Compositions and methods of use for therapeutic low density lipoprotein-related protein 6 (LPR6) multivalent antibodies
A multivalent antibody, antibody technology, applied in the direction of antibody mimics/scaffolds, antibodies, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problems of loss of antibody activity, low efficiency, and troublesome purification of antibodies.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0636] Example 1: Determination of specific binding of anti-LRP6 antibodies to endogenous LRP6 by FACS
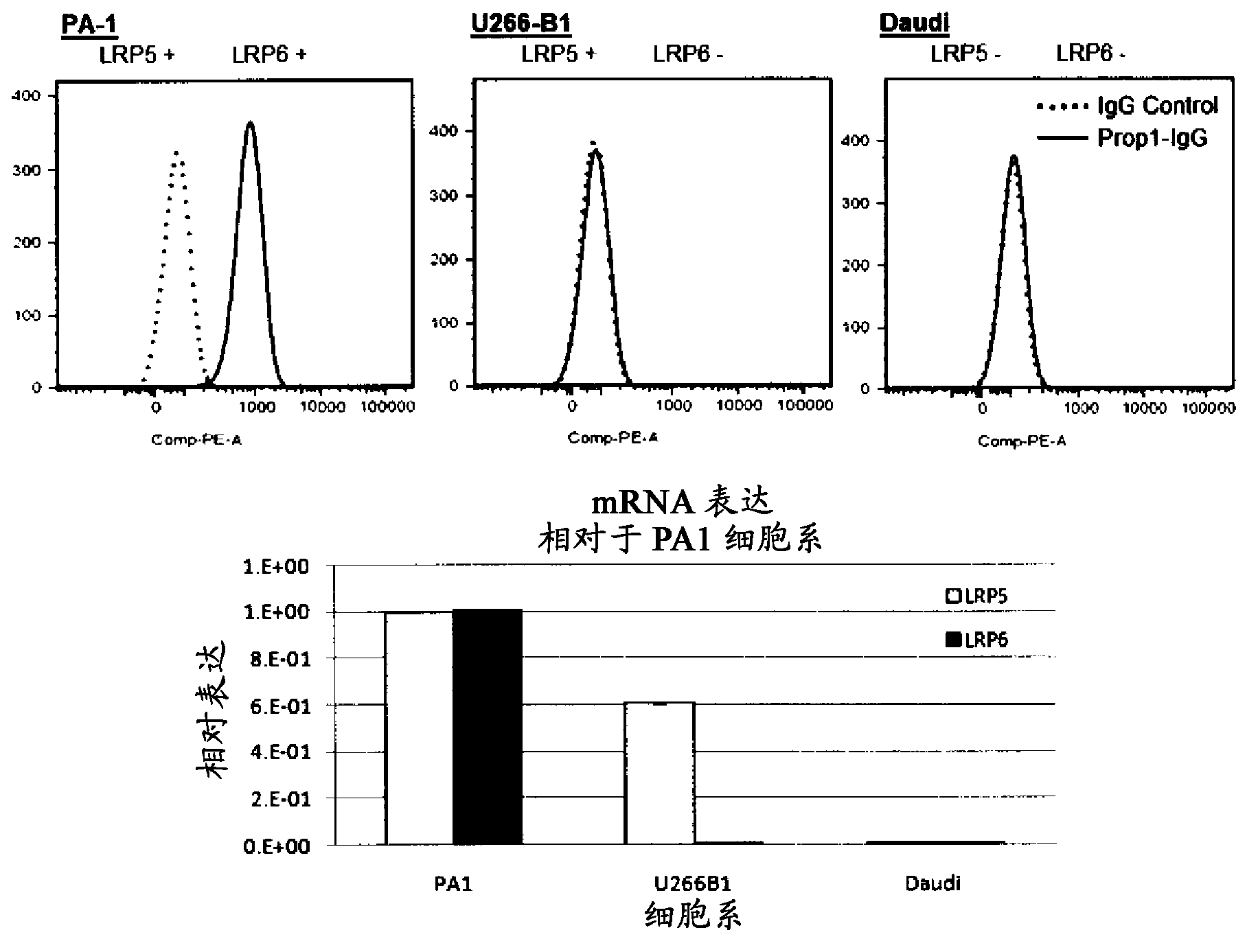
[0637] Detection of endogenous cell surface expression of LRP6 was examined on a number of tumor cells using anti-LRP6 antibodies and FACS analysis. as in Figure 1A As shown in , PA1 cells express LRP5 and LRP6 mRNA, while U266 and Daudi cells do not express LRP6 mRNA. PA1 cells, but not U266 and Daudi cells showed significant staining by Propeller 1 anti-LRP6 IgG. More importantly, U266 cells were not stained by anti-LRP6 antibody, although they expressed LRP6, indicating the specificity of anti-LRP6 antibody. Furthermore, when endogenous LRP6 was depleted using LRP6 shRNA, the staining of PA1 cells by anti-LRP6 antibody was significantly reduced, further indicating the specificity of LRP6 antibody.
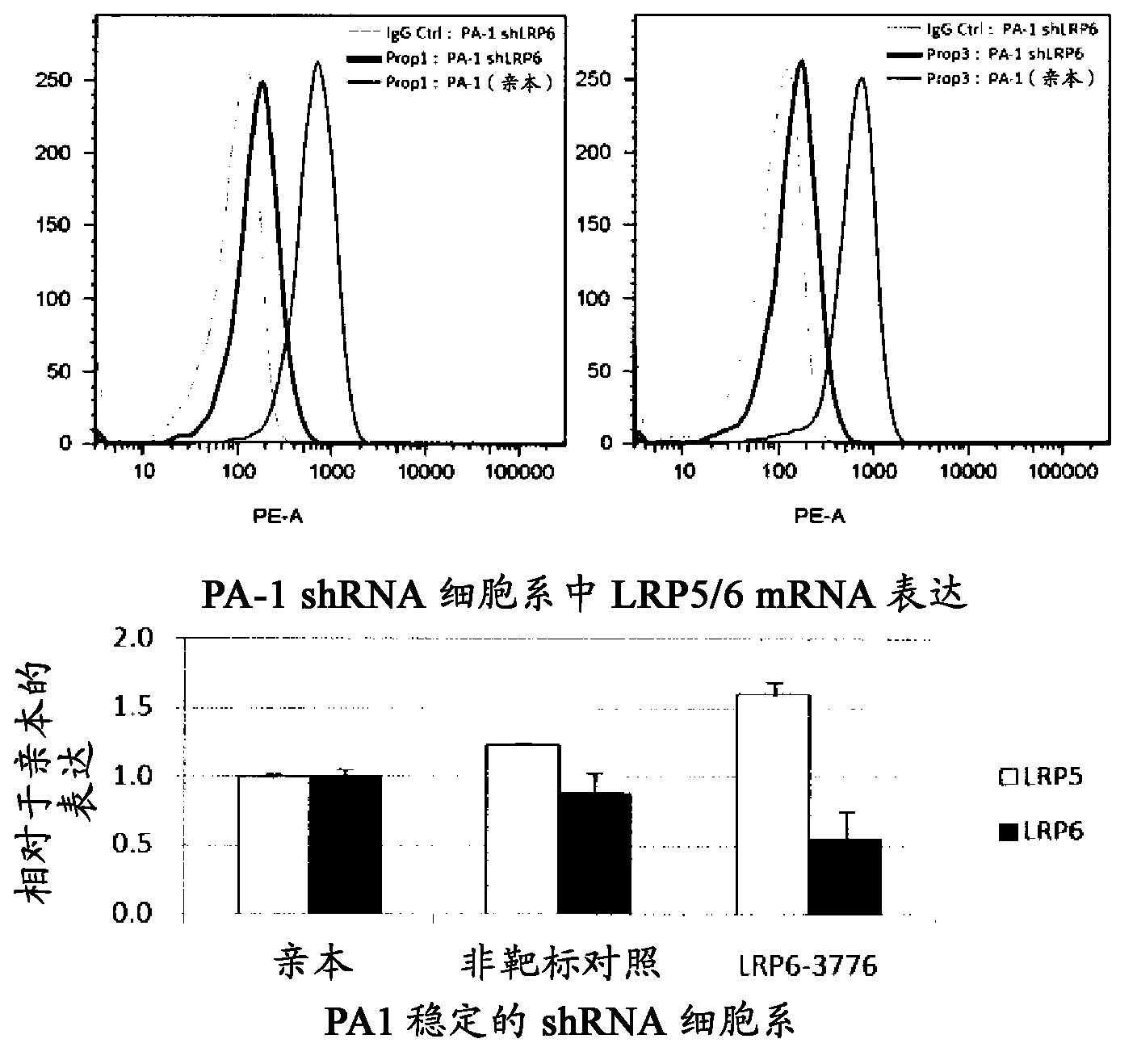
[0638] In other studies, the specificity of Prop1 and Prop3 for LRP6 was further confirmed by shRNA knockdown of LRP6 in PA1 cells (see Figure 1B ). Knockdown was achi...
Embodiment 2
[0639] Example 2: Differential inhibition of Wnt1 and Wnt3a reporter gene assays by Propeller 1 and Propeller 3 anti-LRP6 Fabs
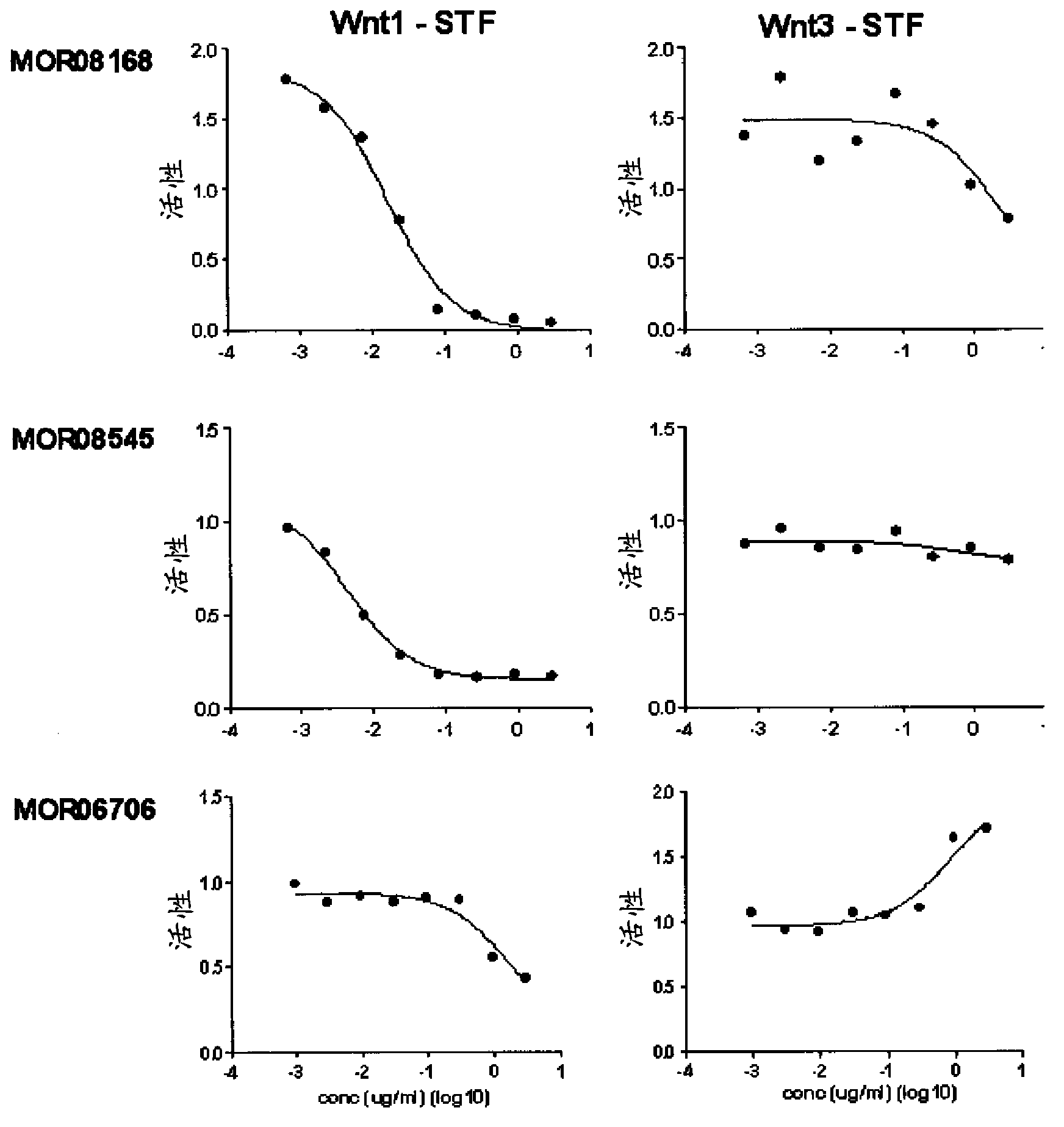
[0640] Different anti-LRP6 Fabs were tested in an in vitro Wnt reporter assay. Wnt1 or Wnt3A ligands (reporter gene assay) were transiently expressed in HEK293T / 17STF cells and treated with different concentrations of anti-LRP6 Fab fragments. STF assays were performed using the method described by Huang et al. (2009), Nature; 461 :614-20 (epublished September 16, 2009). as in Figure 2A As seen in Propeller 1 anti-LRP6 Fabs (MOR08168, MOR08545, MOR06706) specifically reduced Wnt1-dependent signaling without much effect on Wnt3A-dependent signaling. Conversely, as in Figure 2B As shown in Propeller 3 anti-LRP6 Fabs (MOR06475, MOR08193, MOR08473) specifically decreased Wnt3-dependent signal transduction without significant effect on Wnt1-dependent signal transduction. The results indicated that Wnt1 and Wnt3A activities were blocked separately by ...
Embodiment 3
[0641] Example 3: Binding of anti-LRP6 antibodies to LRP6 from different species
[0642] To show cross-reactivity, cells expressing endogenous LRP of human (HEK293T / 17) and mouse origin (NIH 3T3) or transiently transfected HEK293 / T17 cells expressing macaque LRP6 were treated as described above and subjected to Flow Cytometry. image 3 The findings were summarized and shown that all anti-LRP6 antibodies bound human, mouse and macaque LRP6.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com