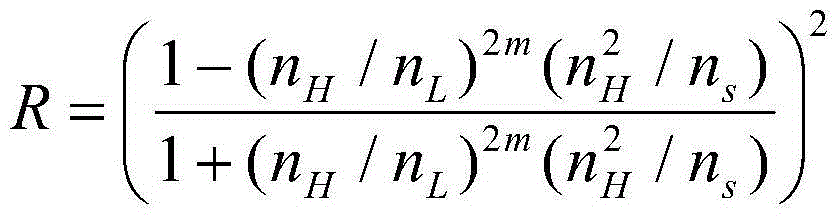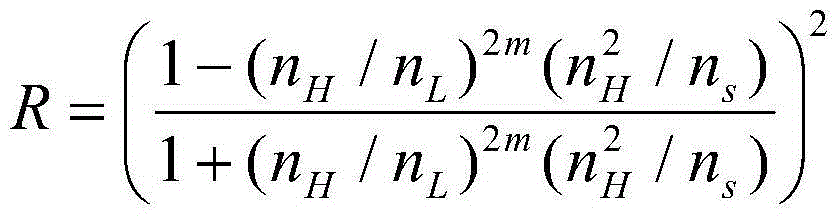Patents
Literature
54 results about "Gravitational wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gravitational waves are disturbances in the curvature of spacetime, generated by accelerated masses, that propagate as waves outward from their source at the speed of light. They were proposed by Henri Poincaré in 1905 and subsequently predicted in 1916 by Albert Einstein on the basis of his general theory of relativity. Gravitational waves transport energy as gravitational radiation, a form of radiant energy similar to electromagnetic radiation. Newton's law of universal gravitation, part of classical mechanics, does not provide for their existence, since that law is predicated on the assumption that physical interactions propagate instantaneously (at infinite speed) – showing one of the ways the methods of classical physics are unable to explain phenomena associated with relativity.
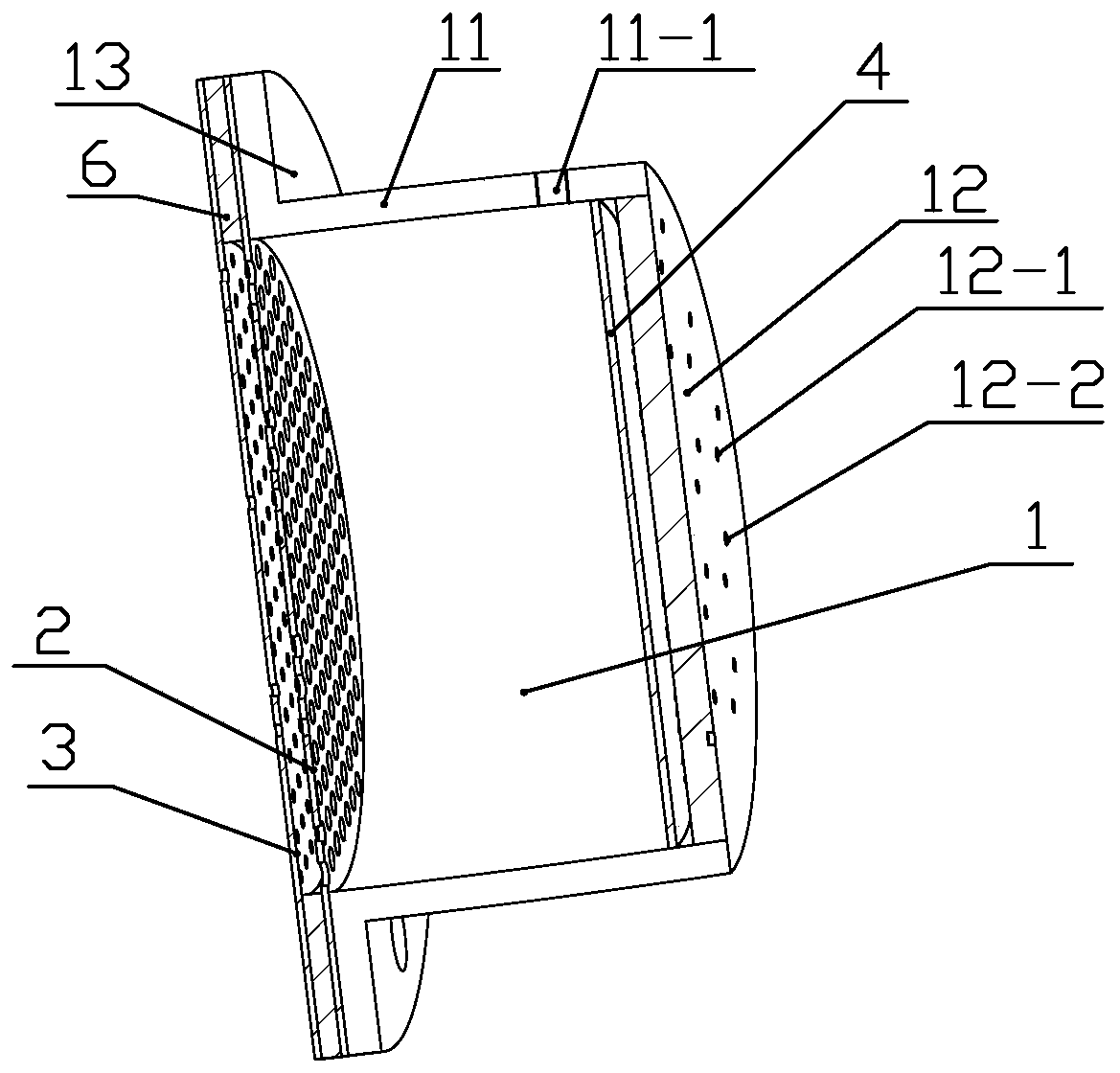
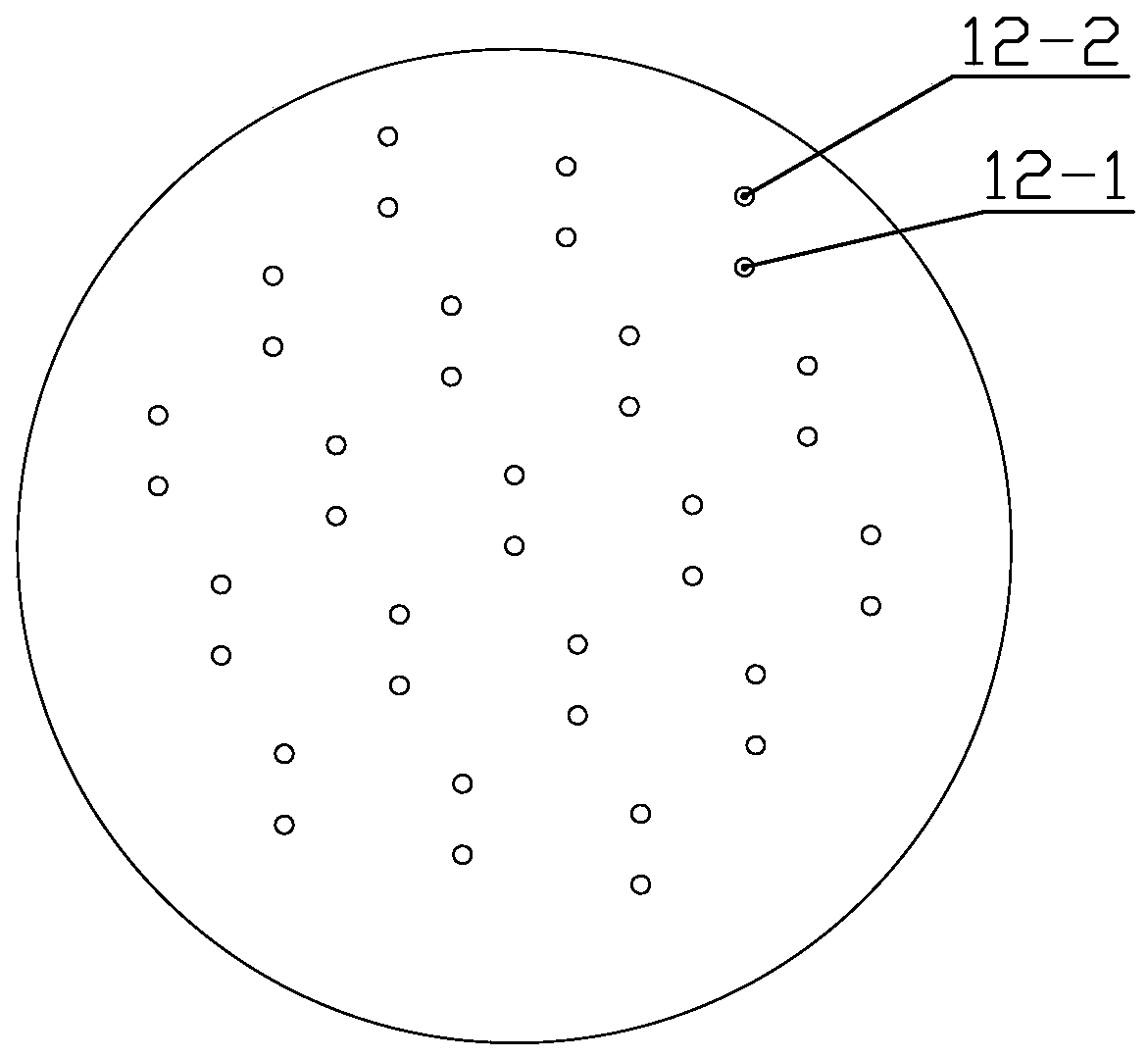
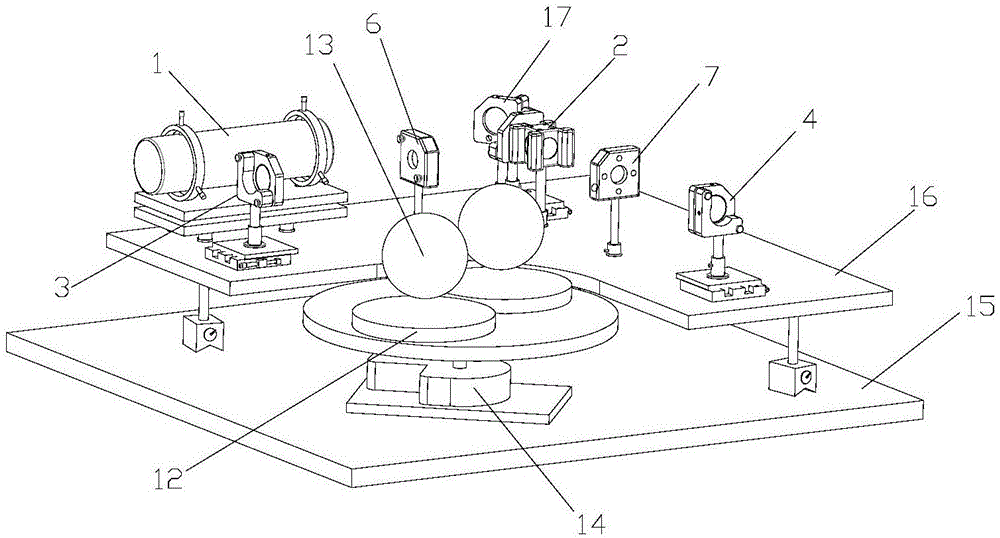
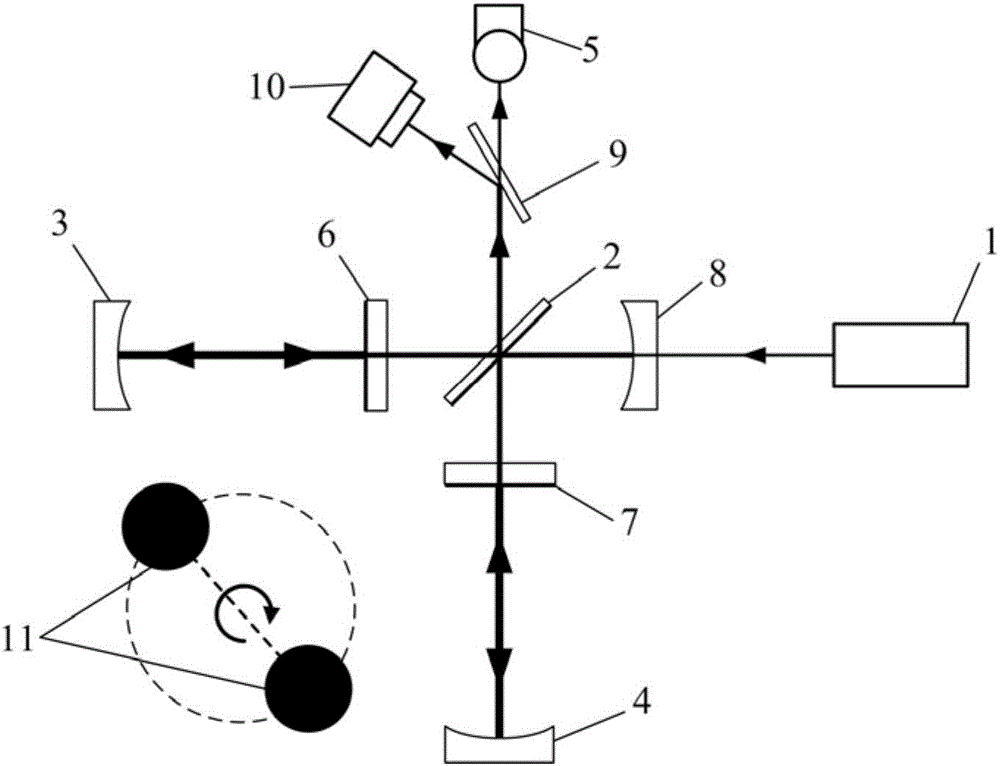
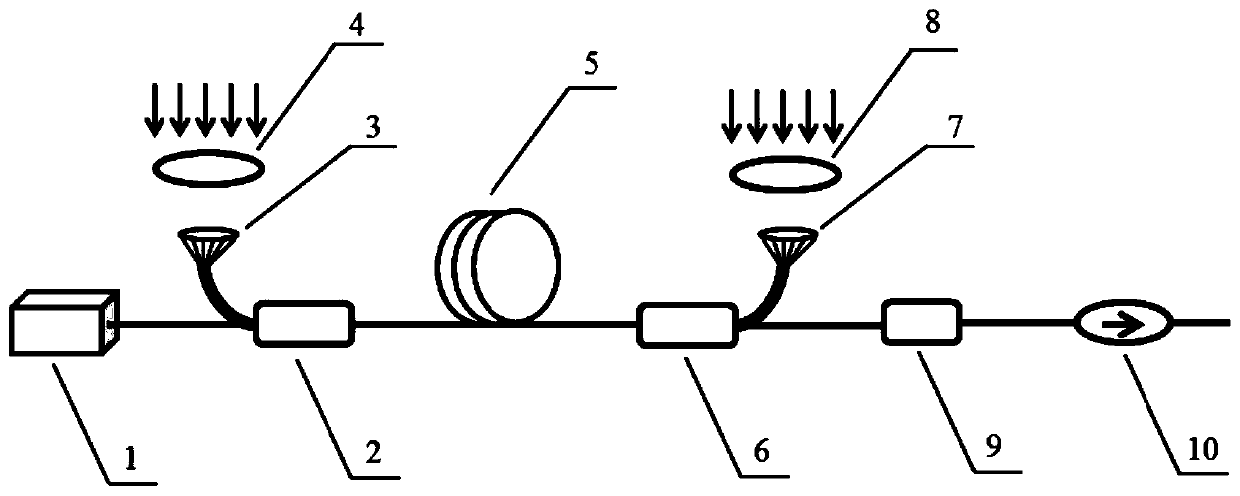
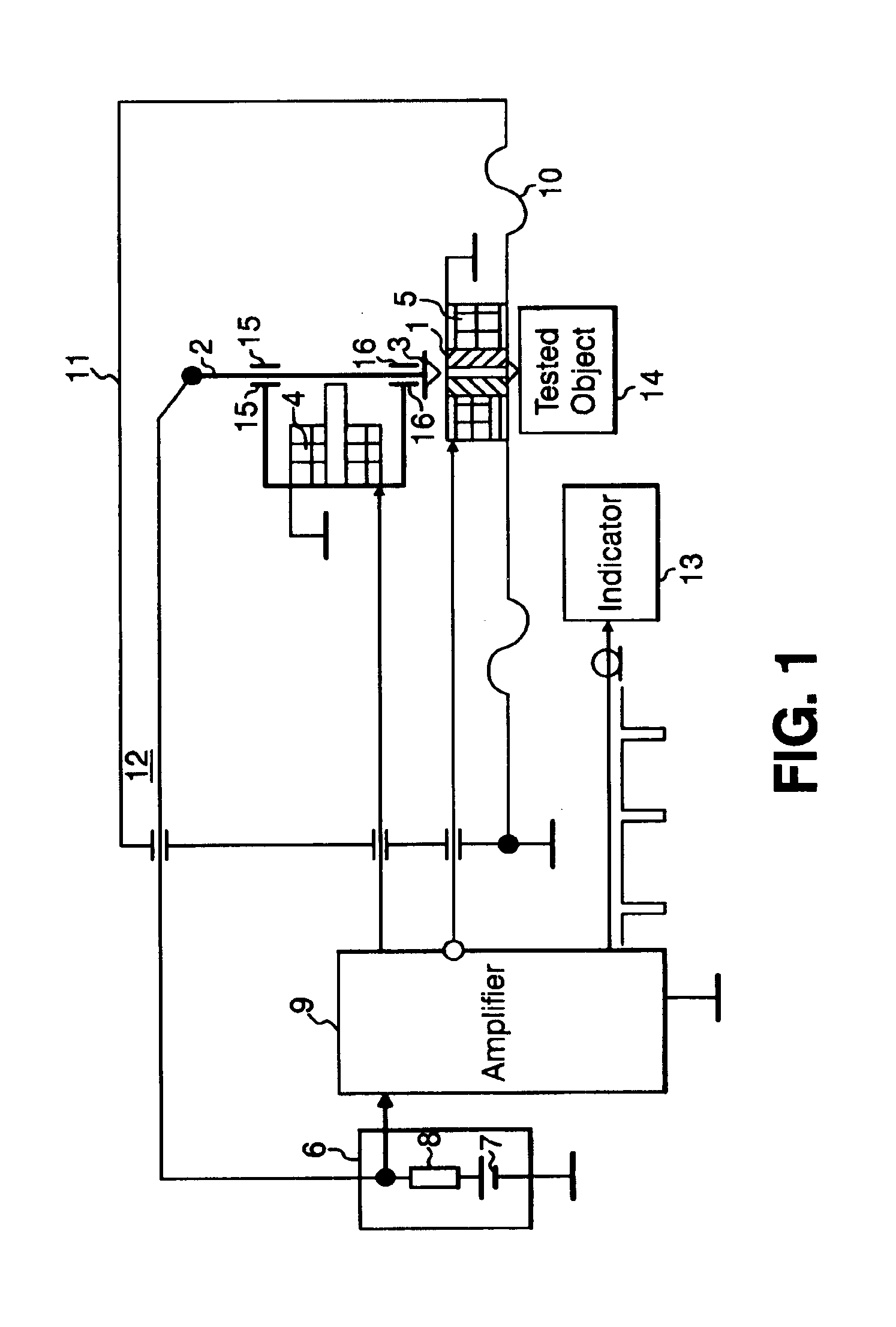
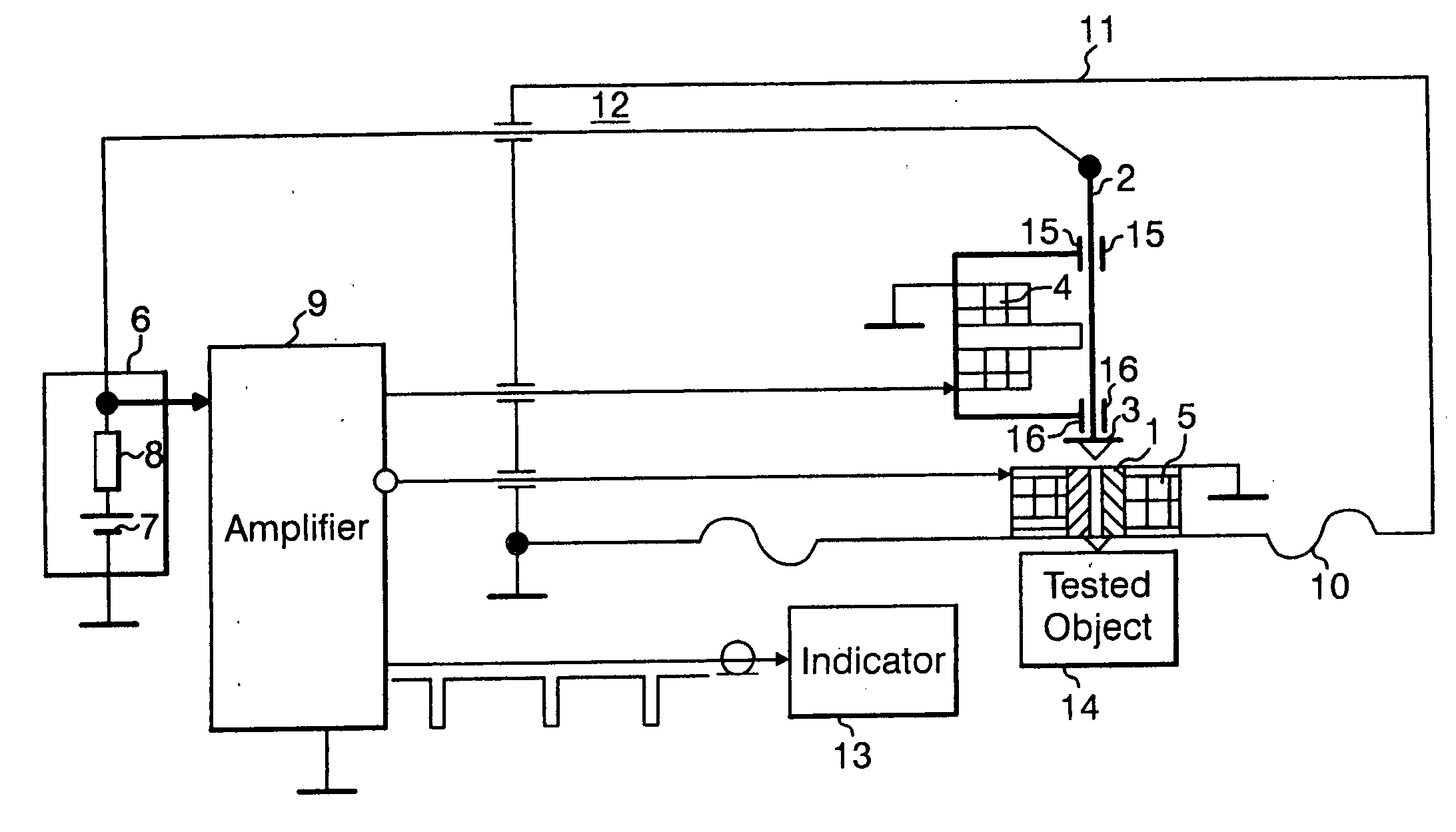
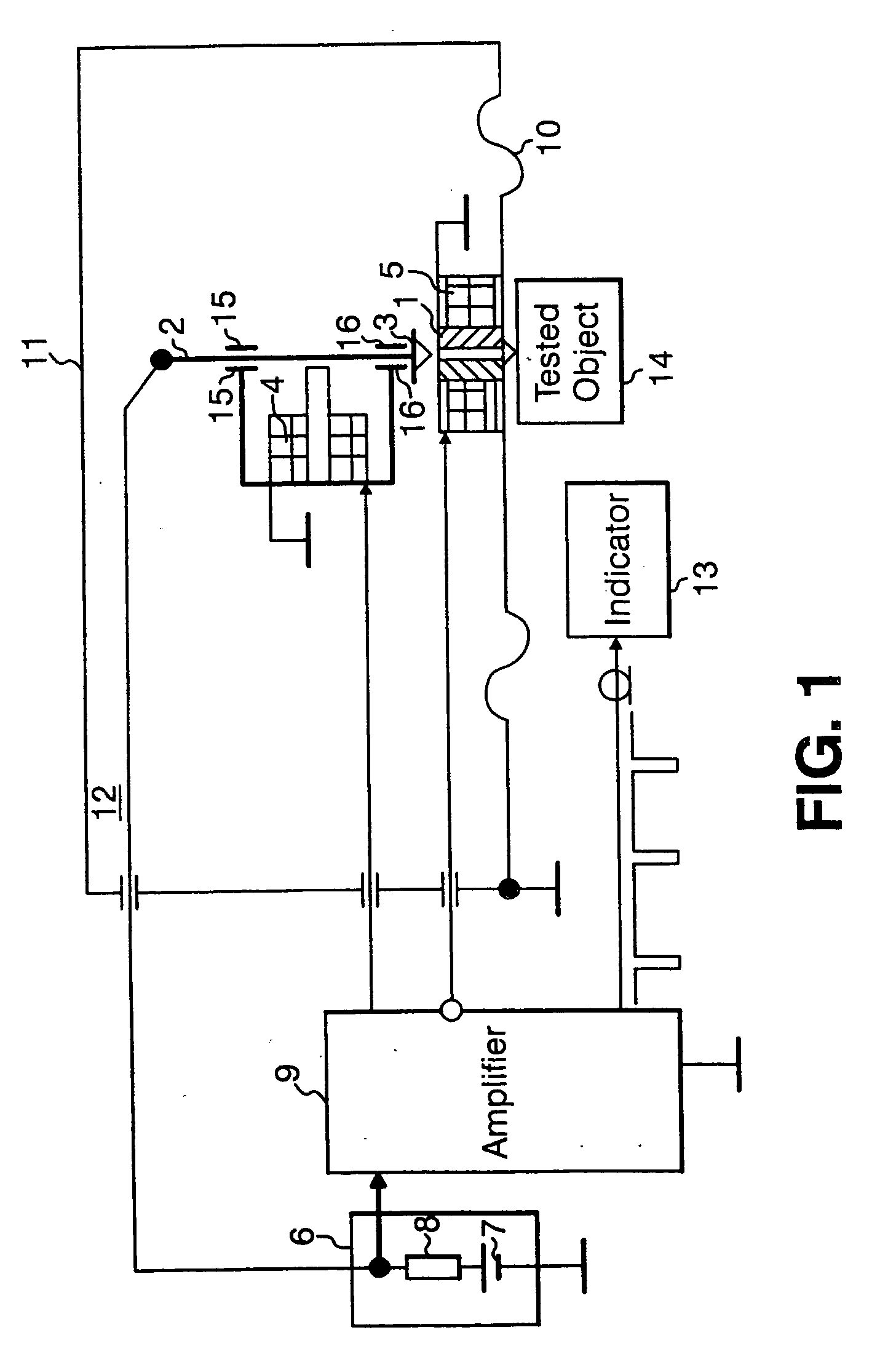
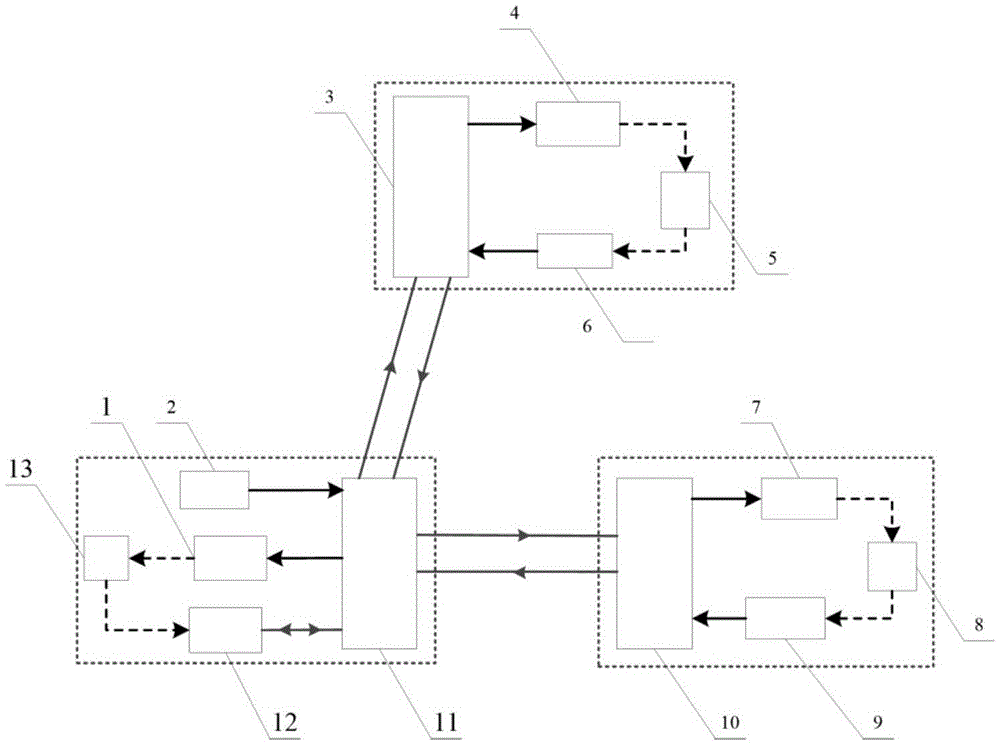
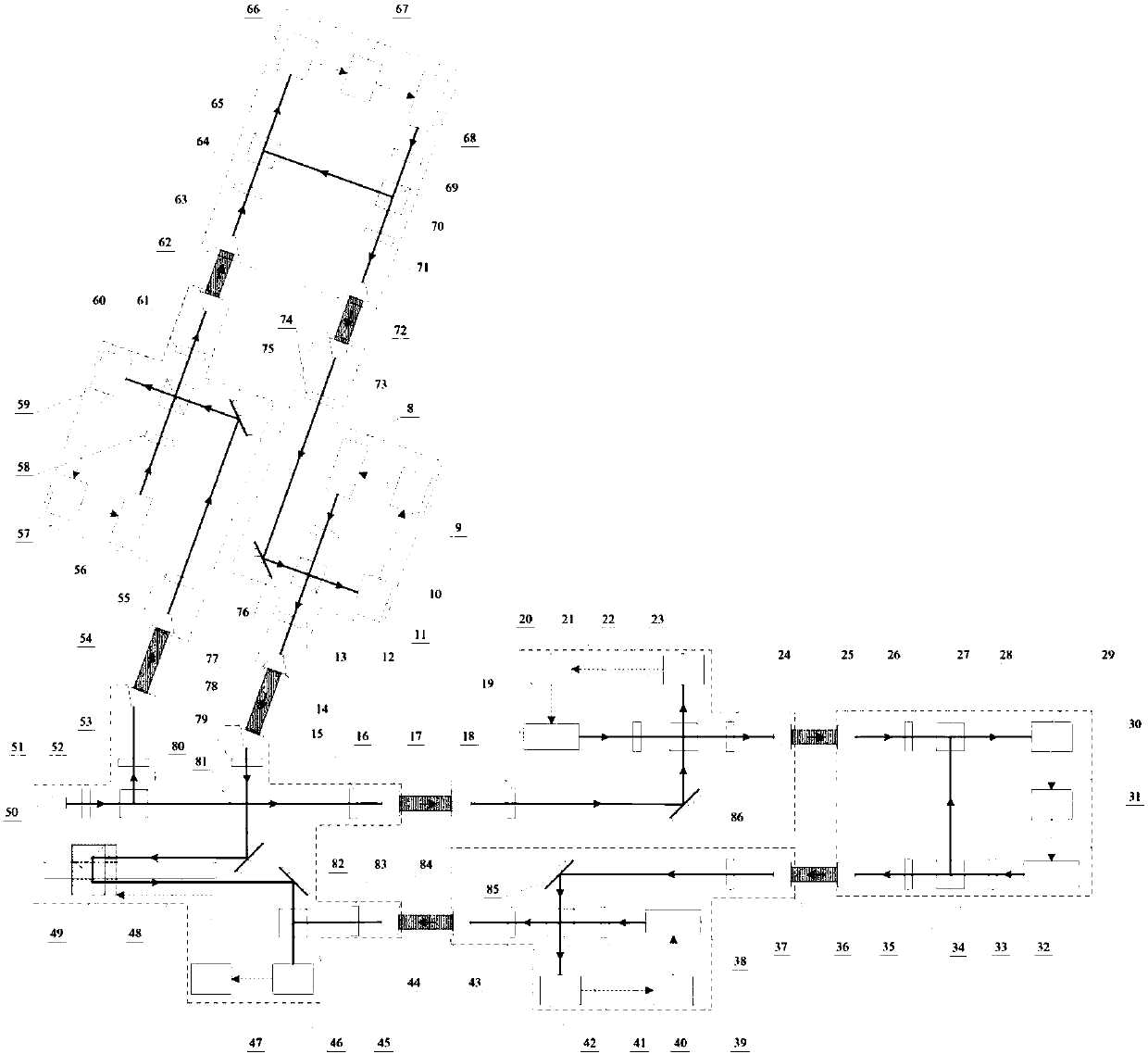
High-precision double star laser interference dynamic distance measuring ground simulation device
InactiveCN103513254AEliminate the effects ofIsolation impactElectromagnetic wave reradiationFrequency stabilizationDouble star
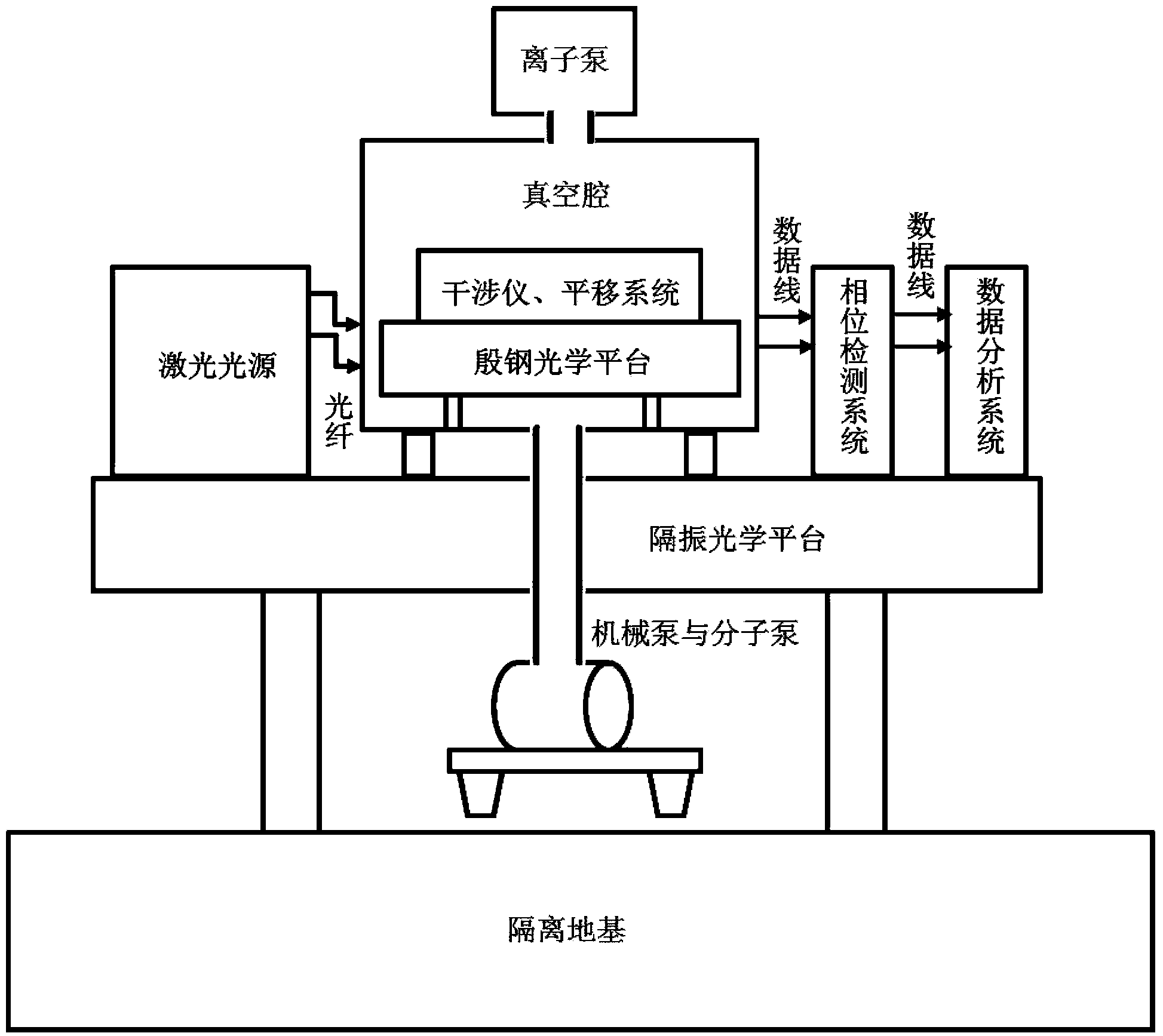
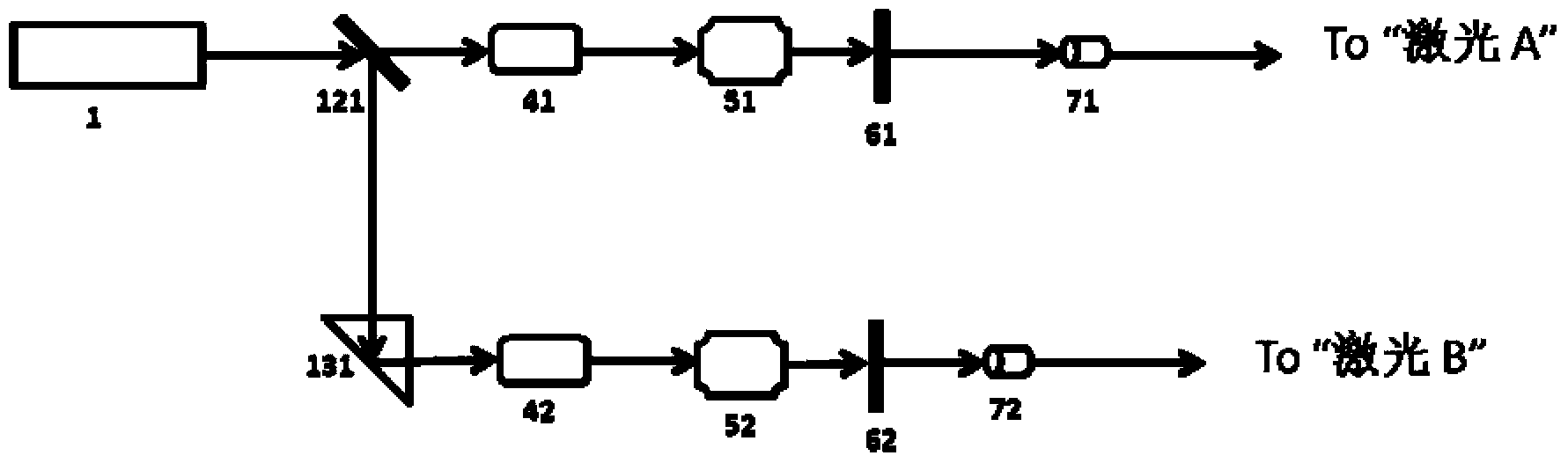
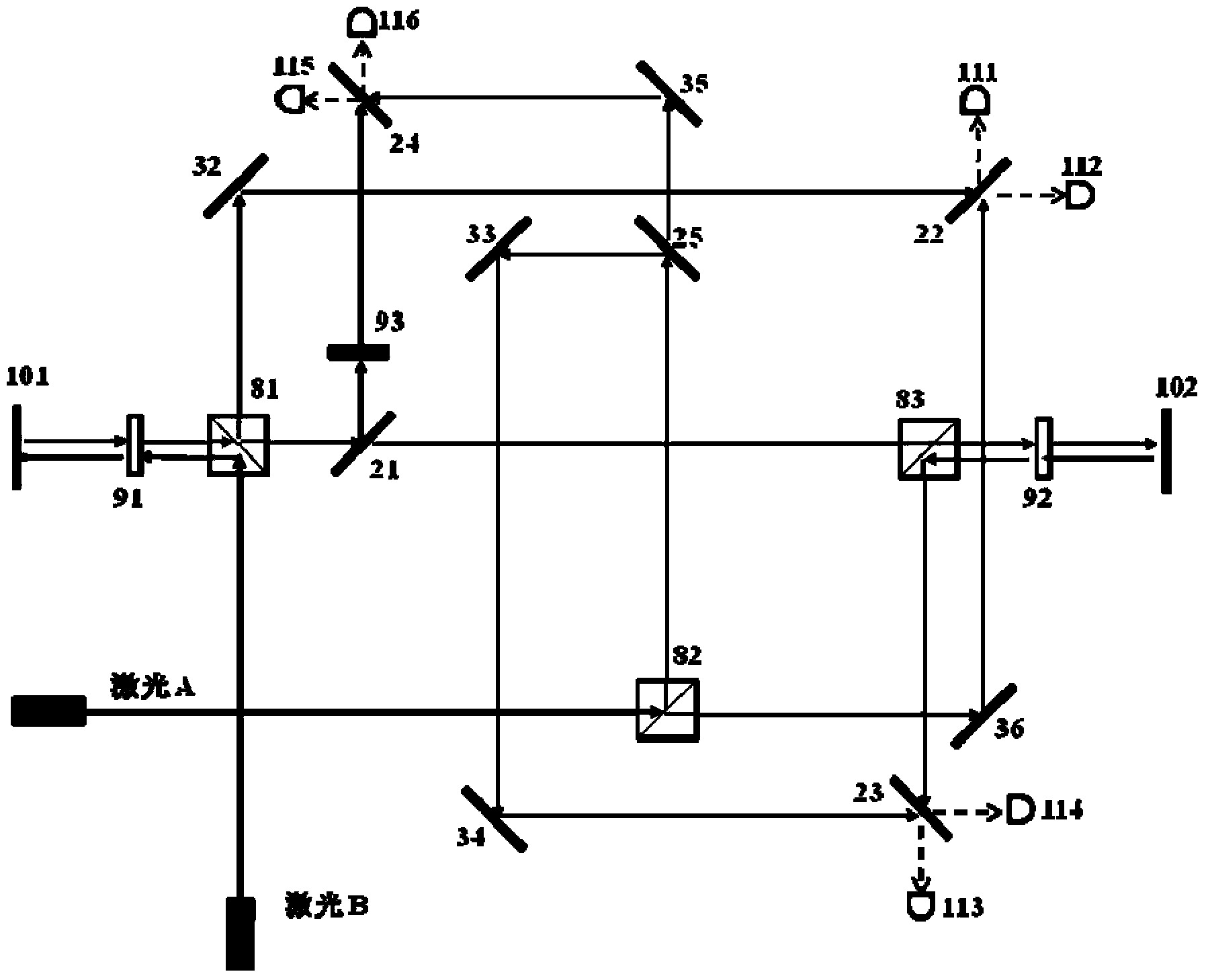
The invention provides a high-precision double star laser interference dynamic distance measuring ground simulation device which at least comprises a vibration-isolation system, a vacuum system, a light source system, an interferometer, a first horizontal moving system, a second horizontal moving system, a phase detection system and a data analyzing system. The vibration-isolation system is used for isolating and filtering outside vibration noise and reducing the vibration noise of a system. The vacuum system is used for reducing thermal noise brought by temperature fluctuation of the system. The light source system is used for providing two laser beams which are high in stability and high in frequency stabilization. The interferometer is used for generating three paths of heterodyning interference signals which have the identical arm length and simulating satellite orbit dissociating motion information and scientific signal information caused by gravitational waves or a gravitational field or the like. The first horizontal moving system is used for simulating scientific signals caused by gravitational waves or a gravitational field or the like. The second horizontal moving system is used for simulating satellite orbit dissociating signals. The phase detection system is used for carrying out phase detection on interference signals, collecting phase information and carrying out inversion displacement. The data analyzing system is used for estimating dynamic distance measuring precision of an interfering system and extracting scientific signals from mixed signals. The high-precision double star laser interference dynamic distance measuring ground simulation device can achieve ground simulation of high-precision double star laser interference dynamic distance measuring.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Micro-Newton-scale ion propulsion device achieving vortex resonant ionization
ActiveCN110230581AExpand the adjustment rangeImprove working fluid utilizationMachines/enginesUsing plasmaEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention discloses a micro-Newton-scale ion propulsion device achieving vortex resonant ionization, and belongs to the field of plasma propulsion. The device solves the problem that an existing micro-Newton-scale thruster cannot meet high-pressure thrust control, wide-range continuous thrust adjustment, ultrahigh thrust resolution ratio and long-service-life on-orbit working required in a gravitational wave detecting task. A quartz protection plate is fixedly arranged in a discharge cavity, a plurality of first through holes and a plurality of second through holes are formed in a bottom plate, and a plurality of incense-coil-shaped antennae are arranged on the end face, close to the quartz protection plate, of the bottom plate. The end, located in the center, of each incense-coil-shaped antenna penetrates through the corresponding first through hole to guide out a high-voltage pole and is connected with an output pole of a radio frequency power source, and the end, located on theperiphery, of each incense-coil-shaped antenna penetrates through the corresponding second through hole to guide out a grounded pole and is connected with the output pole of the radio frequency powersource. A screen grid is connected with positive high voltage, and an acceleration grid is connected with low negative voltage, and air inlet holes are formed in an annular side wall between the quartz protection plate and the screen grid.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Single-frequency fiber laser device with wide single-longitudinal-mode temperature range
InactiveCN107946883AShorten the effective lengthReflectivity Optimization and ImprovementActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionGratingOptical communication
The invention discloses a single-frequency fiber laser device with a wide single-longitudinal-mode temperature range. The laser device is composed of a broadband fiber grating, a highly-doped gain fiber, a narrowband fiber grating, a wavelength division multiplexer, a single-mode semiconductor pump laser device and an optical isolator. The single-mode semiconductor pump laser device is used as a pump source to carry out pumping on a resonant cavity; with the fiber grating with the short grating zone length, the reflectivity of the narrowband fiber grating is optimized and improved; and with the ultra-short highly-doped gain fiber as a grain medium, the effective cavity length of the whole resonant cavity is shortened effectively from many aspects and the space between adjacent longitudinalmodes inside the cavity is increased substantially, so that the laser device is able to realize a stable single-frequency laser output within a wide temperature range. The laser device has the wide single-longitudinal-mode temperature range and is protected from being affected by the external environmental temperature in operation; and the stable single longitudinal mode output is realized. The laser device can be applied to fields of space detection, coherent optical communication, Doppler wind-finding radar, gravitational wave detection, and quantum optics and the like.
Owner:横琴东辉科技有限公司
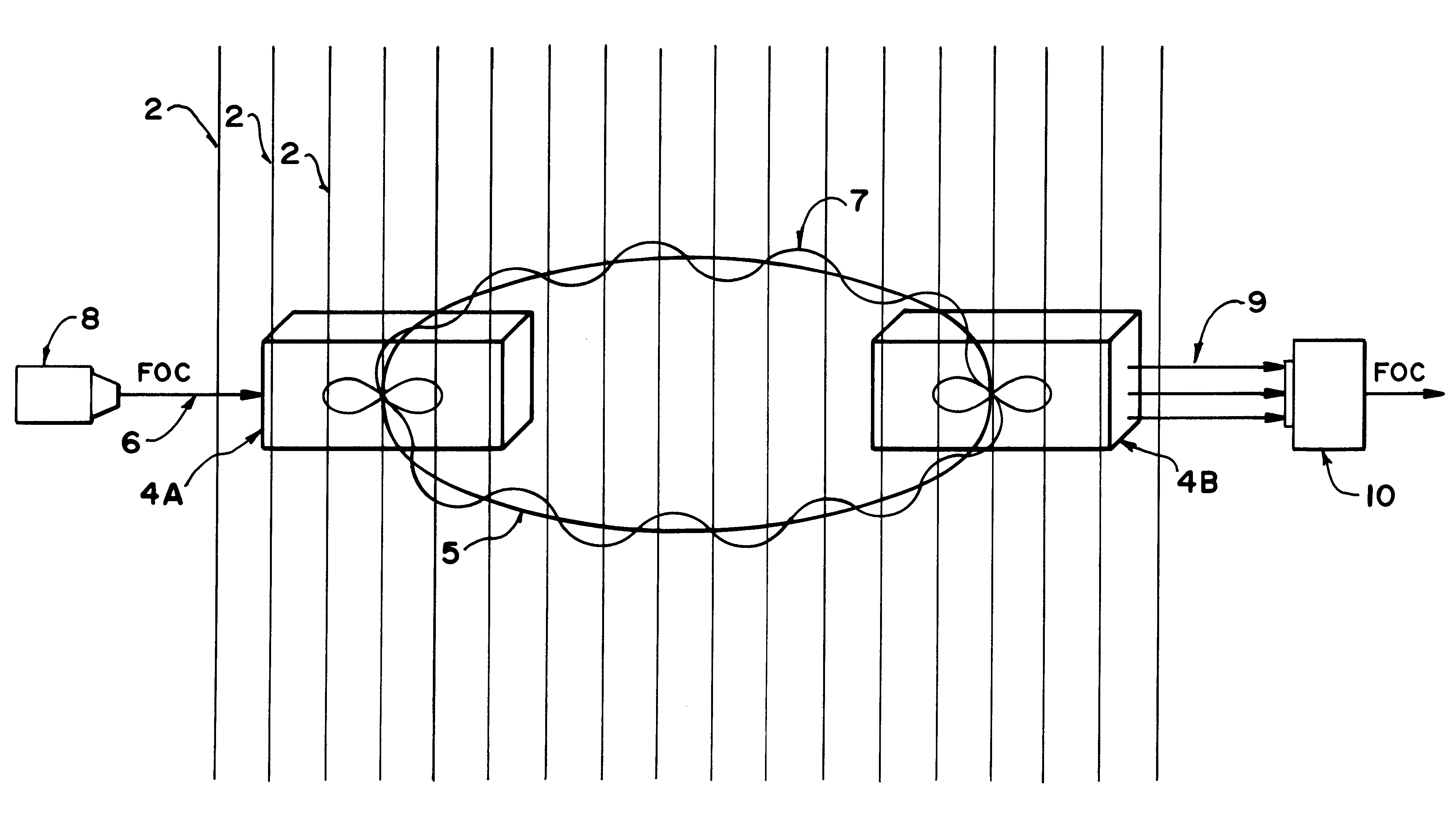
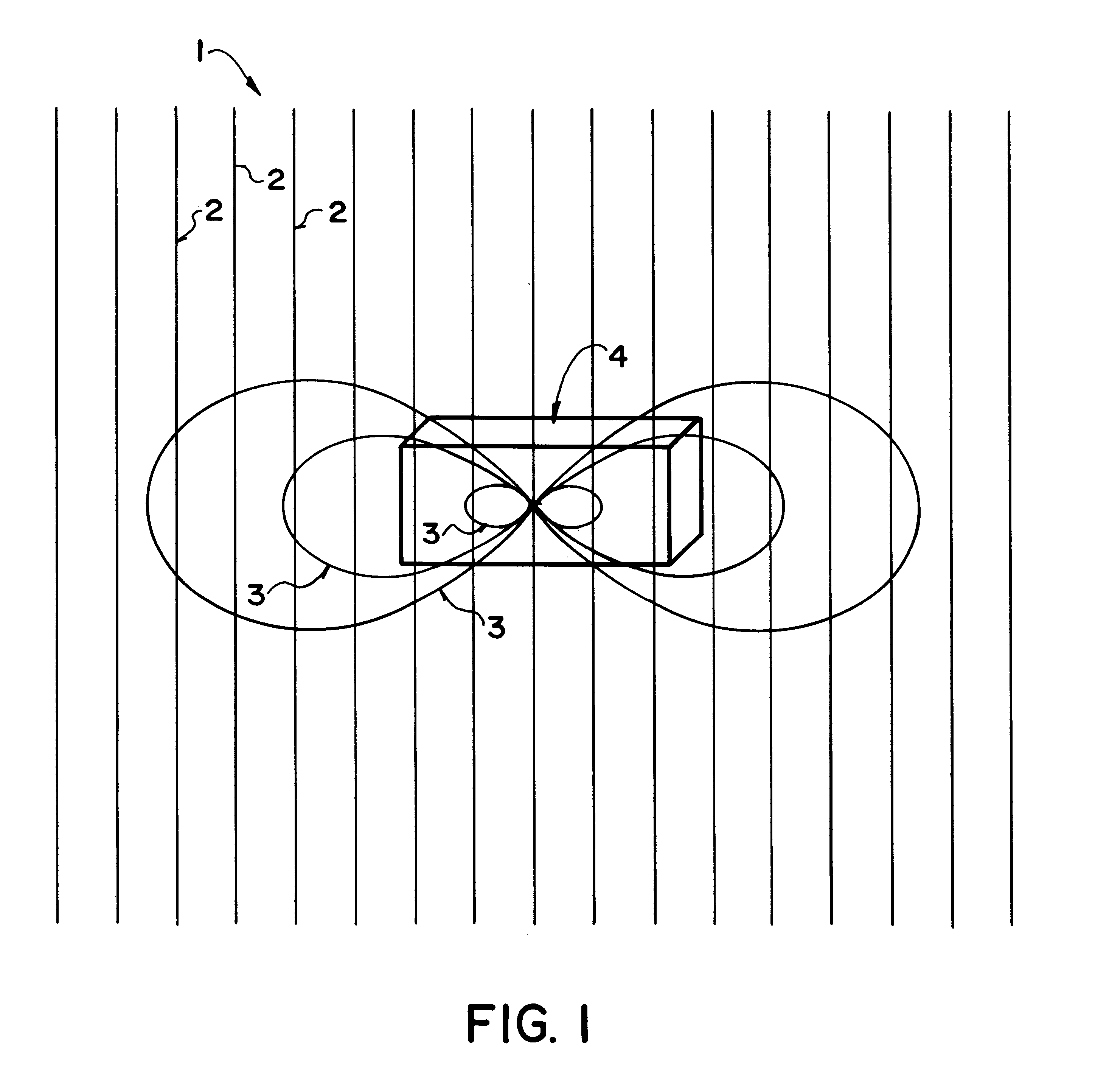
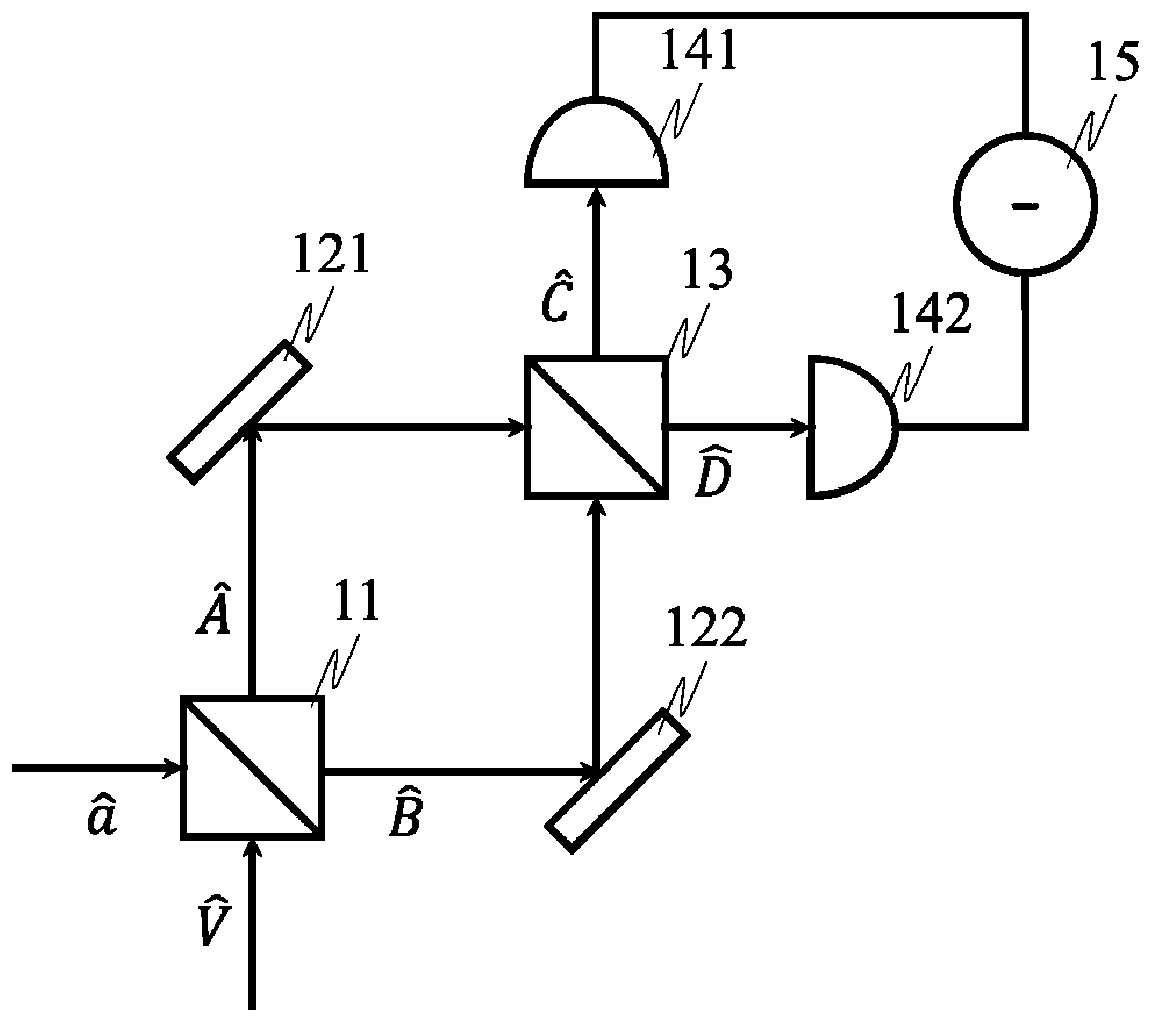
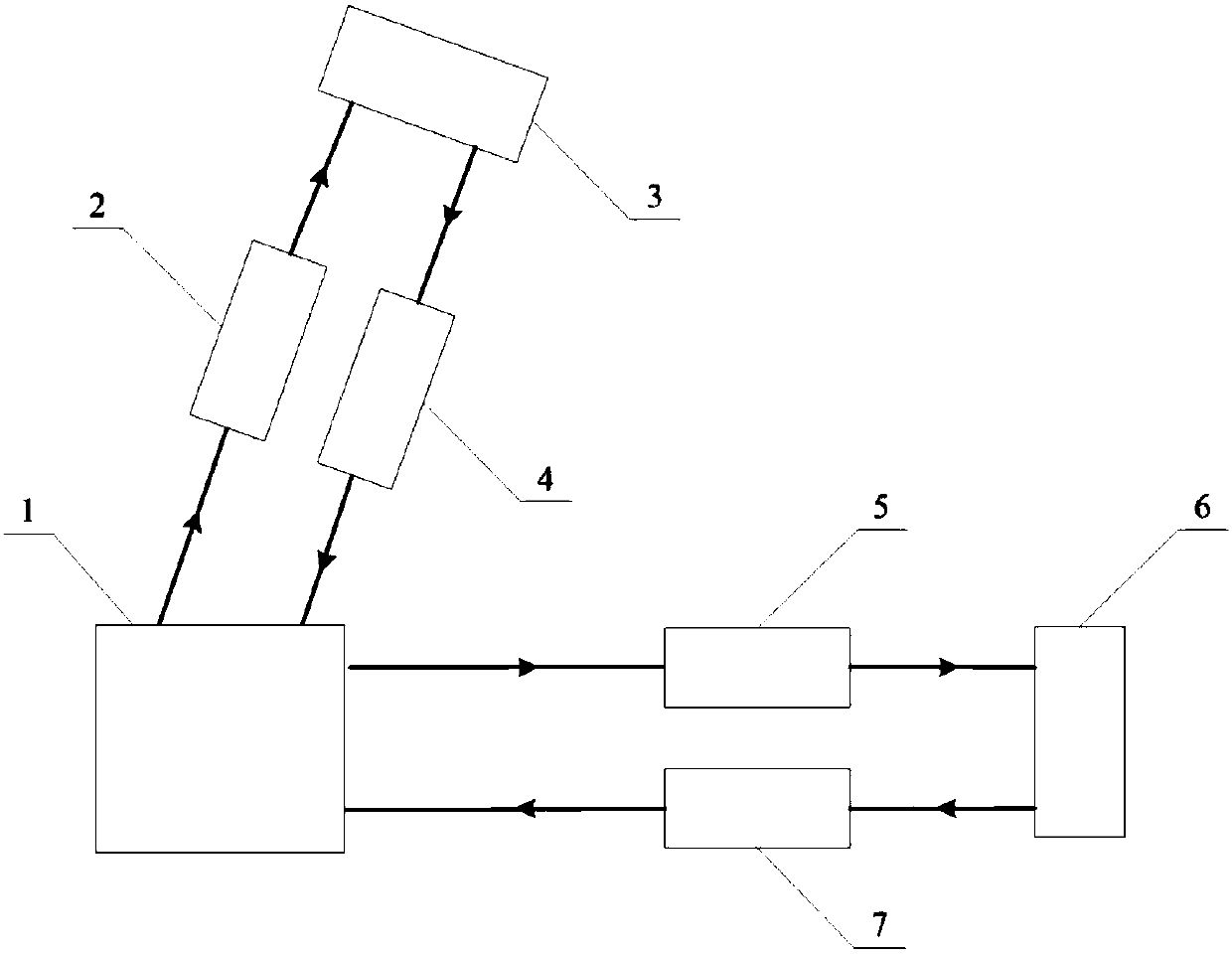
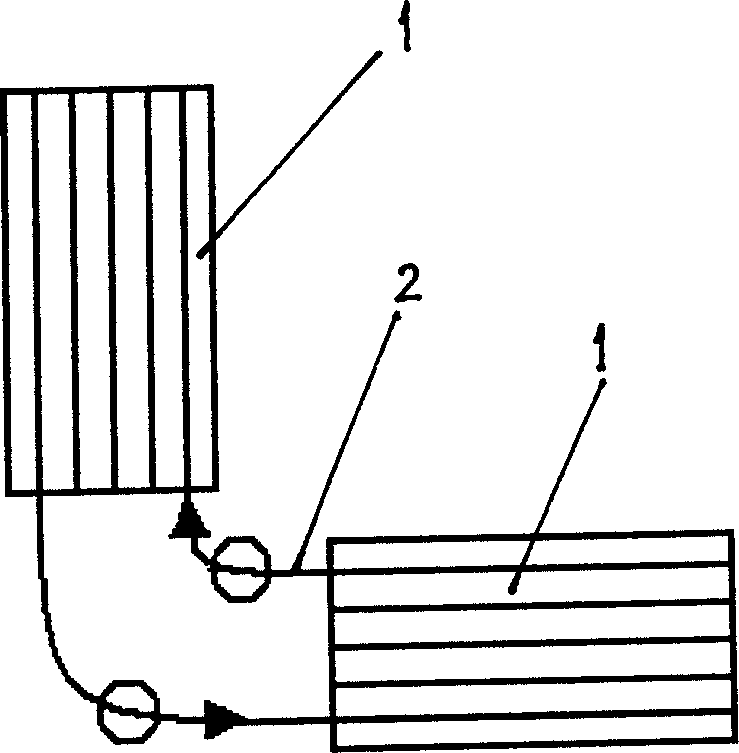
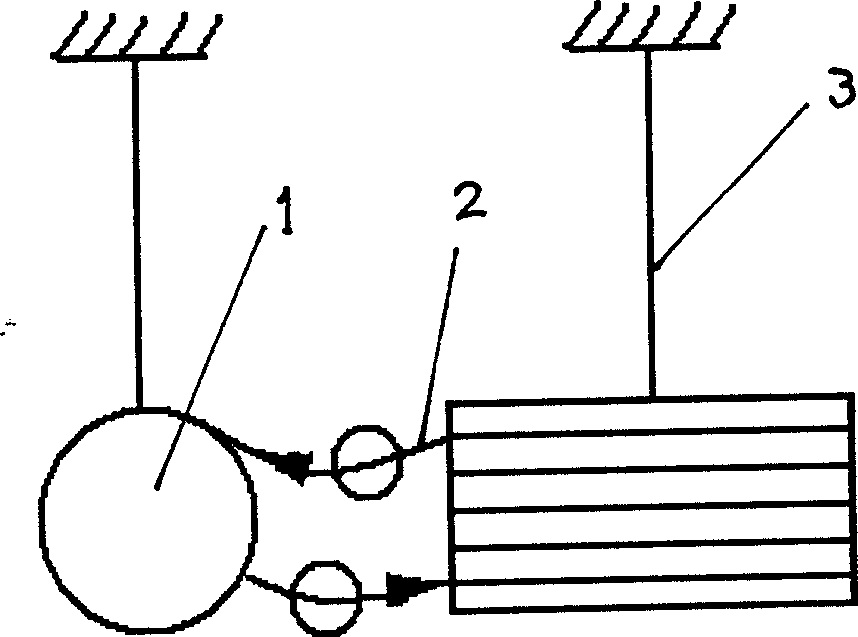
Gravitational wave detecting device
ActiveCN1558255AEnhanced ability to detect gravitational wavesIncrease the optical pathGravitational wave measurementFiberClassical mechanics
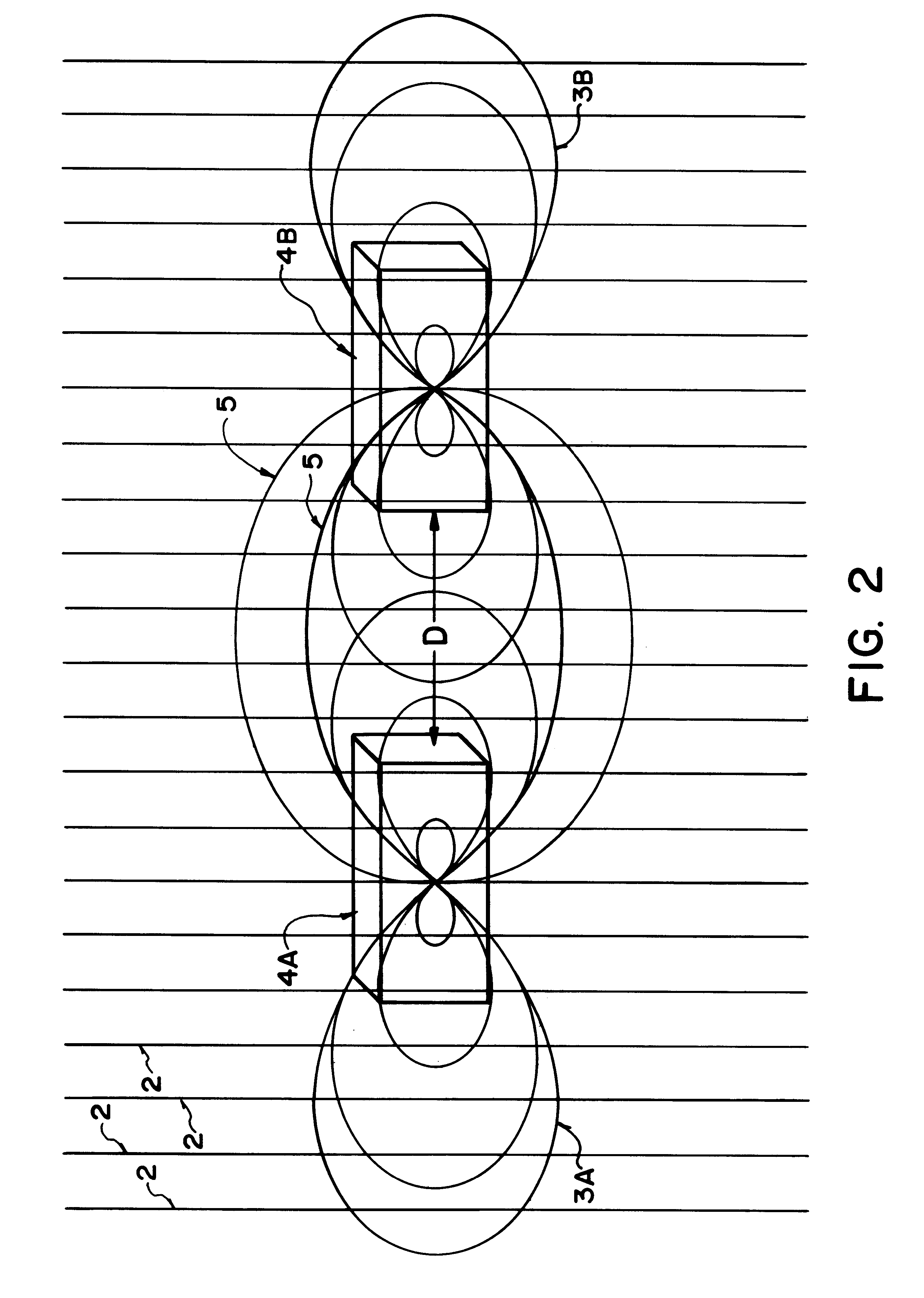
The present invention is gravitational wave detector, and belongs to the field of optical measurement technology. The gravitational wave signal is amplified by means of resonant effect and prolonging optical path, to raise the gravitational wave detecting sensitivity. The present invention has two independent resonant rods suspended with string horizontally with the axial lines perpendicular to each other; two optical fibers, each of which is folded into 1,000-1,000,000 sections and axially wound around or set inside the resonant rod, with the optical fibers on two resonant rods being connected via optical devices to constitute one closed loop. The resonant rods with the optical fibers serve as the resonant mass to amplify the gravitational wave signal by Q times by means of the resonant effect; and the folded fiber increases the optical path greatly to strengthen the gravitational wave detecting capacity, resulting in greatly raised detection sensitivity.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
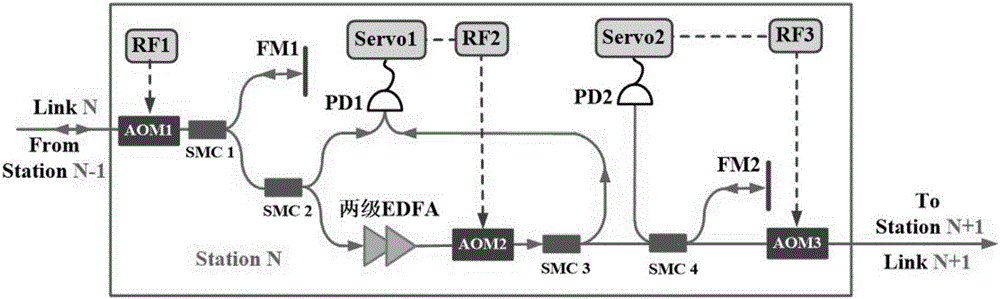
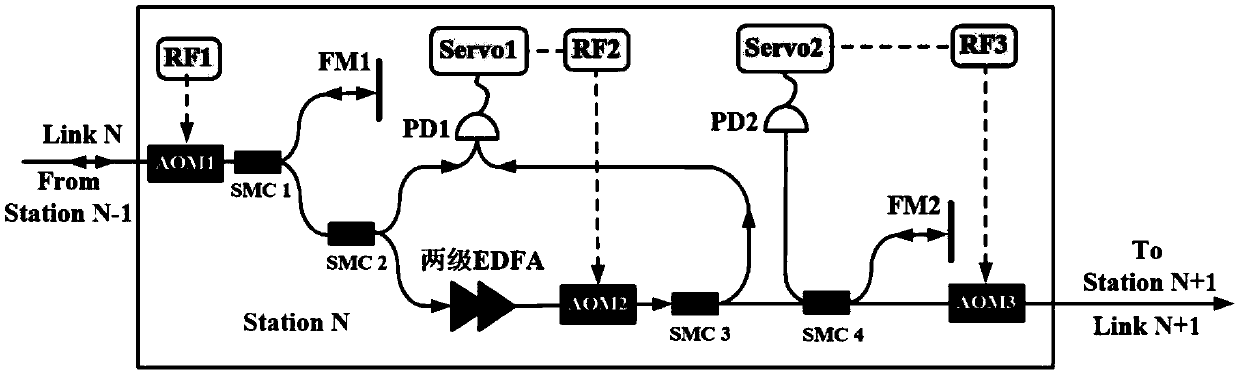
Relay method in optical fiber optical frequency link and relay station for implementing the method
ActiveCN106788750ASolve the problem of controlling bandwidthSuppress noiseElectromagnetic transmissionPhase noiseOptical clock
The invention discloses a relay method in an optical fiber optical frequency link and a relay station for implementing the method. The method comprises the following steps: using the signal of a previous level optical fiber link as seed light to receive and amplify a part of the seed light and send the seed light to the next level optical fiber link; and the other part of the seed light is reflected to return to the previous level link along the original route, a part of return light of the next level optical fiber link is received to serve as beat frequency to inhibit the noise so as to inhibit the import phase noise in an amplification process. By adoption of the relay method disclosed by the invention, the problem of controlling the width of a band in a phase noise inhibition process can be well solved, and the relay method has the advantages of adaptability to complex links, simple structure, low cost, and so on. The relay station of the optical fiber optical frequency link designed in the invention can be applied to optical atom clock comparison, ultra high precision optical clock signal transmission, optical fiber time frequency system networking, gravitational wave detection and other high-tech fields.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Communication system using gravitational waves
InactiveUS6300614B1Radiation/particle handlingMaterial analysis by optical meansCommunications systemGravitational wave
A method and apparatus for communication using gravitational waves is disclosed. The system utilizes a resonant frequency set up between identical masses to transmit information. The communication system uses two pieces of superconducting material, identical in size, mass and shape; means to modify the density of the first piece of superconducting material at a variable frequency; and detection means for sensing the effect of gravitational wave pulses on said second piece of superconducting material.
Owner:PETLAN JIRI JOSEPH
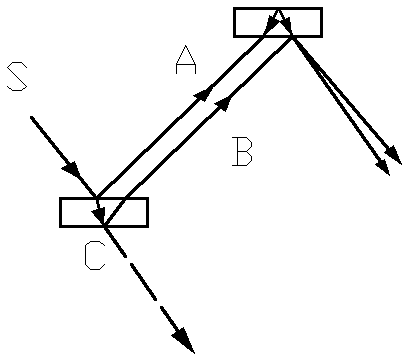
Optical interference measuring device and its method
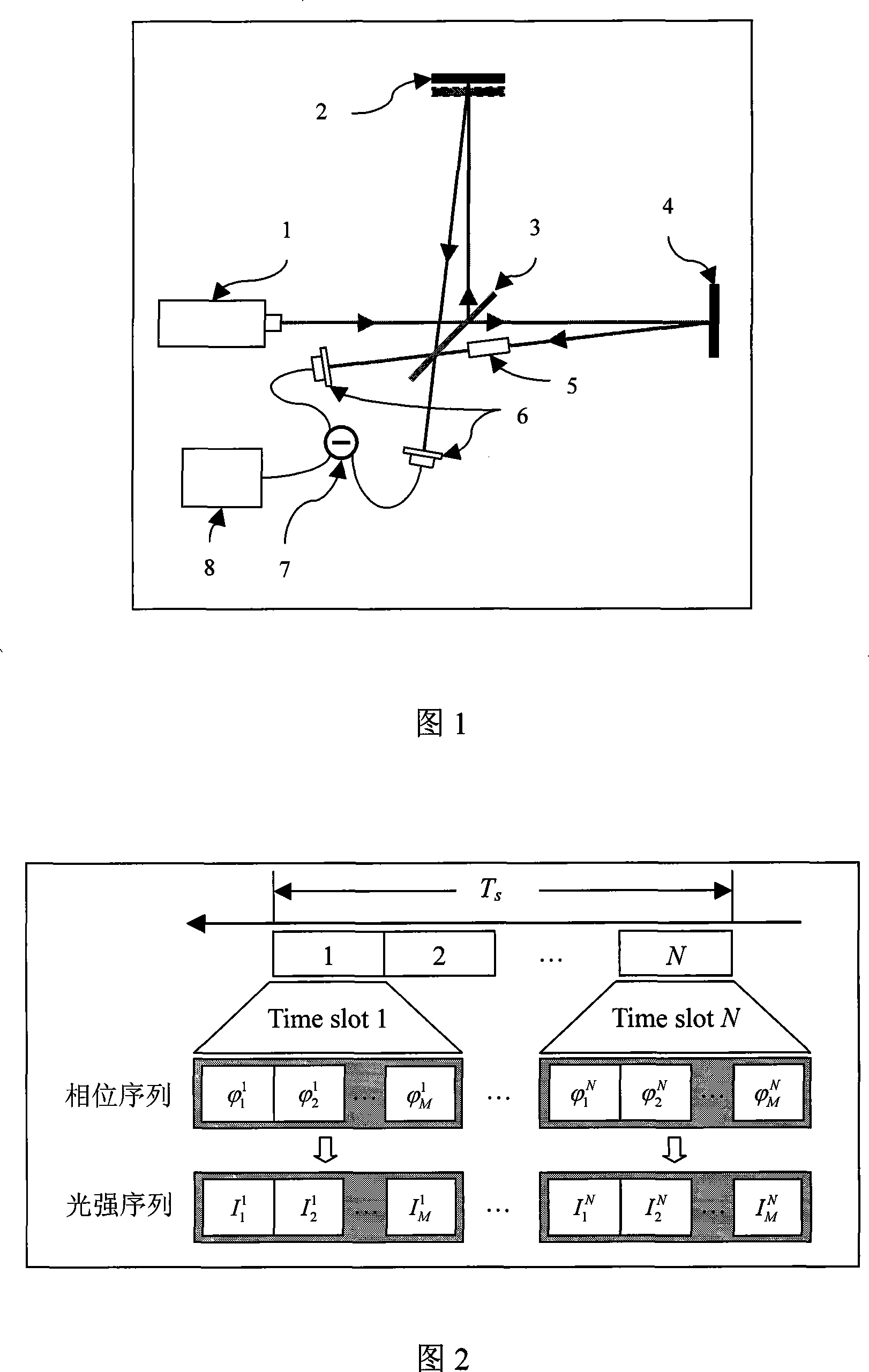
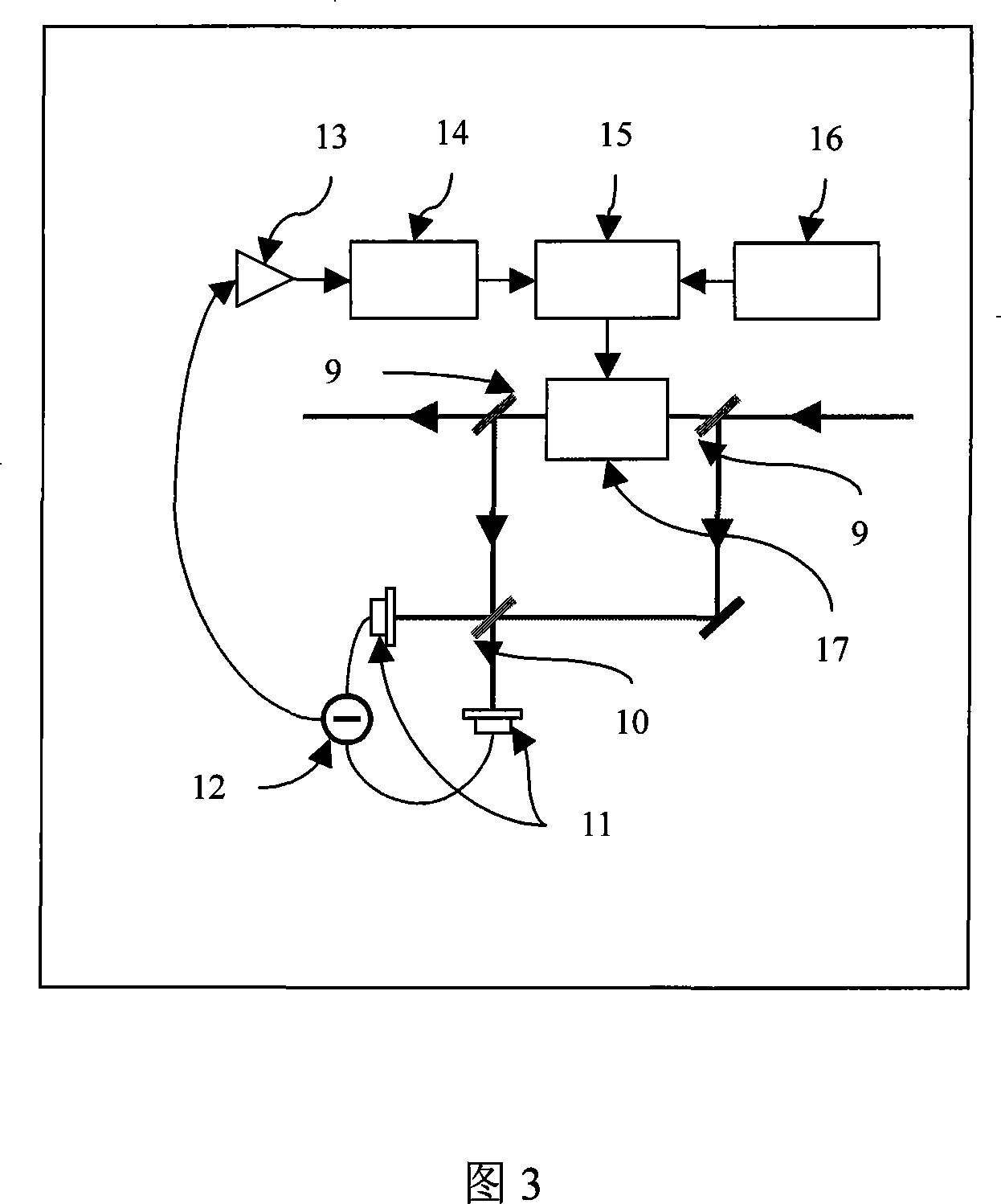
The present invention discloses an optical interference measuring device and the method. The coherent light beam produced by the laser is separated into two coherent light beams by the first transflective beam splitter, wherein a coherent light beam generates a phase change by the moving of the first reflecting mirror, the other coherent light beam enters into the phase modulation component through the reflecting mirror, then the transflective beam splitter passed by the two coherent light beam outputs two interference light beams, the two interference light beam changes to electrical signal by the detection of the detector, the electrical signal realizes the measuring of the phase change by the first difference equipment and relevant instruments. The invention realizes the elevation of the phase sensitivity of the interference measuring using the special-designed pseudorandom phase sequence. It only requires an ordinary coherent light source and the linear optical element, and it has important application foreground in the fields of gravitational wave detection, micro-nanometer displacement measurement, optical fiber gyroscope and optical fiber sonar detection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
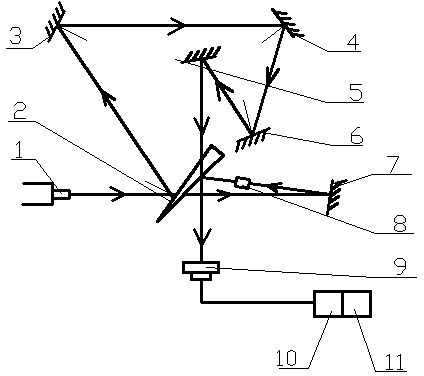
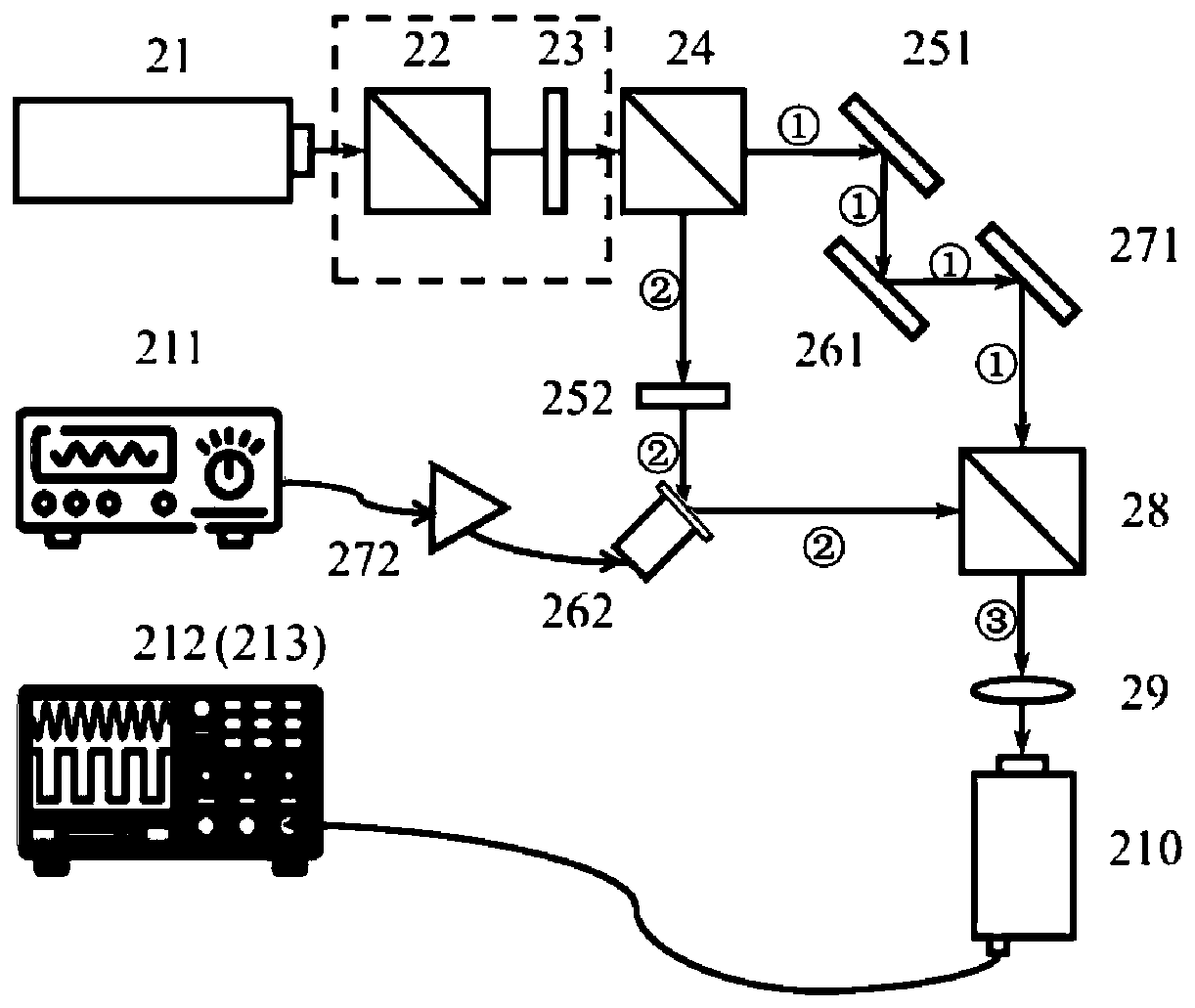
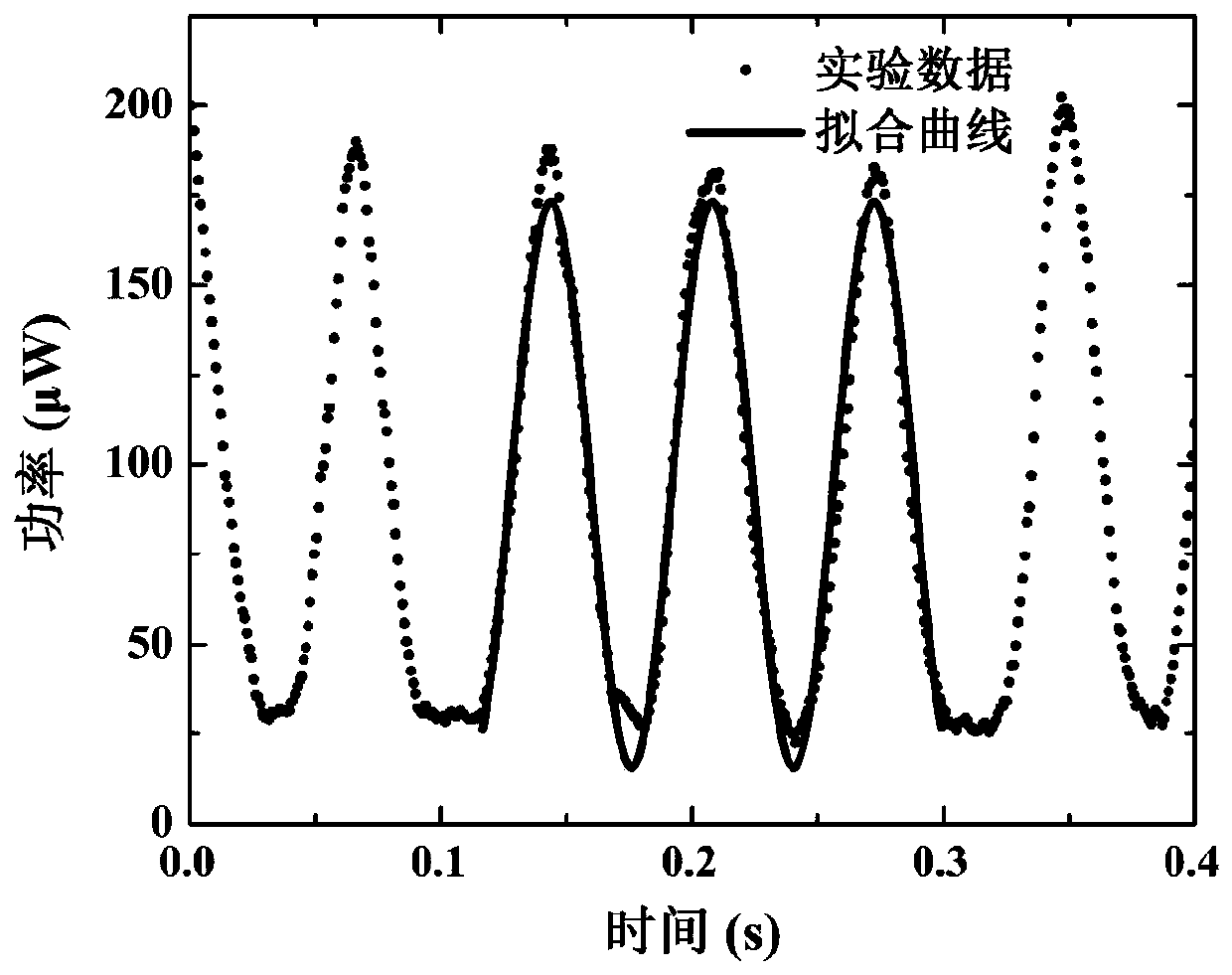
Gravitational wave experiment device
The invention provides a gravitational wave experiment device. The gravitational wave experiment device comprises a laser device and a sound wave source, wherein a light splitting mirror is arranged at a laser emitting end of the laser device; a first reflection mirror is arranged at an outgoing end of a first light beam of the light splitting mirror; a second reflection mirror is arranged at an outgoing end of a second light beam of the light splitting mirror; a first arm is formed between the first reflection mirror and the light splitting mirror; a second arm is formed between the second reflection mirror and the light splitting mirror; a detector capable of obtaining a detection signal is arranged at one side of the light splitting mirror; the detector and the second reflection mirror are arranged at two sides of the light splitting mirror; the sound wave source is arranged in a plane formed between the first reflection mirror and the second reflection mirror of the light splitting mirror; the sound wave source is used for sending sound waves for stimulating gravitational waves to cause length changes of the first arm and the second arm; the detector is used for further detecting light signals caused by the length changes of the first arm and the second arm. According to the experiment device provided by the invention, a gravitational wave transmission manner and a detection principle are demonstrated through the experiment device, and are more visual and clear.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Sunlight-based high-efficiency pumping single-frequency fiber laser
PendingCN110544866AOptimizing Optical ParametersImprove absorption efficiencyActive medium shape and constructionOptical devices for laserSeeds sourceOptical isolator
The invention discloses a sunlight-based high-efficiency pumping single-frequency fiber laser, which includes: a single-frequency laser seed source, a signal pumping combiner, a multimode fiber panel,a sunlight focusing lens, a high-gain fiber, an optical filter module, and an optical isolator. The laser, based on a seed source main oscillation power amplification and multimode cladding pumping scheme, firstly, by designing and optimizing the optical parameters of the high-gain fiber, provides the high-gain fiber with good absorption and energy conversion efficiency for sunlight; secondly, uses the sunlight focusing lens to focus the sunlight as a pumping source, uses the multimode fiber panel to efficiently couple the concentrated sunlight into the multimode fiber, and amplifies the power of the single-frequency signal light by the high-gain fiber, thereby achieving single-frequency fiber laser output based on sunlight high-efficiency pumping. The single-frequency fiber laser directly uses sunlight as a pumping source, and can be used in the fields of space-based gravitational wave detection, laser weapons, space lidar and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
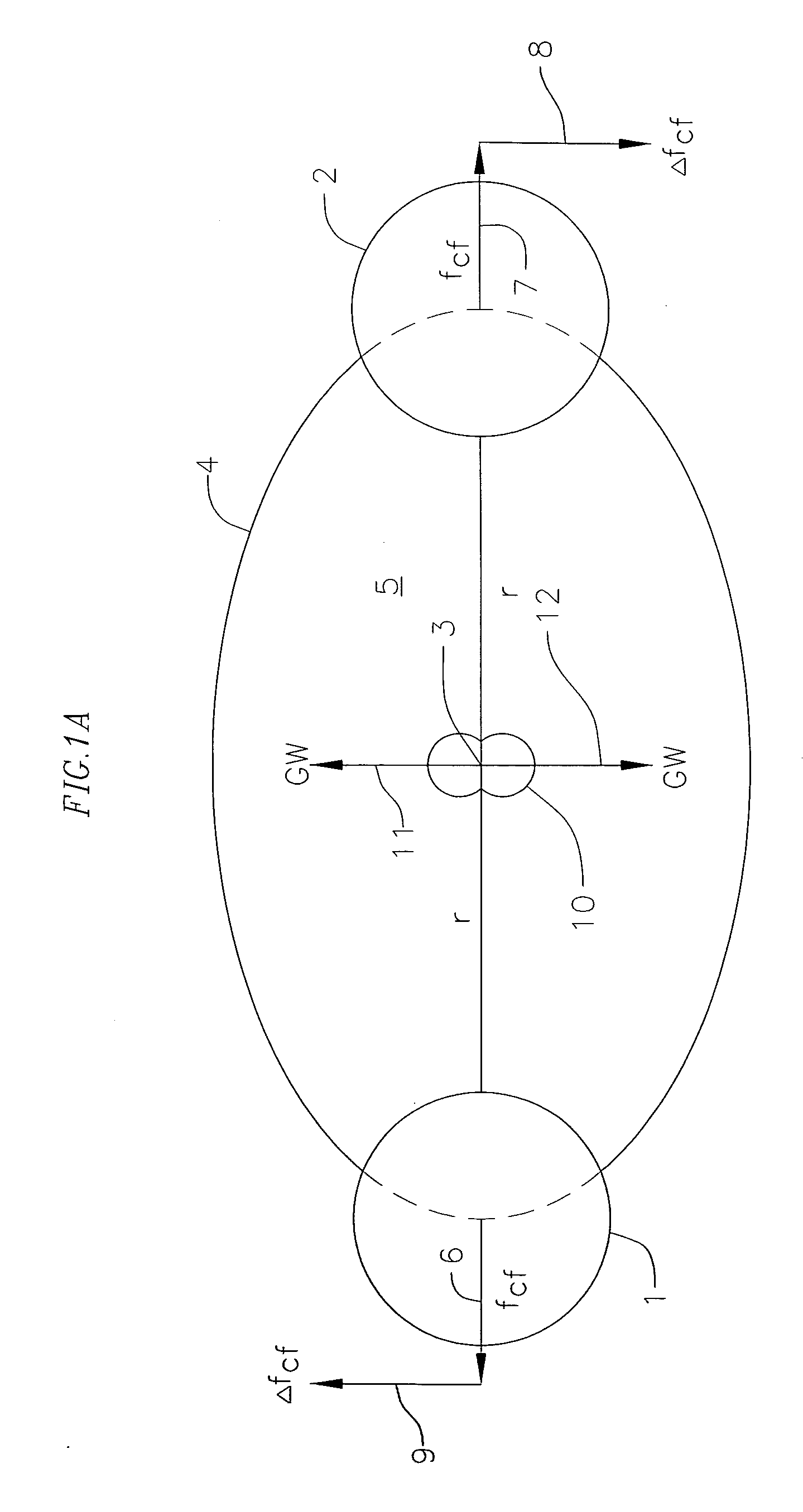
Gravitational wave propulsion
A gravitational wave generating device comprising an energizing means such as magnetrons, which act upon energizable elements such as film bulk acoustic resonators or FBARs. A computer that controls the magnetrons' phase. A gravitational wave generation device that exhibits directivity and forms a gravitational-wave beam. The utilization of a medium in which the gravitational wave speed is reduced in order to effect refraction of the gravitational wave and be a gravitational wave lens. A gravitational wave generator device that can be directed in order to propel an object by its momentum or by changing the gravitational field nearby the object to urge it in a preferred direction and be a propulsion means.
Owner:GRAVWAVE
Full body teleportation system
InactiveUS20060071122A1Constant gainCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsWhole bodyGravitational wave
A pulsed gravitational wave wormhole generator system that teleports a human being through hyperspace from one location to another.
Owner:HECHT ROJAS LUIS A
Micromovement measuring device and method of movement process conversion to an electric signal
InactiveUS6935200B2High sensitivityEliminate processingMagnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansField emission currentElectric signal
A micromovement measuring device records creeping and dynamic infraprocesses both of natural and artificial origin, including seismic processes or infrasound and gravitational waves. The device has a sensitivity for measuring in a wide dynamic range. The device includes a measuring element, a sensitive element, a membrane, a signal conditioner, a fixing electromagnet, and a pulling electromagnet. The pulling electromagnet is located on the membrane which increases the range of the measurable movements. A hermetic housing prevents the formation of oxides or similar films at the working surfaces of the measuring and sensitive elements. A method of converting movement to electric signals is performed by the device, which takes an electronic field emission current to be a characteristic of quantization, and so movements in the range of Angstroms may be recorded.
Owner:A METRICS
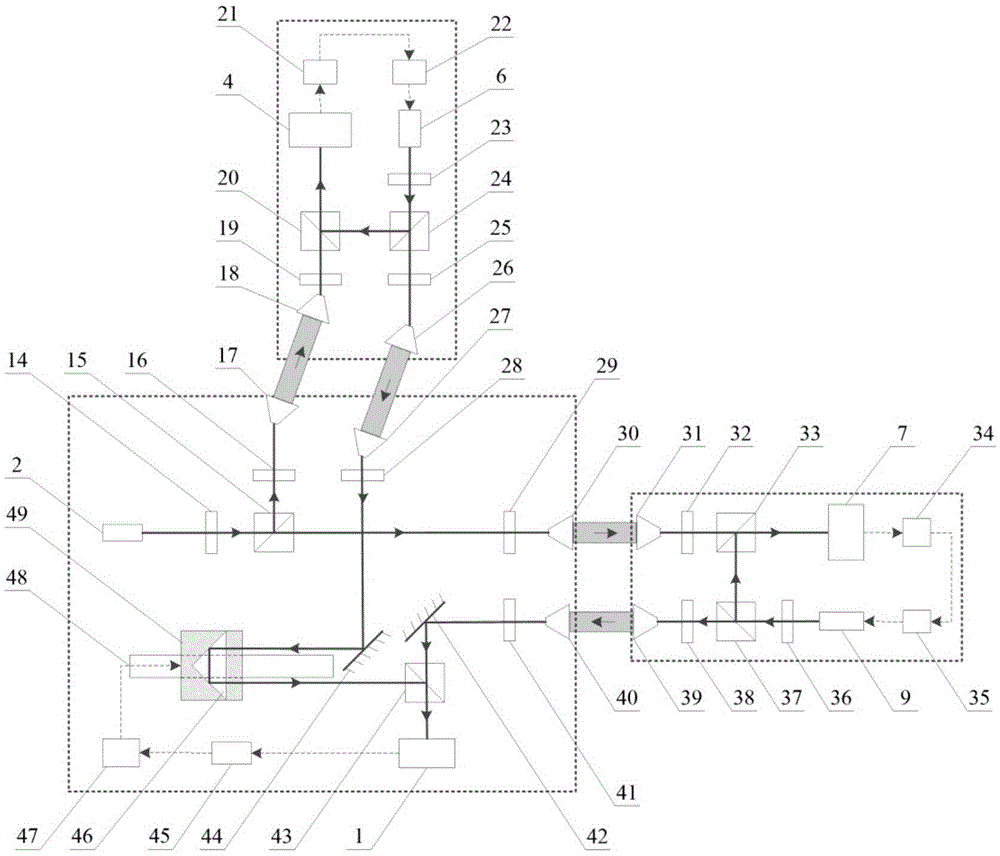
Relay type femtosecond pulse high-precision displacement detection device
ActiveCN105738960ARealize ultra-long-distance dynamic displacement detectionAvoid real-time communicationUsing optical meansGravitational wave measurementLight echoReal-time communication
A relay type femtosecond pulse high-precision displacement detection device belongs to the gravitational wave detection field, and comprises a measurement terminal, a No.1 femtosecond phase lock relay, a No.2 femtosecond phase lock relay and a No.3 femtosecond phase lock relay. The relay type femtosecond pulse high-precision displacement detection device of the present invention adopts a pulse time domain lock type relay measurement structure, amplifies the light power of the measured light by the cascade of the three femtosecond phase lock relays, and transforms the system light echo power from a biquadrate attenuation function of a measured distance into a square attenuation function, realizes the ultra long distance dynamic displacement detection of an outer solar system scale, and realizes the displacement detection of the sub-nanometer sensitivity by the light delay line scanning. The measurement terminal and the three femtosecond phase lock relays are relatively independent, so that the real-time communication and high-precision clock synchronization problem among the far apart satellites is avoided.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Micromovement measuring device and method of movement process conversion to an electric signal
InactiveUS20050274209A1High sensitivityEliminate the electroerosive processes at working surfacesStructural/machines measurementUsing electrical meansMeasurement deviceField emission current
A micromovement measuring device records creeping and dynamic infraprocesses both of natural and artificial origin, including seismic processes or infrasound and gravitational waves. The device has a sensitivity for measuring in a wide dynamic range. The device includes a measuring element, a sensitive element, a membrane, a signal conditioner, a fixing electromagnet, and a pulling electromagnet. The pulling electromagnet is located on the membrane which increases the range of the measurable movements. A hermetic housing prevents the formation of oxides or similar films at the working surfaces of the measuring and sensitive elements. A method of converting movement to electric signals is performed by the device, which takes an electronic field emission current to be a characteristic of quantization, and so movements in the range of Angstroms may be recorded.
Owner:A METRICS
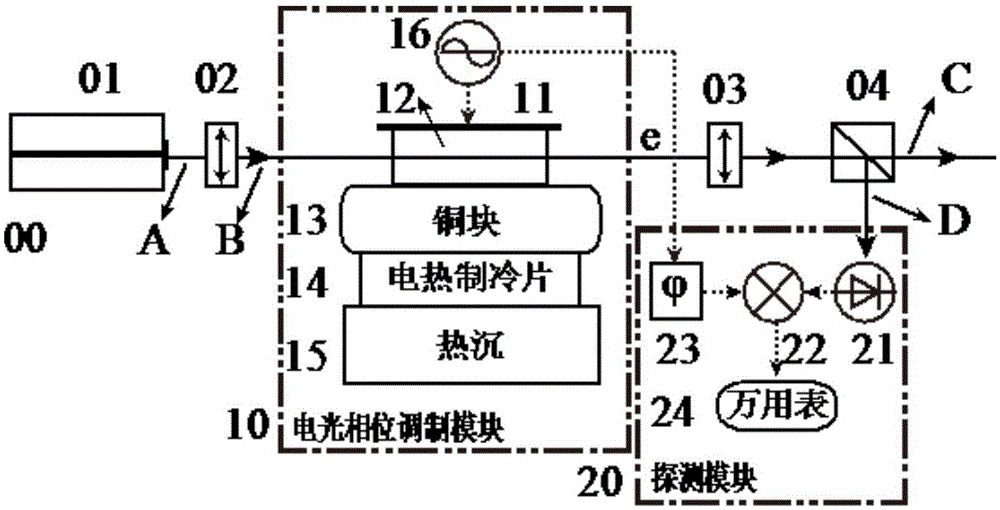
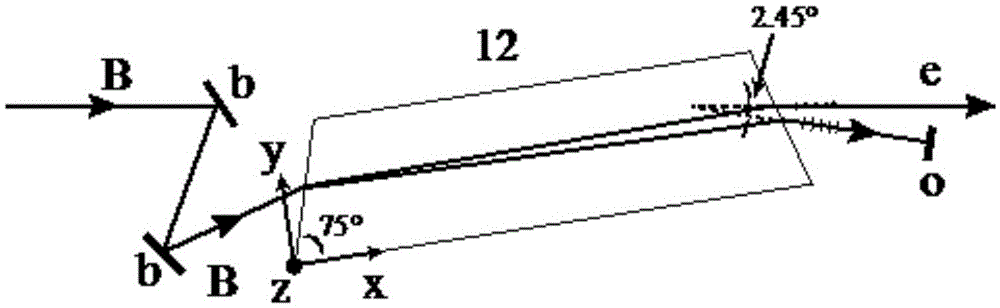
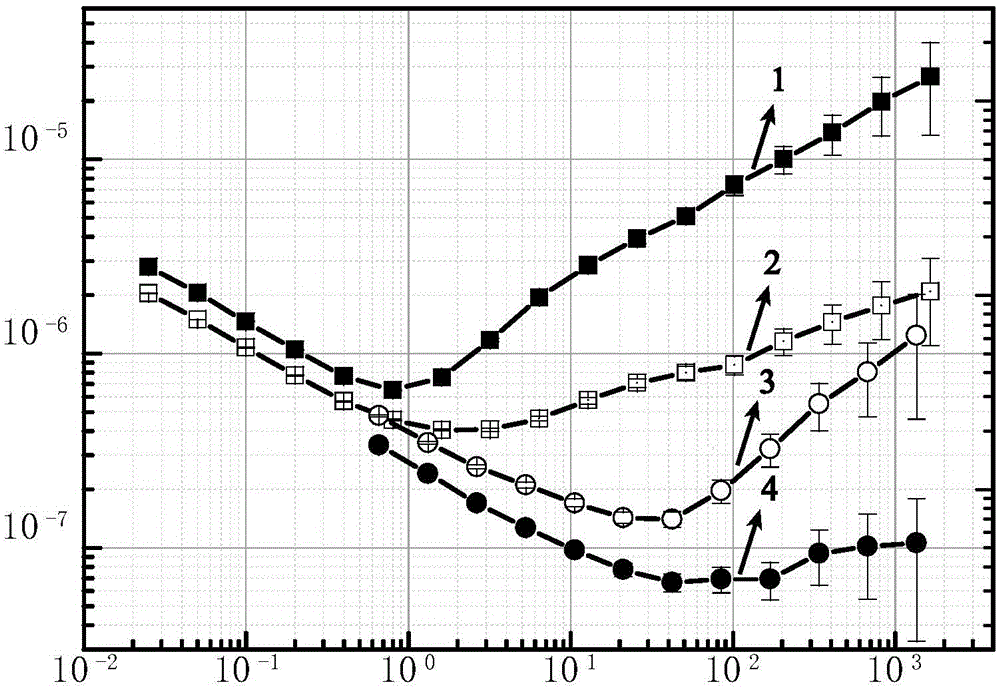
Residual amplitude modulation stabilization device based on wedge angle electro-optic crystal
ActiveCN105576495ASimple structureImprove stabilityLaser detailsNon-linear opticsCopper foilPolarizer
The invention discloses a residual amplitude modulation stabilization device based on a wedge angle electro-optic crystal, and relates to the technical field of laser frequency stabilization. According to the device, an optical path part is formed by a laser device, a polarizer, the electro-optic crystal, a polarization analyzer and a polarization splitting prism which are arranged in turn; an electro-optic phase modulation part is formed by a signal source, a copper foil, the electro-optic crystal, a copper block, a thermoelectric refrigeration piece and a heat sink which are connected in turn; the signal source, a phase shifter and the local end of a frequency mixer are connected in turn so as to acquire local oscillation signals required by demodulation; vertically polarized light of the polarization splitting prism, a photoelectric detector and the radio frequency end of the frequency mixer are connected in turn so as to acquire radio frequency signals; and the intermediate frequency end of the frequency mixer is connected with a digital universal meter so as to acquire residual amplitude modulation signals, wherein the electro-optic crystal is a lithium niobate crystal with a wedge angle, and an inclined angle of 75 degrees is formed between the light-transmitting surface and the optical axis direction. The device is simple in structure, high in stability and easy to realize and can be applied to the field of precision measurement of high-stability laser, laser interference, gravitational wave observation, laser spectroscopy and optical frequency standards.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Bidirectional femtosecond pulse-based deep space gravitational wave detection method and device
ActiveCN105572685ARealize ultra-long-distance deep space explorationRealize differential detectionOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationLight echoOptical delay line
The invention relates to a bidirectional femtosecond pulse-based deep space gravitational wave detection method and device and belongs to the gravitational wave detection field. According to the method, equal-arm length differential detection on gravitational wave signals is realized through scanning optical delay lines, and detection sensitivity can reach a sub nanometer level; and two measuring arms are both of a pulse time-domain lock type bidirectional measurement structure, so that light echo power of a system can be calculated according to a square attenuation function of the distance instead of an original biquadrate attenuation function of the distance, and therefore, detection of deep space gravitational waves at a scale of hundreds of millions of kilometers can be realized. The device comprises a measuring end at a master satellite, a No. 1 active reflector located at a slave satellite A and a No. 2 active reflector located at a slave satellite B. With the method and device adopted, problems in real-time communication and high-accuracy clock synchronization between satellites which are separated from each other by long distances can be solved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Optical interference measurement device design and method thereof based on TRIZ (Theory of the Solution of Inventive Problems)
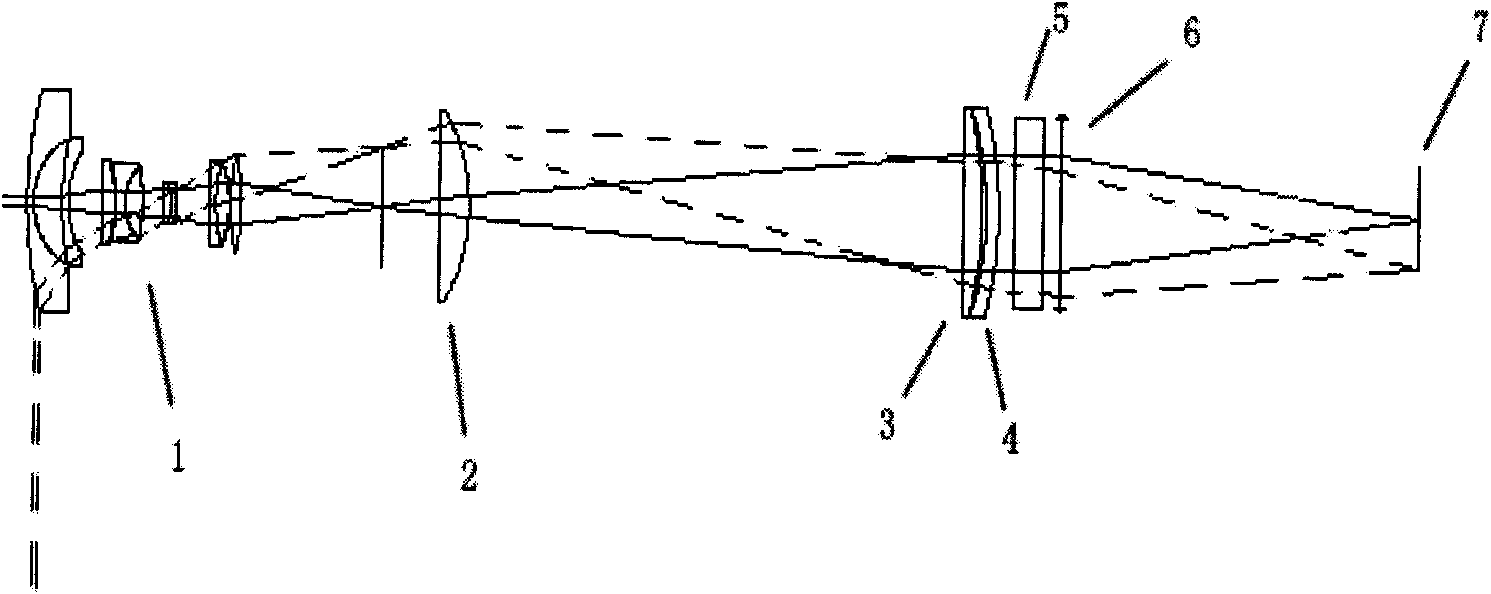
The invention discloses a precise optical interference measurement device and a technical improvement route. A TRIZ (Theory of the Solution of Inventive Problems) and an optical interference principle are utilized in a device design. A laser device of the device produces a coherent light beam to pass through wedge semi-transparent semi-reflecting glass to be divided into two coherent light beams; one coherent light beam passes through four reflecting mirrors to increase the effective length of an interference arm and improve the measurement accuracy; the other coherent light beam passes through a phase modulator to produce a phase difference; the phase modulator is associated with the physical quantity to be tested; the two coherent light beams pass through the wedge semi-transparent semi-reflecting glass to output two interference light beams; interference is caused by the two light beams which are gathered together due to the phase difference and output light intensity changes along with transformation of the phase difference; and accordingly a value of the phase difference can be obtained through measurement of the light intensity and then a value of the physical quantity to be tested can be obtained. The optical interference measurement device design and a method thereof based on the TRIZ have important application prospects in fields of gravitational wave detection, micro-nano displacement measurement, optical fiber gyros, optical fiber sonar detection and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
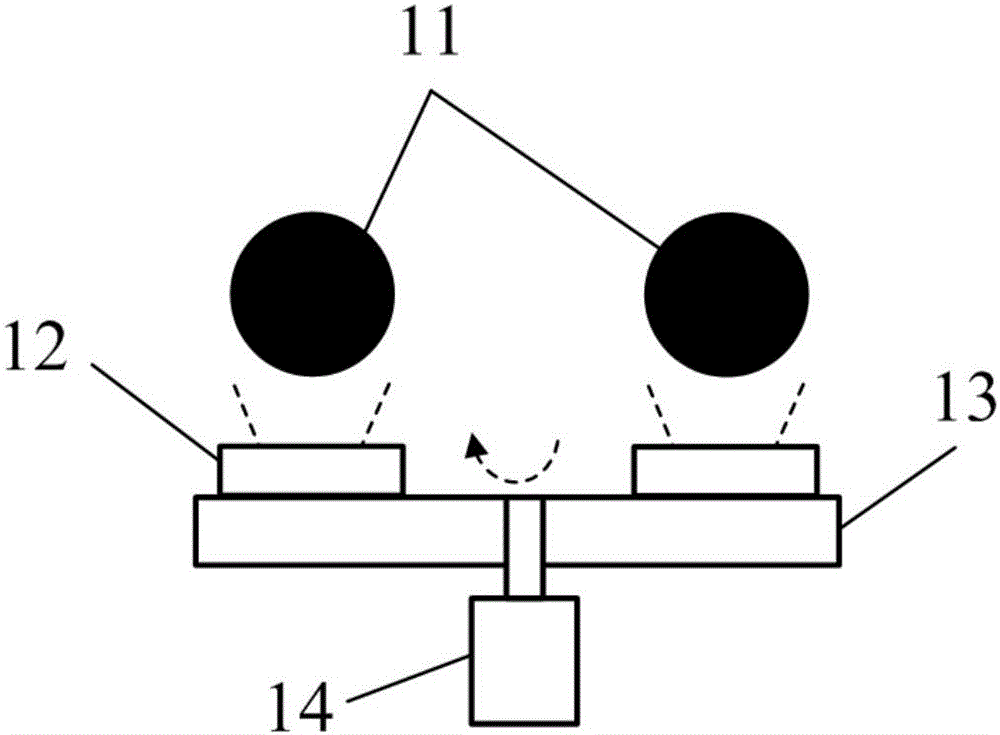
Celestial body running simulation device and method thereof
The invention provides a celestial body running simulation device and a method thereof. The celestial body running simulation device comprises a barrel-shaped body, an elastic film, an air blower, andat least two spheres. The elastic film covers the upper opening edge of the barrel-shaped body. The spheres are placed on the elastic film to simulate celestial bodies or dark matters. Air holes aredensely distributed in the elastic film. The air blower is communicated with the inner space of the barrel-shaped body through an air inlet pipe, and is used for blowing air into the barrel-shaped body to form positive pressure. Gas in the barrel-shaped body is discharged from the air holes to carry partial gravity of the spheres. According to the invention, the device has a simple structure, andcan be used for simulating celestial body running laws such as celestial body revolution, universal gravitation, dark matters, dark energy, cosmic expansion and gravitational waves, clearly displays obscure astronomical knowledge to students, well popularizes astronomical knowledge, and is convenient for general public to understand.
Owner:YANGZHONG INTELLIGENT ELECTRICAL INST NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV
Small quantum interferometer for simulating gravitational waves by using piezoelectric ceramic
The invention discloses a small quantum interferometer for simulating gravitational waves by using a piezoelectric ceramic. A helium-neon laser is used as a laser light source, an interferometer system comprises a 50:50 beam splitter, a mirror, a continuously adjustable attenuator; a gravitational wave simulation system comprises the piezoelectric ceramic with the mirror, a piezoelectric ceramic driving power supply, a signal generator and a high voltage amplifier; a detection system comprises a focusing lens, a silicon-based photodetector, an oscilloscope and a spectrum analyzer. An electricsignal generated by the signal generator is amplified by the high voltage amplifier and input into the piezoelectric ceramic. The piezoelectric ceramic produces corresponding periodic expansion and contraction change, and the influence of the external small change such as the gravitational waves on optical path difference between two light-beams of the M-Z interferometer is simulated. The elementsof the small quantum interferometer are relatively simple and commonly used, and the structure and the optical path design are compact and flexible, adjustment can be carried out as needed, the smallquantum interferometer has the characteristics of small volume, low cost and simple and easy operation, and the small quantum interferometer is a small quantum interferometer system which can be usedfor quantum precision measurement. High research value and application prospects are achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Gravitational wave propulsion and telescope
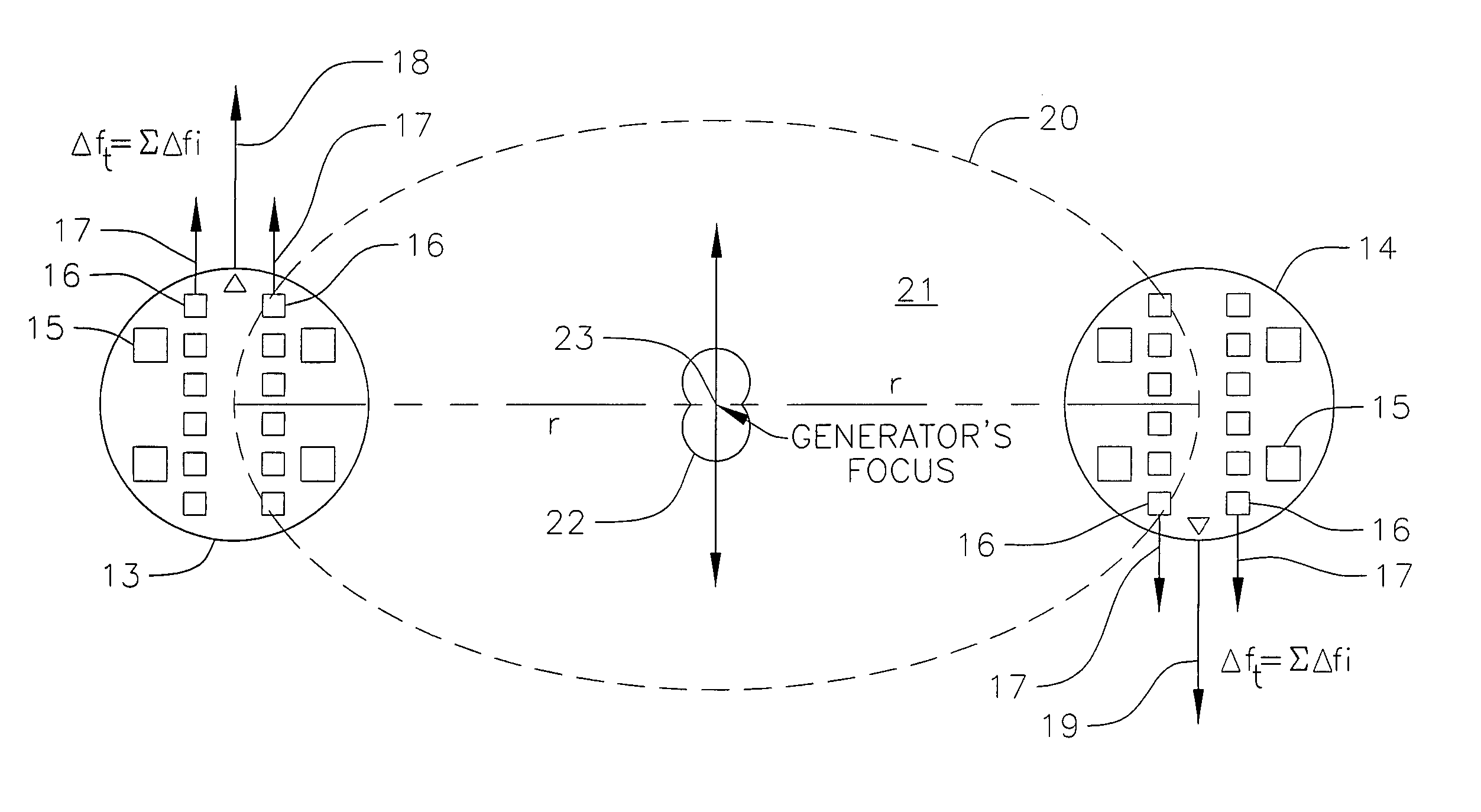
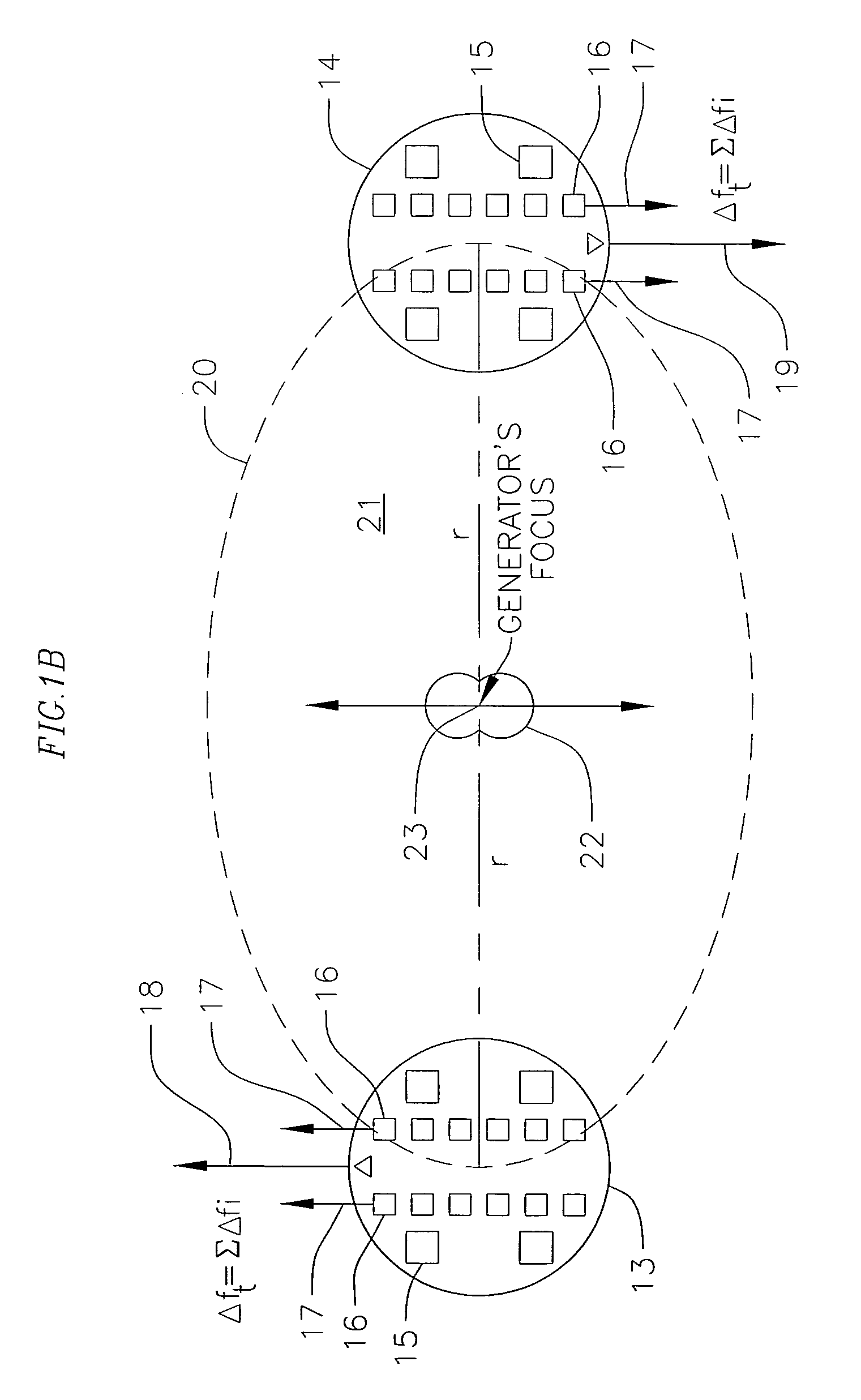
InactiveUS20040130237A1Radiation/particle handlingEnergy storageInformation processingDetector array
A gravitational wave generating device comprising an energizing means such as a particle or electromagnetic beam, which act upon energizable elements such as molecules, atoms, electrons, nuclei or nuclear particles in order to create nuclear reactions or collisions, the products of which can move in a single preferred direction with an attendant impulse (jerk or harmonic oscillation) of an ensemble of target nuclei or other energizable elements over a very brief time period. The target nuclei or energizable elements such as electrons or other submicroscopic particles in a superconductor acting in concert generate a gravitational wave. An information-processing device connected to a computer, controls the particle beam's high-frequency, (approximately GHz to THz or higher) pulse rate and the number of particles in each bunch comprising the pulse in order to produce modulated gravitational waves that can carry information. A gravitational wave generation device that exhibits directivity. A gravitational wave detection device that exhibits directivity and can be tuned. The utilization of a medium in which the gravitational wave speed is reduced in order to effect refraction of the gravitational wave and be a gravitational wave lens. A gravitational wave generator device that can be directed in order to propel an object by its momentum or by changing the gravitational field nearby the object to urge it in a preferred direction and be a propulsion means. A gravitational wave telescope that utilizes a source of gravitational waves and a gravitational wave lens to focus an image on an array of detectors.
Owner:BAKER ROBERT M L JR
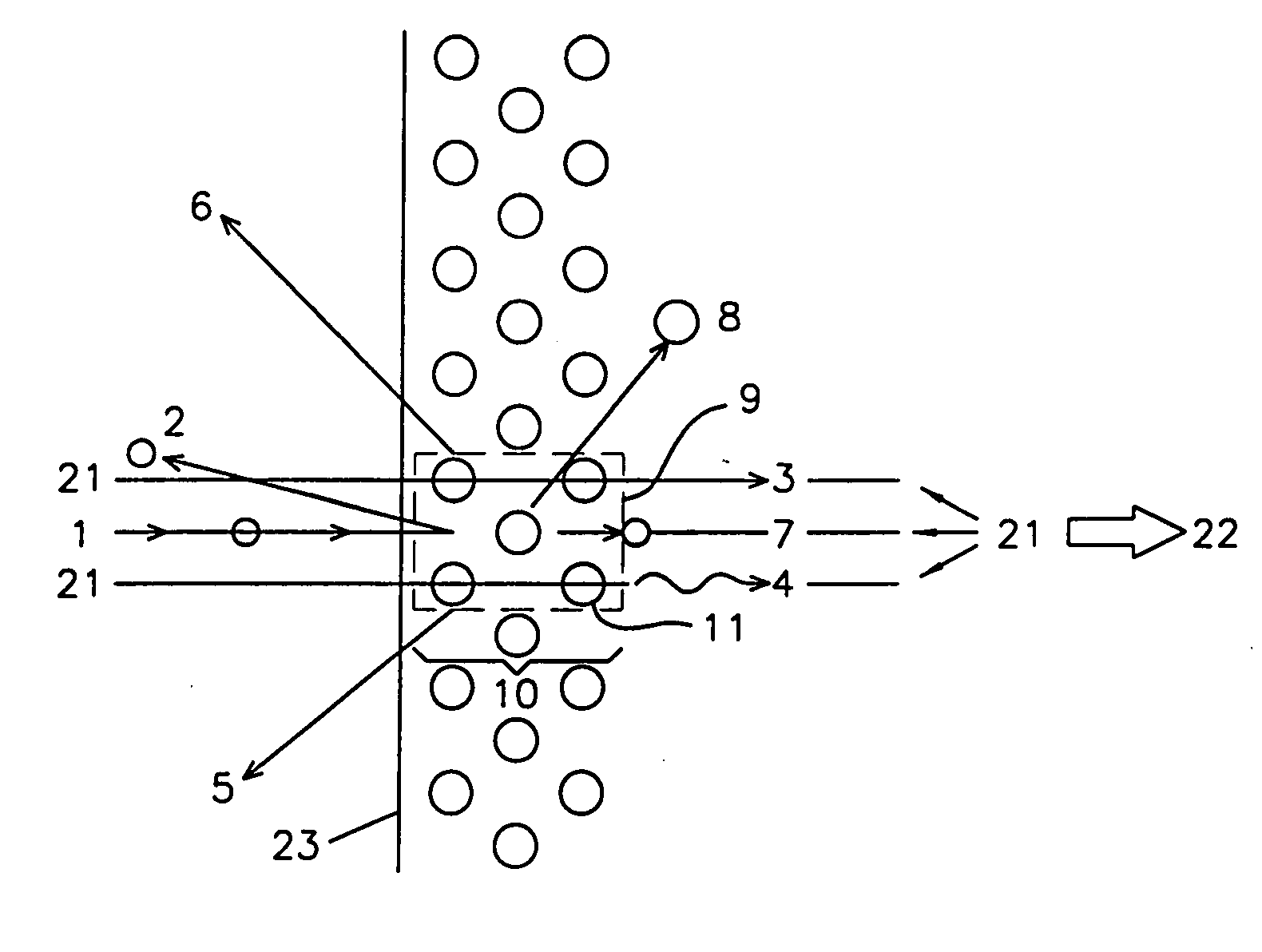
All-sky atmosphere gravitational wave imager
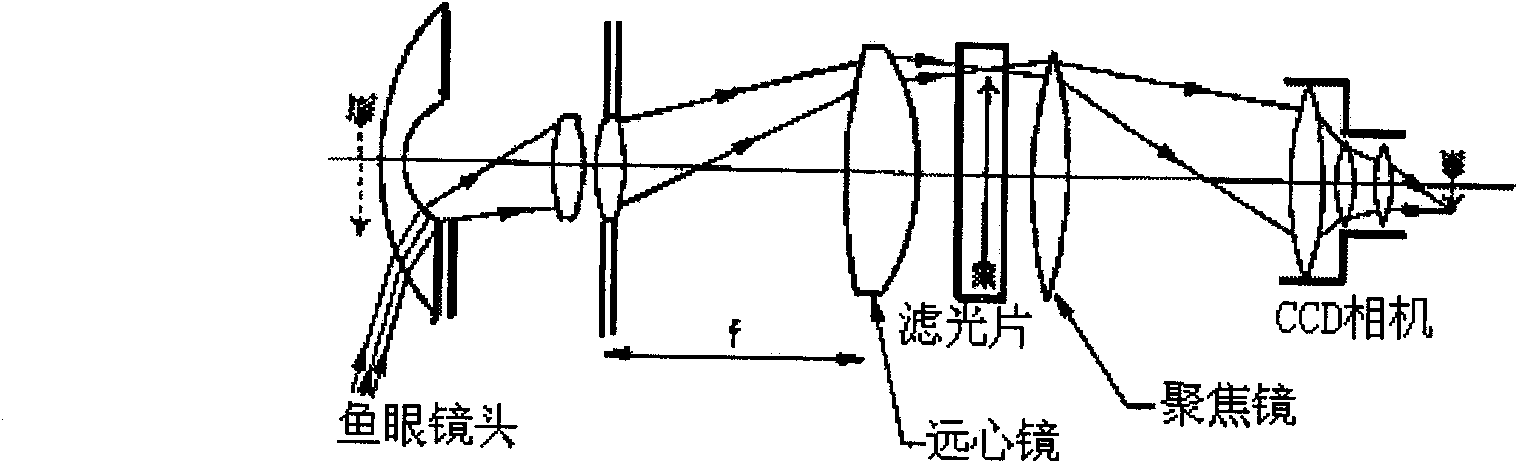
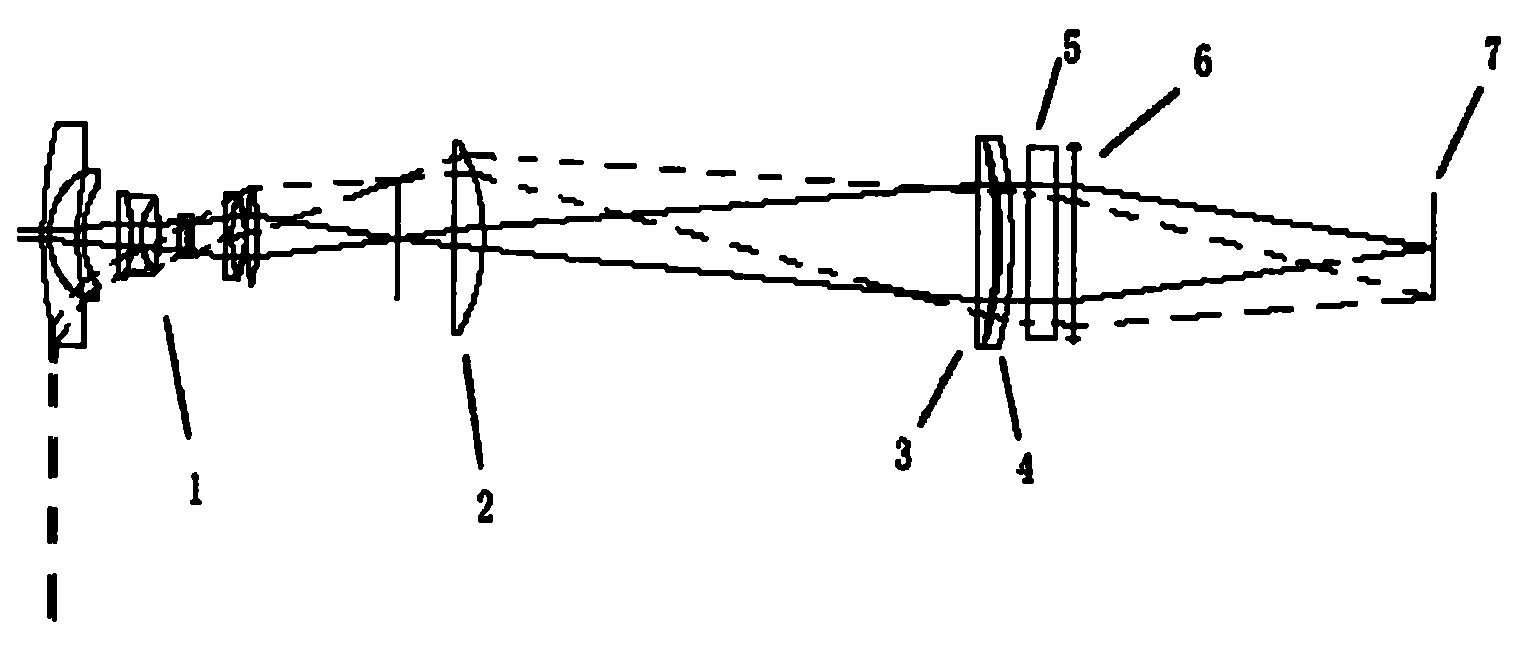
ActiveCN101923179ARealize imaging observationSatisfy the angle requirementGravitational wave measurementCamera lensImaging lens
The invention provides an all-sky atmosphere gravitational wave imager which comprises a fisheye lens, a three-lens light path adjustment lens group, an optical filter, an imaging lens and a scientific CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, wherein the three-lens light path adjustment lens group comprises a first lens, a second lens and a third lens, the first lens is a plus lens and is arranged close to the focal plane of the fisheye lens, the second lens which is a plus lens and the third lens which is a minus lens are arranged behind the first lens, and the third lenses are matched with the fisheye lens mutually so that light emitted from the third lens meets the angular requirement of the band width of the optical filter on incident light, then passes through the optical filter, the imaging lens sequentially and finally reaches the scientific CCD camera connected with the imaging lens, and thus, the all-sky atmosphere gravitational wave imager realizes the all-sky 180-degree atmosphere gravitational wave imaging by taking OH and O2 airglow radiation as a tracer. The all-sky atmosphere gravitational wave imager not only can realize higher-accuracy gravitational wave activity observation, but also can reduce cost and size and has concise structure and high accuracy.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
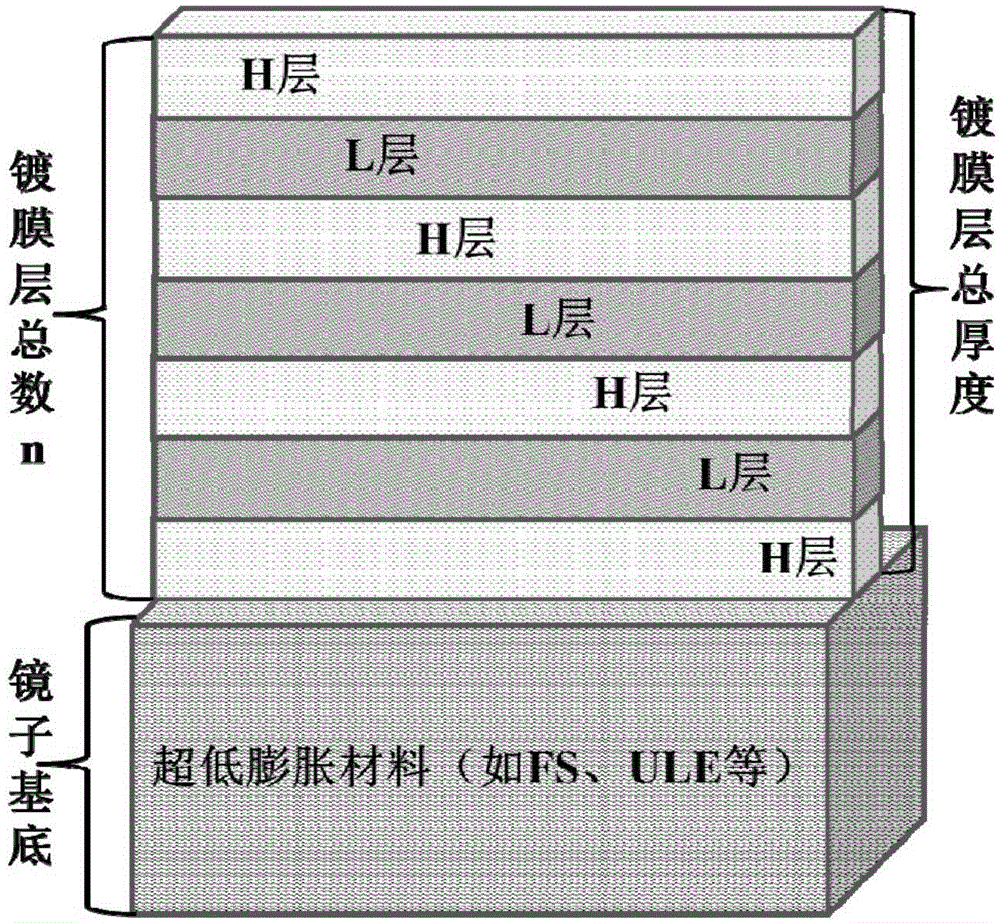
Low-thermal-noise high-reflection type optical combined film structure and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a low-thermal-noise high-reflection type optical combined film structure and a preparation method thereof. The low-thermal-noise high-reflection type optical combined film structure is that a ultralow-expansion optical material is used as a substrate; a film coats the substrate, wherein the film is a multi-layer film formed by a sapphire film layer and a diamond layer which are arranged alternatively and combined by bonding or contact blocking. According to the low-thermal-noise high-reflection type optical combined film structure, the sapphire and diamond materials are used as the film coating layers and have extremely low mechanical loss factors, so that the brown thermal noise of the film coating material can be greatly reduced; meanwhile, the sapphire and diamond materials have a large difference in refraction rate, and therefore, high and low film layers can be formed to achieve high reflection rate; the combined film can be applied to high-tech fields such as an optical reference cavity, an optical interference instrument, an ultralow linewidth laser, an optical atomic clock and gravitational wave detection.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic field reconstruction method based on distance weighted multi-pole expansion method
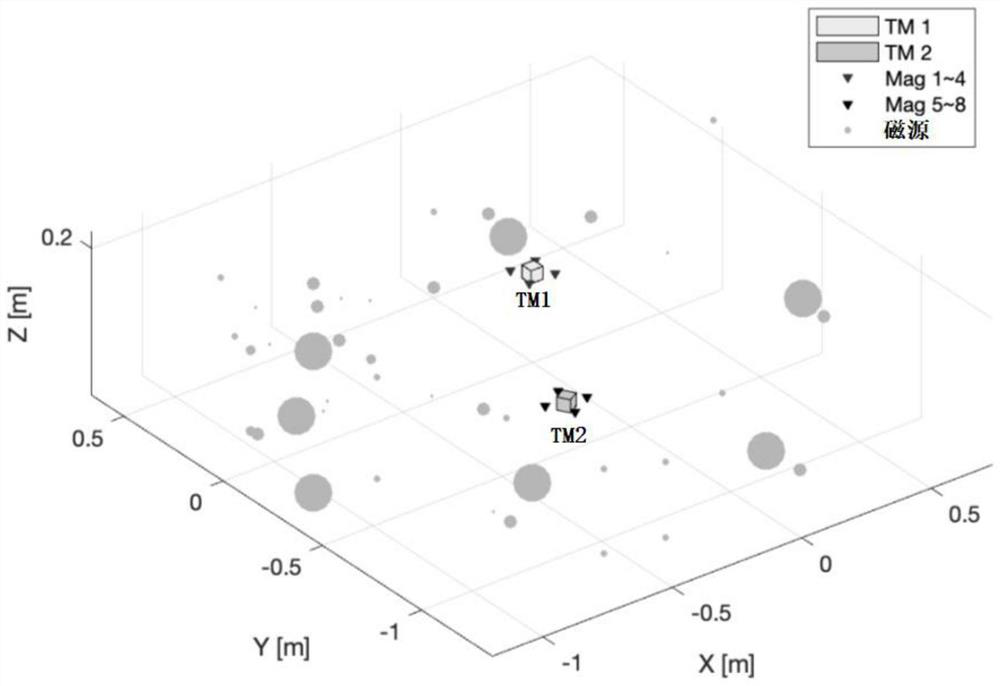
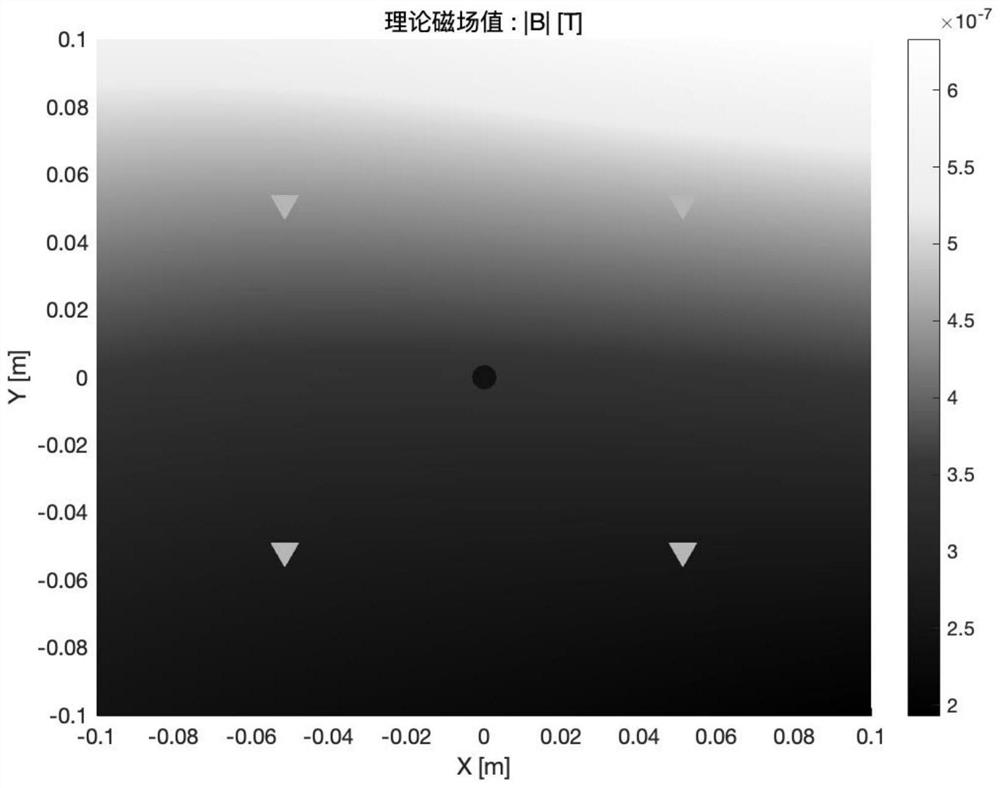
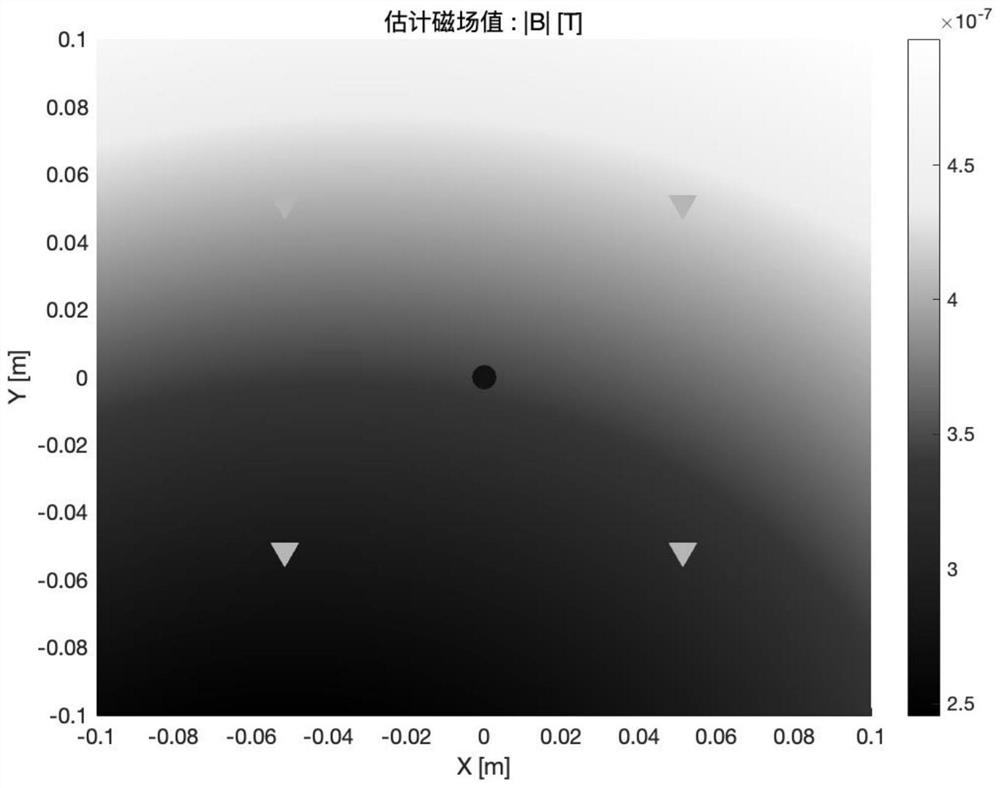
ActiveCN114444299AImprove the accuracy of magnetic field reconstructionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMagnetic field gradientComputational physics
The invention belongs to the technical field of space gravitational wave detection magnetic field reconstruction, and particularly relates to a magnetic field reconstruction method based on a distance weighted multi-pole expansion method, which comprises the following steps of: distributing magnetic components on a satellite outside two inertial sensor areas, enabling the magnetic components on the satellite to be equivalent to one or more magnetic dipoles to form a group of magnetic dipoles, the two inertial sensors respectively comprise a test mass, and four small magnetometers are respectively arranged outside an electrode cage of each test mass; according to a pre-established magnetic dipole theoretical model, obtaining a real magnetic field value of the magnetic field at the position of the to-be-solved test mass and real magnetic field values of the magnetic field at the positions of the eight small magnetometers; and performing distance weighting on the reconstruction error of each magnetometer based on a distance weighting multi-pole expansion method to obtain an optimal estimation multi-pole coefficient, and obtaining an estimated magnetic field value and a corresponding estimated magnetic field gradient value at a to-be-solved test mass position.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
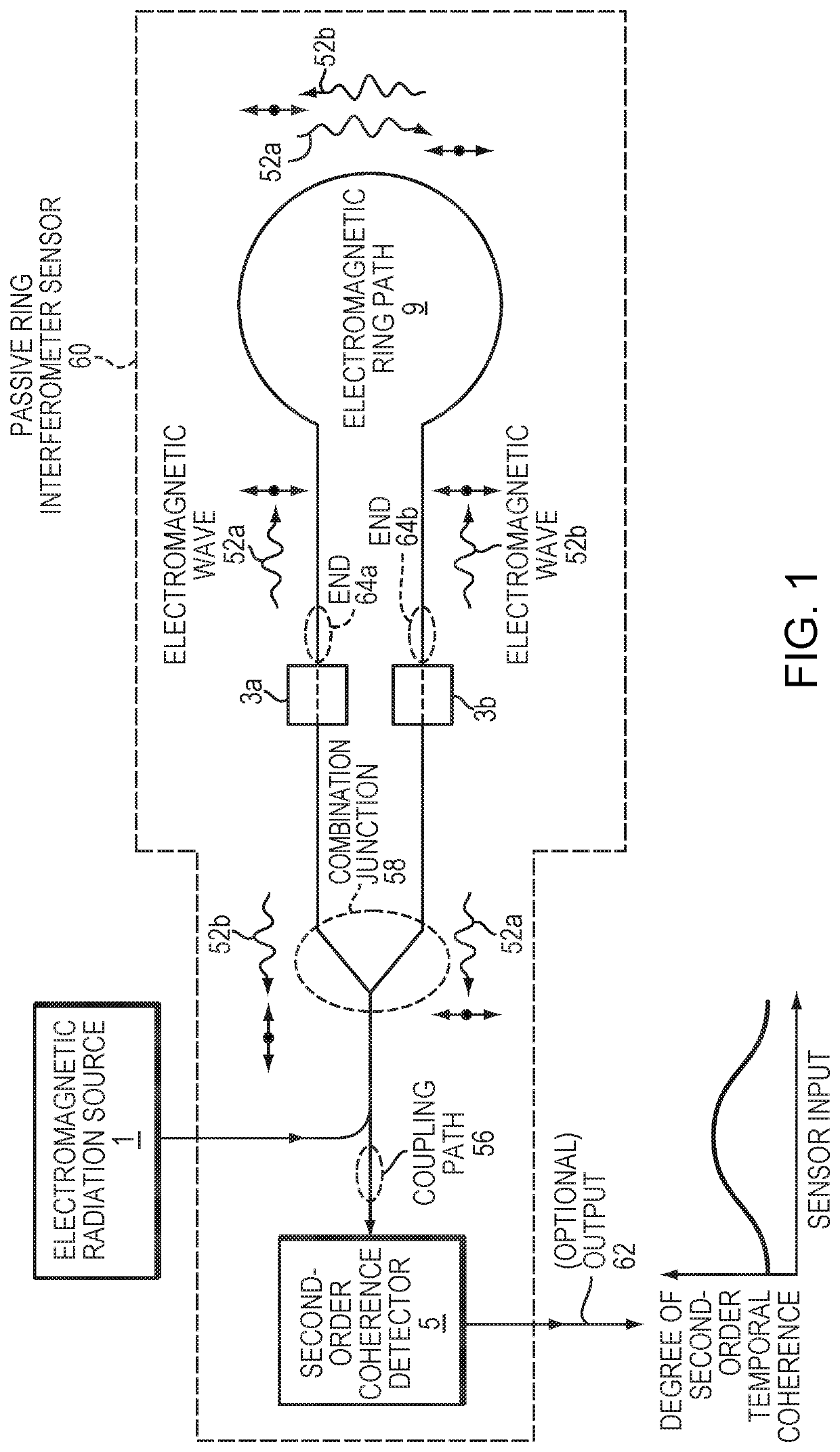
Second-order passive ring interferometer sensor and method
ActiveUS20190383614A1Increases true unambiguous dynamic rangeLinewidth broadeningSagnac effect gyrometersFiberWavelength
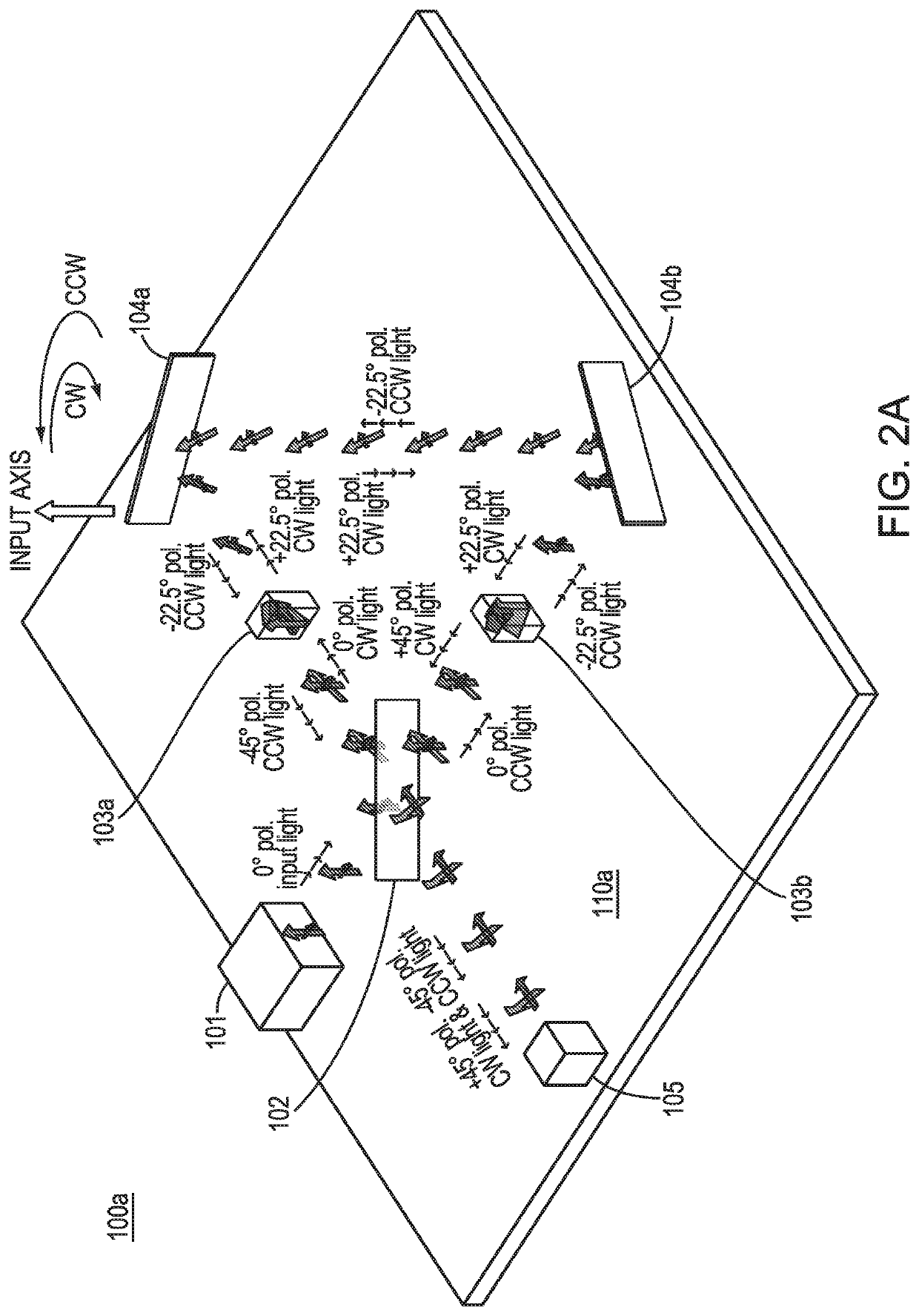
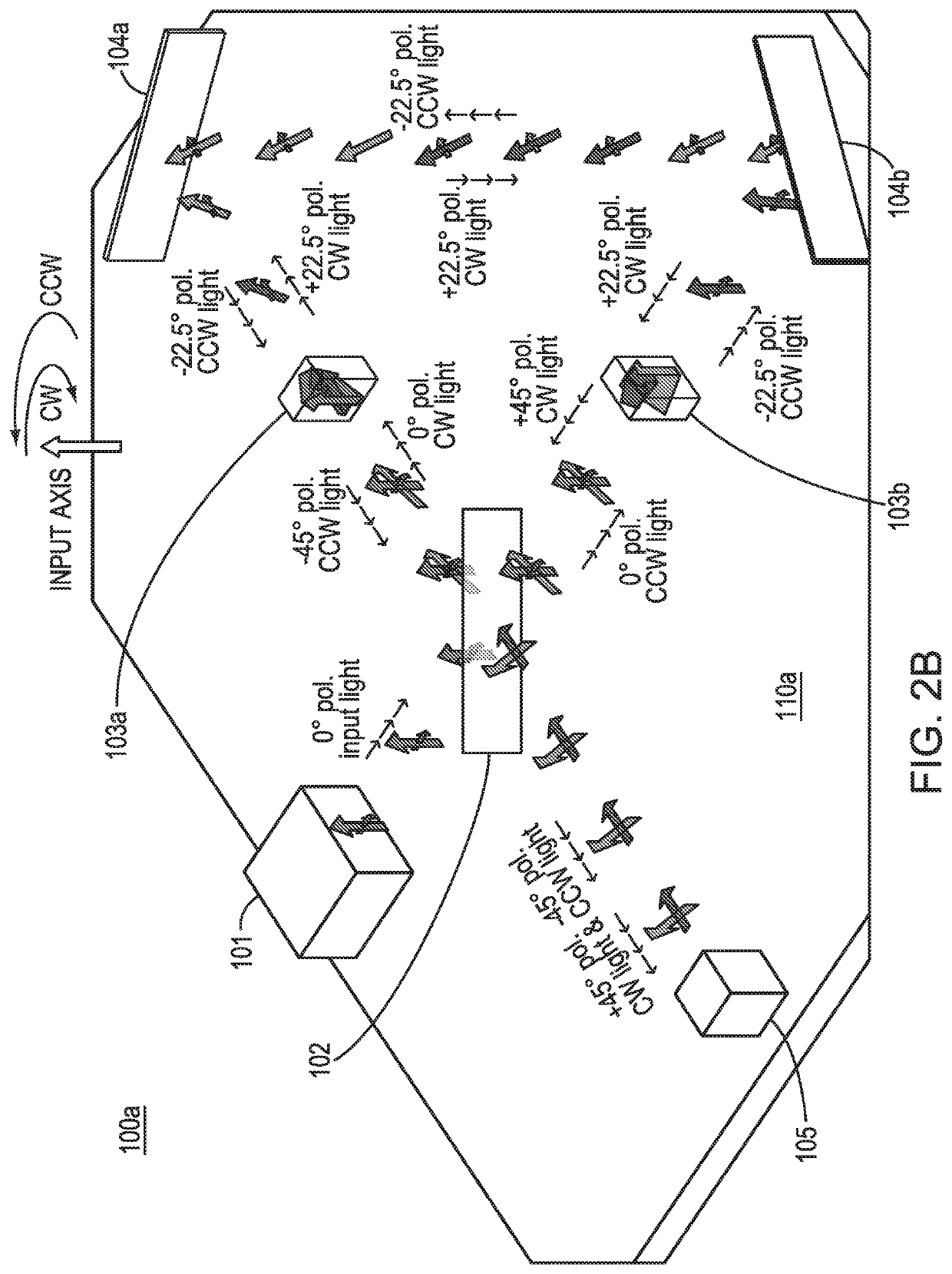
A passive ring interferometer sensor includes an electromagnetic ring path configured to receive a pair of electromagnetic waves from an electromagnetic radiation source and to direct the waves to be counter-propagating within the ring path toward respective ends of the path. A combination junction receives the waves from the respective ends and combines the waves to be co-propagating within a coupling path. Polarization elements are configured to set the waves to be mutually co-polarized within the electromagnetic ring path and to be mutually cross-polarized within the coupling path. A detector is configured to receive the mutually cross-polarized waves from the coupling path and to detect second-order coherence. Embodiments can sense rotation rate as fiber-optic gyroscopes or serve as other types of sensors such as gravitational wave sensors. Embodiments may have greatly increased unambiguous range and decreased sensitivity to any centroid wavelength shift.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
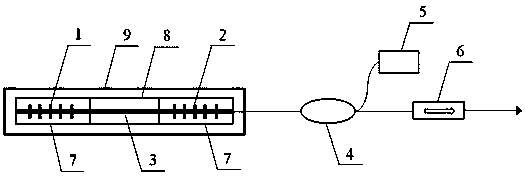
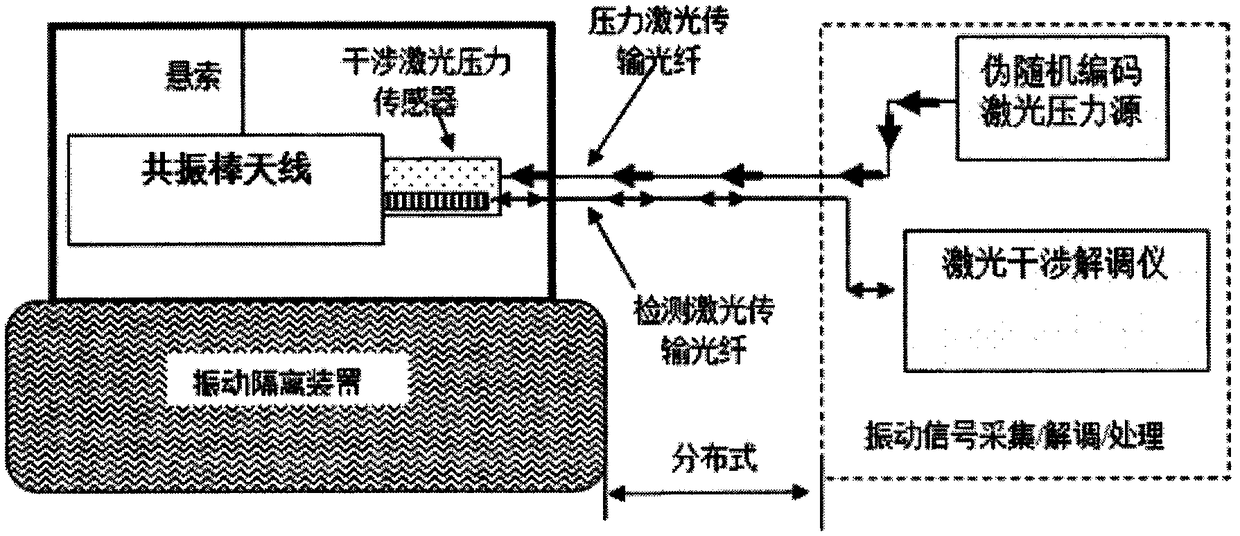
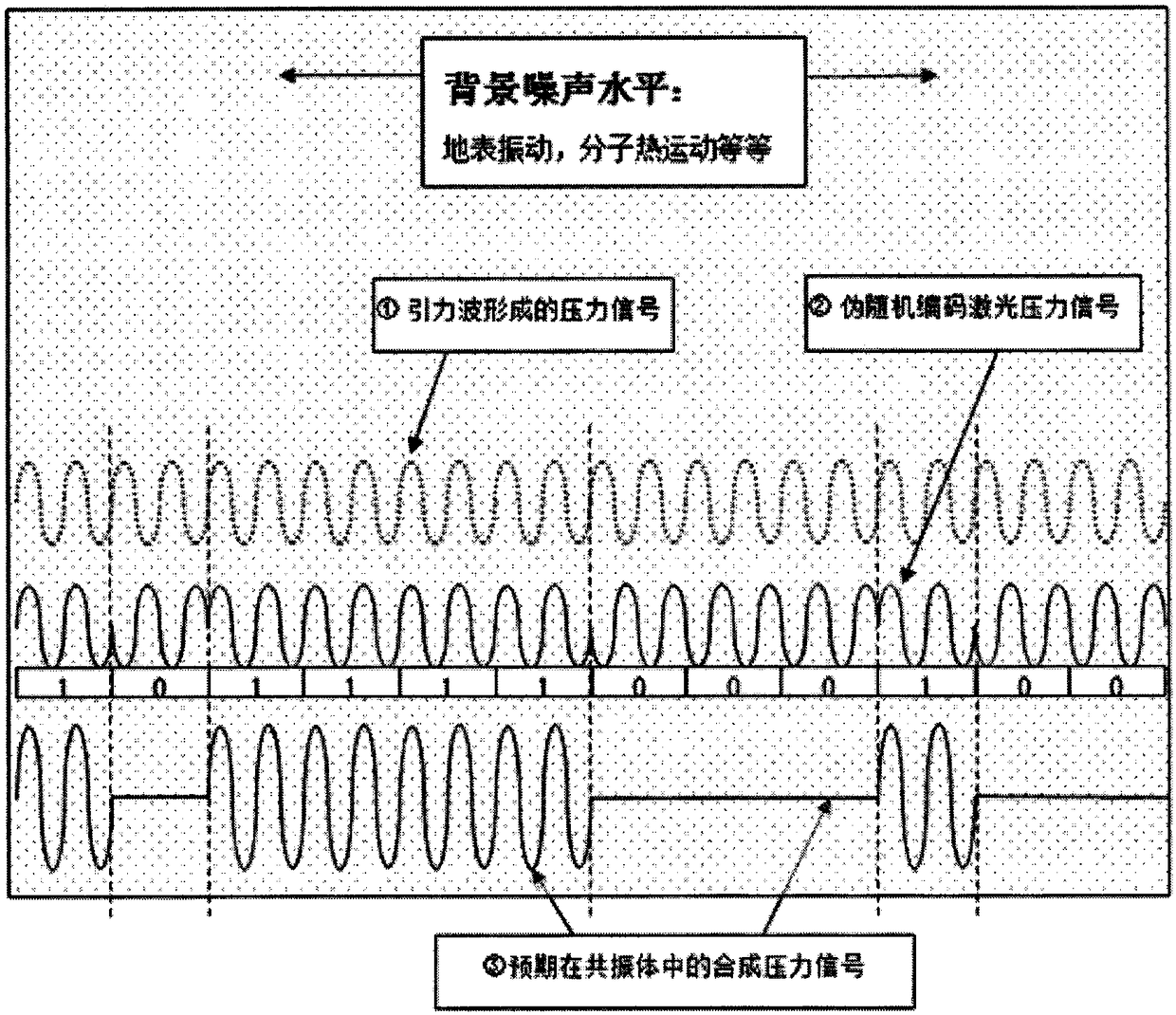
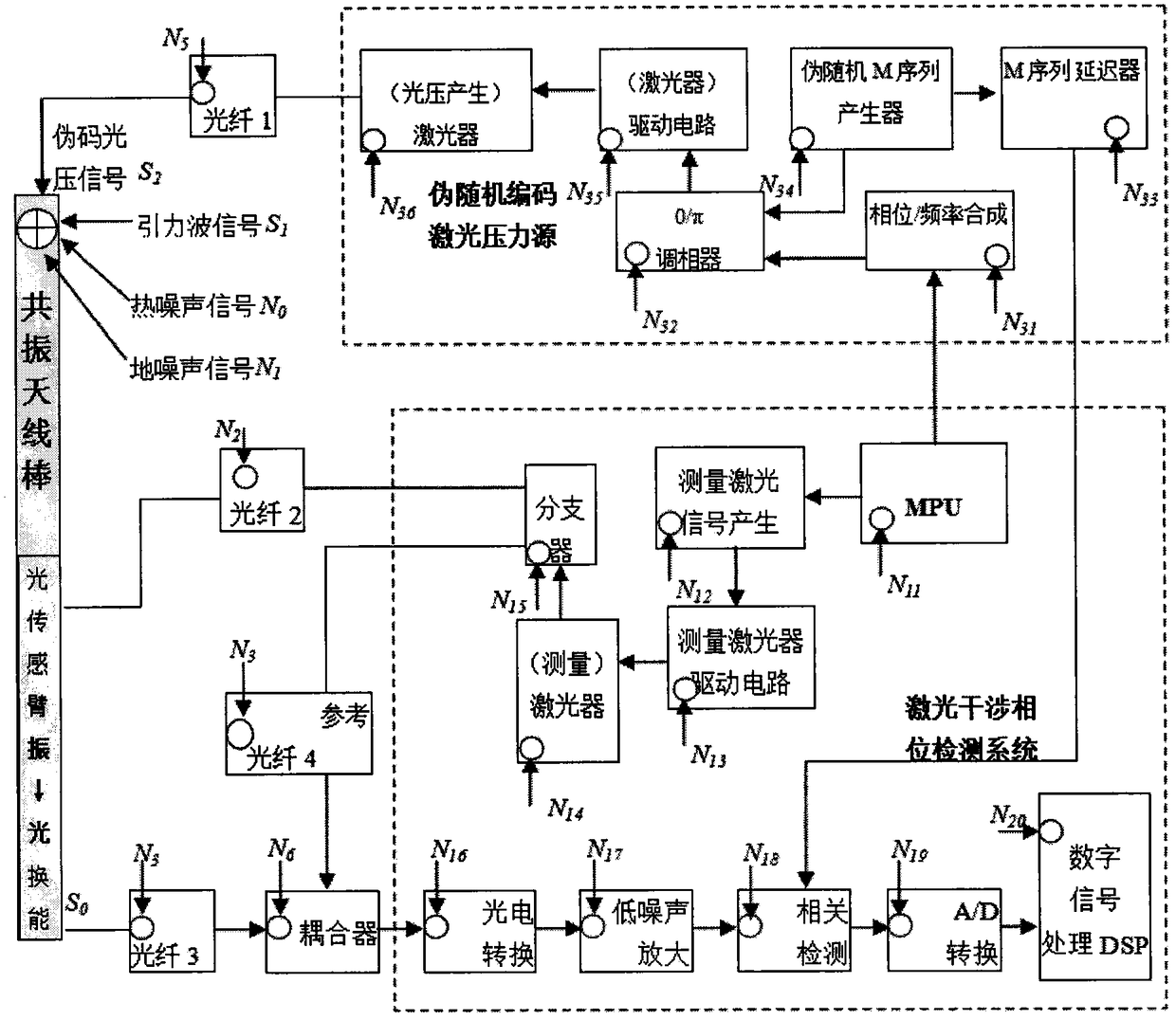
Gravitational wave detecting method based on pseudo random encoding technique
InactiveCN109471188AReduced thermal noise levelEasy to measureGravitational wave measurementNoise levelSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention discloses a gravitational wave detecting method based on a pseudo random encoding technique. A pseudo random encoded laser beam is used for assisting in irradiation to a normal-temperature gravitational wave antenna, resonance having pseudo code characteristics can be formed when the light pressure of encoding laser conforms to the frequency / phase of gravitational wave pressure signals in a detection antenna, and accordingly the capability of detecting weak gravitational wave vibration under the thermal noise background is remarkably improved. Compared with a large resonance rodantenna, huge construction and operation cost for cooling to liquid helium temperature and the brought thermal noise level of the antenna by 2-4 orders of magnitude are reduced. The signal-to-noise ratio gain of 10 orders of magnitude is brought with relatively low cost through a pseudo random technique, and gravitational waves can be increased to the orders of magnitude of 10-4 to 10-5 g, so thatthe measurement level is easily achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A relay method in an optical fiber optical frequency link and a relay station for realizing the method
ActiveCN106788750BSolve the problem of controlling bandwidthSuppress noiseElectromagnetic transmissionPhase noiseOptical clock
The invention discloses a relay method in an optical fiber optical frequency link and a relay station for implementing the method. The method comprises the following steps: using the signal of a previous level optical fiber link as seed light to receive and amplify a part of the seed light and send the seed light to the next level optical fiber link; and the other part of the seed light is reflected to return to the previous level link along the original route, a part of return light of the next level optical fiber link is received to serve as beat frequency to inhibit the noise so as to inhibit the import phase noise in an amplification process. By adoption of the relay method disclosed by the invention, the problem of controlling the width of a band in a phase noise inhibition process can be well solved, and the relay method has the advantages of adaptability to complex links, simple structure, low cost, and so on. The relay station of the optical fiber optical frequency link designed in the invention can be applied to optical atom clock comparison, ultra high precision optical clock signal transmission, optical fiber time frequency system networking, gravitational wave detection and other high-tech fields.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Deep space gravitational wave detection device based on relay femtosecond pulse
ActiveCN105700035BRealize the detection of gravitational waves in deep spaceRealize differential detectionGravitational wave measurementTime domainClock synchronization
A deep space gravitational wave detection apparatus based on repeating type femtosecond pulses is disclosed and comprise a measuring end, a number one femtosecond phase lock repeater, a number two femtosecond phase lock repeater, a number three femtosecond phase lock repeater, a number four femtosecond phase lock repeater, a number five femtosecond phase lock repeater and a number six femtosecond phase lock repeater. The deep space gravitational wave detection apparatus can be used for conducting equal arm length differential detection on gravitational wave signals, detection sensitivity can reach a sub-nanometer magnitude, each of two measuring arms adopts a pulse time domain locking type repeating measurement structure, the luminous power of measuring light is amplified by cascading three femtosecond phase lock repeaters, deep space gravitational wave detection on the scale of the outer solar system, the measuring end is independent of the six femtosecond phase lock repeaters, and problems of real time communication between satellites that are far apart and high-precision clock synchronization can be addressed.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
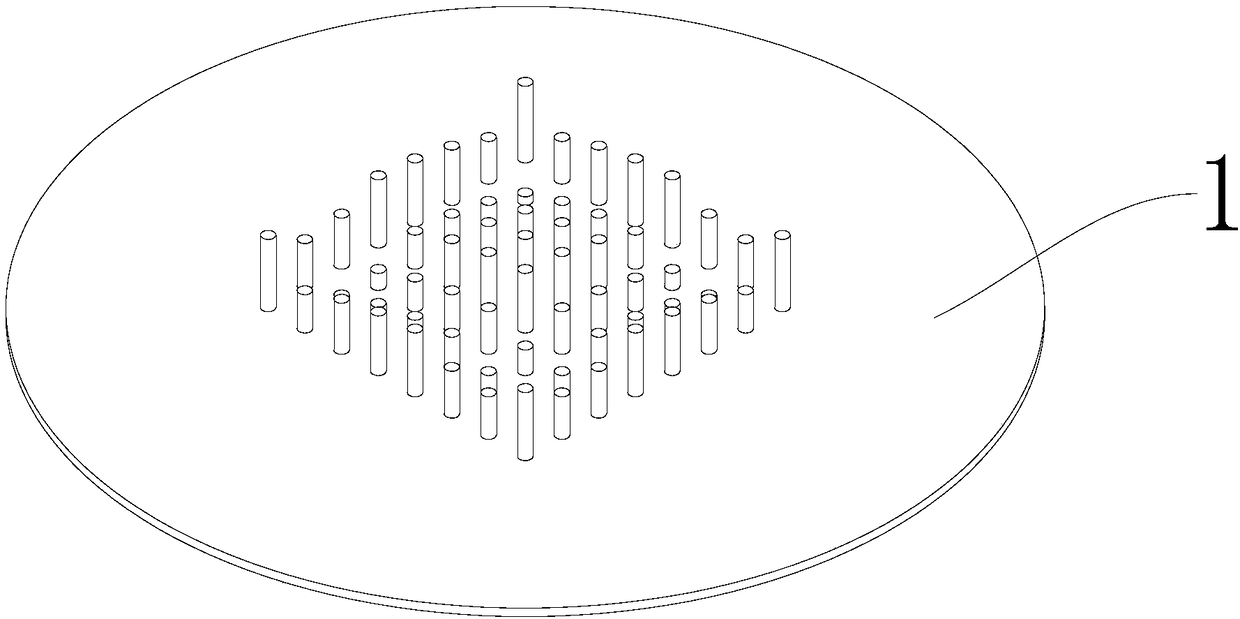
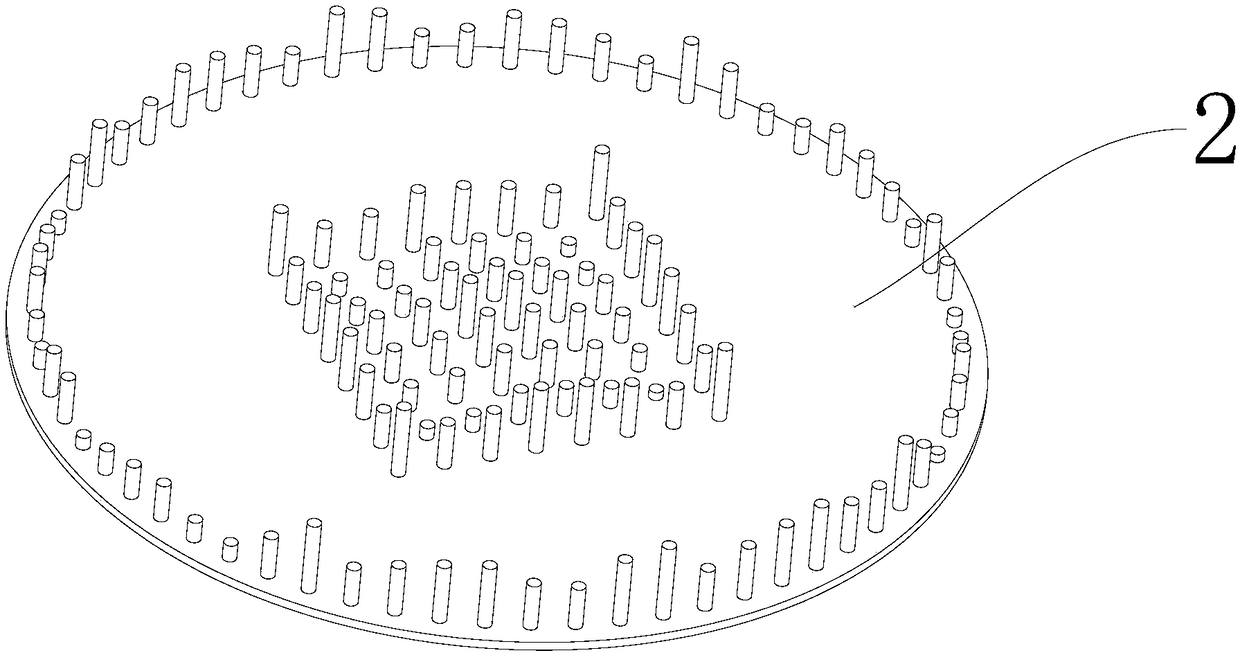
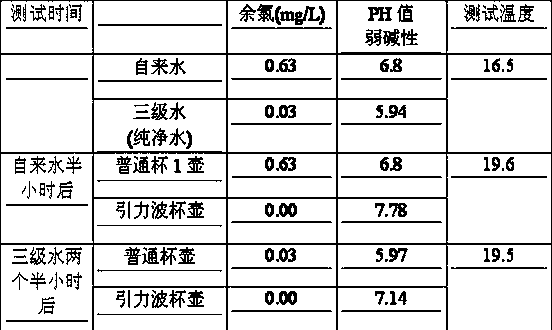
Gravitational wave cup or gravitational wave kettle
PendingCN108851864ASpeed up the dissipationHeating fastDrinking vesselsGravitational waveTheoretical physics
The invention discloses a gravitational wave cup or a gravitational wave kettle. The gravitational wave cup or the gravitational wave kettle has the advantages that dechlorination can be accelerated,water becomes small molecular water and alkalescent water, and a gravitational wave effect is achieved. The top face of the cup bottom of the gravitational wave cup or the top face of a bottom plate in the gravitational wave kettle is provided with a square column array composed of 64 protruding column bodies with different heights, the square column array is a mode that the 64 column bodies are evenly arranged in an 8*8 square matrix; the gravitational wave cup is internally provided with the square column array, so that the dissipation of chlorine in the water can be accelerated; the bottomplate in the gravitational wave kettle is provided with the square column array, so that each column body can dissipate heat when the water is heated; the water is heated by using heights with different proportions of the column array, heating is fast, energy is saved, tumbling is more complete, the dechlorination is accelerated, and the water becomes small molecular water and alkalescent water, so that the gravitational wave cup or the gravitational wave kettle has a health care effect.
Owner:熊浩祖
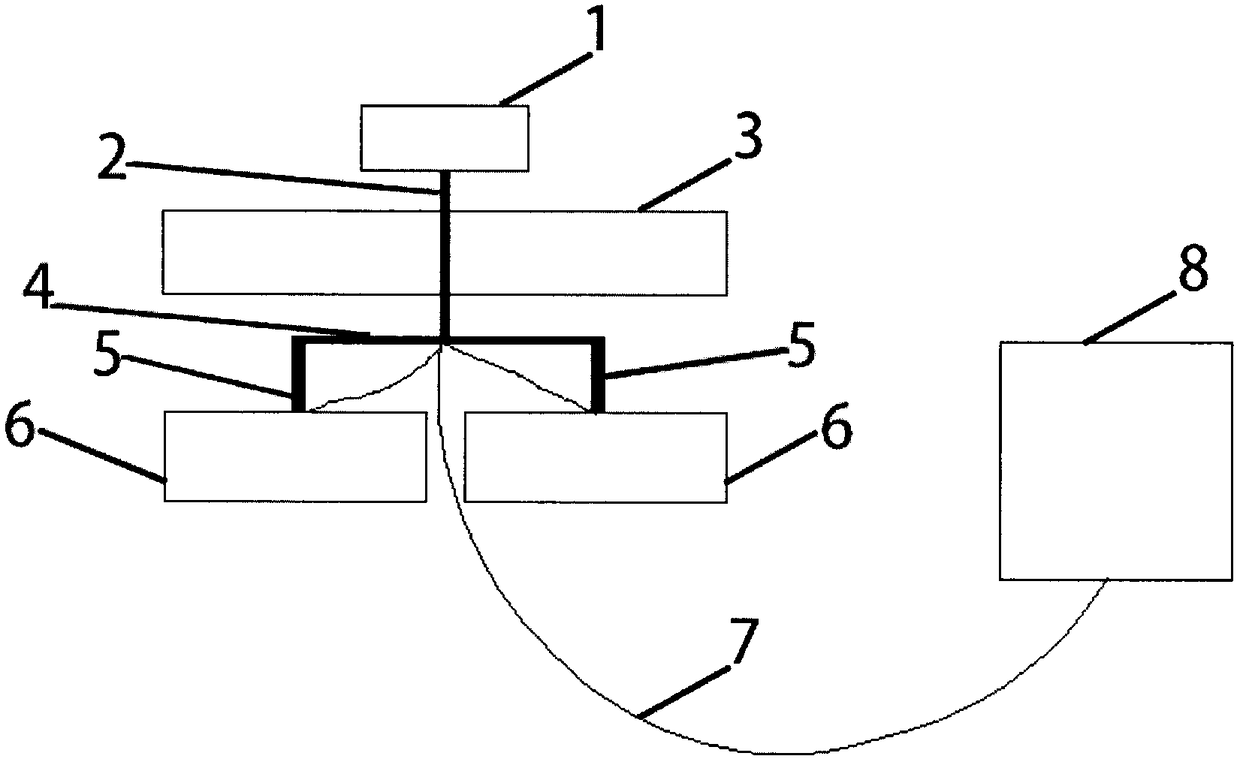
Gravitational wave energy field water purifying device
PendingCN108793435AIncrease the speed of microcirculationReasonable structural designWater/sewage treatment apparatusBiological water/sewage treatmentEngineeringElectromagnetic field
The invention provides a gravitational wave energy field water purifying device which is characterized by comprising a rotating shaft, a swing arm, an energy field generating device, an electric wireand a power source, wherein the rotating shaft is connected with the swing arm; a water allocation floating bucket is fixed on the swing arm; the swing arm is connected with an electromagnetic field generating device; the energy field generating device is capable of allowing water to flow therein; one end of the electric wire is connected with the energy field generating device, and the other endof the electric wire is connected with the power source. The gravitational wave energy field water purifying device is simple in structure and convenient to use, realizes the purposes of purifying water and removing algae, and reduces energy consumption.
Owner:陈雷
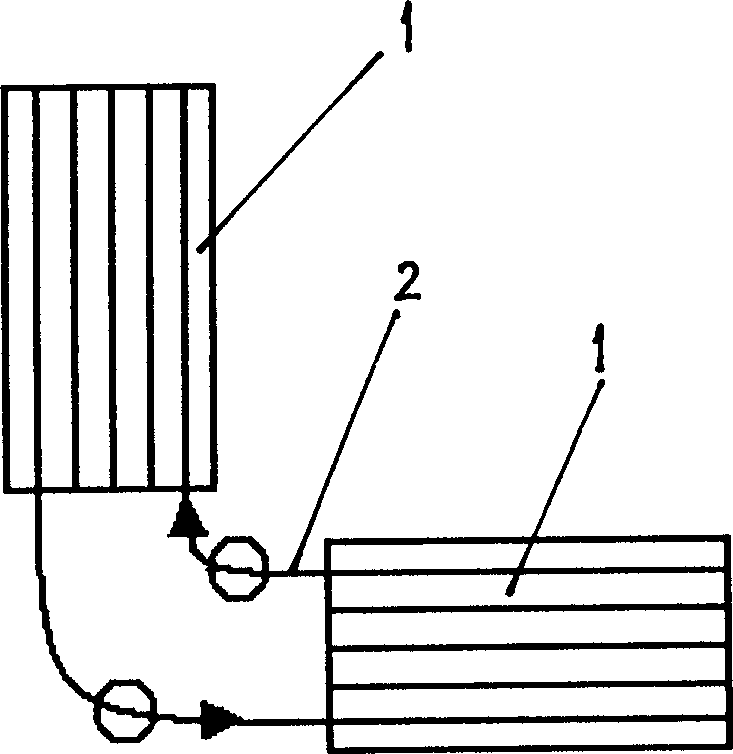
Gravitational wave detecting device
ActiveCN1234019CEnhanced ability to detect gravitational wavesIncrease the optical pathGravitational wave measurementFiberClosed loop
The gravitational wave detection device belongs to the field of optical measurement technology, which not only utilizes the resonance effect but also utilizes the extended optical path to amplify the gravitational wave signal, so as to improve the sensitivity of detecting gravitational wave. In the present invention, the two resonant rods are independently hung horizontally through the center by strings, and their central axes are perpendicular to each other; corresponding to the two resonant rods, the optical fiber is divided into two sections, and each section is folded into N subsections, 1,000≤N ≤1,000,000, and wound along the axis of the resonant rod and fixed on the resonant rod, or placed in the resonant rod along the axis of the resonant rod, the ends of the optical fibers on the two resonant rods are connected by optical devices, and the entire optical fiber forms a closed loop. The resonant rod and the optical fiber on it act as a resonant mass, and use the resonance effect to amplify the gravitational wave signal by Q times; at the same time, the optical fiber folding is used to greatly increase the optical path of the optical signal, and the response of the resonant rod to the gravitational wave is accumulated to enhance the detection of gravitational waves. ability to further amplify the gravitational wave signal and greatly improve the detection sensitivity.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com