A method for efficiently utilizing fatty acids to produce mevalonate and the constructed genetically engineered bacteria
A technology for mevalonate and fatty acid, applied in genetic engineering, microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as rare raw materials, high cost, and environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The construction of long-chain fatty acid transporter gene (fadL) and acyl-CoA synthetase gene (fadD) co-expression vector, the specific process is as follows:
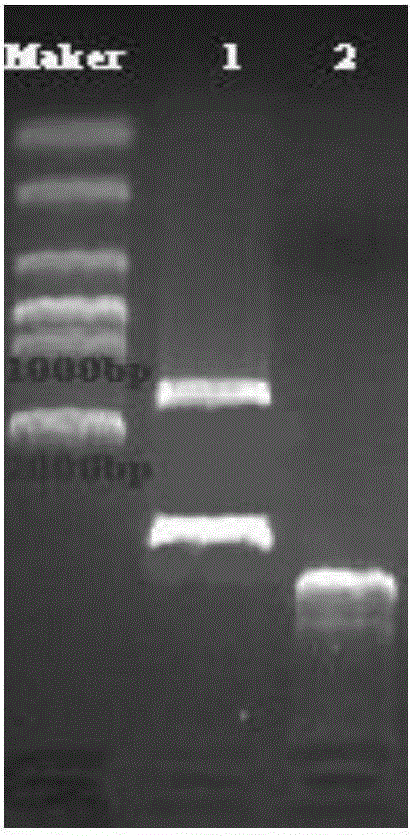
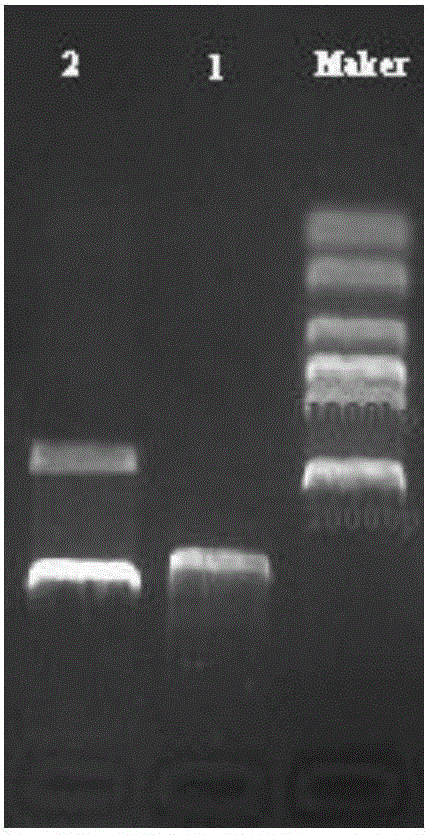
[0036] The long-chain fatty acid transferase ( fadL), and introduced EcoI and HindIII restriction sites at the 5' end and 3' end, respectively, and then cloned the gene into the pET-30a vector with the above restriction sites to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET-fadL( figure 1 ); using oligonucleotides 5'-GGGAATTCCATATGACCGCTCAGGTTACATGCG-3' and 5'-CCGCTCGAGTTAAACCAGACGAACTTCGTGC-3' as primers, using Escherichia coli genomic DNA as a template, acyl-CoA synthesis was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) enzyme (fadD), and introduced KpnI and BamHI restriction sites at the 5' end and 3' end, respectively, and then cloned the gene into the pET-fadL vector using the above restriction sites to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET-fadL-fadD ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 2
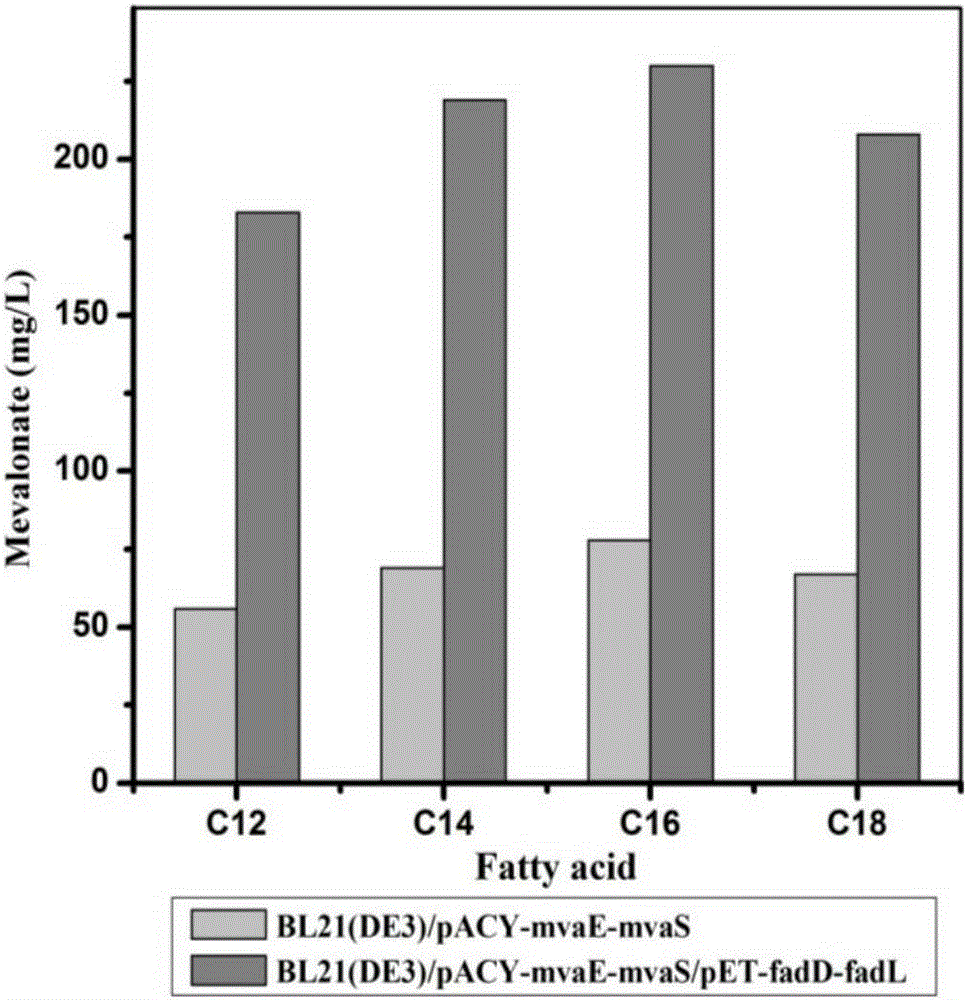
[0038] The preparation of engineering Escherichia coli strain BL21(DE3) / pET-fadL-fadD / pYJM11 for synthesizing mevalonate, and using the strain to ferment and transform fatty acid into mevalonate, the specific process is as follows:
[0039] The recombinant plasmid pET-fadL-fadD constructed in Example 1 and the recombinant plasmid pYJM11 (Jianming Yang et al., BioresourceTechnology 104, 642-647, 2012) constructed in this laboratory were extracted by alkaline lysis, and 5 μl of recombinant plasmids were recombined by heat shock transformation Transform the plasmid into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) competent cells, and then take 50 μl of the transformed bacterial solution and spread it on a medium containing 34 μg·mL -1 Chloramphenicol with 50 μg·mL -1 Positive clones were screened on the ammonia LB plate, and the grown colonies were recombinant Escherichia coli strains co-expressing long-chain fatty acid transferase and fatty acyl-CoA synthetase. Pick a single colony of recombin...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Preparation of engineering Escherichia coli strain W3110 / pET-fadL-fadD / pYJM11 for synthesizing mevalonate, and using this strain to ferment and convert fatty acids into mevalonate, the specific process is as follows:
[0042] The recombinant plasmid pET-fadL-fadD constructed in Example 1 and the recombinant plasmid pYJM11 (Jianming Yang et al., BioresourceTechnology 104, 642-647, 2012) constructed in this laboratory were extracted by alkaline lysis, and 5 μl of recombinant plasmids were recombined by heat shock transformation The plasmid was transformed into Escherichia coli W3110 competent cells, and then 50 μl of the transformed bacteria liquid was applied to the cells containing 34 μg·mL -1 Chloramphenicol and 50 μg·mL -1 Positive clones were screened on the ammonia LB plate, and the grown colonies were recombinant Escherichia coli strains co-expressing long-chain fatty acid transferase and fatty acyl-CoA synthetase. Pick a single colony of recombinant Escherichia c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com