Distributed fault location method for overhead line-cable hybrid circuit
A hybrid line and fault location technology, applied to fault locations, emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as complex calculations, large errors, and overhead line faults, and achieve good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
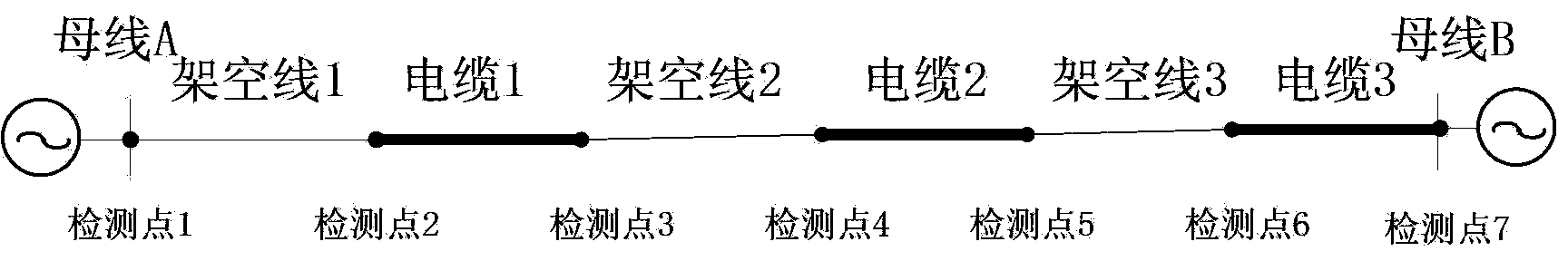
[0098] The fault occurred on hybrid circuit cable 1. The fault occurred 0.245s after the system was started. It was a single-phase ground fault, and the fault resistance was 50 ohms. By analyzing the fault traveling wave current detected by detection points 1-7, the current polarity can be obtained as shown in Table 1.
[0099] Table 1 Current polarity analysis of each detection point
[0100] check Point
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
polarity
+
+
-
-
-
-
-
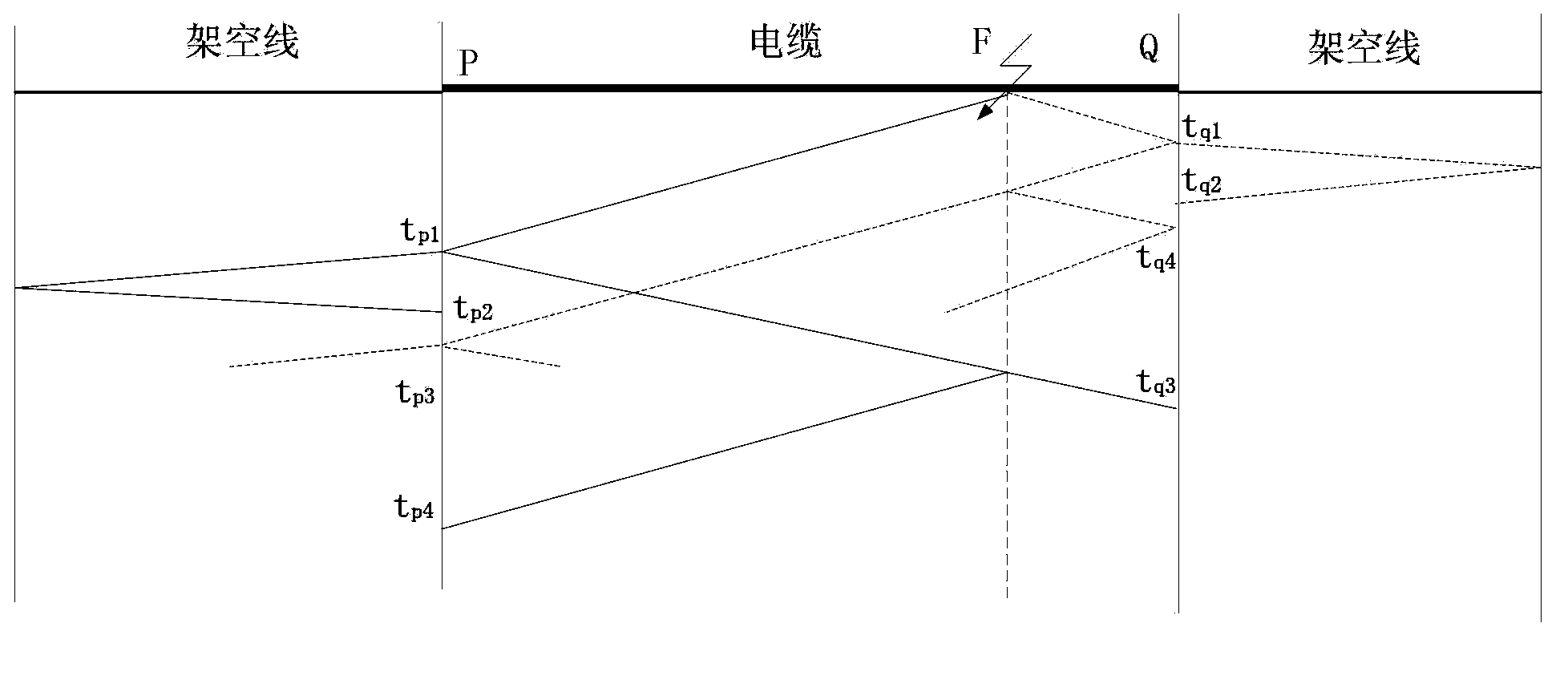
[0101] It can be seen from Table 1 that the fault occurred between detection points 2 and 3, that is, cable 1.
[0102] The arrival time of the first fault traveling wave detected by detection point 2 is 0.245200s, and the arrival time of the first fault traveling wave detected by detection point 3 is 0.245064s, so the fault occurs in the lower half of cable 1. Set the cable wave velocity v b =1.5×10 8 m / s, the velocity of the overhead line wave is v a =...
Embodiment 2
[0104] The fault occurred on the overhead line 3 of the hybrid circuit. The fault occurred 0.240s after the system was started. It was a two-phase ground fault, and the fault resistance was 500 ohms. By analyzing the fault traveling wave current detected by detection points 1-7, the current polarity can be obtained as shown in Table 2.
[0105] Table 2 Current polarity analysis of each detection point
[0106] check Point
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
polarity
+
+
+
+
+
-
-
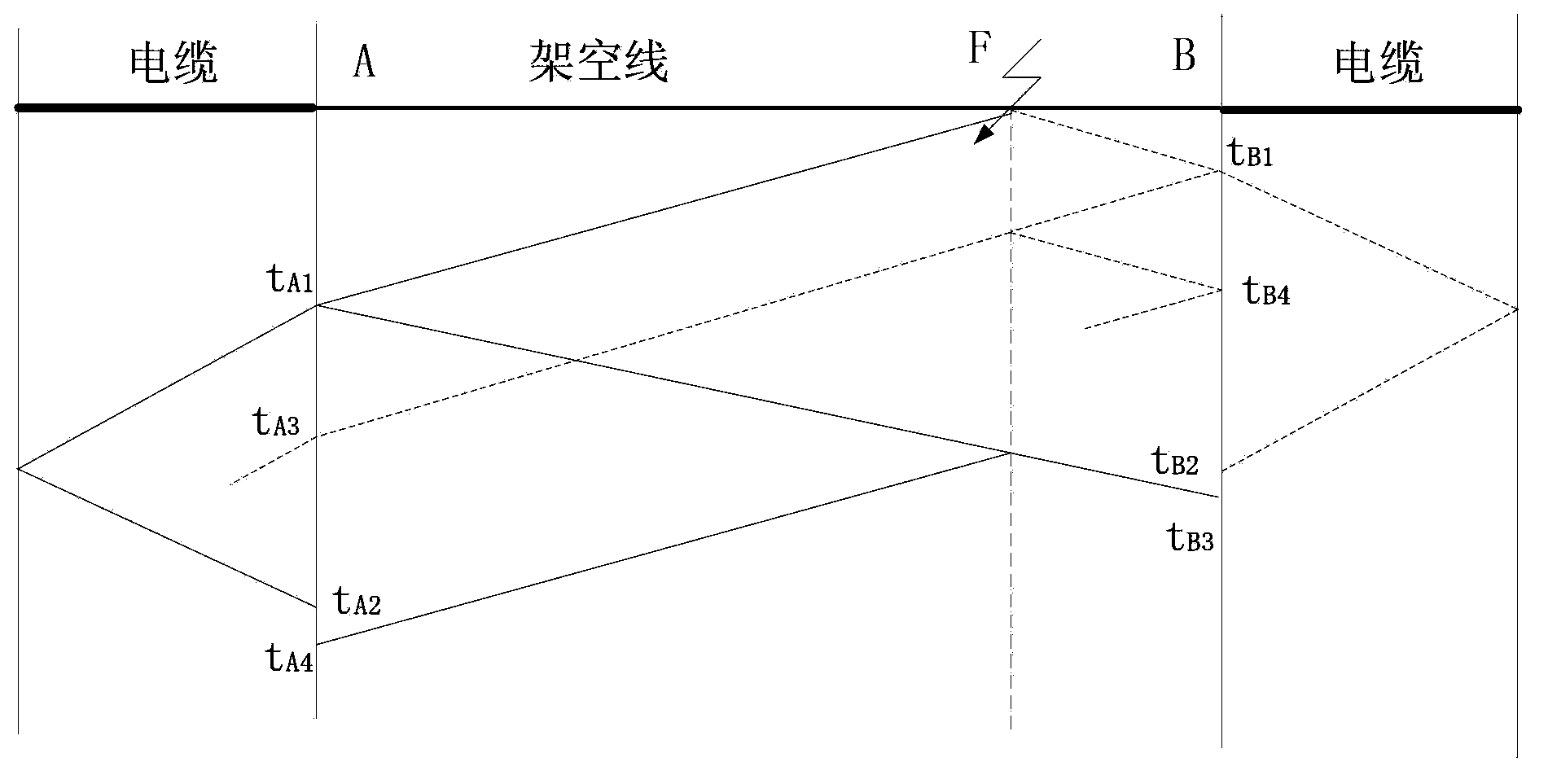
[0107] It can be seen from Table 2 that the fault occurred between detection points 5 and 6, that is, overhead line 3.
[0108] The arrival time of the first fault traveling wave detected by detection point 5 is 0.240030s, and the arrival time of the first fault traveling wave detected by detection point 6 is 0.240098s, so the fault occurred in the upper half of overhead line 3. Set the cable wave velocity v b =1.5×10 8 m / s, the velocity ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com