Attitude and position estimation method based on vision and inertia information
An attitude and inertial technology, applied in the field of attitude and position estimation based on visual and inertial information, can solve the problems of small moving speed, difficult zero speed detection, estimation drift, etc., and achieve less computing resources, small amount of calculation, and good robustness sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] In order to describe the present invention in more detail, the technical solution of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
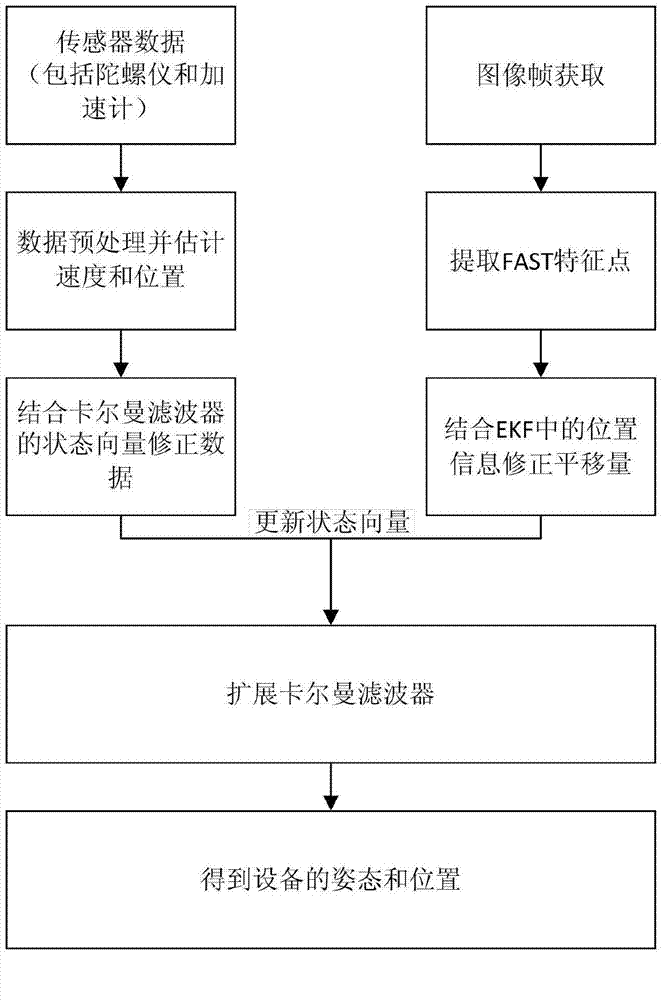
[0027] The method of the present invention is implemented on a smart phone, and the camera and sensor data on the phone are used to calculate the position and posture, such as figure 1 As shown, the specific implementation is as follows:
[0028] A. Perform joint calibration of the camera and sensor on the device to obtain the internal parameters and distortion parameters of the camera, and at the same time obtain the positional relationship between the sensor and the camera in the world coordinate system, so that the sensor and the camera are aligned in the world coordinate system.
[0029] B. Set the origin of the world coordinate system for the initial position of the camera, set the initial state vector of the extended Kalman filter (EKF) in the initial state, set...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com