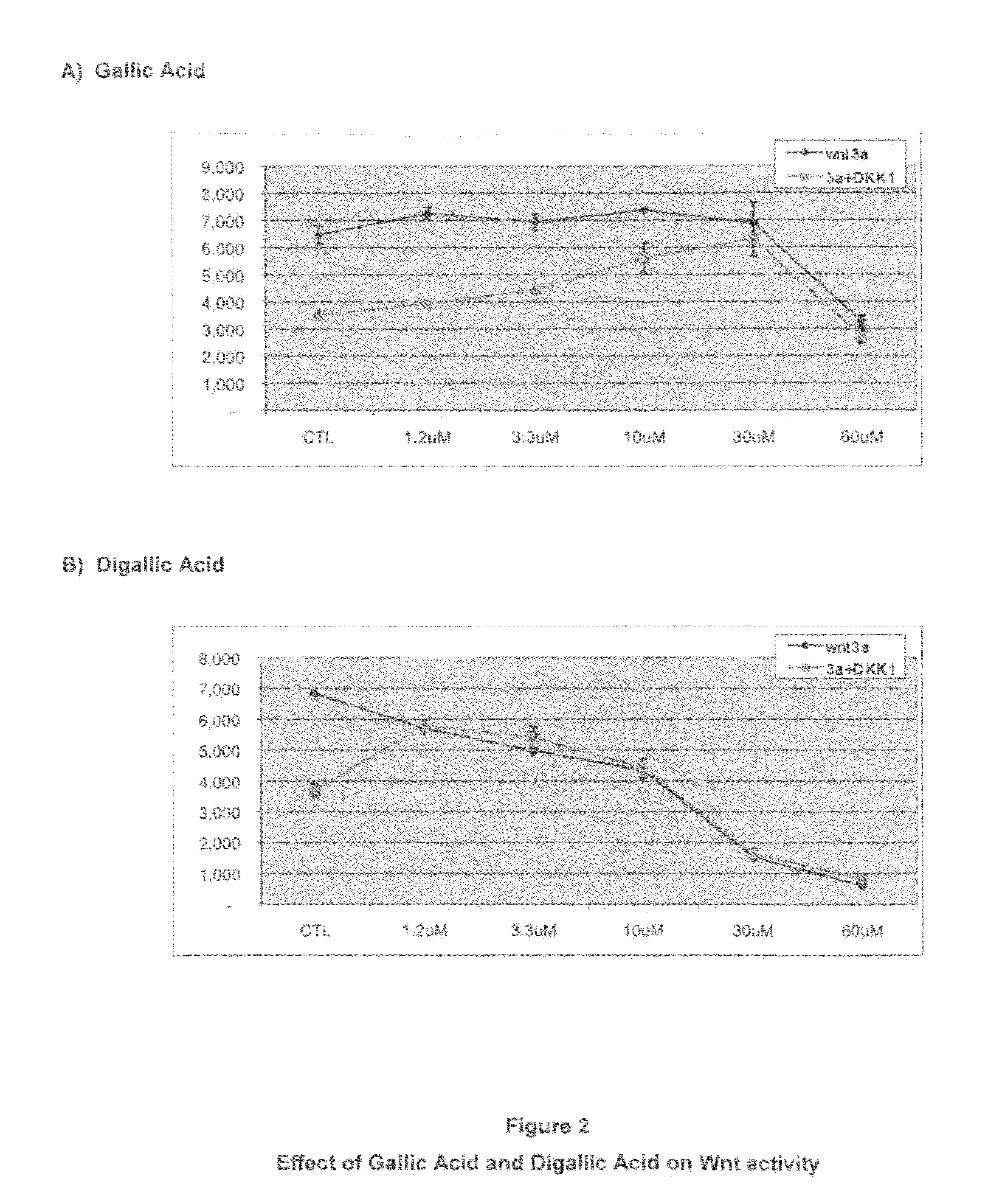
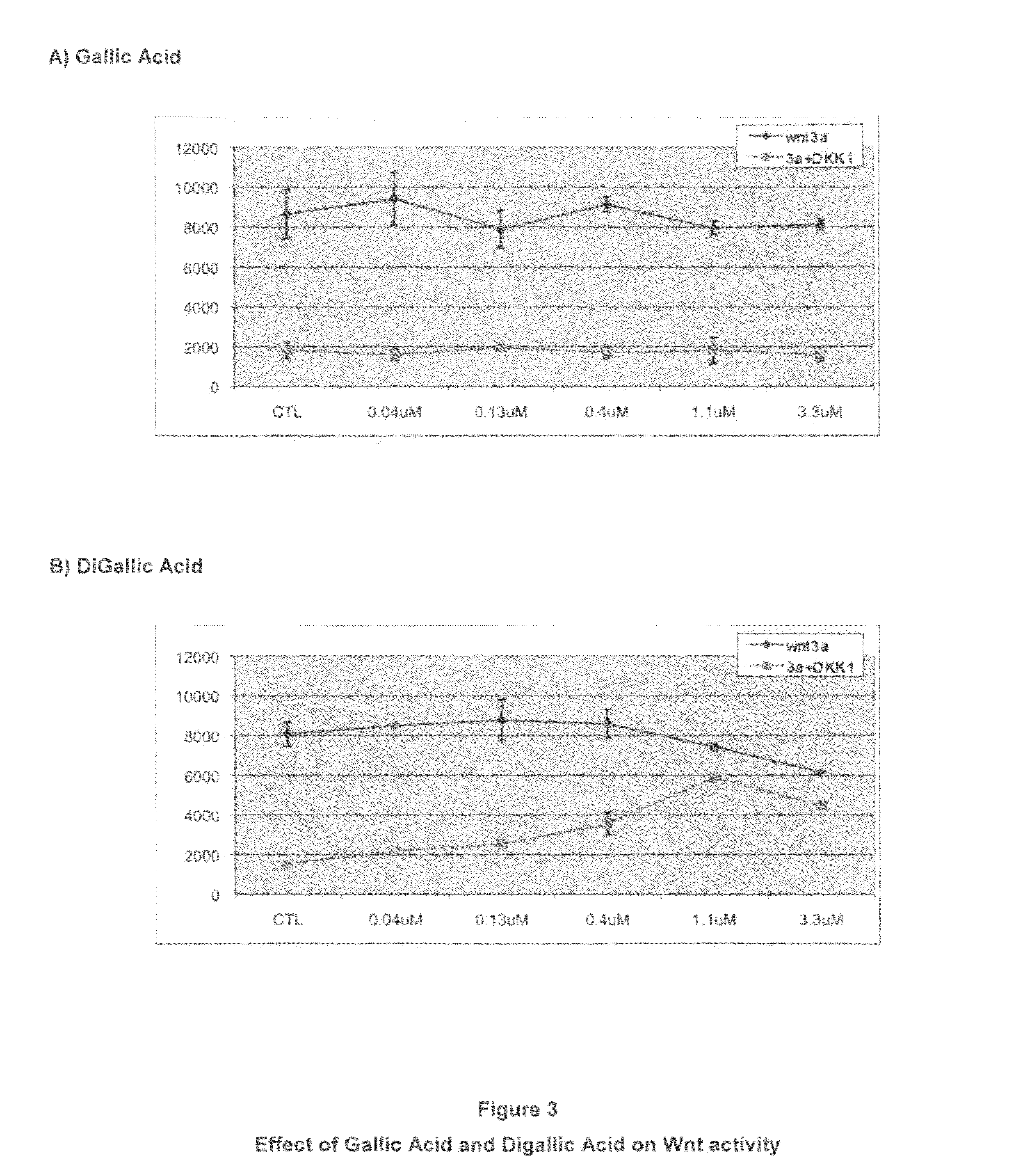
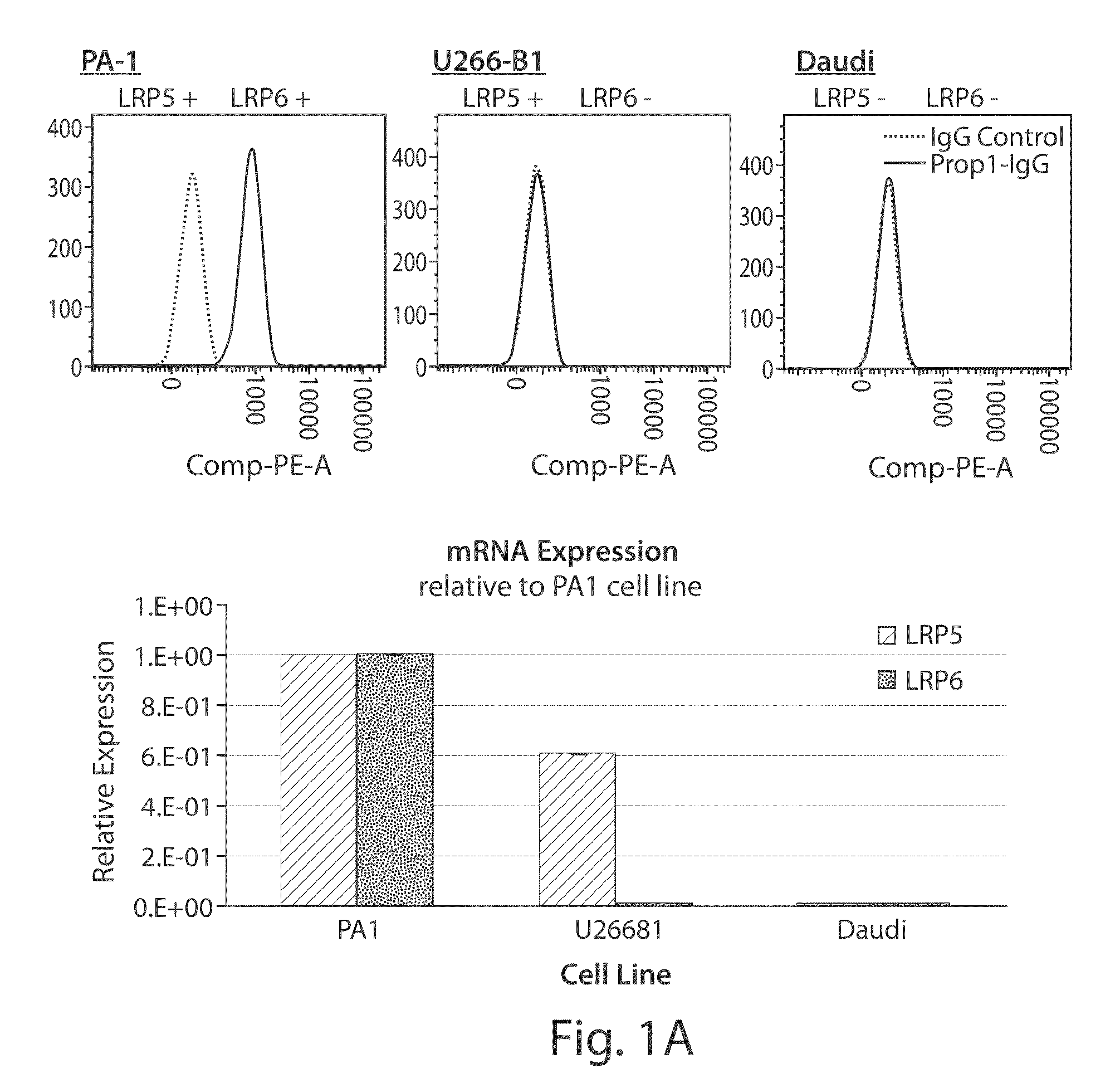
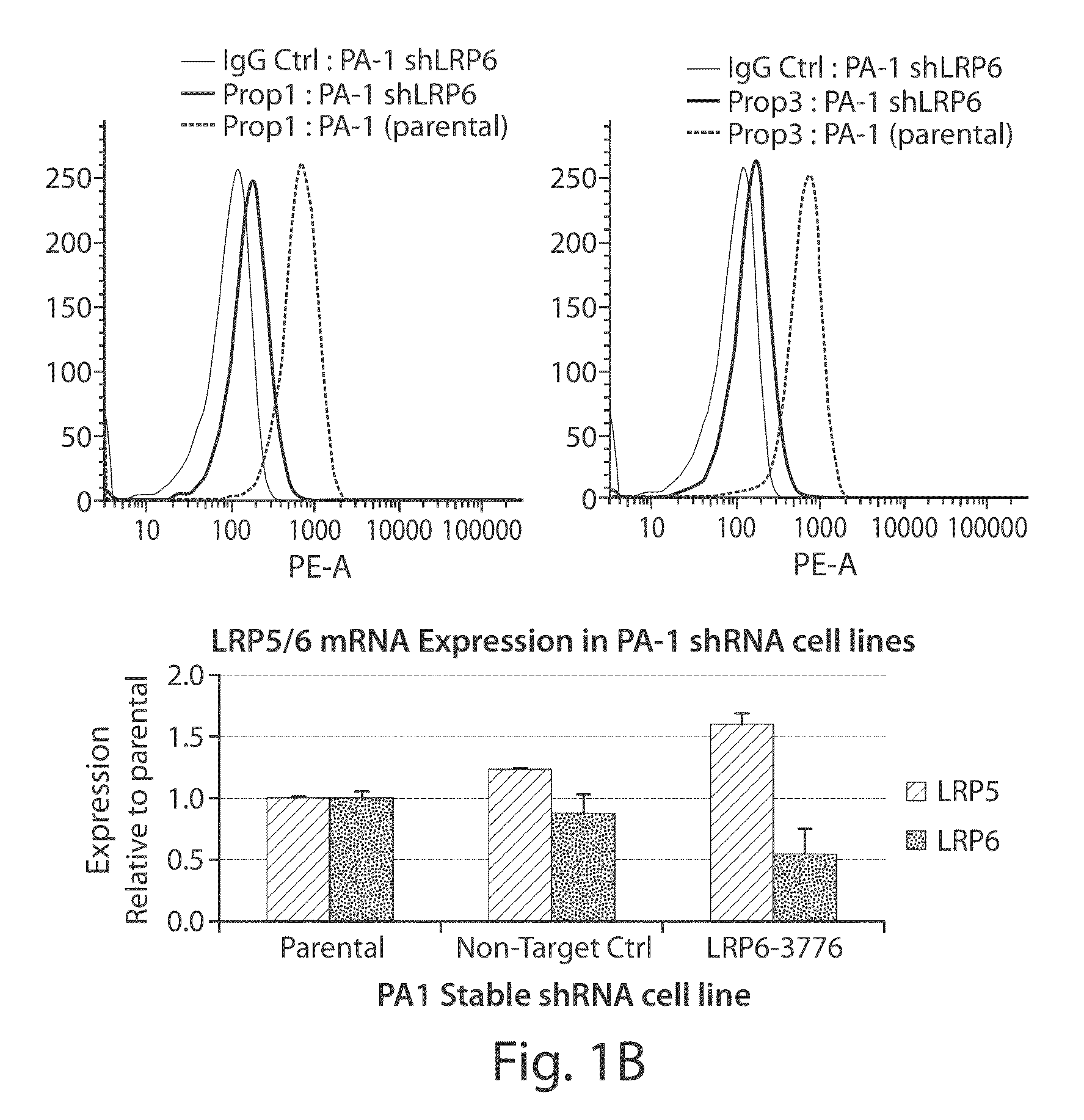
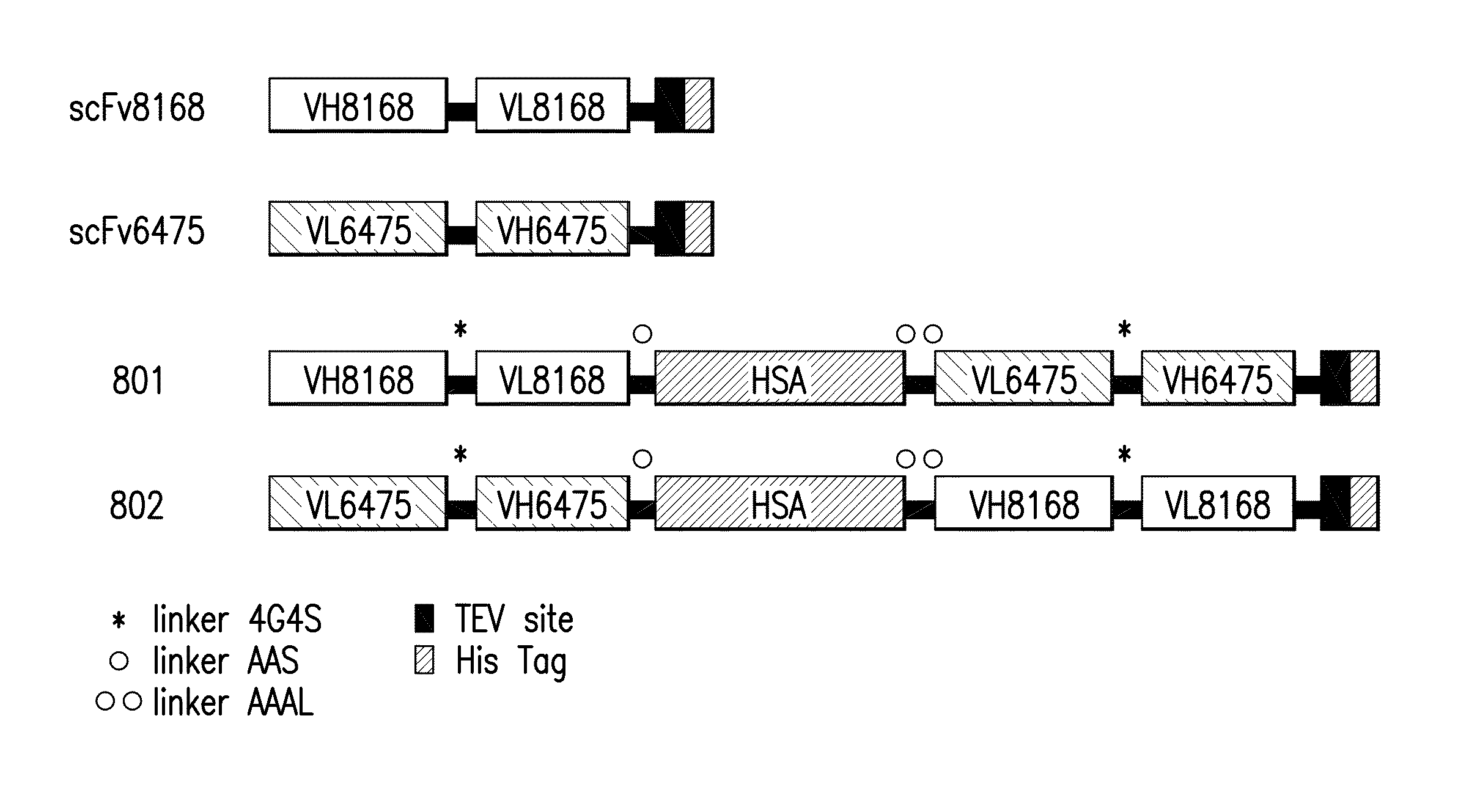
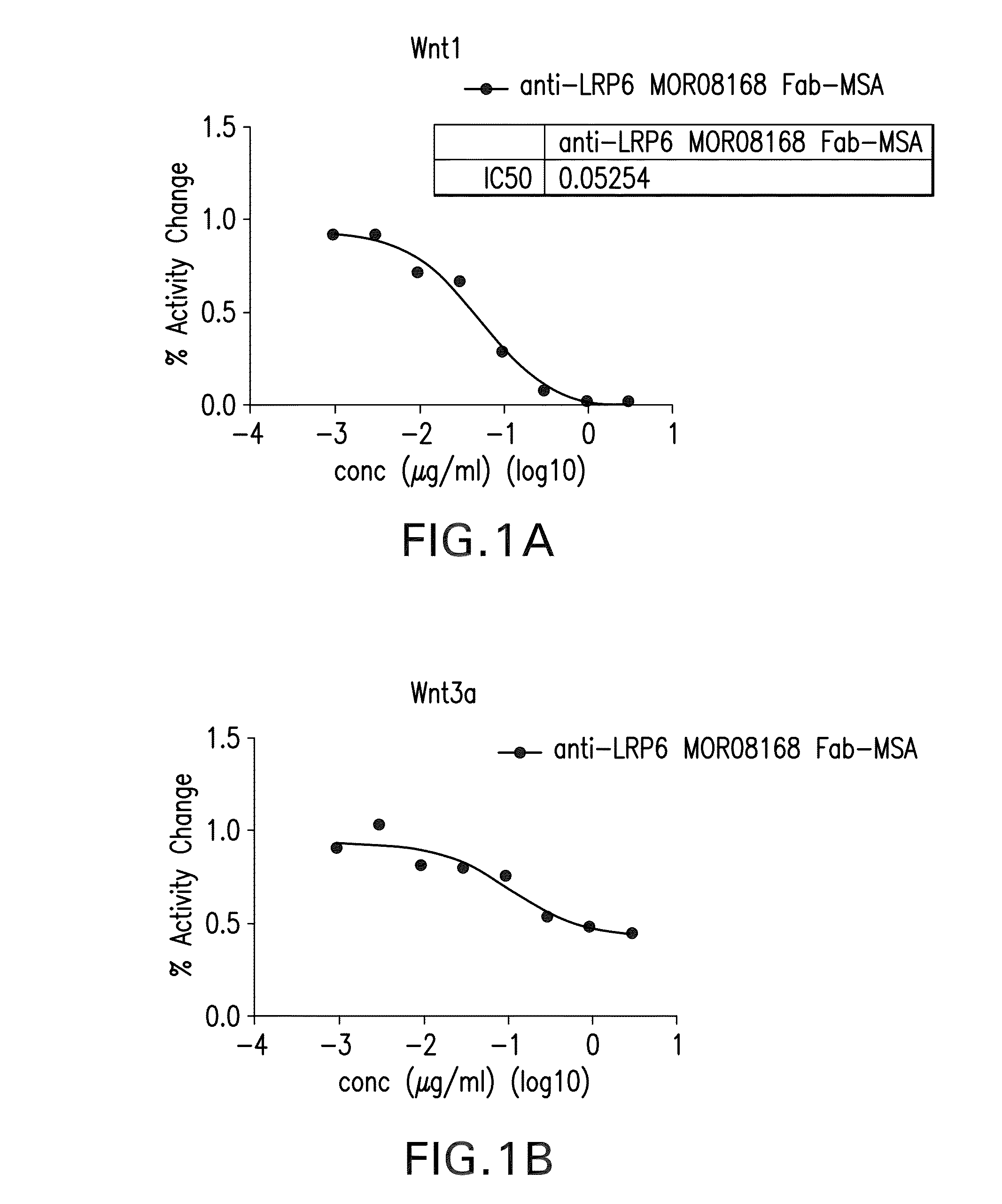
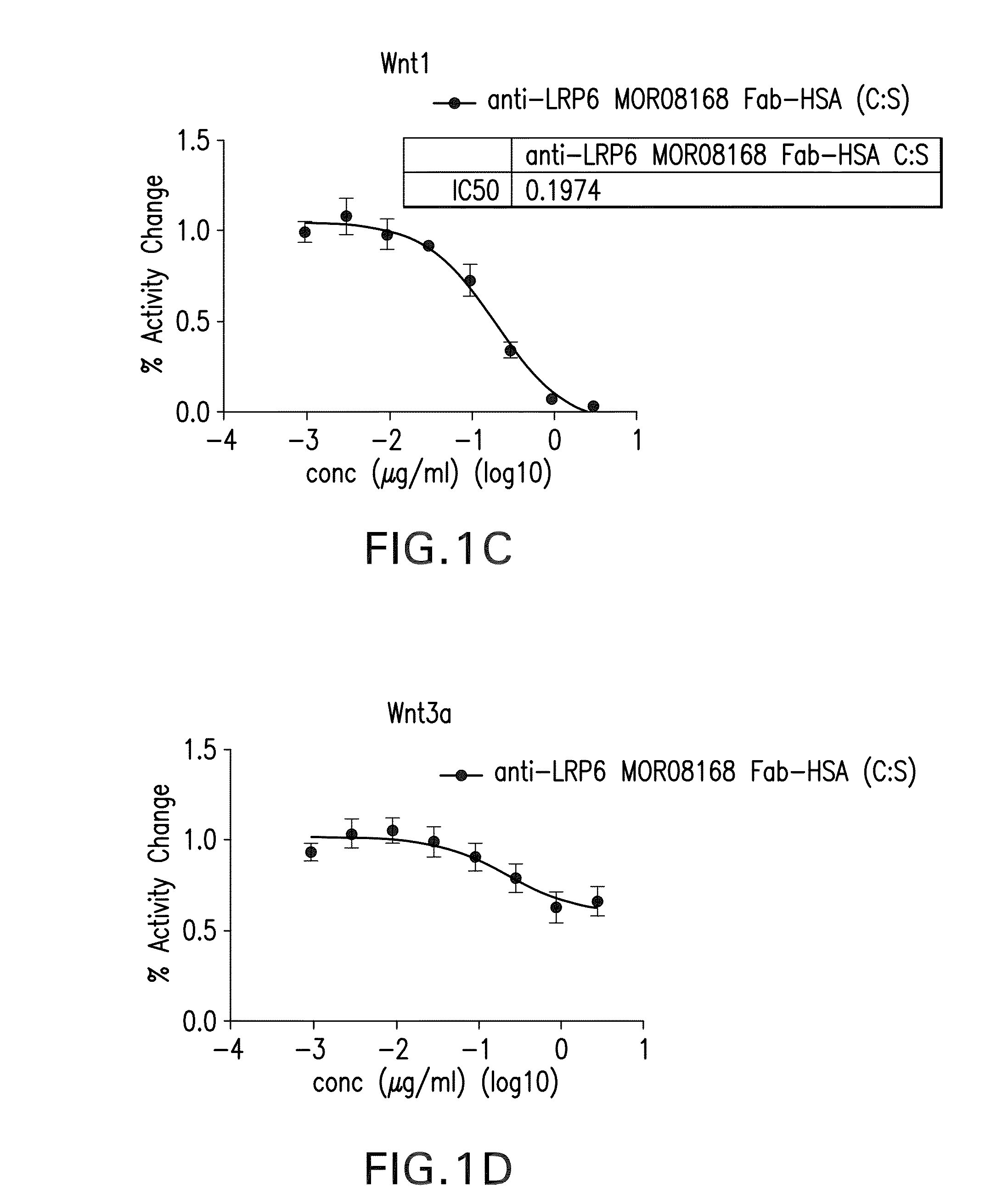
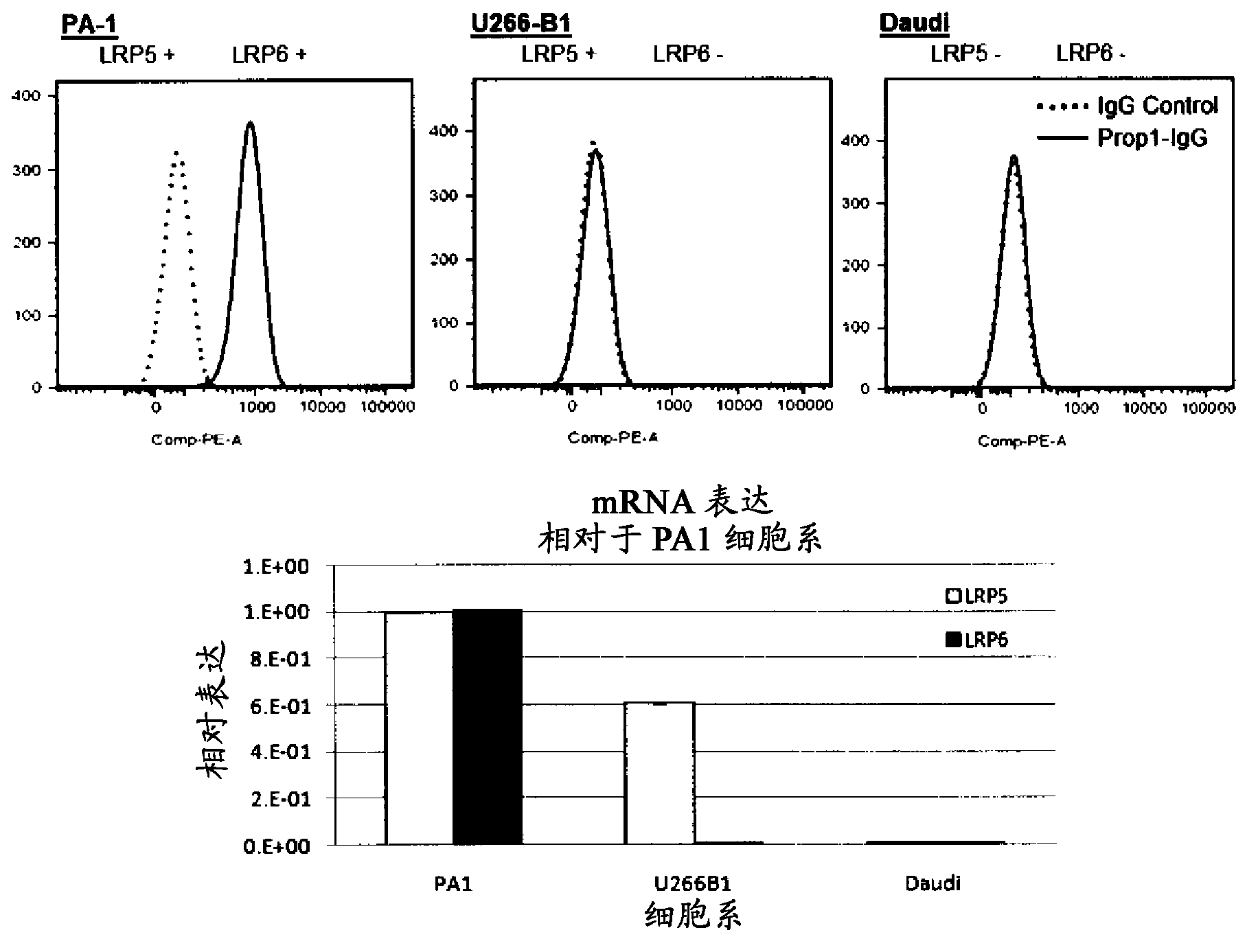
Patents
Literature
33 results about "LRP6" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
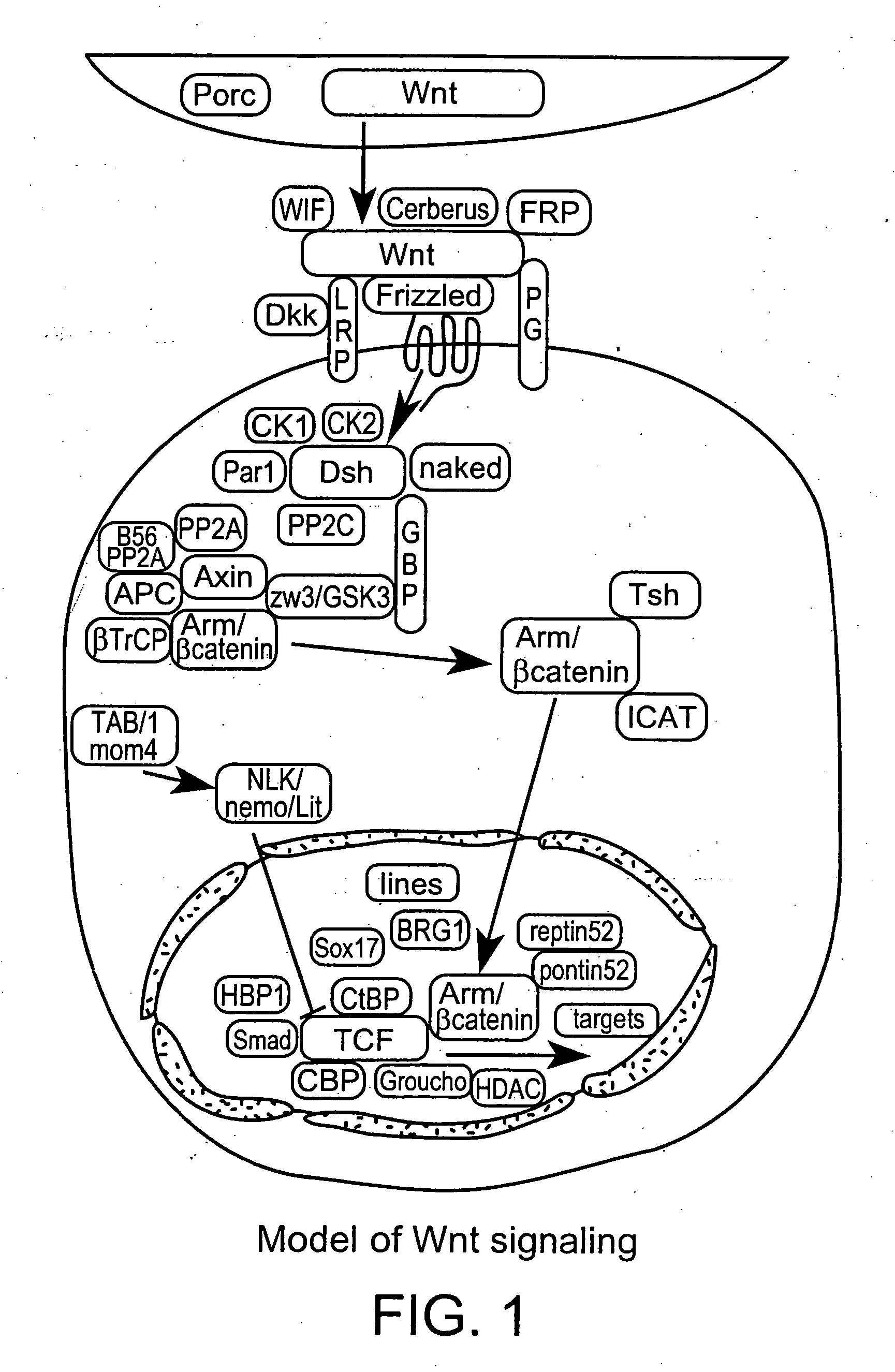
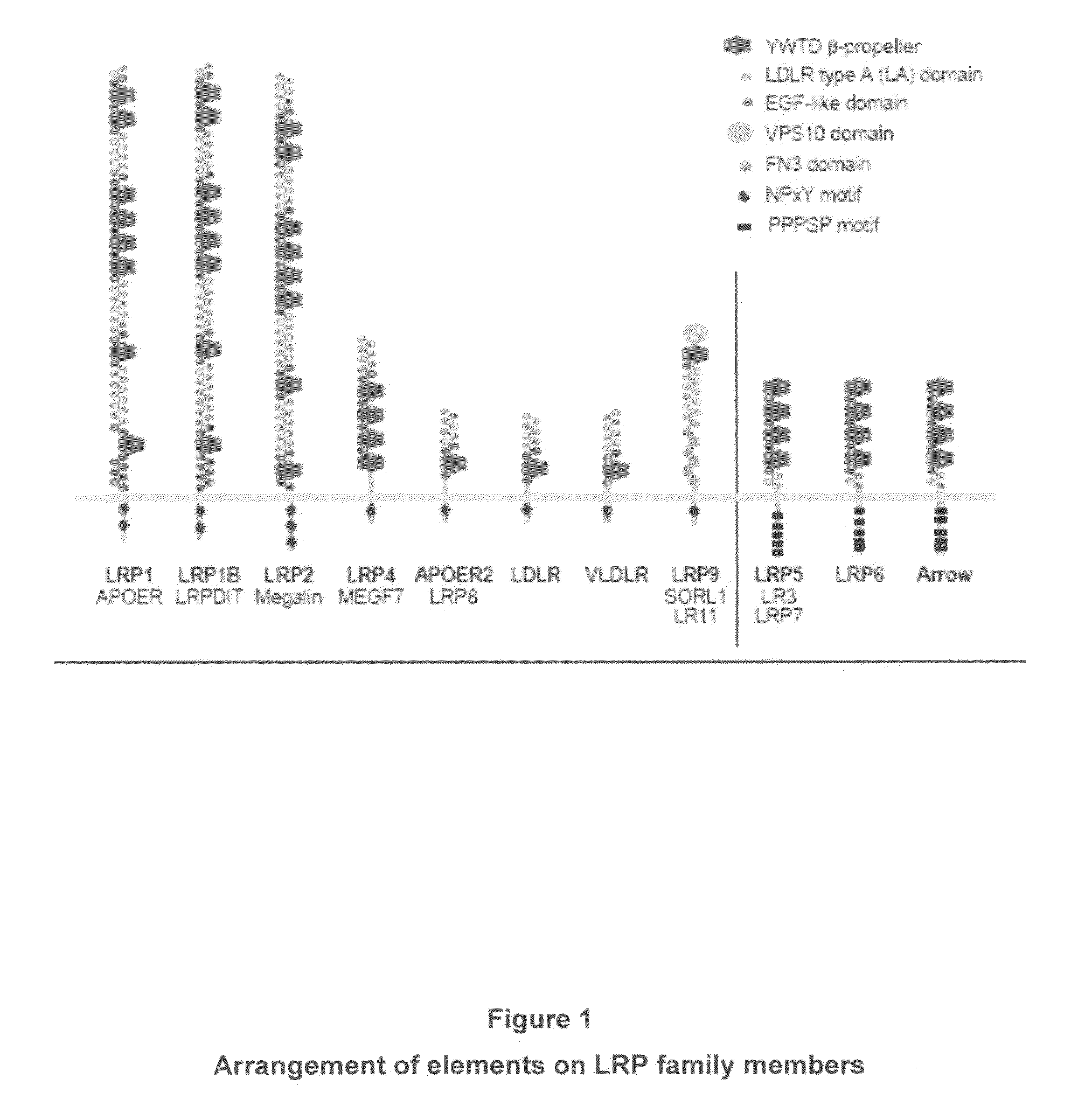
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRP6 gene. LRP6 is a key component of the LRP5/LRP6/Frizzled co-receptor group that is involved in canonical Wnt pathway.
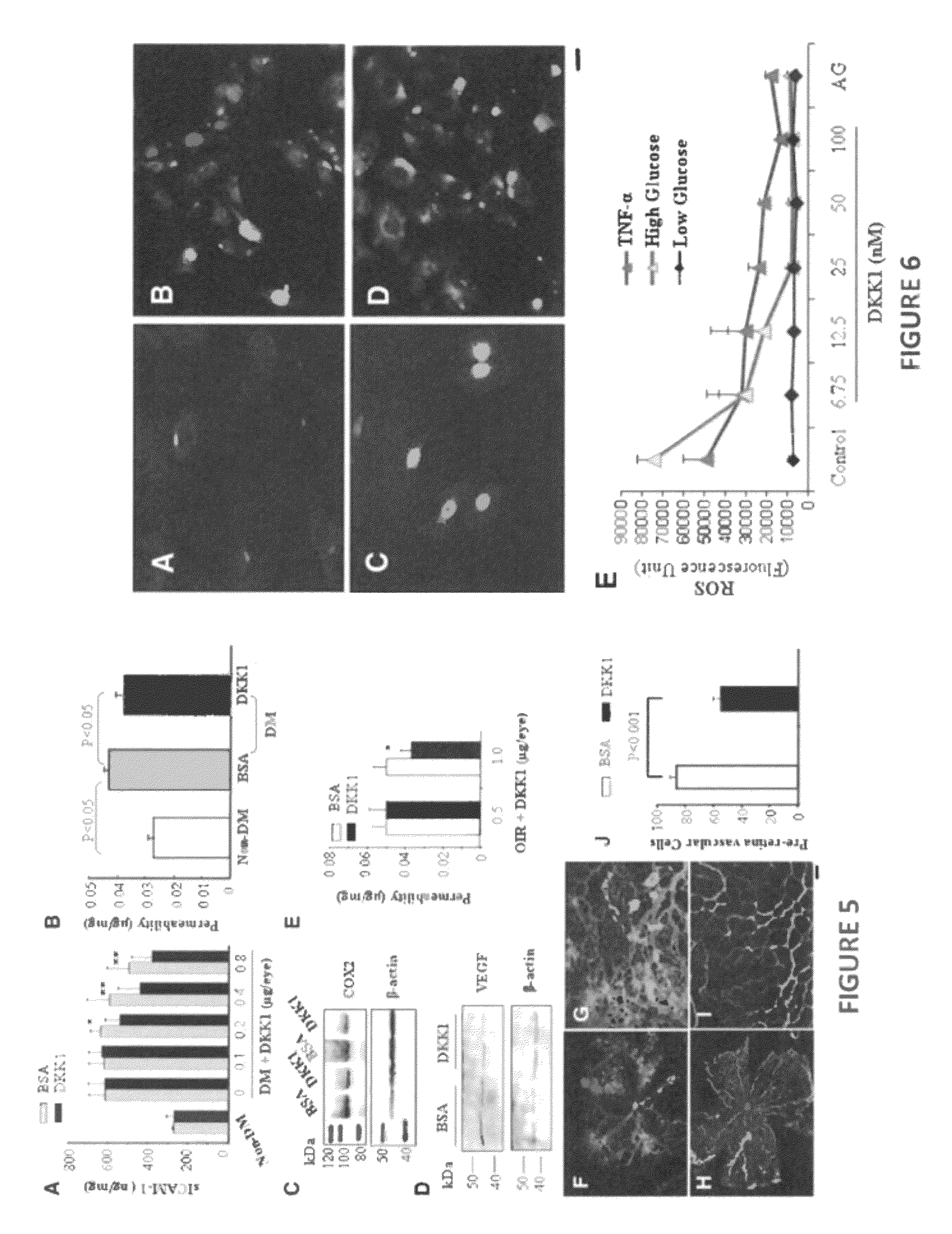
Reagents and method for modulating Dkk-mediated interactions
The present invention provides reagents, compounds, compositions, and methods relating to novel interactions of the extracellular domain of LRP5, HBM (a variant of LRP5), and / or LRP6 with Dkk, including Dkk-1. The various nucleic acids, polypeptides, antibodies, assay methods, diagnostic methods, and methods of treatment of the present invention are related to and impact on Dkk, LRP5, LRP6, HBM, and Wnt signaling. Dkk, LRP5, LRP6, HBM, and Wnt are implicated in bone and lipid cellular signaling. Thus, the present invention provides reagents and methods for modulating lipid levels and / or bone mass and is useful in the treatment and diagnosis of abnormal lipid levels and bone mass disorders, such as osteoporosis.
Owner:GENOME THERAPEUTICS
Reagents and method for modulating Dkk-mediated interactions
The present invention provides reagents, compounds, compositions, and methods relating to novel interactions of the extracellular domain of LRP5, HBM (a variant of LRP5), and / or LRP6 with Dkk, including Dkk-1. The various nucleic acids, polypeptides, antibodies, assay methods, diagnostic methods, and methods of treatment of the present invention are related to and impact on Dkk, LRP5, LRP6, HBM, and Wnt signaling. Dkk, LRP5, LRP6, HBM, and Wnt are implicated in bone and lipid cellular signaling. Thus, the present invention provides reagents and methods for modulating lipid levels and / or bone mass and is useful in the treatment and diagnosis of abnormal lipid levels and bone mass disorders, such as osteoporosis.
Owner:GENOME THERAPEUTICS
Low-density lipoprotein receptor 6 (LRP6) as a mammary stem cell marker and related methods
A method for enriching a population of somatic mammary stem cells or mammary tumor stem cells based on low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 (LRP6). Also included are methods for screening for LRP6 modulators, as well as methods for reducing Wnt signaling, for treating Wnt signaling-related diseases, for detecting mammary basal-like cells, for diagnosing basal-like breast cancer, and for inhibiting proliferation of a tumor expressing LRP6, and compositions thereof.
Owner:VAN ANDEL RES INST
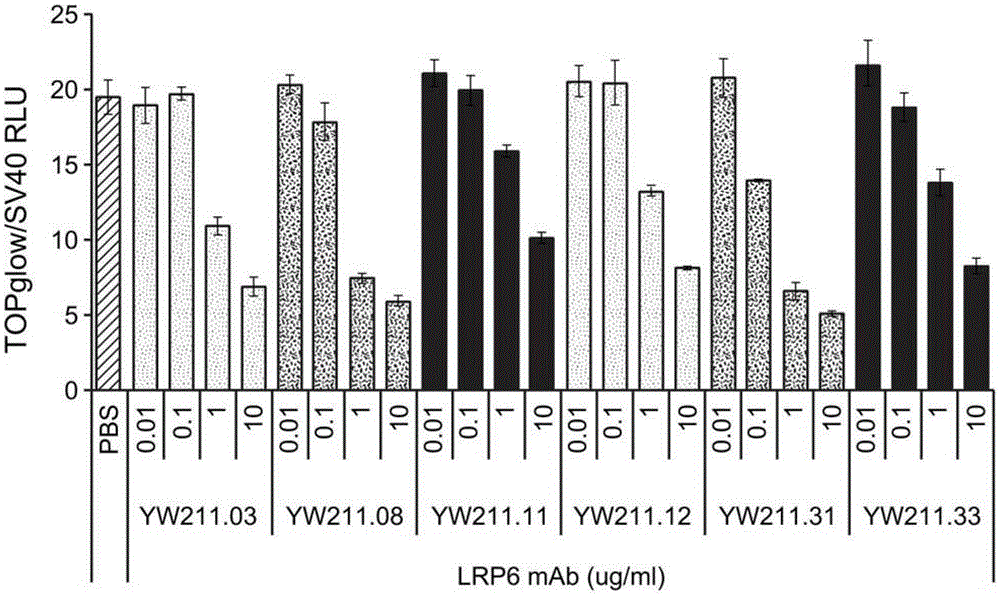
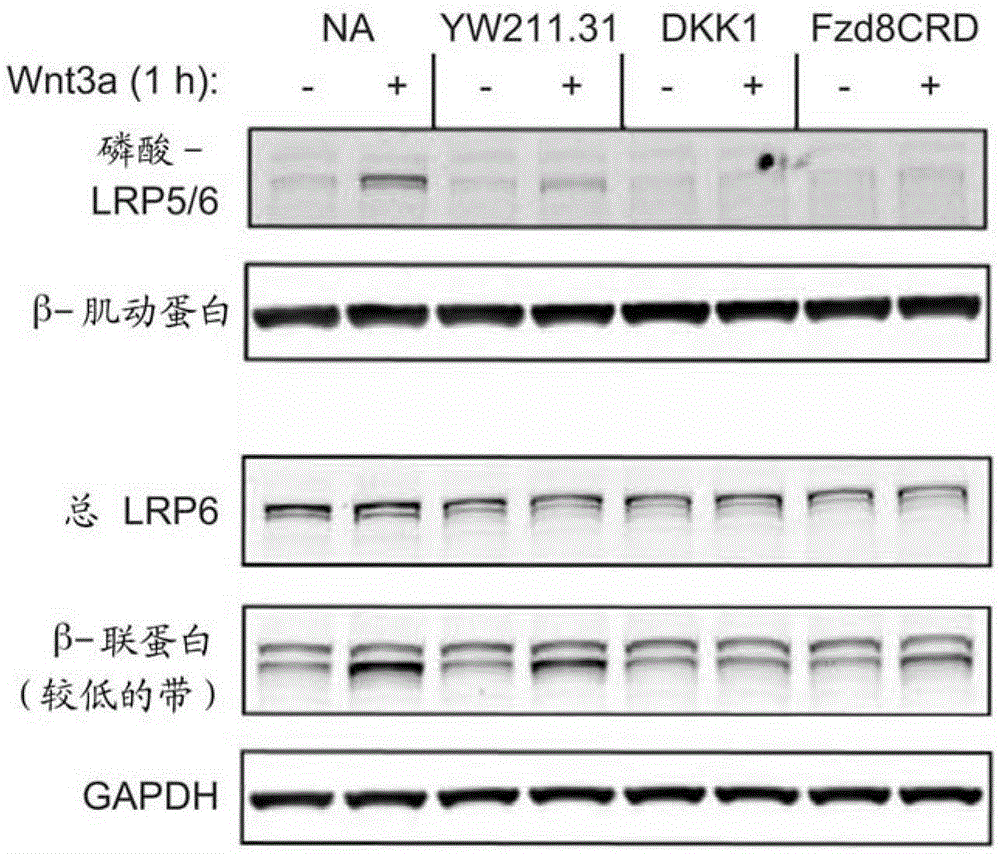
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES THAT INHIBIT THE Wnt SIGNALING PATHWAY AND METHODS OF PRODUCTION AND USE THEREOF
Monoclonal antibodies against LRP6 and that block the Wnt signaling pathway are disclosed. Methods of production and use thereof are also disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Methods for treating inflammation
The present invention relates to the field of therapeutic methods, compositions and uses thereof, that affect, directly or indirectly, the behavior of LRP receptors. These compositions and methods result in the treatment of inflammatory, immunological and metabolic conditions. More particularly, the methods and compositions of the invention are directed to the identification of small molecules, drugs and / or pharmacological agents that affect the Wnt pathway by affecting normal complex formation among various signaling receptors, the LRP5 and LRP6 receptor, and related ligands.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
Therapeutic low density lipoprotein-related protein 6 (LRP6) multivalent antibodies
ActiveUS9290573B2Expanded repertoireImprove effectivenessAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMuscular disorderAntigenVery low-density lipoprotein
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Low density lipoprotein - related protein 6 (LRP6) - half life extender constructs
ActiveUS20140050725A1Extended half-lifeInhibiting Wnt signalingPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLRP6A lipoprotein
The present invention relates to LRP6 constructs that bind to LRP6 receptor. The LRP6 constructs comprise at least one LRP6 binding moiety and a half-life extender molecule such that the LRP6 construct inhibit the Wnt signaling pathway without potentiation of the Wnt signal. The LRP6 constructs also have an increased half-life to provide more time for the therapeutic benefit.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Compositions and methods of use for therapeutic low density lipoprotein-related protein 6 (LPR6) multivalent antibodies
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
HBM variants that modulate bone mass and lipid levels
The present invention relates to methods and materials used to express an HBM-like polypeptide derived from HBM, LRP5 or LRP6 in animal cells and transgenic animals. The present invention also relates to transgenic animals expressing the HBM-like polypeptides. The invention provides nucleic acids, including coding sequences, oligonucleotide primers and probes, proteins, cloning vectors, expression vectors, transformed hosts, methods of developing pharmaceutical compositions, methods of identifying molecules involved in bone development, and methods of diagnosing and treating diseases involved in bone development and lipid modulation. In preferred embodiments, the present invention is directed to methods for treating, diagnosing and preventing osteoporosis.
Owner:GENOME THERAPEUTICS +1
Mutant Lrp5/6 Wnt-Signaling Receptors in Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment
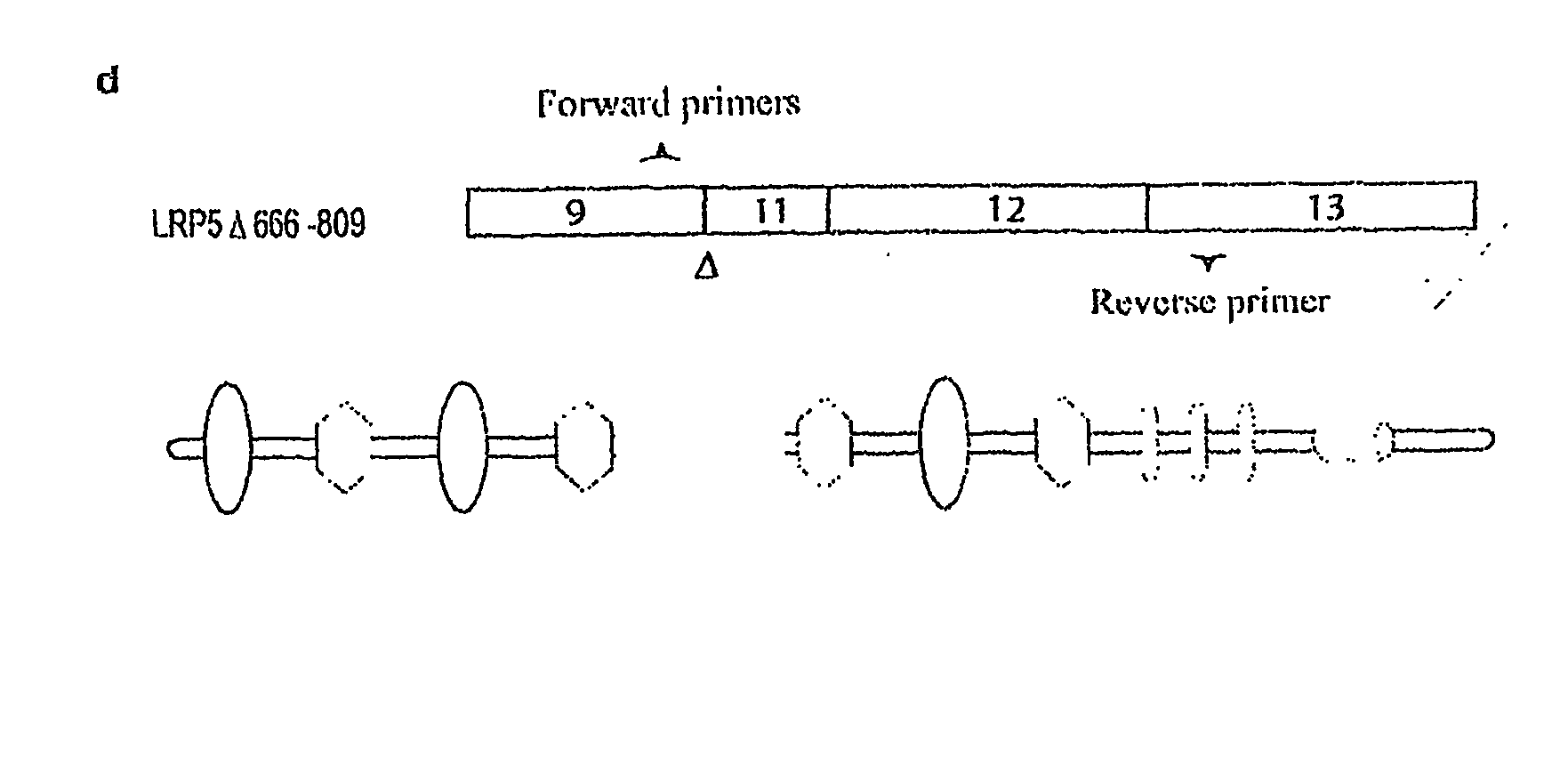
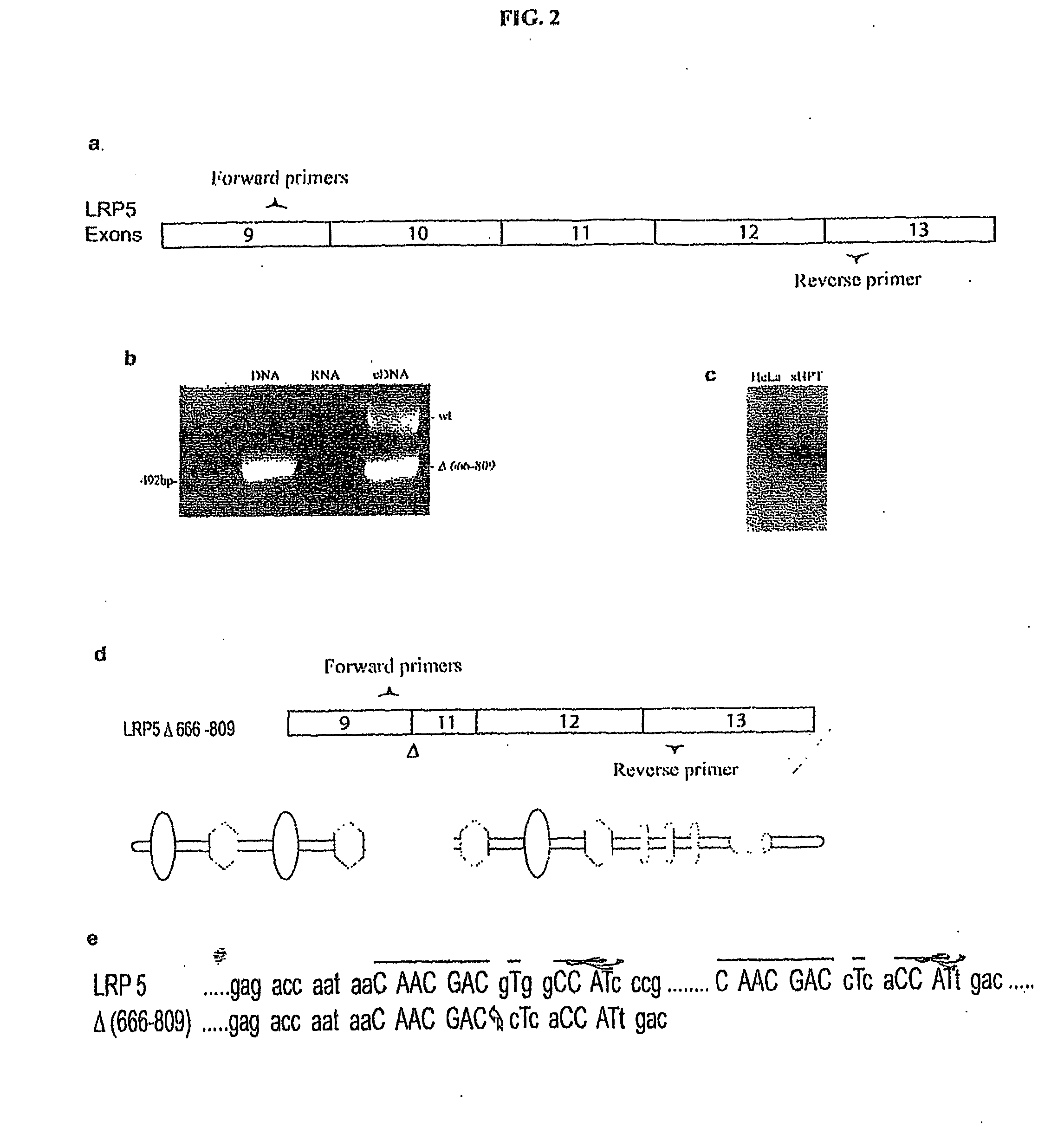
A novel mutant form of lrp5 and lrp6 genes, the mutant LRP5 and LRP6 receptor proteins expressed therefrom, and a cell line which expresses the mutant LRP5 and / or LRP6 receptor proteins. Methods of diagnosing, prognosing and treating LRP5 related diseases, specifically hyperthyroidism and parathyroid tumors, and kits suitable for rapid on-site testing. Finally, methods of screening for agents capable of modulating the mutant LRP5 or LRP6 receptor proteins and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the selected agents.
Owner:BIOINVENT INT AB
Monoclonal antibodies that inhibit the wnt signaling pathway and methods of production and use thereof
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Method for regulating cellular pathway by using plant hormone ABA (Abscisic Acid) and small molecular substance PYR (Pyrabactin)
InactiveCN108410909AAvoid damageConvenient inductionVectorsVector-based foreign material introductionPlant hormoneCellular pathways
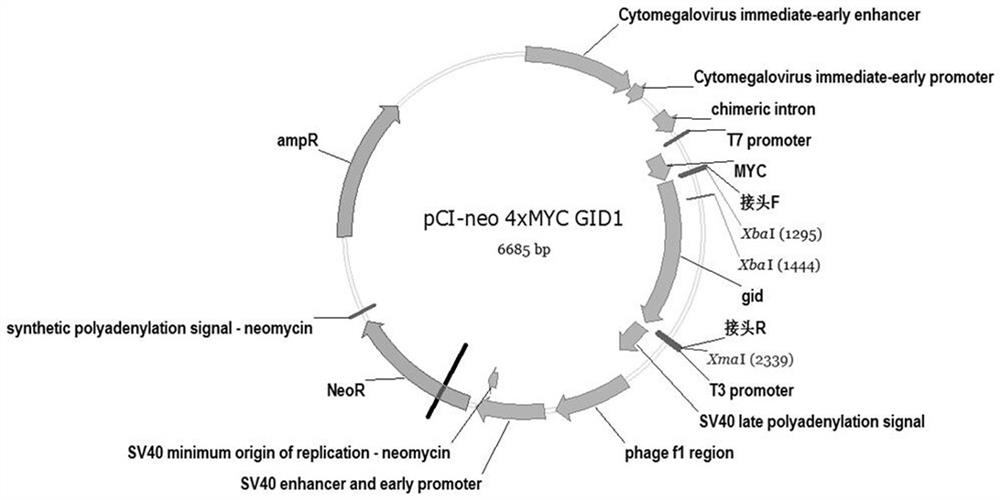
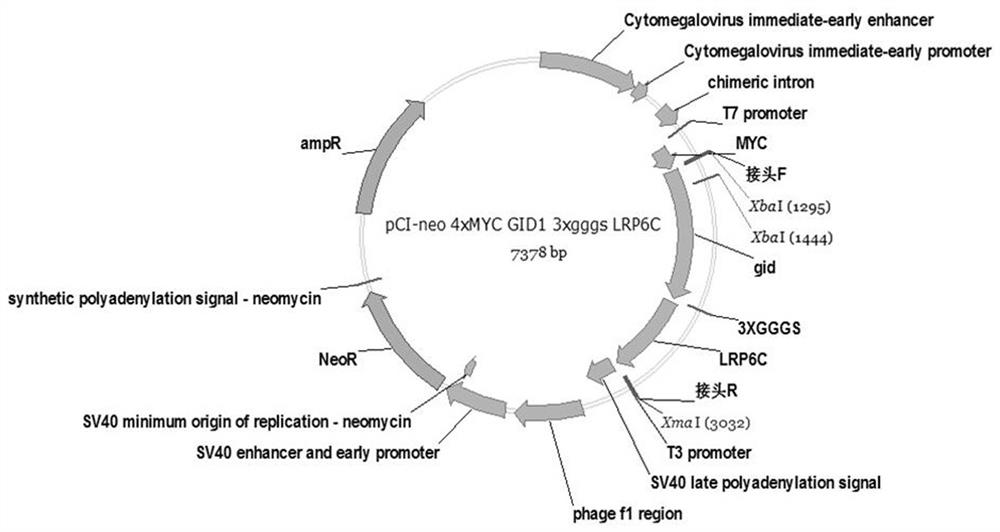
The invention provides a method for regulating a cellular pathway by using plant hormone ABA (Abscisic Acid) and a small molecular substance PYR (Pyrabactin). The method comprises the following steps:constructing ABA receptor proteins ABI1 and PYR1 in Arabidopsis thaliana on a human cell expression vector, then transferring into HEK293T cells respectively, adding ABA in order that the two receptor proteins undergo induced interaction, and adding a PYR inhibitor in order that the interaction degree is weakened; fusing other human cell signal pathway key proteins with the two receptor proteins,and making the two receptor proteins undergo interaction under the induction of the ABA, so that a fused signal pathway also undergoes ABA induced aggregation. According to the method provided by theinvention, a key protein LRP6 on a human Wnt pathway is selected. After fusion expression of an ABA receptor and LRP6, LRP6 aggregates under the induction of ABA, thereby promoting the production ofbeta-catenin and opening up an intracellular signal pathway. After the PYR inhibitor is added, the production amount of the beta-catenin is reduced, and the cellular pathway is closed.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for detecting LRP6 to be target gene of miR-29a by adopting dual luciferase reporter gene
The method for detecting that LRP6 is the target gene of miR-29a by using a dual-luciferase reporter gene, the purpose of the present invention is to confirm that miR-29a can be negatively expressed by targeting the 3'UTR of the LRP6 gene through a dual-luciferase reporter gene system Regulates the expression of LRP6. A method for detecting LRP6 as a target gene of miR-29a using a dual-luciferase reporter gene, the method comprising the following steps: (1) constructing a plasmid vector and performing point mutations: (2) dual fluorescence detection. The present invention The beneficial effects are as follows: provide a new method for verifying that miR-29a can negatively regulate the expression of LRP6 by targeting the 3'UTR of the LRP6 gene, and contribute to miR-29a, LRP6 and Wnt / -catenin signaling pathways Elucidation of the pathogenesis of osteogenesis-related diseases involved; contribute to the development of potential drugs for osteogenesis-related diseases involved in miR‑29a, LRP6 and Wnt / ‑catenin signaling pathways and the screening of biomarkers.
Owner:THE UNIV OF HONG KONG SHENZHEN HOSPITAL
Method for treating inflammation by administering a compound which binds LDL-receptor-related protein (LRP) ligand binding domain
The present invention relates to the field of therapeutic methods, compositions and uses thereof, that affect, directly or indirectly, the behavior of LRP receptors. These compositions and methods result in the treatment of inflammatory, immunological and metabolic conditions. More particularly, the methods and compositions of the invention are directed to the identification of small molecules, drugs and / or pharmacological agents that affect the Wnt pathway by affecting normal complex formation among various signaling receptors, the LRP5 and LRP6 receptor, and related ligands.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
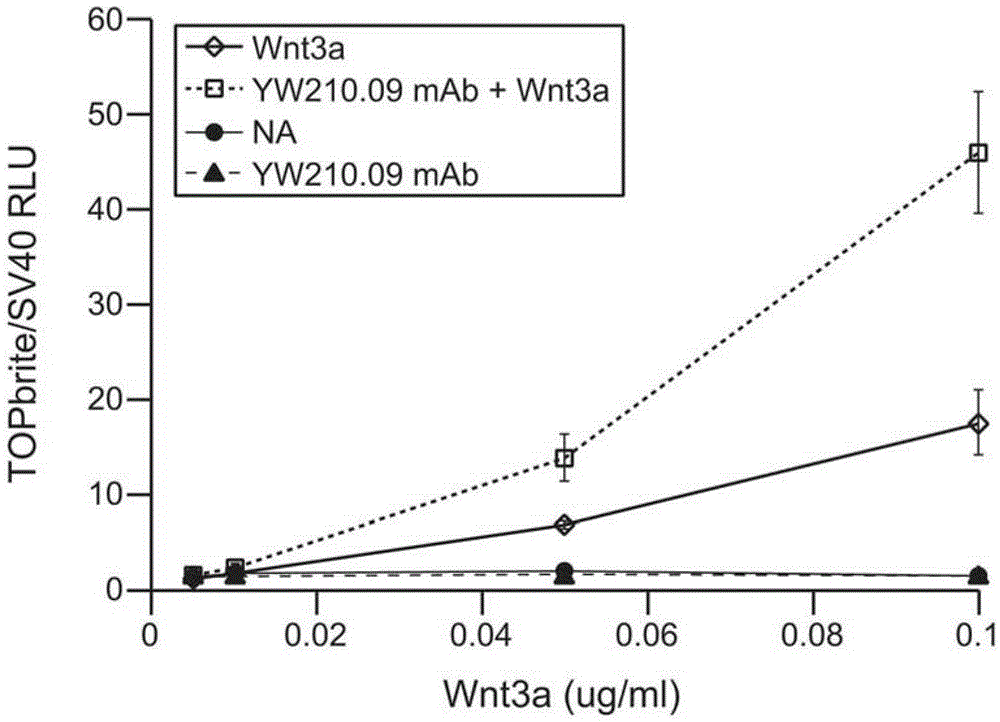
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR MODULATING THE Wnt PATHWAY
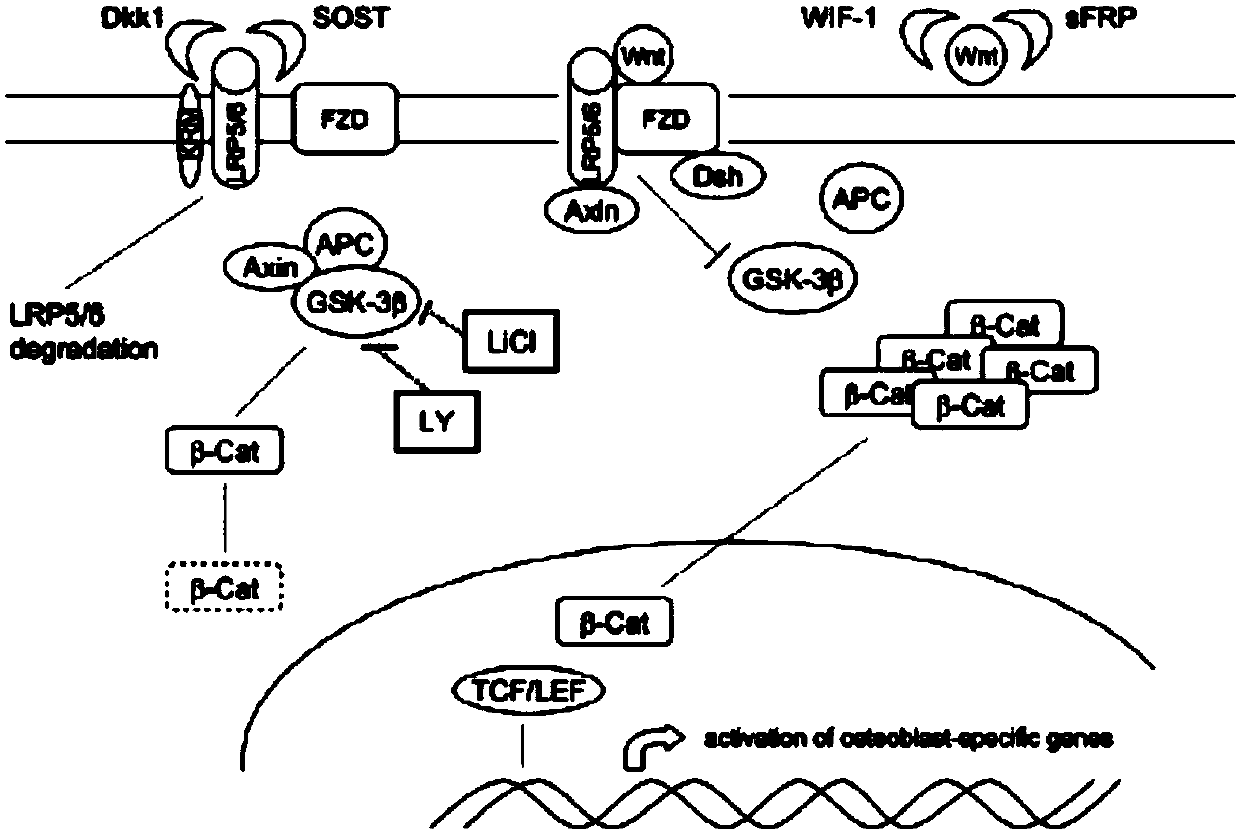
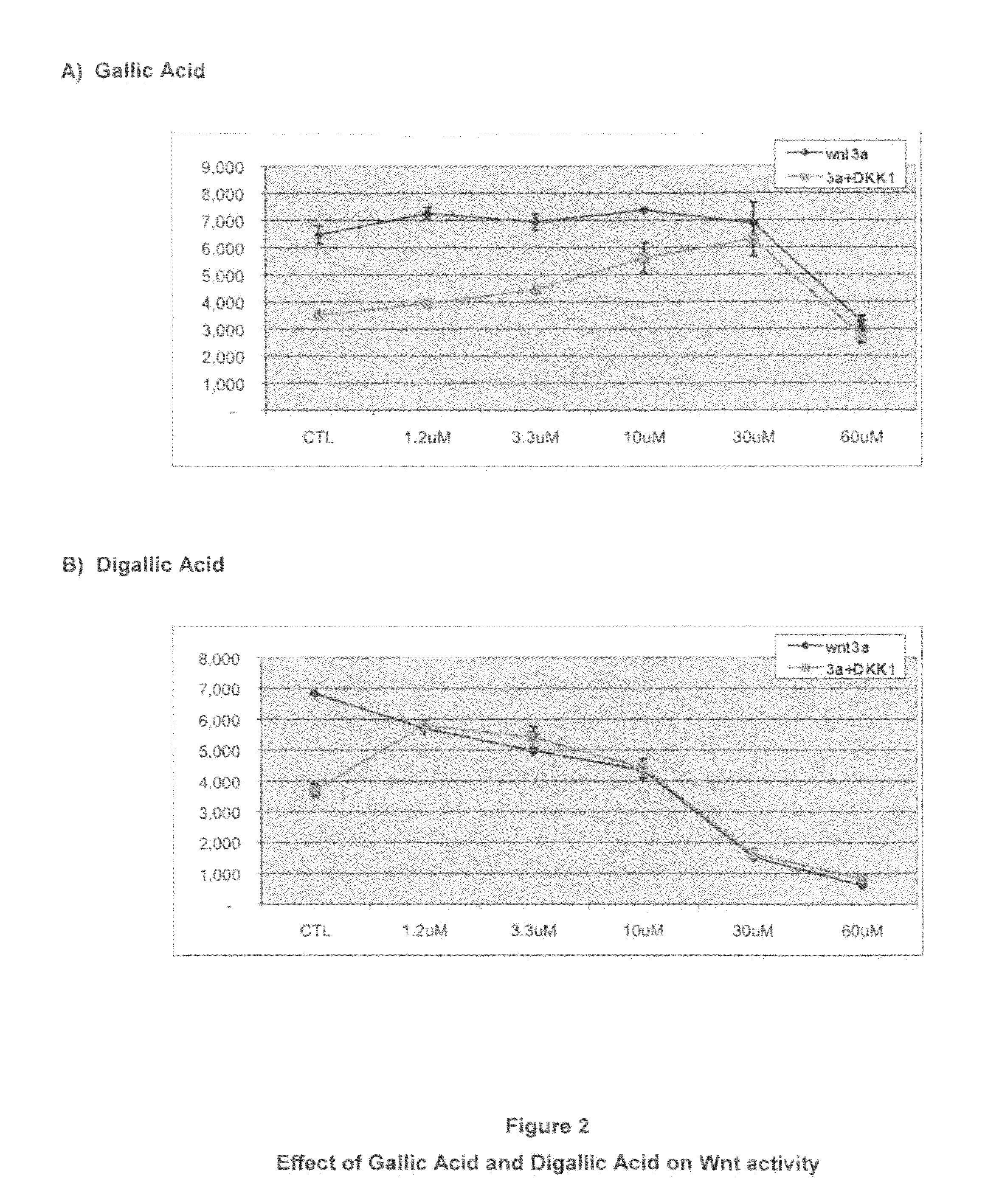
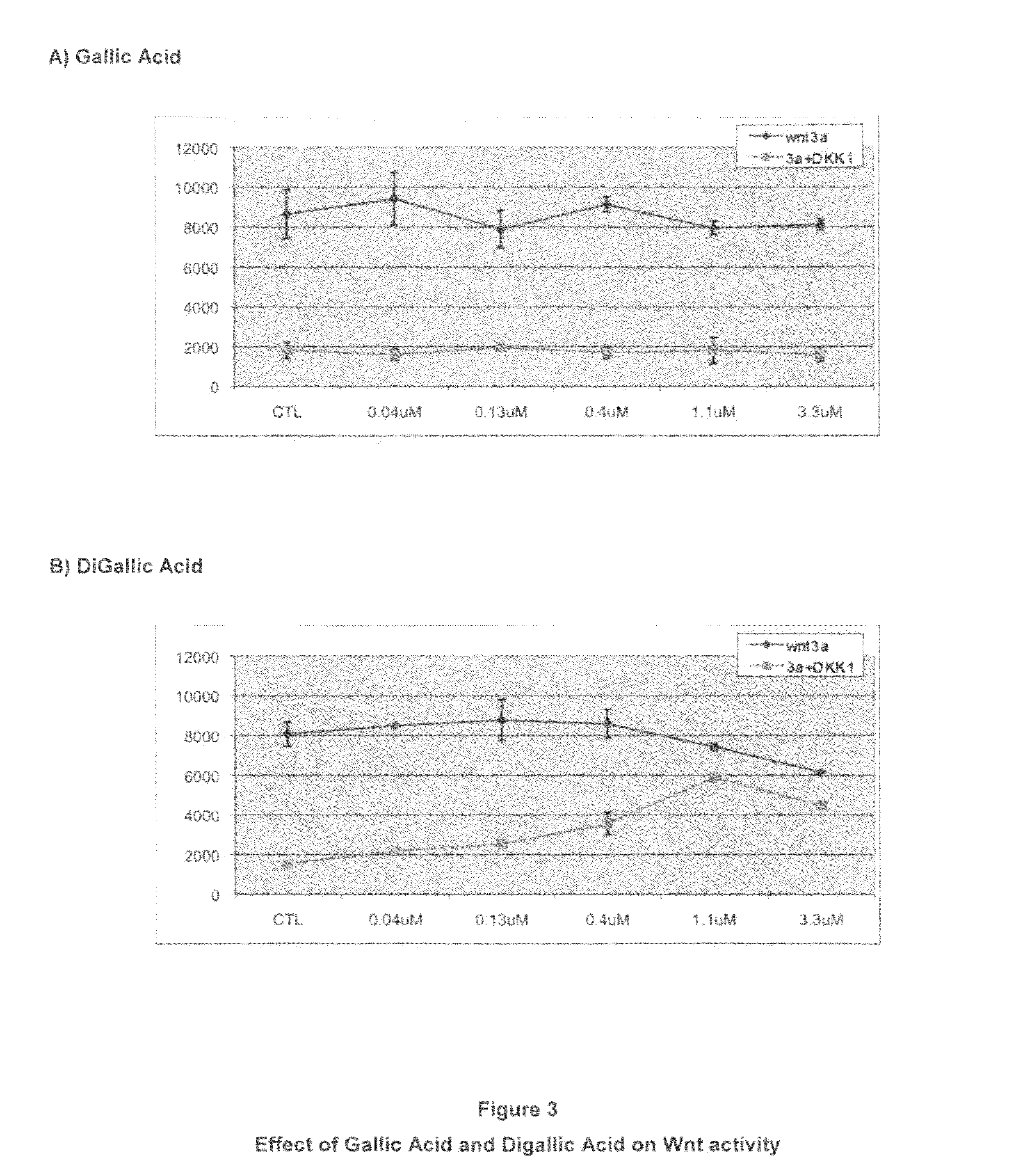
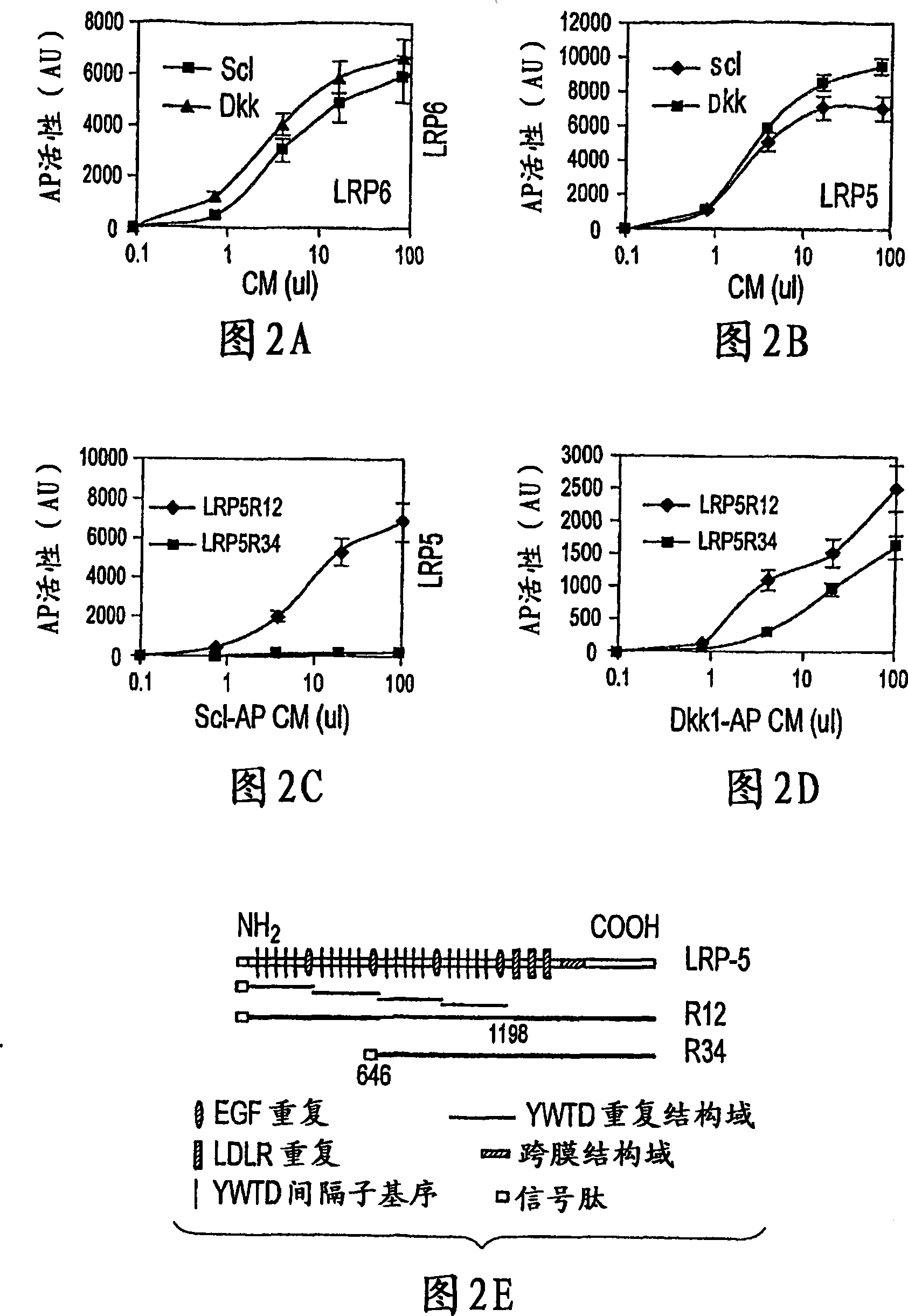
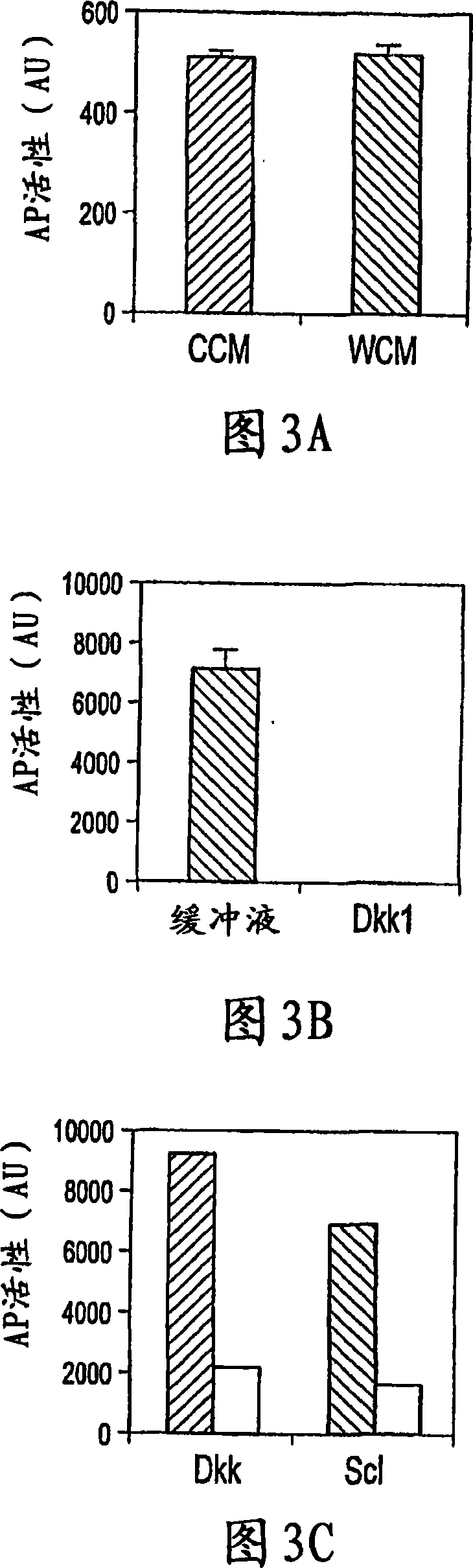
The invention provides methods and compositions for modulating the Wnt signaling pathway, in particular by interfering with binding of Dkk1 or SOST with LRP5 and / or LRP6.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Sclerostin and the inhibition of wnt signaling and bone formation
InactiveCN101888849AAvoid combiningBinding blockCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLRP6Bone formation
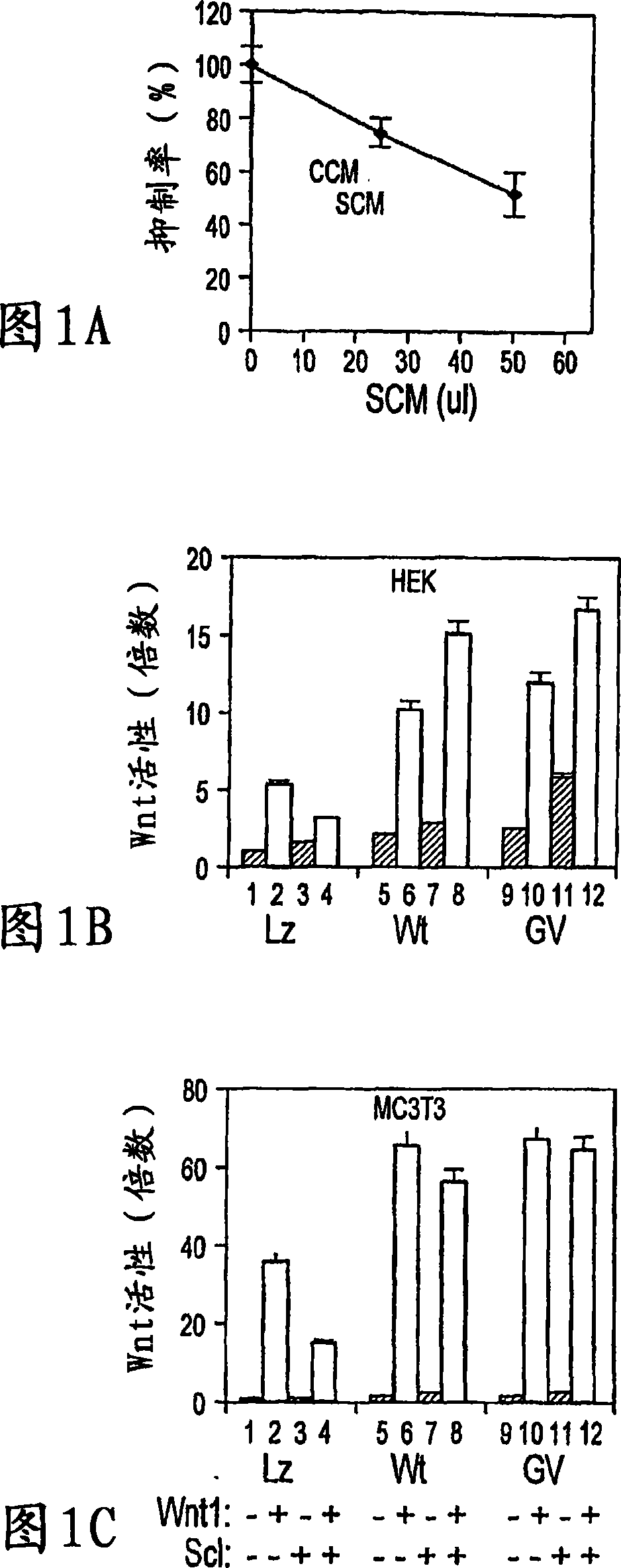
The loss of the SOST gene product sclerostin leads to sclerosteosis characterized byihigh bone mass (HBM). In this report, we found that sclerostin could antagonize canonical, Wnt signaling in human embryonic kidney A293 cells and mouse osteoblastic MC3T3 cells. This sclerostin-mediated antagonism could be reversed by over-expression of Wnt coreceptor LRP5. In addition, we found that sclerostin bound to LRP5 as well as LRP6 and identified the first two YWTD-EGF repeat domains of LRP5 as being responsible for the binding. Although these two repeat domains are required for transducing canonical Wnt signals, canonical Wnt did not appear to compete with sclerostin for binding to LRP5. Examination of the expression of sclerostin and Wnt7b, an autocrine canonical Wnt, during primary calvarial osteoblast differentiation revealed that sclerostin is expressed at the late stages of osteoblast differentiation coinciding with the expression of osteogenic marker osteocalcin and trailing after the expression of Wnt7b. Given the plethora of evidence indicating that canonical Wnt signaling stimulates osteogenesis, we believe that the HBM phenotype associated with the loss of sclerostin may at least in part be attributed to an increase in canonical Wnt signaling resulting from the reduction in sclerostin-mediated Wnt antagonism.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Biparatopic polypeptides antagonizing Wnt signaling in tumor cells
ActiveUS10597449B2Easy to manufactureIncrease concentrationSenses disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseLRP6
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Compositions and methods relating to induction of intestinal stem cell homeogenesis and/or regeneration
ActiveUS9827290B2Reduce sensitivityIncrease host tolerancePeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemLRP6Medicine
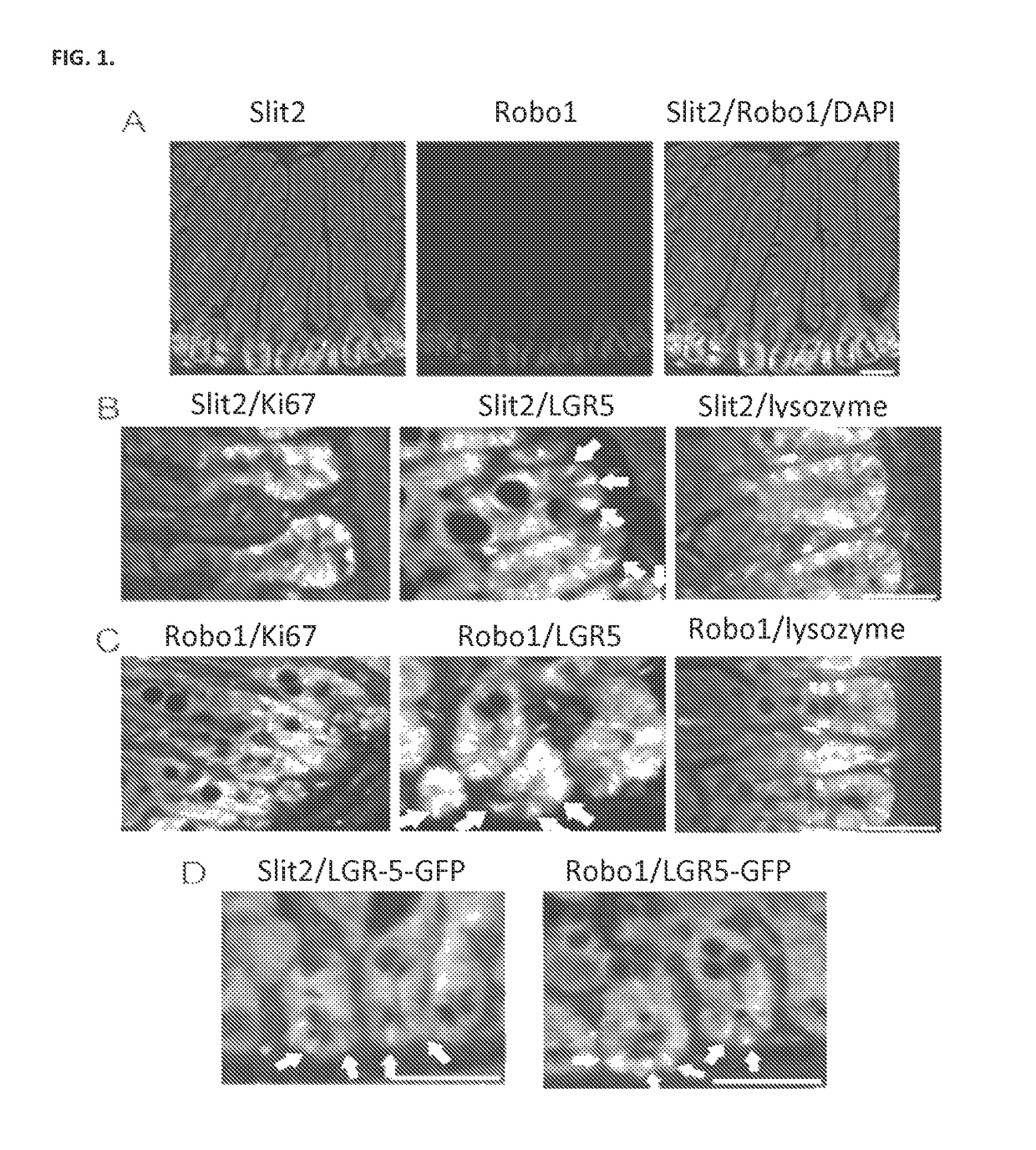
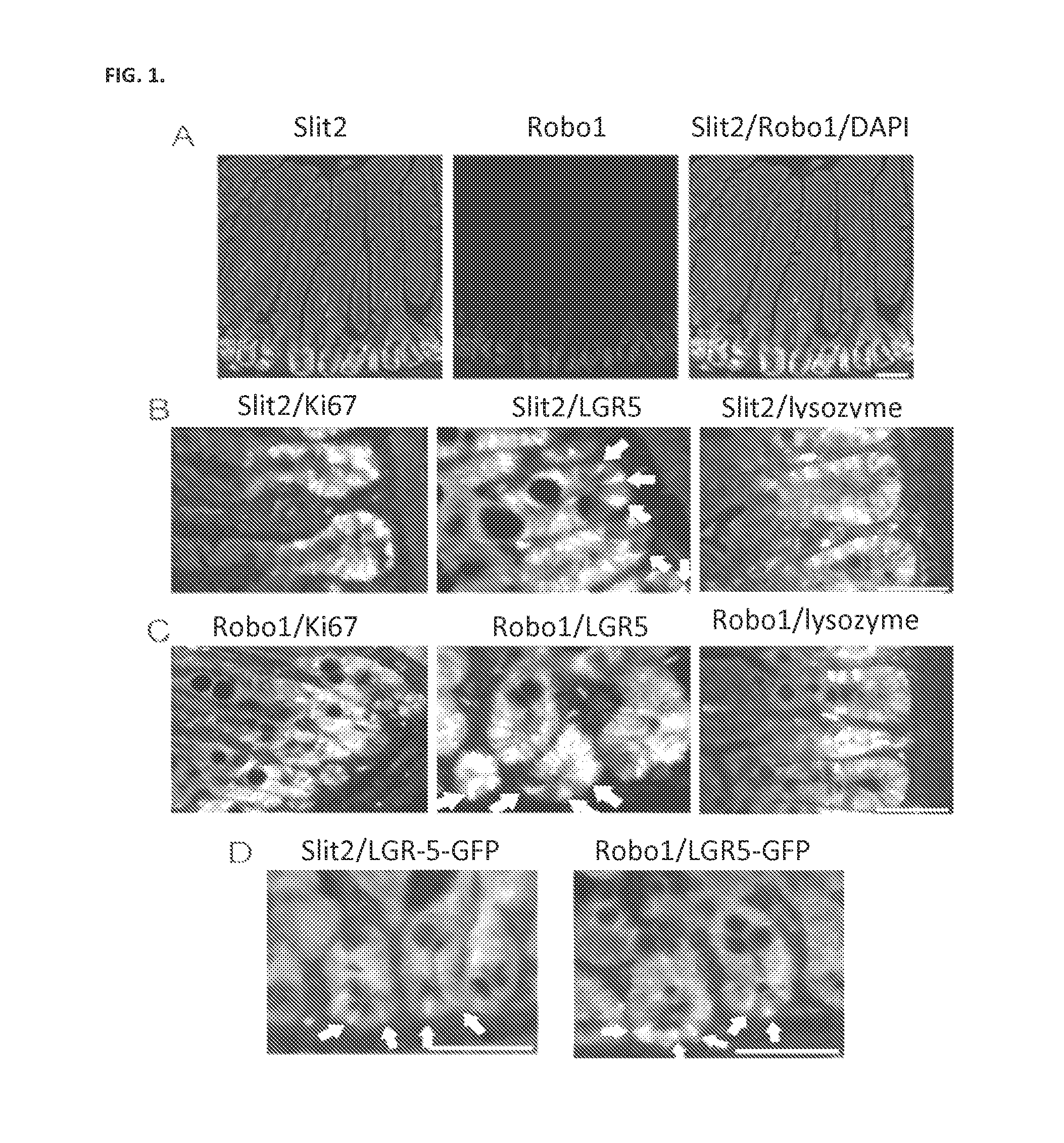
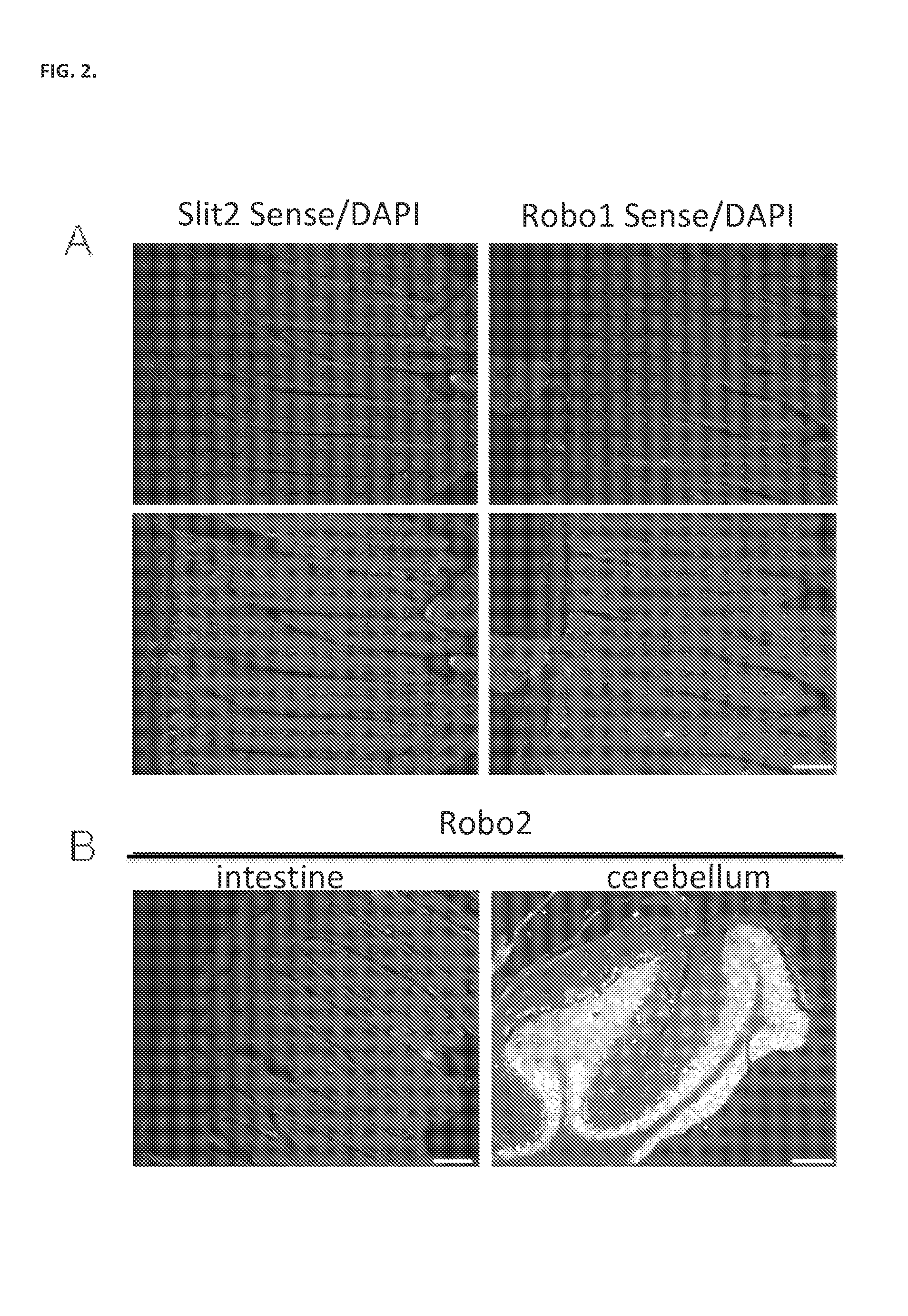
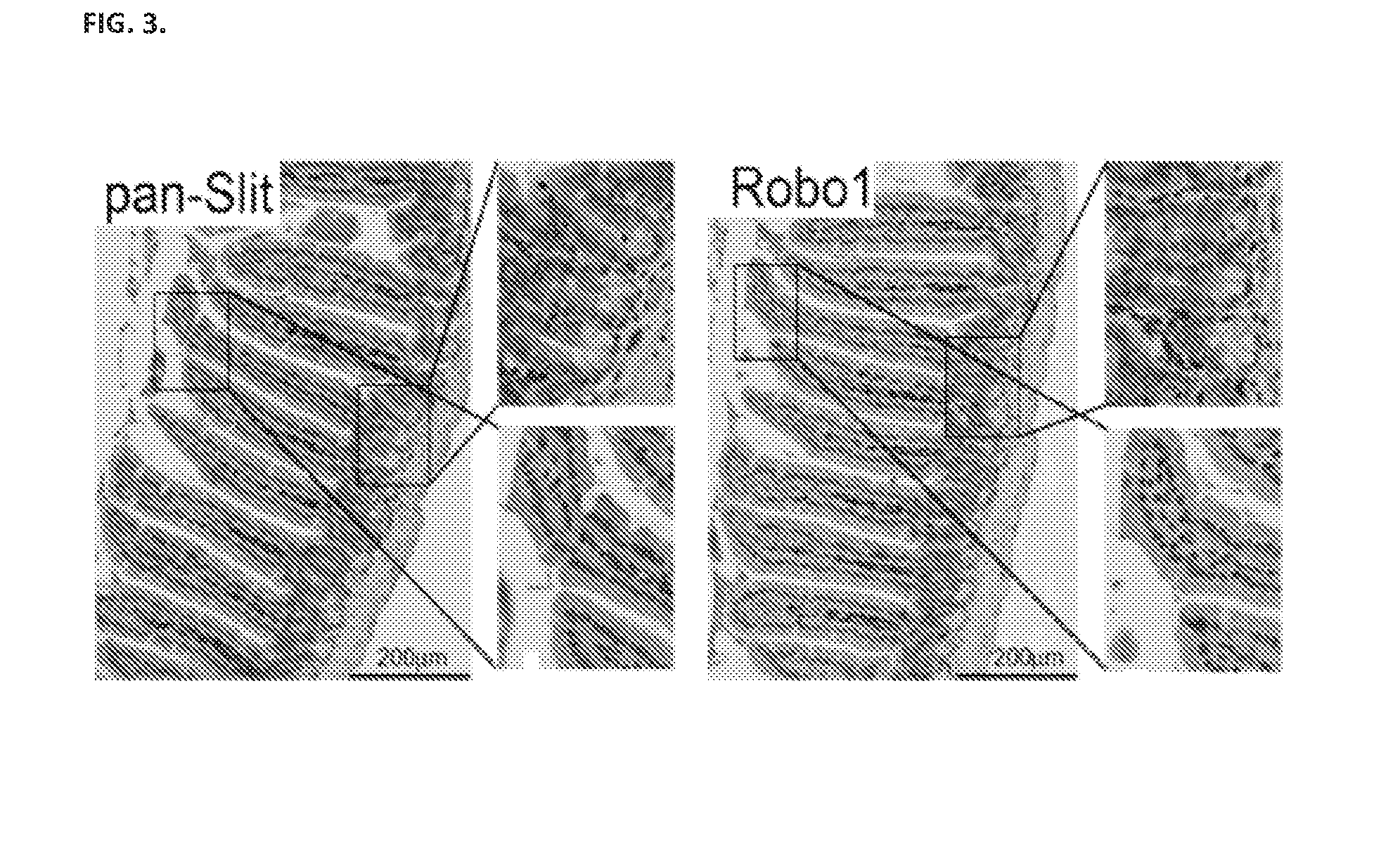
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for inducing intestinal stem cell homeogenesis and / or regeneration within intestinal tissue expressing Robo1 through administration of a Rspo1 agent and a Slit2 agent. Administration of such agents results in, for example, binding of the Rspo1 agent and Slit2 agent with Robo1, resulting in, for example, binding of the CC3 motif of Robo1 with LRP6, resulting in phosphorylation of LRP6, and ultimately, induction of intestinal stem cell homeogenesis and / or regeneration. In certain embodiments, such administration of a Rspo1 agent and a Slit2 agent is used to protect and / or prevent intestinal tissue damage resulting from exposure to an intestinal tissue damaging event (e.g., radiation). The agents and related compositions additionally find use in diagnostic and research settings.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Compositions and methods relating to induction of intestinal stem cell homeogenesis and/or regeneration
ActiveUS20160000865A1Reduce lethal tissue damageMitigates chemoradiation-induced tissue injuryPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemLRP6Phosphorylation
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for inducing intestinal stem cell homeogenesis and / or regeneration within intestinal tissue expressing Robo1 through administration of a Rspo1 agent and a Slit2 agent. Administration of such agents results in, for example, binding of the Rspo1 agent and Slit2 agent with Robo1, resulting in, for example, binding of the CC3 motif of Robo1 with LRP6, resulting in phosphorylation of LRP6, and ultimately, induction of intestinal stem cell homeogenesis and / or regeneration. In certain embodiments, such administration of a Rspo1 agent and a Slit2 agent is used to protect and / or prevent intestinal tissue damage resulting from exposure to an intestinal tissue damaging event (e.g., radiation). The agents and related compositions additionally find use in diagnostic and research settings.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
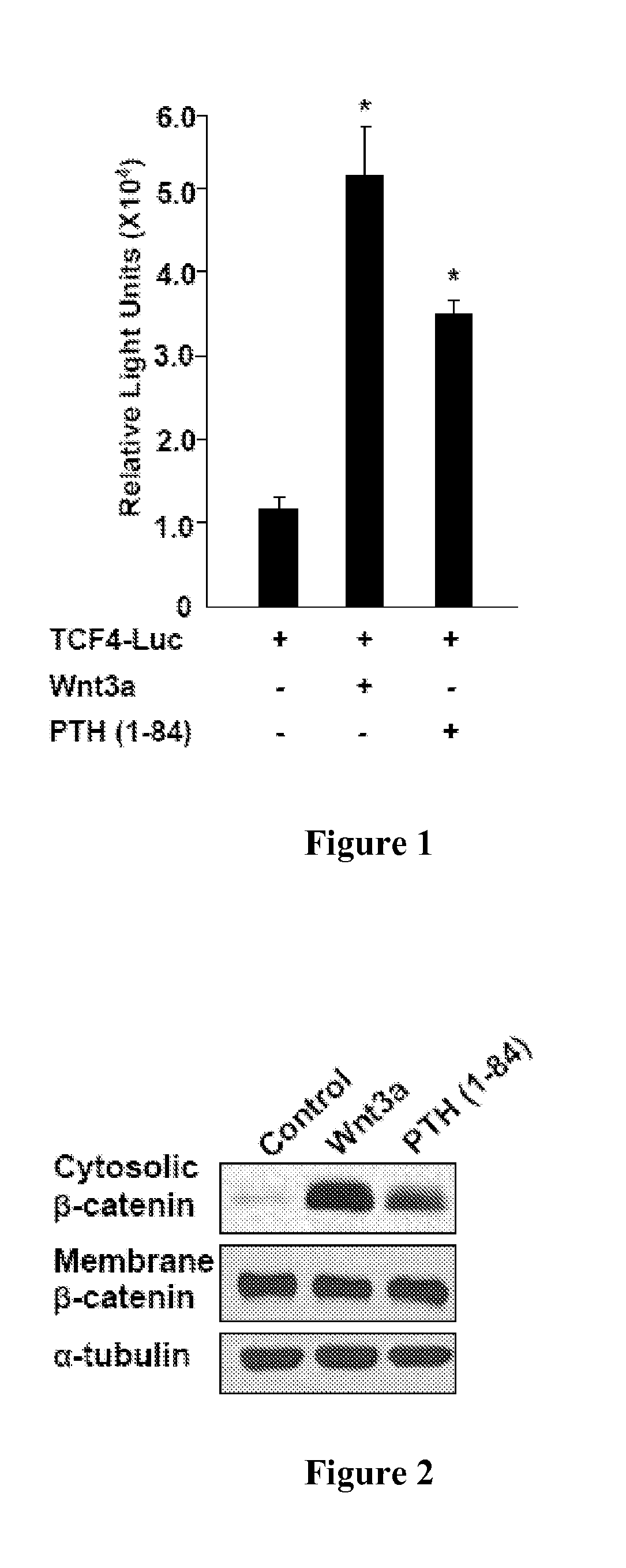
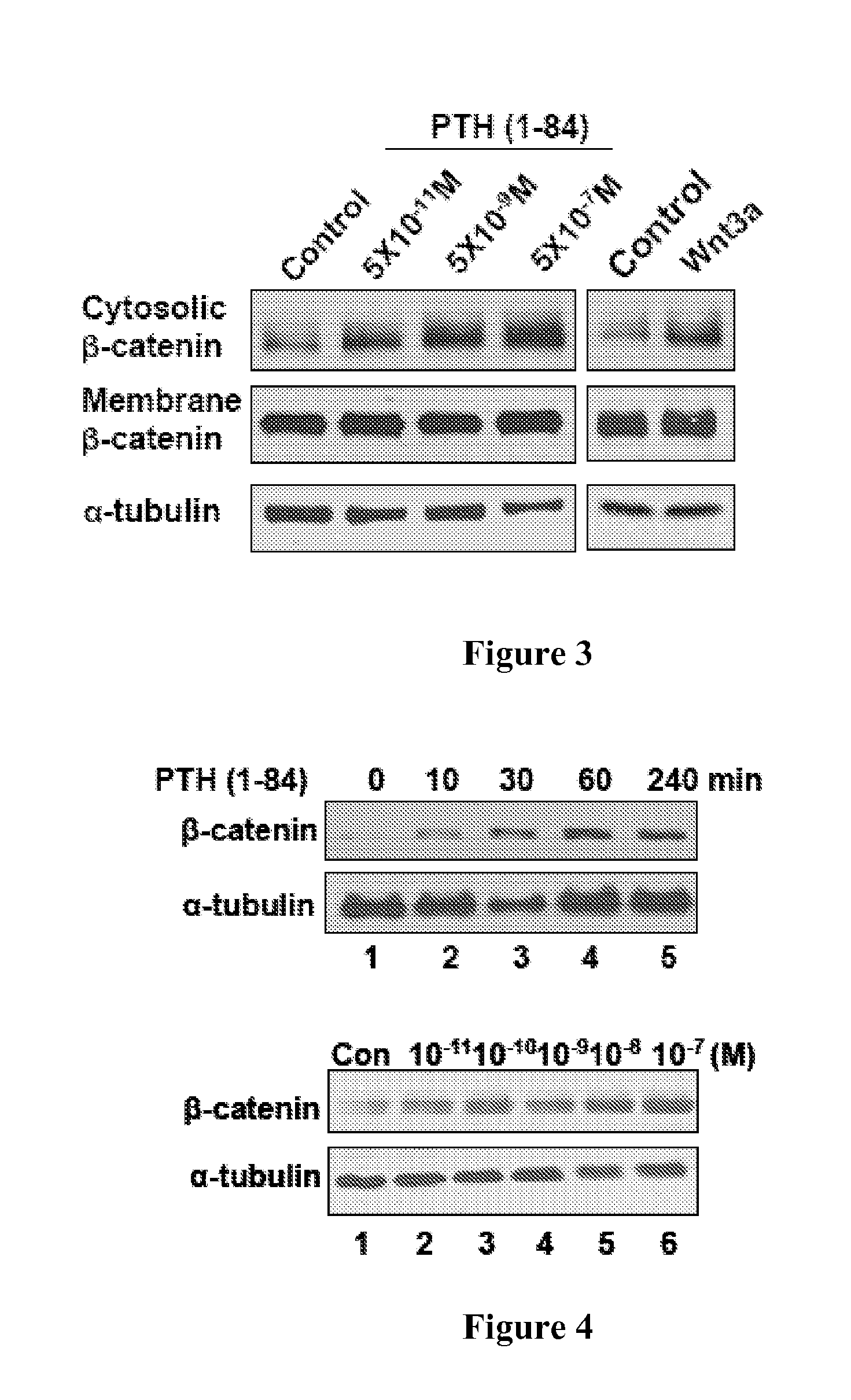
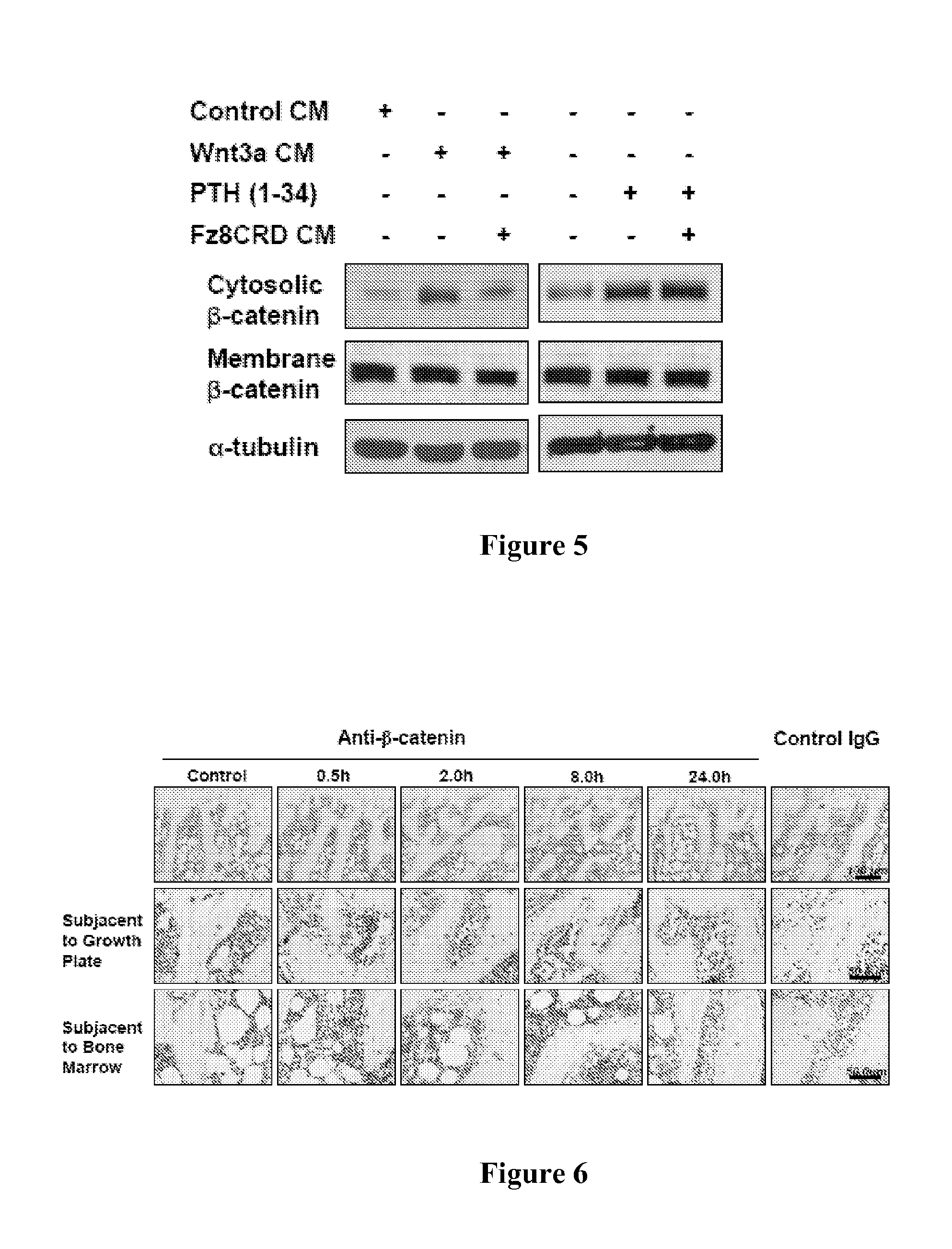
Identifying parathyroid hormone agonists and antagonists
InactiveUS20110256557A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionDiseaseSkeletal disorder
Provided herein are methods of screening for an agent that is a PTH agonist or antagonist. For example, provided is a method of screening for an agent that is a PTH agonist or antagonist, the method comprising contacting a cell with LRP6 and the agent to be screened, wherein the cell comprises a PTH1R, and determining the level of LRP6 binding to the PTH1R. An increased level of LRP6 binding to the PTH1R compared to a control indicates the agent is a PTH agonist. A decreased level of LRP6 binding to the PTH1R compared to a control indicates the agent is a PTH antagonist. Also provided are methods of treating a skeletal disorder in a subject, wherein the skeletal disorder is characterized by proliferative bone growth or reduced bone density.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND +1
Biparatopic polypeptides antagonizing wnt signaling in tumor cells
ActiveUS20200199222A1Easy to manufactureMore solubleSenses disorderImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseLRP6
The invention provides novel biparatopic LRP5 / LRP6 cross-reactive binding polypeptides, and more specifically novel biparatopic LRP5 / LRP6 cross-reactive immunoglobulin single variable domain constructs which can inhibit Wnt signaling pathways. The invention also relates to specific sequences of such polypeptides, methods of their production, and methods of using them, including methods of treatment of diseases such as cancer.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM INT GMBH
Modified DKK2 protein, nucleic acid encoding the same, preparation method thereof, and use thereof
ActiveUS10259850B2High affinityPromote angiogenesisPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseLRP6
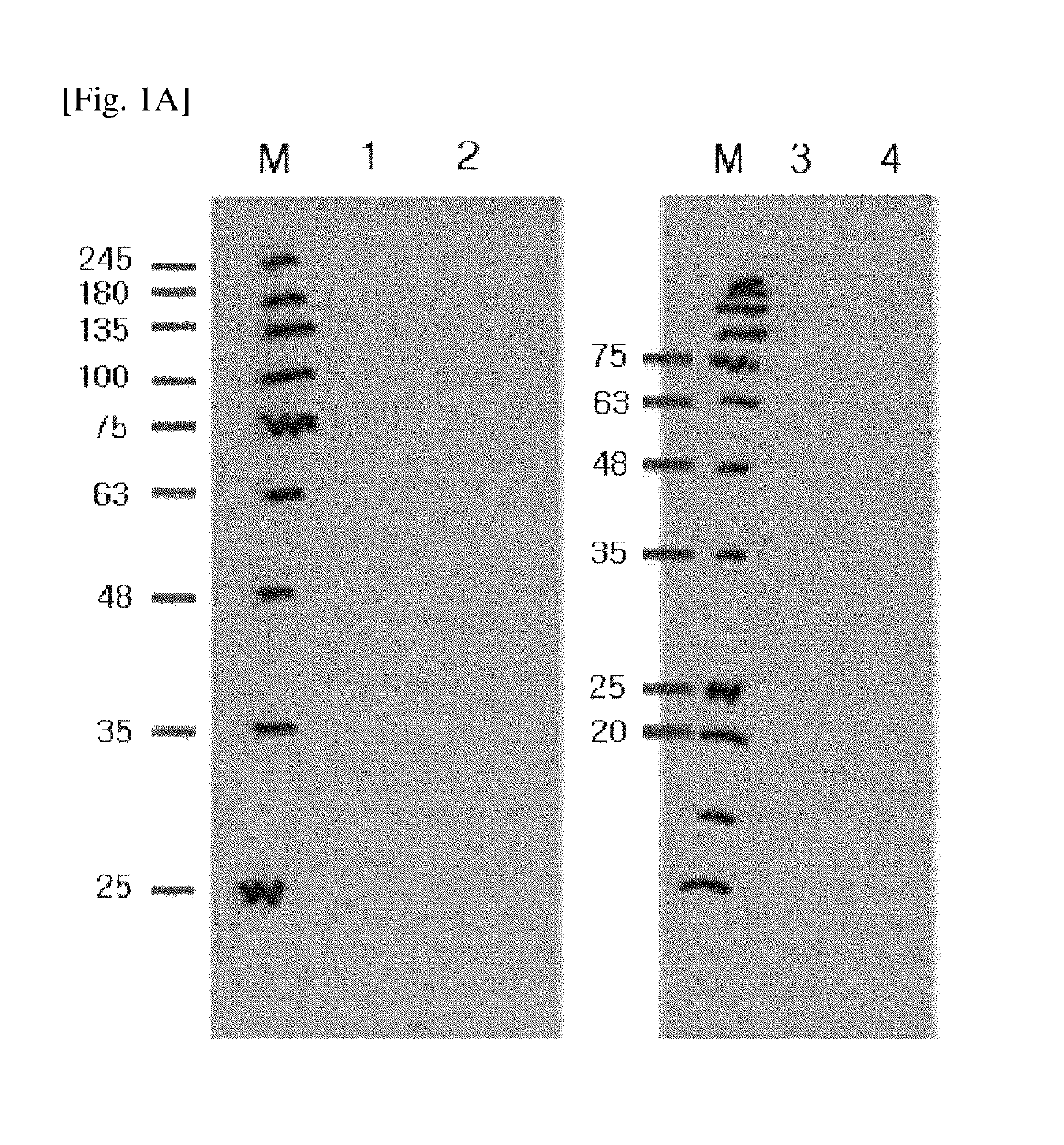
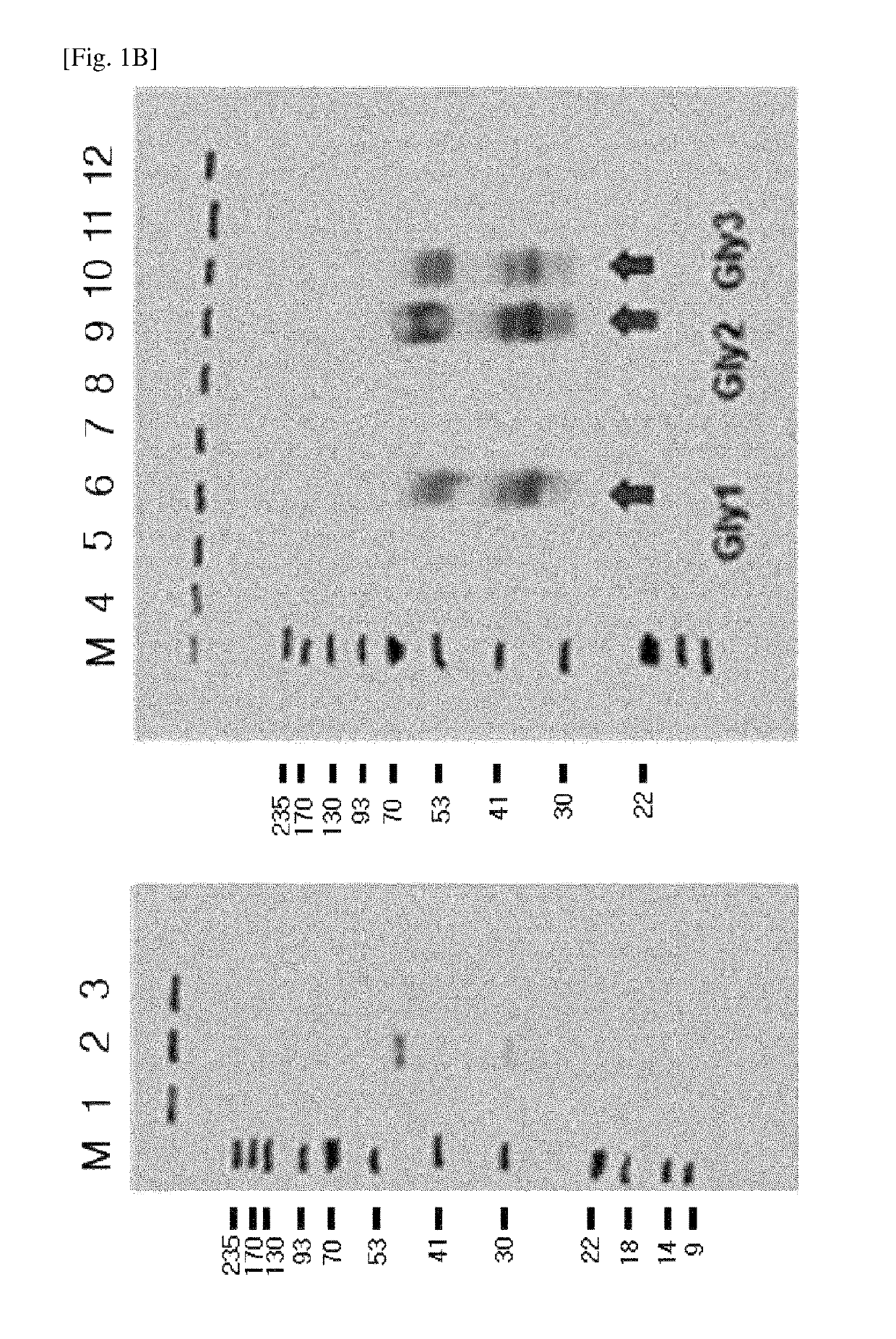
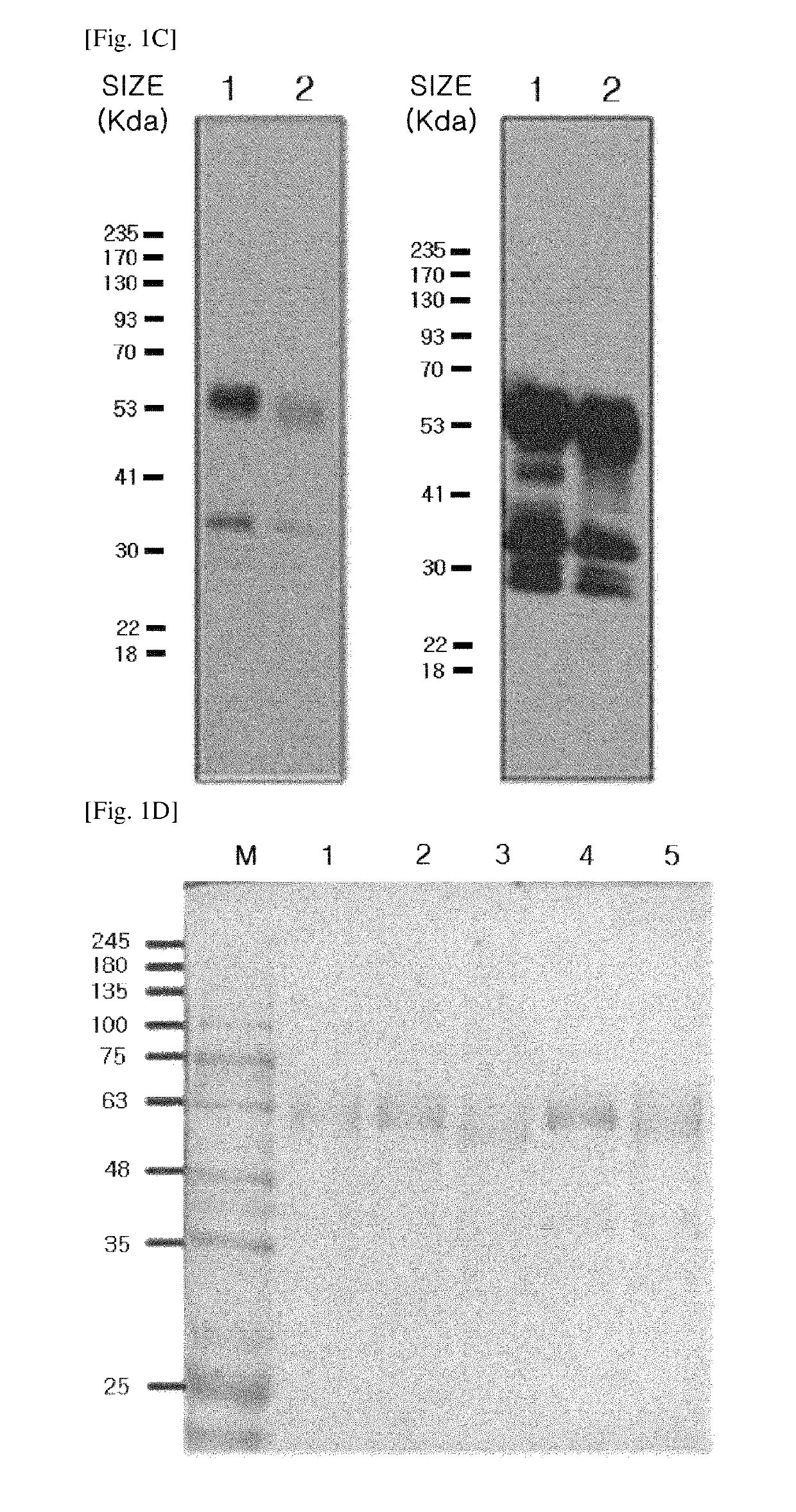
Provided are a modified DKK2 polypeptide according to an aspect, a nucleic acid encoding the same, a preparation method thereof, and use thereof. Accordingly, a modified DKK2 protein having an additional glycosyl group or improved binding affinity for a substrate LRP6 may be efficiently prepared, thereby being used for promoting angiogenesis or preventing or treating vascular permeability-related diseases.
Owner:BIOCOMPLETE INC
Antibodies for modulating binding between lrp and wise
InactiveUS20190194314A1Inhibit bindingCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsLRP6LRP5
Owner:STOWERS INST FOR MEDICAL RES
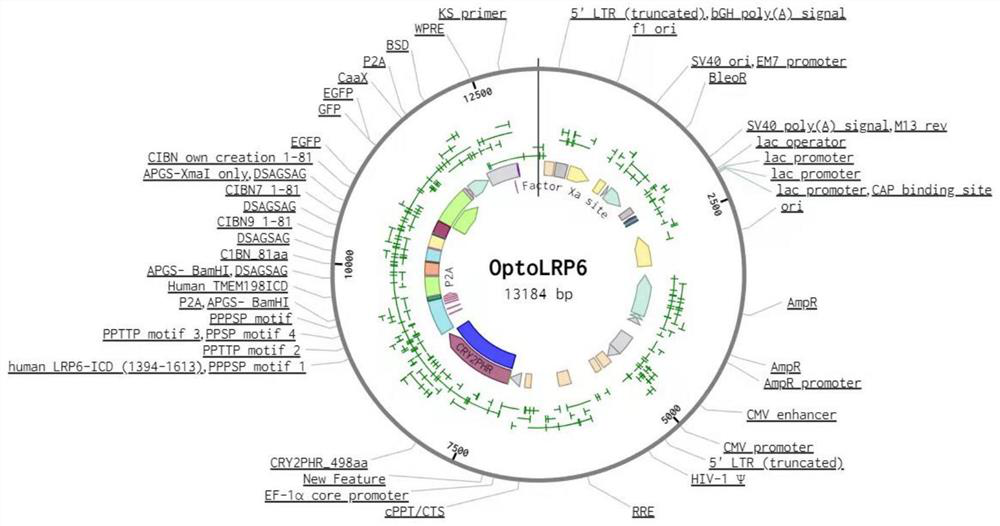
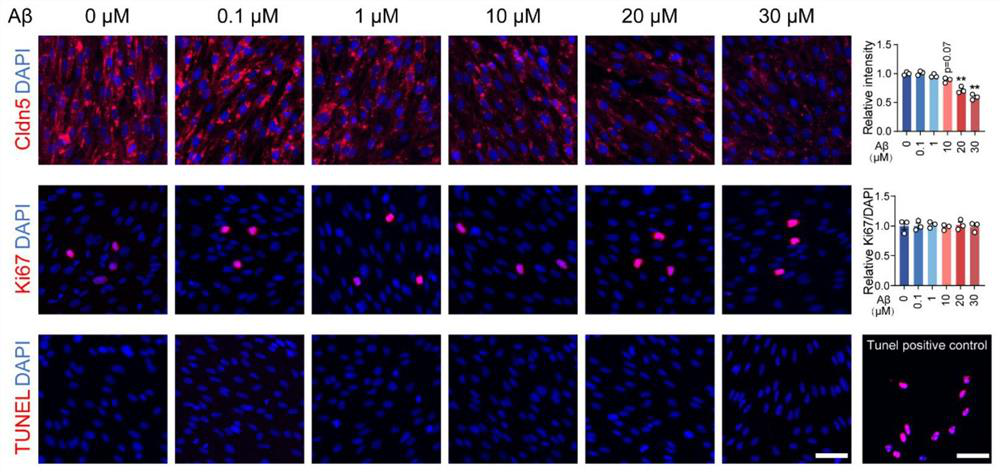
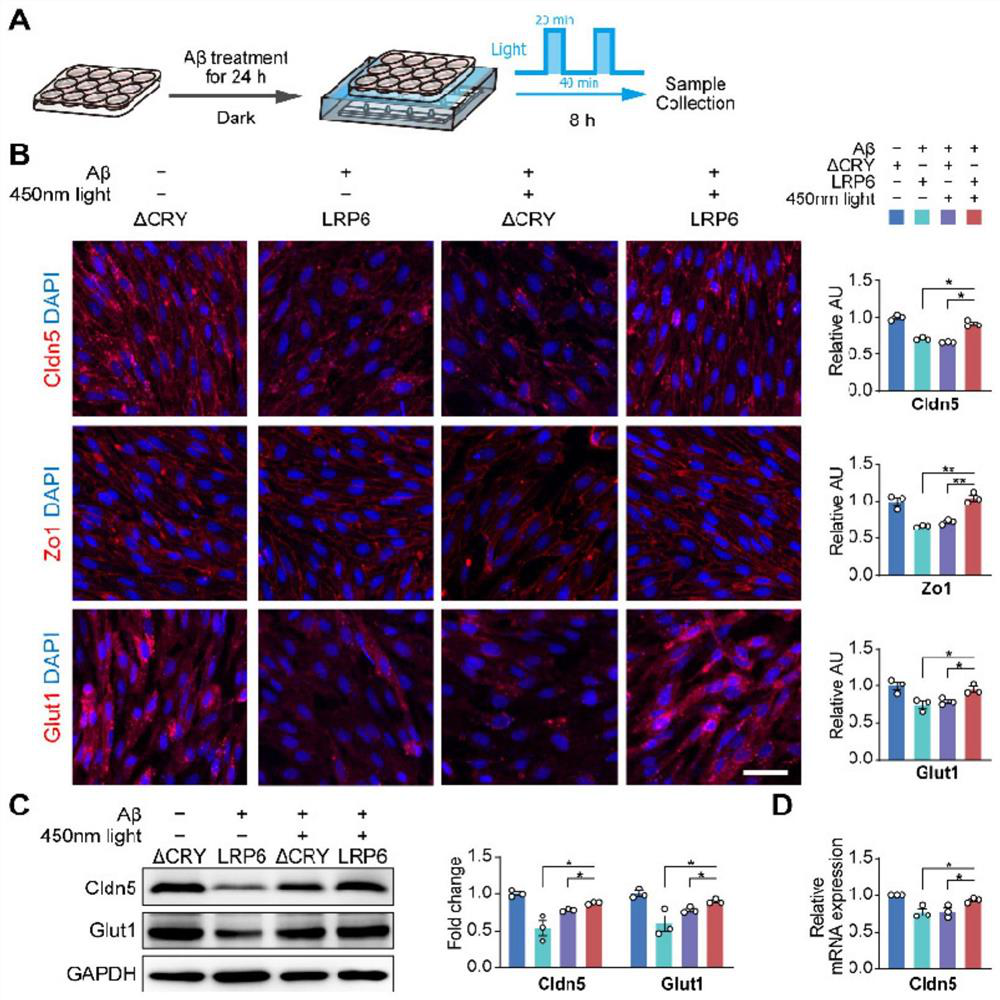
Application of tool for targeted activation of LRP6 in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating Alzheimer's disease
PendingCN114832106ARepair damageMitigating Functional DamageNervous disorderPhotodynamic therapyOptogeneticsLRP6
The invention discloses application of a tool for repairing and maintaining a blood-brain barrier function based on targeted activation of LRP6 in preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating Alzheimer's disease, in particular to early intervention and prevention of the Alzheimer's disease. Based on the research of the invention, an optogenetics tool OptoLRP6 is utilized to target LRP6, the blood brain barrier injury can be repaired, the blood brain barrier function can be maintained, and the brain microenvironment steady state in the AD disease course can be remodeled, so that the brain endothelial cell function damage caused by A beta oligomer can be relieved, and the method can be applied to treatment and early intervention prevention of Alzheimer's disease. Therefore, development of a tool for repairing and maintaining the blood-brain barrier function based on targeted activation of the LRP6, such as an optogenetics tool, has a very good application prospect in prevention and / or treatment of the Alzheimer's disease.
Owner:THE SEVENTH AFFILIATED HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV SHENZHEN
anti-lrp6 antibody
InactiveCN102906117BPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntiendomysial antibodiesLRP6
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
A method for regulating cell pathways by using plant hormone GA and small molecular substance pac
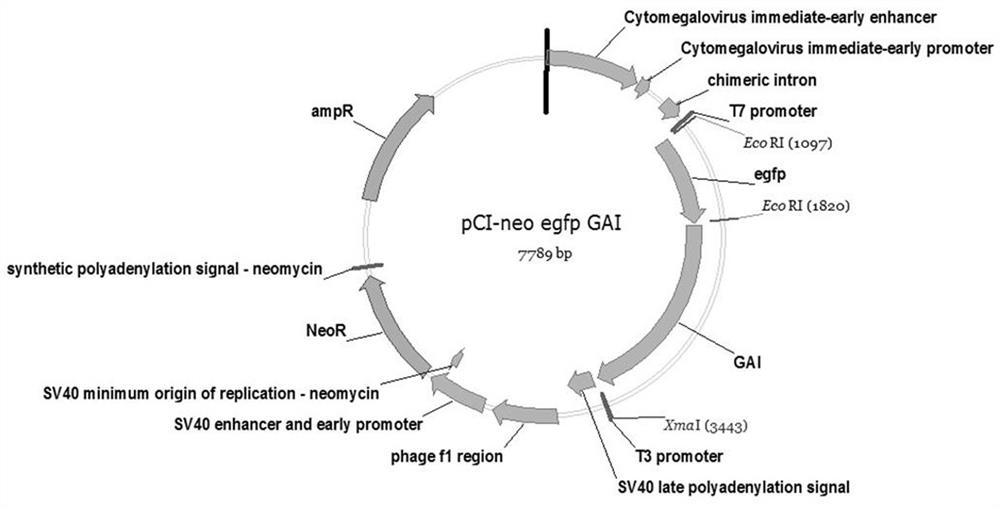
The invention provides a method for regulating cell pathway by using plant hormone GA and small molecular substance PAC, and realizes the regulation switch of signal pathway in human cells. The GA receptor proteins GID1 and GAI in Arabidopsis thaliana were constructed on a human cell expression vector, and then transferred into HEK293T cells together. GA was added to induce the interaction between the two proteins. After adding the inhibitor PAC, the degree of interaction would be weakened. In this way, the key proteins in the human cell signaling pathway are fused and expressed with these two receptor proteins. The two receptor proteins interact under the induction of GA, and the fusion signaling pathway is also induced by GA. The present invention selects the key protein LRP6 on the human Wnt pathway. After the fusion expression of GA receptor and LRP6, LRP6 will aggregate under the induction of GA, thereby promoting the production of β-catenin and opening the intracellular signaling pathway. After adding PAC inhibition, the production of β-catenin is reduced and the cell pathway is closed.
Modified dkk2 protein, nucleic acid encoding the same, preparation method thereof, and use thereof
ActiveUS20180016313A1Promote angiogenesisPreventing and treating vascular permeability-related diseasePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseLRP6
Provided are a modified DKK2 polypeptide according to an aspect, a nucleic acid encoding the same, a preparation method thereof, and use thereof. Accordingly, a modified DKK2 protein having an additional glycosyl group or improved binding affinity for a substrate LRP6 may be efficiently prepared, thereby being used for promoting angiogenesis or preventing or treating vascular permeability-related diseases.
Owner:BIOCOMPLETE INC
Cancer patient selection for administration of wnt signaling inhibitors using rnf43 mutation status
InactiveUS20170306409A1Good surface smoothnessAddress bad outcomesOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementZNRF3 GeneLRP6
Disclosed are biomarkers, methods and assay for the identification of cancer patients who are predicted to benefit from the therapeutic administration of Wnt antagonist. The biomarkers include detection of RNF43 and ZNRF3 gene deletion, reduced RNF43 and ZNRF3 mRNA expression, reduced RNF43 and ZNRF3 protein expression, RNF43 and ZNRF3 inactivation mutation, phosphorylated LRP6, phophorylated Dishevelleds, and the expression of Frizzleds. These biomarkers can be associated with the better outcome for cancer patients treated with Wnt pathway inhibitors.
Owner:IRM +1
Antibodies for modulating binding between lrp and wise
InactiveUS20200339675A1Inhibit bindingCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesLRP6
Owner:STOWERS INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com