A Calculation Method of Real-time Normal Vector in 3D Scanning Point Cloud
A 3D scanning and normal vector technology, applied in computing, image data processing, 3D modeling, etc., can solve problems such as normal vector errors, and achieve the effect of reducing overhead time, avoiding recalculation, and reducing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
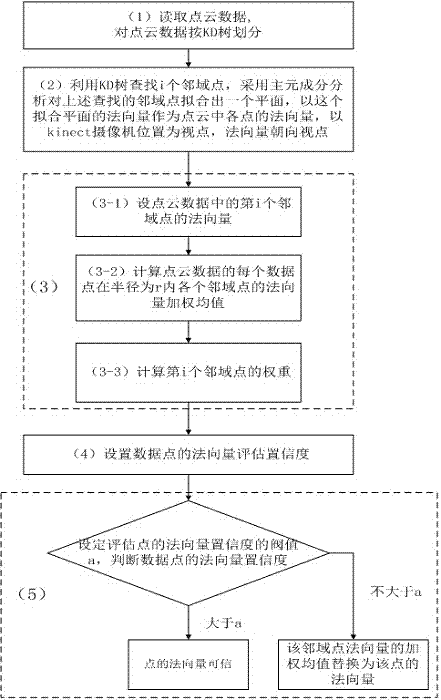
[0047] A method for calculating real-time normal vectors in a three-dimensional scanning point cloud of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the steps are:
[0048] (1). Use the kinect camera for physical scanning, such as figure 2 As shown, read point cloud data, such as image 3 shown. , divide the point cloud data according to the KD tree, and obtain k neighborhood points of each point cloud data;
[0049] (2). For each point of the point cloud data, use the KD tree of the point cloud data to find i neighbor points, where The value of is a positive integer in the interval [5-20], where, According to the principal component analysis (PCA), a plane is fitted to the above-mentioned searched neighborhood points, and the normal vector of the fitted plane is used as the normal vector of each point of the point cloud data, and the posit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com