Execution method and system in production of aviation maintenance, repair and overhaul (MRO) industry
A manufacturing execution system and manufacturing execution technology, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, resources, etc., can solve the problems of big data analysis that is difficult to realize aviation MRO, and achieve the effect of rapid and effective management
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The principles and features of the present invention are described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, and the examples given are only used to explain the present invention, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
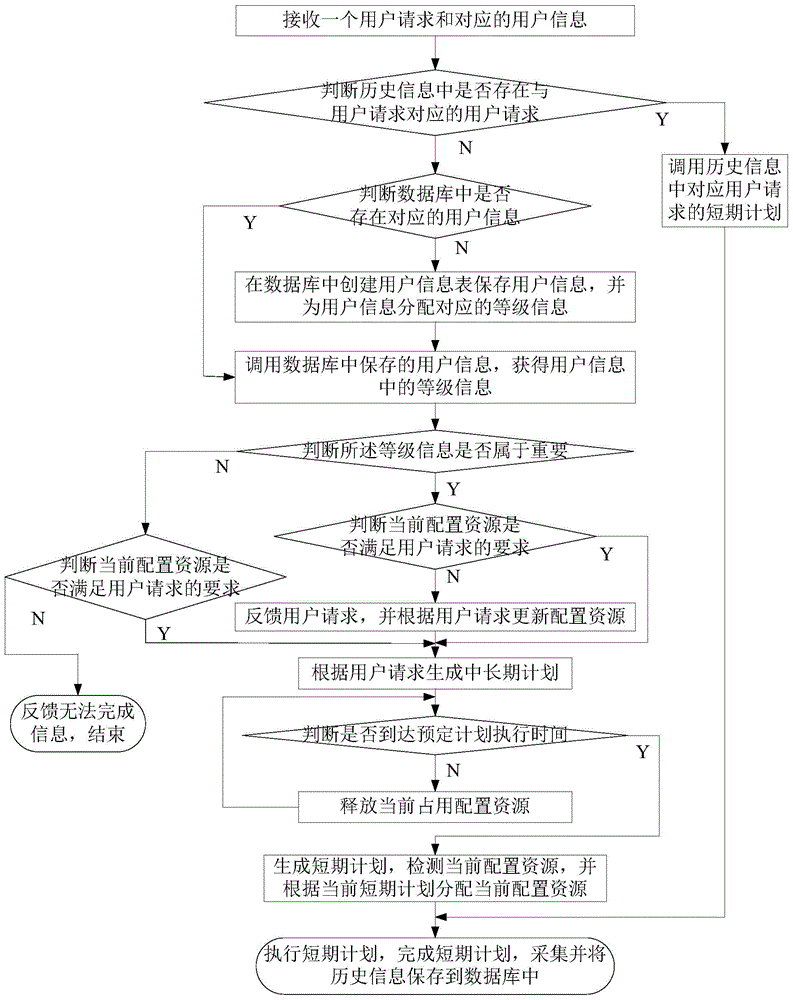
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a manufacturing execution method in the aviation MRO industry described in a specific embodiment of the present invention, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0045] Step 1: Receive a user request and corresponding user information;
[0046] Step 2: Compare the user request with the historical information in the database, and determine whether there is a user request corresponding to the user request in the historical information, if yes, perform step 3; otherwise, perform step 4;
[0047] Step 3: call the short-term plan corresponding to the user request in the historical information, and execute step 15;
[0048] Step 4: Determine whether there is correspond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com