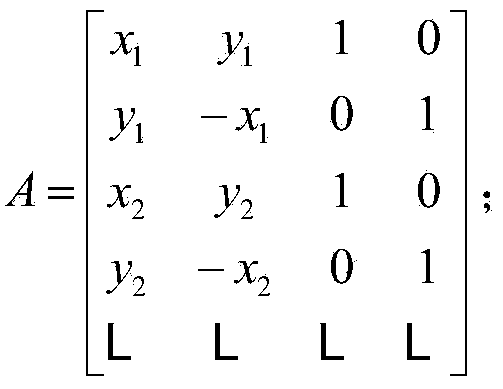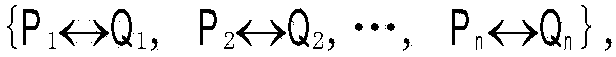Frequency domain shape description method for image matching, recognition and retrieval
A shape description and image technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve problems such as high computational complexity, robustness to noise and deformation, and inability to obtain tangent vectors, achieving a wide range of application prospects, computing low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
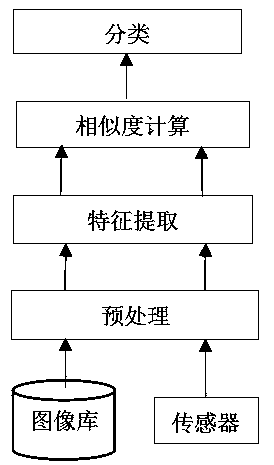
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Step 1: Extract feature points from an input image, and calculate the shape descriptor of each feature point, let P={P 1 ,P 2 ,...,P K} and {f(F(P k ))|k=1,2,…,K} represent the obtained feature points and their corresponding shape descriptors respectively. The calculation steps of shape descriptors are as follows:
[0020] (a) Choose a feature point P k ∈P is used as a reference point to make statistics on the spatial distribution of other feature points to obtain a corresponding histogram, denoted as h(P k ); here, the specific calculation method of the histogram is as follows: with reference point P k As the center, divide the space where the smallest circumscribed circle of the image is into a grid of M×N, calculate the number of feature points falling into each interval of the grid to obtain a histogram, and M and N are all natural numbers; As a reference point, a histogram is obtained corresponding to each feature point, and a total of K histograms {h(P k )|k...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Step 1: same as step 1 of embodiment 1;
[0066] Step 2: All the feature points P={P obtained in step 1 1 ,P 2 ,...,P K} corresponding shape descriptor [f(F(P 1 )), f(F(P 2 )),…,f(F(P K ))] matrix addition to get G(P)=f(F(P 1 ))⊕f(F(P 2 )),…,⊕f(F(P K )), where the operator "⊕" represents the addition of the elements of the corresponding positions of each matrix involved in the operation, and G(P) represents all K matrices f(F(P 1 )), f(F(P 2 )),…,f(F(P K )) The elements with the same subscript are added together, and G(P) is the shape descriptor that is finally used for image matching, recognition, and retrieval;
[0067] Step 3: same as step 2 of embodiment 1;
[0068] Step 4: All the feature points Q={Q obtained in step 3 1 ,Q 2 ,...,Q L} corresponding shape descriptor f(F(Q 1 )), f(F(Q 2 )),…,f(F(Q L )) matrix addition to get G(Q)=f(F(Q 1 ))⊕f(F(Q 2 )),…,⊕f(F(Q K ));
[0069] Step 5: Straighten the matrices G(P) and G(Q) into vectors respectively...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com