Method and system for detecting and distinguishing passive synthetic aperture target signal
A technology of target signal and synthetic aperture, which is applied in radio wave measurement system, system for determining direction or offset, orientator for determining direction, etc. It can solve the problem of unapplied and ineffective detection and resolution of underwater target signal and phase estimation. Factor error and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
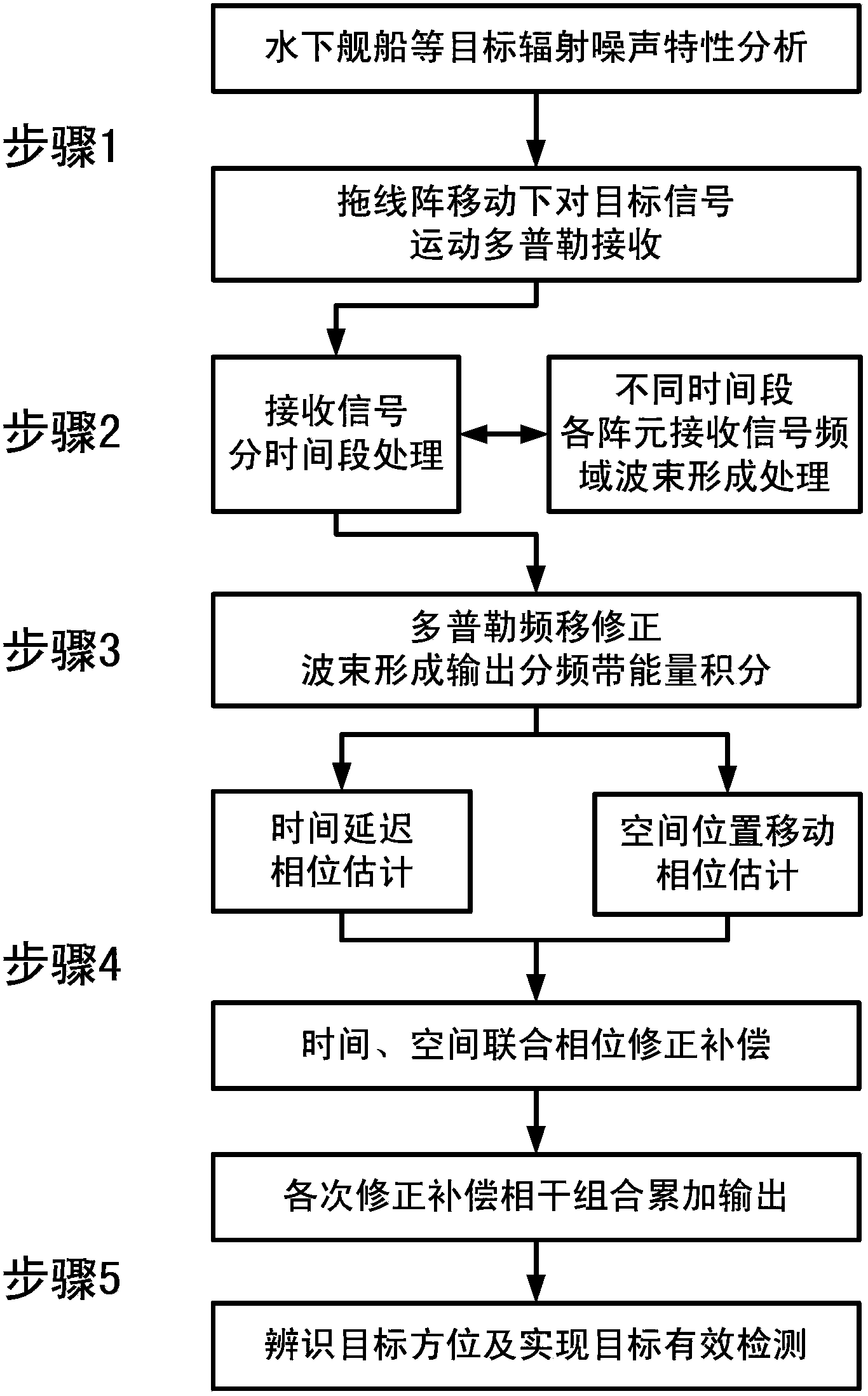
Embodiment
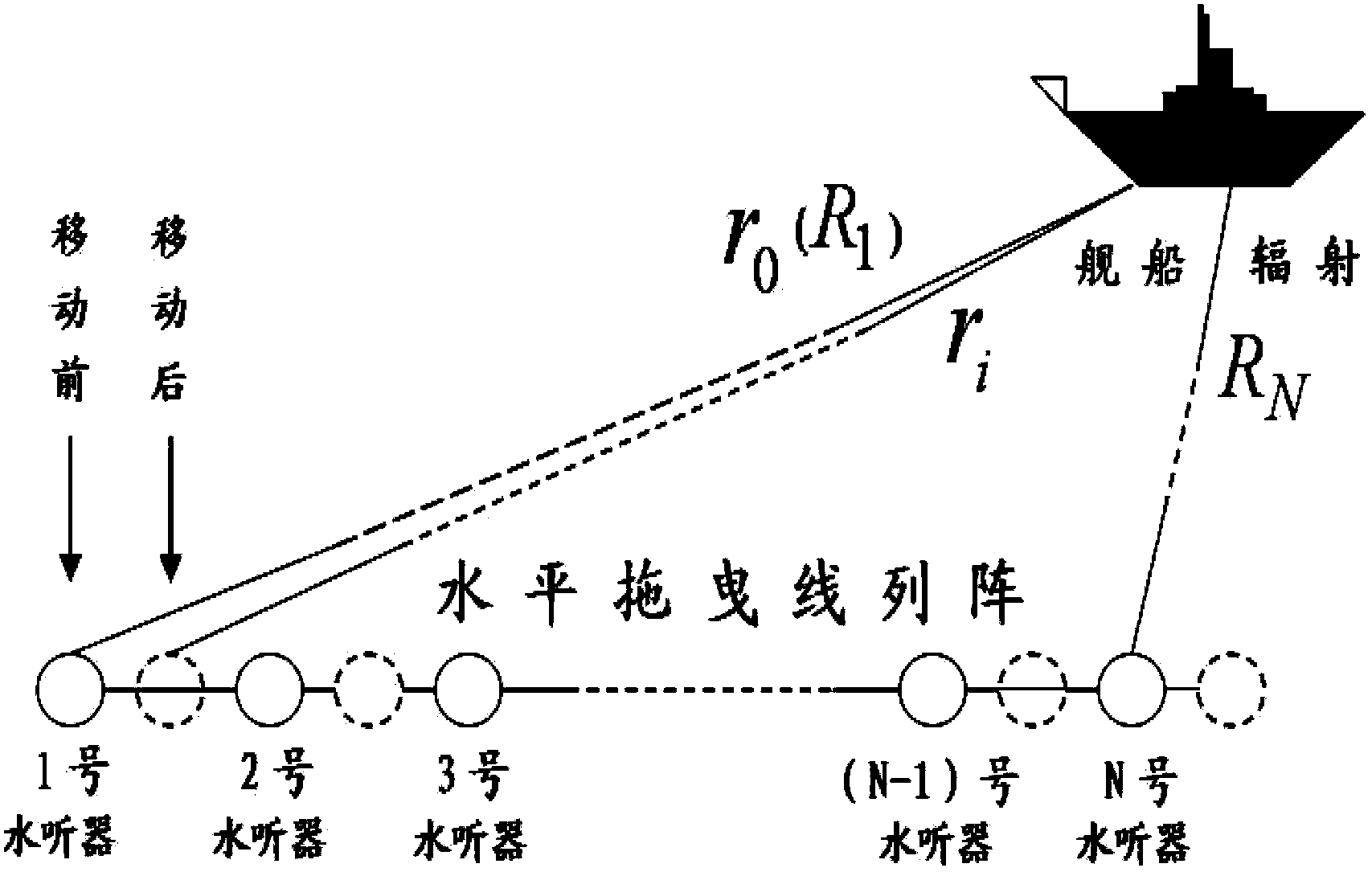
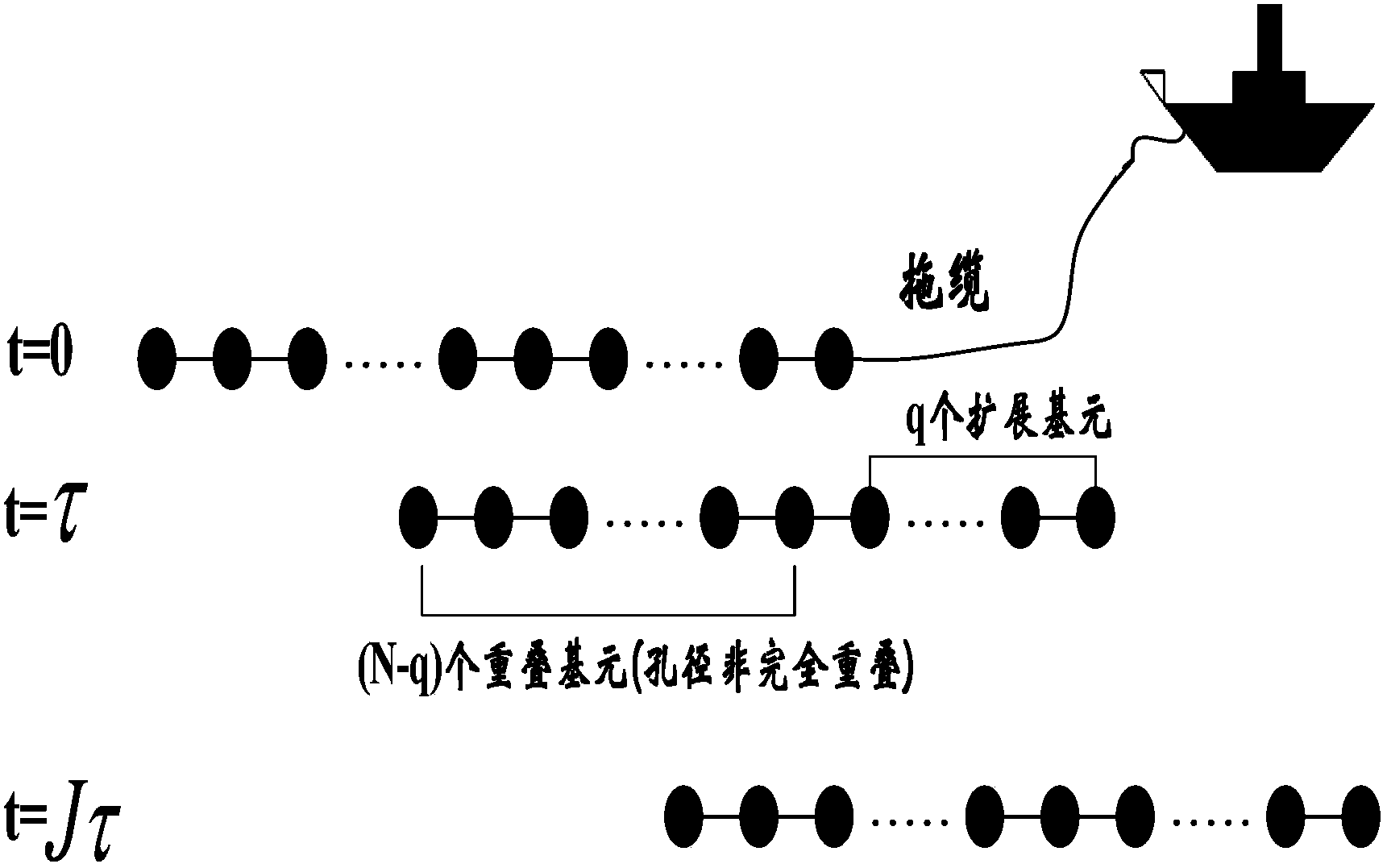
[0113] Such as figure 1 As shown in Fig. 1, when the underwater ship or the measured target passes through the horizontal line array, each array element samples the noise signal, and due to the existence of dragging speed, the frequency of the received signal and the radiated sound source are inconsistent. combine figure 2 The base array of the linear array moves in a straight line. For N isotropic linear arrays with an equal distance of d, the speed is v. The first array element receives the ship radiation noise signal at time t=0 as the reference standard, and the second The propagation delay of each array element relative to the first array element is △τ, then the signal received by the nth array element is
[0114] x n (t i )=Aexp[j2πf(t i -τ n )]+ξ n (t i )
[0115] In the formula, A-amplitude; f-frequency; t i - i-th sampling time, τ n is the propagation delay of the nth hydrophone element relative to the first element
[0116] τ n =(R n -R 1 ) / c
[0117]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com