The slider brake mechanism of the linear guide assembly and the lifting device of the bar cutter
A technology of linear guide rail and brake mechanism, applied in the field of brake device, slider brake mechanism, lifting device of bar cutting machine, and bar cutting machine, which can solve the problems of inconspicuous effect and increased production cost, etc. To achieve the effect of convenient operation, improve flatness and avoid swing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
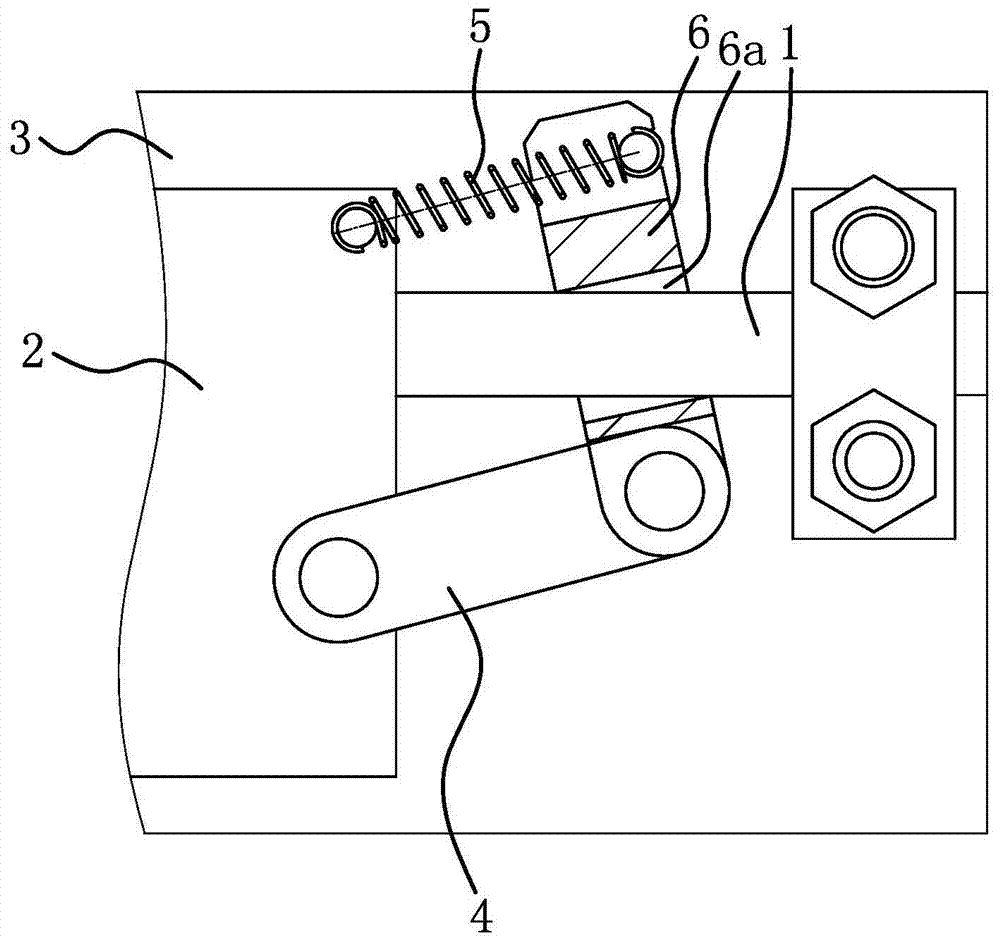
[0040] like figure 1 As shown, the linear guide rail 1 in the slider brake mechanism of the linear guide rail assembly is fixed on a base plate 3 .
[0041] like figure 1 As shown, the slider brake mechanism of the linear guide assembly includes a pull rod 4 , a tension spring 5 and a brake swing rod 6 .
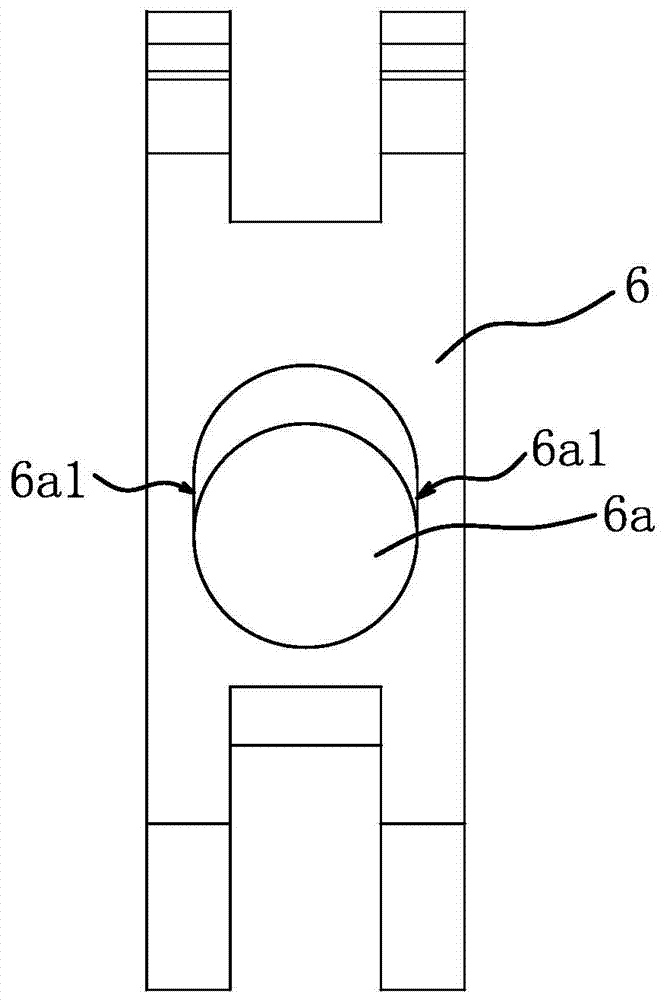
[0042] like figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the brake rocker 6 has a snap-in hole 6a with two guide sides 6a1. The cross section of the linear guide 1 is circular, the cross section of the occlusal hole 6a is strip-shaped, the outer side of the linear guide 1 is dependent on the two guide sides 6a1, and the upper and lower sides of the occlusal hole 6a are arc-shaped.
[0043] The linear guide rail 1 passes through the occlusal hole 6a; the pull rod 4 and the brake swing rod 6 are both straight rods, one end of the pull rod 4 is hinged to the slider 2, and the other end of the pull rod 4 is hinged to one end of the brake swing rod 6; the tension spring 5 One end of the...
Embodiment 2
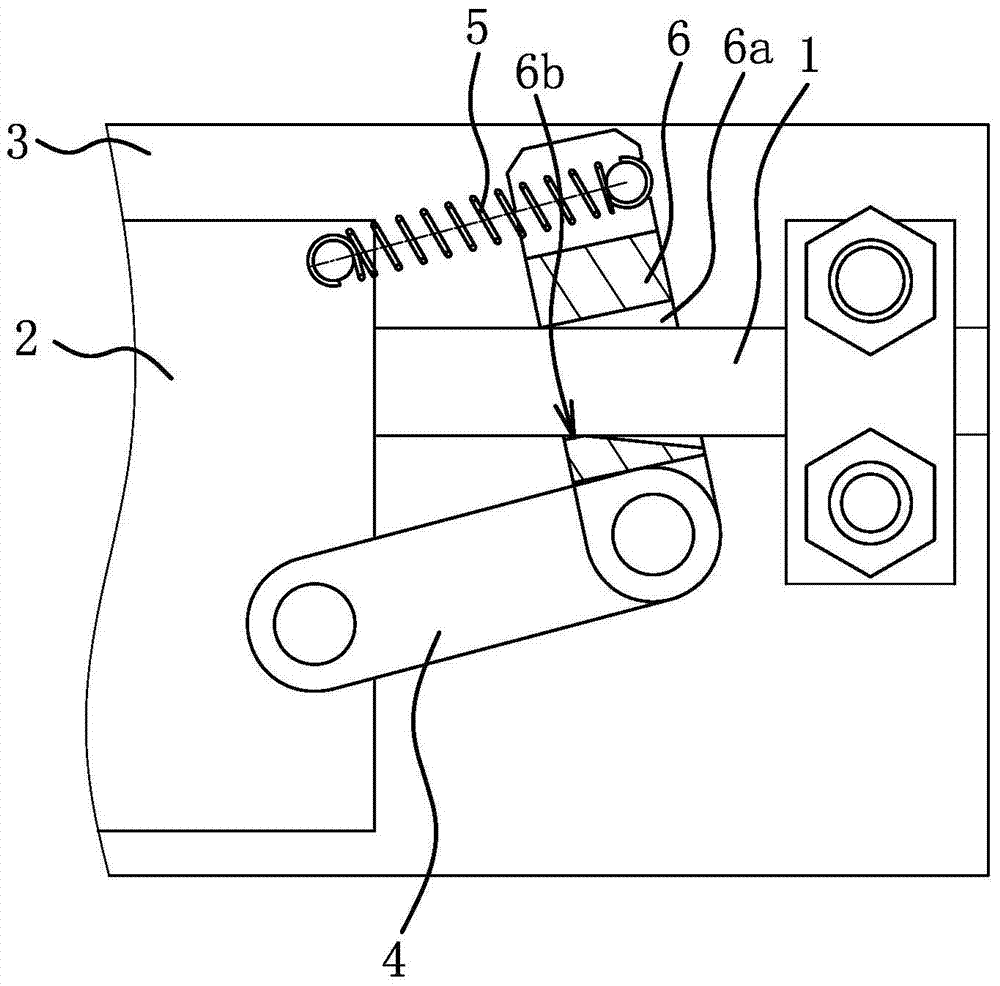
[0055] The structure and principle of this embodiment are basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that: image 3 and Figure 4 As shown, the cross-section of the linear guide 1 is rectangular, and the cross-section of the bite hole 6a is also rectangular. The cross-sectional width of the bite hole 6a is the same as that of the linear guide 1. the cross-sectional length. The outer surface of the linear guide rail 1 and the two guiding side surfaces 6a1 are in one-to-one correspondence. There is an engaging tooth 6b on the lower side wall of the engaging hole 6a. Under the elastic force of the extension spring 5, the engaging tooth 6b and one end hole of the engaging hole 6a The edges and corners on the mouth all abut against the linear guide rail 1 to form a pre-occlusion.
Embodiment 3
[0057] The structure and principle of this embodiment are basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, the difference is that: Figure 7 As shown, the automatic unlocking mechanism includes an unlocking member 14 that is fixed on the lifting slider 9 and can push the other end of the brake swing lever 6 to swing. The unlocking part 14 is a cylinder or an electromagnet. Both the unlocking part 14 and the driving part 10 are electrically connected to controllers such as a PLC or a single-chip microcomputer. The controller first controls the action of the unlocking part 14, and after the unlocking part 14 pushes the other end of the brake lever 6 to swing to unlock, the controller then controls the driving part 10. Action, the driving part 10 drives the lifting slider 9 to move and realizes loosening the metal bar.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com