Method for monitoring activity state of underground fault
A technology of active states and faults, used in geophysical measurements, instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
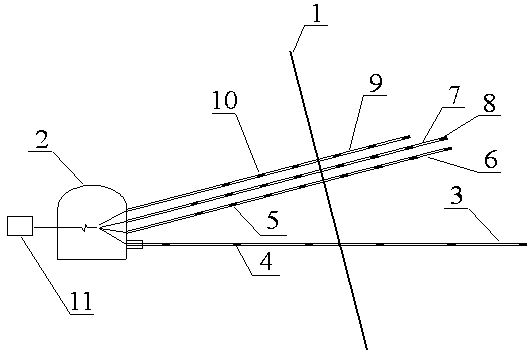
[0022] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-2 Shown, a kind of downhole fault active state monitoring method, the concrete steps of described method are as follows:
[0023] A. Excavate observation chamber 2 in the footwall of normal fault 1 or the upper wall of reverse fault 1′;
[0024] B. Arrange horizontal medium-deep holes in the observation chamber 2, wherein the medium-deep holes pass through the fault plane for a certain distance S 1 And a multi-point displacement gauge 3 is installed in the middle and deep holes;
[0025] C. Arrange three medium-deep holes perpendicular to the fault plane, among which the medium-deep holes pass through the fault plane for a certain distance S 2 And the anchor multi-point stress gauge 6, the drilling multi-point stress gauge 7, and the microseismic monitoring system 9 are respectively installed in the three medium and deep holes;
[0026] D. Multi-point displacement meter 3, bolt multi-point stress meter 6, drilling multi-point stress meter...
Embodiment 2
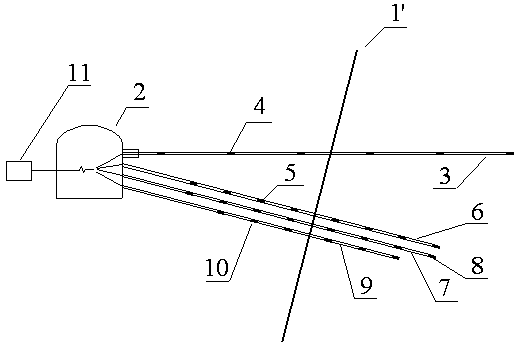
[0036] Embodiment 2: as Figure 1-2 Shown, a kind of downhole fault active state monitoring method, the concrete steps of described method are as follows:
[0037] A. Excavate observation chamber 2 in the footwall of normal fault 1 or the upper wall of reverse fault 1′;
[0038] B. Arrange horizontal medium-deep holes in the observation chamber 2, wherein the medium-deep holes pass through the fault plane for a certain distance S 1 And a multi-point displacement gauge 3 is installed in the middle and deep holes;
[0039] C. Arrange three medium-deep holes perpendicular to the fault plane, among which the medium-deep holes pass through the fault plane for a certain distance S 2 And the anchor multi-point stress gauge 6, the drilling multi-point stress gauge 7, and the microseismic monitoring system 9 are respectively installed in the three medium and deep holes;
[0040] D. Multi-point displacement meter 3, bolt multi-point stress meter 6, drilling multi-point stress meter...
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3: as Figure 1-2 Shown, a kind of downhole fault active state monitoring method, the concrete steps of described method are as follows:
[0051] A. Excavate observation chamber 2 in the footwall of normal fault 1 or the upper wall of reverse fault 1′;
[0052] B. Arrange horizontal medium-deep holes in the observation chamber 2, wherein the medium-deep holes pass through the fault plane for a certain distance S 1 And a multi-point displacement gauge 3 is installed in the middle and deep holes;
[0053] C. Arrange three medium-deep holes perpendicular to the fault plane, among which the medium-deep holes pass through the fault plane for a certain distance S 2 And the anchor multi-point stress gauge 6, the drilling multi-point stress gauge 7, and the microseismic monitoring system 9 are respectively installed in the three medium and deep holes;
[0054] D. Multi-point displacement meter 3, bolt multi-point stress meter 6, drilling multi-point stress meter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com