DVFS-based energy-saving dispatching method for large-scale parallel tasks
A scheduling method and large-scale technology, applied in the field of distributed computing, can solve problems such as the inability to meet the dynamic needs of users and the inability to dynamically adjust the execution performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0064] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention is described in further detail:
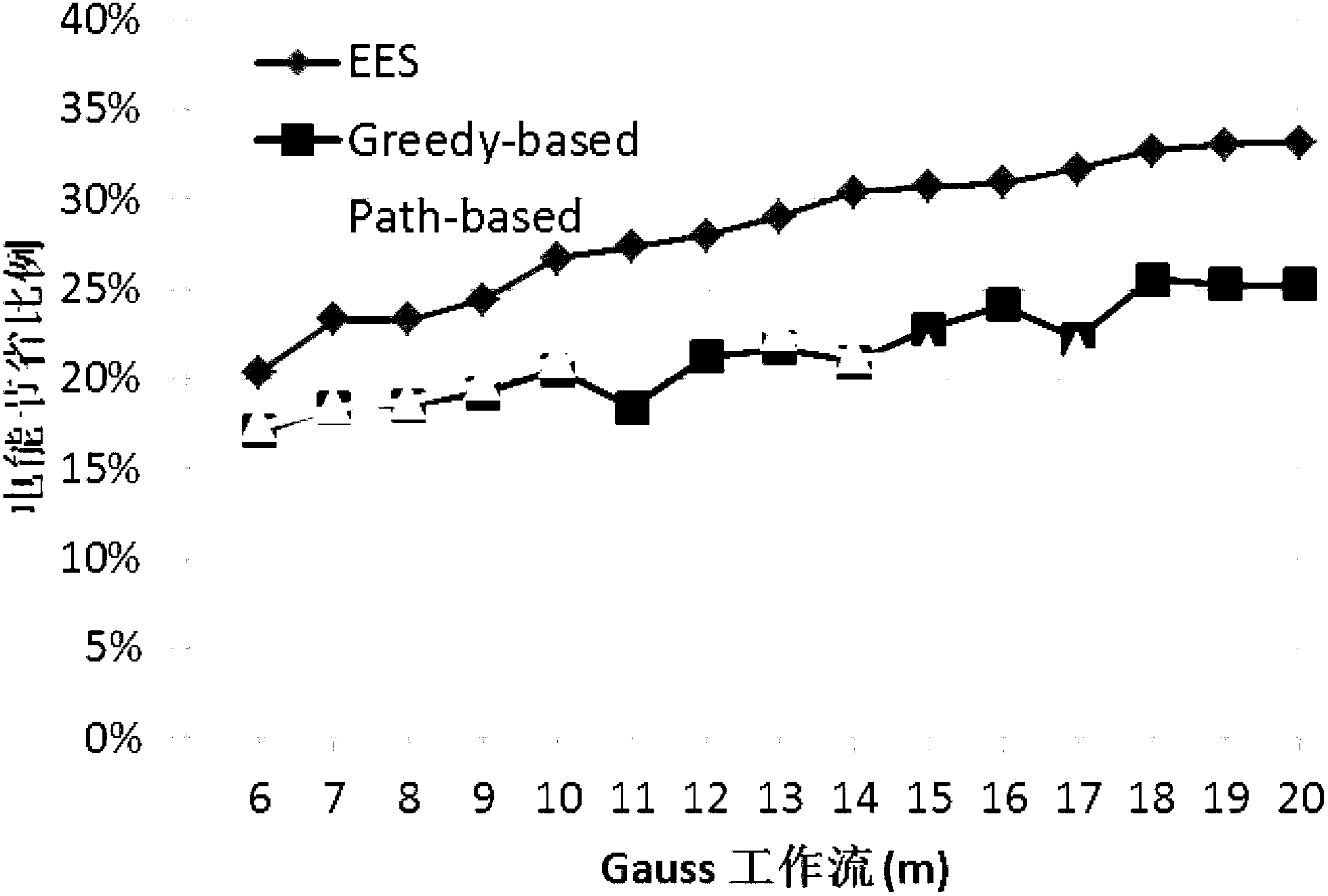
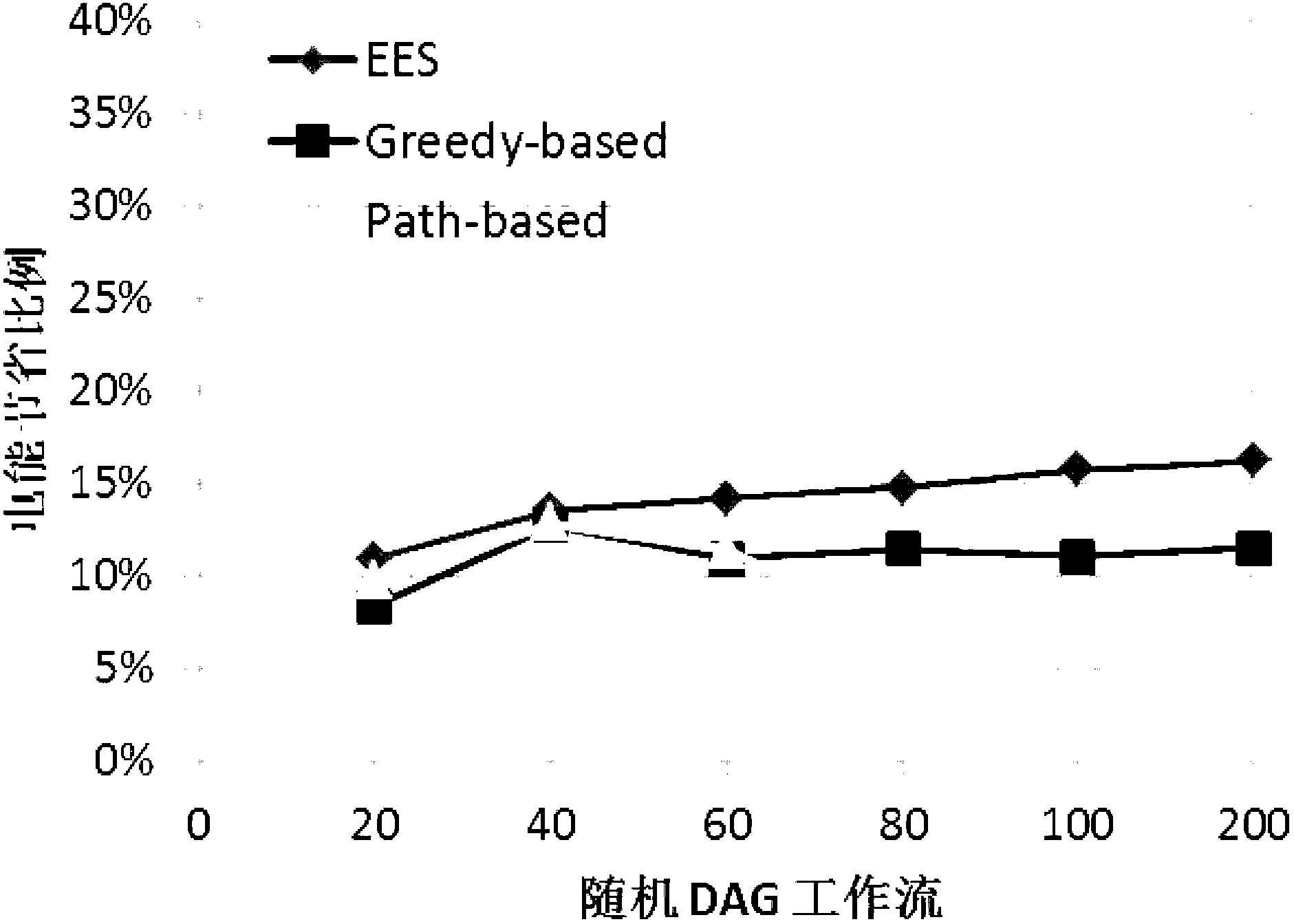
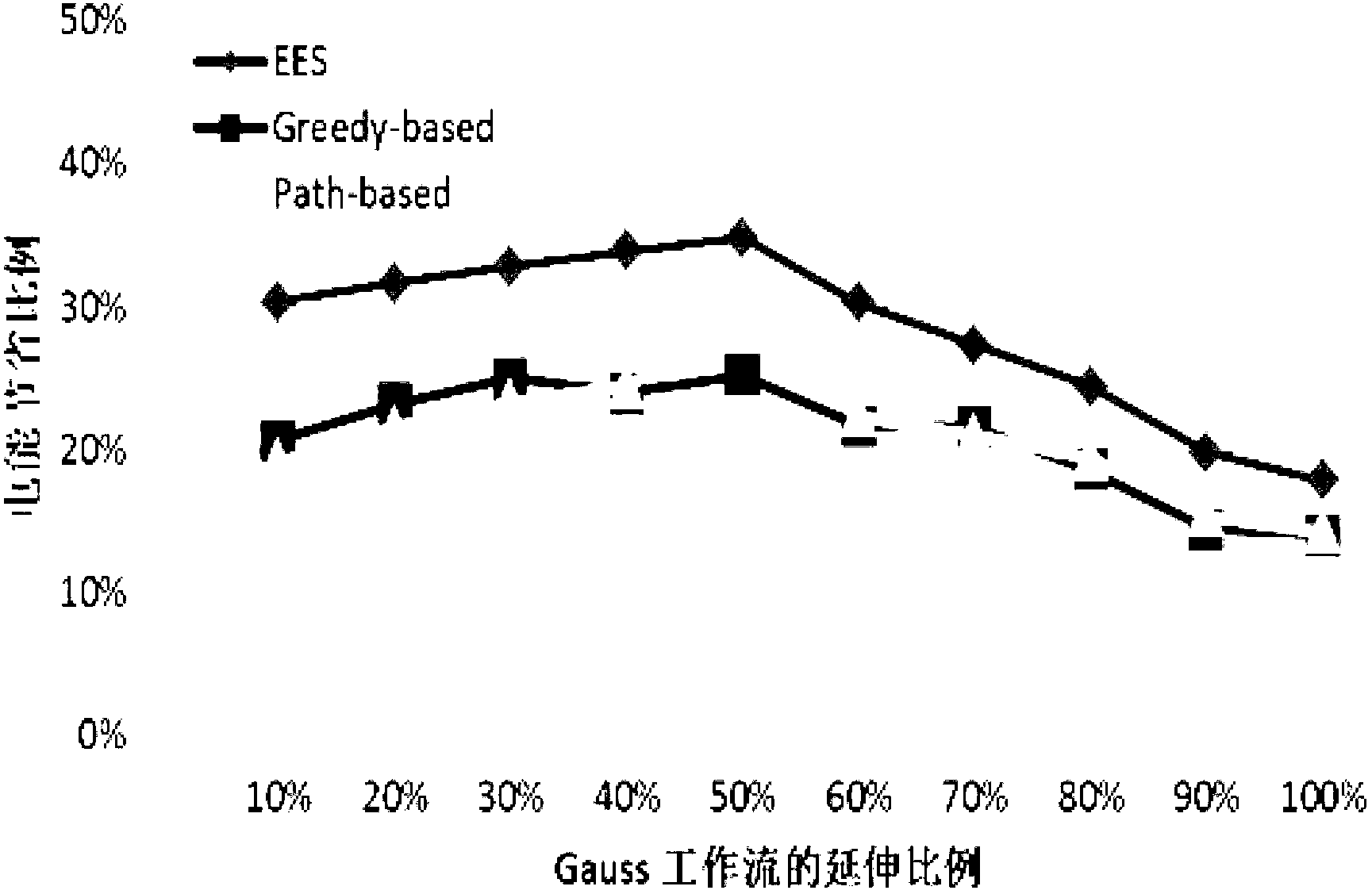
[0065] The present invention requires the server of the underlying cloud computing platform to support the DVFS technology. With the support of DVFS technology, a task scheduling model and an energy consumption model of parallel tasks are established, and a new heuristic energy-efficient scheduling method (Enhanced Energy-efficient Scheduling, referred to as EES) is proposed according to the model (which is the method of the present invention. English name, to facilitate the description of the comparison method later).
[0066] The formal description of the parallel task scheduling problem is as follows:
[0067] ●Distributed processing system: the collection of heterogeneous server processors in the system is denoted as P={p 1 ,p 2 ,...,p n}, for processor p i There are corresponding voltage and frequency sets: V i ={v i,1 , v i,2 ,...,v i,m}, F i ={f i,1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com