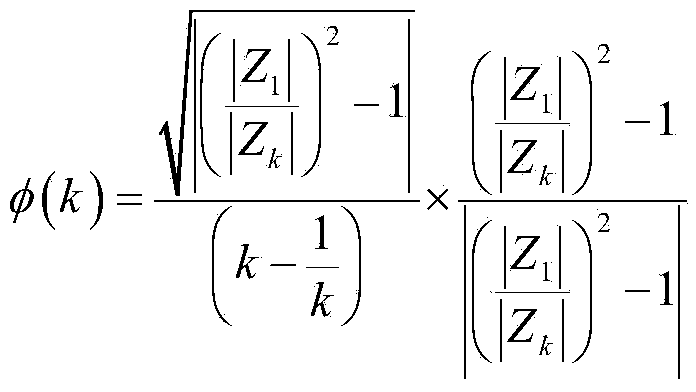Method for constructing harmonic wave impedance characteristic function
A technology of harmonic impedance characteristics and construction methods, applied in the field of data processing, can solve problems such as system island misjudgment, failure to reflect island load characteristics, etc., and achieve a wide range of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] In the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the harmonic impedance characteristic function construction method is carried out as follows:
[0023] A), function construction
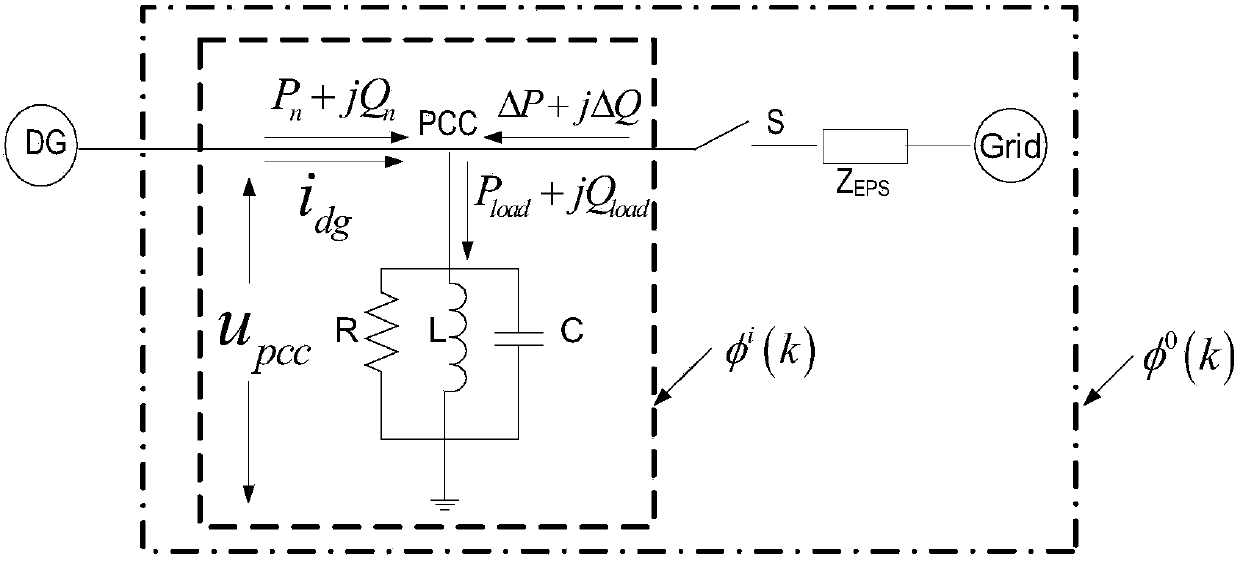
[0024] When an island situation occurs, figure 1 The switch S in is off, then the impedance at the point of common coupling (PCC) when the system is stable is:
[0025] Z i ( jω ) = 1 1 R + j ( ωC - 1 ωL ) - - - ( 1 )
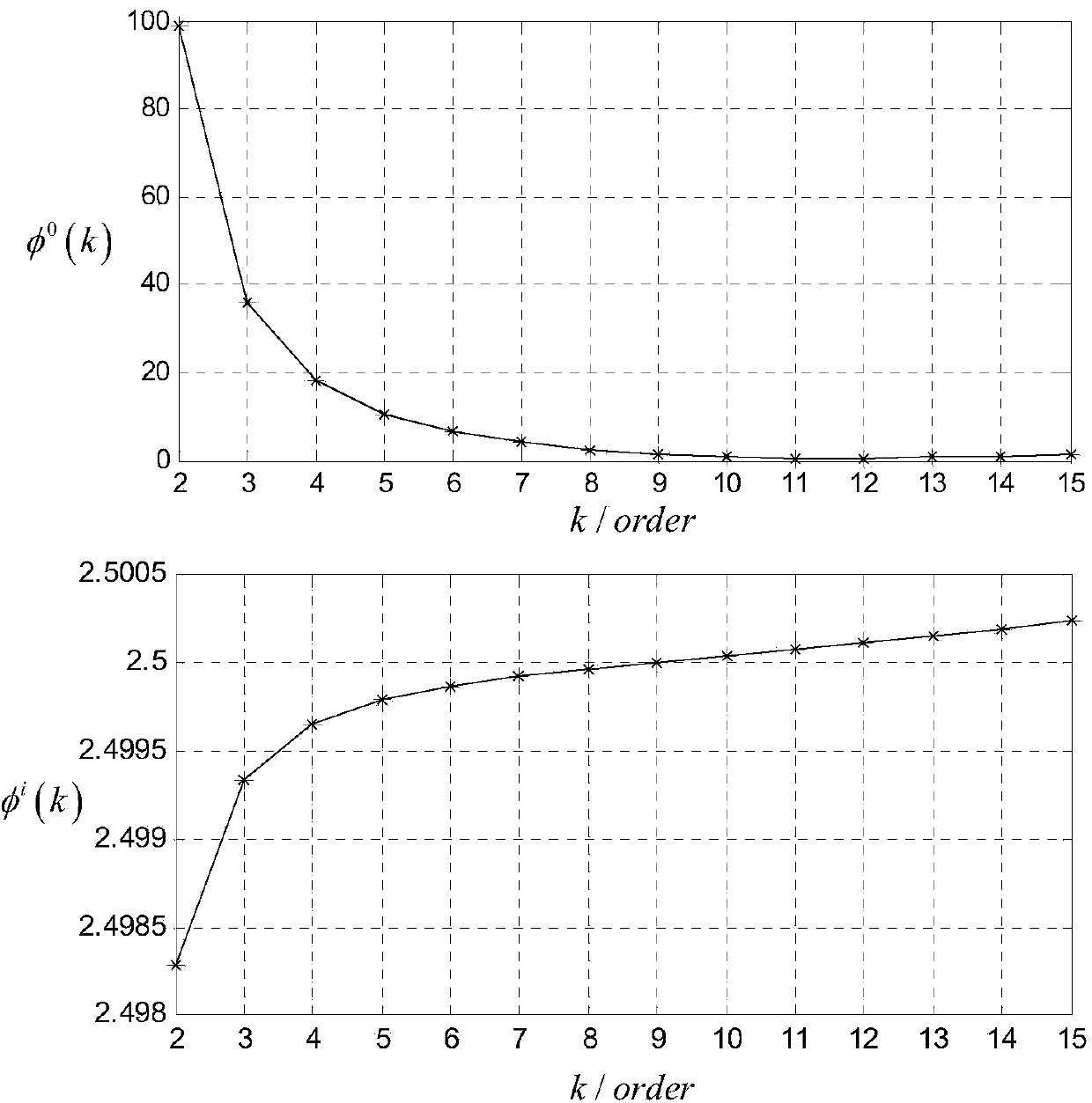
[0026] Due to the local load figure of merit ω 0 Represents the local load resonance angular frequency, then the output impedance amplit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com