Encoding and decoding method and device for Ethernet physical layer
An encoding method and encoding device technology, applied in code conversion, transmission data organization to avoid errors, digital transmission system, etc., can solve the problem of difficulty in achieving optimal (synchronous) header overhead control, and the inability to flexibly select information groups to be encoded Issues such as length and (sync) header redundancy overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
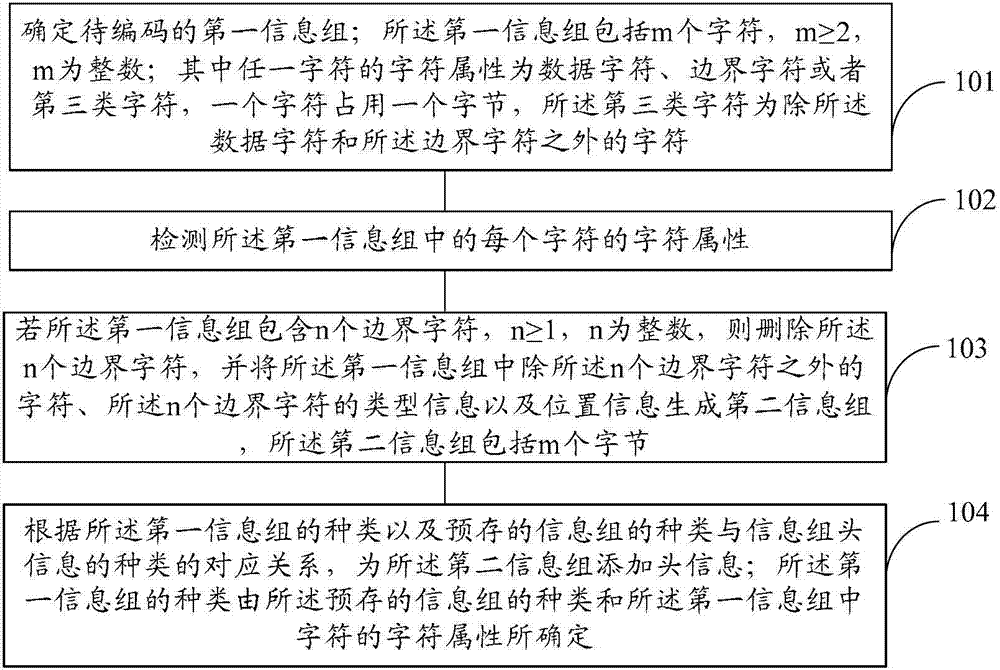
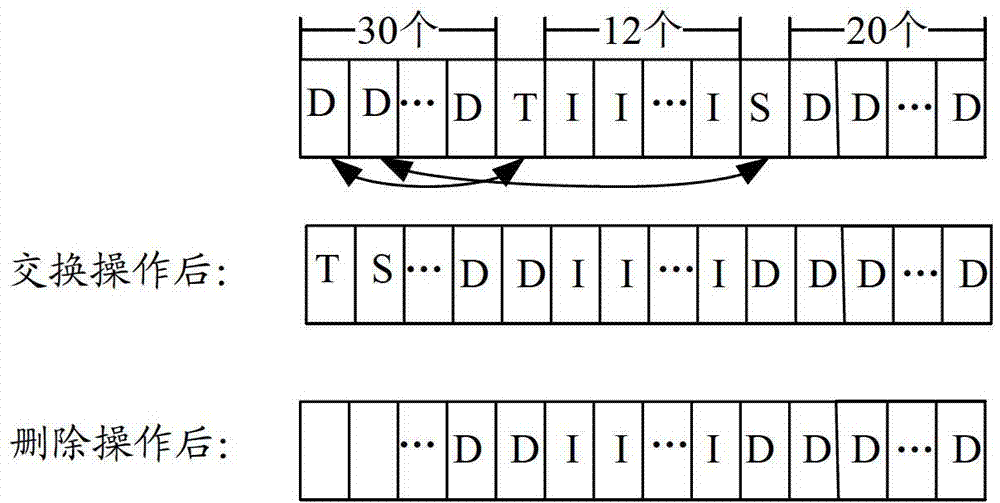
[0202] It is assumed that the types of the second information group are: full data character type (type A), boundary character type (type B) and all third type character type (type C). Table 2 shows the relationship between the type of the second information group and the header information of the second information group.
[0203] see Figure 6 ,include:
[0204] 601: Determine the second information group to be decoded and the header information of the second information group;
[0205] Exemplarily, the header information of the second information group includes: any one of A:01, B:10, and C:00.
[0206] 602: Detect header information of the second information group;
[0207] 603: If the header information of the second information group is: A:01, use the second information group as the first information group;
[0208] 604: If the header information of the second information group is: C:00, then delete the type information of the second information group recorded in the...
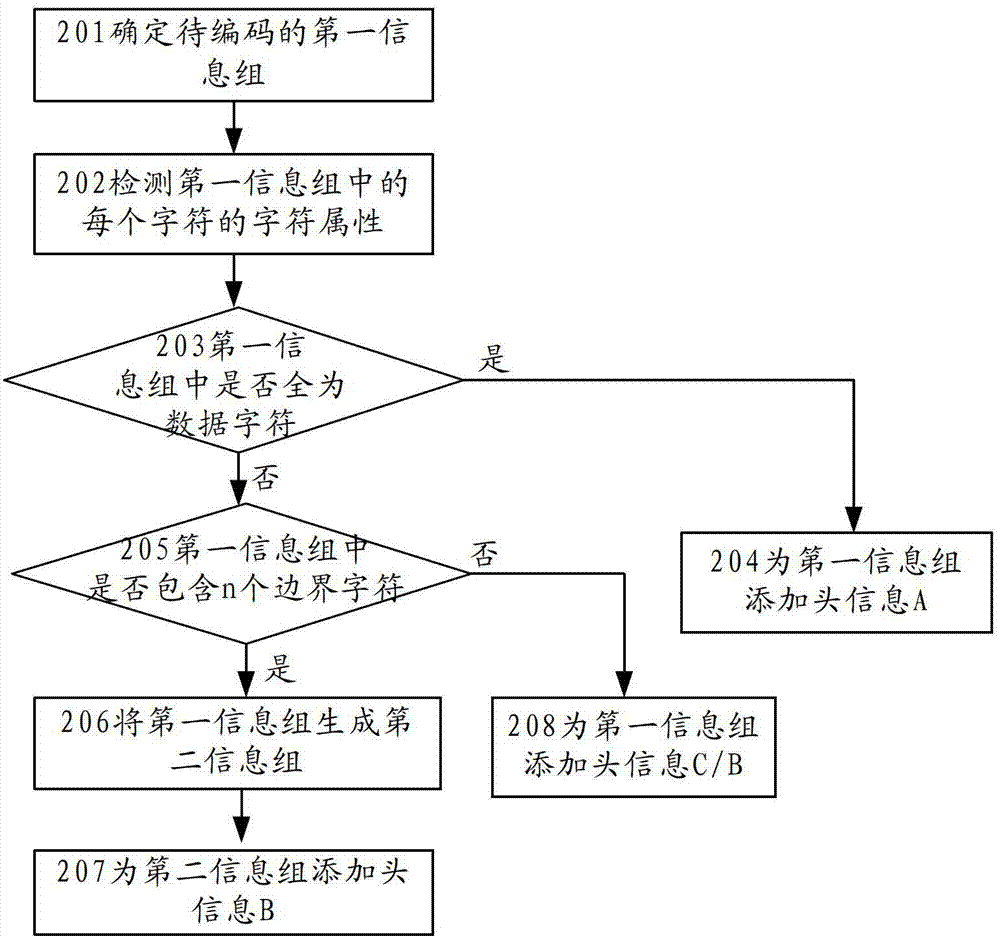
Embodiment 2
[0213] Assuming that the header information type of the second information group is header information 0 in Table 3, if the second information group is a non-data symbol type, the type information of the second information group is recorded in the first two bits of the second information group. characters, represented by 00 / 01 / 10 / 11 respectively.
[0214] see Figure 7 ,include:
[0215] 701: Determine the second information group to be decoded and the header information of the second information group;
[0216] 702: Detect header information of the second information group;
[0217] 703: If the header information of the second information group is: A:0, use the second information group as the first information group;
[0218] 704: If the header information of the second information group is: B:1, then judge whether the first two bits of the second information group are 00;
[0219] 705: If yes, delete the type information of the second information group recorded in the fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com