A method for improving the antibacterial properties and stability of cationic short peptides
A peptide antibacterial and cationic technology, applied in the field of antibacterial drugs, can solve the problems of poor stability and low antibacterial properties of cationic short peptides, and achieve the effects of improving stability, increasing action strength, and good antibacterial properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] 1. Preparation of cationic short peptide:
[0030] The synthesis of short cationic peptides can be achieved by a standard microwave-assisted solid-phase method: using amide resin as the substrate, using 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-protected L-amino acids as raw materials, and dried N,N-dimethylformamide (purity greater than 99.5%) is the reaction solvent, benzotriazole-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate is the coupling reagent, and N,N-diisopropylethylamine is The activator is used for amino acid condensation coupling reaction, and piperidine is used as the deprotection reagent to remove the 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl group. The corresponding 9-fluorenyl moxycarbonyl-protected L-amino acid is sequentially coupled on the surface of the amide resin through repeated steps such as condensation coupling of L-amino acid and removal of the 9-fluorenyl moxycarbonyl protecting group.
Embodiment 1-1
[0032] Synthesis of tert-butyloxycarbonyl-4-azophenyl-L-phenylalanine: 2g tert-butyloxycarbonyl-4-amino-L-phenylalanine was dissolved in 200mL of glacial acetic acid, and then Quickly add 1.156g of nitrosobenzene and stir at room temperature for 8h. After the reaction was completed, 300 mL of saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution was added to the reaction solution, and the above solution was extracted 3 times with ethyl acetate, and the ethyl acetate phase was collected and dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the obtained filtrate was filtered and concentrated, and the crude product was analyzed with a silica gel column. Purify. The developer dichloro:methanol=1:1 (volume ratio), and 1.64 g of a yellow solid product was obtained with a yield of 65%.
[0033] Synthesis of 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-4-azophenyl-L-phenylalanine: take 1g of tert-butyloxycarbonyl-4-azophenyl-L-phenylalanine obtained above and 50mL di Chloromethane was added into a 250mL round-bott...
Embodiment 1-2
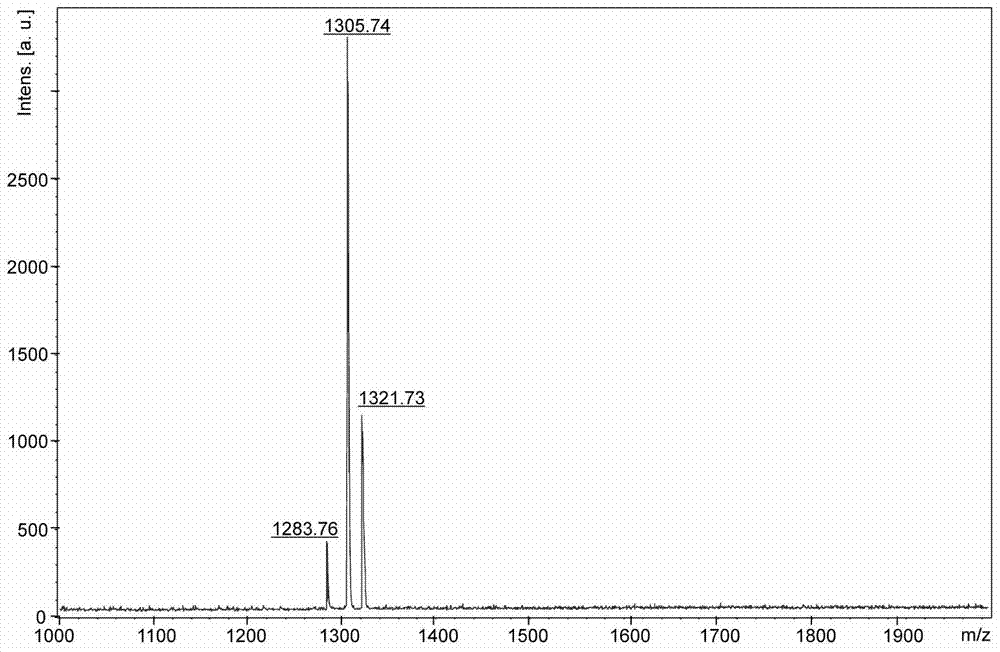
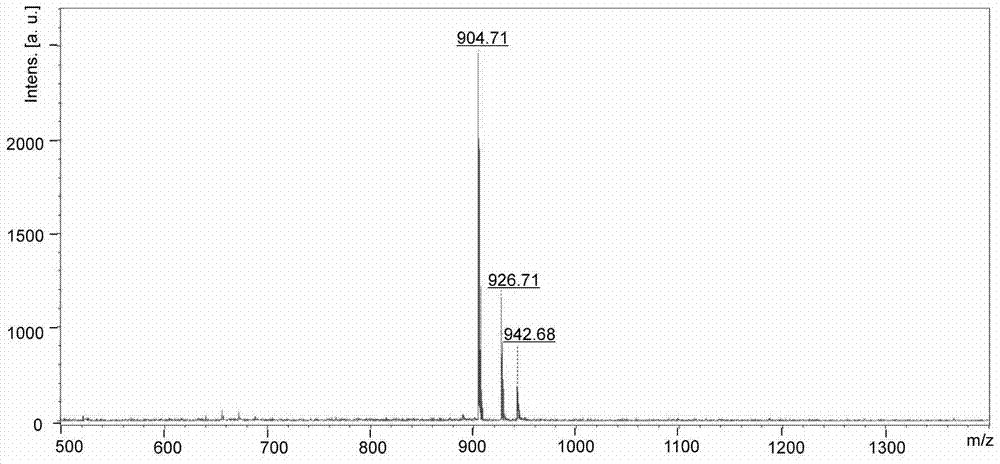
[0036] Synthesis of KazoKazoK (molecular weight 903.5g / mol): As shown in Example 1-1, other conditions remain unchanged, and 9-fluorene is sequentially coupled on the amide resin according to the deprotection and coupling reaction steps described in Example 1-1 Methoxycarbonyl-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine, 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-4-azophenyl-L-phenylalanine, 9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl-tert-butyloxycarbonyl- L-lysine, 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-4-azophenyl-L-phenylalanine, 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine. After the reaction is complete, add 3 mL of a mixed solution containing trifluoroacetic acid, anisole, water, and triisopropylsilane (volume ratio 88:5:5:2) to the reaction tube, and In a constant temperature shaker at 25°C, shake continuously for 3 h. After the reaction was completed, the filtered solution was added to 10 mL of glacial ether, and centrifuged for 3 minutes in a centrifuge with a rotation speed of 9,000 rpm to obtain a crude Ka...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com