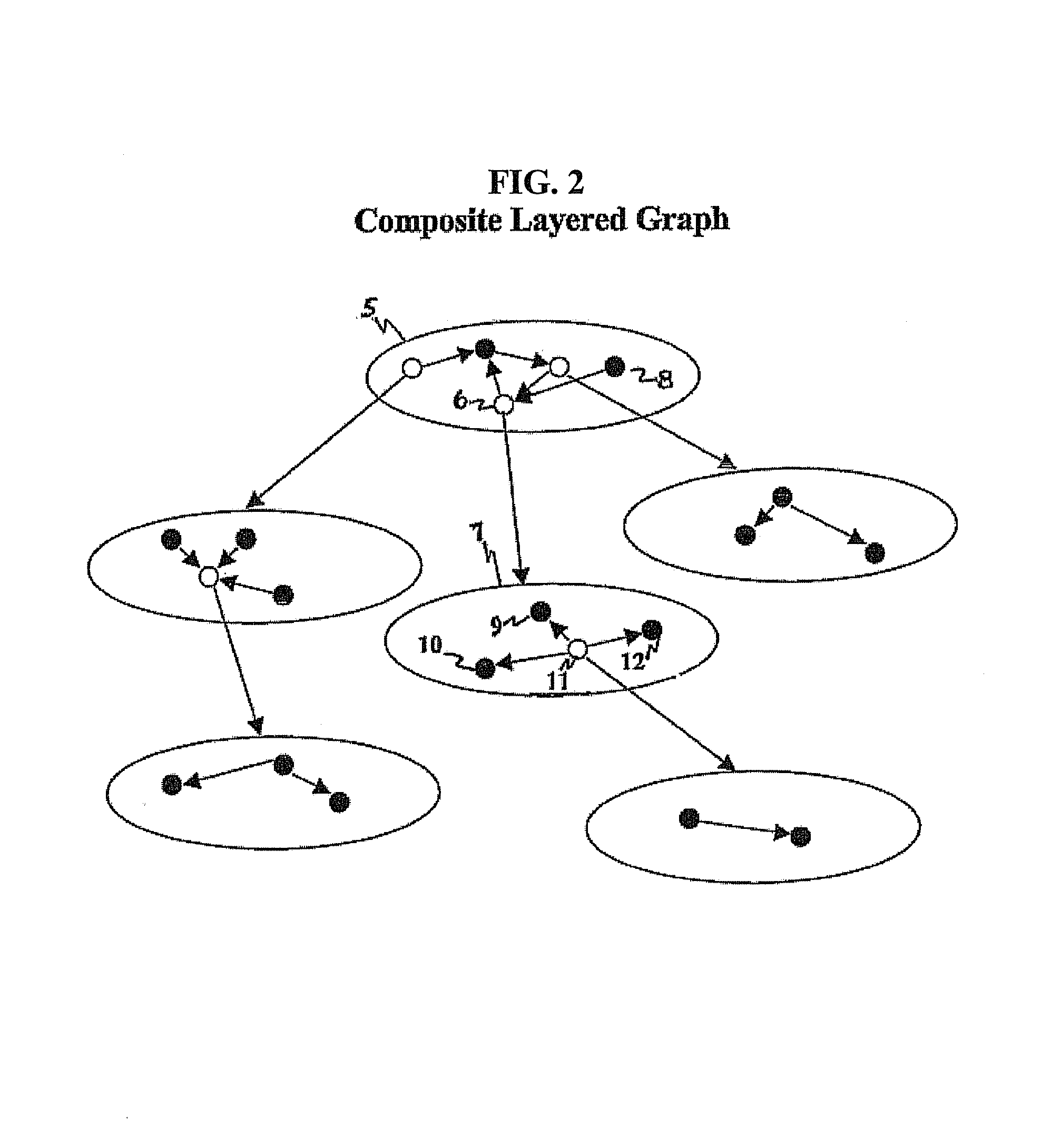
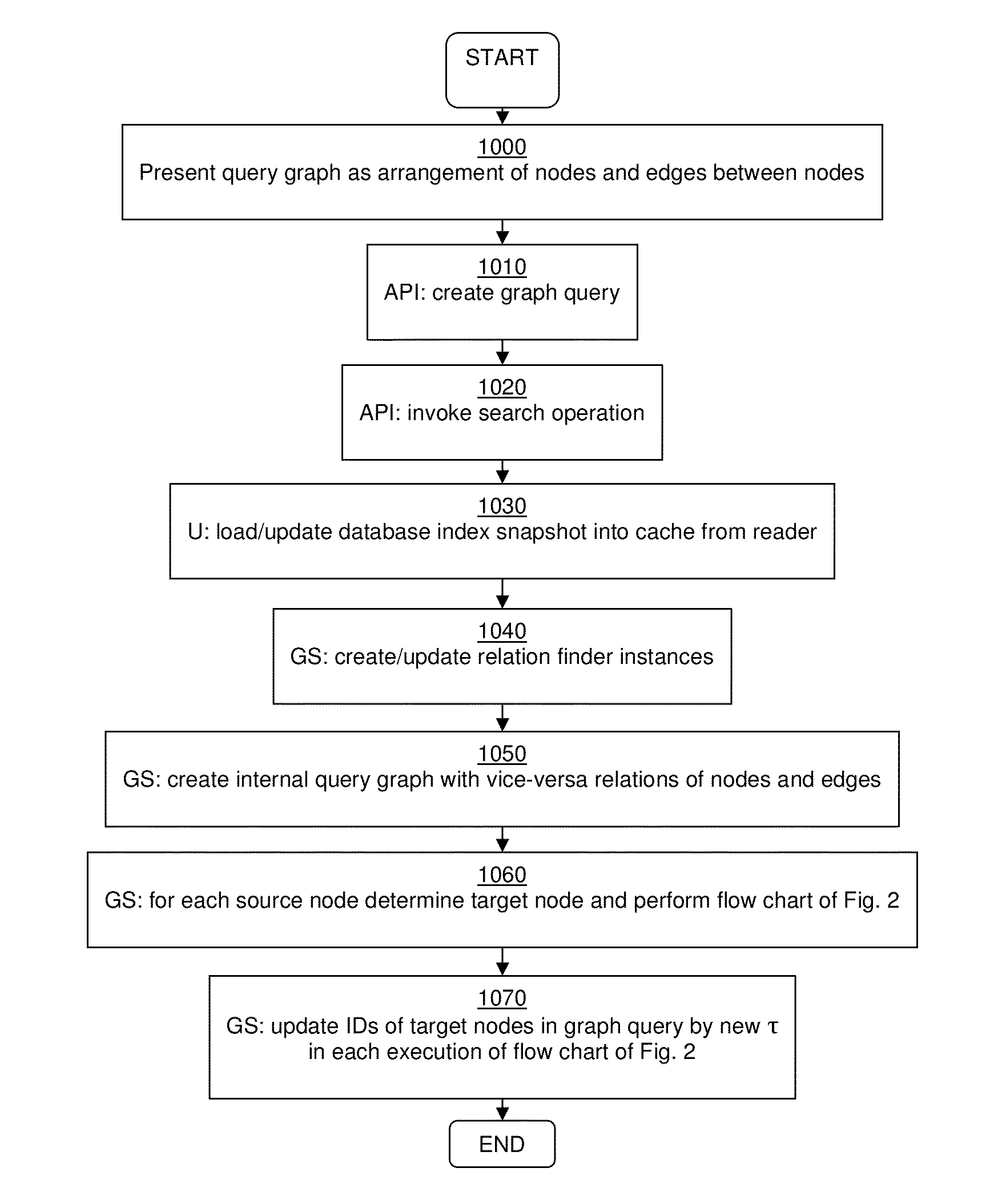
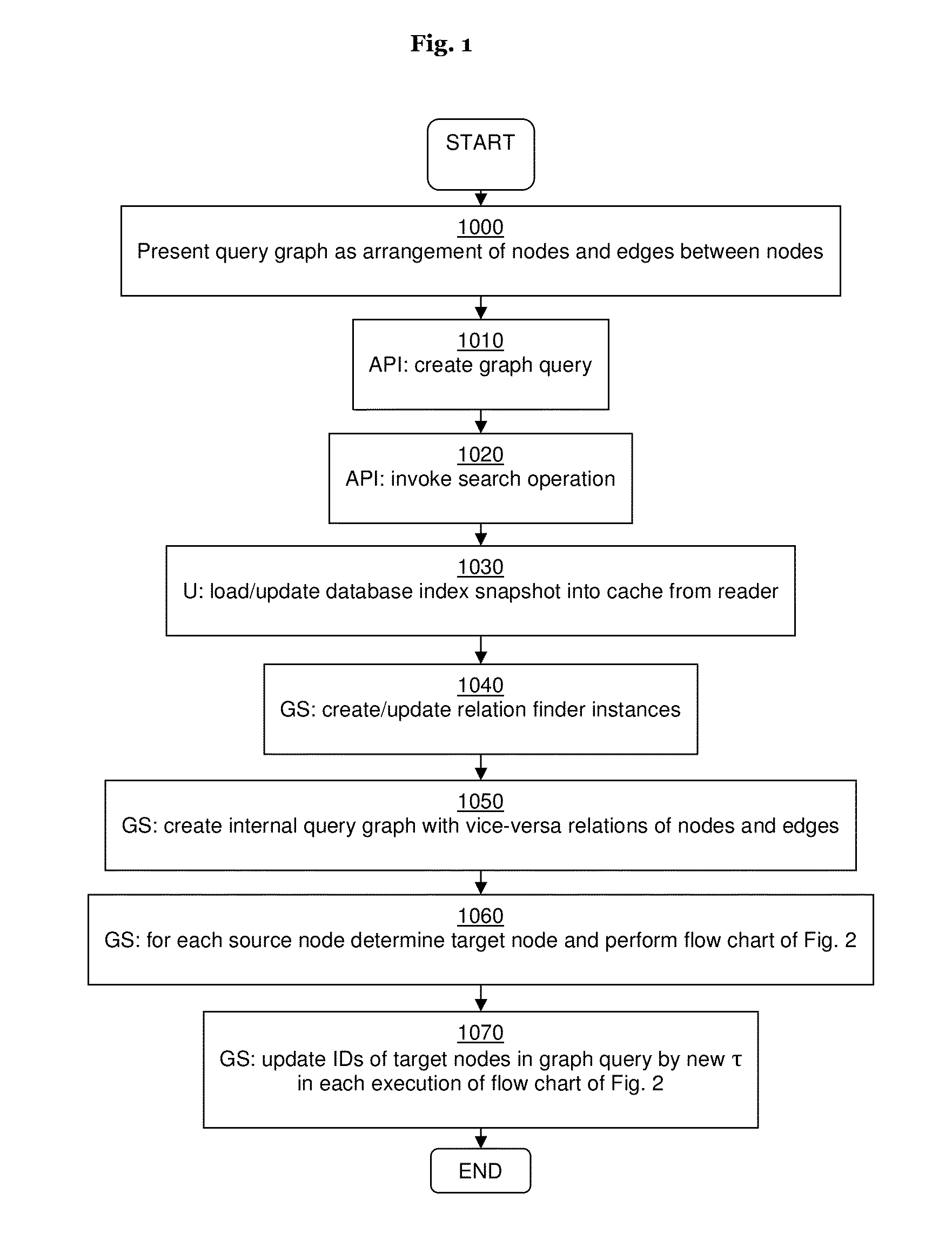
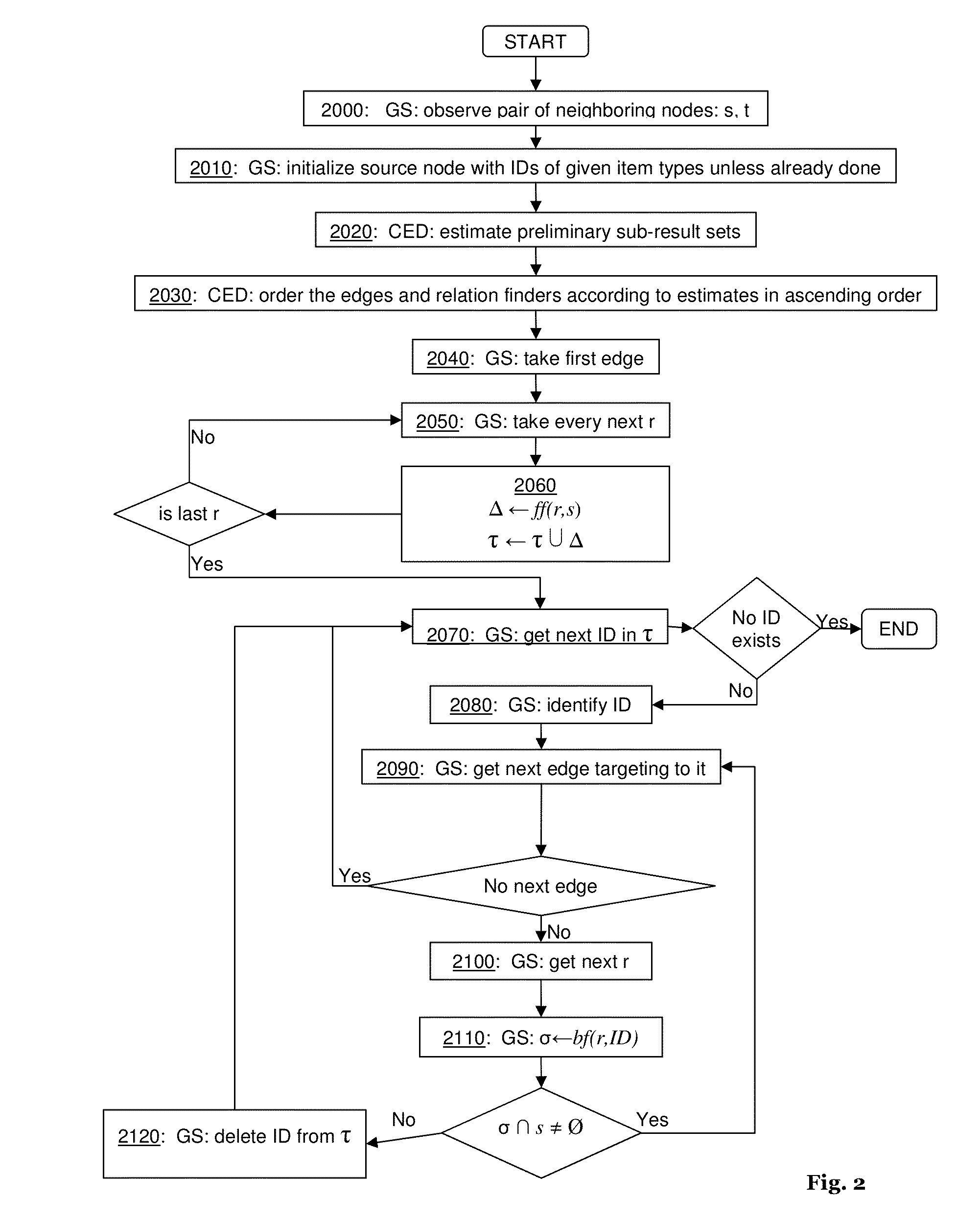
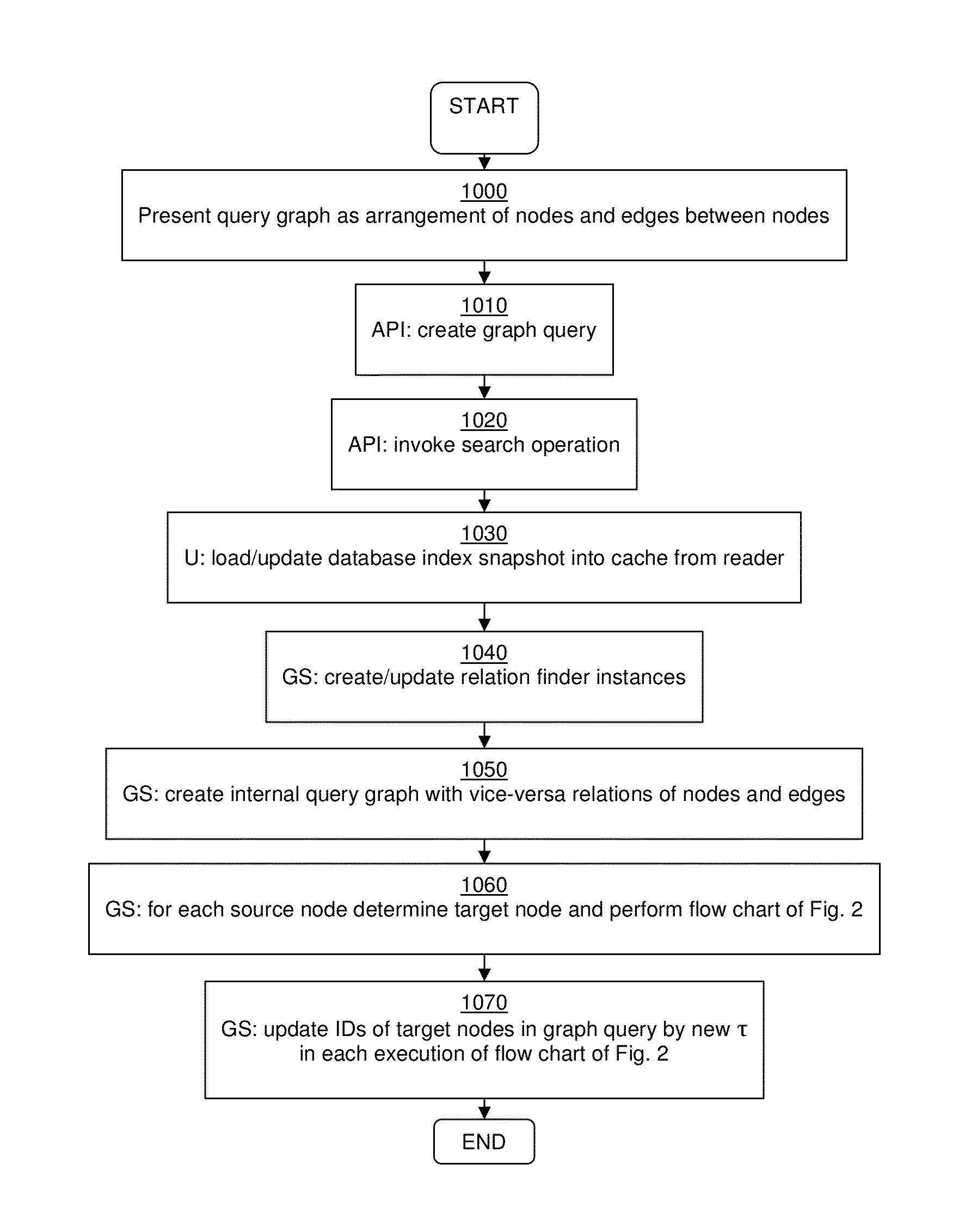
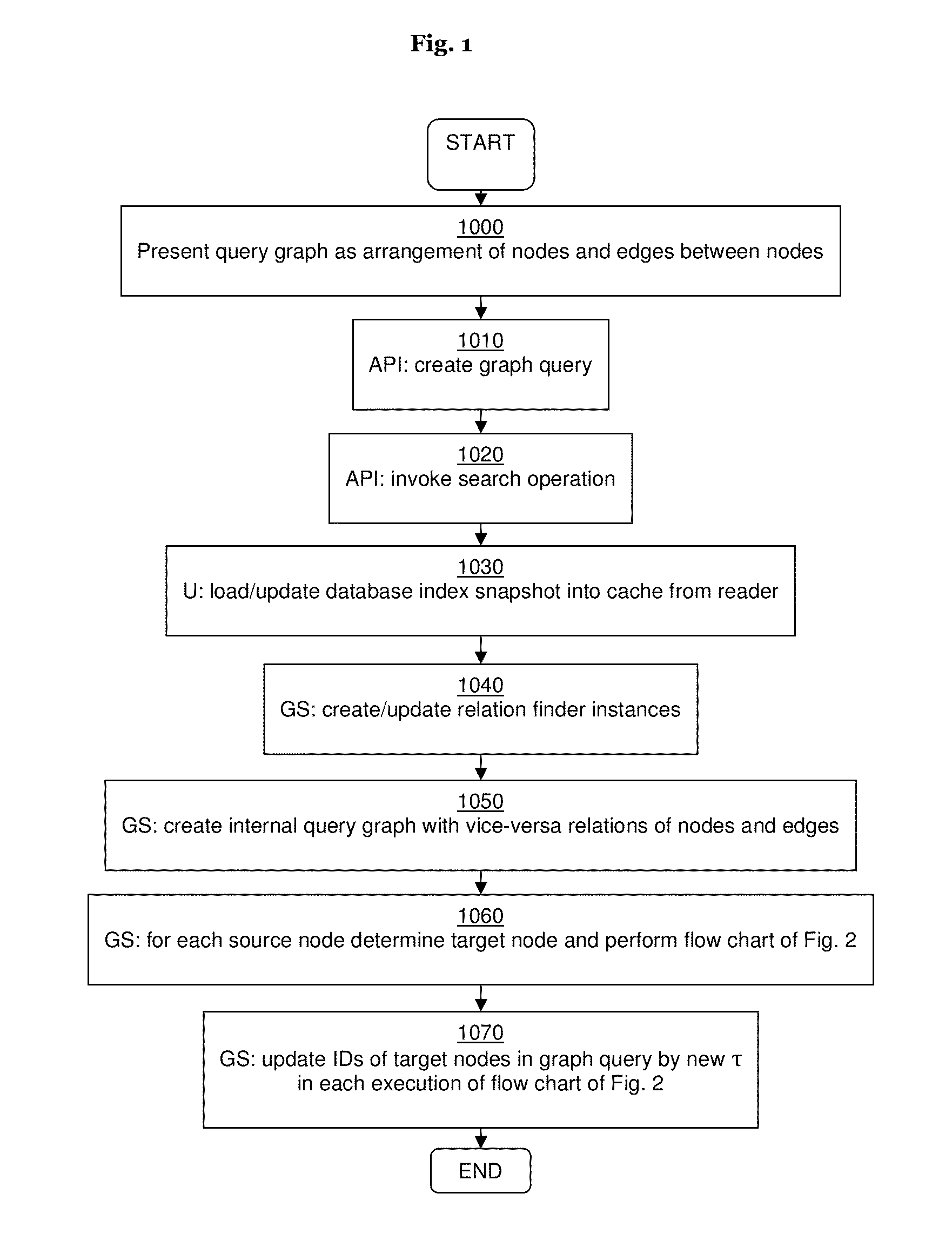
Method and system for processing graph queries
ActiveUS20140136520A1Efficient processingMinimize consumptionDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGraphicsProject type
In certain example embodiments, a graph query retrieves data items from a data source by indicating a source node, a target node, and a plurality of edges between the source and target nodes. Each edge includes one or more relation conditions. Each relation condition defines a mapping between items of one of the source item types and items of one of the target item types. The edges are selected and traversed from the source node to the target node in accordance with the relation condition(s), producing an intermediate set of result items including items of the data source that belong to the at least one target item type and fulfill the corresponding relation condition(s). Items from the intermediate set of result items that do not fulfill the corresponding relation condition(s) are deleted as further traversals are made. The intermediate set ultimately is returned as the graph query result.
Owner:SOFTWARE AG
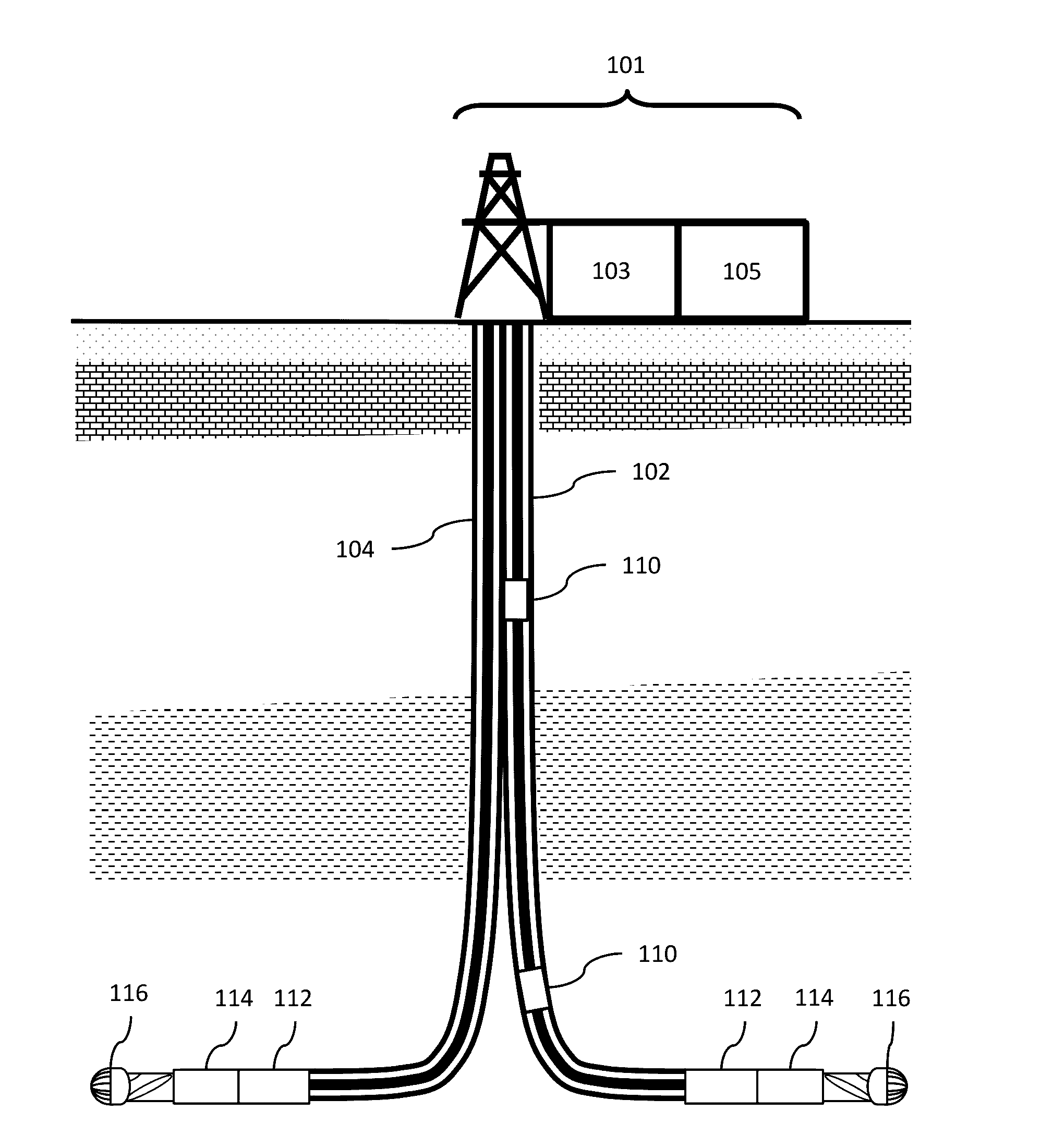
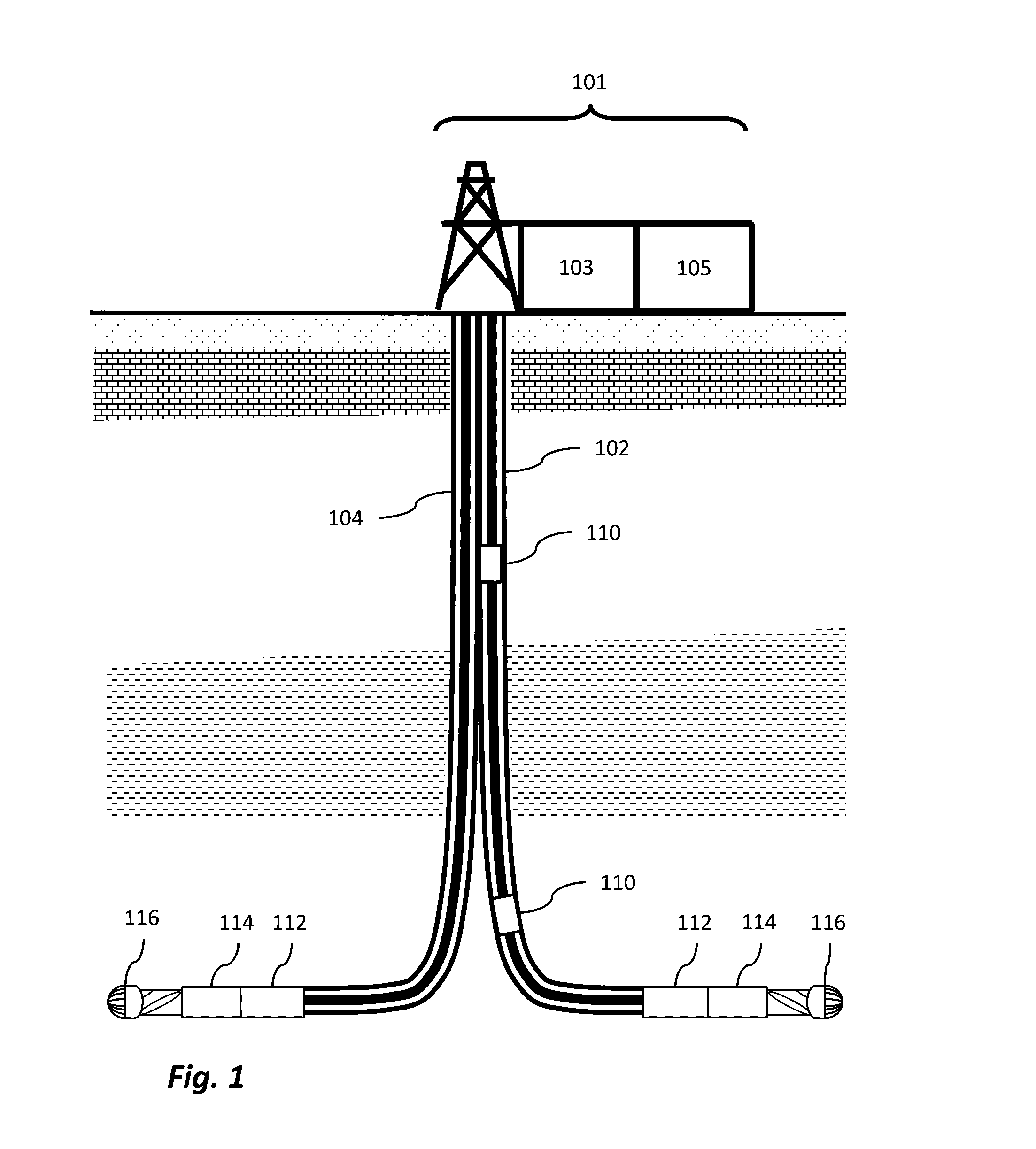
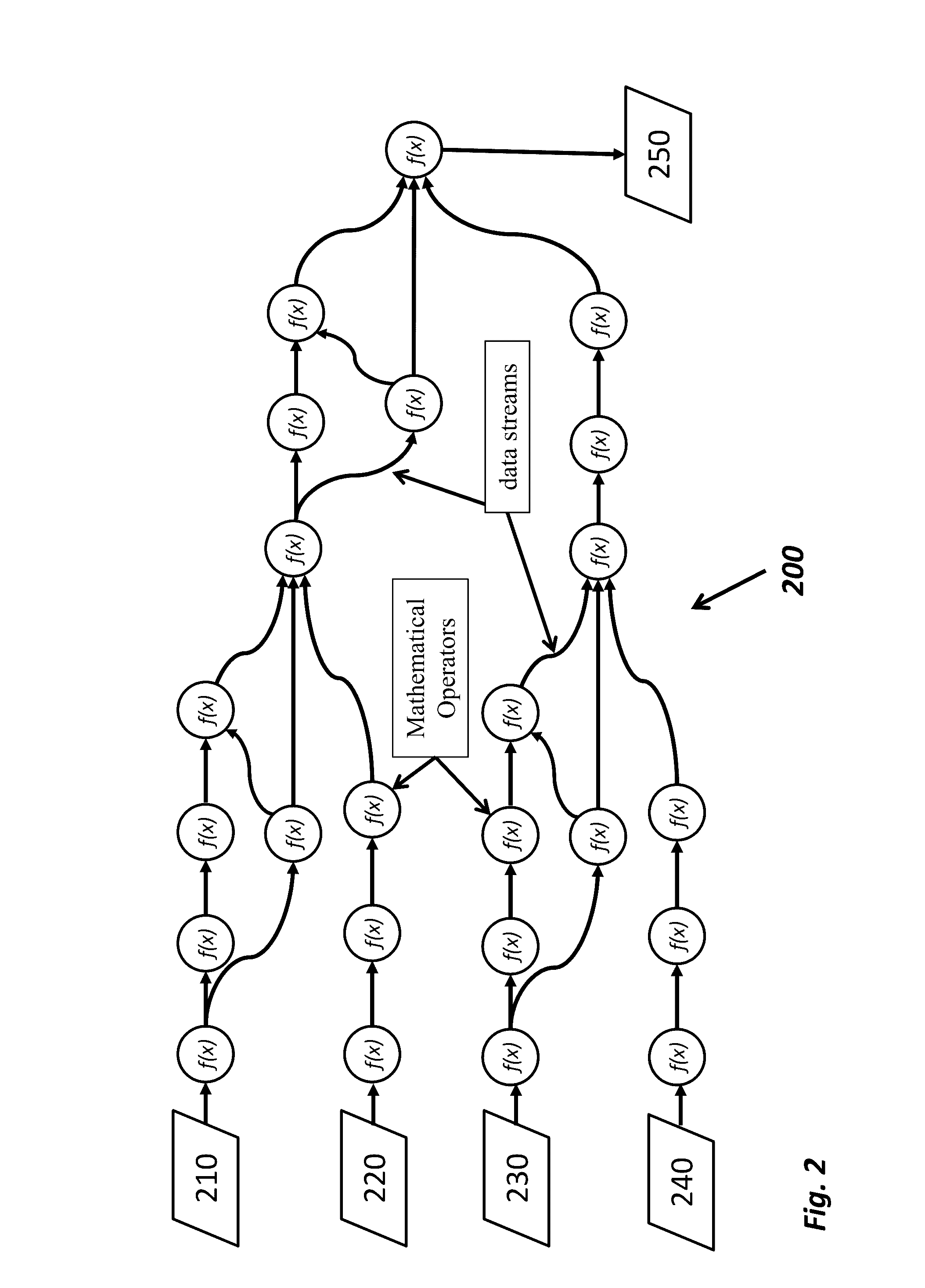
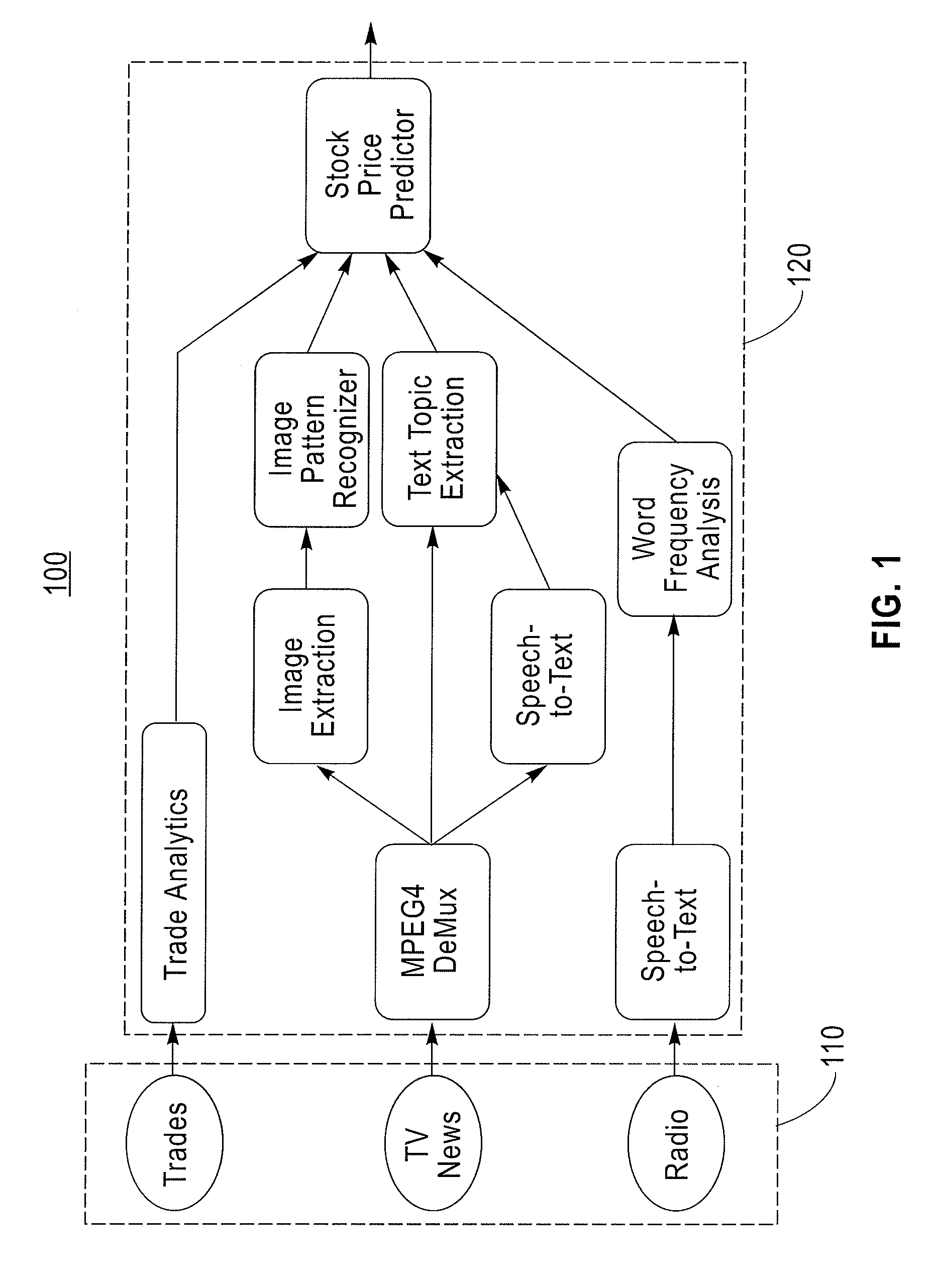
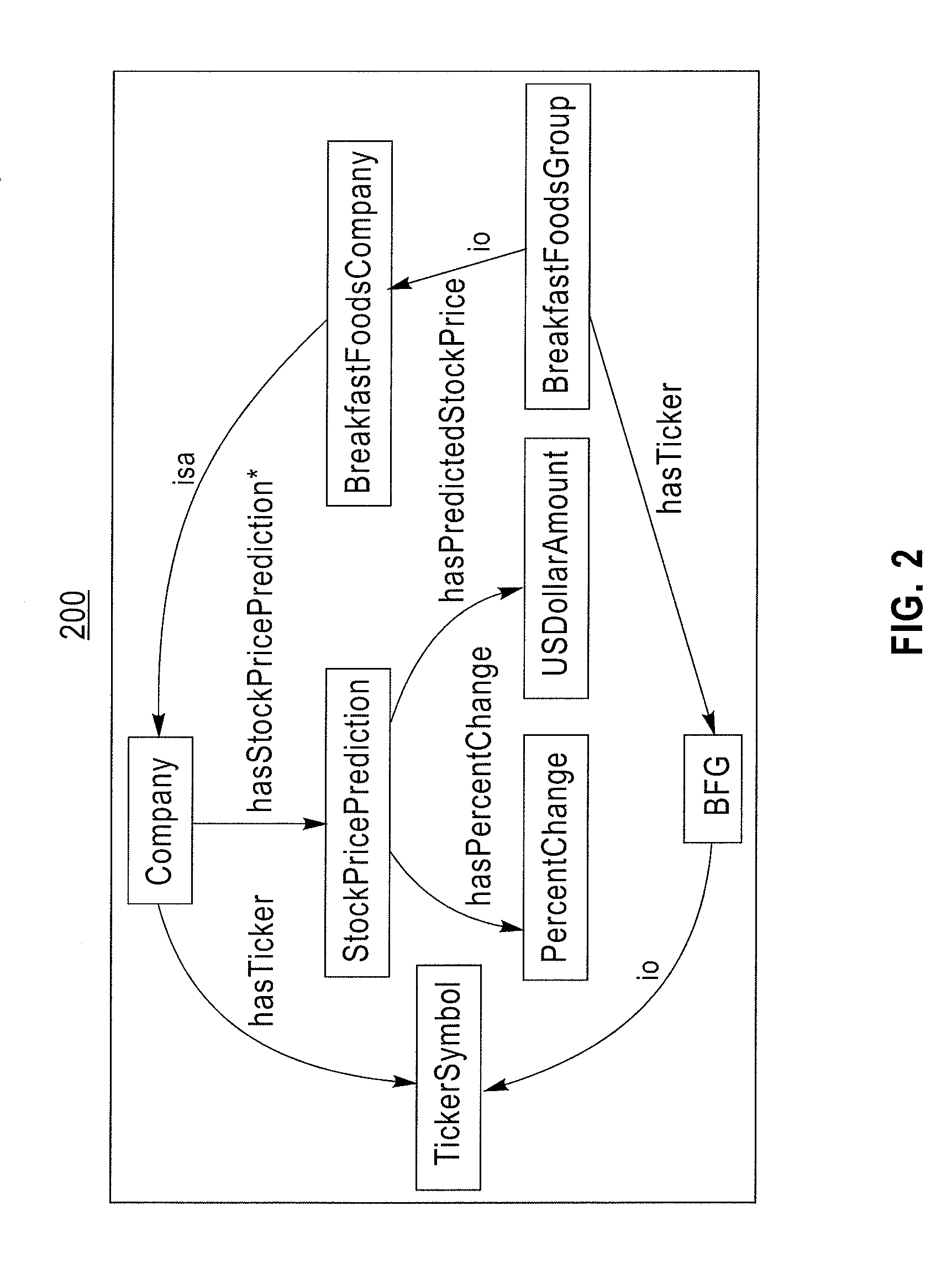
Big drilling data analytics engine
ActiveUS20160333673A1Reduced dysfunctionProgramme controlComputer controlMathematical OperatorsData stream
The invention relates to systems, processes and apparatuses for determining a rig-state of a drilling rig during a wellbore drilling operation and detecting and mitigating drilling dysfunctions. These systems, processes and apparatuses provide a computer with a memory and a processor, a plurality of sensors associated with a wellbore drilling operation for acquiring time series data wherein the data are formatted for sample and bandwidth regularization and time-corrected to provide substantially time-synchronized data, a processing graph of data-stream networked mathematical operators that applies continuous analytics to the data at least as rapidly as the data are acquired to determine dynamic conditions of a plurality of rig conditions associated with the wellbore drilling operation and determining a rig-state from the plurality of rig conditions.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
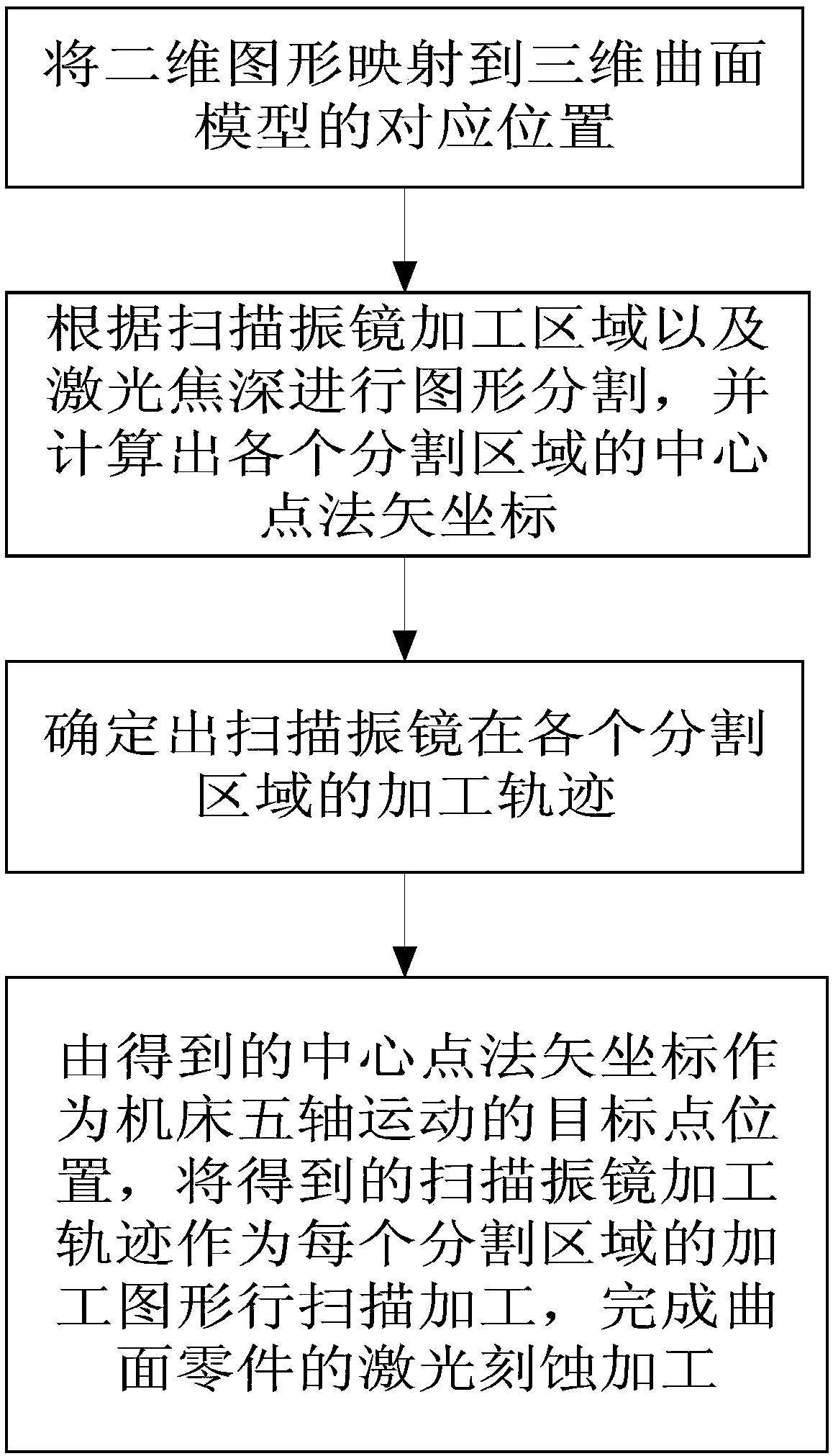
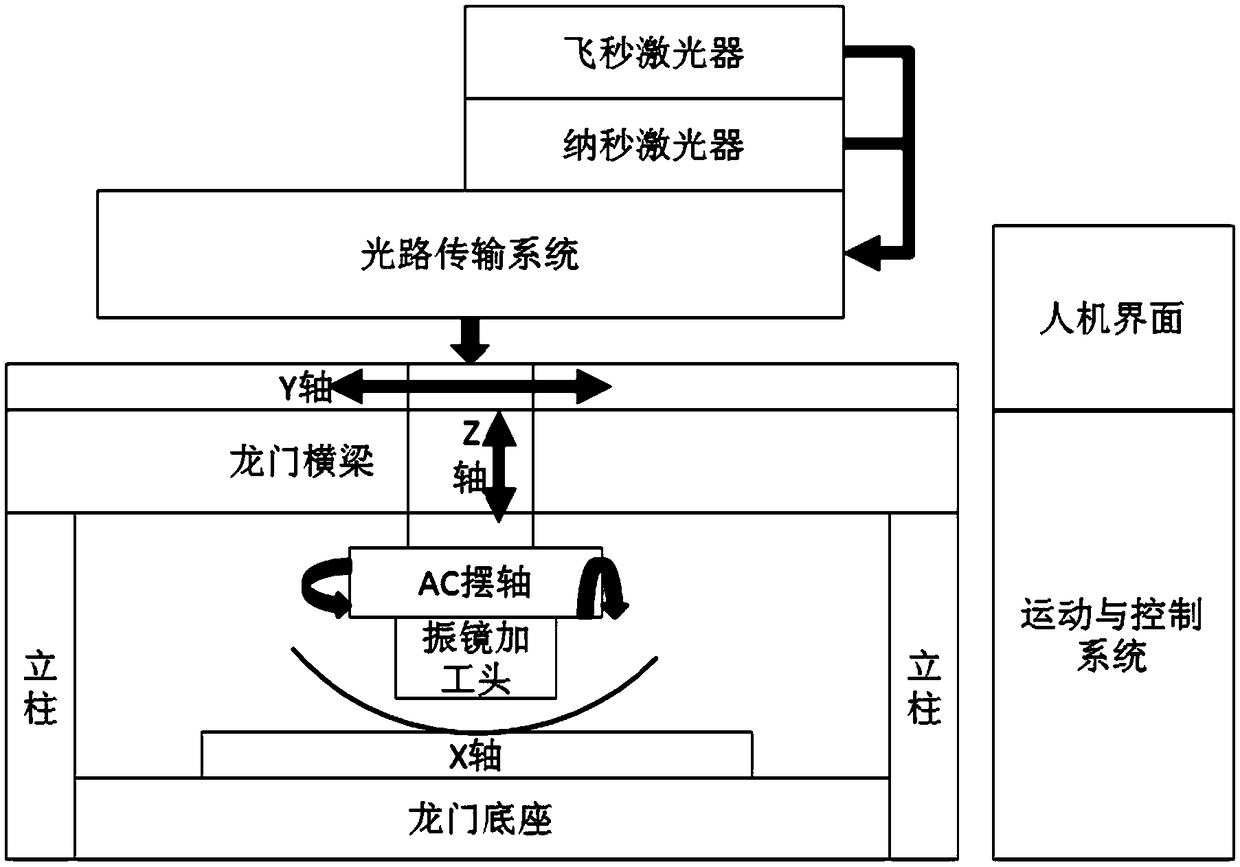
Laser etching method of three-dimensional curved surface
ActiveCN108838551ACorrect angle deviationImprove accuracyLaser beam welding apparatusLaser etchingTwo-dimensional graph
The invention relates to a laser etching method of a three-dimensional curved surface, is applied to the fields of aerospace, electronic and optical devices, and solves the problem that ideal texturegraphs cannot be acquired as a conventional three-dimensional curved surface laser processing method can only be utilized to process parts with to-be-processed surface texture characteristics and processed graphs have angle change. The laser etching method comprises the following steps that: (1) a two-dimensional graph is mapped to a corresponding position of a three-dimensional curved surface model; (2) the graph is cut according to a processing region of a scanning galvanometer and laser focus depth, and central point normal vector coordinates of cut regions are calculated; (3) processing tracks of the scanning galvanometer in the cut regions are confirmed; and (4) the central point normal vector coordinates acquired in the step (2) are adopted as target point positions of five-shaft motion of a machine tool, the processing tracks of the scanning galvanometer acquired in the step (3) are adopted as processing graphs of the cut regions, scanning processing is carried out, and laser etching processing of curved surface parts is achieved.
Owner:XIAN MICROMACH TECH CO LTD
Graph data processing method, device and system
ActiveCN108132838AImprove acceleration performanceGuaranteed normal processingResource allocationDatabase distribution/replicationAlgorithmComputer science
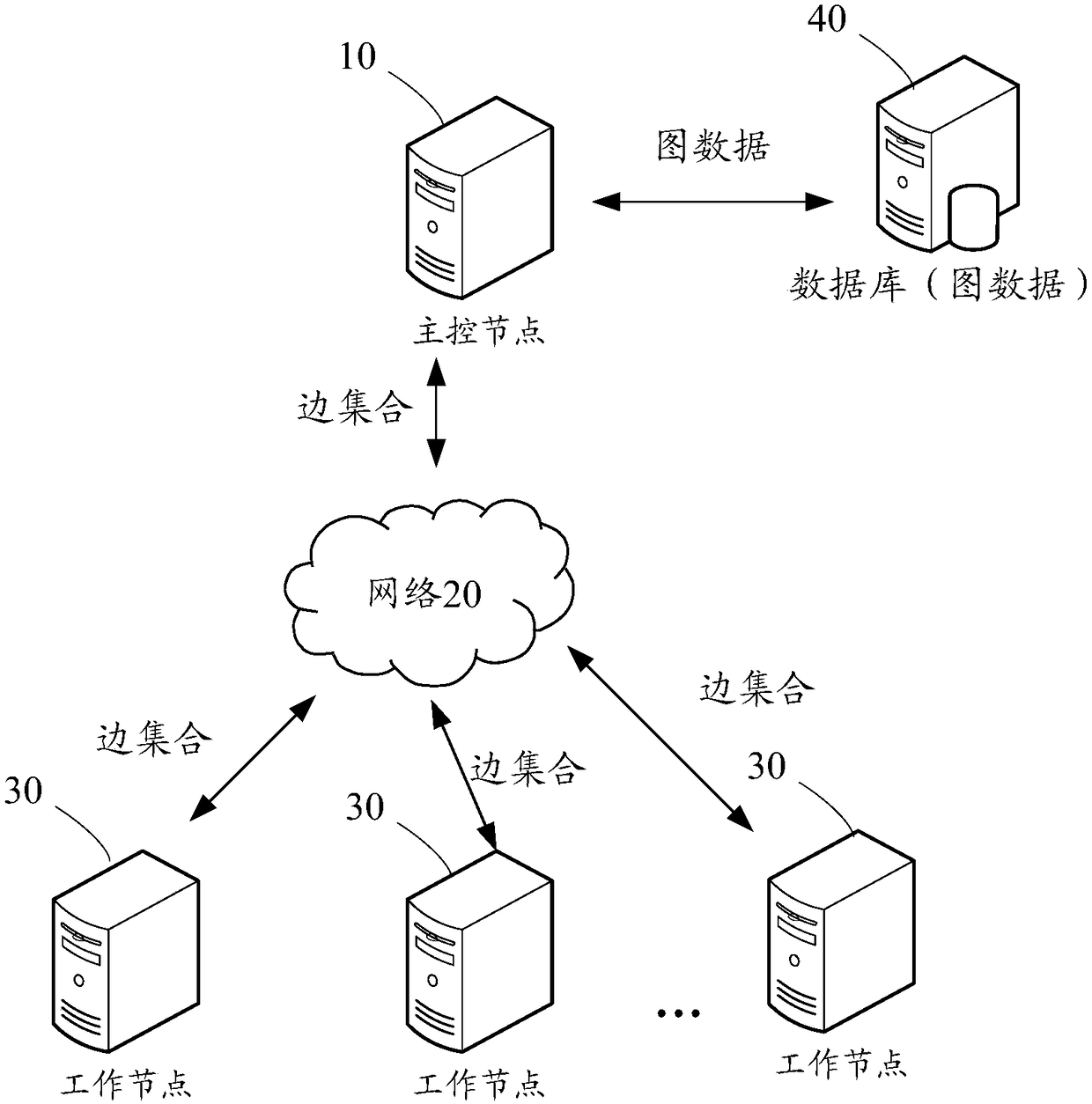
The invention discloses a graph data processing method applied to a distributed system which comprises a master control node and multiple work nodes. The method includes the steps that the master control node acquires graph data and segments the graph data to obtain P fragments, wherein P is a positive integer, and the P fragments include the first fragment and the second fragment; at least two edge sets are determined from each fragment; the edge sets included in the first fragment of the P fragments are scheduled to at least two work nodes for processing; incidence edge sets included in thesecond fragment are scheduled to the work nodes for processing, wherein the incidence edge sets are edge sets including outgoing edges of a target vertex corresponding to the first fragment. By meansof the graph data processing method in the embodiment, a great deal of memory resources of the distributed system can be utilized for processing graph data, the overall throughput capacity of the system is increased, and the IO overhead can be reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
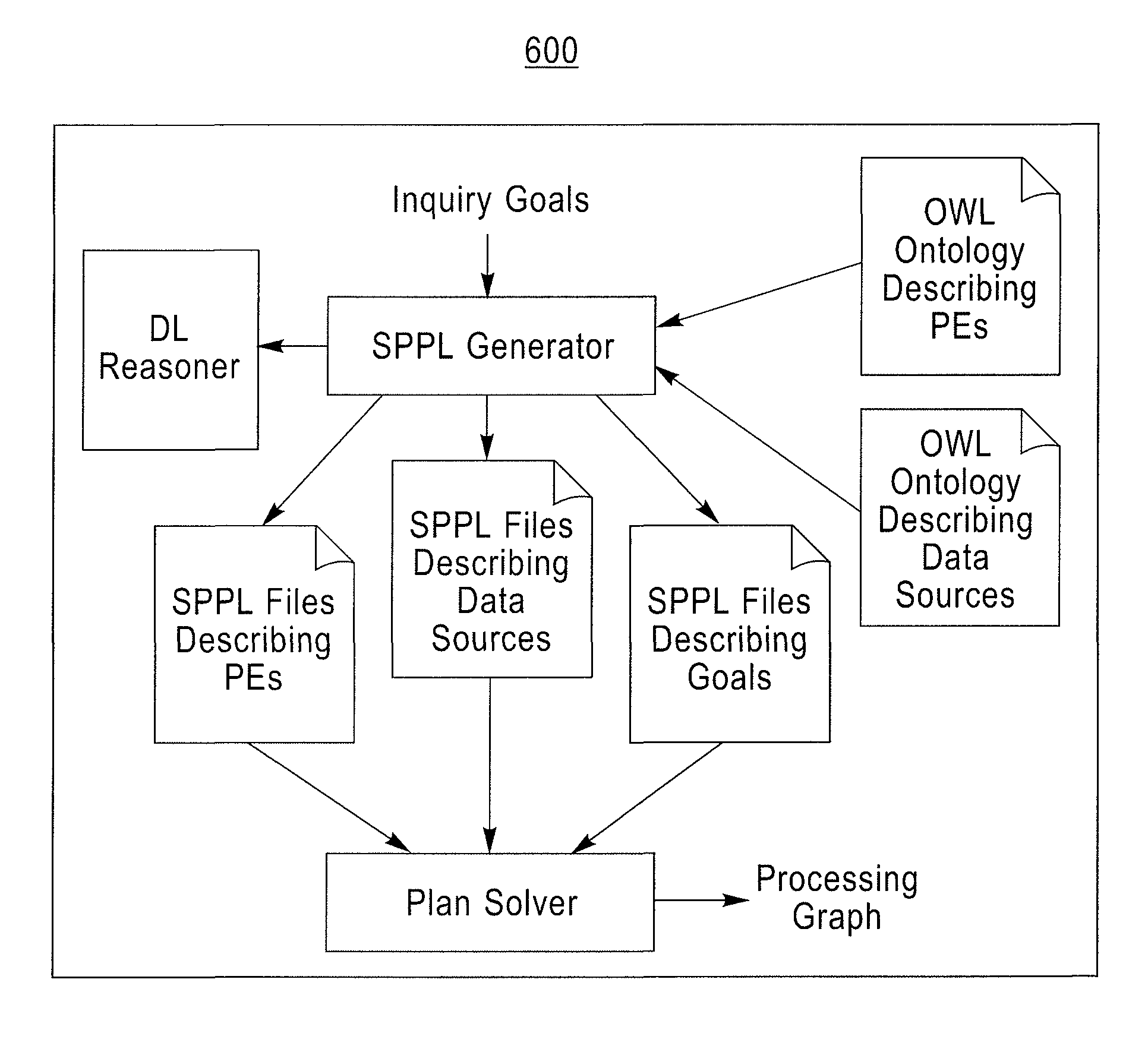
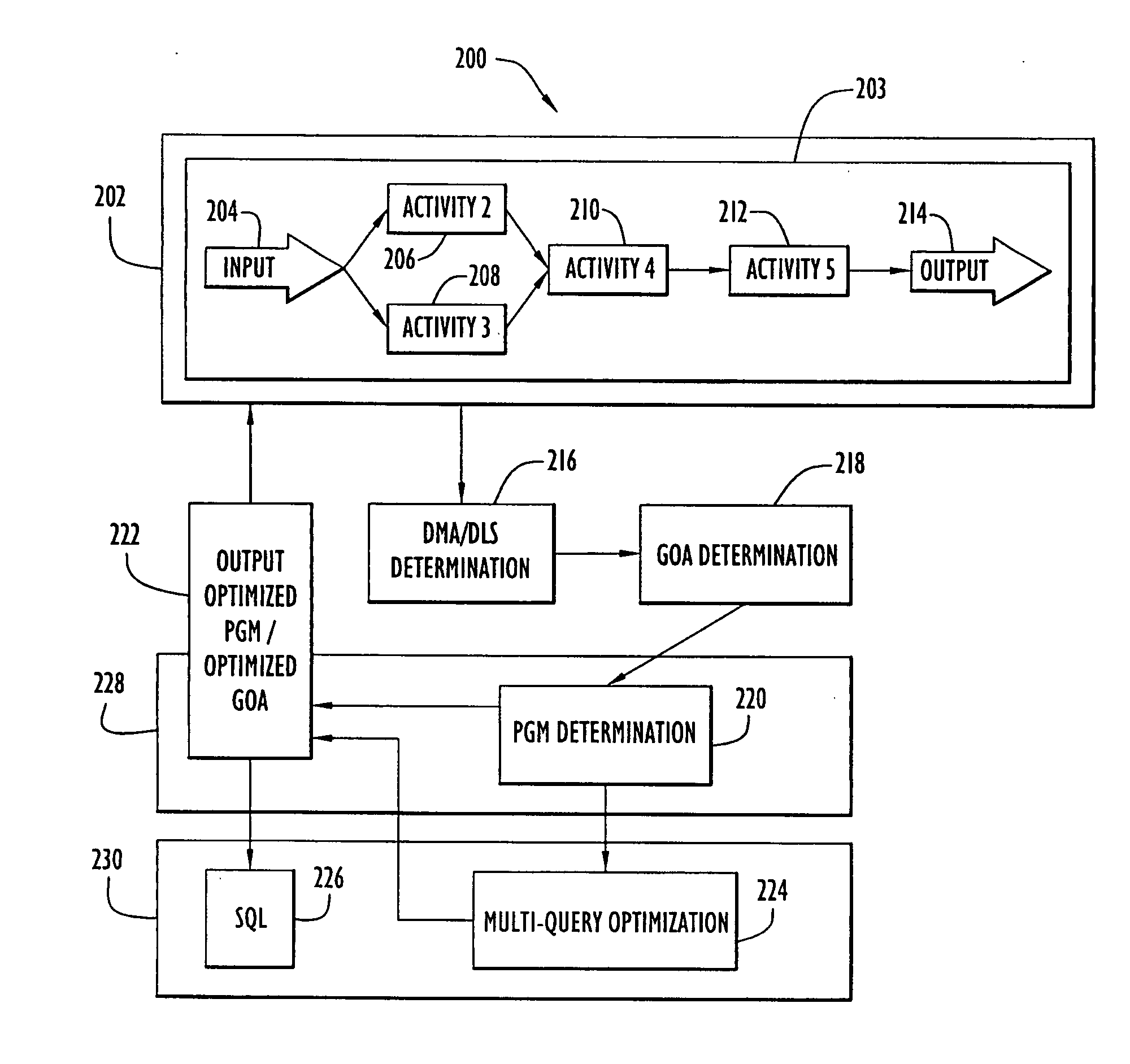
Method and apparatus for optimization in workflow management systems
ActiveUS20070055557A1Improve performanceDigital data processing detailsResourcesWorkflow management systemSemantics
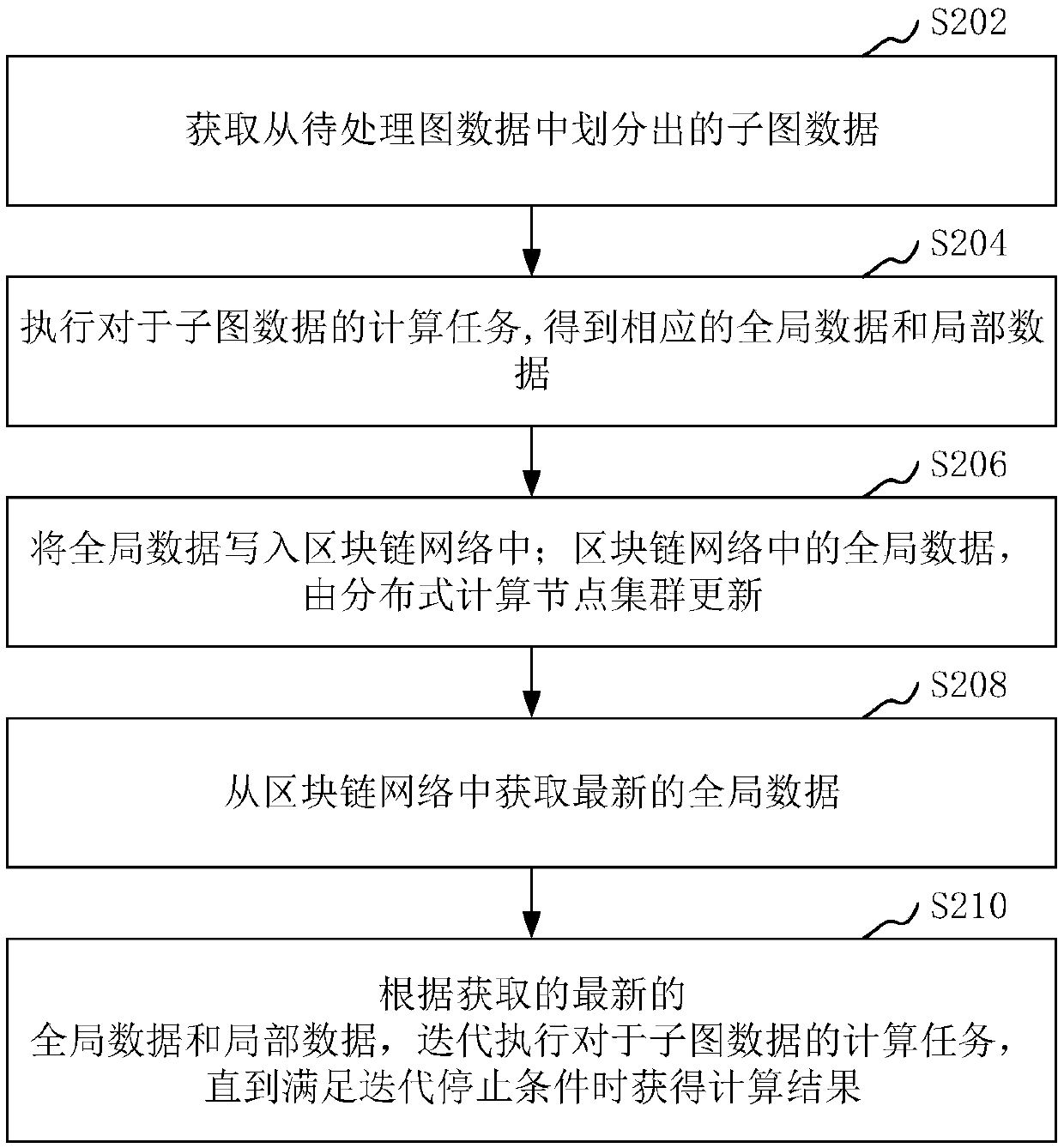
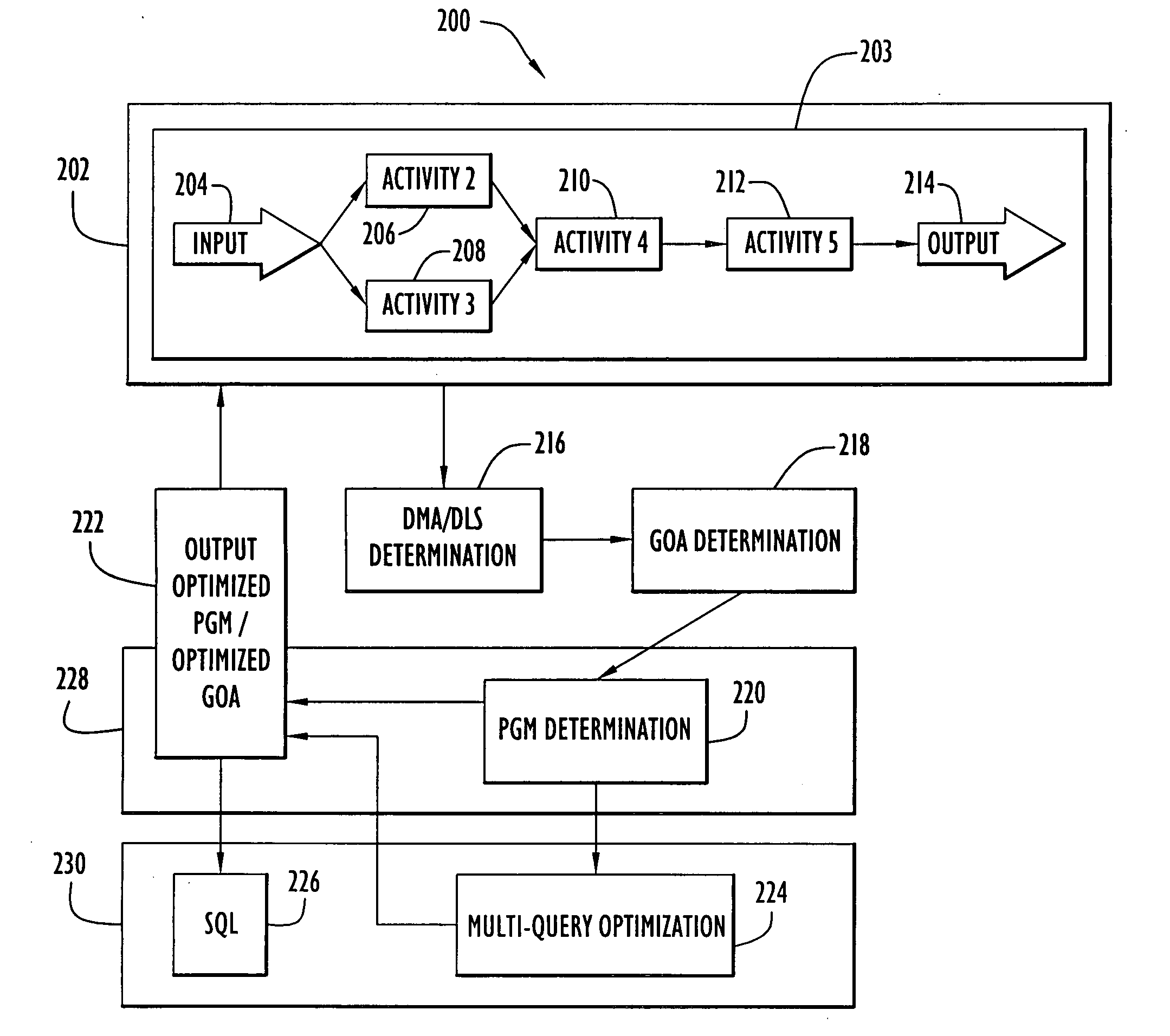
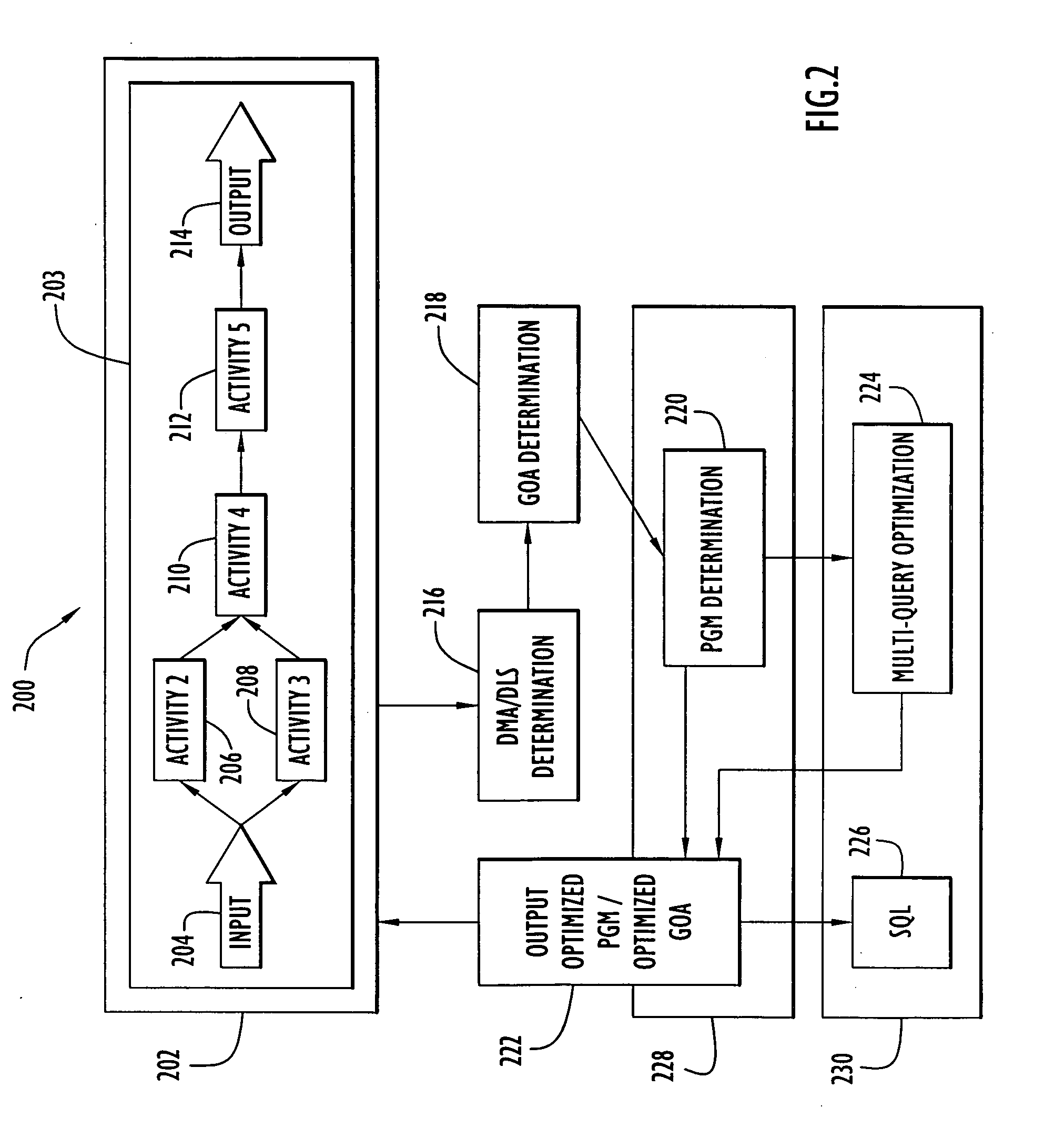
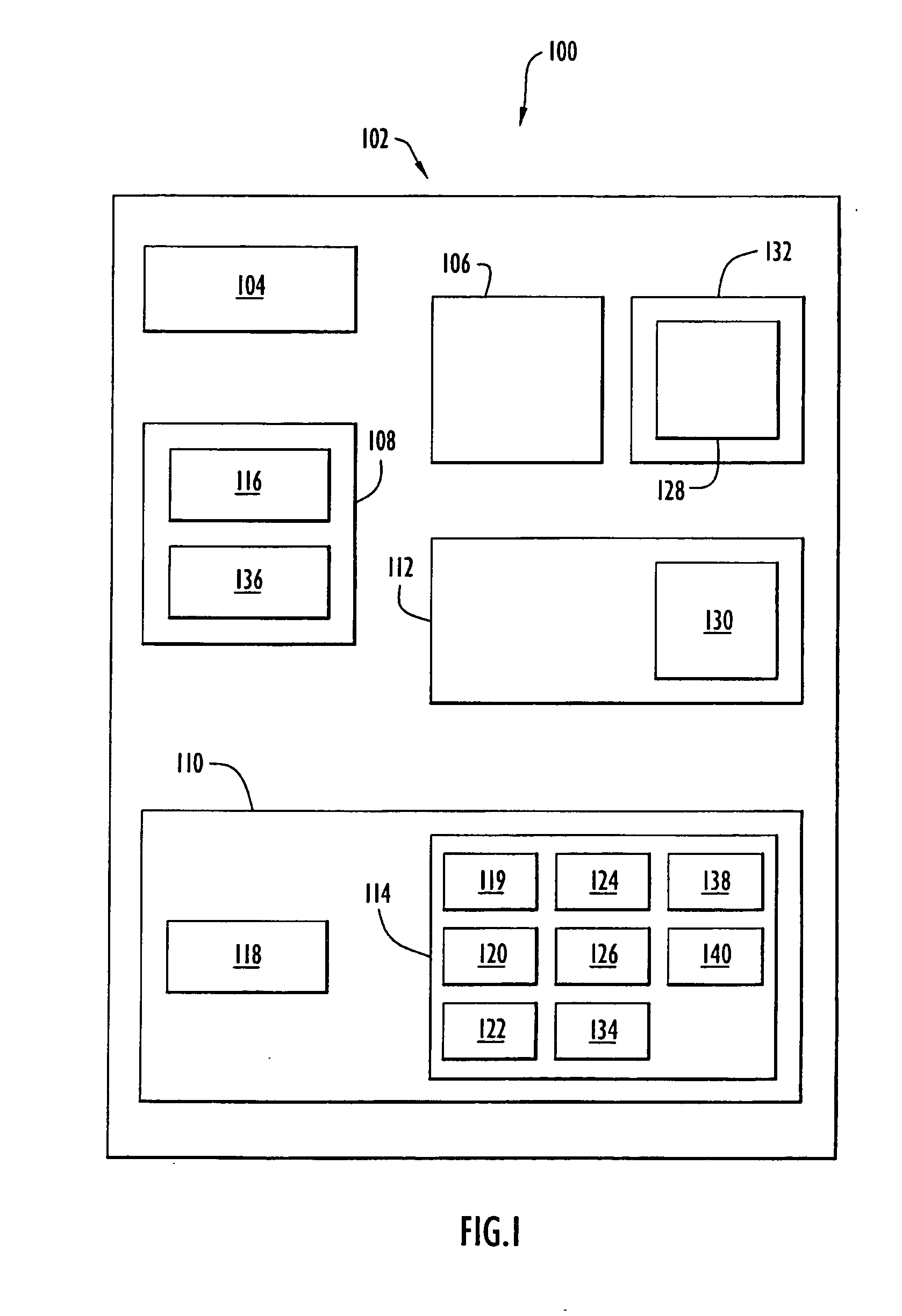
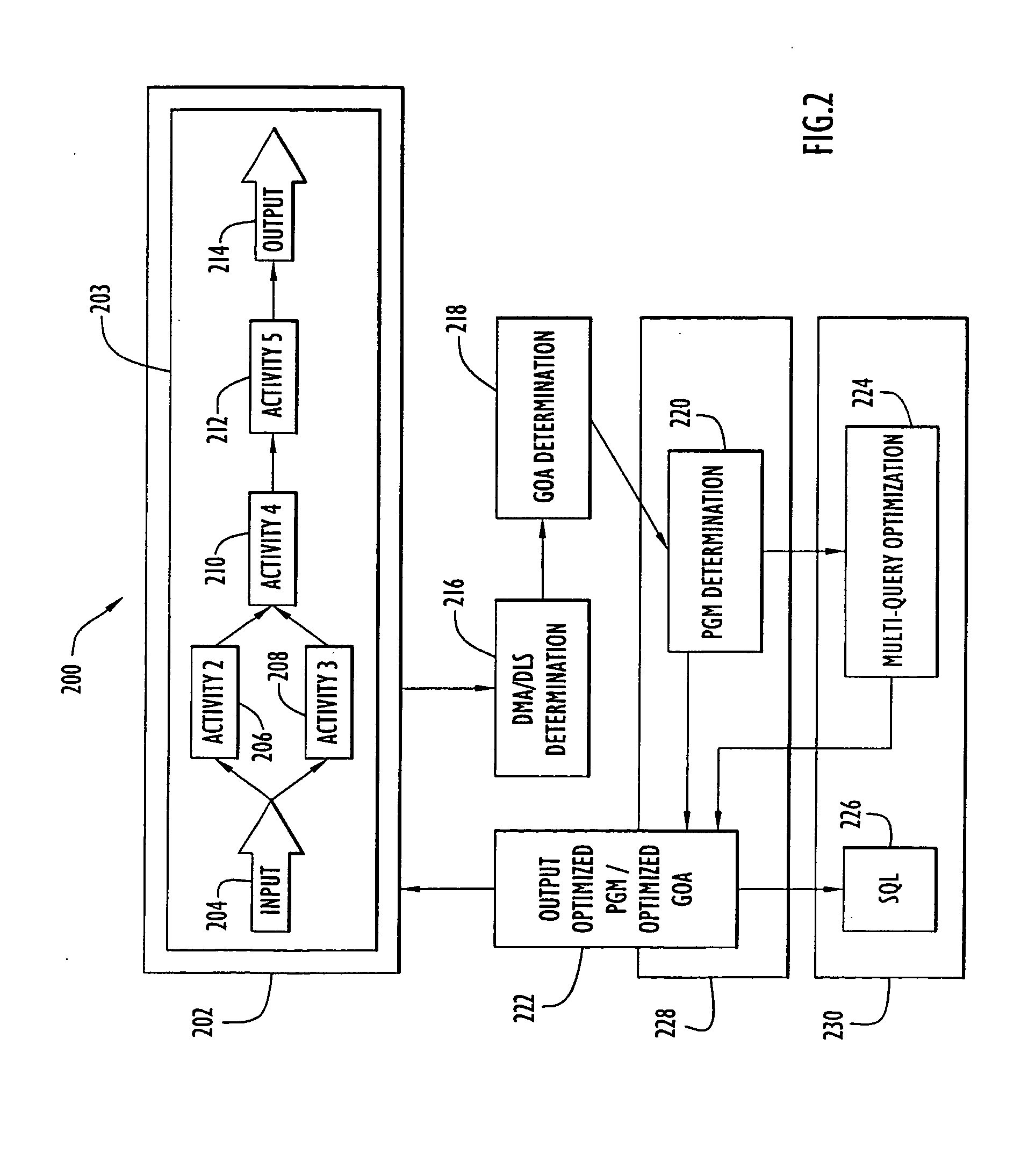
Activities within a workflow are either data management activities (DMAs) or non-DMAs. A workflow is typically carried out by a system by executing one activity after the other. This can, however, be very time consuming. A method and system are provided for optimizing a group of activities (GOA) comprising a DMA, whereby the GOA is comprised in the workflow to improve the overall performance. The method determines the DMAs, and for each DMA, a data level statement (DLS). The GOA is determined and a process graph model (PGM) is determined from the GOA so that the DLS is comprised in the PGM and the semantics of the PGM are identical to those of the GOA. The PGM is optimized for which an optimized GOA is determined. The semantics of the optimized GOA are identical to those of the GOA. In the workflow, the GOA is replaced by the optimized GOA.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for assembling information processing applications based on declarative semantic specifications
InactiveUS20080244540A1Program controlRequirement analysisProgramming languageInformation processing
A method for assembling an information processing application, includes: inputting a plurality of component descriptions, wherein each of the component descriptions includes a graph pattern that semantically describes an applicability condition of a component and a graph pattern that semantically describes an inclusion effect of the component; inputting a processing request, wherein the processing request includes a goal that is represented by a graph pattern that semantically describes a desired processing outcome; assembling a processing graph, wherein the processing graph includes at least one component that satisfies the desired processing outcome; and outputting the processing graph.
Owner:IBM CORP
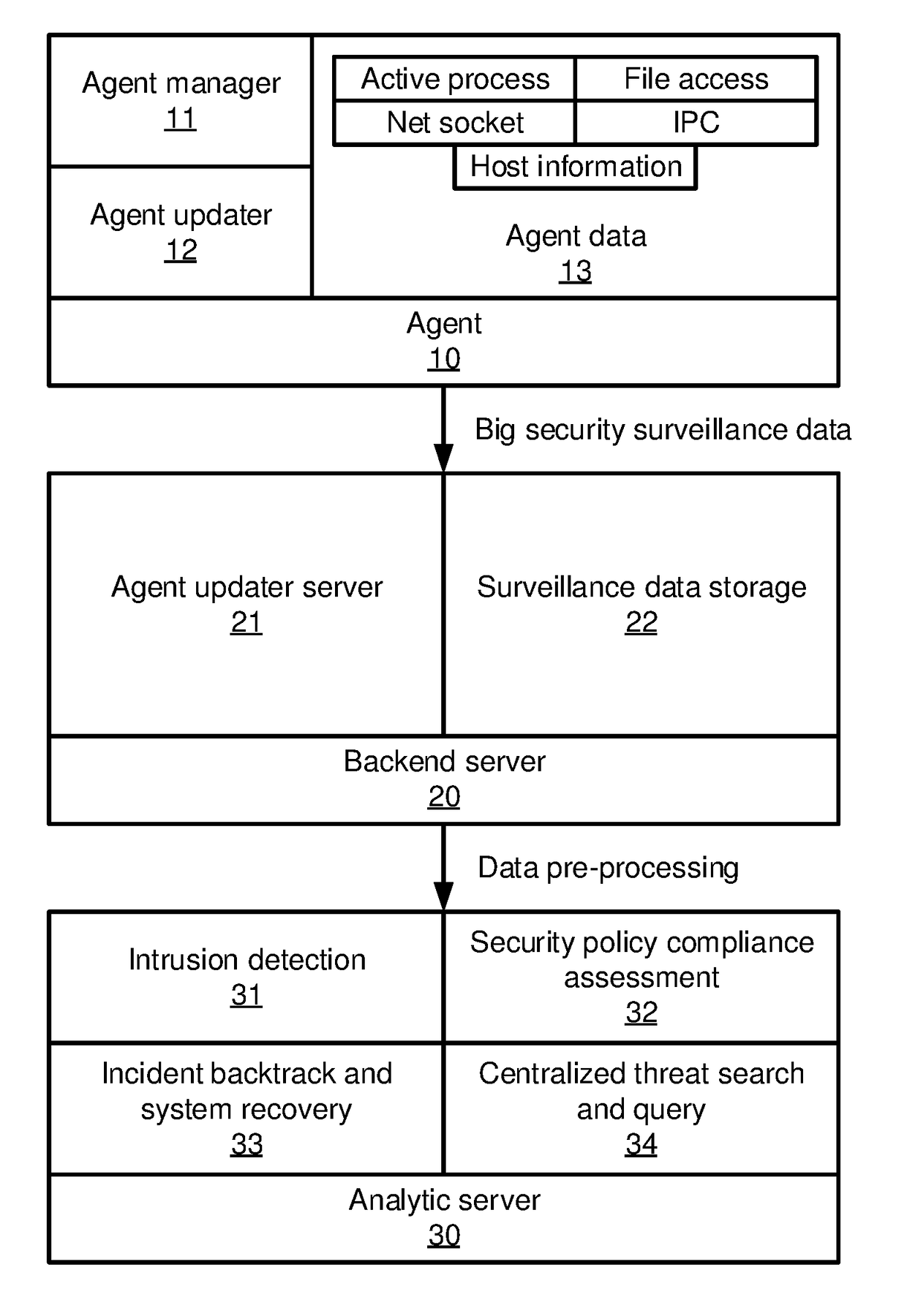
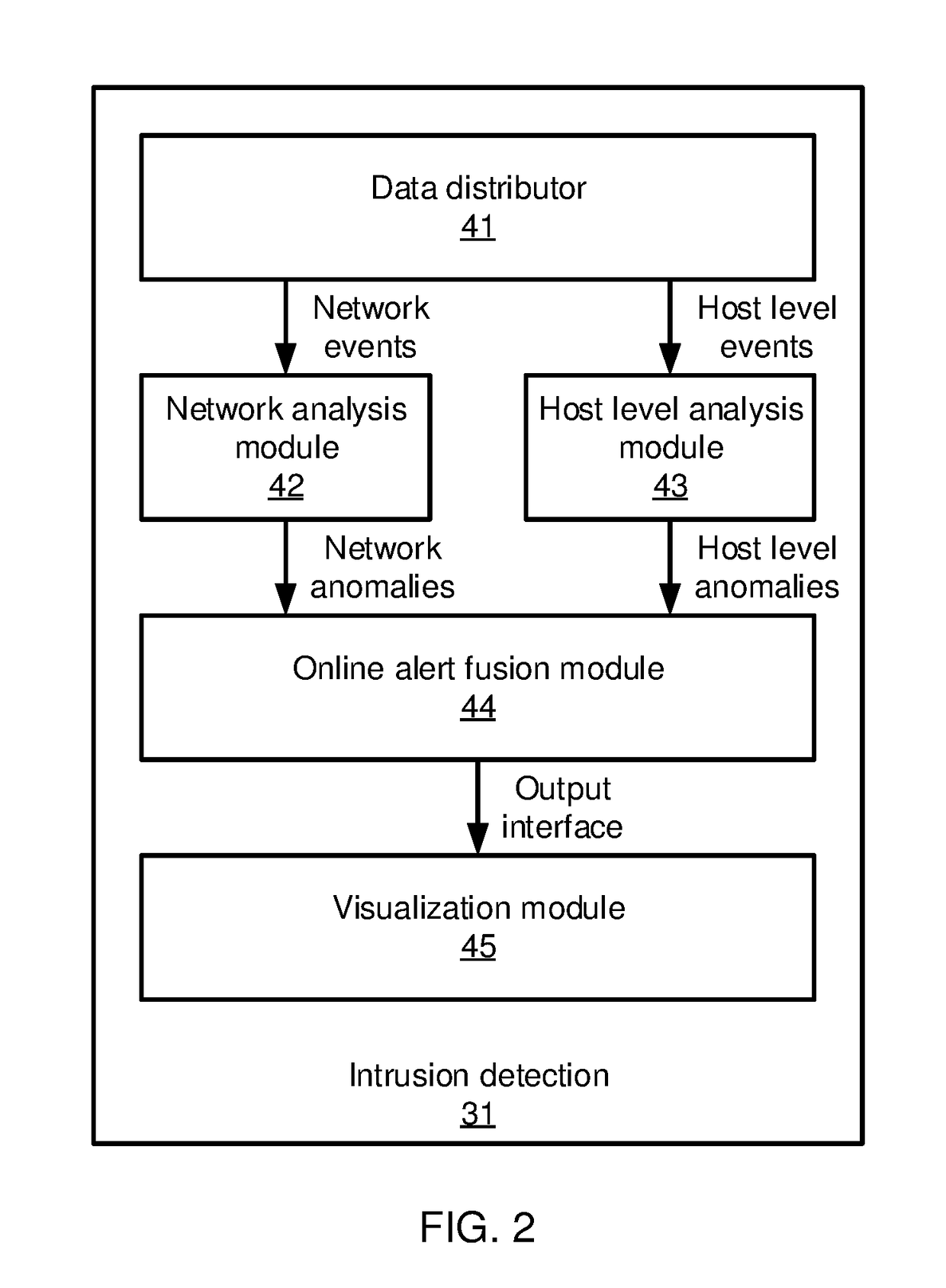
Blue print graphs for fusing of heterogeneous alerts
Methods and systems for reporting anomalous events include building a process graph that models states of process-level events in a network. A topology graph is built that models source and destination relationships between connection events in the network. A set of alerts is clustered based on the process graph and the topology graph. Clustered alerts that exceed a threshold level of trustworthiness are reported.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and system for processing graph queries
ActiveUS9092481B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsGraphicsProject type
In certain example embodiments, a graph query retrieves data items from a data source by indicating a source node, a target node, and a plurality of edges between the source and target nodes. Each edge includes one or more relation conditions. Each relation condition defines a mapping between items of one of the source item types and items of one of the target item types. The edges are selected and traversed from the source node to the target node in accordance with the relation condition(s), producing an intermediate set of result items including items of the data source that belong to the at least one target item type and fulfill the corresponding relation condition(s). Items from the intermediate set of result items that do not fulfill the corresponding relation condition(s) are deleted as further traversals are made. The intermediate set ultimately is returned as the graph query result.
Owner:SOFTWARE AG
Method, system and apparatus to associate and transform processes
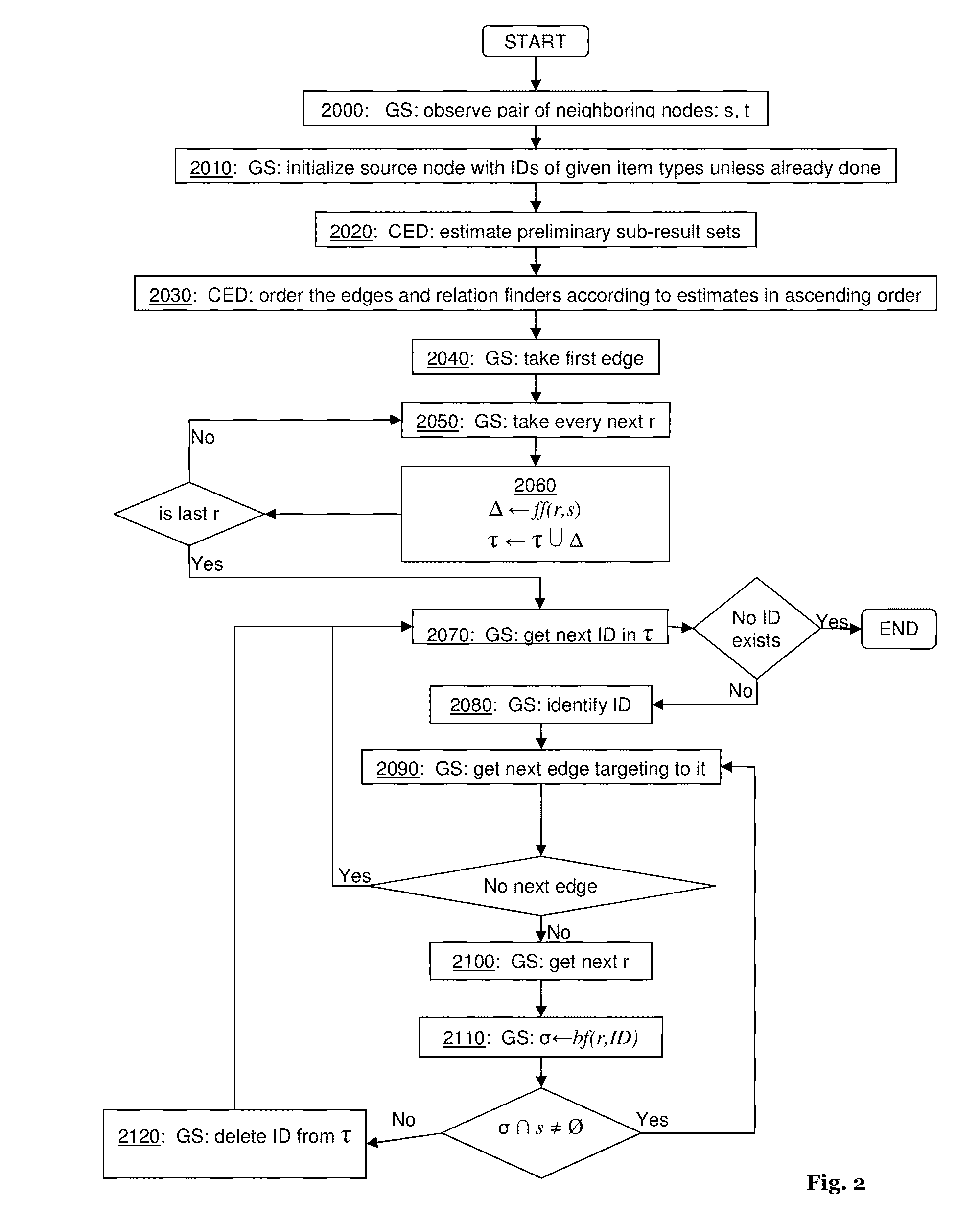
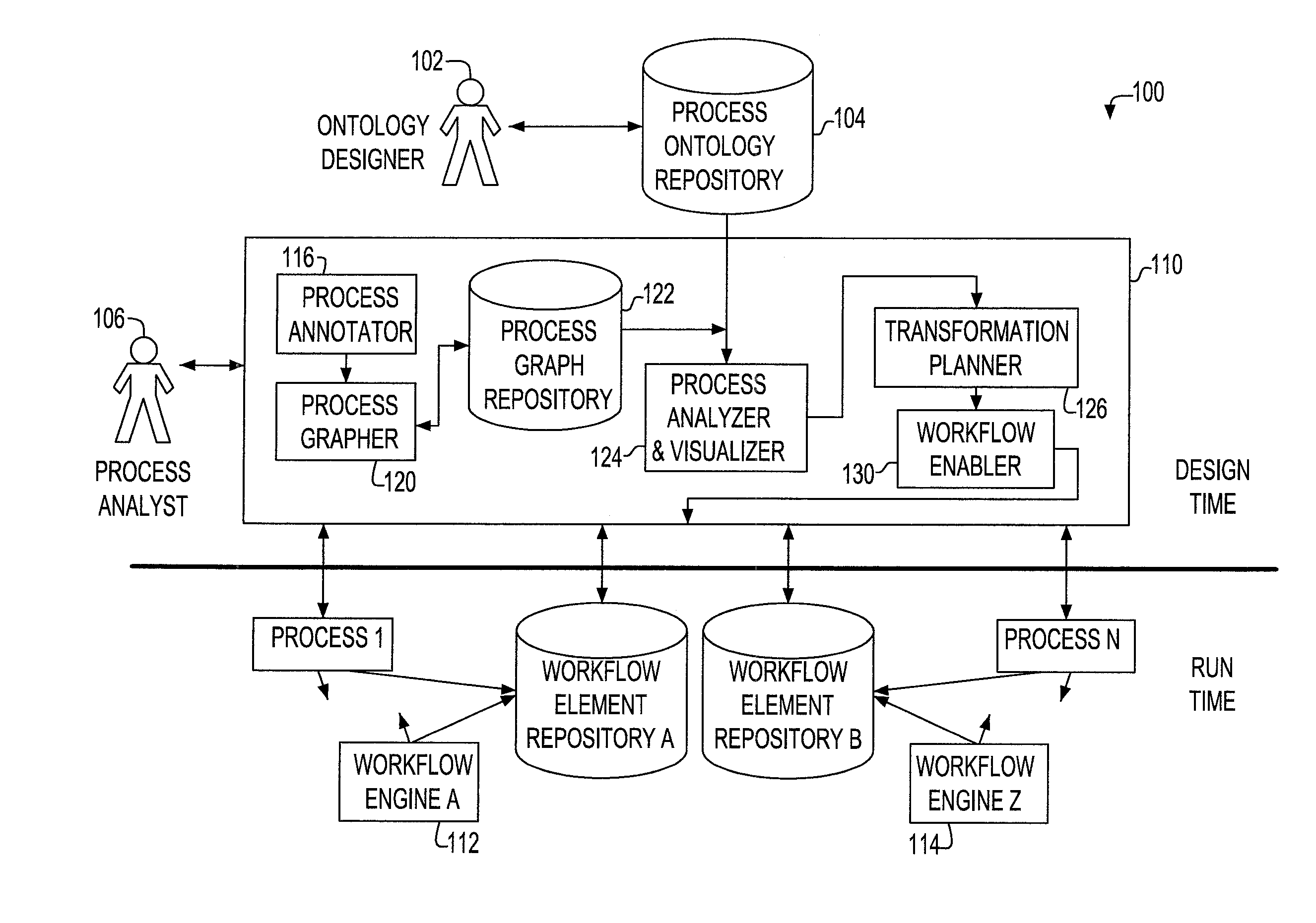
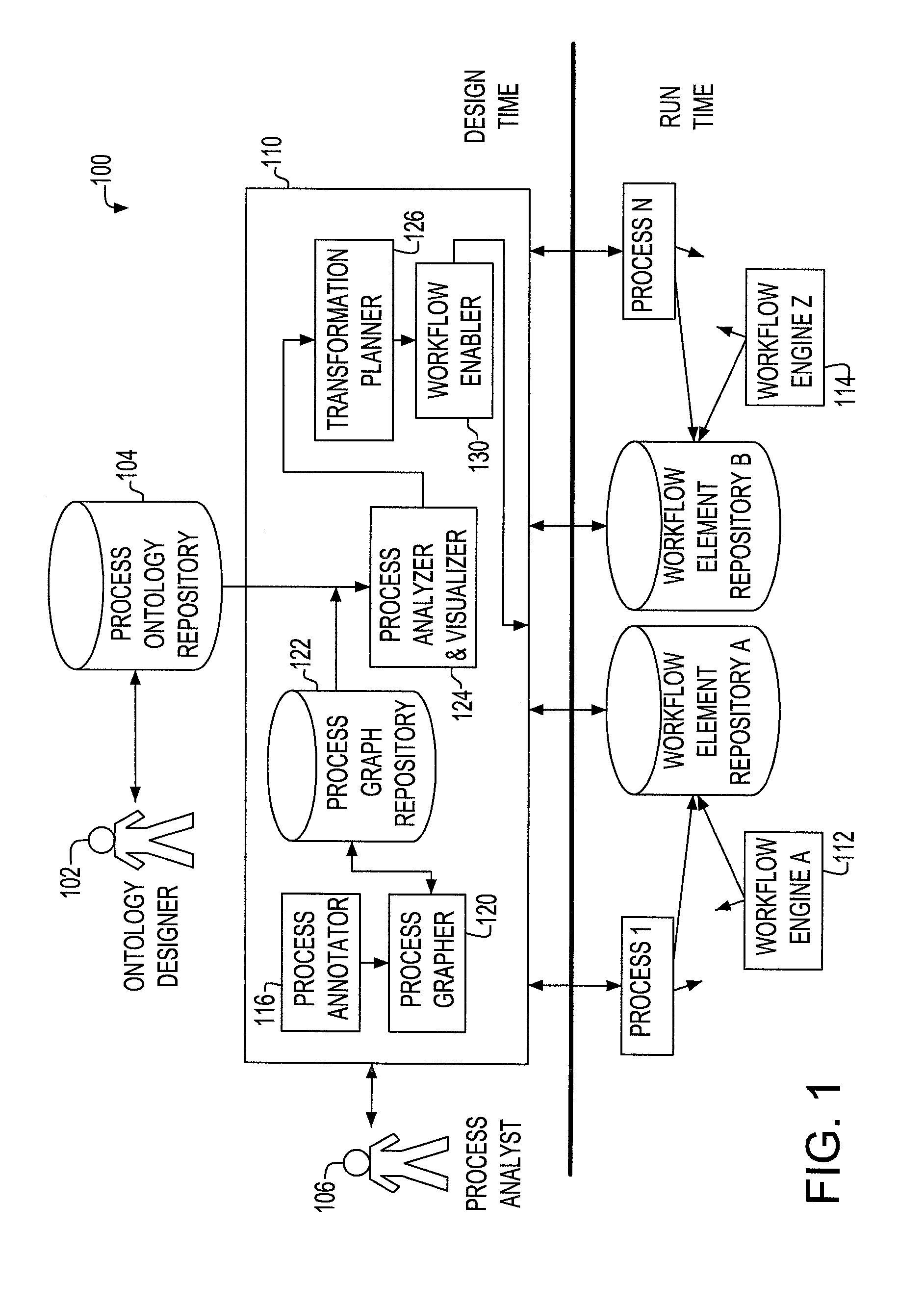
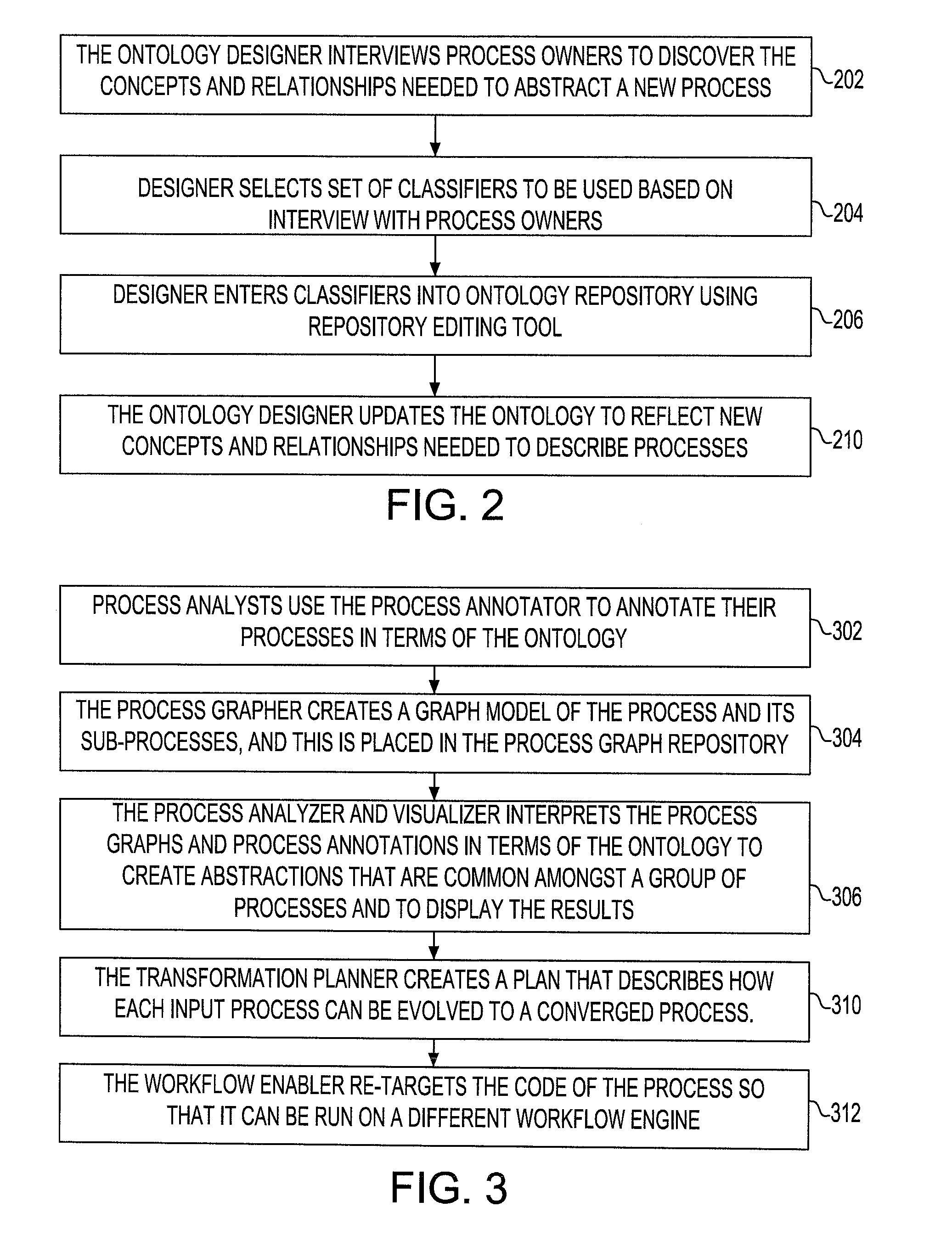
InactiveUS20080178164A1Stay flexibleAgility and speed-to-marketOffice automationProgram controlWork flowWorkflow engine
Described are a method, system and apparatus for the association of an existing process with a reference process and ontology so that the process may be manipulated to the advantage of the process owner. Specifically, once integrated and associated into the process ontology repository and the process graph repository the invention describes how the processes can be expressed so as to show the relationship between process elements at different levels; permit queries against them; provide a way to find similar process elements based on the ontology; facilitate the creation of transformation plans that express how divergent processes can be converged based on similarities identified by the process analysis; associate processes to canonical workflow elements; and retarget process workflows to different workflow engines based on these associations.
Owner:IBM CORP
Wafer-supporting platform
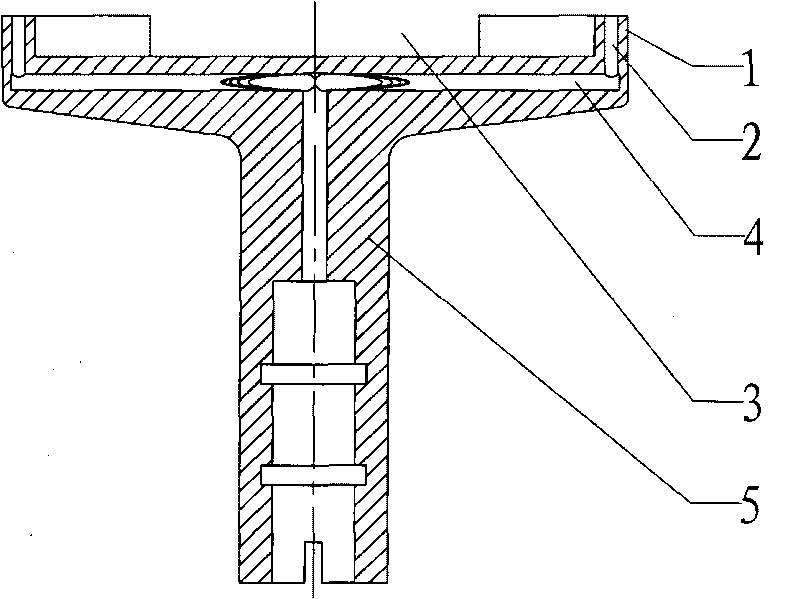
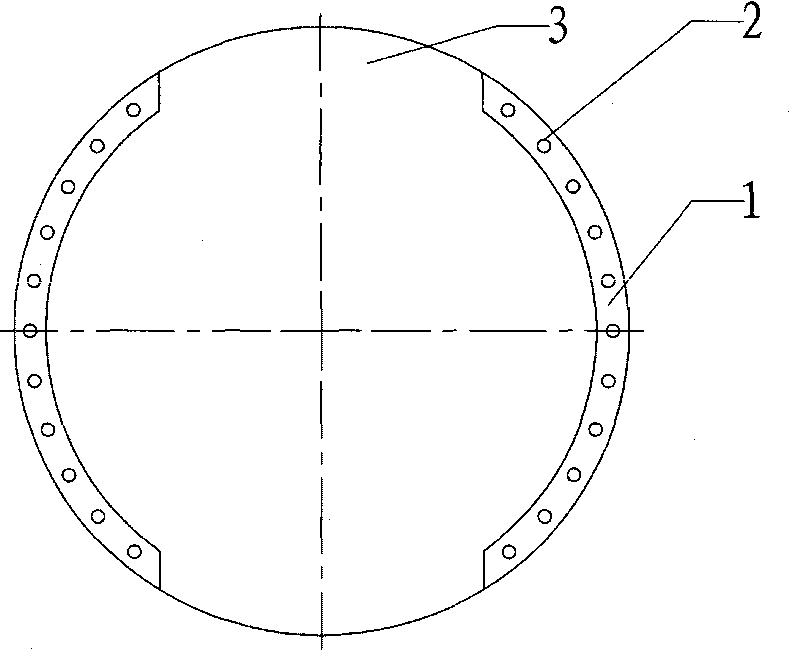
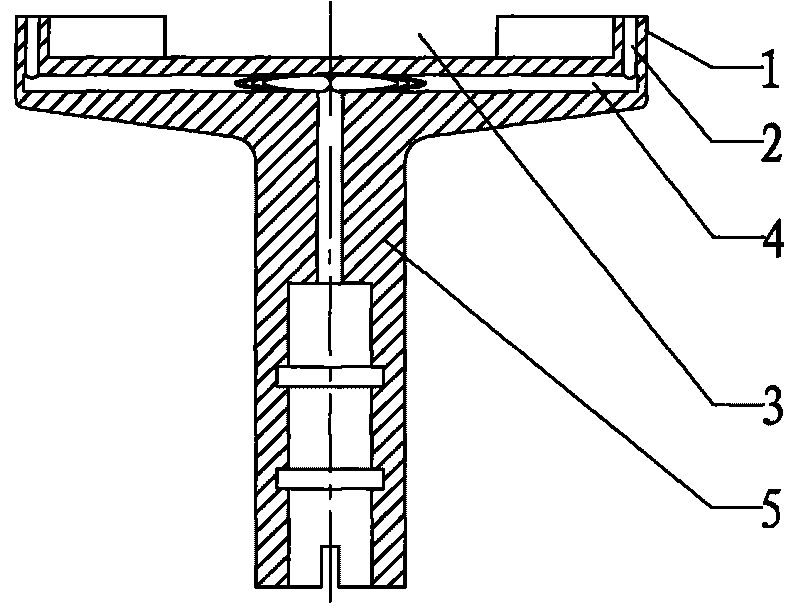
InactiveCN101728296AWafer fixationEasy to fixSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess graphManipulator
The invention relates to the field of semiconductor, in particular to a wafer-supporting platform. The wafer-supporting platform can be used when wafer edges can only contact the wafer-supporting platform according to process requirements during rotary processing in the semiconductor industry to ensure that the central graphic area of a wafer does not contact the wafer-supporting platform, thereby preventing damages to a processed graph caused by the problems of the wafer-supporting platform. The wafer-supporting platform is provided with an annular platform, vacuum sucking discs, a groove, vacuum channels and a body, wherein the top of the body is provided with the annular platform; the annular platform is provided with the groove which is convenient for an I-shaped mechanical hand to enter to fetch and deliver the wafer; the vacuum sucking discs are distributed on the upper surface of the annular platform; and the inside of the body is provided with the vacuum channels communicated with the vacuum sucking discs. The wafer-supporting platform only carries out vacuum adsorption on annular belts on wafer edges and does not contact the graphic areas of the wafers, thereby obtaining high reliability and stable wafer adsorption without causing excursion, wafer drop, and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG KINGSEMI CO LTD
Subgraph query method and device and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveCN108388642AThe query result is accurateReduce the number of query matchesSpecial data processing applicationsUser inputAlgorithm
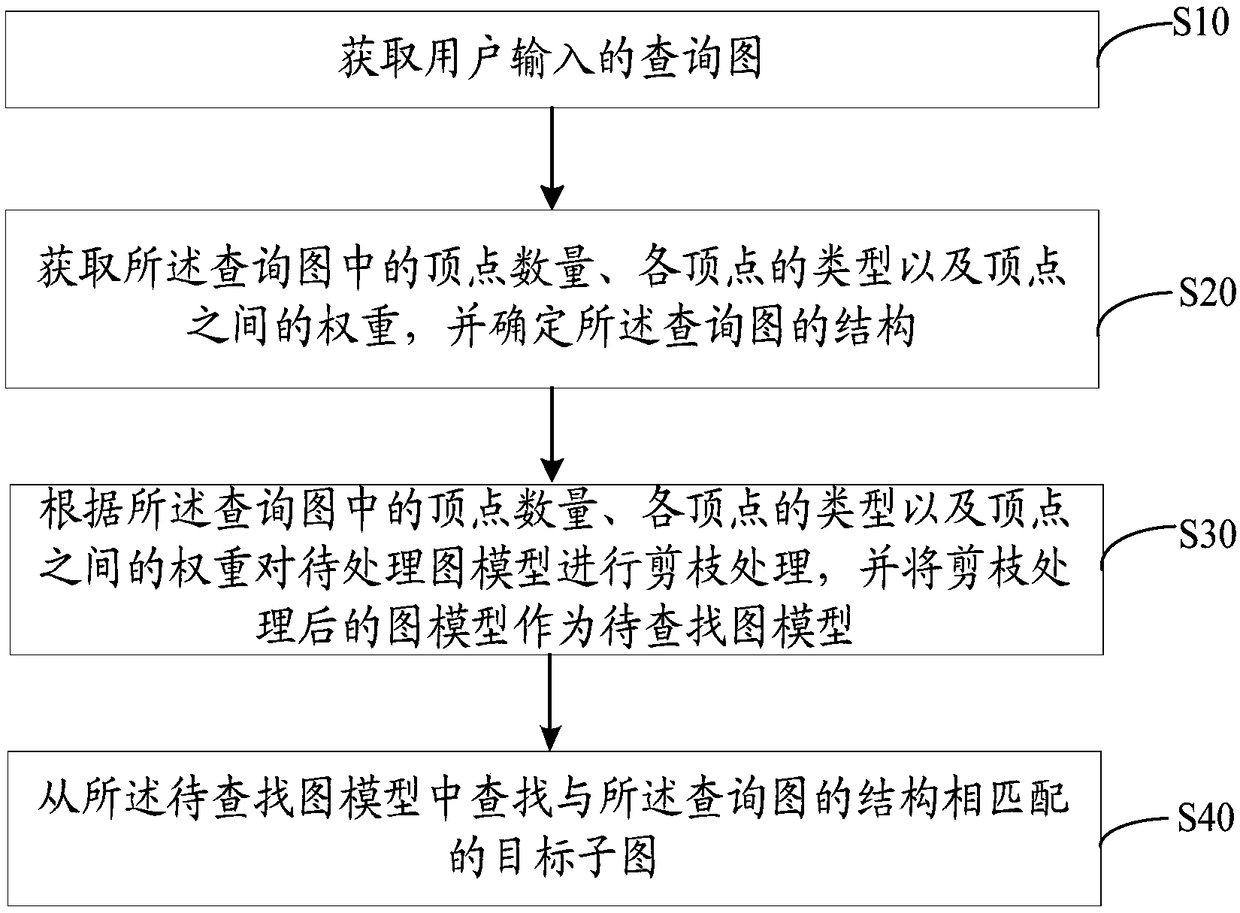
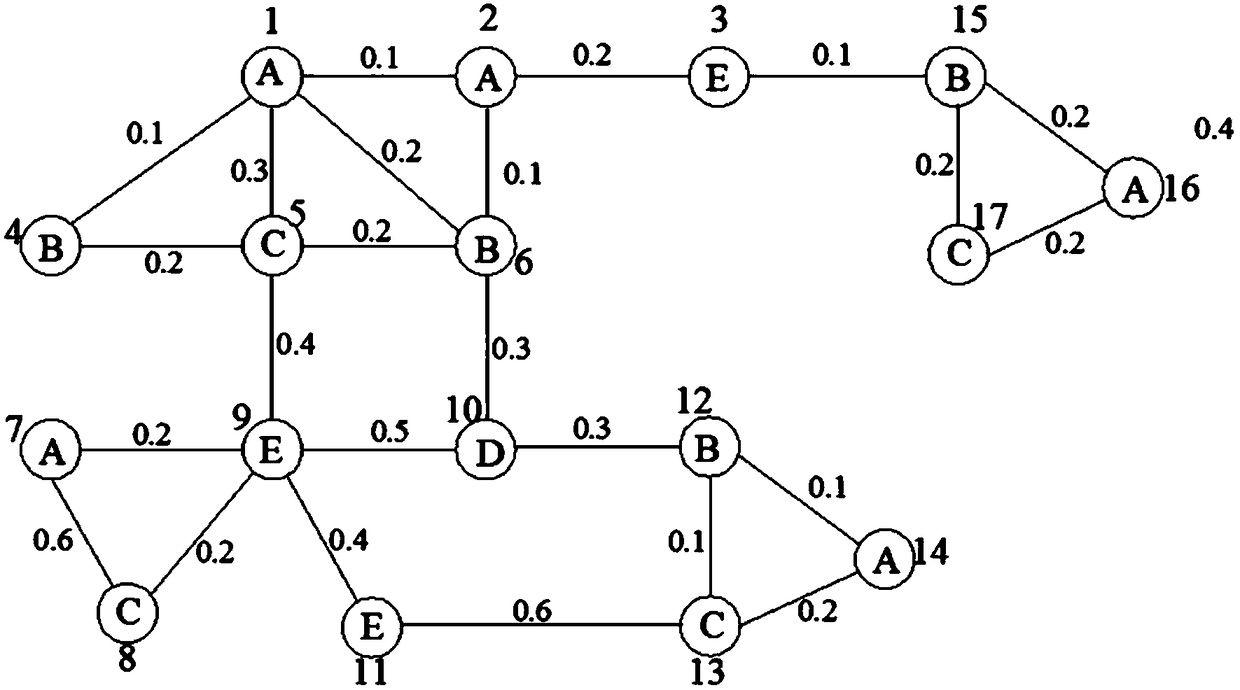
The invention discloses a subgraph query method and device and a computer-readable storage medium. The subgraph query method comprises the following steps of firstly obtaining a query graph input by auser, after determining the quantity of vertexes, the types of all the vertexes and weights among the vertexes in the query graph and obtaining the structure of the query graph, carrying out pruningprocessing on a to-be-processed graph model according to the quantity of the vertexes, the types of all the vertexes and the weights among the vertexes in the query graph, so as to reduce unnecessaryquery matching times, using the graph model subjected to the pruning processing as a to-be-found graph model, and finally finding a target subgraph, matched with the structure of the query graph, in the to-be-found graph model. Thus, when the query graph input by the user contains a specific query condition, quickly and effectively carrying out subgraph query on a to-be-processed graph is realized, and an accurate subgraph query result is obtained.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Object process graph relational database interface
InactiveUS7493335B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDatabase interfaceSoftware system
A computer software system is provided, namely an Object Process Graph Relational Database Interface (OPGRDI) system. The OPGRDI defines and updates relational database tables based on an OPG and stores and retrieves data in the tables as an OPG-defined application is run. The OPGRDI also defines and updates OPG persistent data object elements based on relational database table schemas. The OPGRDI functions can be enabled by users who want to store and retrieve application information in a relational database system, such as Oracle, Sybase, SQL Server, etc. The OPGRDI alters relational database tables as a user changes the structure of an OPG-defined application.
Owner:GRAPHLOGIC INC
Method and system for assembling information processing applications based on declarative semantic specifications
InactiveUS8863102B2Program loading/initiatingRequirement analysisInformation processingProgramming language
A method for assembling an information processing application, includes: inputting a plurality of component descriptions, wherein each of the component descriptions includes a graph pattern that semantically describes an applicability condition of a component and a graph pattern that semantically describes an inclusion effect of the component; inputting a processing request, wherein the processing request includes a goal that is represented by a graph pattern that semantically describes a desired processing outcome; assembling a processing graph, wherein the processing graph includes at least one component that satisfies the desired processing outcome; and outputting the processing graph.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and device for processing graph data
InactiveCN105677755AImprove computing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsData capacityAlgorithm
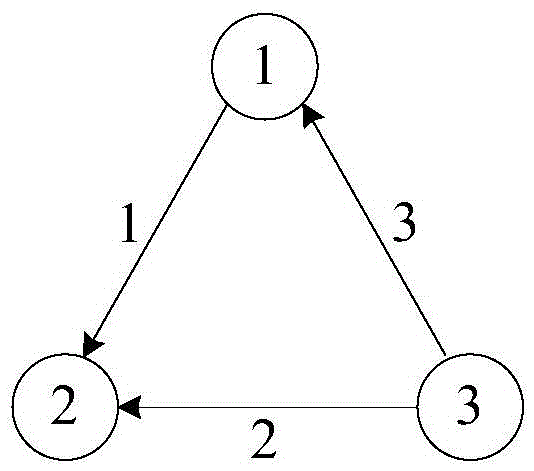
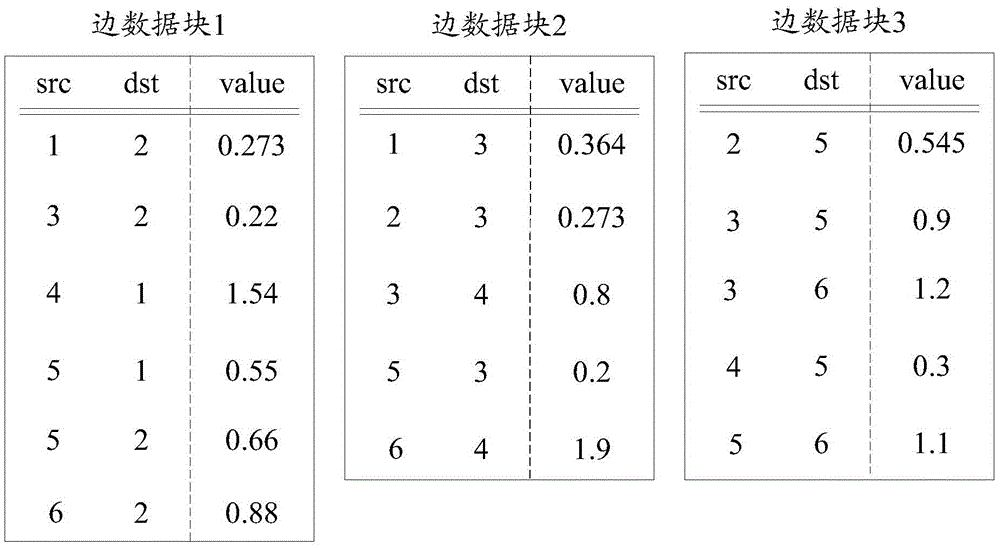
The embodiments of the invention disclose a method and a device for processing graph data, and relates to the technical field of data mining for increasing graphic calculation efficiency. The method comprises: obtaining edge data in the graph data and a computational algorithm for conducting graphic calculation on the graph data; based on the computational algorithm, determining a partitioning algorithm for partitioning the edge data in the graph data, the partitioning algorithm referring to an algorithm which partitions the edge data in the graph data in accordance with nodes which constitute the edge data, the nodes constituting the edge data referring to source nodes and / or destination nodes that constitute the edge data; partitioning the edge data in the graph data into N initial edge data blocks in accordance with the partitioning algorithm and memory capacity of local memory, each initial edge data block of the N initial edge data blocks having a data capacity less than the memory capacity, wherein N is equal to or greater than 1 and is an integer; arranging the edge data of each initial edge data block of the N initial edge data blocks in accordance with the nodes the constitute the edge data, and obtaining N target edge data blocks.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUAWEI DIGITAL TECH
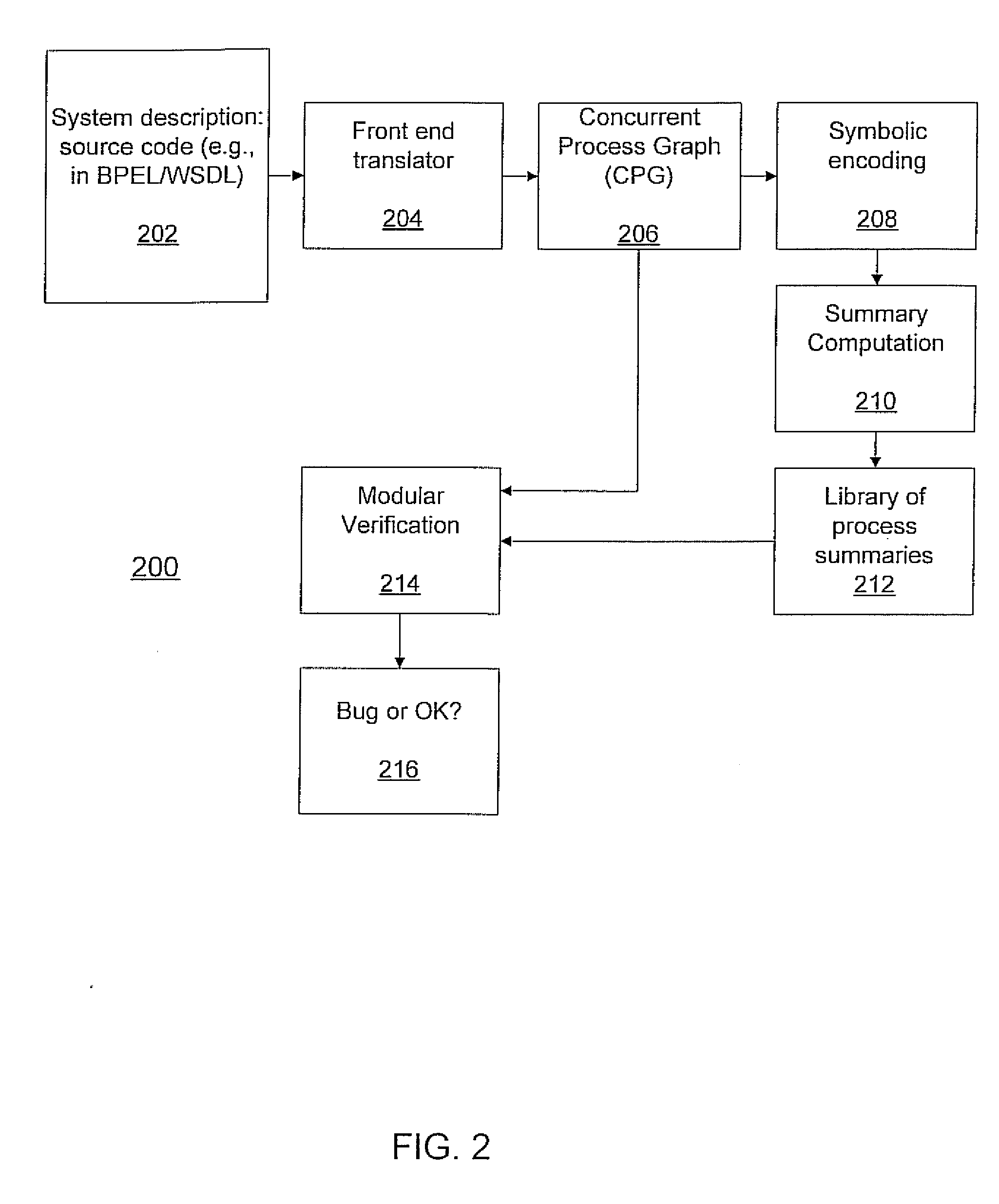
Modular verification of web services using efficient symbolic encoding and summarization
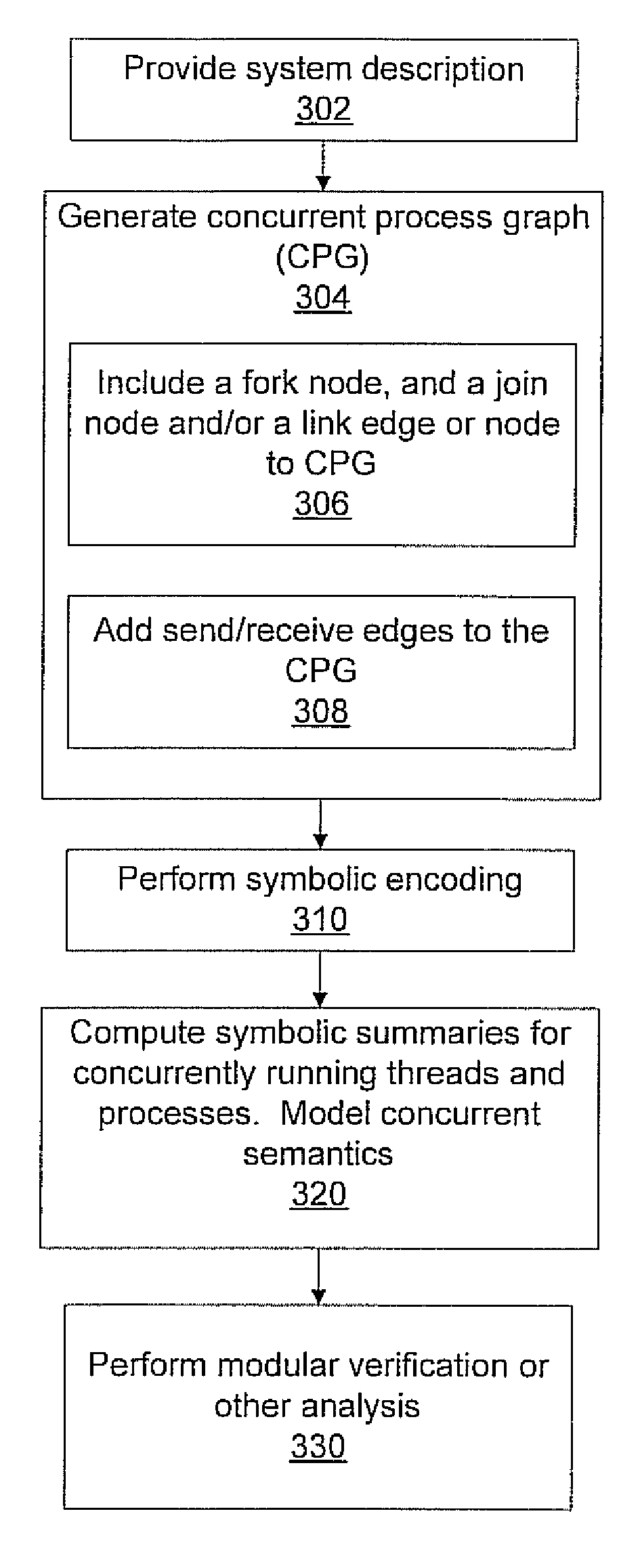
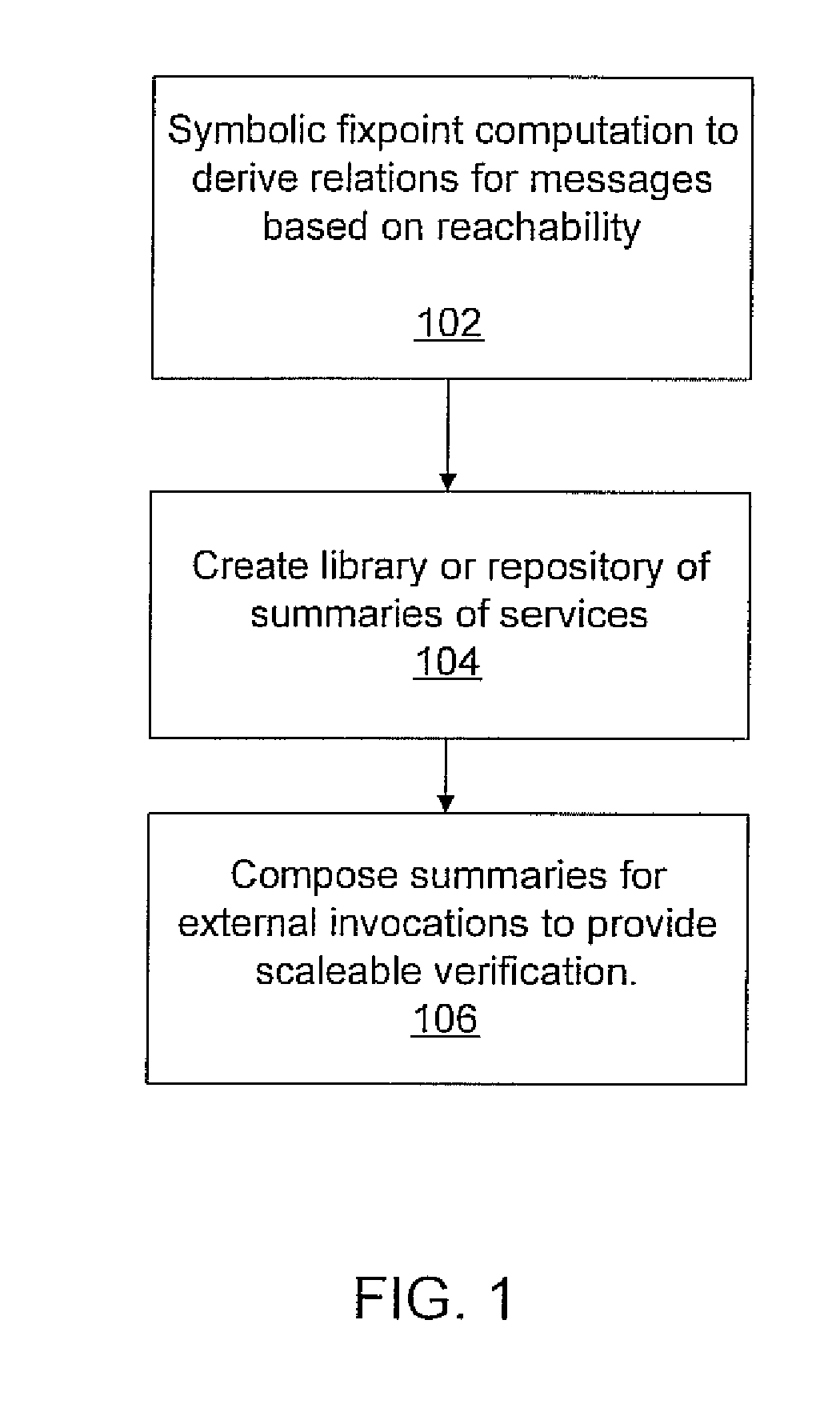
InactiveUS20090222249A1Simple definitionAvoids unnecessary additionError detection/correctionAnalogue computers for electric apparatusWeb serviceReachability
A system and method for verifying a composition of interacting services in a distributed system includes generating a concurrent process graph (CPG) for processes in a system and symbolically encoding the CPG of each process to perform a reachability analysis. Symbolic summaries are generated for concurrently running processes based on the reachability analysis. Modular verification is conducted by utilizing the symbolic summaries of the processes to verify a system of interrelated processes.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Methods and systems for using map-reduce for large-scale analysis of graph-based data
ActiveUS8943011B2Improve memory usageDigital data processing detailsBiological testingCluster algorithmGraphics
Embodiments are described for a method for processing graph data by executing a Markov Clustering algorithm (MCL) to find clusters of vertices of the graph data, organizing the graph data by column by calculating a probability percentage for each column of a similarity matrix of the graph data to produce column data, generating a probability matrix of states of the column data, performing an expansion of the probability matrix by computing a power of the matrix using a Map-Reduce model executed in a processor-based computing device; and organizing the probability matrix into a set of sub-matrices to find the least amount of data needed for the Map-Reduce model given that two lines of data in the matrix are required to compute a single value for the power of the matrix. One of at least two strategies may be used to computing the power of the matrix (matrix square, M2) based on simplicity of execution or improved memory usage.
Owner:SALESFORCE COM INC
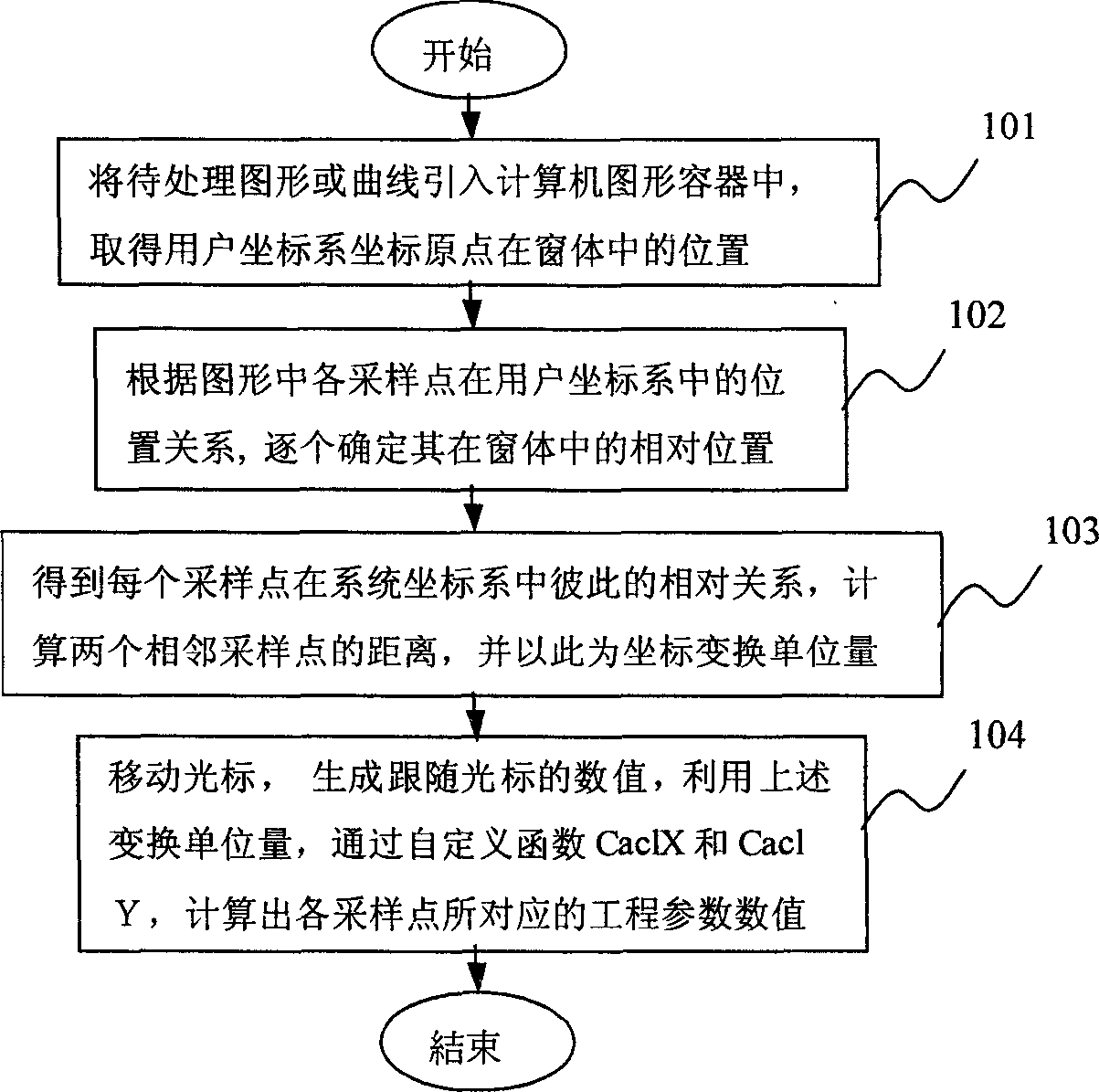
Method for automatic obtaining engineering parameter values of sampling points in graph by using computer
InactiveCN1797409ASimple programmingEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsComputational science
The invention advances a method for automatically obtain engineering parameter values of sampling points from a graph by computer, obtaining the engineering parameter values of sampling points in the graph by conversion and calculation for a reference frame. And the method comprises the steps of: leading an to-be-processed graph or curve into a computer graph container, and obtaining the origin position of a user reference frame where the graph exists; according to the in-window position relation of all sampling points in the graph in the user reference frame, one by one determining their relative positions in the window; obtaining the relation between all the sampling points in a system reference frame, and calculating a distance between every two adjacent sampling points and using this as reference frame transform unit quantities of the system and user reference frames; moving a cursor to generate a cursor following value and using the unit quantities to obtain corresponding engineering parameter values to all sampling points.
Owner:李强
Method and Apparatus for Optimization in Workflow Management Systems
Activities within a workflow are either data management activities (DMAs) or non-DMAs. A workflow is typically carried out by a system by executing one activity after the other. This can, however, be very time consuming. A method and system are provided for optimizing a group of activities (GOA) comprising a DMA, whereby the GOA is comprised in the workflow to improve the overall performance. The method determines the DMAs, and for each DMA, a data level statement (DLS). The GOA is determined and a process graph model (PGM) is determined from the GOA so that the DLS is comprised in the PGM and the semantics of the PGM are identical to those of the GOA. The PGM is optimized for which an optimized GOA is determined. The semantics of the optimized GOA are identical to those of the GOA. In the workflow, the GOA is replaced by the optimized GOA.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
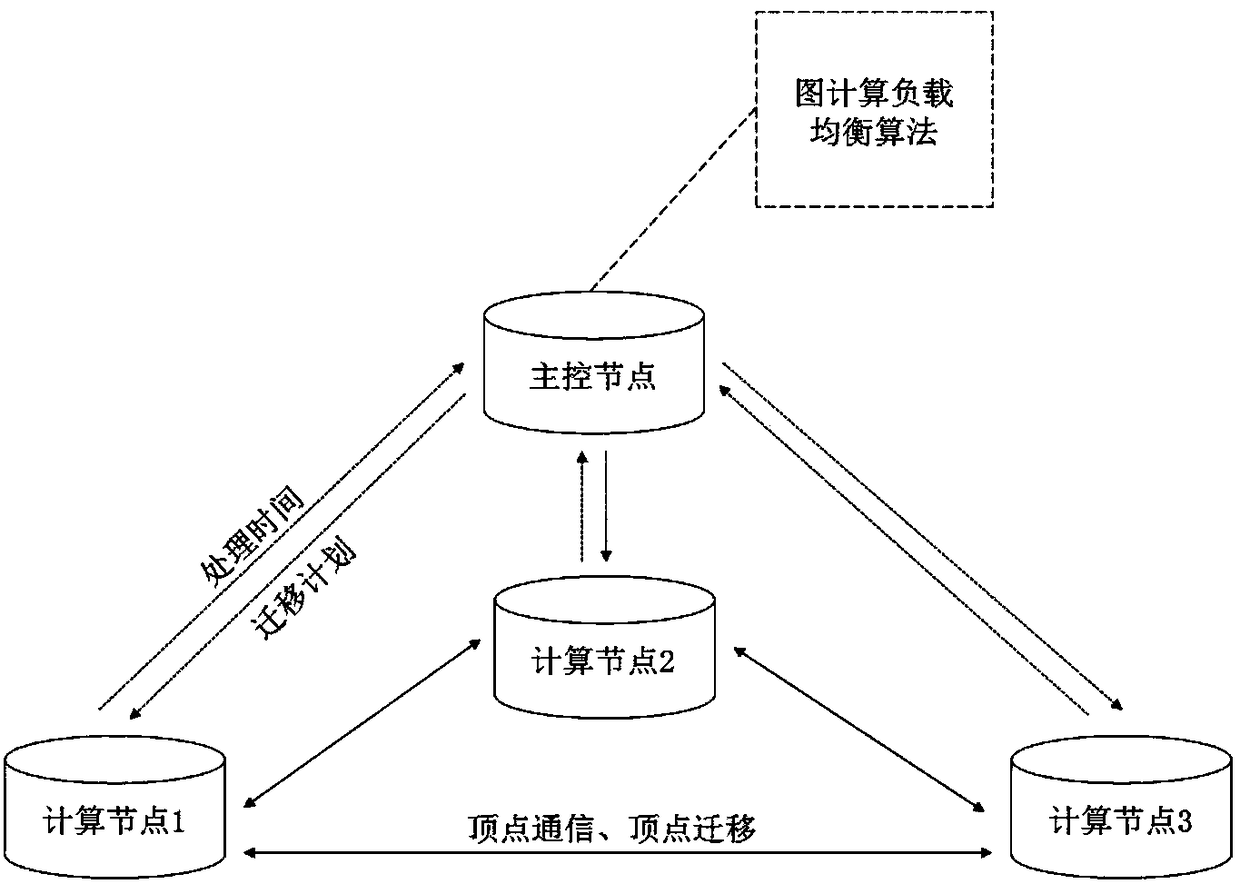
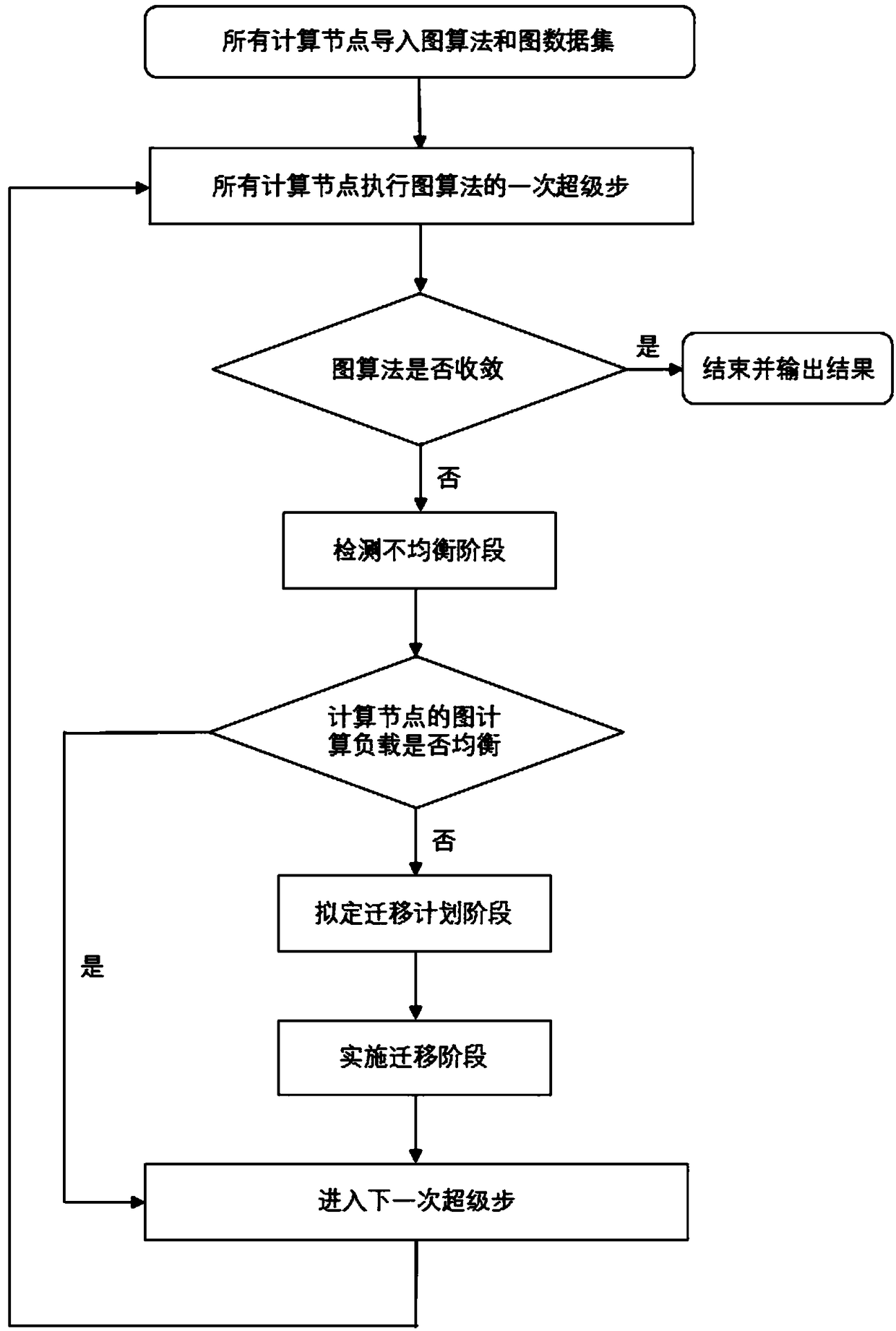
Heterogeneous server structure-oriented graph calculation load balancing method
ActiveCN108089918AReduce synchronization overheadReduce running timeProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationResource utilizationParallel computing
The invention discloses a heterogeneous server structure-oriented graph calculation load balancing method. The method includes: calculating a variation coefficient of all processing times in a currentsuper step by a main control node according to the times used by processing graph calculation loads by all calculation nodes in the super step; if variation coefficients in two consecutive super steps are greater than a preset threshold value, determining that the graph calculation loads of all the calculation nodes in running are not balanced, and the graph calculation loads on the calculation nodes need to be re-assigned after the current super step ends; and otherwise, continuing to execute a next super step by all the calculation nodes. According to the method of the invention, vertex migration is utilized to balance processing times of the calculation nodes in each super step, thus synchronization overheads of all the calculation nodes in each super step are effectively reduced, a running time of a graph calculation task is shortened, and a resource utilization rate of each calculation node in running is increased.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
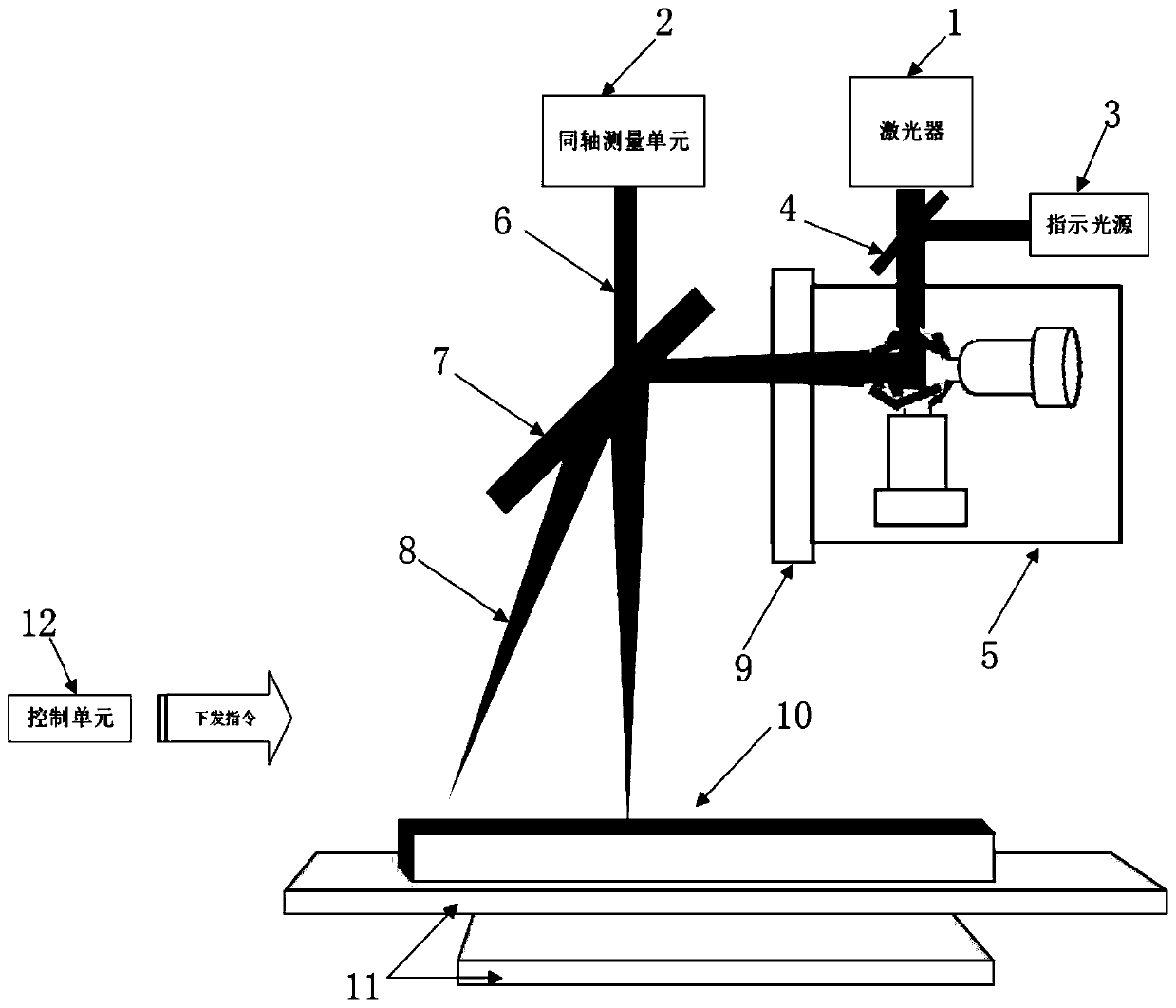
Graph on-line splicing method and system for laser processing of large format
ActiveCN109702319AUnlimited Positioning AccuracyHigh precision splicingLaser beam welding apparatusGraphicsLaser processing
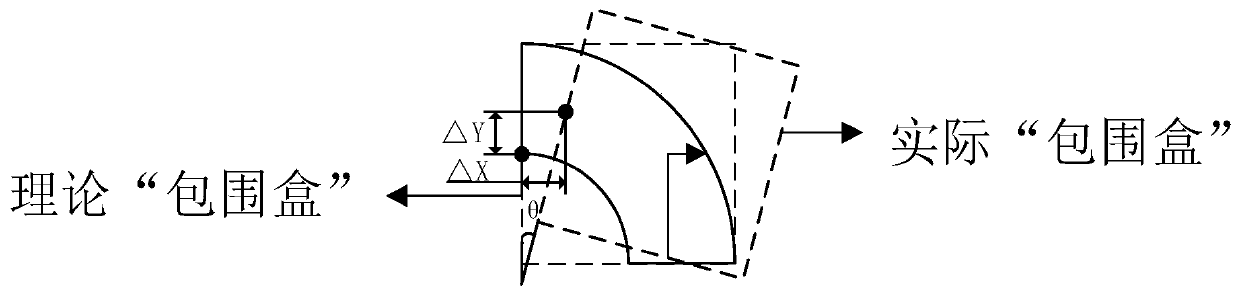
The invention relates to a graph on-line splicing method and system for laser processing of a large format, and solves the problem that the splicing accuracy of an existing on-line splicing method cannot meet the processing requirement. The graph on-line splicing method comprises the following steps of 1) dividing a to-be-processed graph into N sub graphs, and acquiring the coordinate of the center point of each sub graph and the smallest rectangular region containing each sub graph; 2: turning on an indication power supply, enabling light beam emitted by the indication power supply to reach an X to-be-processed area, and scanning the boundary of the X to-be-processed area; 3) observing the X to-be-processed areas by a coaxial measuring unit, acquiring the images of the X to-be-processed areas, and obtaining the actual bounding box of the X to-be-processed areas by the control unit according to the acquired image; 4) comparing a theory bounding box with an actual bounding box; 5) adjusting the positions of X sub graphs in the control unit; and 6) completing the graph scanning of the X processing areas; and 7) repeating the step 2 to the step 6.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Graph data processing method and apparatus
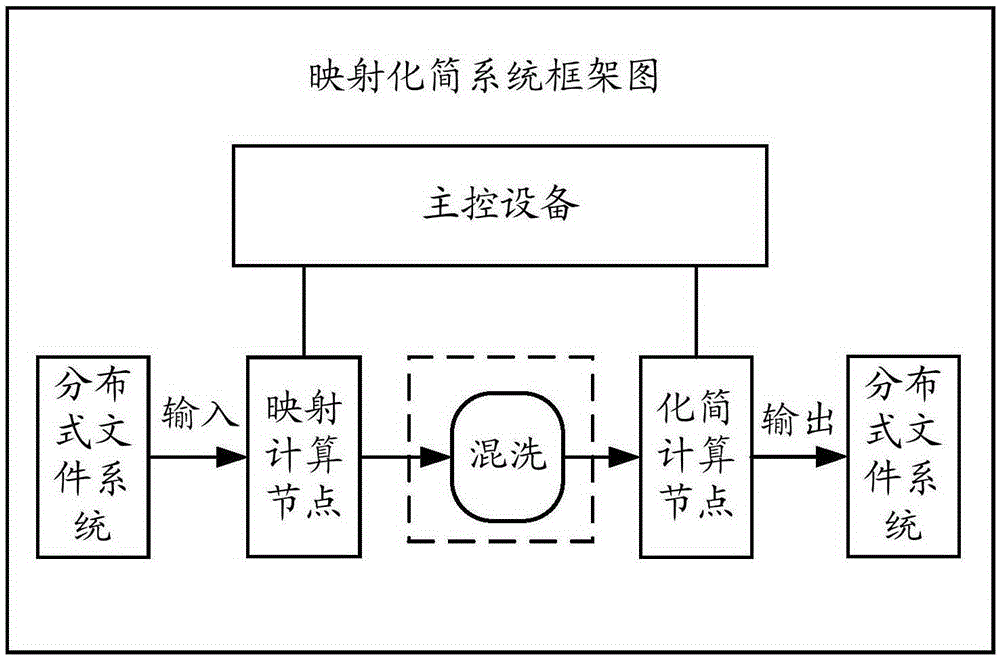
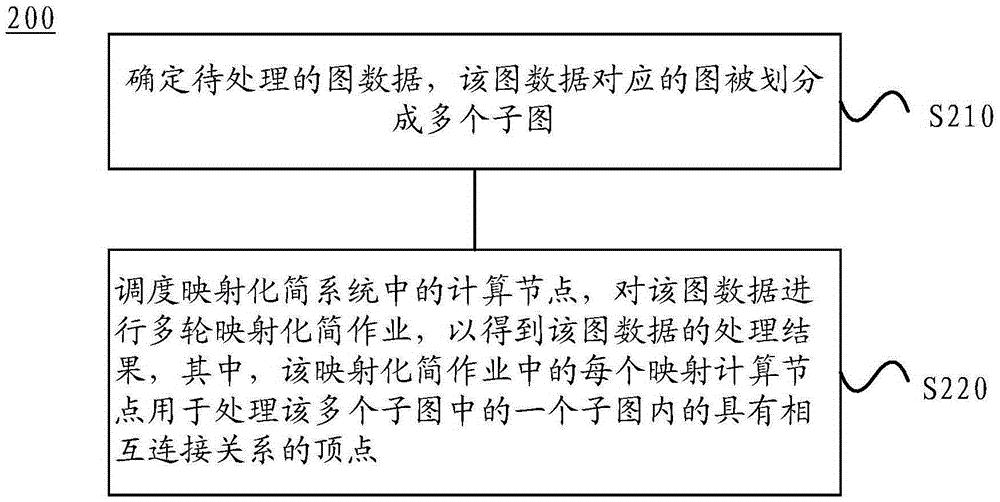
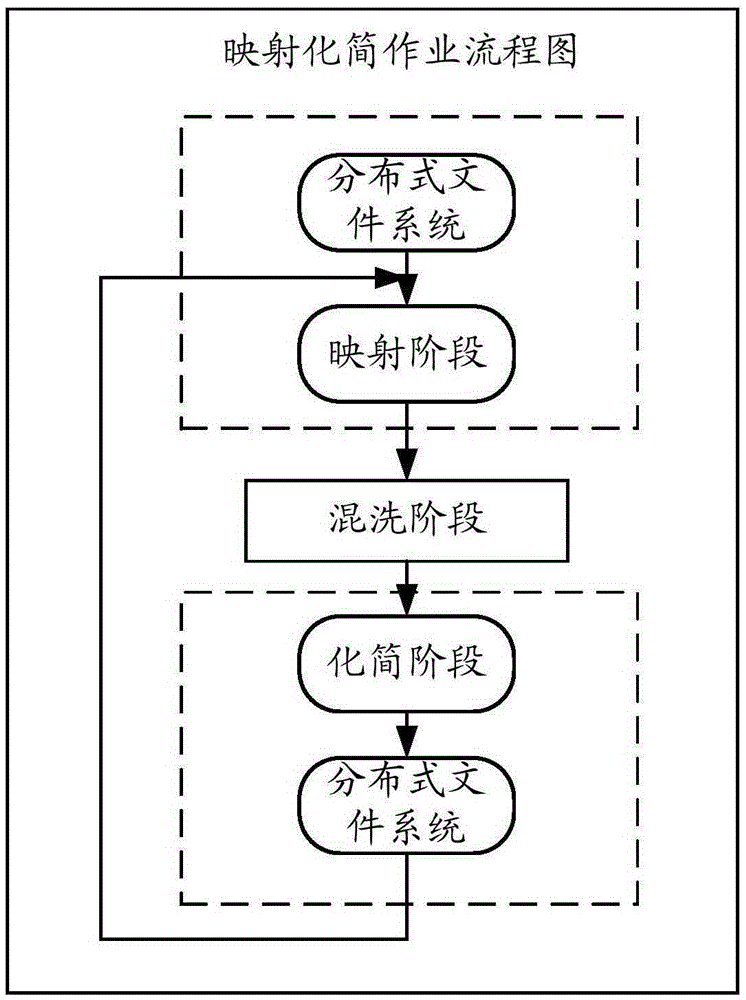
ActiveCN106649391AImprove processing efficiencyReduce the number of roundsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmProcess graph
Embodiments of the invention disclose a graph data processing method and apparatus. The method comprises the steps of determining to-be-processed graph data, and dividing a graph corresponding to the graph data into a plurality of sub-graphs; and dispatching computing nodes in a MapReduce system, and performing multi-round MapReduce operations on the graph data to obtain a processing result of the graph data, wherein each Map computing node in the MapReduce operation is used for processing vertexes with a mutual connection relationship in one of the sub-graphs. According to the method and the apparatus provided by the embodiments of the invention, the graph data processing efficiency can be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method for rotatingly displaying picture
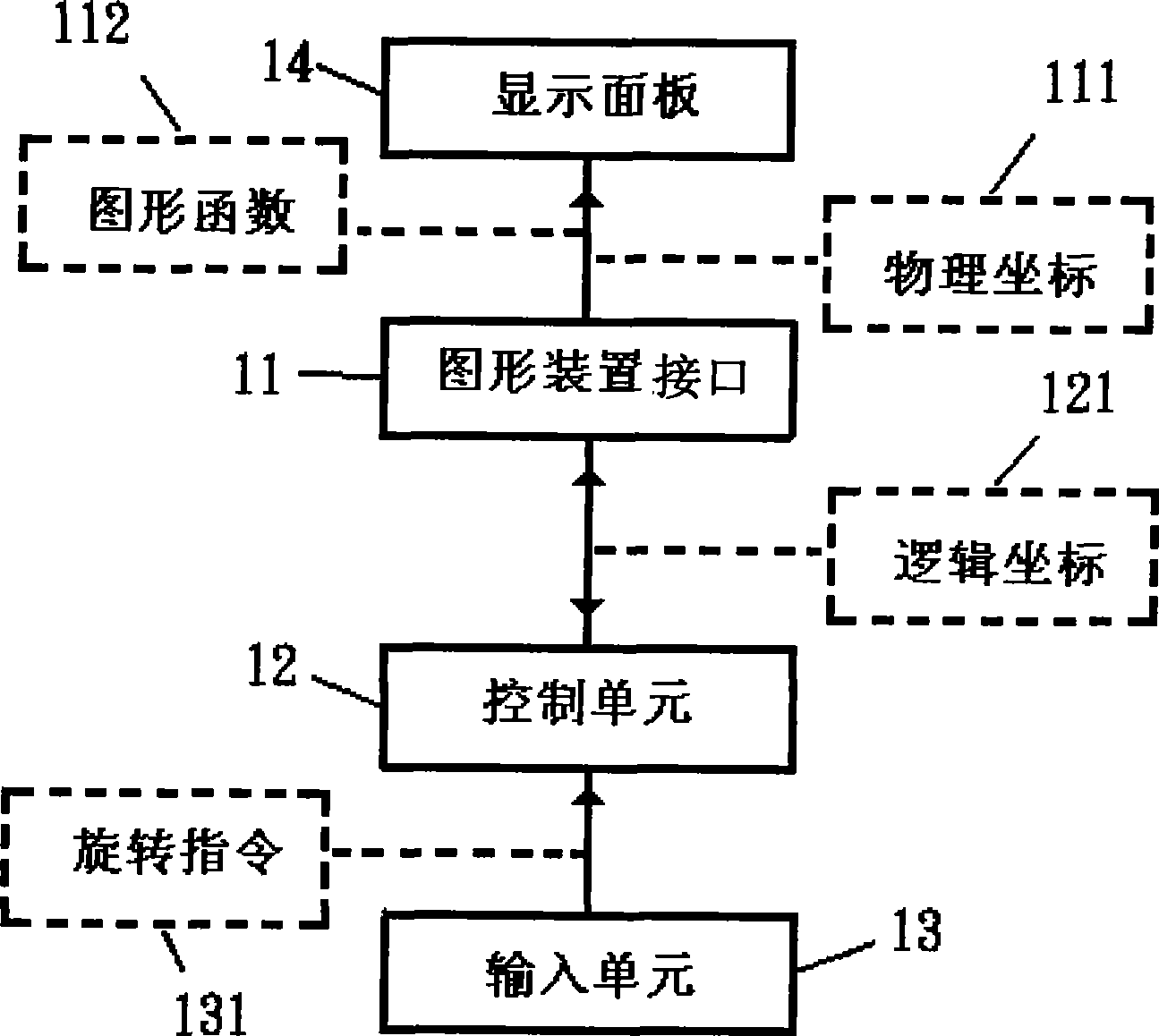
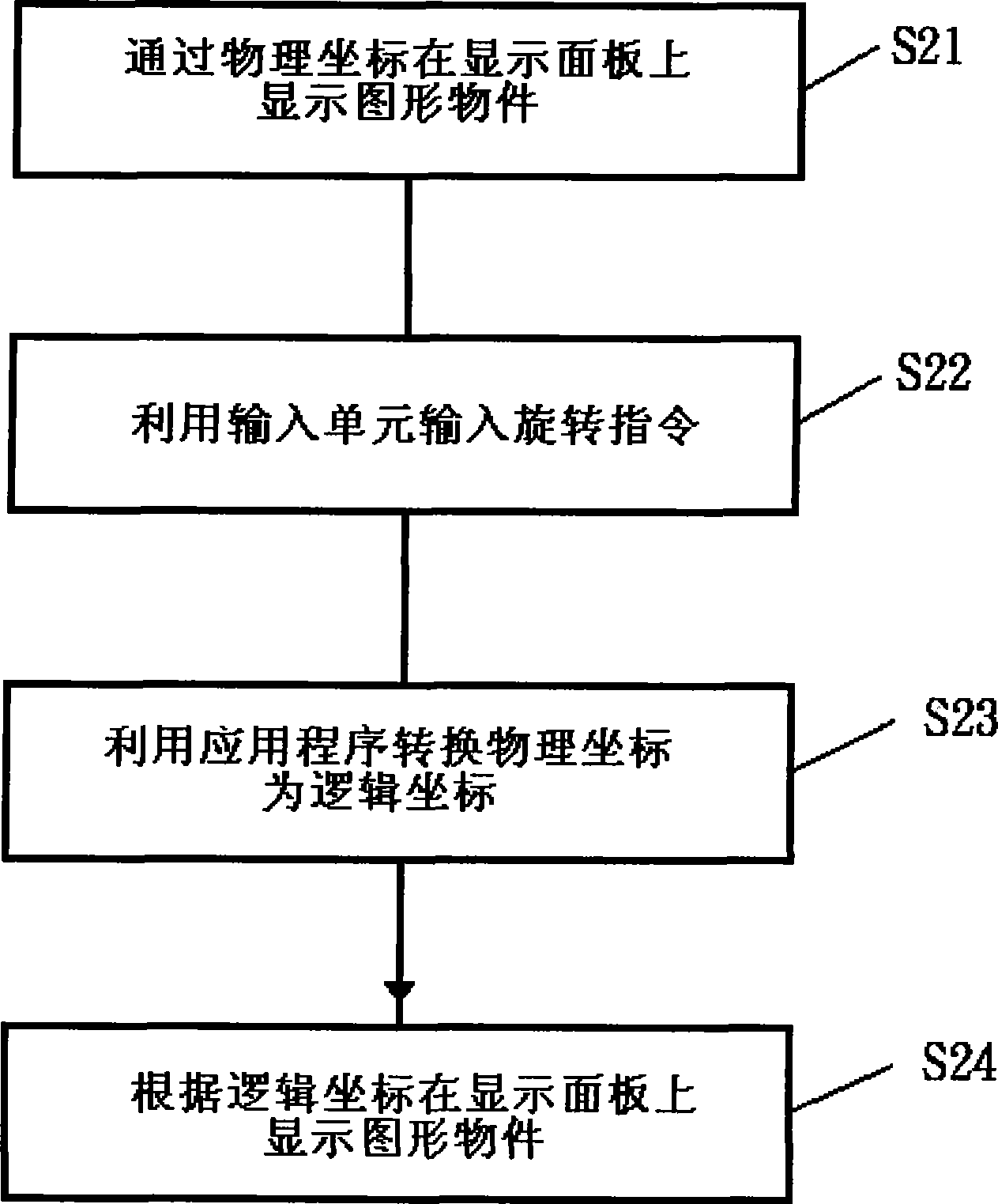
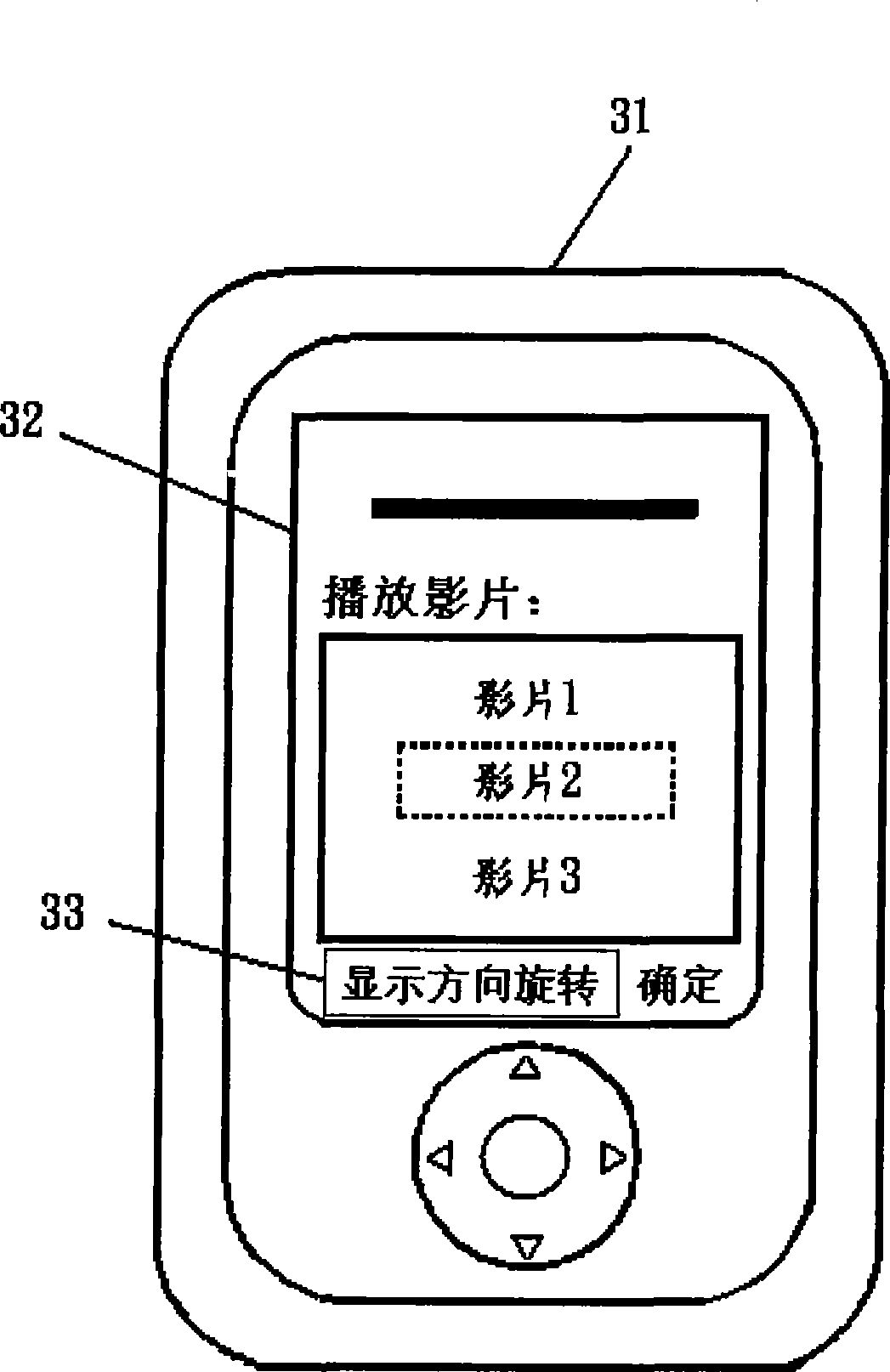
InactiveCN101425015ASpecific program execution arrangementsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsApplication software
The invention relates to a system and a method for rotating a display picture. The system comprises a graphical device interface, a control unit and an input unit, wherein the graphical device interface comprises a plurality of graphical functions which are used for processing graph objects, and the graph objects are displayed on a display panel through physical coordinates; the control unit is used for executing an application program, and the application program converts the physical coordinates into logical coordinates according to rotation instructions so as to rotate the graph objects; the input unit is used for inputting the rotation instructions, and the input unit is accessed to the control unit which is accessed to the graphical device interface. The invention causes a user to freely rotate the displayed graph objects on the display panel according to the demands, and is convenient and fast.
Owner:WUDI SCI & TECH (XIAN) CO LTD
Graph processing method, device and apparatus and storage medium
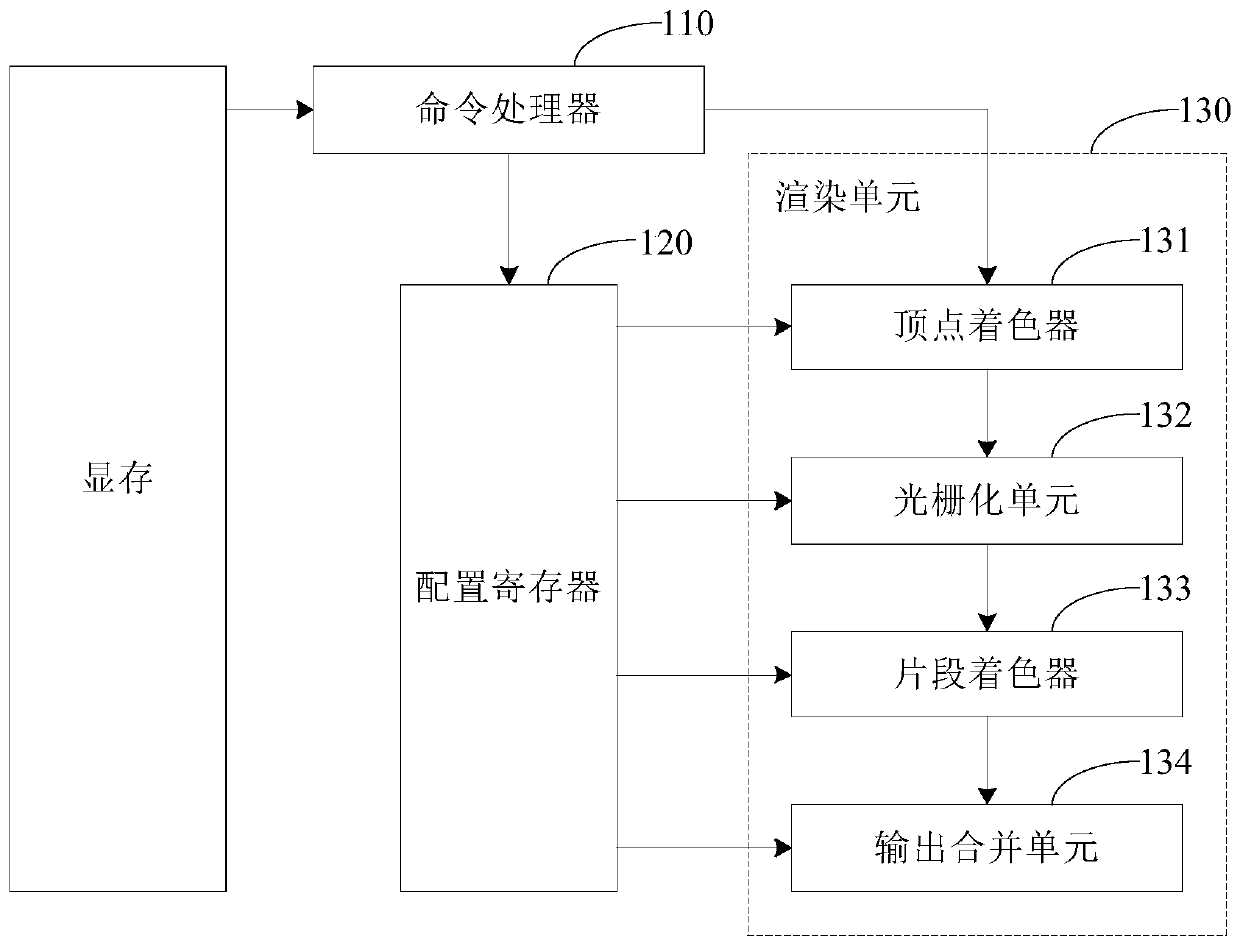
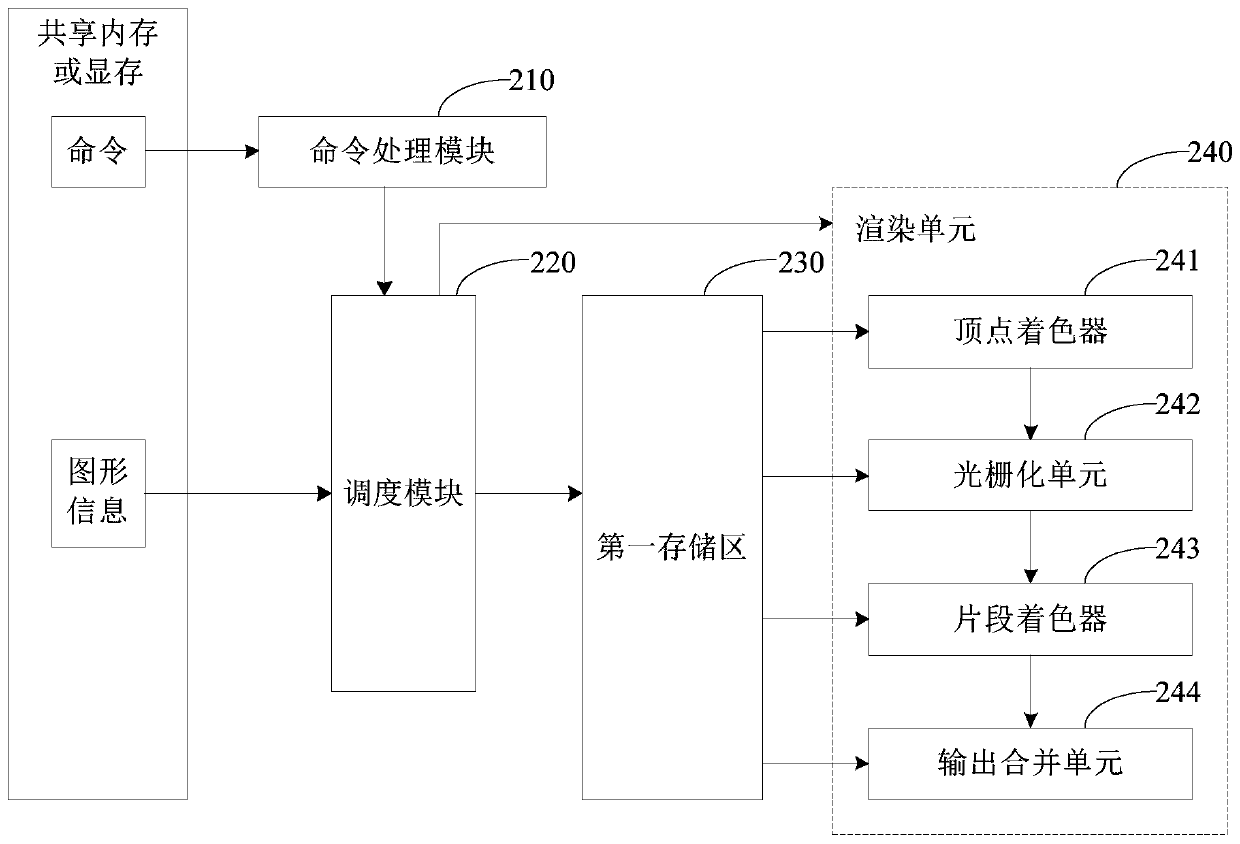
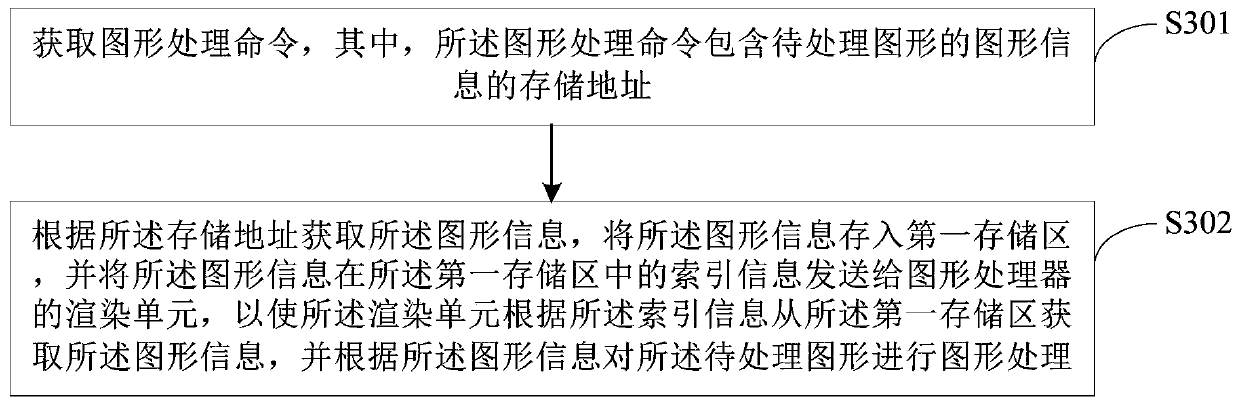
ActiveCN110415161AReduce overheadAvoid writingImage memory managementProcessor architectures/configurationGraphicsProcessor register
The embodiment of the invention provides a graphic processing method, device and apparatus and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a graphic processing command which comprises a storage address of graphic information of a to-be-processed graph; acquiring the graphic information according to the storage address, storing the graphic information into a first storage area,and sending index information of the graphic information in the first storage area to a rendering unit of a graphic processor, so that the rendering unit acquires the graphic information from the first storage area according to the index information and performs graphic processing on the to-be-processed graphic according to the graphic information. According to the embodiment of the invention, therendering unit of the graphic processor can obtain the required graphic information without configuring a register, so that the register is prevented from writing a command in the graphic processingprocess, and the command overhead is reduced.
Owner:龙芯中科(合肥)技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com