Kurtosis-based variable-step-size self-adaptive blind source separation method
A blind source separation and self-adaptive technology, applied in the field of signal processing, can solve the problems of large steady-state error, slow convergence speed, algorithm convergence speed and steady-state error cannot be satisfied at the same time, etc., to solve the problem of convergence speed and steady-state error. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
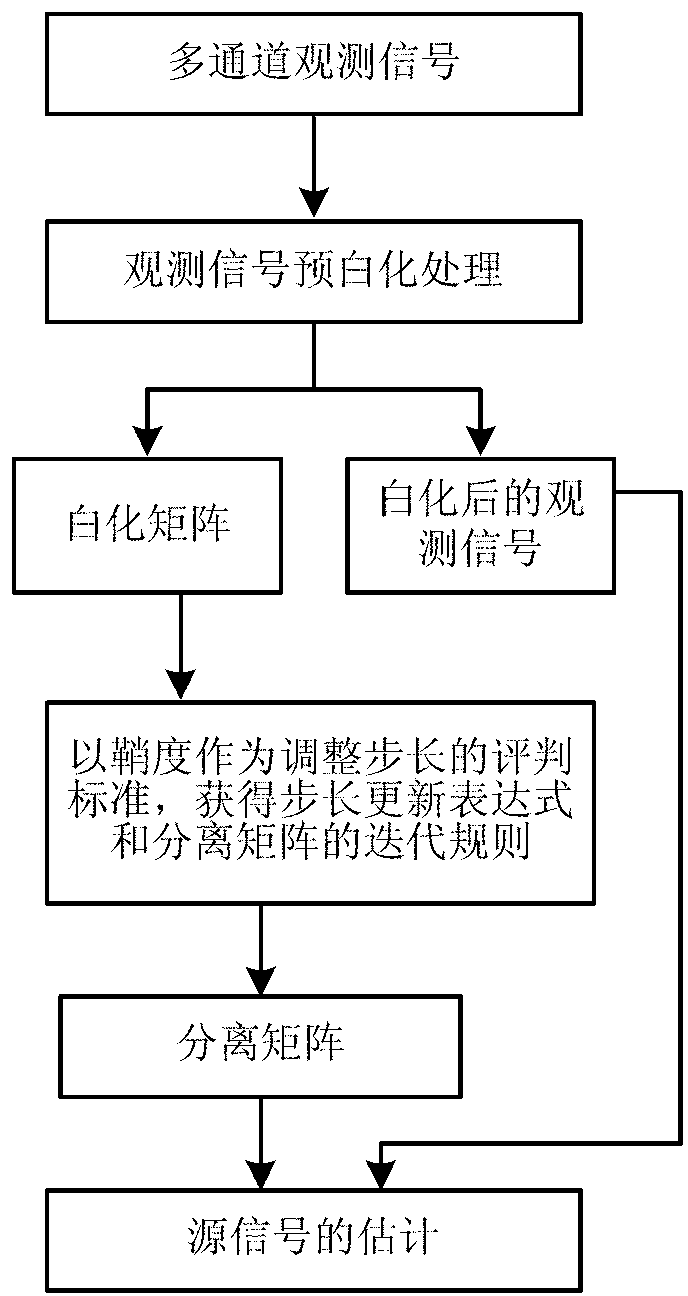
[0026] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific embodiment the present invention is described in further detail:
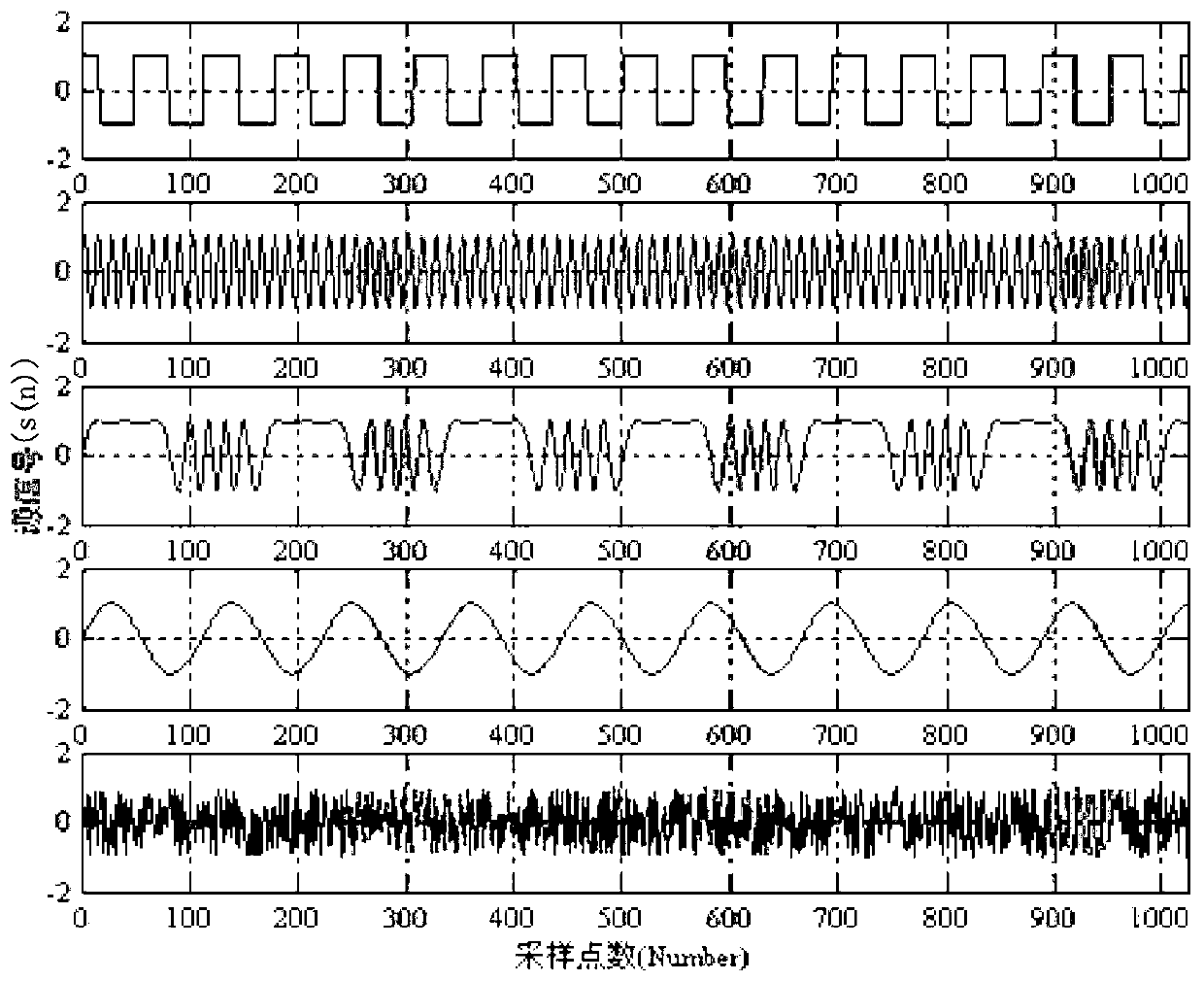
[0027] The present invention uses the change of kurtosis to adjust the step size online, and achieves the purpose of self-adaptation by continuously optimizing the separation matrix. The specific process is as follows figure 1 shown. Construct the following five source signals s1=sign(cos(2*π*155*x)), s2=sin(2*π*800*x), s3=sin(2*π*300*x+6*cos (2*π*60*x)), s4=sin(2*π*90*x), s5=2*rand(1,4000)-1
[0028] Combining the above five signals into a source signal S in sequence, the source signal is as follows figure 2 Shown, and multiply S by a randomly generated matrix A, the random matrix A is:
[0029]
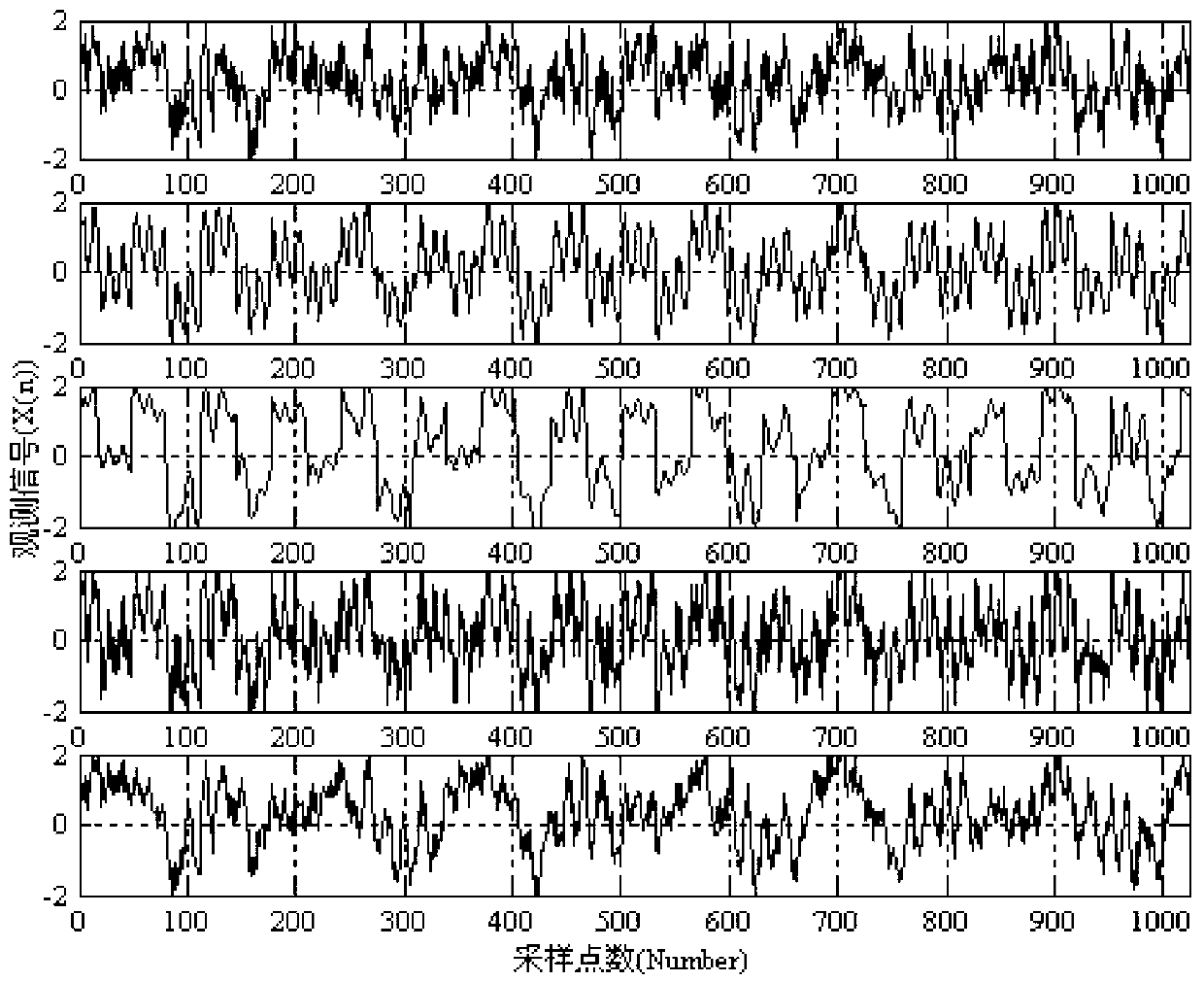
[0030] The resulting mixed signal is image 3 As shown, this is used as the observed signal for blind source separation. The results of blind source separation using the traditional EASI algorithm are as follows: Figure 4 shown.
[0031] T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com