Method for calculating short-half-life daughter nucleus bank deposit external irradiation dose of long-lived radioactive nuclide
A technology for radionuclides and radioactive daughter nuclei, which is applied in the field of calculating the external radiation dose of short half-life daughter nuclei of long-lived radionuclides deposited on the shore. Effects of technical issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
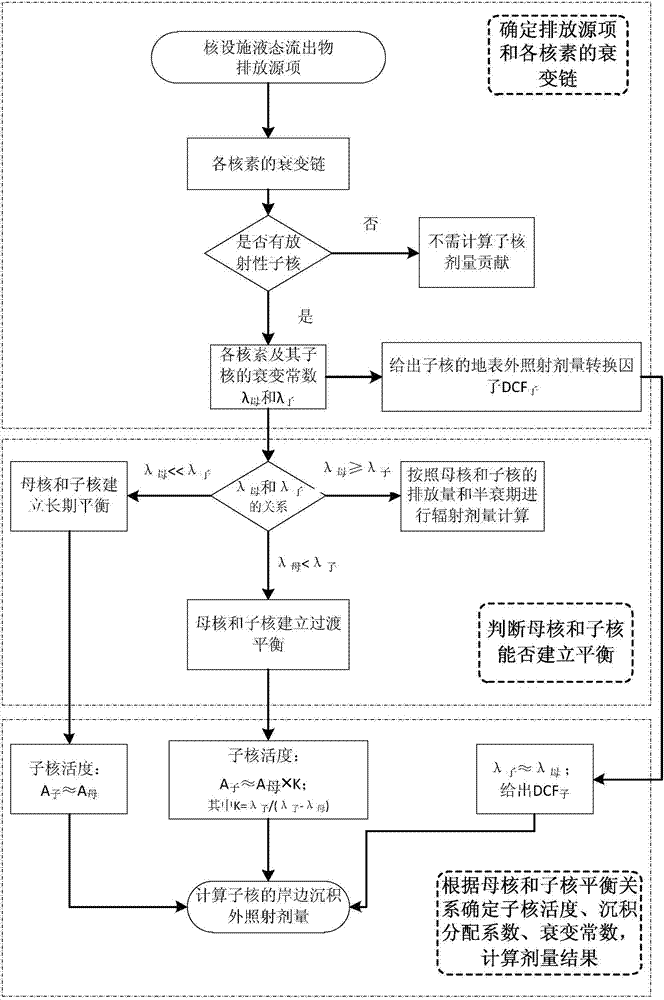
[0028]Taking the mother nucleus Ce-144 and its daughter nucleus Pr-144 as an example, the relevant calculations and assumptions carried out according to the steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0029] The first step is to judge whether Ce-144 has a radioactive daughter nucleus. After judging that there is a radioactive daughter nucleus Pr-144, the λ can be found from the public information Ce-144 =1.02E-4 / h, λ Pr-144 =2.41 / h, the surface deposition external radiation dose conversion factor DCF of the daughter nucleus Pr-144 Pr-144 =1.44E-12Sv m 2 / Bq h;
[0030] The second step is to judge whether the balance relationship between the mother nucleus Ce-144 and the daughter nucleus Pr-144 can be established: by λ Ce-144 Pr-144 , it can be considered that the parent nucleus Ce-144 and the daughter nucleus Pr-144 have established a long-term equilibrium relationship at the deposition site;
[0031] In the third step, according to the equilibrium relationship establ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com