Experimental method for scientific prediction of action science
An experimental method and functional technology, applied in prediction, data processing application, calculation, etc., can solve problems such as error, uselessness, impracticality, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] Example 1 Dripping water effect experiment
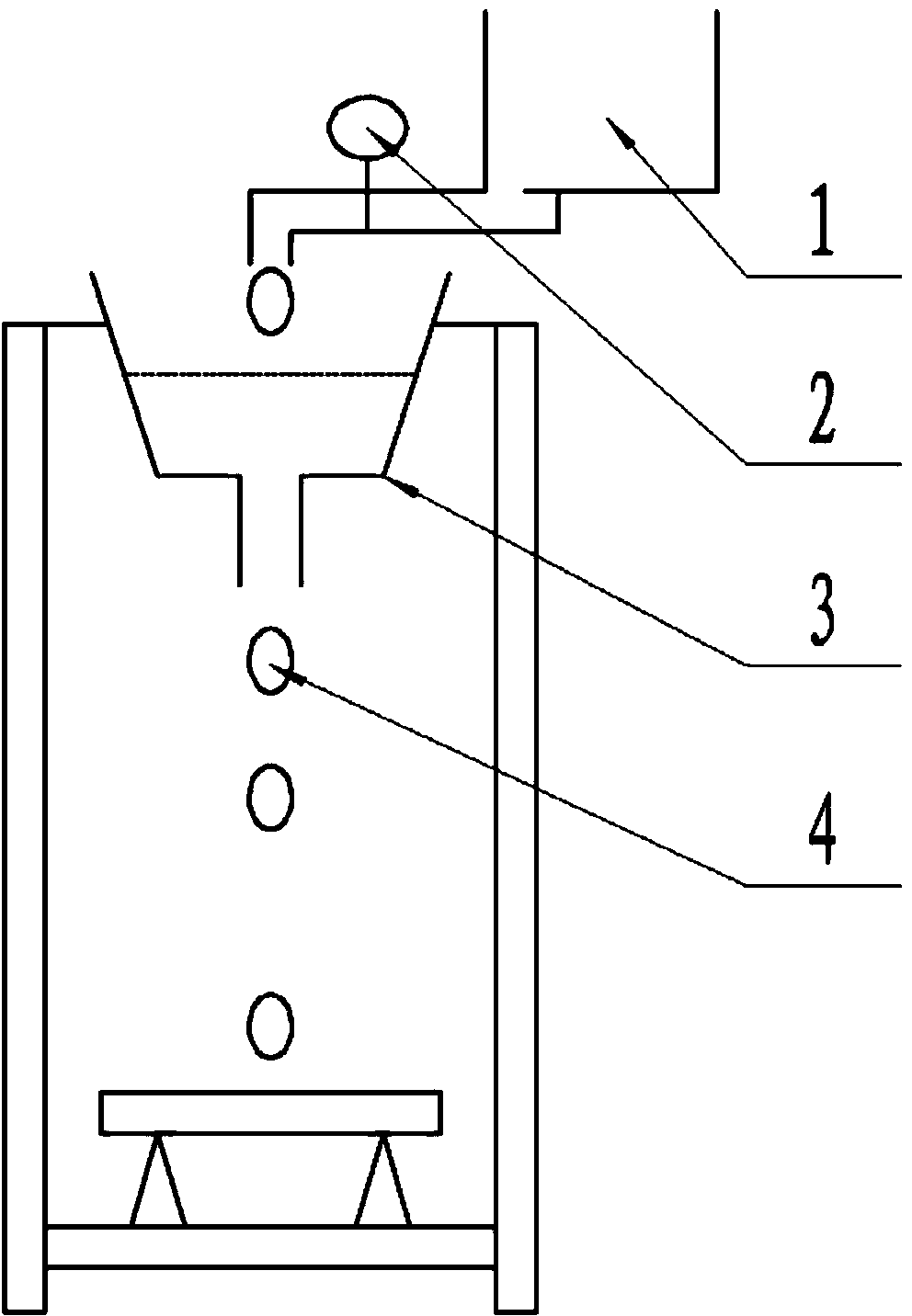
[0087] Under the condition of dripping, the deformation performance of different rock formations is very different. This difference in deformation is mainly determined by the different properties of different formations. The phenomenon of dripping water through rocks was discovered very early in history, and it seems that everyone knows the truth. However, people have never known the quantitative relationship among dripping action, rock properties, and rock deformation. How many drops of water can penetrate a rock of a certain nature? This is a question that no one can answer at present. To answer this question, we must rely on the results of the drip test.
[0088] The water supply valve 2 of the water supply tank 1 drips water to the drip tank 3, and the drip tank 3 drips water downwards, and the dripping speed is the same. The water droplets 4 finally drop onto the test piece, and act on the test piece, causing the test pi...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Example 2 Extrusion Experiment
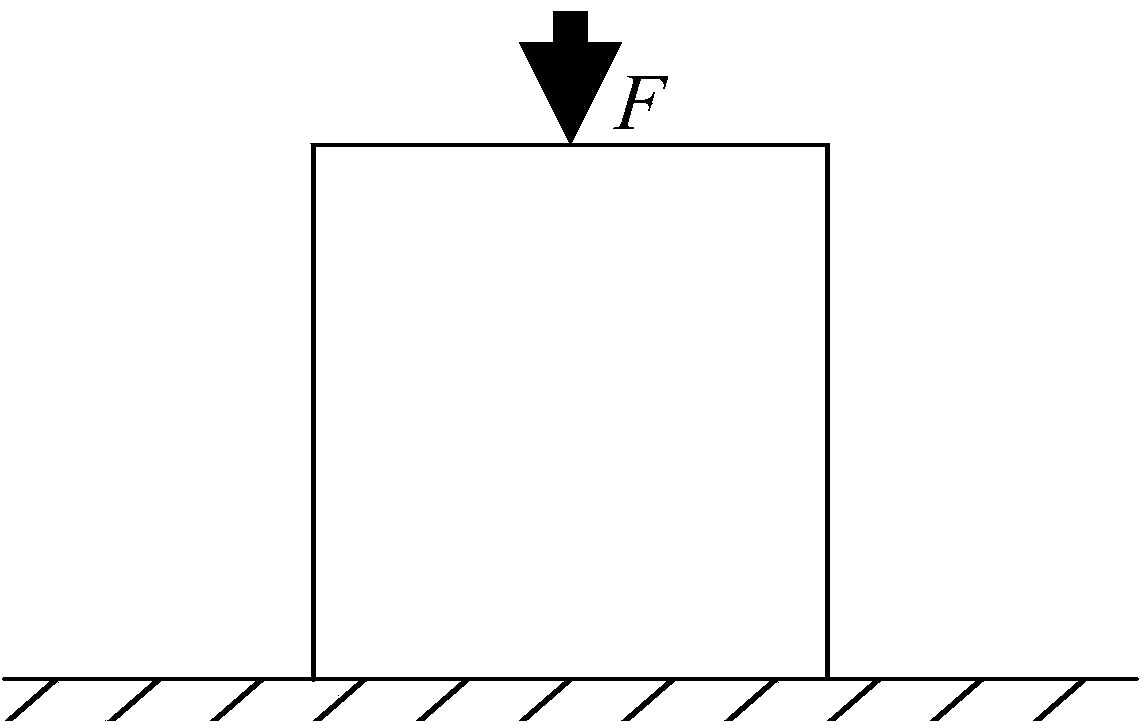
[0100] In order to explore the essential law of the relationship between material properties and extrusion, an experiment on the relationship between compression and deformation is introduced here. The specimen deforms under the action of squeezing and changes its properties at the same time. If the speed of action (the amount of action produced per unit time, that is, the amount of pressure) does not change, within a certain action time or deformation time, materials with different material components and structures will deform due to their different resistance to deformation or variable properties. The amount is different.
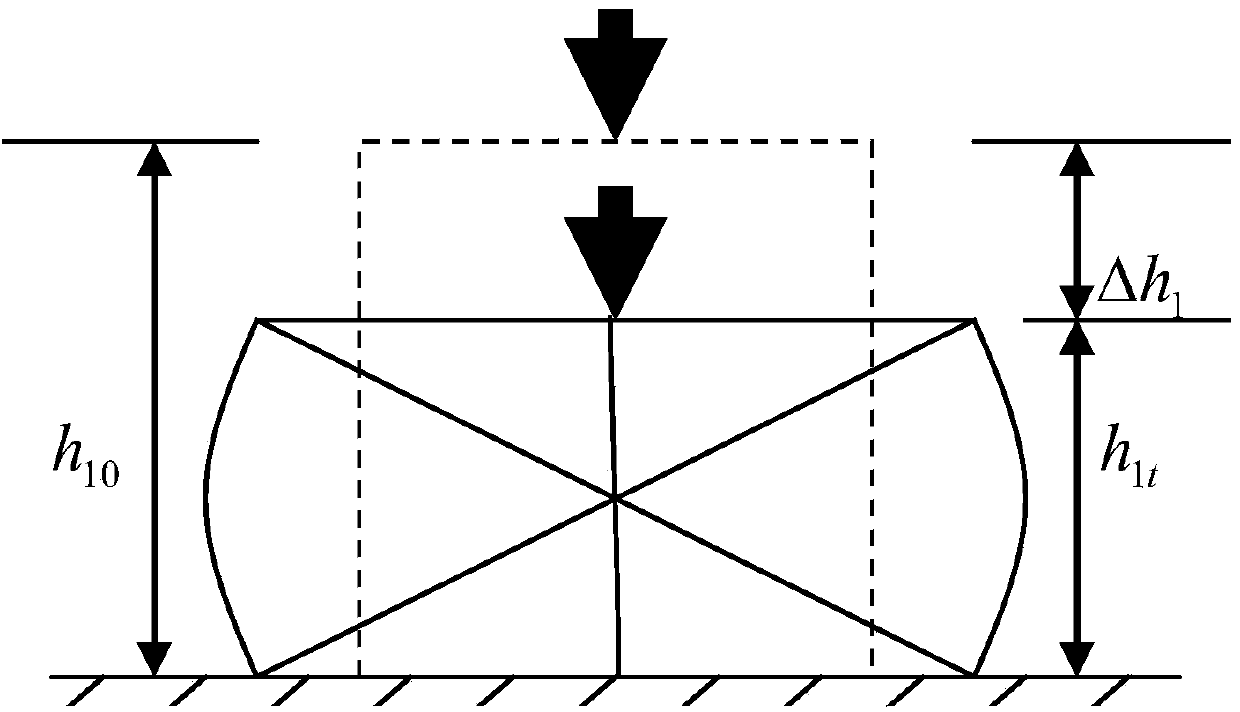
[0101] image 3 Specimen shown (specimen 1) and Figure 4 The specimen shown (specimen 2) deforms under the same operating speed (ie, the same force) and the same operating environment, but the amount of deformation of the two is different. The compression deformation of specimen 1 is Δh 1 =h 1t -h 10 , The compressio...
Embodiment 3
[0121] Example 3 Material property change test experiment
[0122] Both the variable and immutable properties of materials change with the change of conditional factors such as the intensity and time of action. That is to say, the characteristic value of variable properties and the characteristic value of invariable properties of materials are not constant constants, but variables that both change with changing conditions. However, changes in material properties also obey certain objective laws. Let us understand this rule through the tensile test.
[0123] Such as Figure 5-7 As shown, the affected specimen deforms under the action. During the deformation process under the control of the action, the properties of the specimen are constantly changing. In order to describe this property change law, the experiment introduces the concepts of material variable property change rate and anti-change property change rate, denoted as β and α respectively.
[0124] According to research, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com