Rigid scope optical assembly and rigid endoscope
An optical system and rigid mirror technology, applied in the direction of endoscopes, optics, optical components, etc., can solve the problems of enlarged focal power distribution of the diffractive surface, decreased diffraction efficiency, and inability to ensure that it can achieve a good correction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
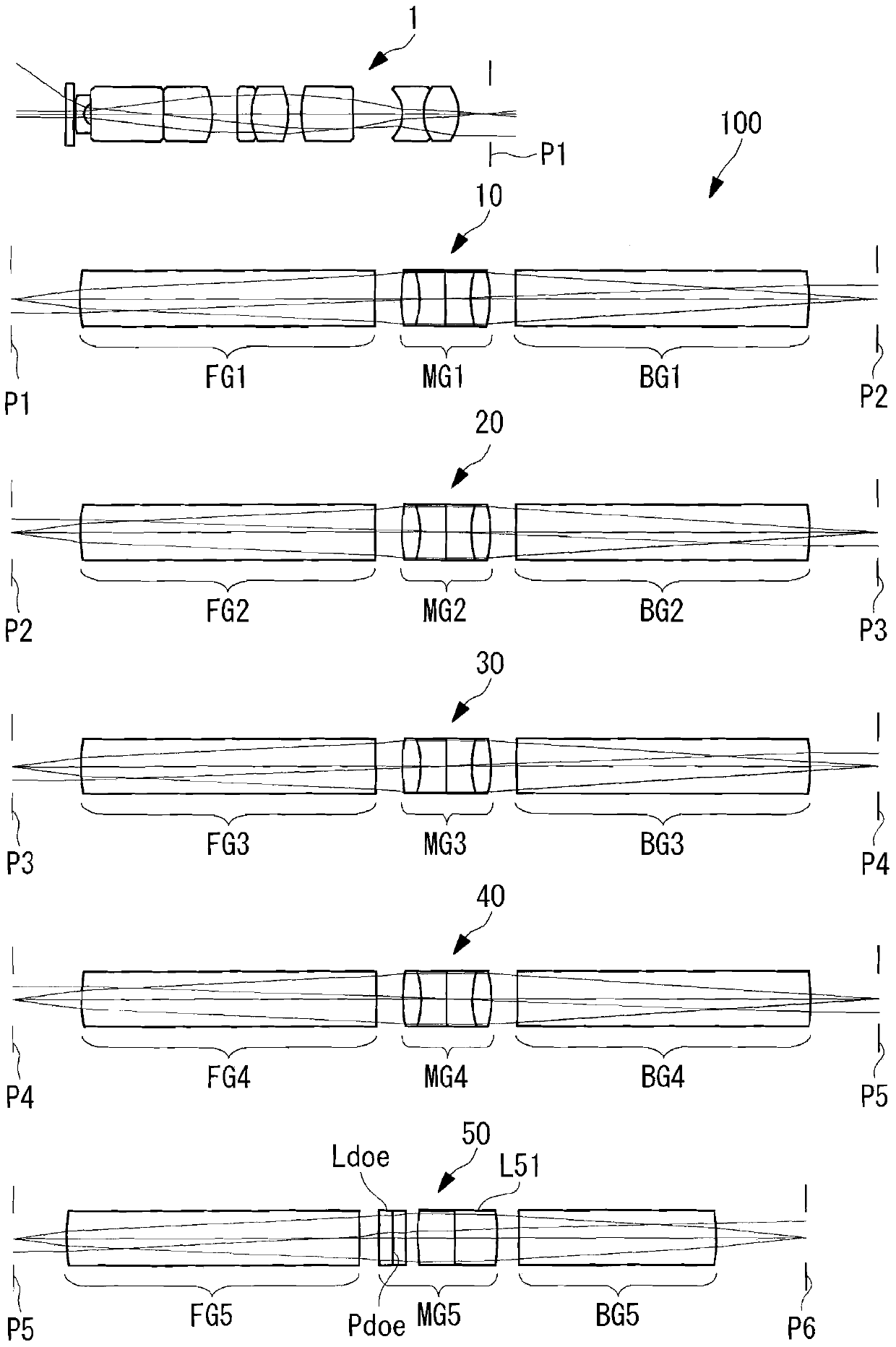
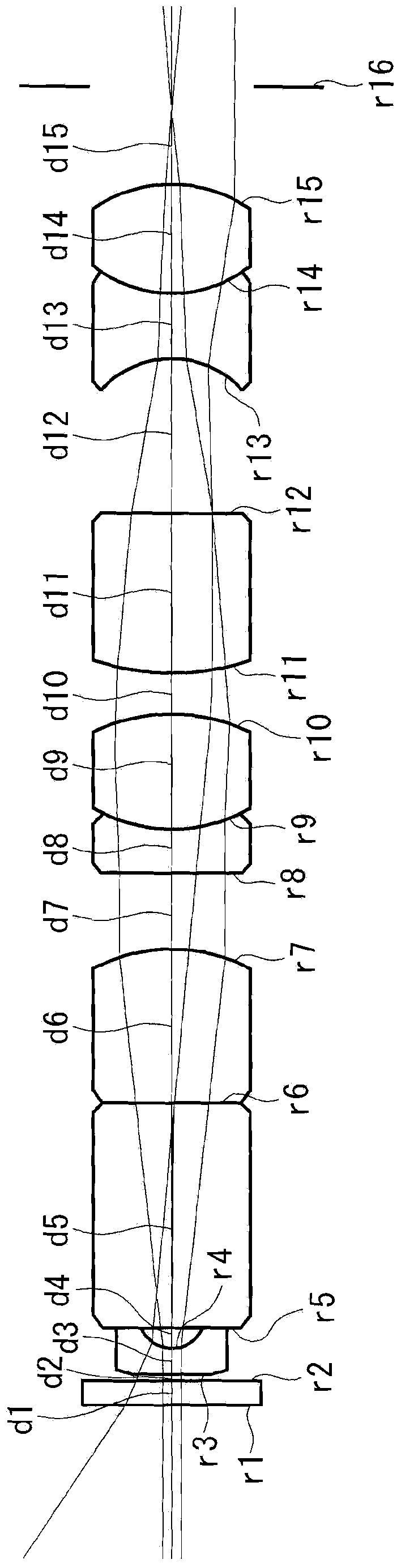
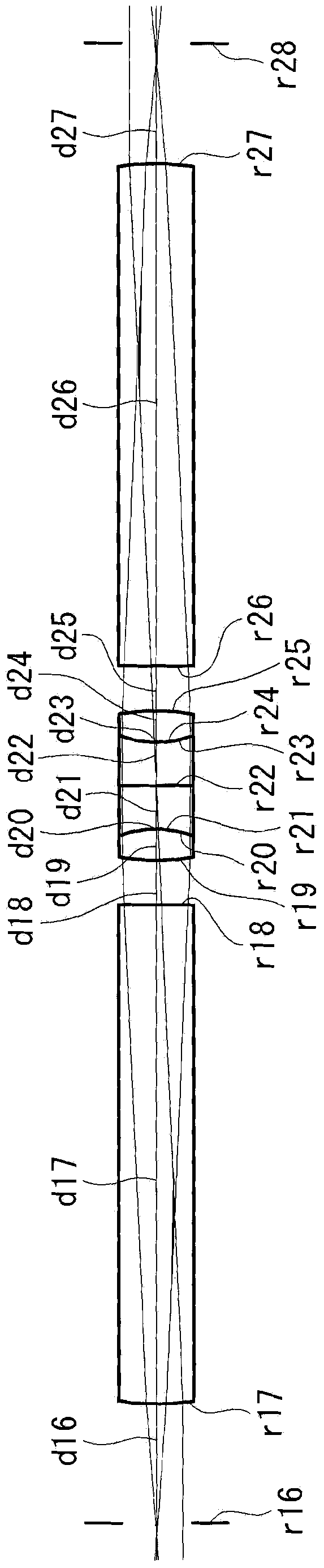
[0069] The optical system for rigid mirrors related to Embodiment 1 of the present invention is as follows: Figure 2 to Figure 7 As shown, an objective optical system and first to fifth relay optical systems are provided in this order from the object side.
[0070] The first to fourth relay optical systems include, in order from the object side, a positive front group consisting of a plano-convex lens with a convex surface facing the object side, a positive middle group consisting of a cemented lens, and a plano-convex lens having a convex surface facing the image side. Positive rear group formed. The fifth relay optical system includes, in order from the object side, a positive front group consisting of a plano-convex lens with a convex surface facing the object side, a positive middle group consisting of a diffractive optical element and a cemented lens, and a plano-convex lens with a convex surface facing the image side. Positive rear group composed of convex lens. The l...
Embodiment 2
[0082] The optical system for rigid mirrors related to Embodiment 2 of the present invention is as follows: Figure 9 and Figure 10 As shown, the lens structure of the objective optical system (face numbers 1 to 15) and the fifth relay optical system (face numbers 65 to 78) differs from the rigid mirror optical system of Example 1 mainly. In the fifth relay optical system, the diffractive optical element is sandwiched by two cemented lenses in the direction of the optical axis. The lens configurations of the first to fourth relay optical systems are substantially the same as those of the rigid mirror optical system of the first embodiment, and therefore illustration thereof is omitted. The lens data of the rigid mirror optical system according to this embodiment are as follows.
[0083] Figure 11 An axial chromatic aberration diagram of the rigid mirror optical system configured in this way is shown. According to the optical system for a rigid mirror of this embodiment, ...
Embodiment 3
[0093] The optical system for rigid mirrors related to Embodiment 3 of the present invention is as follows: Figure 12 As shown, the fifth relay optical system (surface numbers 65 to 78) is mainly different from the rigid mirror optical system of Example 2 in the lens structure. The lens configurations of the objective optical system and the first to fourth relay optical systems are substantially the same as those of the rigid mirror optical system of the second embodiment, and therefore illustration thereof is omitted. The lens data of the rigid mirror optical system according to this embodiment are as follows.
[0094] Figure 13 An axial chromatic aberration diagram of the rigid mirror optical system configured in this way is shown. According to the optical system for a rigid mirror of this embodiment, the axial chromatic image between the C-line (C-line) and the F-line (F-line) can be corrected by the cemented lens included in the first to fourth relay optical systems. Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com