Optical fiber coupling member and method for producing same
A technology for optical fiber coupling and optical components, applied in the field of optical fiber coupling components and their manufacturing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
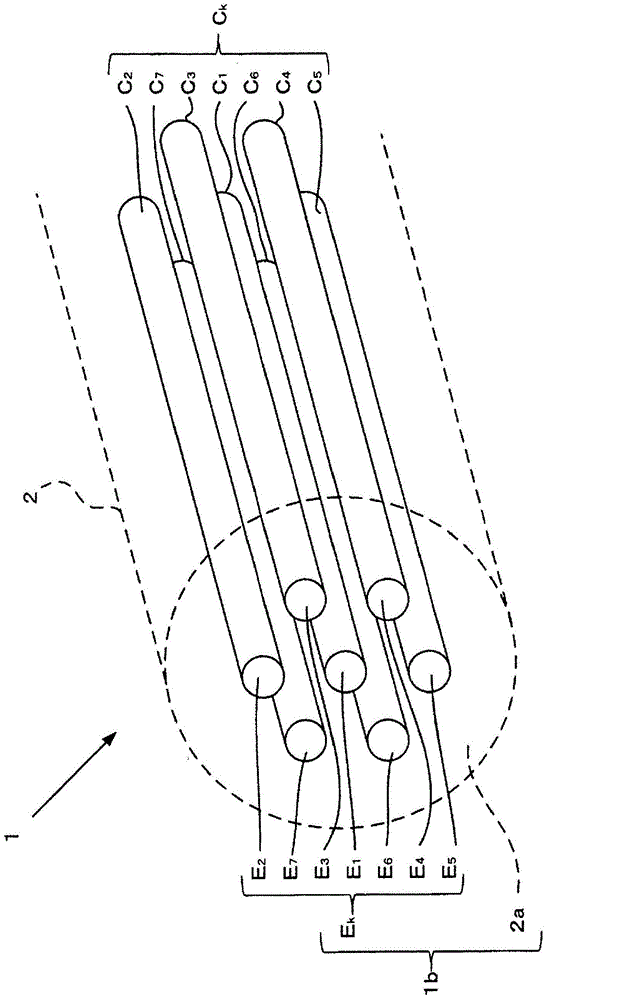
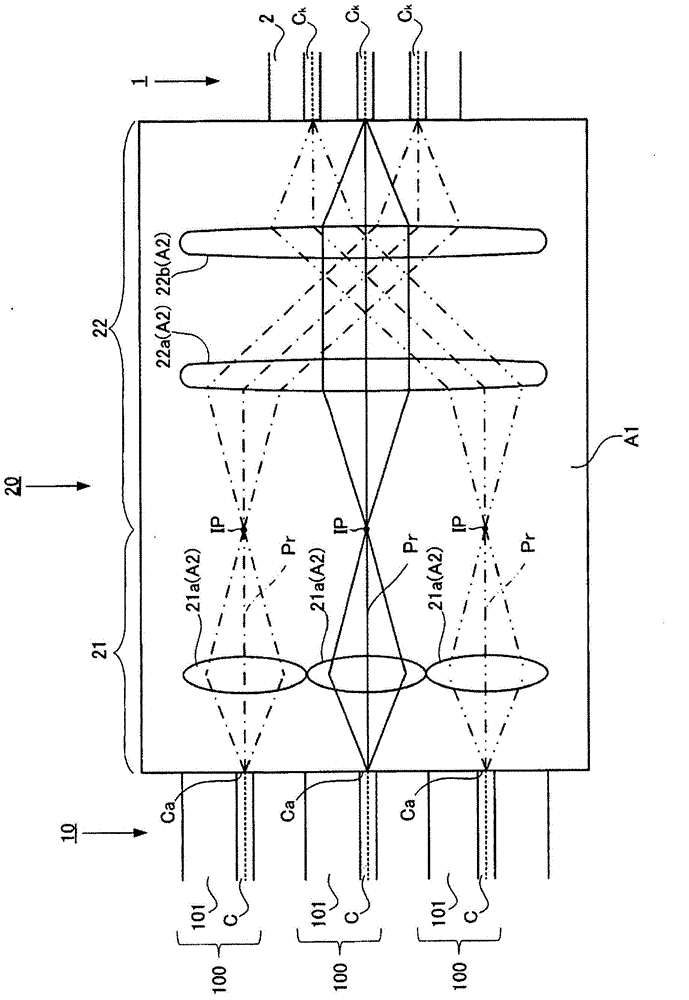
[0055] Next, refer to Figure 2 ~ Figure 4H , the structure and manufacturing method of the coupling member 20 of the first embodiment will be described. The coupling member 20 is arranged between the first optical waveguide and the second optical waveguide. The first optical waveguide is formed by bundling a plurality of one core (optical path) covered with a cladding. The second optical waveguide is composed of a plurality of cores each covered with a cladding. The coupling member 20 optically couples the first optical waveguide and the second optical waveguide. The coupling member 20 in this embodiment couples the optical fiber bundle 10 serving as a first optical waveguide and the multi-core optical fiber 1 serving as a second optical waveguide. figure 2 It is a conceptual diagram showing axial cross-sections of the coupling member 20 , the optical fiber bundle 10 , and the multi-core optical fiber 1 .
[0056] [Structure of Fiber Bundle]
[0057] The optical fiber b...
no. 2 approach
[0108] Next, refer to Figure 5 , the structure of the coupling member 20 of the second embodiment will be described. Figure 5 It is a conceptual diagram showing axial cross-sections of the coupling member 20 , the optical fiber bundle 10 , and the multi-core optical fiber 1 . In this embodiment, an example using a GRIN lens as the first optical system 21 and the second optical system 22 constituting the coupling member 20 will be described. In addition, a detailed description of the same configuration as that of the first embodiment and the like will be omitted.
[0109] [Structure of the coupling part]
[0110] The coupling member 20 in this embodiment has a GRIN lens. A GRIN lens is a lens of a refractive index distribution type that bends diffused light by ion-exchanging the medium constituting the lens to adjust the refractive index distribution inside the lens and concentrates the light. That is, the GRIN lens can adjust the refractive index distribution by ion exch...
no. 3 approach
[0128] Next, refer to Figure 6 , the structure of the coupling member 20 of the third embodiment will be described. Figure 6 It is a conceptual diagram showing axial cross-sections of the coupling member 20 , the optical fiber bundle 10 , and the multi-core optical fiber 1 . In this embodiment, a description is given of using a plurality of optical fibers F as the first optical system 21 constituting the coupling part 20. k , An example in which the GRIN lens SL2 is used as the second optical system 22 . In addition, detailed descriptions of the same configurations and the like as those of the first embodiment and the second embodiment are omitted.
[0129] [Structure of the coupling part]
[0130] The coupling member 20 in this embodiment has the 1st optical system 21 and the 2nd optical system 22 similarly to 1st embodiment and 2nd embodiment.
[0131] In the first optical system 21, as a medium, there are a plurality of optical fibers F k (k=1~n). Fiber F k One end...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com