Multi-target optimization method for dispatching of automatic stereoscopic warehouse with limitation on storage time
A multi-objective optimization, three-dimensional warehouse technology, applied in the field of multi-objective optimization of automatic three-dimensional warehouse scheduling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
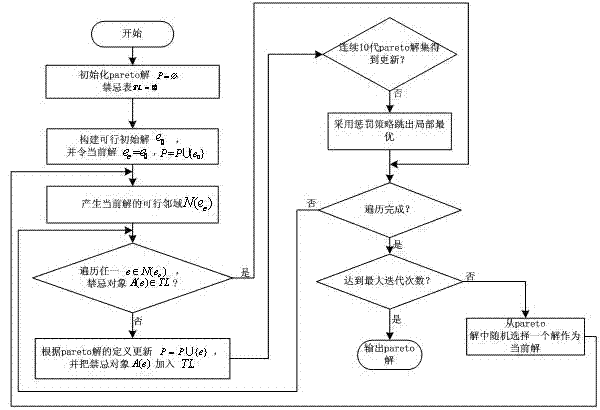
[0055] see figure 1 , the multi-objective optimization method for automatic three-dimensional warehouse scheduling with limited storage time is characterized by the following specific steps:
[0056] (1) Analyze the constraints existing on the industrial site and the goals to be optimized, and abstract them into mathematical models;
[0057] (2) Let pareto unset , Taboo Table ;
[0058] (3) Construct a feasible initial solution , and let the current solution , ;
[0059] (4) Generate the current solution feasible neighborhood of ;
[0060] (5) traverse any , if the taboo object , then update according to the definition of Pareto solution , and put join in ; otherwise do not update ;
[0061] (6) If during the search process, the Pareto solution has not been updated for 10 consecutive generations, the penalty strategy is enabled to make the search jump out of the local optimum;
[0062] (7) If the search does not reach the maximum number of iterat...
Embodiment 2
[0065] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
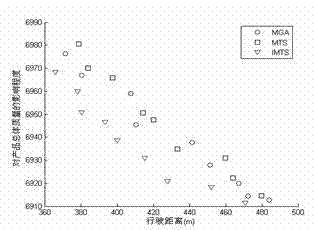
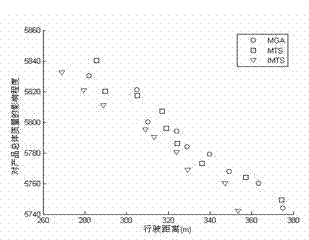
[0066] 1 The mathematical model established in step (1) is established based on the following considerations: Delays in and out of storage have different impacts on products of different processes; Based on the principle of energy saving and consumption reduction, the storage path of the stacker is optimized, so the optimization goals include product quality and product storage path. The mathematical model is expressed as follows:
[0067]
[0068]
[0069]
[0070] in The degree of impact on product quality when the task is completed; The total distance traveled by the stacker to complete the task; is the target to be optimized; , Respectively, the quantity of products entering and exiting the warehouse; is the capacity of the stacker; for the first The time it takes for a product to complete its entry and exit; for the first The time between...
Embodiment 3
[0087] see figure 1 , the multi-objective optimization method for automatic three-dimensional warehouse scheduling with limited storage time, the specific steps are as follows:
[0088] (1) Establish goals and establish optimization models
[0089] The warehouse scheduling problem in this example has the following characteristics:
[0090] a. There are m storage tasks, and their positions in the warehouse are expressed as ( , , ,..., );
[0091] b. There are n outbound tasks, and their positions in the warehouse are expressed as ( , , ,..., );
[0092] The number of products that the stacker can carry each time is , the process for the stacker to perform inbound and outbound operations is: the quantity taken out by the stacker from the inbound buffer zone is less than or equal to warehousing products, and then put them into the corresponding warehouse, and take out the quantity to be out of the warehouse less than or equal to products into the outbou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com