Floating-point adder circuitry
A circuit, floating-point number technology, applied in the field of dynamic bit expansion and shifting technology, can solve problems such as expensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
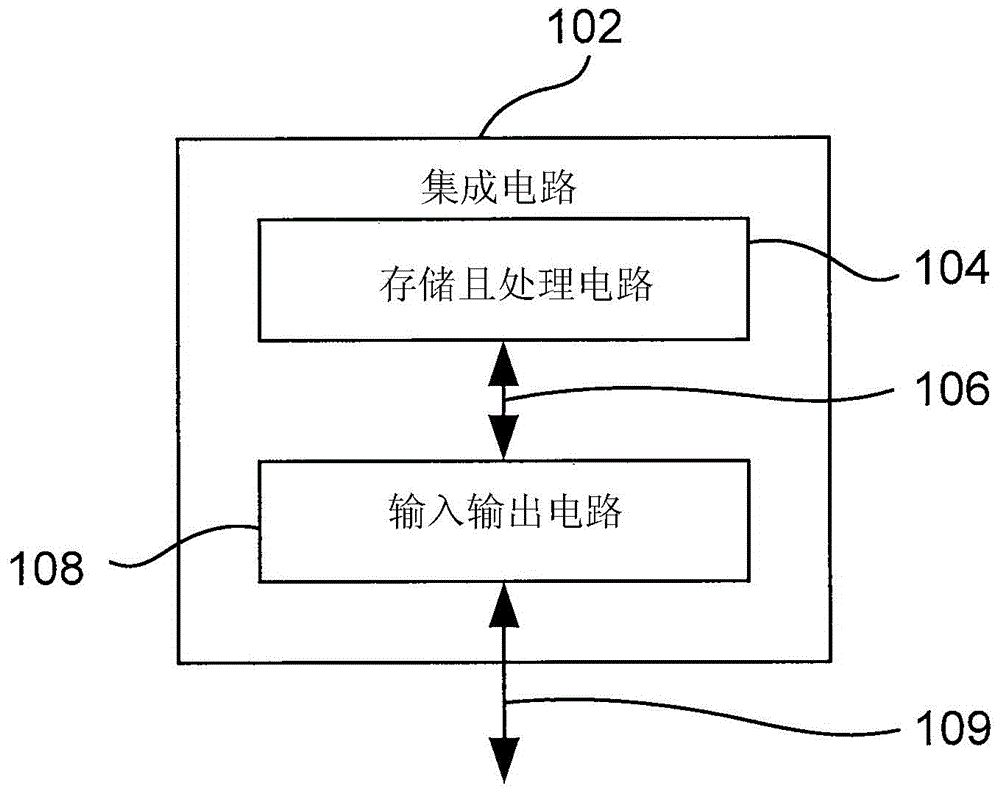
[0019] Embodiments of the present invention relate to performing floating point arithmetic operations in integrated circuits, and more particularly to dynamic bit extension and shifting techniques for floating point operations.
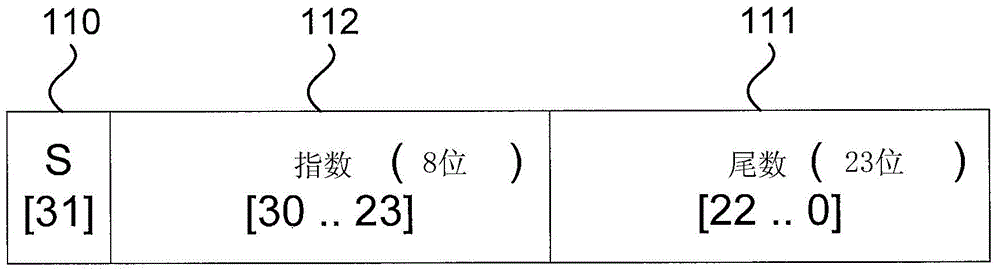
[0020] Floating point arithmetic is typically implemented according to the IEEE754 standard, which defines floating point numbers as having a sign, mantissa, and exponent, and where it is required that the mantissa be always normalized because the standard implies a leading "1". Furthermore, floating-point addition and subtraction require the mantissas of the floating-point operands to be aligned in such a way that the exponents of the floating-point operands are equal.
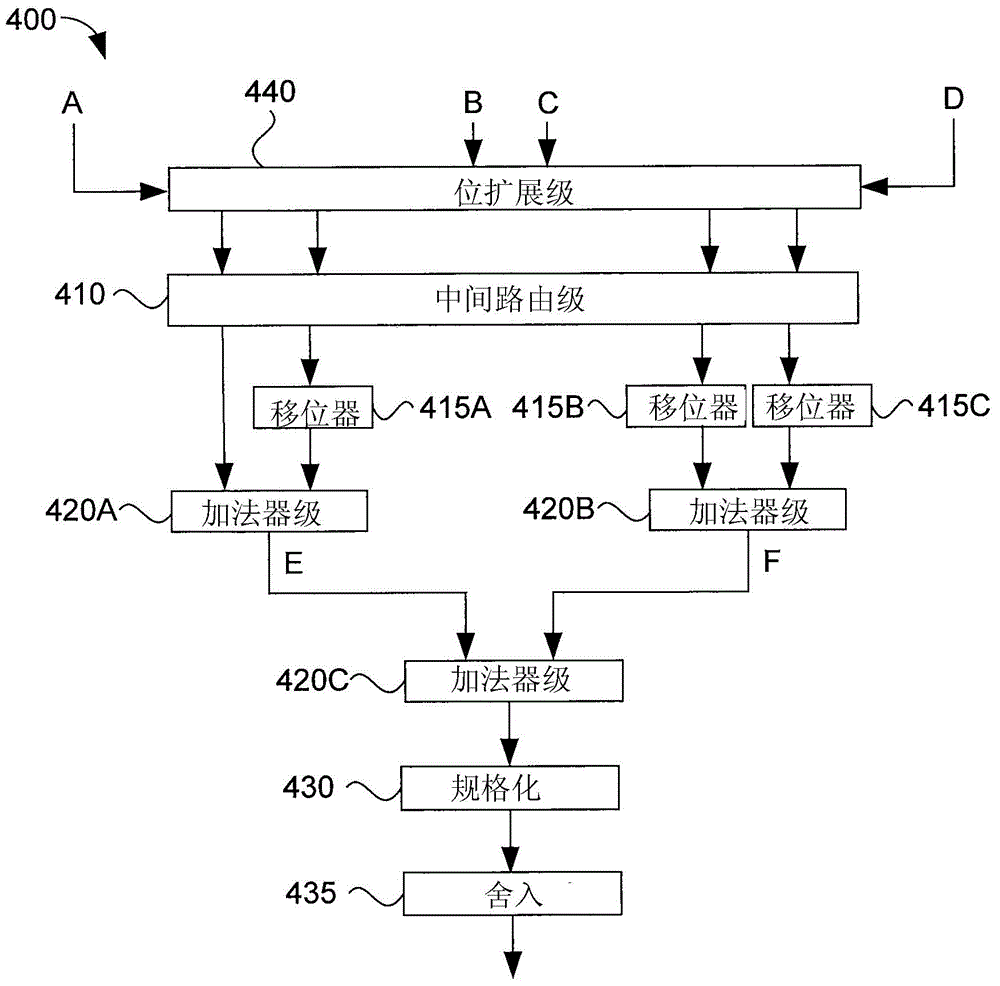
[0021] Situations in which several floating-point addition or subtraction operations are performed sequentially (for example, addition of two or more numbers in a tree structure) frequently arise. Such sequential addition or subtraction operations require normalization of the mantiss...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com