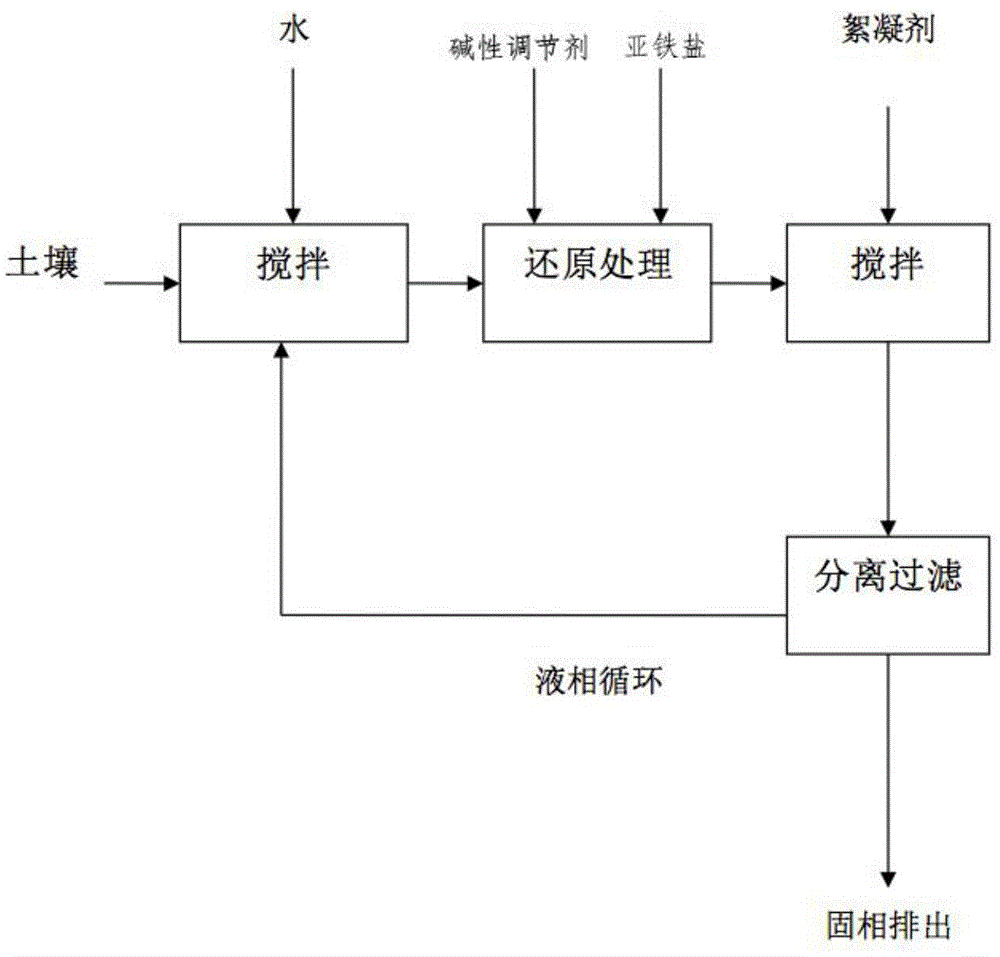
Method for removing hexavalent chromium from polluted soil
A technology for chromium-contaminated soil and hexavalent chromium, which is applied in the field of removing hexavalent chromium pollution in soil, can solve problems such as inability to reduce hexavalent chromium content, inability to achieve metal chromium transfer and separation, inability to effectively remove secondary pollution, etc., to achieve reduction Effect of hexavalent chromium concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Embodiment 1: the effect of washing hexavalent chromium polluted soil
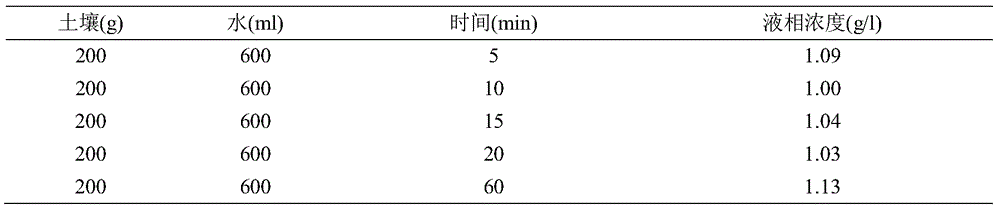
[0027] 200g of soil was used respectively, and the liquid-solid ratio was 3:1, and the washing experiments were carried out according to 5, 10, 15, 20, and 60 minutes. The specific experimental data are shown in Table 1.
[0028] Table 1 The leaching effect of hexavalent chromium under different washing time
[0029]
[0030] As can be seen from Table 1, most of the hexavalent chromium in the soil can be rapidly dissolved in the liquid phase, and as the washing time prolongs, the rising trend of the concentration of hexavalent chromium in the liquid phase is not significant, so the method washing time of the present invention is controlled at 10-60min is sufficient, preferably 30-60min.
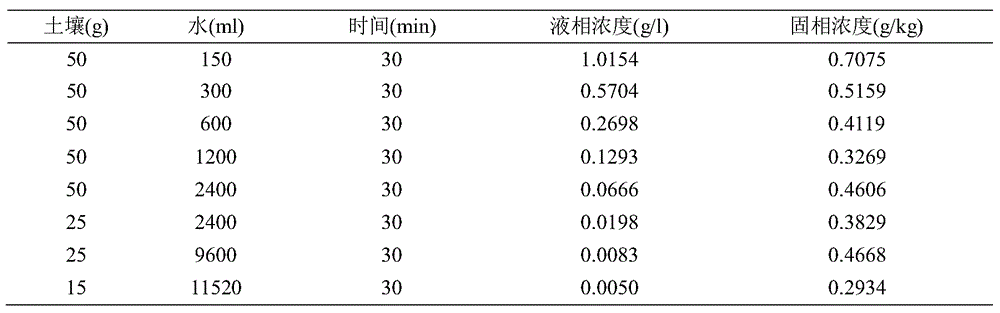
[0031] On the basis of the above, in order to further investigate the distribution of hexavalent chromium in the liquid phase and solid phase in the reaction, the liquid-solid ratios were respectively 3:1, 6:1,...
Embodiment 2
[0034] It can be seen from Table 2 that with the increase of the liquid-solid ratio in the washing process, the concentration of hexavalent chromium in the liquid phase and the solid phase gradually decreased, but when the liquid-solid ratio in the reaction increased to 768:1, the liquid phase Hexavalent chromium in the soil is reduced to 5mg / l. At this time, the concentration of hexavalent chromium in the separated solid phase is still as high as 293.4mg / kg. Only washing with water to remove hexavalent chromium in the soil cannot reach the preset value, and the water consumption is huge. ; Taking water consumption and removal effect into consideration, the ratio of soil to water consumption is 1:3-24, and the unit effect is the largest at the ratio of 1:3. Embodiment 2: the effect of ferrous sulfate washing hexavalent chromium polluted soil
[0035] According to the results of Example 1, the liquid-solid ratio was kept at 3:1, ferrous sulfate was added to carry out reducing w...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: the addition of quicklime (slaked lime) affects the removal rate of hexavalent chromium in soil
[0048] Quicklime was selected as a regulator to precipitate the reduced trivalent chromium in alkaline conditions. The liquid-solid ratio was selected to be 3:1 in the whole experiment, and the data are shown in Table 6 below.
[0049] Table 6 Experimental data table of the influence of quicklime on the reaction
[0050]
[0051] Keep the amount of ferrous sulfate constant, and add different amounts of quicklime to adjust the pH. From the experimental results, with the increase of the amount of quicklime, the concentration of hexavalent chromium in the liquid phase gradually increases, while the concentration of hexavalent chromium in the solid phase It shows a trend of increasing first and then decreasing, so it can be inferred that quicklime increases the desorption capacity of soil for hexavalent chromium, resulting in an increase in the concentration of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com