Patents
Literature
41 results about "Theoretical physics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental physics, which uses experimental tools to probe these phenomena.
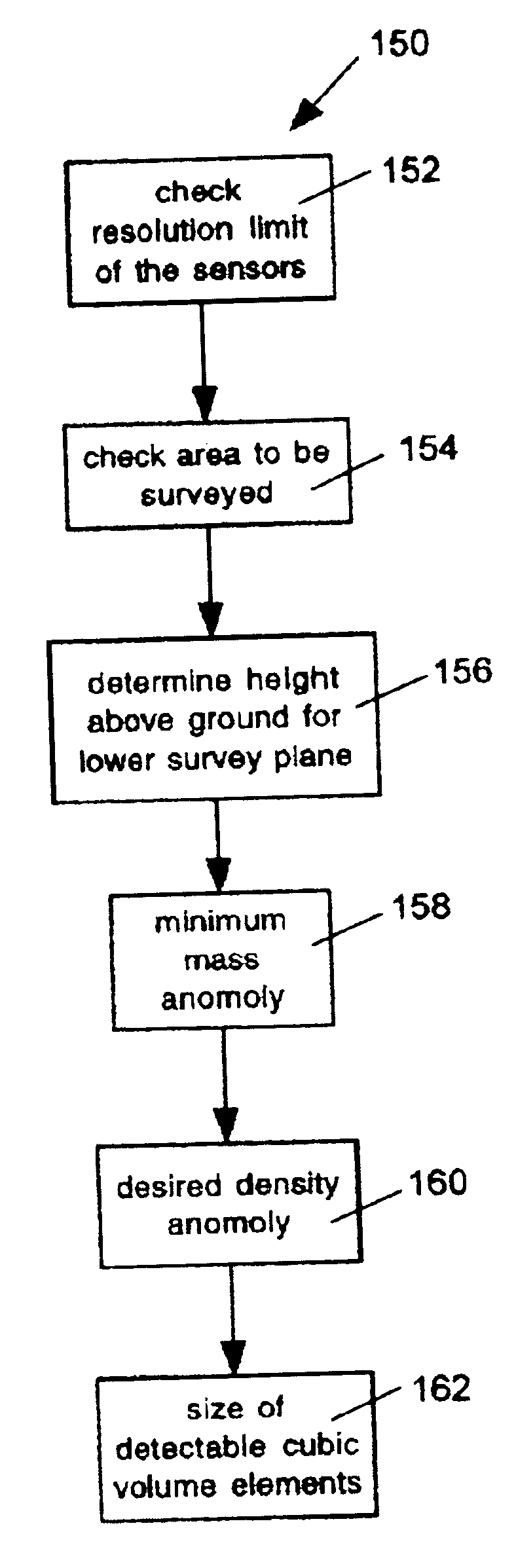
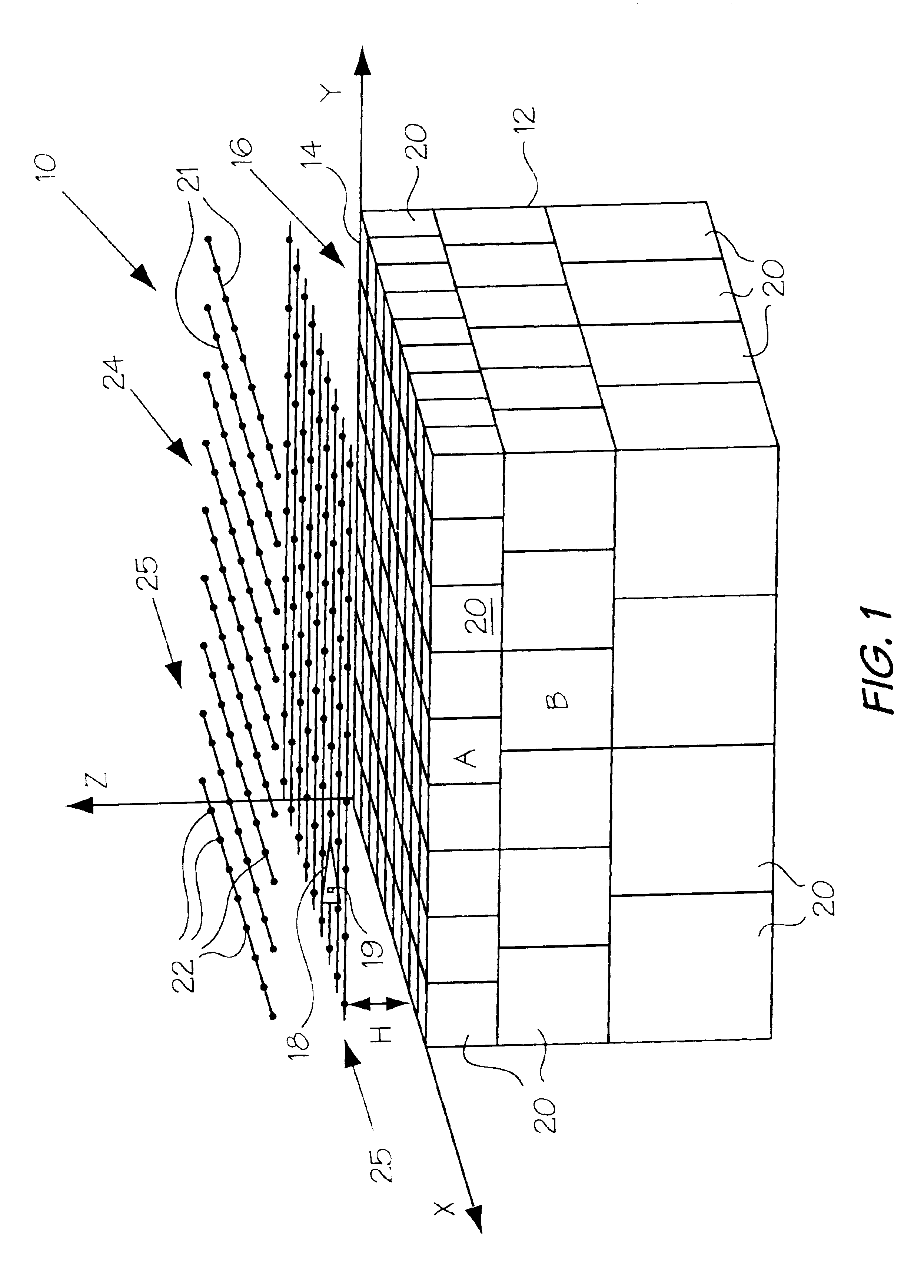
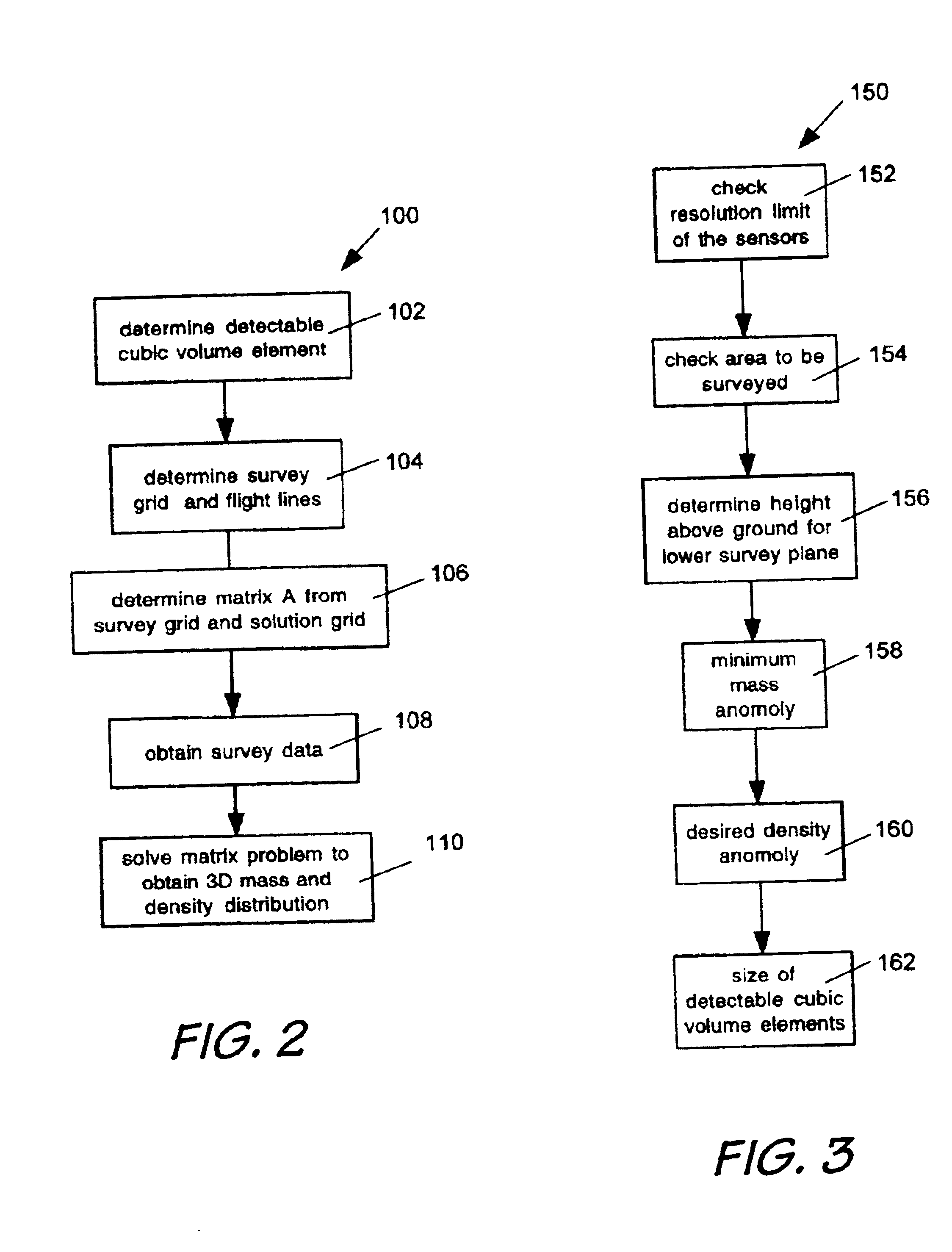
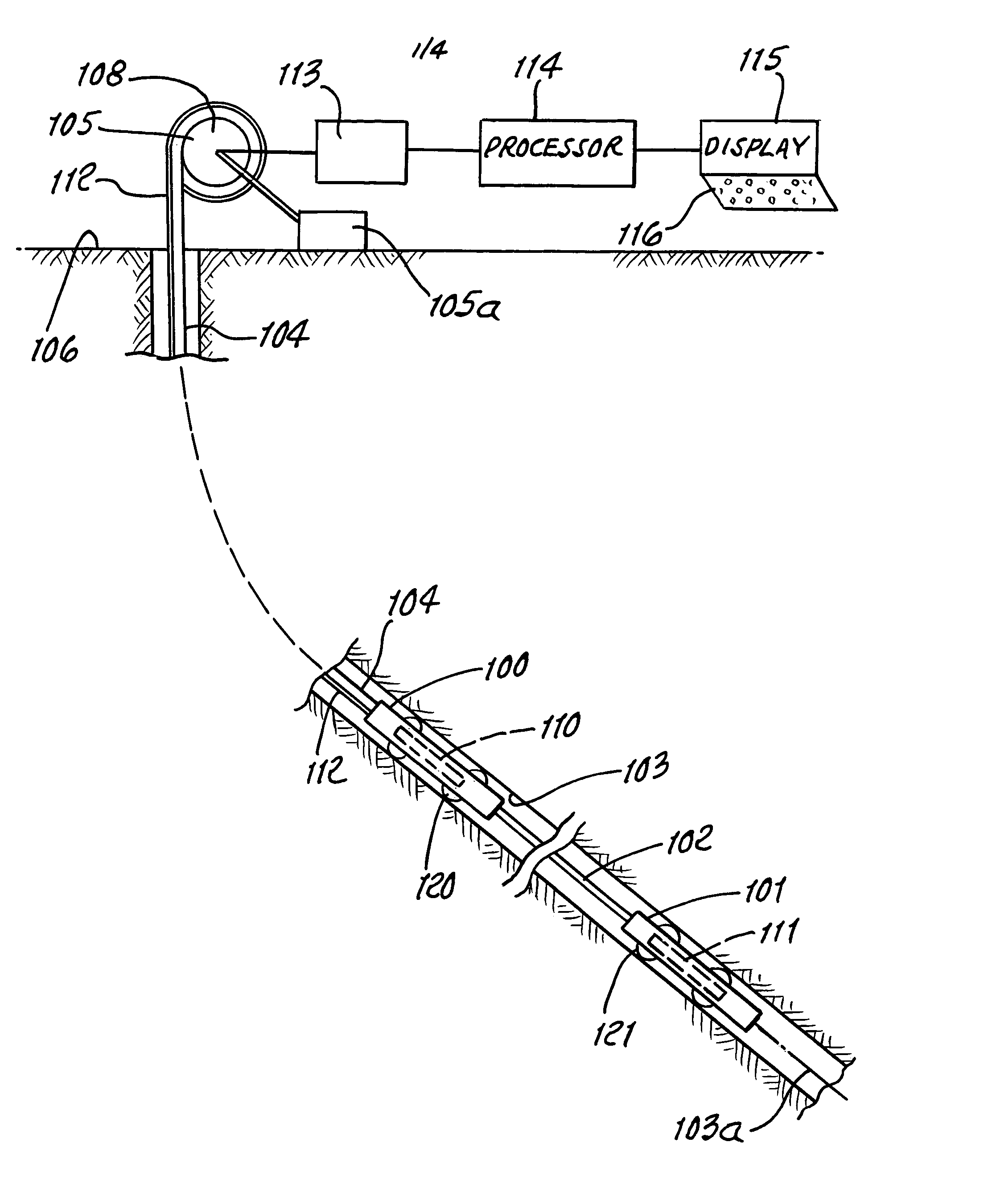
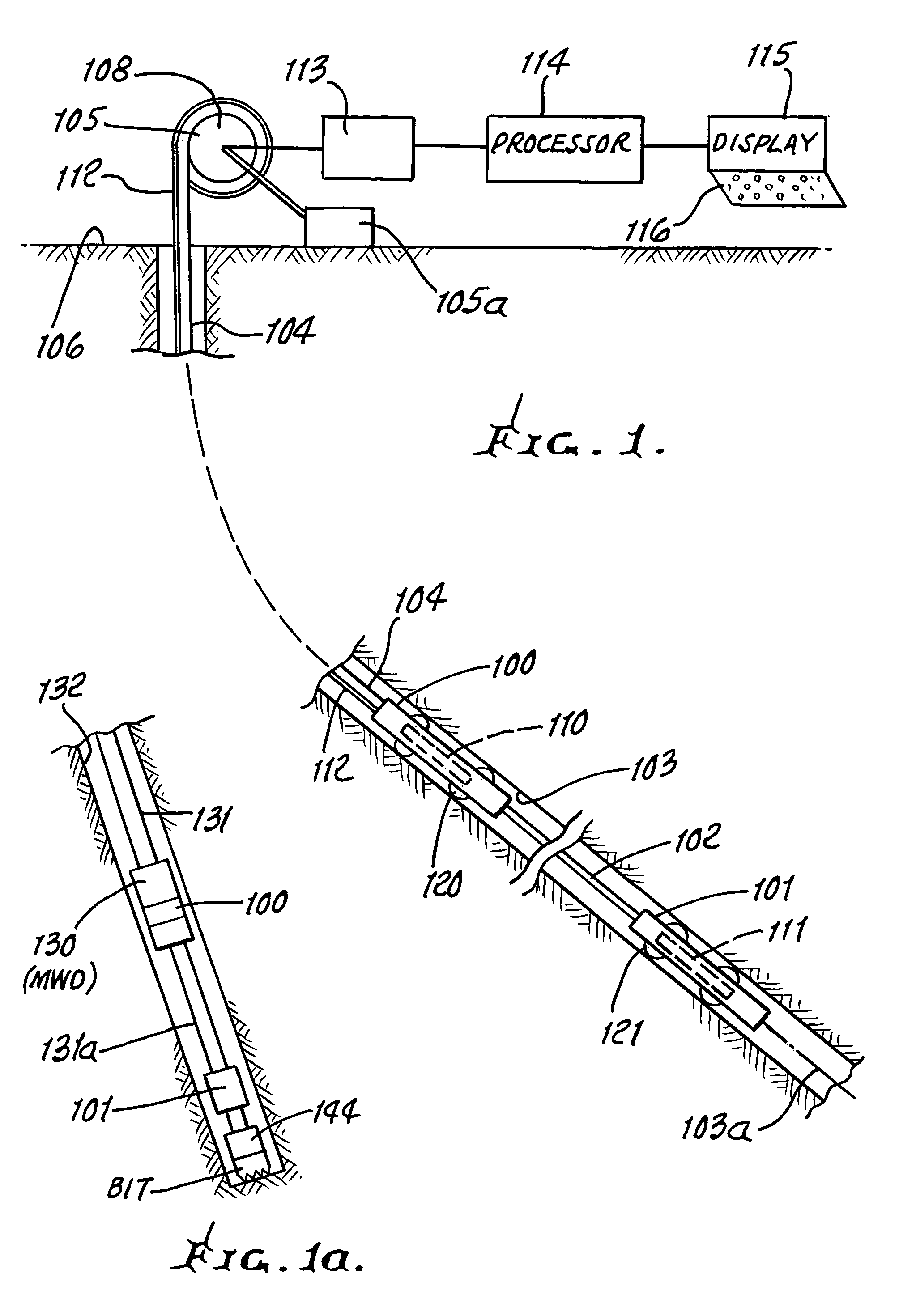
System and method for surveying underground density distributions
ActiveUS6954698B2Special data processing applicationsGravitational wave measurementMassive gravityMagnetic susceptibility
Owner:GEDEX
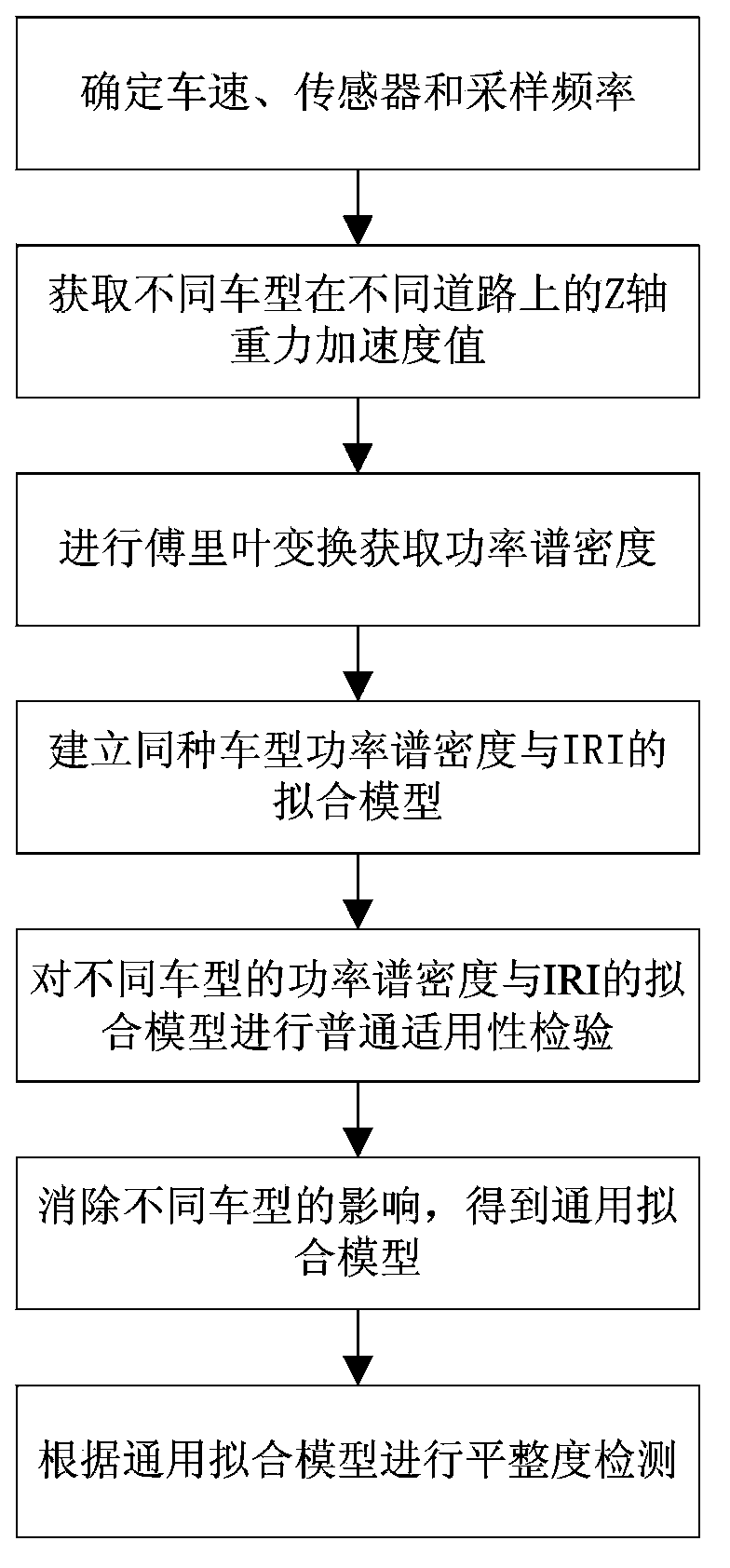
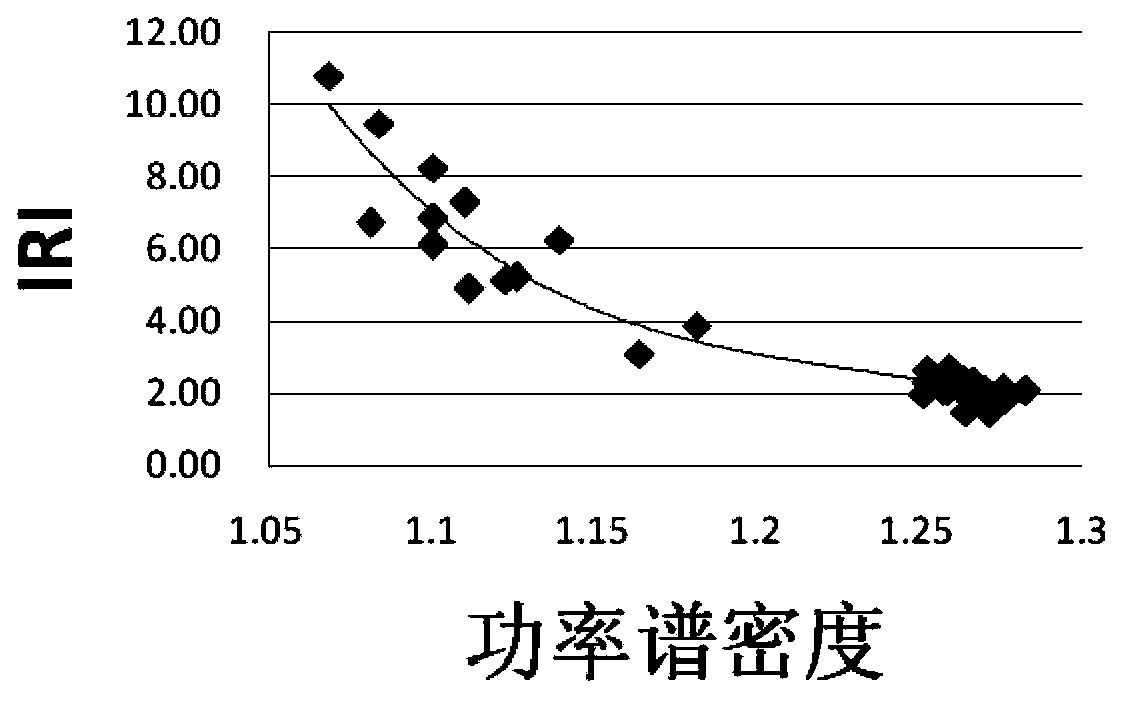
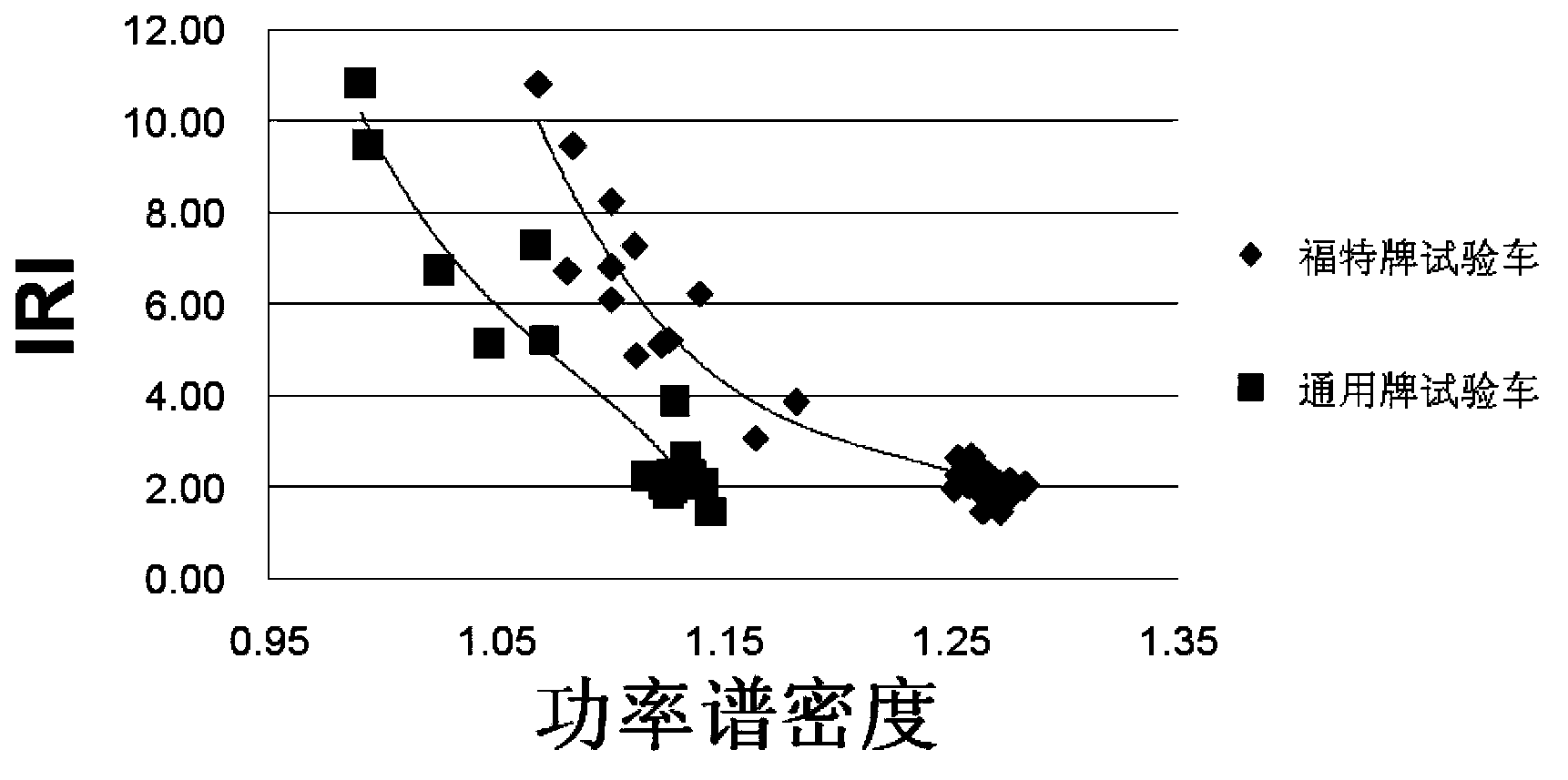
Gravitational acceleration sensor based road surface flatness detection method
The invention relates to a gravitational acceleration sensor based road surface flatness detection method which comprises the following steps: determining the detection vehicle speed, a gravitational acceleration sensor and a sampling frequency; using different models of test vehicles to run on roads with different road surface flatness to obtain gravitational acceleration values of the gravitational acceleration sensor; performing Fourier transform on the collected gravitational acceleration values to obtain power spectral density; establishing a fitting model of the power spectral density of same model of test vehicles and IRI (international roughness index); performing general applicability tests on the fitting model of the same model of test vehicles to obtain a fitting model of the power spectral density of the different models of test vehicles and the IRI; performing general applicability tests on the fitting model of the power spectral density of the different models of test vehicles and the IRI; and according to a universal fitting model and the collected gravitational acceleration values, performing road surface flatness detection. Compared with the prior art, the road surface flatness detection method based on the gravitational acceleration values can solve the problems that a laser flatness detection vehicle in the prior art is expensive and is complicated in detection process.
Owner:上海祎个科技有限公司
Method for computation of differential azimuth from spaced-apart gravity component measurements
InactiveUS7028409B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyMeasurement deviceGravitational force
A method is provided for computing the differential azimuth between two sets of spaced-apart gravity component measurement devices in a borehole, employing multiple rotation angles. The method includes modeling relationships of axes as defined; forming equations relating rotation angles to outputs of gravity measuring devices; solving such equations to derive the values representative of all of the rotation angles, using measured values of the outputs from the first and second sets of gravity component measuring devices, and computing from the values of the rotation angles the differential azimuth angle between the first set and the second set of gravity measuring devices.
Owner:SCIENCE DRILLING INTERNATIONAL INC
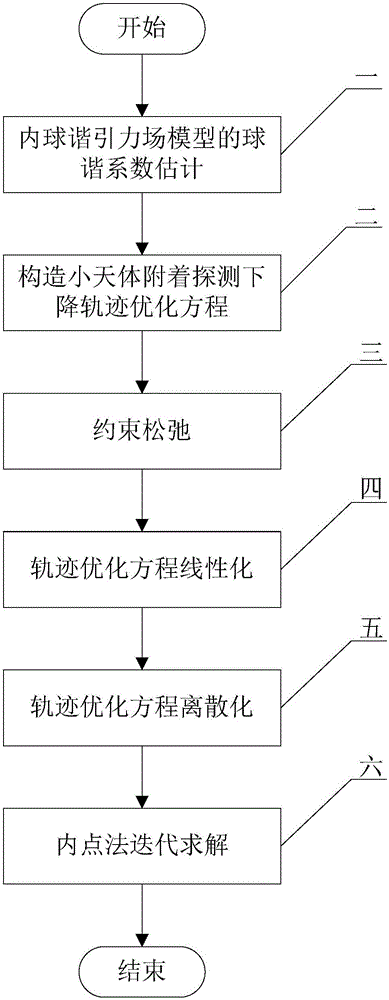
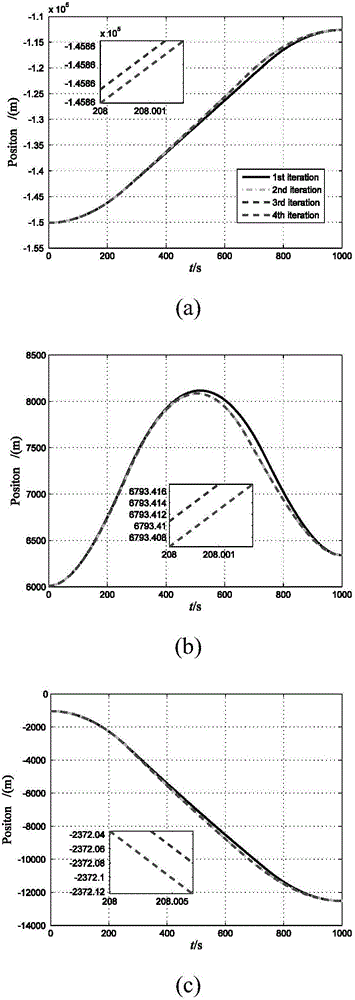
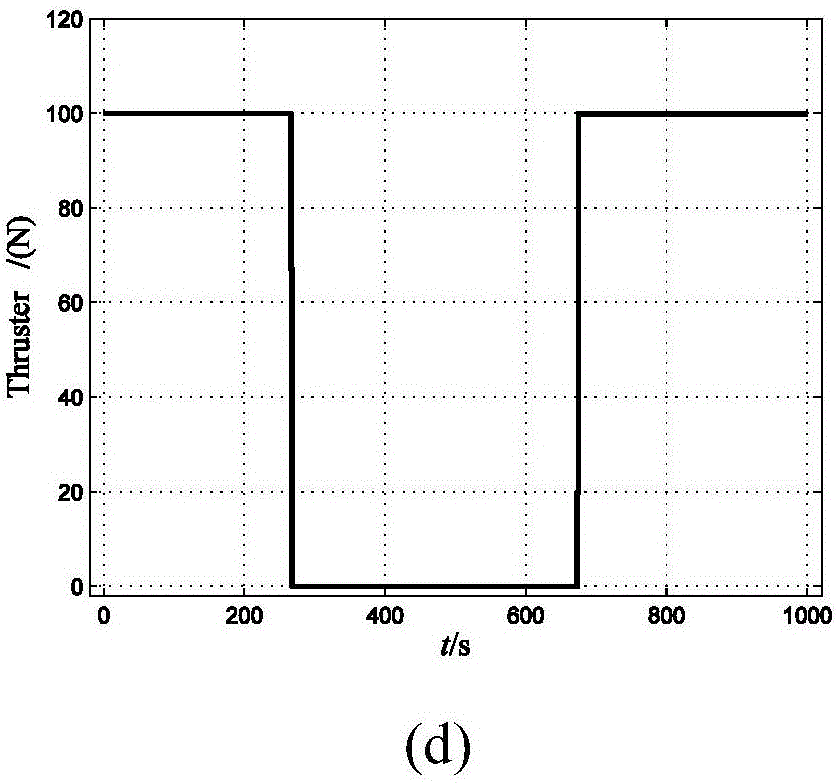
Small celestial body attachment detection descending trajectory optimization method
ActiveCN106778012AAvoid complicating the derivationAvoid questions that have no physical meaning and are not easy to guessInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsAviationState variable
The invention relates to a small celestial body attachment detection descending trajectory optimization method, and belongs to the field of aviation and aerospace. According to the method, an internal spherical harmonic gravitational field model is adopted for estimating gravitational acceleration near a target small celestial body, and a convex optimization algorithm is adopted for solving the optimal control problem. By adopting the internal spherical harmonic gravitational field model for estimating the gravitational acceleration near the target small celestial body, the advantage of being high in computational efficiency is achieved. By adopting the convex optimization algorithm for solving the optimal fuel control problem, the problems that derivation of a indirection method is complicated, and co-state variables are free of physical meaning and not likely to guess are avoided, the derivation step is simple, the computing time is saved, the estimation optimization method is rapid and high in precision, and the obtained result conforms to initial and end state constraint, dynamic constraint and control constraint.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
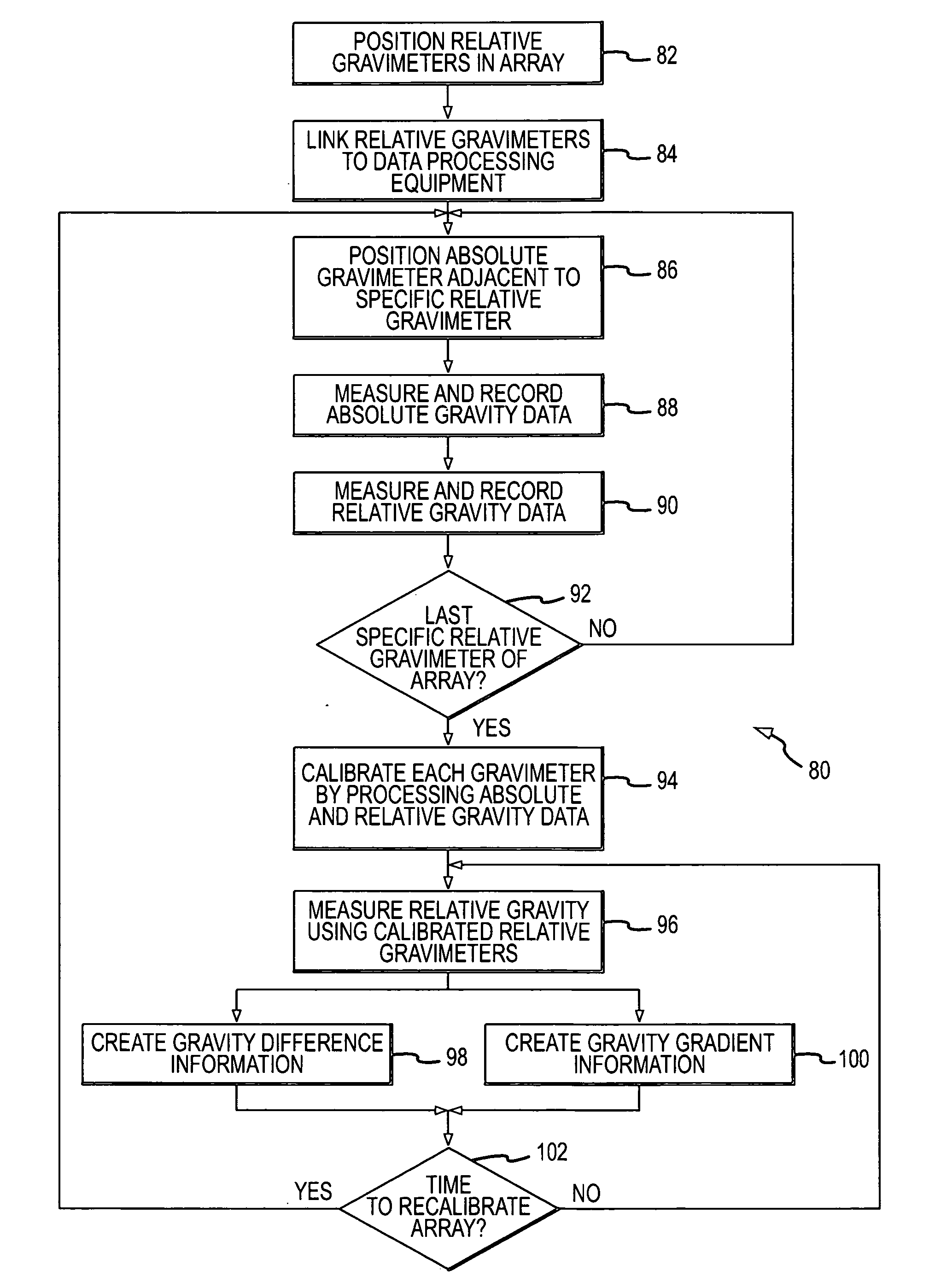
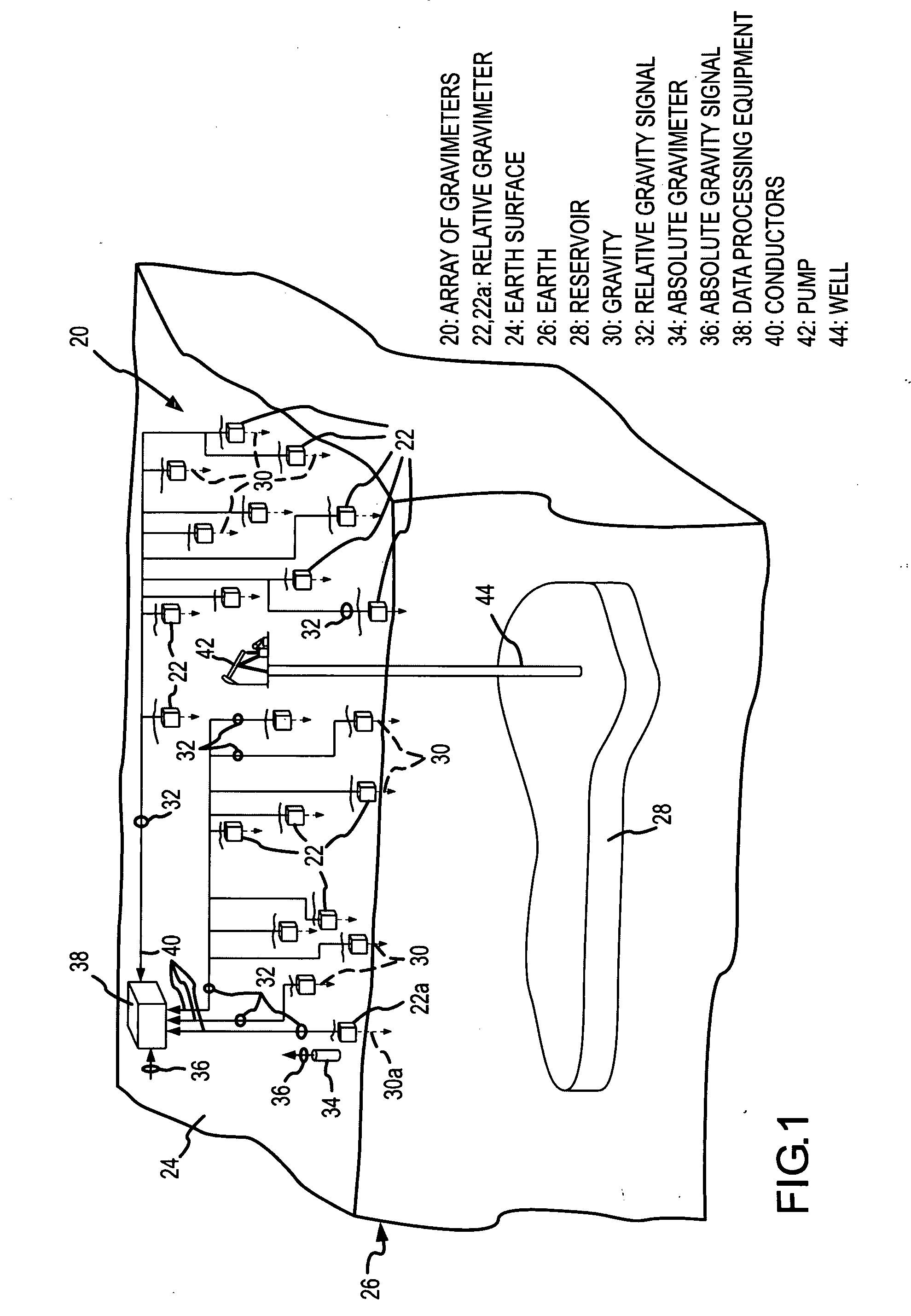
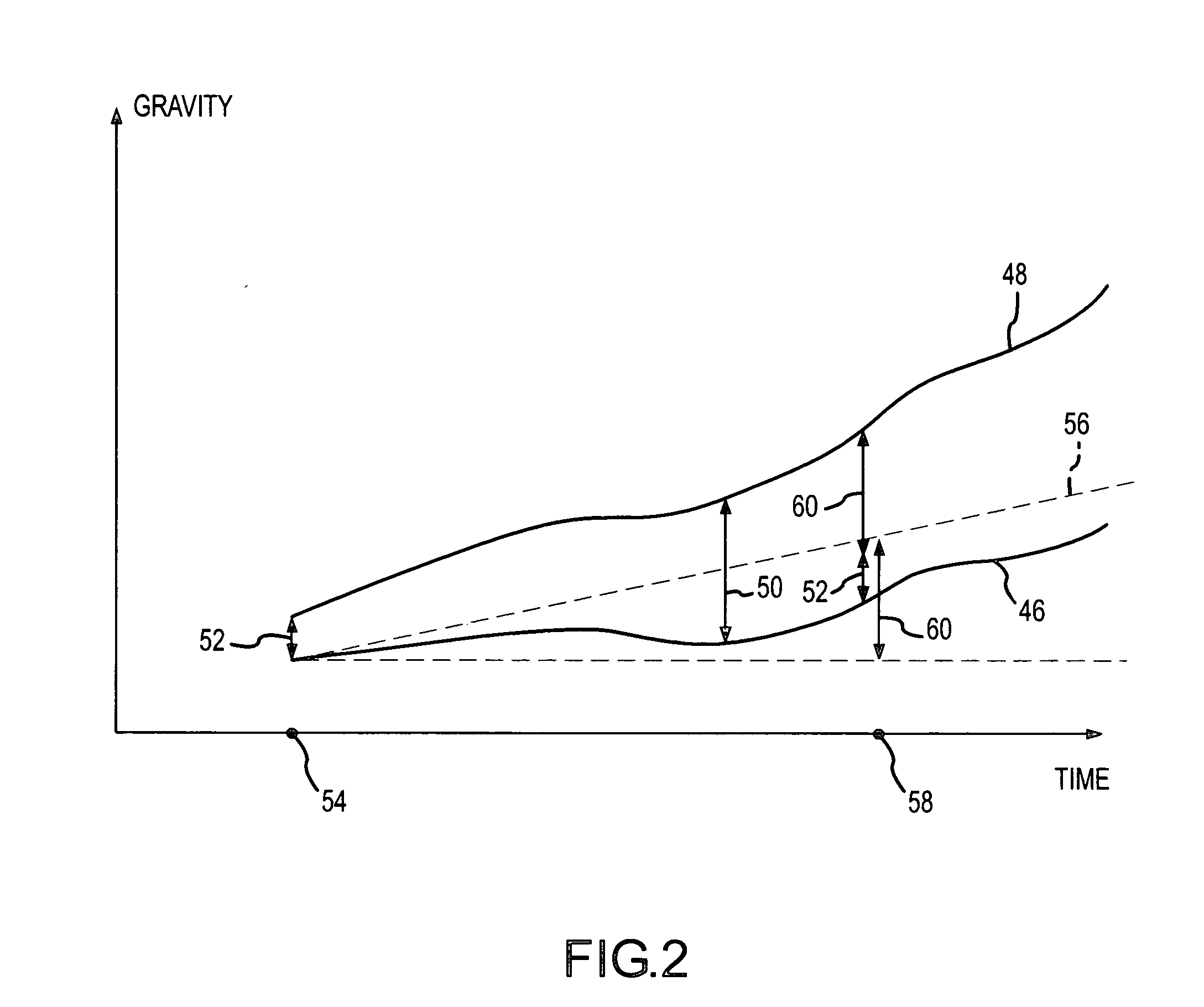
Accurate dynamic gravity measurement method and apparatus
InactiveUS20080015803A1Comparable accuracyElectrical measurementsTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesAbsolute gravityTheoretical physics
Gravity information for a gravity survey is obtained by using an array of relative gravimeters whose relative gravity measurement signals have been calibrated by using an absolute gravimeter to approximate absolute gravity measurements.
Owner:MICRO G LACOSTE
Gravity field or magnetic field data based geologic body three-dimensional visualized modeling and interpretation method
InactiveCN102901989AImprove reliabilityRealize the optimal designElectric/magnetic detectionGravitational wave measurementGeophysical prospectingGravitation
The invention provides a gravity field or magnetic field data based geologic body three-dimensional visualized modeling and an interpretation method. Spatial characteristic and attributive analysis of a geologic body is completed by means of the three-dimensional forward fitting method and the interactive visualized technology; and various visualization schemes for anomalous body models, gravity field or magnetic field data curves and field axis sections are provided, models are integrally or locally subjected to translation, zooming, rotation, subdivision and the like by means of three-dimensional interaction, and functions of integral and local contrastive analysis, user-defined multimode display and the like of airborne geophysical prospecting data are realized.
Owner:CHINA AERO GEOPHYSICAL SURVEY & REMOTE SENSING CENT FOR LAND & RESOURCES
Calculation method for constructing gravitational gradient field of complex body
ActiveCN107273566AEasy to analyzeImprove the display effectDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsRectangular coordinatesCharged body
The invention relates to a calculation method for constructing a gravitational gradient field of a complex body. The method is technically characterized by comprising the following steps of enabling the complex body to be equivalent to a charged insulator, enabling a gravitational field to be equivalent to an electric field, and performing mesh division on a model; calculating a gravitational field between two objects, enabling the density to be equivalent to charge density of a charged body, and multiplying the density by a conversion coefficient to obtain a gravitational field around the complex body; and performing derivation on gravitational components along three coordinate axes in a rectangular coordinate system, regarding the gravitational components as deformation of the objects in three coordinate directions, and calculating out strain generated under the deformation, wherein linear strain corresponds to a linear gravitational gradient, and shear strain corresponds to a cross gravitational gradient. The method realizes calculation of the gravitational gradient around any three-dimensional mass body, is suitable for directive calculation of a self gradient of a gravity gradiometer, a basic gradient of a lab and artificial gradient excitation generated by an experiment apparatus, and lays a solid foundation for gravity gradient inversion and geological interpretation.
Owner:中国船舶重工集团公司第七〇七研究所
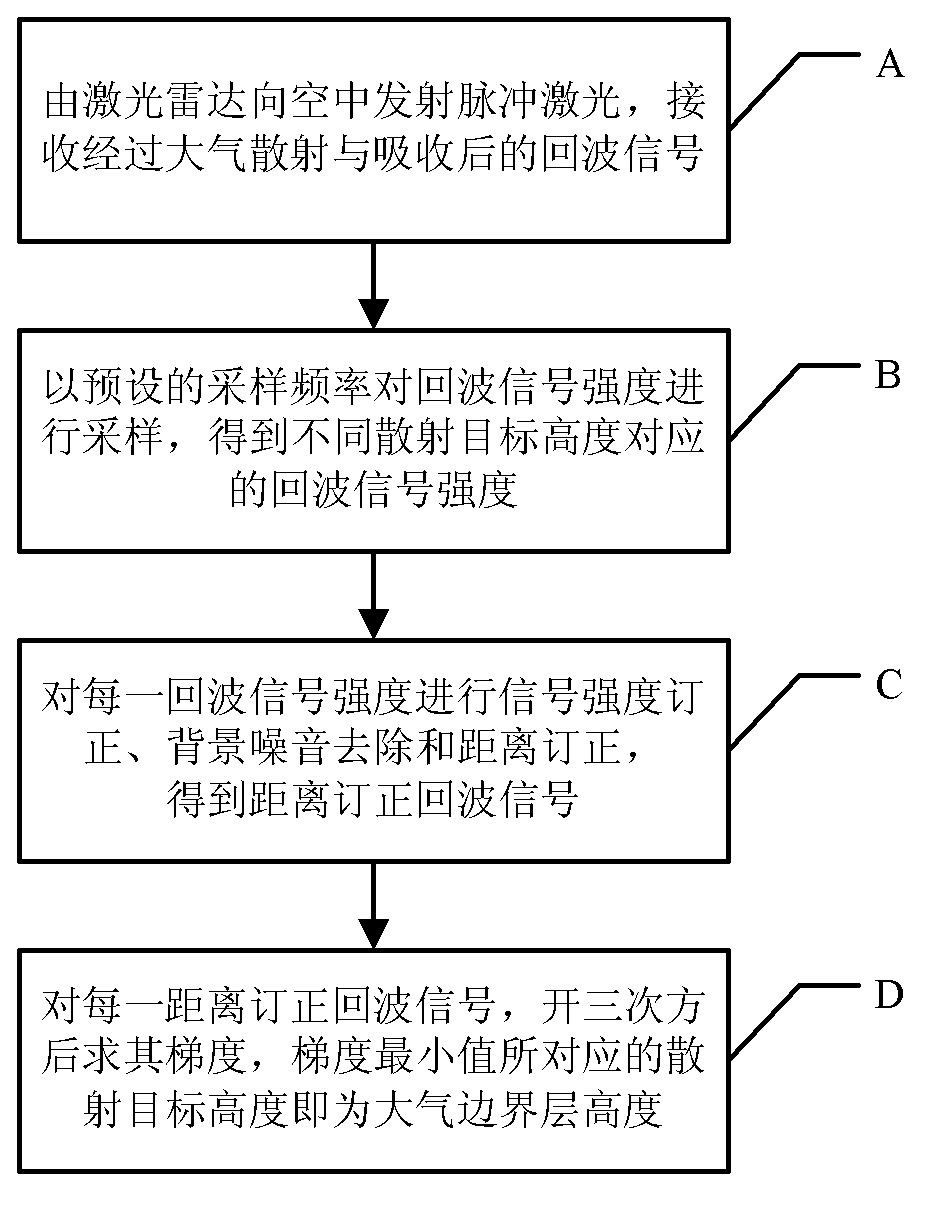
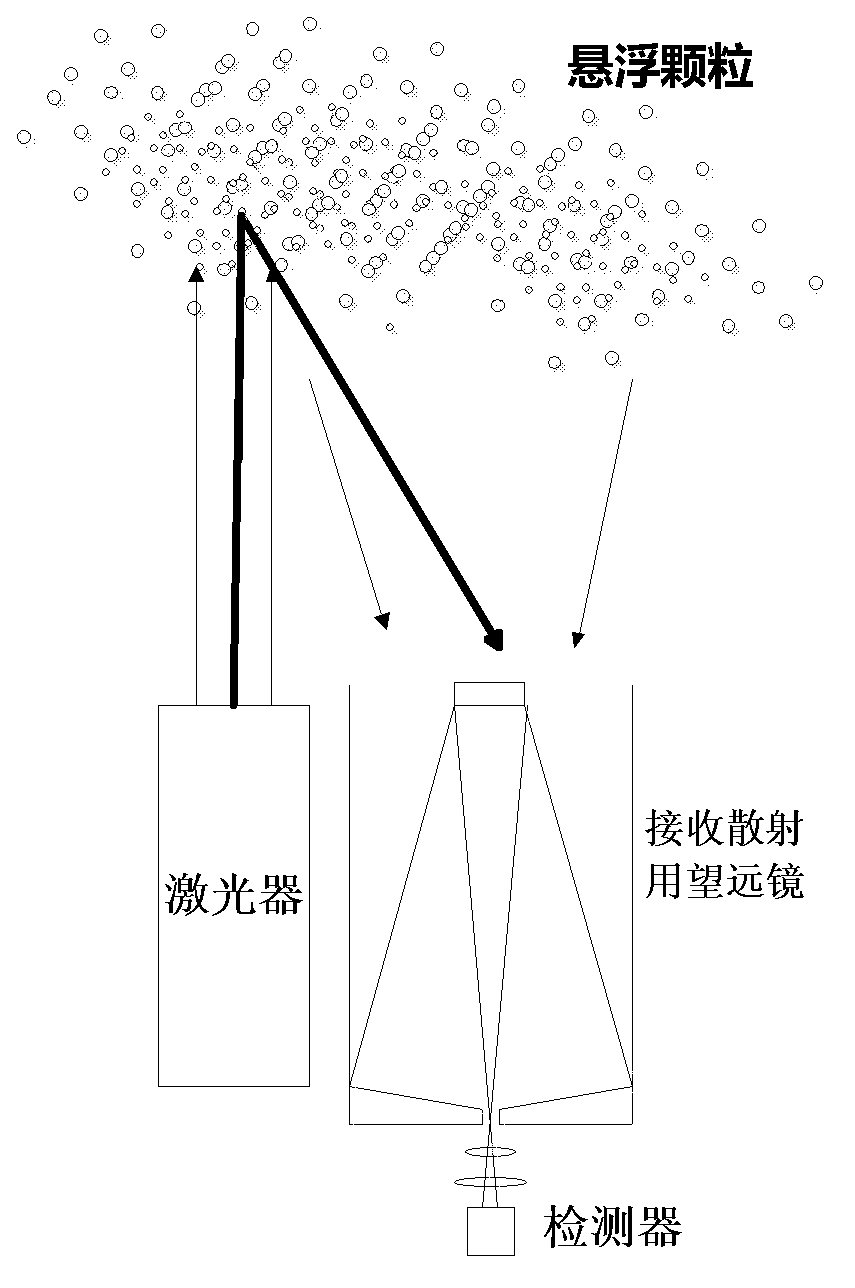
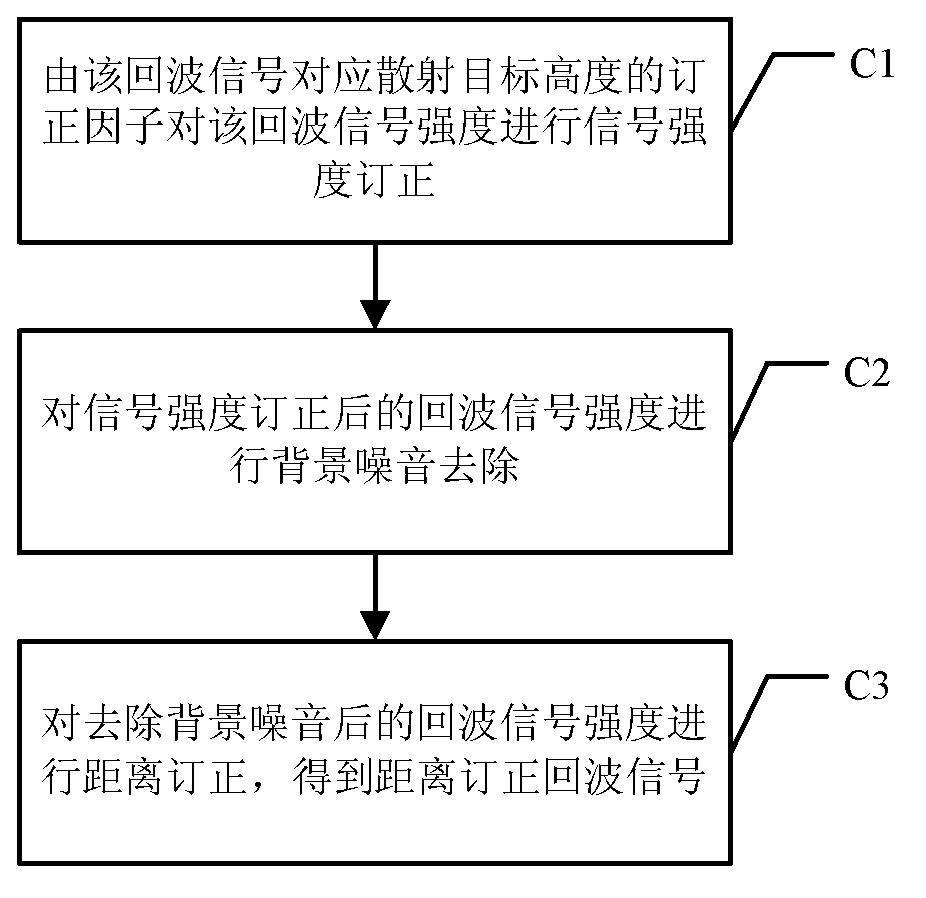
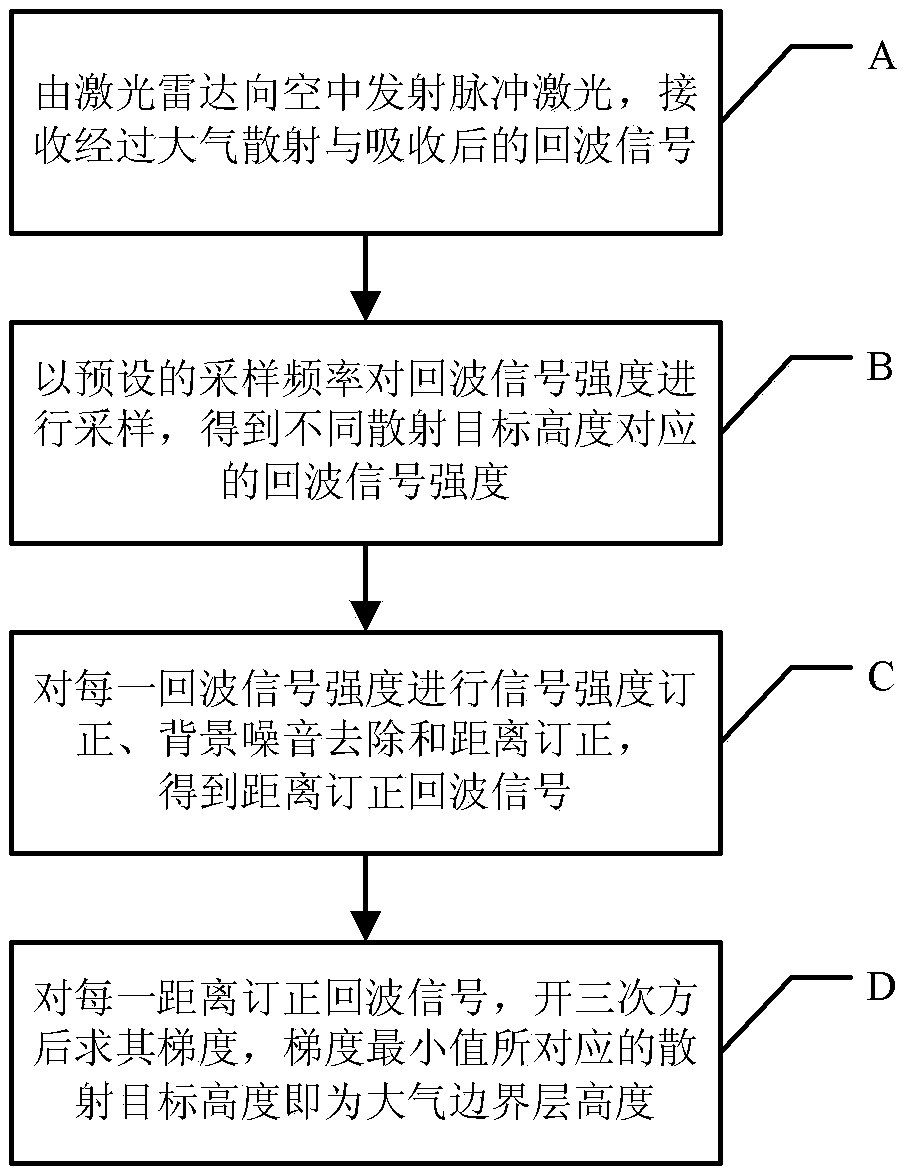
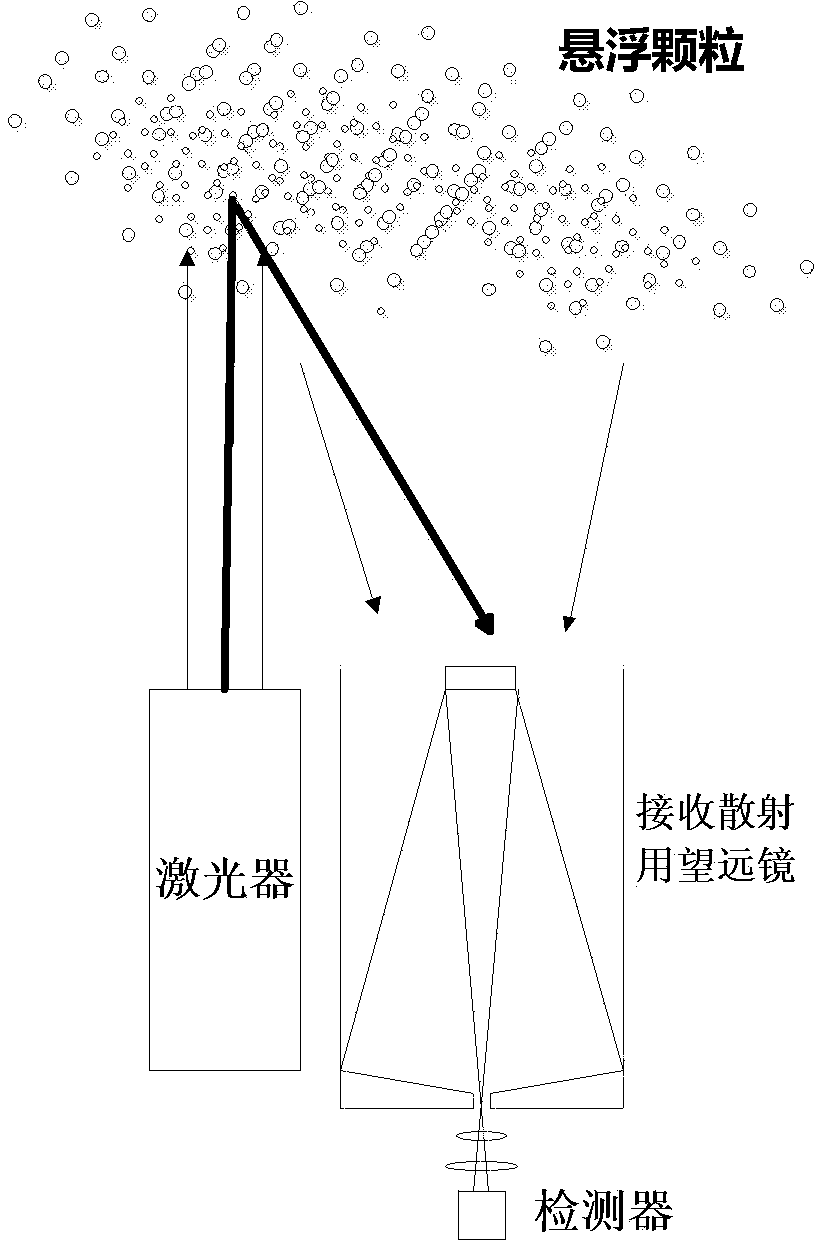
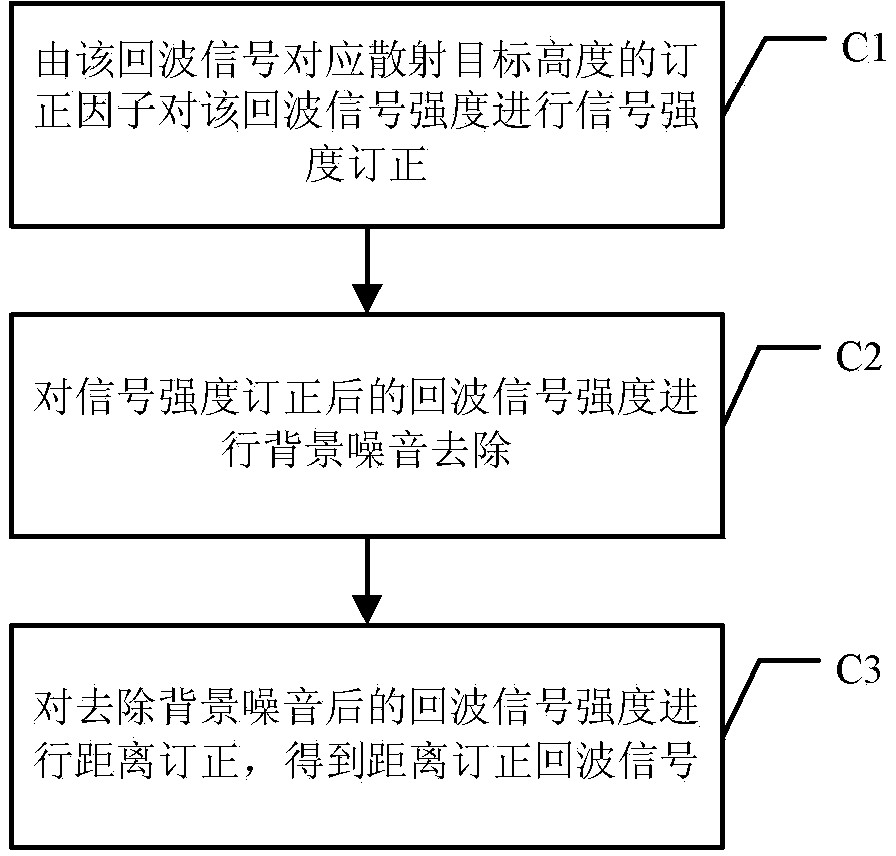
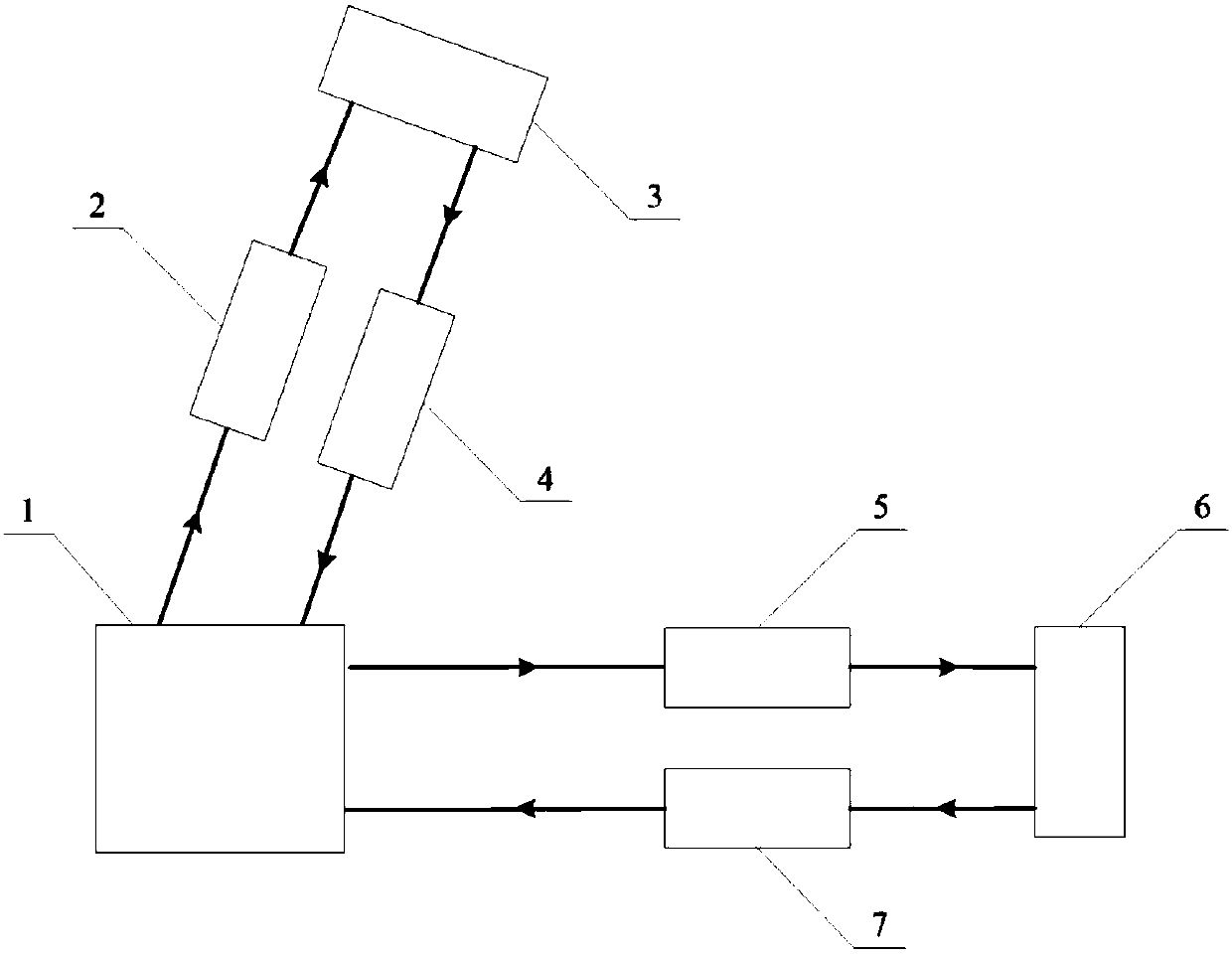
Method for measuring height of atmospheric boundary layer
InactiveCN103135113AImprove accuracyEliminate distractionsElectromagnetic wave reradiationHaze pollutionTheoretical physics
The invention provides a method for measuring the height of an atmospheric boundary layer. An original algorithm based on a gravitational wave theory is adopted in the method, namely the gravitational wave gradient method is used for obtaining the height of the boundary layer and directly enabling aerosols which are distributed vertically under the effect of gravitational waves to be led to a theory of algorithms. The method is more suitable for obtaining the height of the real boundary layer of China high dust-haze pollution environment at present.
Owner:INST OF ATMOSPHERIC PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY SCI
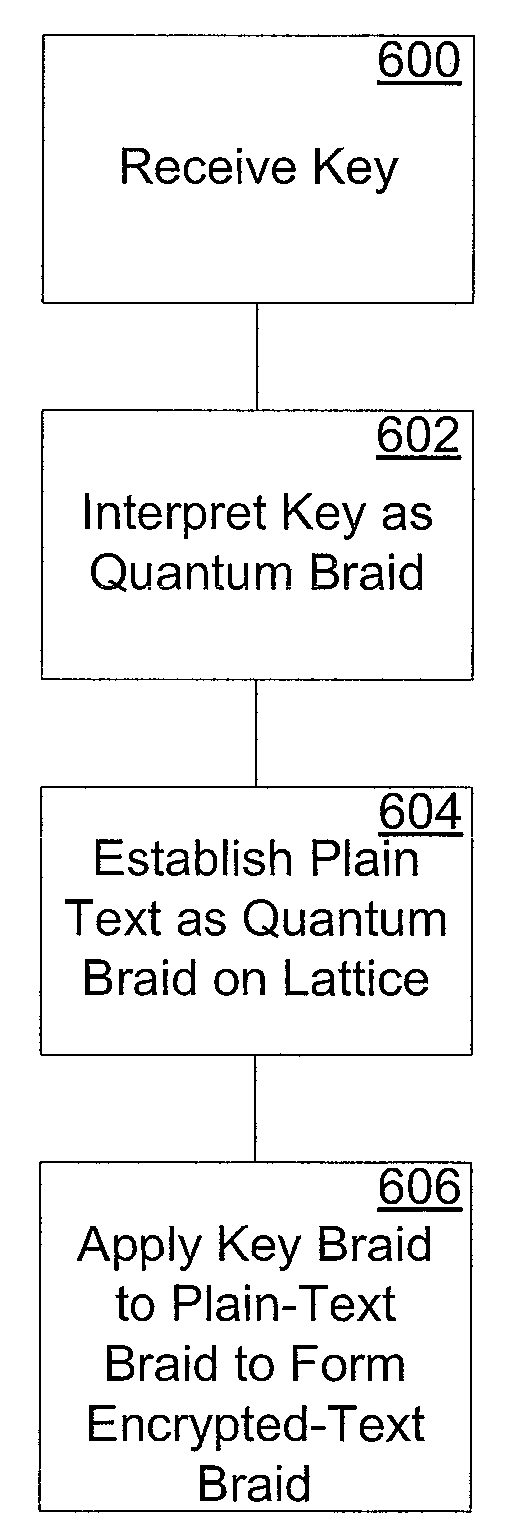
Quantum Computational Systems
InactiveUS20090097652A1Quantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationUniversal quantum simulatorTheoretical physics
Apparatus and methods for performing quantum computations are disclosed. Such quantum computational systems may include quantum computers, quantum cryptography systems, quantum information processing systems, quantum storage media, and special purpose quantum simulators.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
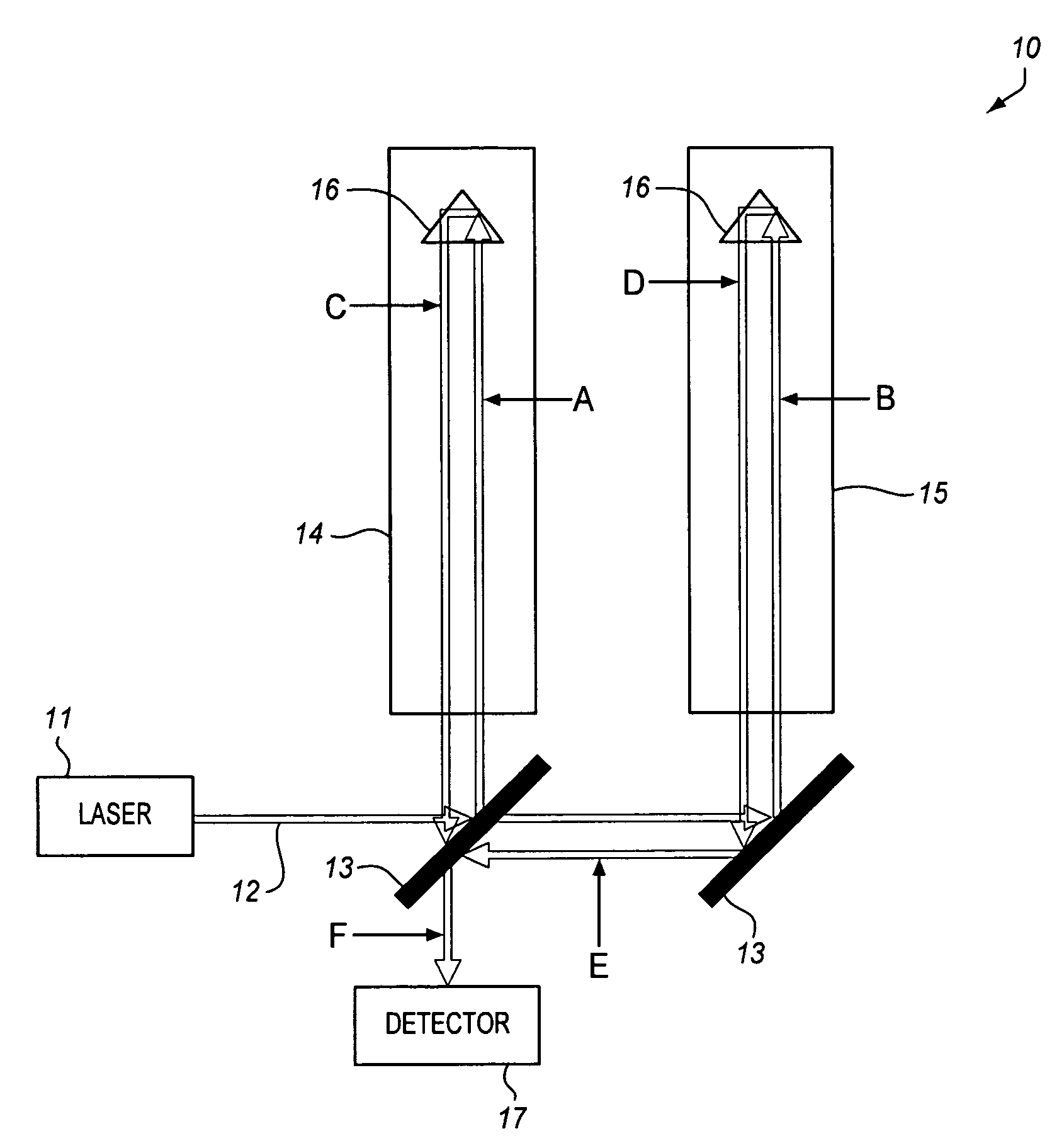
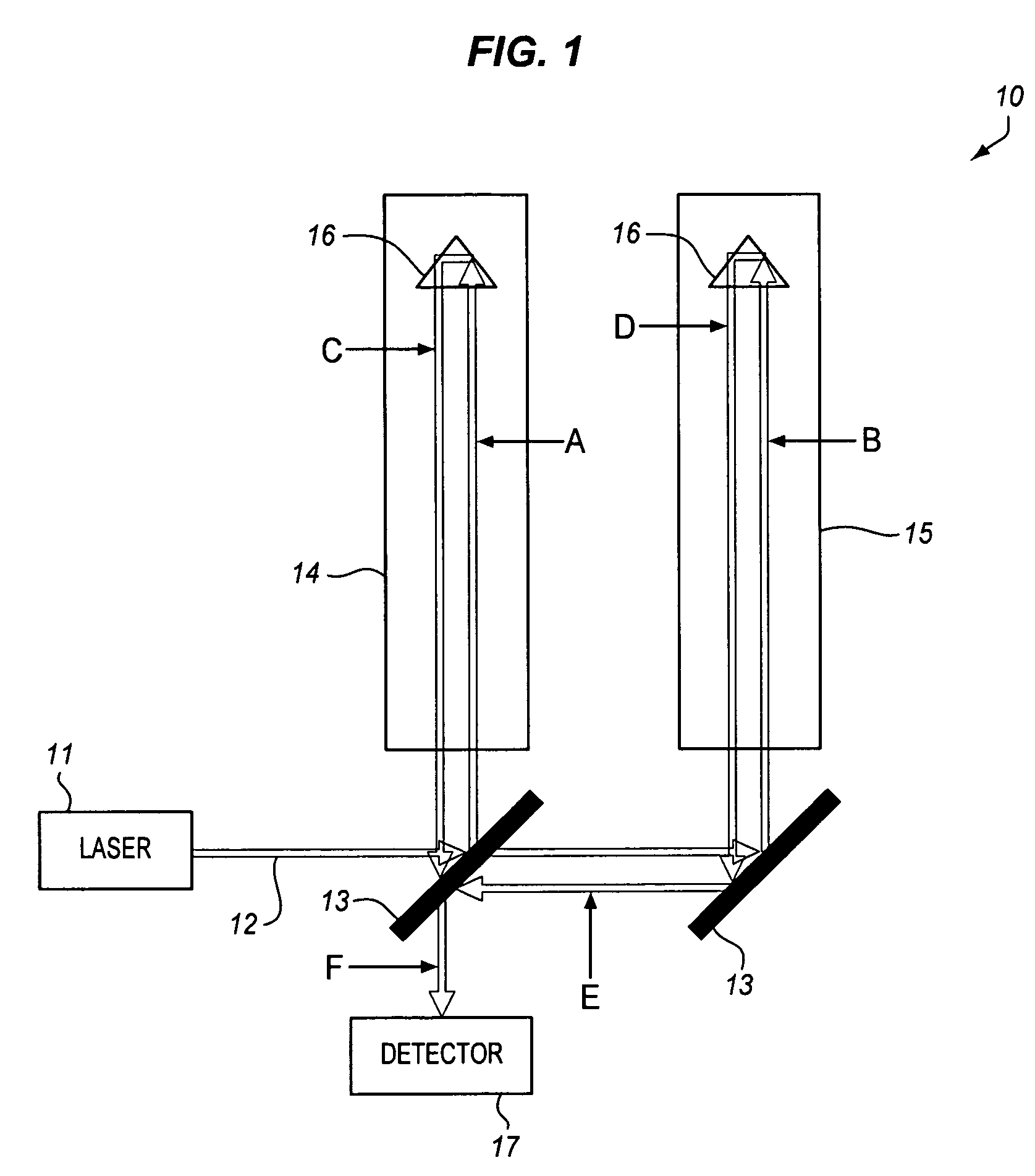
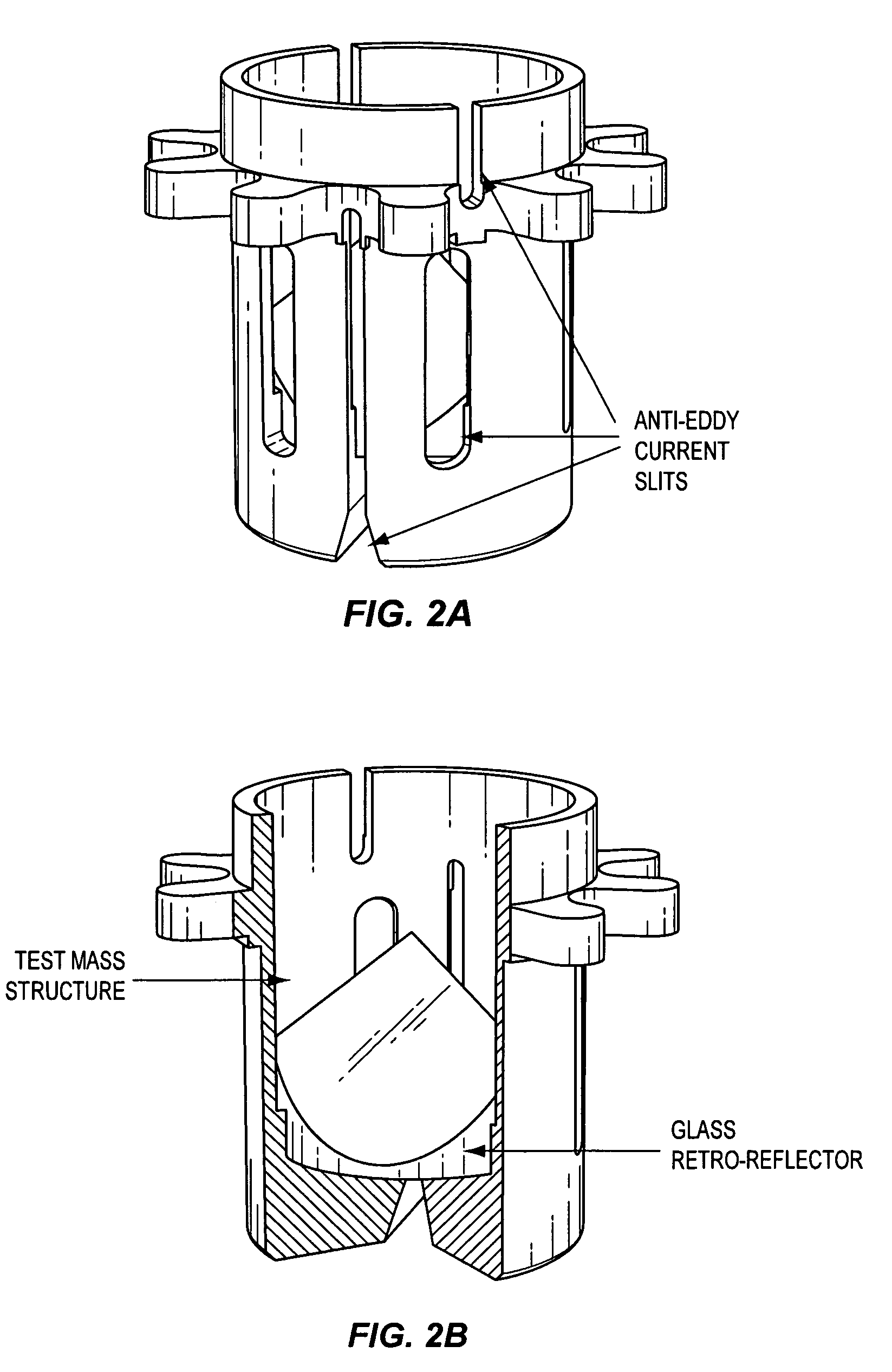
Test mass for gravimeters and gradiometers
InactiveUS20060130575A1Reducing and eliminating source of systematic errorReduce the impactMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsAbsolute gravityTest quality
The present invention provides devices and methods for reducing or eliminating sources of systematic errors in the measurement of absolute gravity or gravity field gradients; specifically, an improved test mass for an interferometer is disclosed that reduces the influence of nearby electromagnetic fields on a freefalling test mass.
Owner:MICRO G LACOSTE
Wind tunnel experiment simulation method for cavity flow-induced vibration and flow-induced noise coupling characteristics
ActiveCN110287643AGuaranteed correctnessIntegrity guaranteedGeometric CADSustainable transportationData setStructural dynamics
The invention relates to the crossing field of aerodynamics, experimental fluid mechanics, aeroacoustics and structural dynamics and discloses a wind tunnel experiment simulation method for cavity flow-induced vibration and flow-induced noise coupling characteristics. The method comprises the following steps of establishing a cavity flow-induced vibration and flow-induced noise coupling characteristic control equation and boundary conditions by using an equation analysis method; converting the physical quantity parameters with dimensions into a similarity criterion data set of the physical quantity parameters without dimensions, and performing wind tunnel experiment model design, incoming flow condition selection and wind tunnel experiment result data correction based on the similarity criterion data set. The defect of the research capability of the cavity flow-induced vibration and flow-induced noise coupling characteristic problem in the prior art is effectively overcome. Completeness of wind tunnel experiment simulation parameters, effectiveness of an experiment data correction method and wind tunnel experiment simulation precision are ensured. Mutual influence rules among experimental results are effectively obtained; and the influence of cavity structure vibration can be simulated, so that the wind tunnel experiment simulation capability of the cavity configuration aircraft part is improved.
Owner:INST OF HIGH SPEED AERODYNAMICS OF CHINA AERODYNAMICS RES & DEV CENT
Three-dimensional nondestructive measurement method and three-dimensional nondestructive measurement device for object with complex outline
InactiveCN104792283AAccurate displacement requirementsSolve bottlenecksUsing fluid meansMathematical modelReconstruction method
The invention discloses a three-dimensional nondestructive measurement method and a three-dimensional nondestructive measurement device for an object with a complex outline. The three-dimensional nondestructive measurement method comprises the following steps of layering and dividing a measured object into a plurality of ordered small grid bodies by using a grid dividing method; measuring volumes of the small grid bodies of each layer in different directions by using a precise displacement control system and a volume measurement system; establishing a mathematical model; performing smart calculation so as to solve three-dimensional coordinate dimensions of the small grid bodies of the object by using a genetic algorithm and the like; and designing a three-dimensional reconstruction method based on a layering feature so as to perform graph reconstruction on the small grid bodies of the object. By the measurement method, the measured object is not damaged, all materials which cannot be dissolved in water, do not have closing holes and are in the complex shapes can be measured conveniently, the cost is low, obtained three-dimensional coordinate point cloud data are layered orderly, reconstruction is simple, and objects can be measured automatically. A theory of the technology can be used for the fields of computer aided design and manufacture, rapid prototyping, virtual reality and the like, technological difficulties of reverse engineering and rapid prototyping in the prior art are solved, and the three-dimensional nondestructive measurement method and the three-dimensional nondestructive measurement device for the object with the complex outline have quite important theoretic value and a wide application prospect.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Communication system using gravitational waves
InactiveUS6300614B1Radiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by optical meansCommunications systemGravitational wave
A method and apparatus for communication using gravitational waves is disclosed. The system utilizes a resonant frequency set up between identical masses to transmit information. The communication system uses two pieces of superconducting material, identical in size, mass and shape; means to modify the density of the first piece of superconducting material at a variable frequency; and detection means for sensing the effect of gravitational wave pulses on said second piece of superconducting material.
Owner:PETLAN JIRI JOSEPH
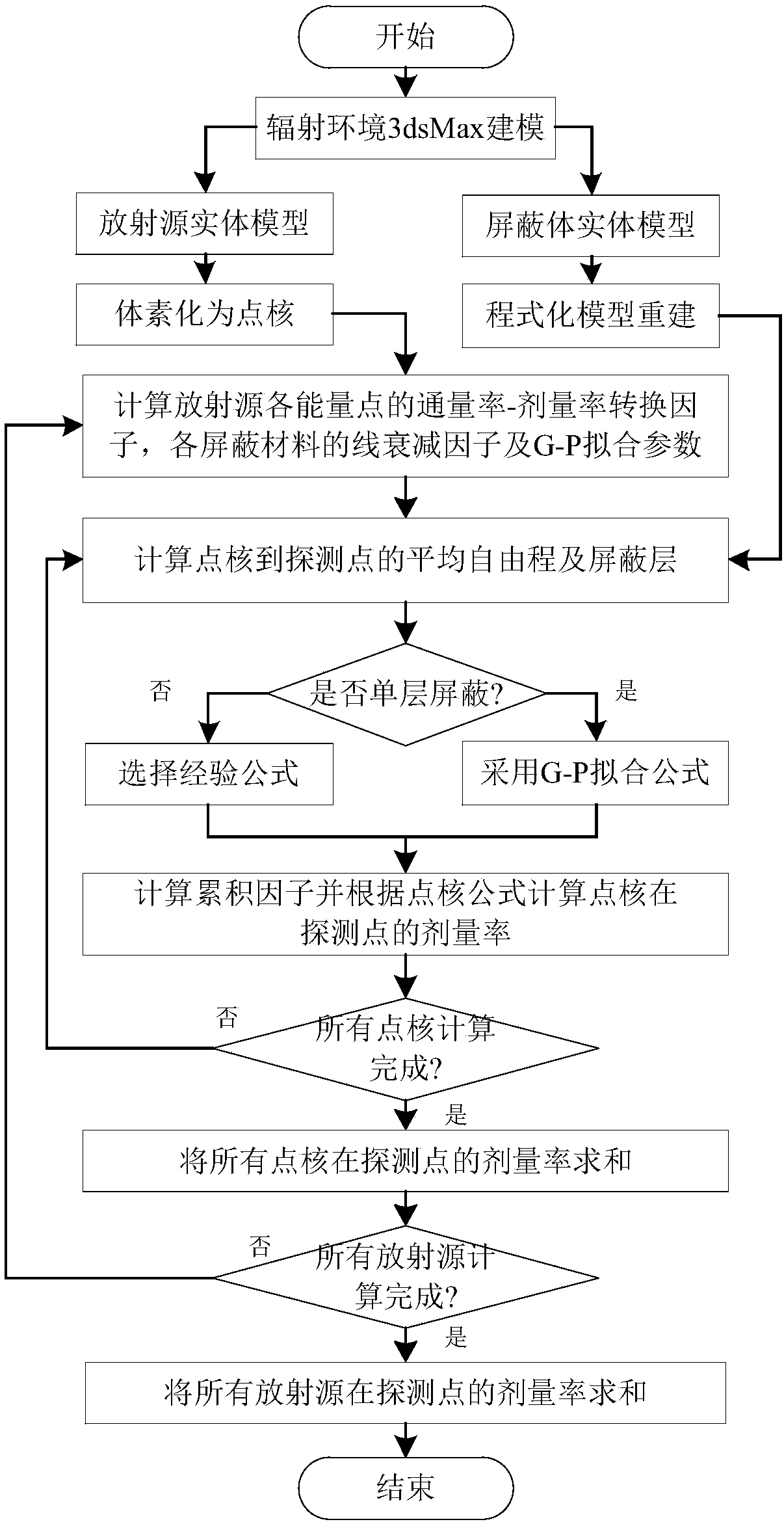
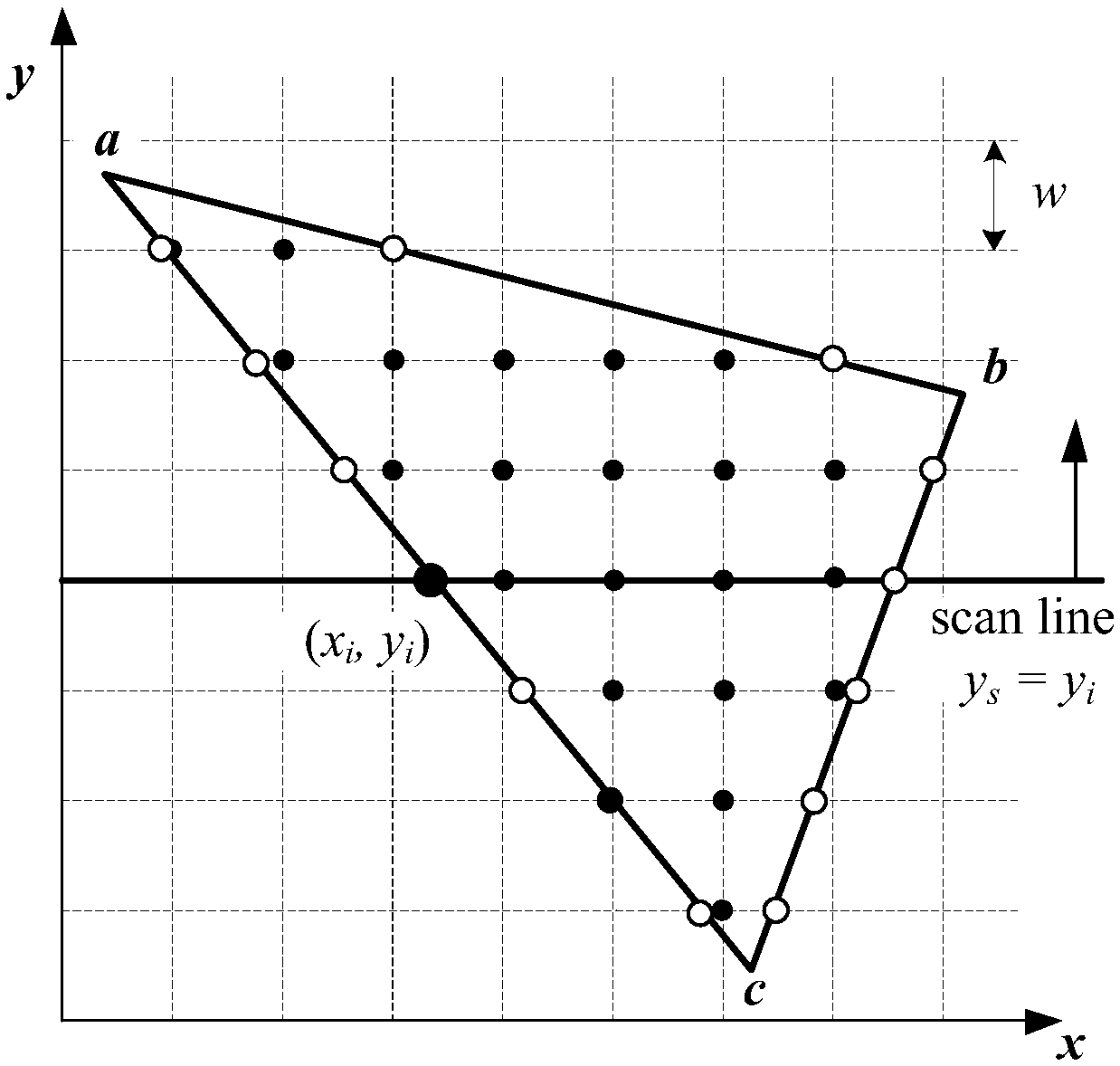
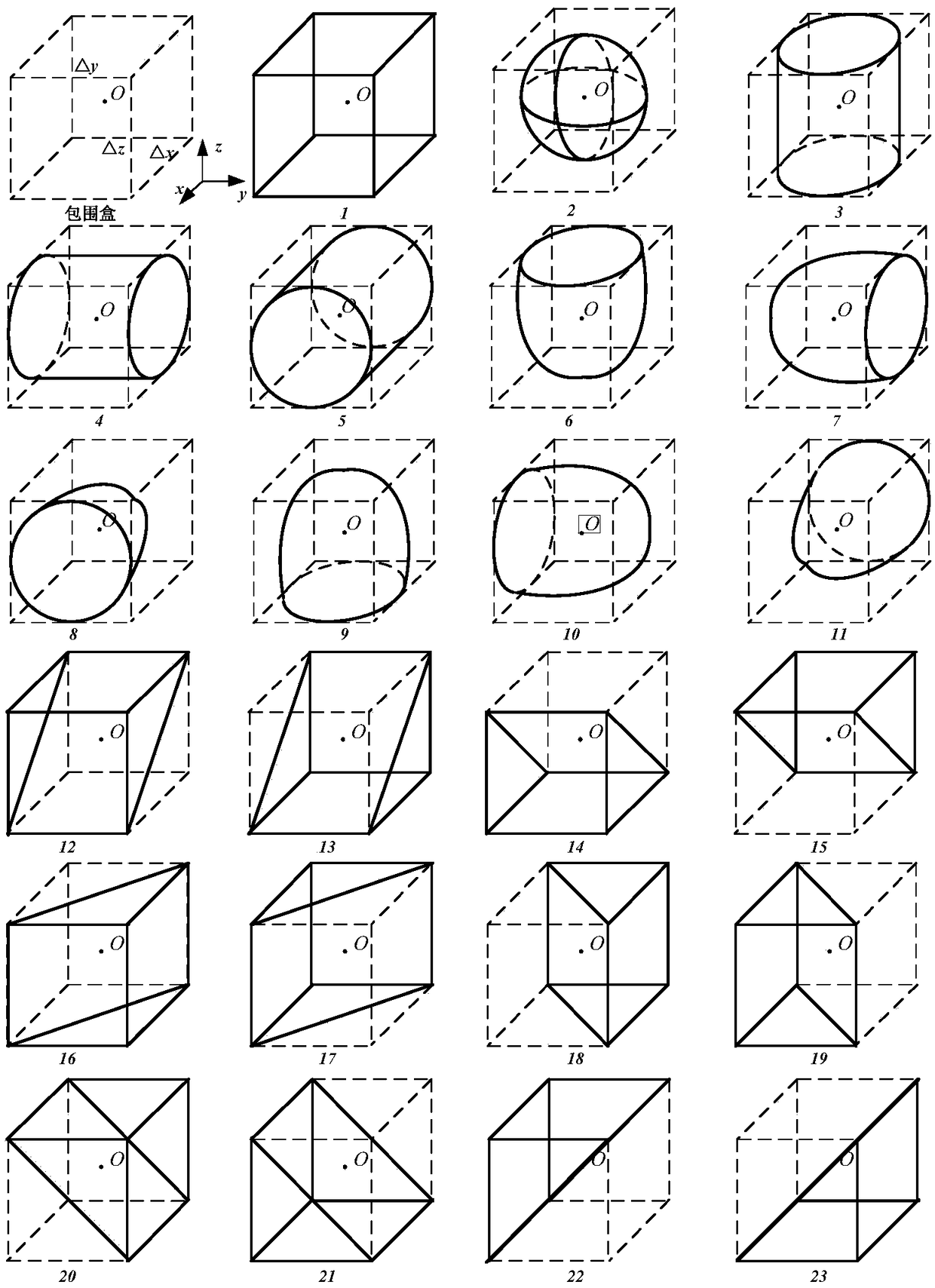
A radiation shielding calculation and simulation method of arbitrary shape radiation sources
ActiveCN109190144ARealize computingAutomate the processDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsVoxelMathematical model
The invention relates to a radiation shielding calculation and simulation method of arbitrary shape radioactive sources, which relates to the nuclear decommissioning simulation field, in particular toa radiation shielding calculation and simulation method for arbitrary shape radioactive sources. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) constructing a model according to a nuclear facilityand obtaining model parameters; (2) constructing the bounding box and tetrahedron of the radiation source model; (3) calculating the intersection points of the scanning plane and the edges of the tetrahedron to obtain a series of planar triangles; (4) discrete planar triangles are voxels; (5) dispersing the radioactive source into point cores; (6) constructing a mathematical model of the shield according to the bounding box of the shield model; (7) determining an external programming model of the shield object according to the number of vertices of the shield object in the programming model; (8) establishing the internal programming model according to the shell thickness of the shield model; (9) calculating the dosimetric distribution of radiation field by the point kernel integration method. The automatic and visual modeling of radiation dose calculation software for arbitrary shape radioactive source is realized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Full body teleportation system
InactiveUS20060071122A1Constant gainCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsWhole bodyGravitational wave
A pulsed gravitational wave wormhole generator system that teleports a human being through hyperspace from one location to another.
Owner:HECHT ROJAS LUIS A
Design method of multifunctional space gravitational wave detector based on TRIZ
InactiveCN103675935AThe principle is simpleEasy to operateGravitational wave measurementIsoetes triquetraDifferentiator
The invention discloses a design method of a multifunctional space gravitational wave detector based on the TRIZ. Seven inventive principles recommended by the TRIZ serve as technological evolution paths, a ground laser interference gravitational wave detector can be evolved into a multifunctional space gravitational wave detector. The multifunctional space gravitational wave detector comprises devices such as spacecrafts. As shown in the figure, the multifunctional space gravitational wave detector is characterized in that the three spacecrafts form an equilateral triangle constellation with the 103-109km side length, the center of the equilateral triangle constellation moves on the earth orbit, an optical table on each spacecraft and an optical table on the adjacent spacecraft can have interference through coherent light beams generated by lasers, if gravitational waves scan the spacecrafts, the strength of light passing through photodiodes of photodetectors changes, a differentiator and a correlator are used for calculating the relation between the strength of the light and the phase position, and the value of the gravitational waves to be measured is obtained. The multifunctional space gravitational wave detector is characterized in that the low and medium frequency gravitational waves are detected, and a double-star system, large-mass black holes and random background gravitational waves are surveyed.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
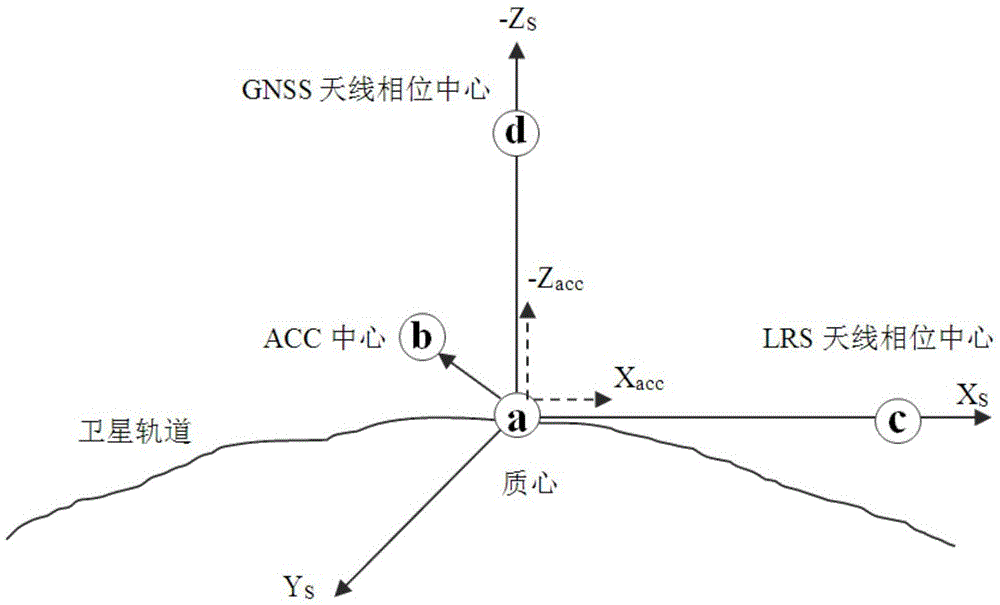
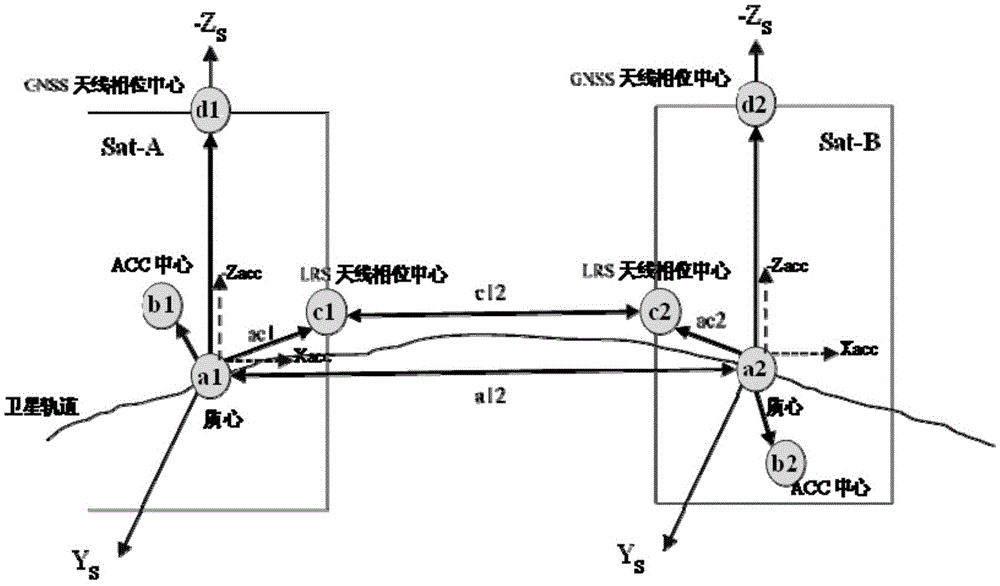
Low-low tracking gravity measurement satellite four-point three-line model and establishment method thereof
InactiveCN105652333ARealize distributionExact abstract descriptionSpecial data processing applicationsGravitational wave measurementSatellite trackingTarget line
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite gravity measurement, and particularly relates to a low-low tracking gravity measurement satellite "four-point three-line" model and an establishment method thereof. The model structure includes centers of mass, an accelerometer mass inspection center, LRS antenna phase centers and a GNSS antenna phase center of two tracking satellites, and a datum line, a measurement line and inertial lines. The datum line is the connecting line of the centers of mass of the two tracking satellites, i.e. the datum line is a satellite gravity measurement target line. The measurement line is the connecting line of the LRS antenna phase centers of the two tracking satellites. The inertial lines are the connecting lines between the centers of mass of the tracking satellites and the LRS antenna phase centers. Accurate and abstract description of a system prototype can be realized so that the reliable basis can be provided for the design of a low-low satellite-to-satellite tracking gravity measurement system; and multiple key technologies of the low-low satellite-to-satellite tracking gravity measurement system are comprehensively combed with the basis acting as the cutting point so that comprehensive distribution of multiple complex errors existing in the gravity measurement system can be realized, and thus the model has important guiding significance for subsequent satellite gravity data processing.
Owner:西安测绘研究所
Method for detecting underground tunnels
ActiveUS8510048B2Reduce degradationReduce readDigital computer detailsUsing electrical meansUnderground tunnelVector field
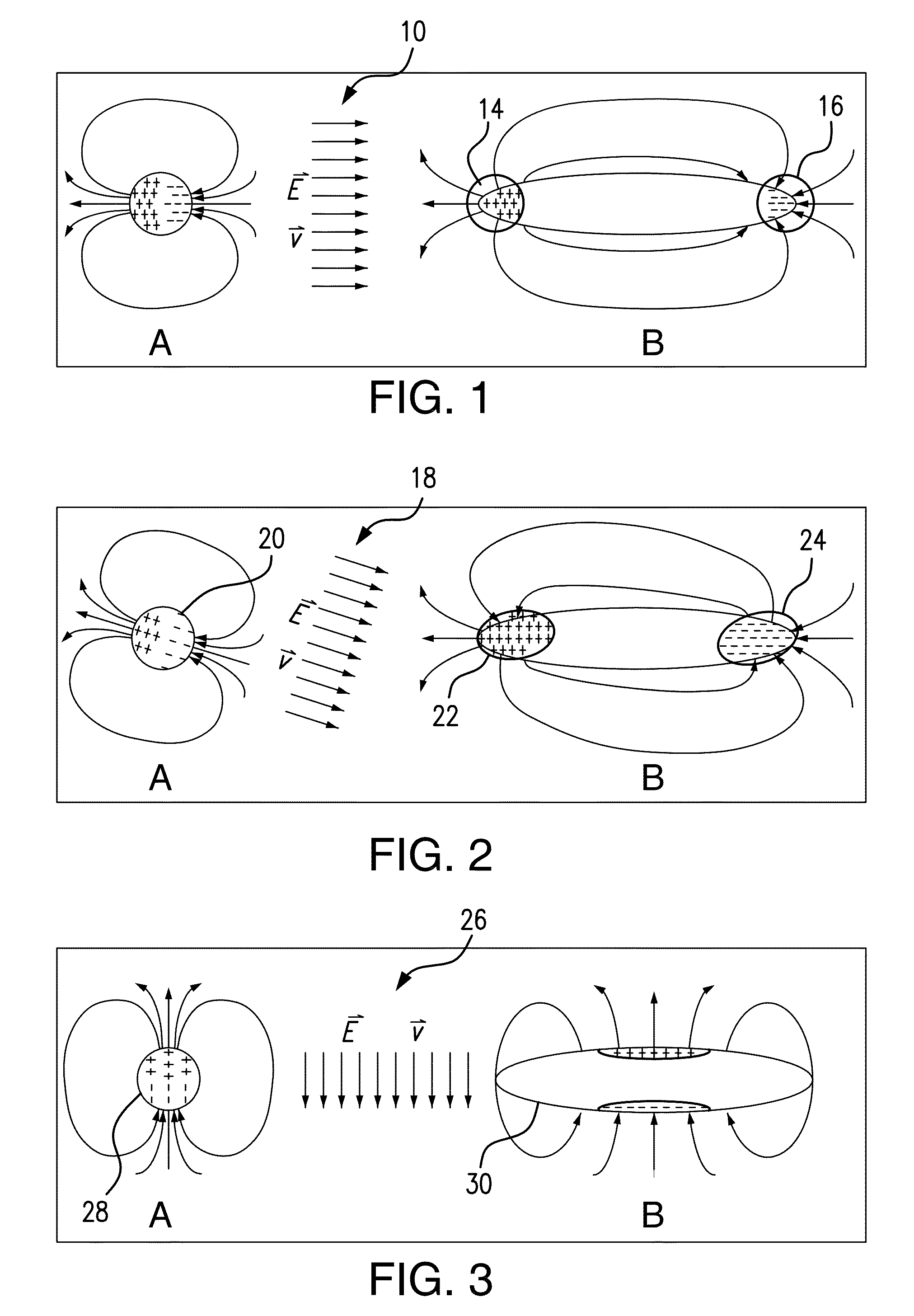
A method for detecting tunnels within an area comprising in one embodiment the steps of providing horizontal tensor gravity gradients for the area, calculating a plurality of gravity gradient vector field pairs from the horizontal tensor gravity gradients, each gravity gradient vector field pair including one gravity gradient vector field and a respective orthogonal gravity gradient vector field, detecting dipolar points and polar source points in each of the one and respective orthogonal gravity gradient vector fields for each gravity gradient vector field pair, identifying the polar source points that are present in one but not in both of the one gravity gradient vector field and the respective orthogonal gravity gradient vector field for each gravity gradient vector field pair to identify endpoints, and distinguishing the endpoints resulting from surface features from the endpoints resulting from tunnels. The polar source points form the endpoints of the tunnels.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Gravity gradiometer with correction of external disturbance
InactiveUS20130055808A1Accurate correctionReduce impactGravitational wave measurementGravitational forceGradiometer
The present disclosure provides a method of detecting a change in gravity gradient using a gravity gradiometer. The gravity gradiometer comprises a detector for detecting the change in gravity gradient. The gravity gradiometer further comprises a sensor for generating a disturbance signal in response to an external disturbance. The method comprises the steps of exposing the gravity gradiometer to the external disturbance during operation of the gravity gradiometer. Further, the method comprises the steps of detecting the disturbance signal and receiving an output signal from the detector of the gravity gradiometer. The method also comprises the step of numerically correcting the output signal for an impact that a component of the gravity gradiometer experiences, as a consequence of the external disturbance using a response parameter that associates the external disturbance with a disturbance experienced by that component.
Owner:TECH RESOURCES PTY LTD
High-precision micro-gravity acceleration measurement device and method based on quantum weak measurement
ActiveCN109061755AAccurate measurementHigh measurement accuracyGravitational wave measurementAviationMeasurement device
The invention discloses a high-precision micro-gravity acceleration measurement device and a method based on a quantum weak measurement; the micro-gravity acceleration measurement device comprises a gravity sensing unit, a Sagnac interferometer, a laser emitting unit, a light receiving and detecting unit and a data processing unit, wherein coupling the gravity sensing unit with the Sagnac interferometer based on the quantum weak measurement, amplifying micro-displacement changes in different gravitational field environments of cantilever beam through deflection of polarized light in the Sagnacinterferometer, so that accurate measurement of gravitational acceleration micro changes is realized; the gravity acceleration measurement precision can reach 10<-10>, and the high-precision micro-gravity acceleration measurement device has very high measurement precision, can be applied to gravity assisted navigation in mine exploration, passive navigation technology, ocean gravity measurement,aviation gravity measurement and the like, and has an important application prospect.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Test mass for gravimeters and gradiometers
InactiveUS7451645B2Reducing and eliminating source of systematic errorReduce impactMachines/enginesLevel indicatorsAbsolute gravityTest quality
The present invention provides devices and methods for reducing or eliminating sources of systematic errors in the measurement of absolute gravity or gravity field gradients; specifically, an improved test mass for an interferometer is disclosed that reduces the influence of nearby electromagnetic fields on a freefalling test mass.
Owner:MICRO G LACOSTE
Gravitational wave propulsion and telescope
InactiveUS20040130237A1Radiation/particle handlingEnergy storageInformation processingDetector array
A gravitational wave generating device comprising an energizing means such as a particle or electromagnetic beam, which act upon energizable elements such as molecules, atoms, electrons, nuclei or nuclear particles in order to create nuclear reactions or collisions, the products of which can move in a single preferred direction with an attendant impulse (jerk or harmonic oscillation) of an ensemble of target nuclei or other energizable elements over a very brief time period. The target nuclei or energizable elements such as electrons or other submicroscopic particles in a superconductor acting in concert generate a gravitational wave. An information-processing device connected to a computer, controls the particle beam's high-frequency, (approximately GHz to THz or higher) pulse rate and the number of particles in each bunch comprising the pulse in order to produce modulated gravitational waves that can carry information. A gravitational wave generation device that exhibits directivity. A gravitational wave detection device that exhibits directivity and can be tuned. The utilization of a medium in which the gravitational wave speed is reduced in order to effect refraction of the gravitational wave and be a gravitational wave lens. A gravitational wave generator device that can be directed in order to propel an object by its momentum or by changing the gravitational field nearby the object to urge it in a preferred direction and be a propulsion means. A gravitational wave telescope that utilizes a source of gravitational waves and a gravitational wave lens to focus an image on an array of detectors.
Owner:BAKER ROBERT M L JR
Assessment method of short-baseline relative orbit perturbation gravitational field measurement performance
ActiveCN105549105AHigh precisionOvercome timeGravitational wave measurementRelative orbitGravity anomaly
The invention provides an assessment method of short-baseline relative orbit perturbation gravitational field measurement performance. The relations between the short-baseline relative orbit perturbation gravitational field measurement performance and task parameters are established in an analysis mode, so that by only obtaining the gravitational field measurement task parameters and inputting the gravitational field measurement task parameters into an analysis relational expression, the gravitational field measurement performance, such as a gravitational field measurement effective order, geoid surface precision and gravity abnormity precision, can by rapidly analyzed and obtained. The method has the advantages that the analysis speed is high, the optimized design of gravitational field measurement task parameters can be conveniently and rapidly carried out, and the defects caused by a conventional numerical simulation method that the calculation time is long and the influence rules of the task parameters on the gravitational field measurement performance are difficult to obtain are overcome.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Contactor bounce feature calculation method considering structural thermal field effect
ActiveCN110232211AImplement featuresGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElement modelCollision dynamics
The invention discloses a contactor bounce feature calculation method considering a thermal field effect. The contactor bounce feature calculation method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a thermal field mathematical model, an electromagnetic feature mathematical model and a vibration collision mechanical model of a contactor; then establishing a thermal field finite element model, an electromagnetic finite element model and a vibration collision dynamics numerical model of the contactor; naming the thermal field finite element model, the electromagnetic finite element modeland the vibration collision dynamics numerical model of the contactor respectively as a thermal field module, an electromagnetic module and a vibration collision module; carrying out module connection on MATLAB / Simulink according to an action relation data interaction mode among electric-magnetic, electric-magnetic-thermal, and electric-magnetic-structural field; and finally, calculating the bounce feature of the contactor according to an electric-magnetic-thermal-structural multi-physical field model. The contactor bounce feature calculation method has key significance for perfecting the establishment of the contactor bounce model and deeply carrying out multi-physical field coupling calculation and bounce mechanism research on the contactor.
Owner:贵州振华群英电器有限公司(国营第八九一厂)
Method for reducing radiation environment model indeterminacy influences on material performance evaluation
ActiveCN108319777AReduce or avoid uncertaintyGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsSpacecraft designOrbit
The invention discloses a method for reducing radiation environment model indeterminacy influences on material performance evaluation. Based on an existing earth radiation belt model, radiation belt environmental parameters of a spacecraft in some orbit and task cycle during an in-orbit period are determined, thereby determining the selected parameters in carrying out spacecraft designs or evaluations, and a ground-based simulation experiment or numerical simulation are utilized to obtain performance changes and a change rule of the spacecraft and spacecraft sensitive materials; based on determined uncertainty factors, exposure material performance under certain uncertainty factors is compared with performance of not considering uncertainty, the selected gedanken experiment parameters areobtained referring to removing or reducing influences brought by space radiation environment model uncertainty. The required simulation experiment parameters of a space radiation environment model can be explicitly decreased or avoided.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Experimental method for scientific prediction of action science
The invention relates to an experimental method for scientific prediction of the action science, and belongs to the research field of natural science basic theory, material science and predication science. The experimental method mainly includes the following steps: A, measuring active action in an experiment; B, according to the relationship between deformation and force in traditional theories of material mechanics, engineering mechanics and rock and soil mechanics, measuring and recording deformation of a material under measured action conditions at any time; C, creating a relation equation between the action and the deformation; D, calculating virtuality and solidity parameter values of the material; E, calculating change rates of virtuality and solidity; F, predicting service life of the material. The experimental method has the advantages that experimental data completely identical to the reality and the engineering application method are provided, and scientific experiments are truly scientific, systematical, theorized and practical; the parameters and the method both needed by practical problem solutions can be provided, and the type and the number of natural science parameters are greatly reduced.
Owner:蓬莱金王耐磨物料有限公司
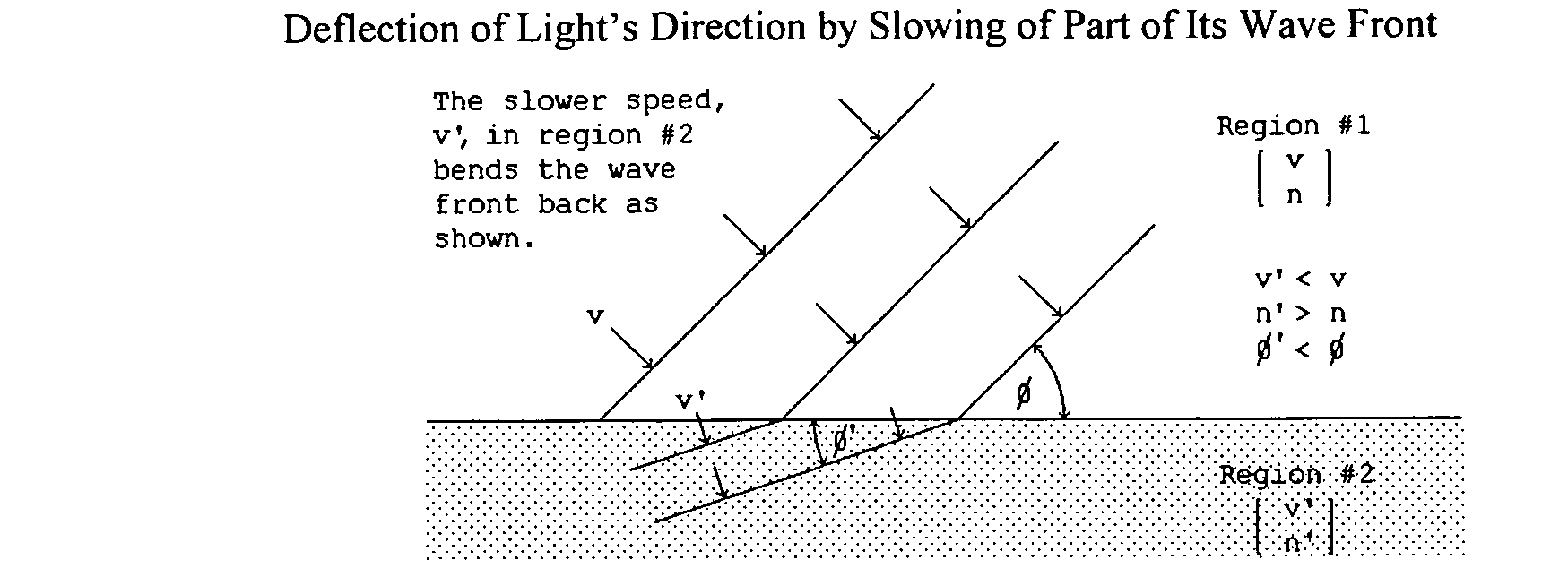
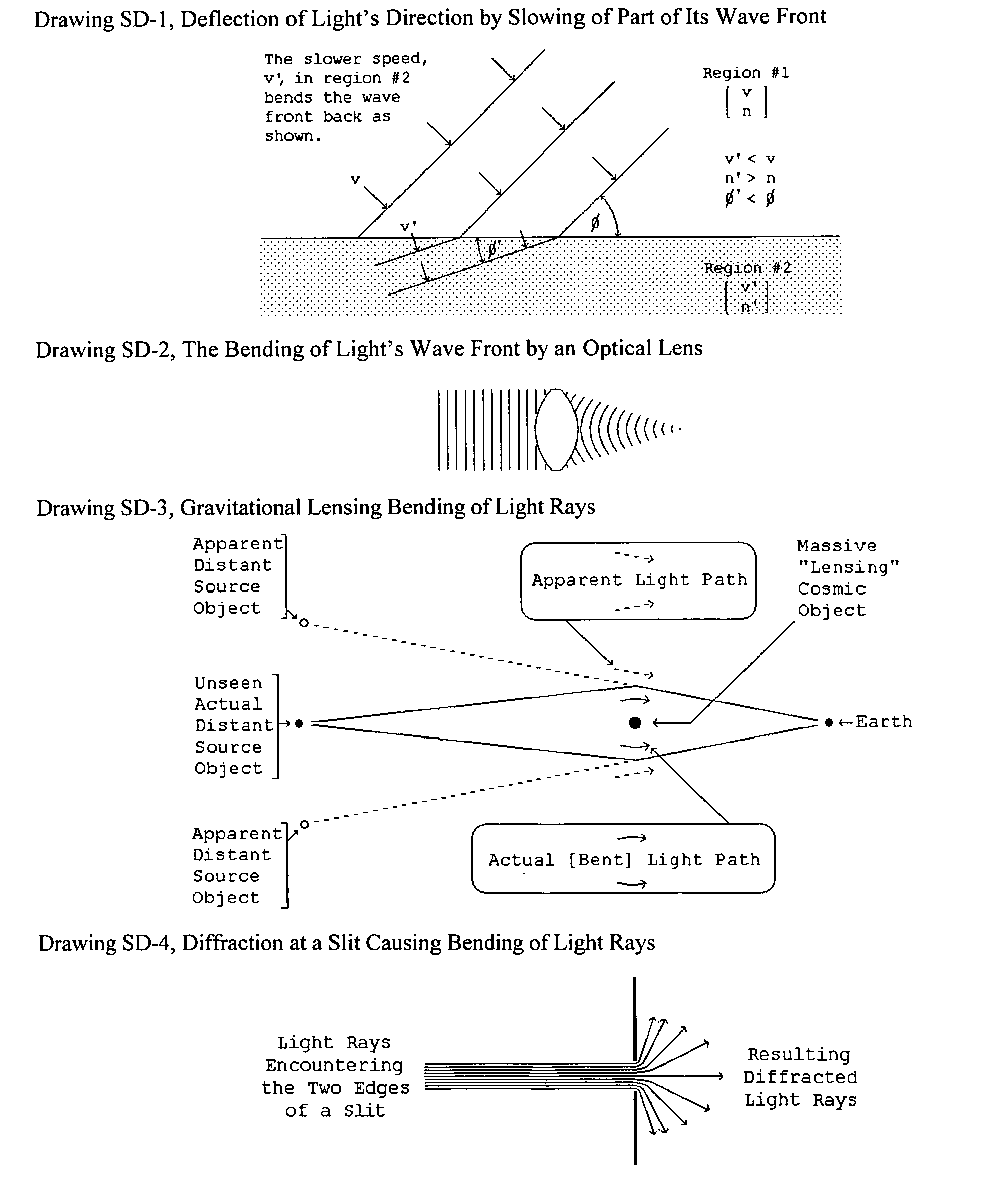
Gravitation deflecting mechanisms
InactiveUS20090214884A1Bending is greaterSlowing is greaterPolycrystalline material growthLayered productsMassive gravityLight diffraction
This disclosure presents and claims means for the modification of local gravitation by reducing its strength, speed of propagation, and / or its direction of action and presents and claims various uses of those means. The new technology involved is the recognition that light and gravitation flow in the same medium; that the observed effects of gravitational lensing and light diffraction demonstrate the gravitational field of atoms deflecting the flow of that common light / gravitation medium; that a suitable arrangement of atoms thus could produce a desired deflection of gravitation; and that the atomic structure of a cubic crystal [for example Silicon] is suitable for that application.
Owner:ELLMAN ROGER
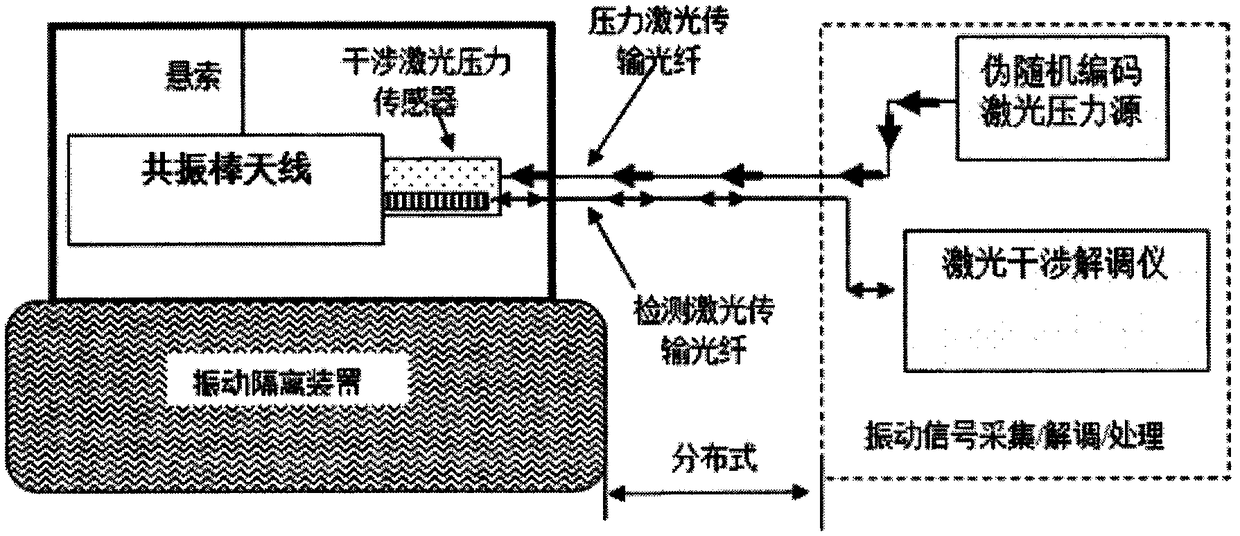
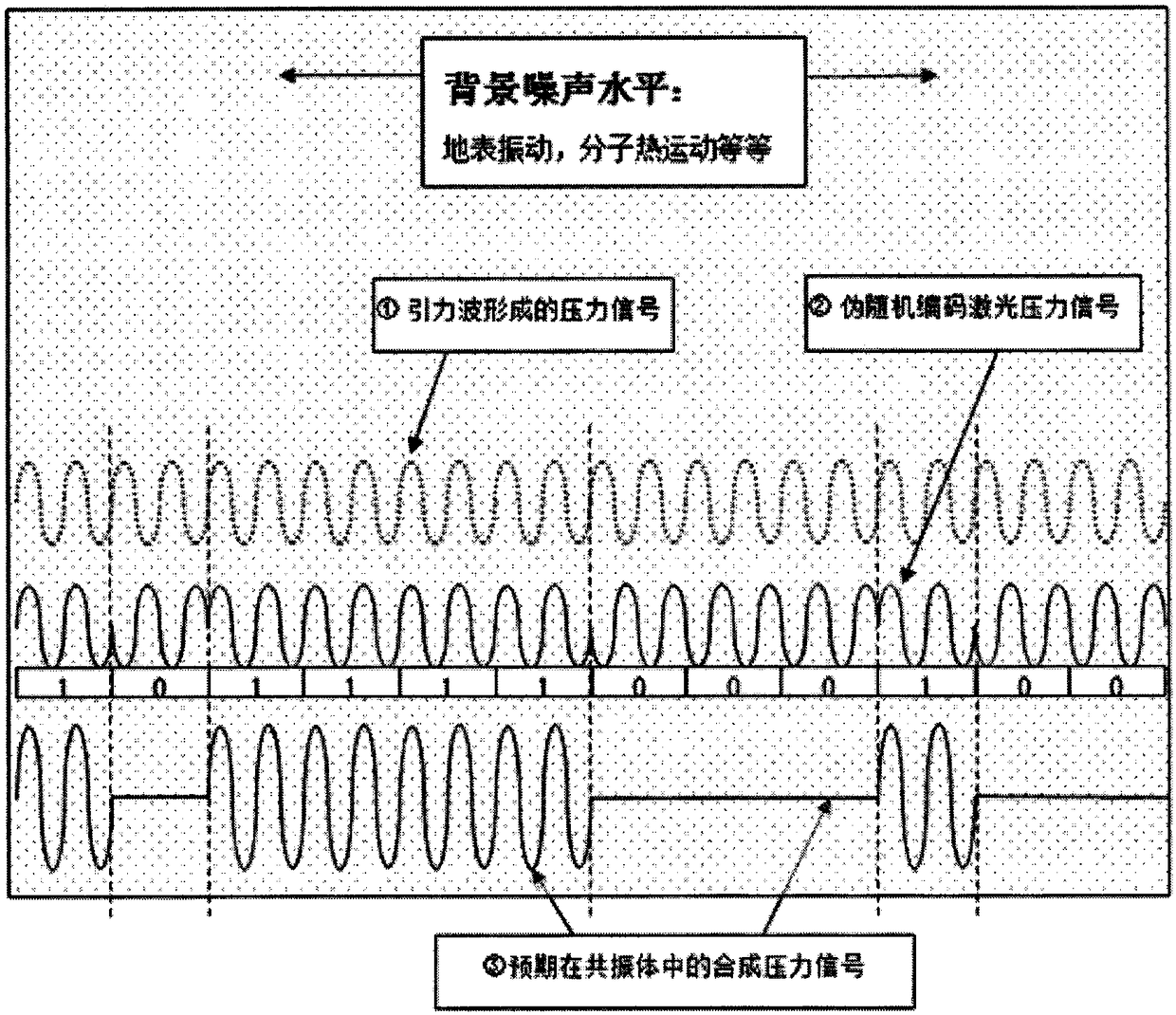
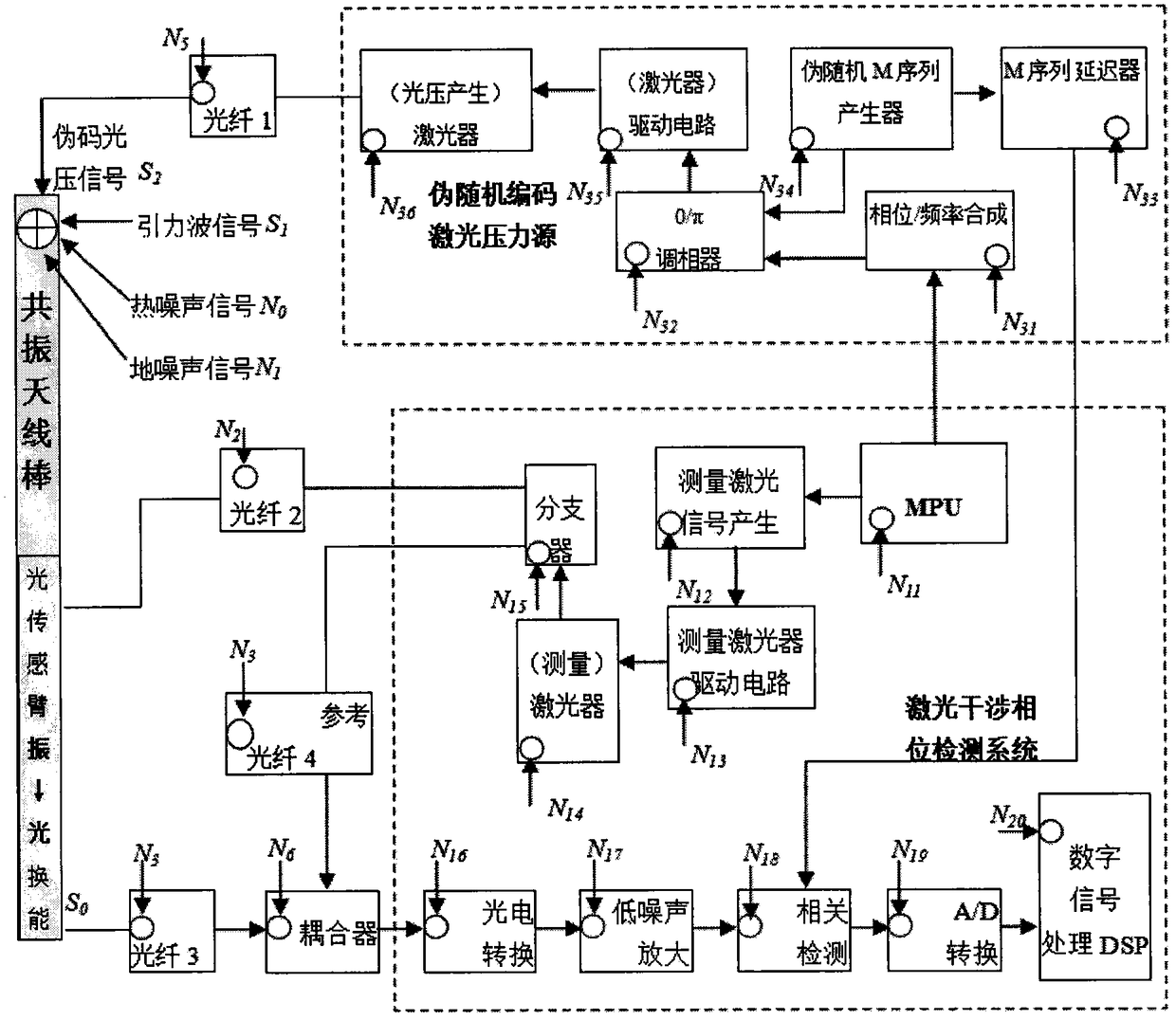
Gravitational wave detecting method based on pseudo random encoding technique
InactiveCN109471188AReduced thermal noise levelEasy to measureGravitational wave measurementNoise levelSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a gravitational wave detecting method based on a pseudo random encoding technique. A pseudo random encoded laser beam is used for assisting in irradiation to a normal-temperature gravitational wave antenna, resonance having pseudo code characteristics can be formed when the light pressure of encoding laser conforms to the frequency / phase of gravitational wave pressure signals in a detection antenna, and accordingly the capability of detecting weak gravitational wave vibration under the thermal noise background is remarkably improved. Compared with a large resonance rodantenna, huge construction and operation cost for cooling to liquid helium temperature and the brought thermal noise level of the antenna by 2-4 orders of magnitude are reduced. The signal-to-noise ratio gain of 10 orders of magnitude is brought with relatively low cost through a pseudo random technique, and gravitational waves can be increased to the orders of magnitude of 10-4 to 10-5 g, so thatthe measurement level is easily achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for measuring height of atmospheric boundary layer
InactiveCN103135113BImprove accuracyEliminate distractionsElectromagnetic wave reradiationHaze pollutionTheoretical physics
The invention provides a method for measuring the height of an atmospheric boundary layer. An original algorithm based on a gravitational wave theory is adopted in the method, namely the gravitational wave gradient method is used for obtaining the height of the boundary layer and directly enabling aerosols which are distributed vertically under the effect of gravitational waves to be led to a theory of algorithms. The method is more suitable for obtaining the height of the real boundary layer of China high dust-haze pollution environment at present.
Owner:INST OF ATMOSPHERIC PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY SCI
Deep space gravitational wave detection device based on relay femtosecond pulse
ActiveCN105700035BRealize the detection of gravitational waves in deep spaceRealize differential detectionGravitational wave measurementTime domainClock synchronization
A deep space gravitational wave detection apparatus based on repeating type femtosecond pulses is disclosed and comprise a measuring end, a number one femtosecond phase lock repeater, a number two femtosecond phase lock repeater, a number three femtosecond phase lock repeater, a number four femtosecond phase lock repeater, a number five femtosecond phase lock repeater and a number six femtosecond phase lock repeater. The deep space gravitational wave detection apparatus can be used for conducting equal arm length differential detection on gravitational wave signals, detection sensitivity can reach a sub-nanometer magnitude, each of two measuring arms adopts a pulse time domain locking type repeating measurement structure, the luminous power of measuring light is amplified by cascading three femtosecond phase lock repeaters, deep space gravitational wave detection on the scale of the outer solar system, the measuring end is independent of the six femtosecond phase lock repeaters, and problems of real time communication between satellites that are far apart and high-precision clock synchronization can be addressed.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com