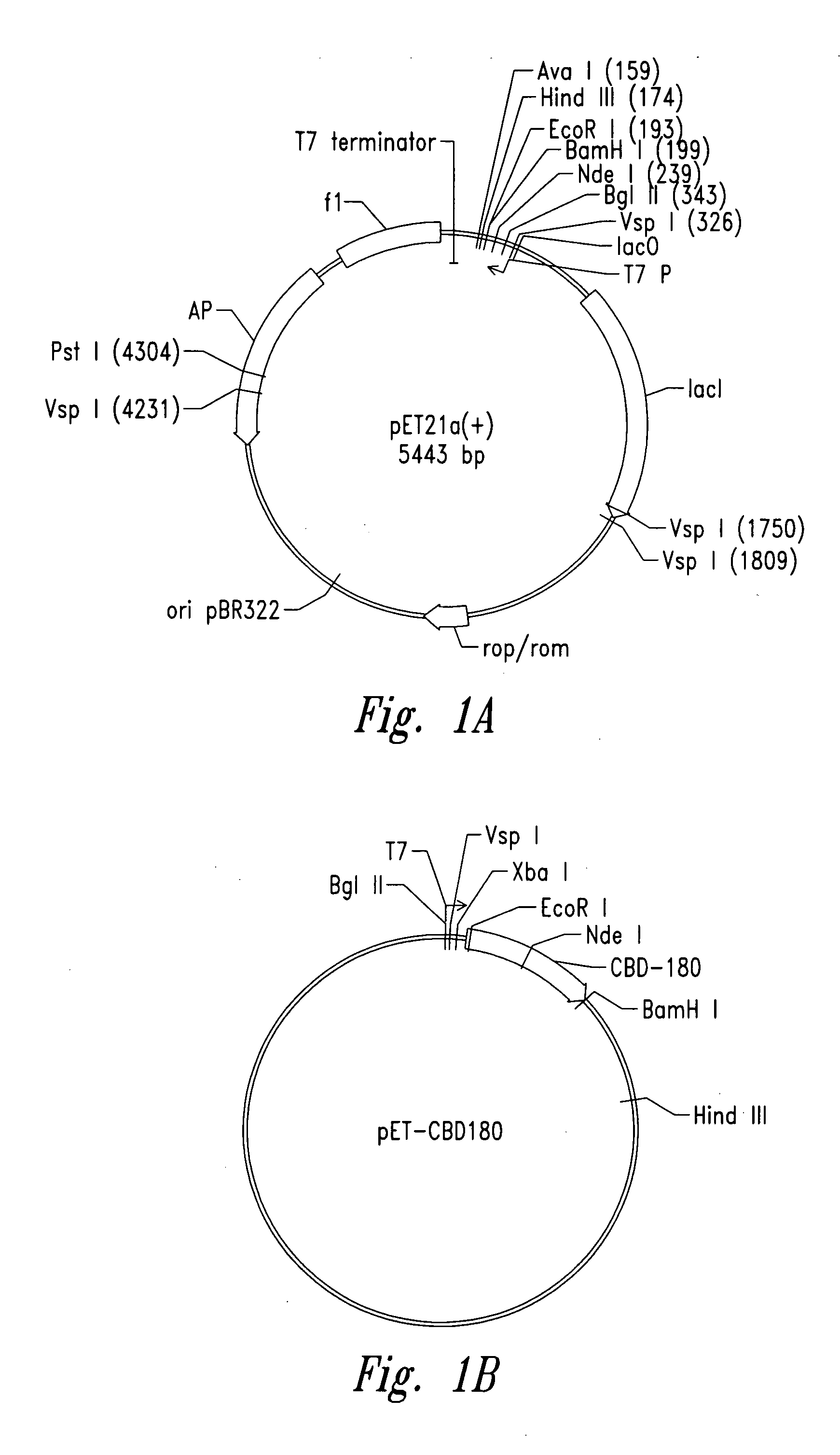
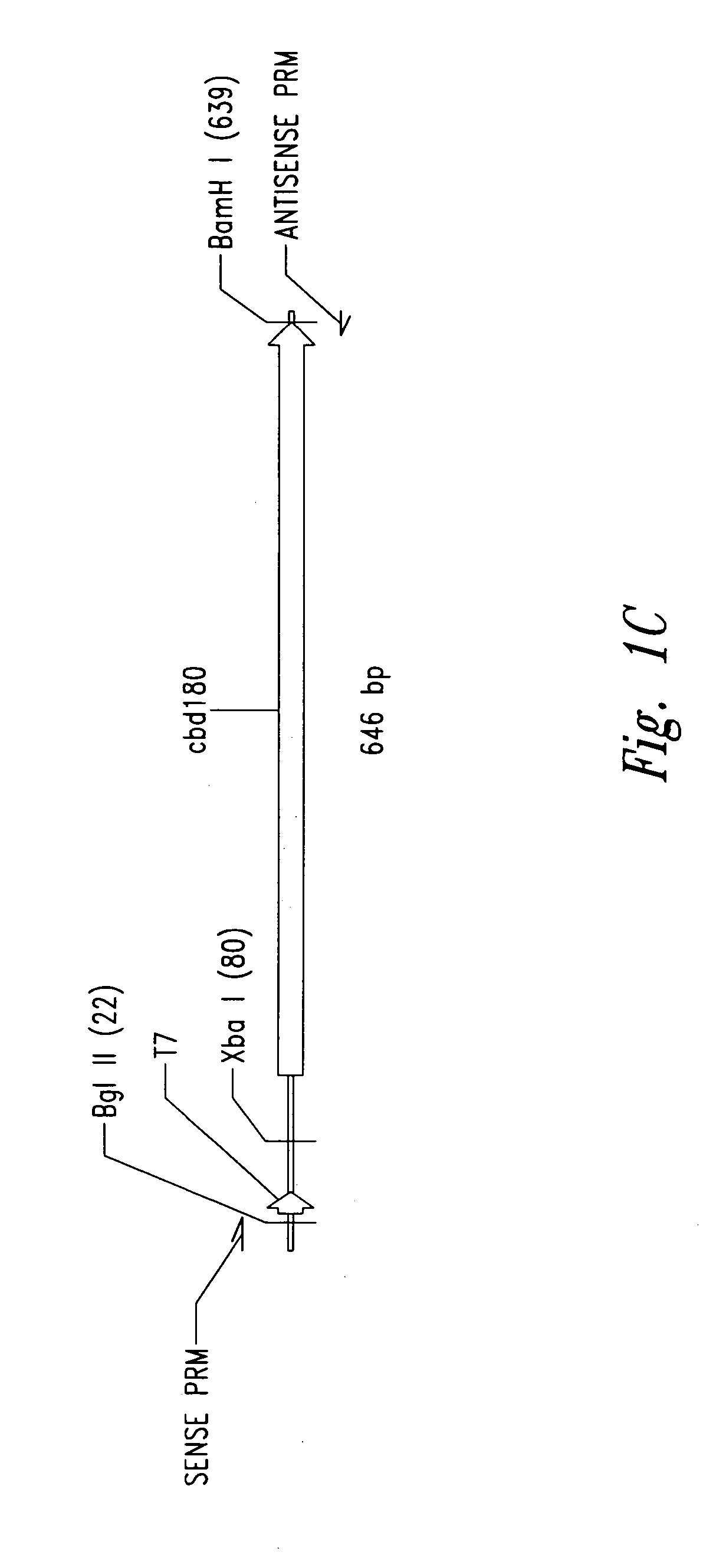
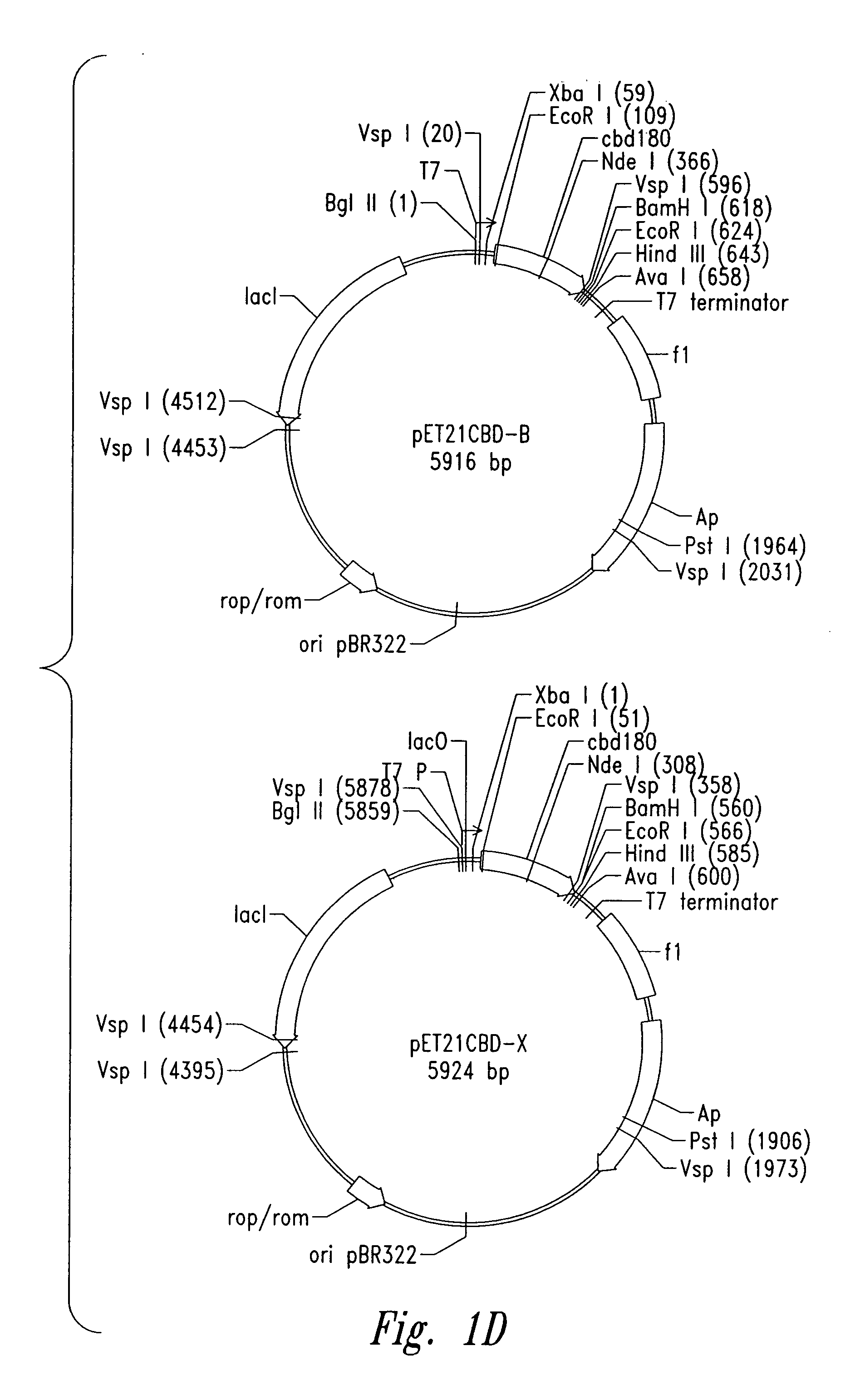
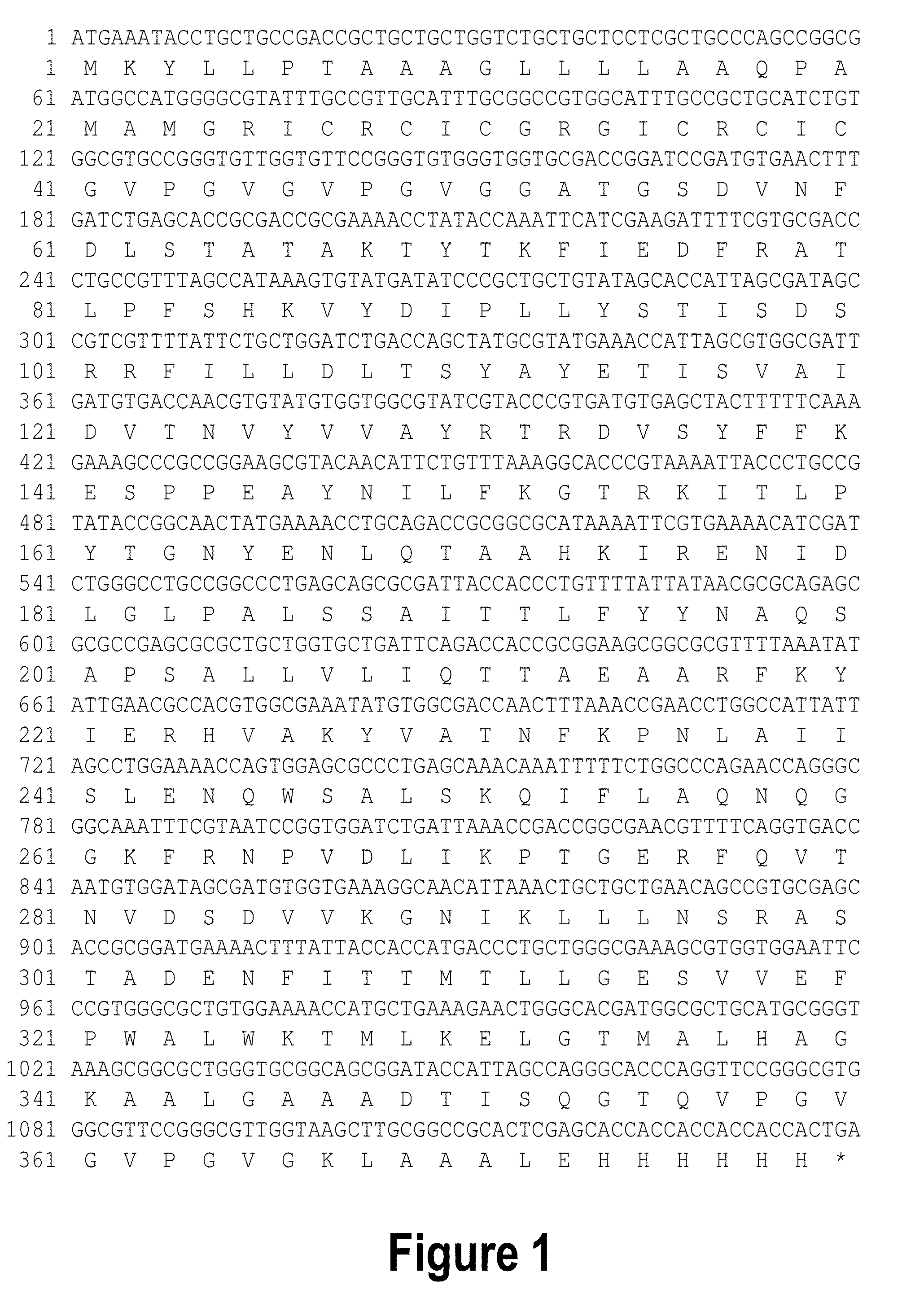Patents
Literature
59 results about "Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cationic antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are gene-encoded peptides of the host defence system made up of 12-50 amino acids, with at least 2 positive charges conferred by lysine and arginine residues and about 50% hydrophobic amino acids (Hancock and Scott 2000).
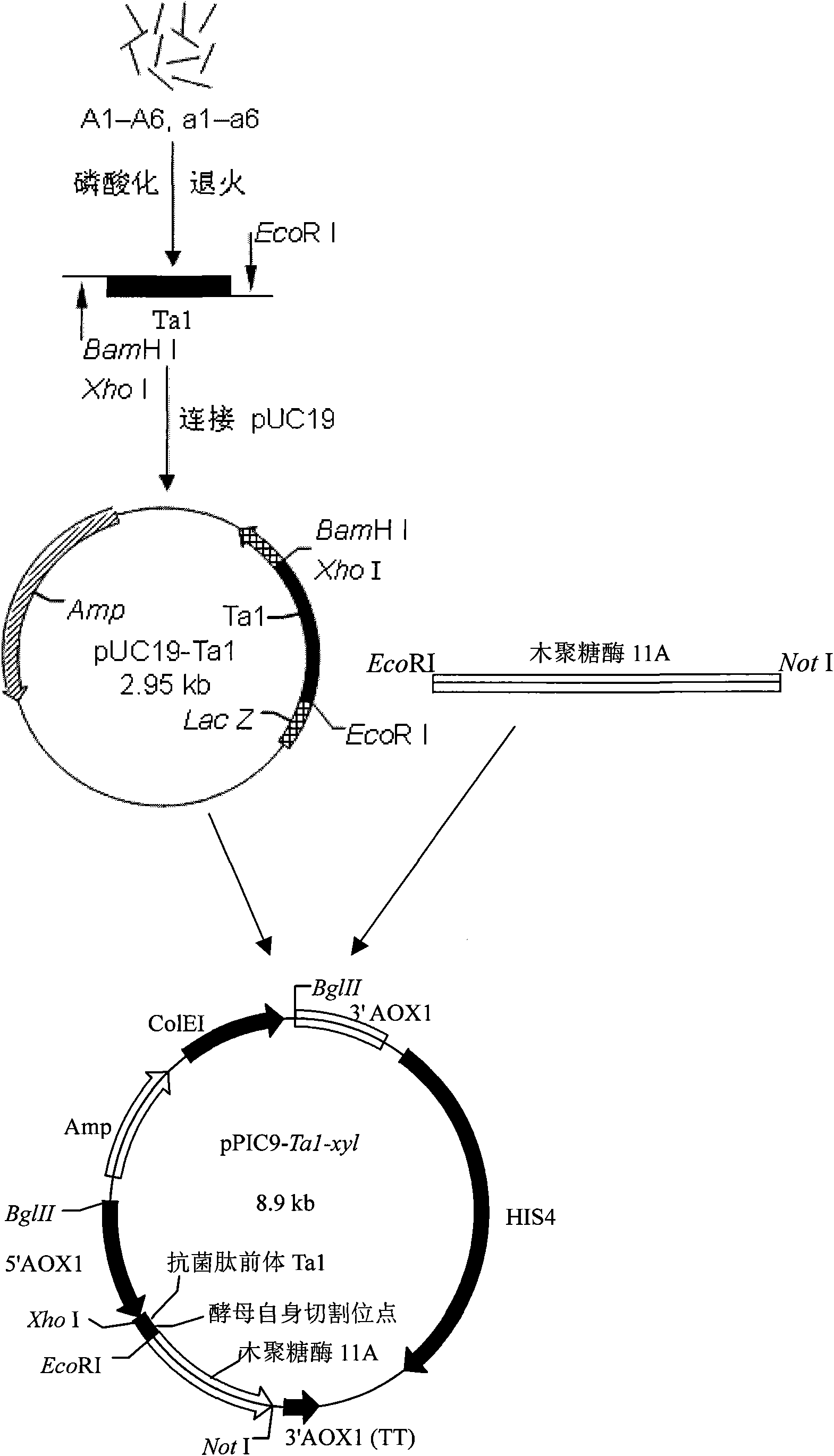
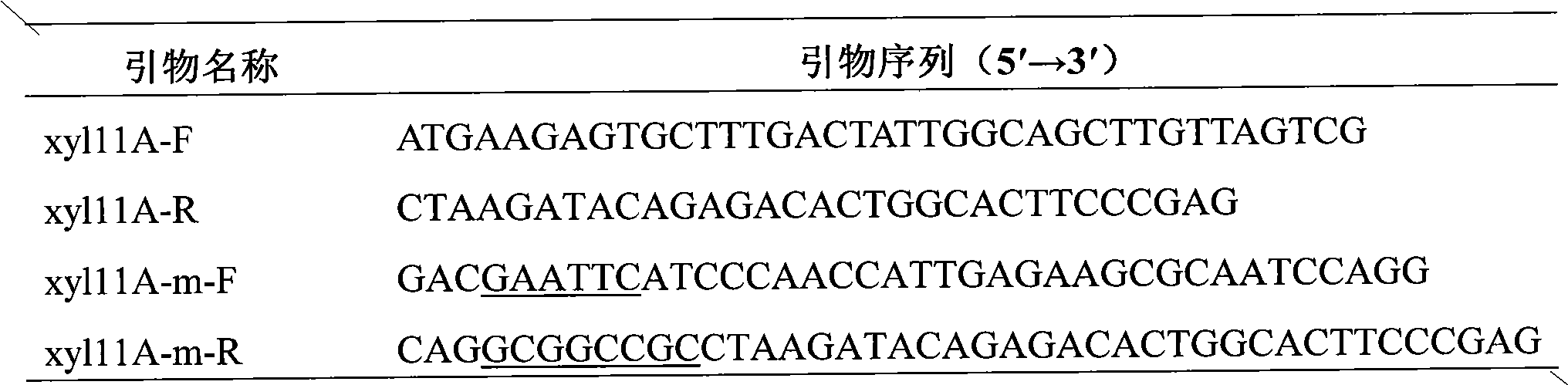
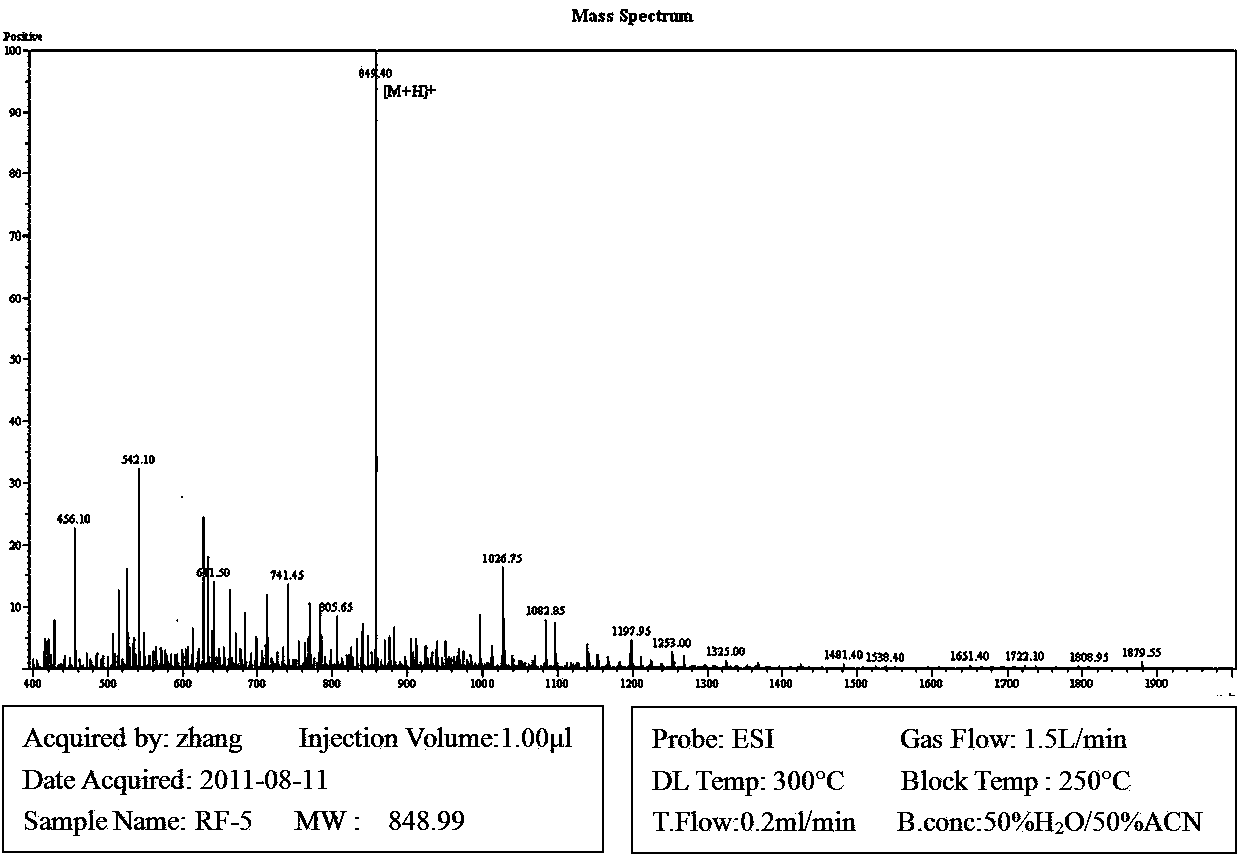
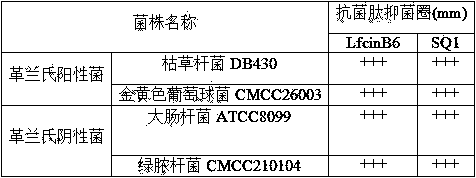
Method for effectively expressing cationic antibacterial peptides in pichia pastoris
ActiveCN101914565AHigh expressionToxic reductionFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisProteinase activity
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a method for effectively expressing cationic antibacterial peptides in pichia pastoris. In the method, the cationic antibacterial peptides can be driven to be expressed by acid enzyme; a large amount of acidic amino acid of the acid enzyme can neutralize the alkaline amino acid of the cationic antibacterial peptides to keep the cationic antibacterial peptides out of the attack of host protease; the yield of antibacterial peptides can be judged directly by the activity of expressed recombinase; moreover, expressed products and the antibacterial peptides can be directly applied at the same time.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Micromolecule synthesized anti-microbial peptide, as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104292301ASimple structureReduce manufacturing costAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisAntibiosis
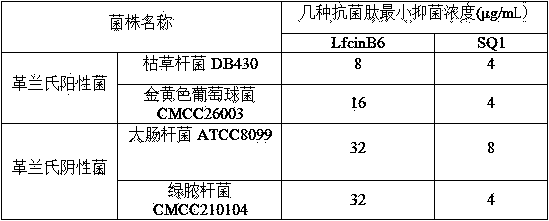
The invention discloses a micromolecule synthesized anti-microbial peptide, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The sequence of a cationic anti-microbial peptide is SQ1: R-W-W-R-F-NH2 (Arg-Arg-Trp-Trp-Arg-NH2), and the preparation method is the solid-phase chemosynthesis method. The micromolecule synthesized anti-microbial peptide has broad-spectrum cytotoxicity to gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria, has stronger bactericidal activity than a natural anti-microbial peptide, is simple in structure, convenient for artificial synthesis without any modification and connection, has the advantages of small hemolytic toxicity and no poison effects on animal and plant cells, and has an important value in development and application of antimicrobial agents.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Cation antibacterial peptides, their preparation method and application
ActiveCN102766196AImprove the bactericidal effectAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsCombinatorial chemistryAntibacterial activity
The invention belongs to the field of medicines and specifically relates to a set of cation antibacterial peptides with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity, their preparation method and an application thereof. The general formula of an amino acid sequence of the cation antibacterial peptides provided by the invention is X-(C)m-(B)n-His-X.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +2
Cation antibacterial peptide
An anionic antibacterial peptide used as the medicine for treating the diseases caused by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria and fungus is composed of an alkaline amino acid cluster consisting of 2-4 continuous alkaline amino acids and a neutral amino acid fragment consisting of 8-9 neutral amino acids. It has high antibacterial activity and low hemolytic activity.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Efficient methods for producing antimicrobial cationic peptides in host cells
Owner:COMPHARE TRUST COMPANY
Method for representing activity relationships of antibacterial proteins or polypeptides
InactiveCN102663271AFit closelyGood forecastSpecial data processing applicationsAntibacterial proteinTopological index
The invention discloses a method for representing activity relationships of antibacterial proteins or polypeptides. The method is characterized in that starting from 85 structural parameters and topological indexes of representation molecules, a characteristic descriptor comprising 166 amino acid systems is obtained through principle component analysis (PCA), namely a principle component score vector of structural and topological variable (VSTPV).. The VSTPV is applied to study of the quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR) of 101 antibacterial cationic peptides and 28 hydrolyzed bovine lactoferricins (BPPs), the models have better fitting and forecasting capabilities, and the cross validation related coefficients and related coefficients are above 0.70. The study shows that the VSTPV can well represent coded and uncoded amino acids and establish polypeptides with stronger forecasting capabilities and derivative QSAR models thereof.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Targeted Delivery of Antimicrobial Agents
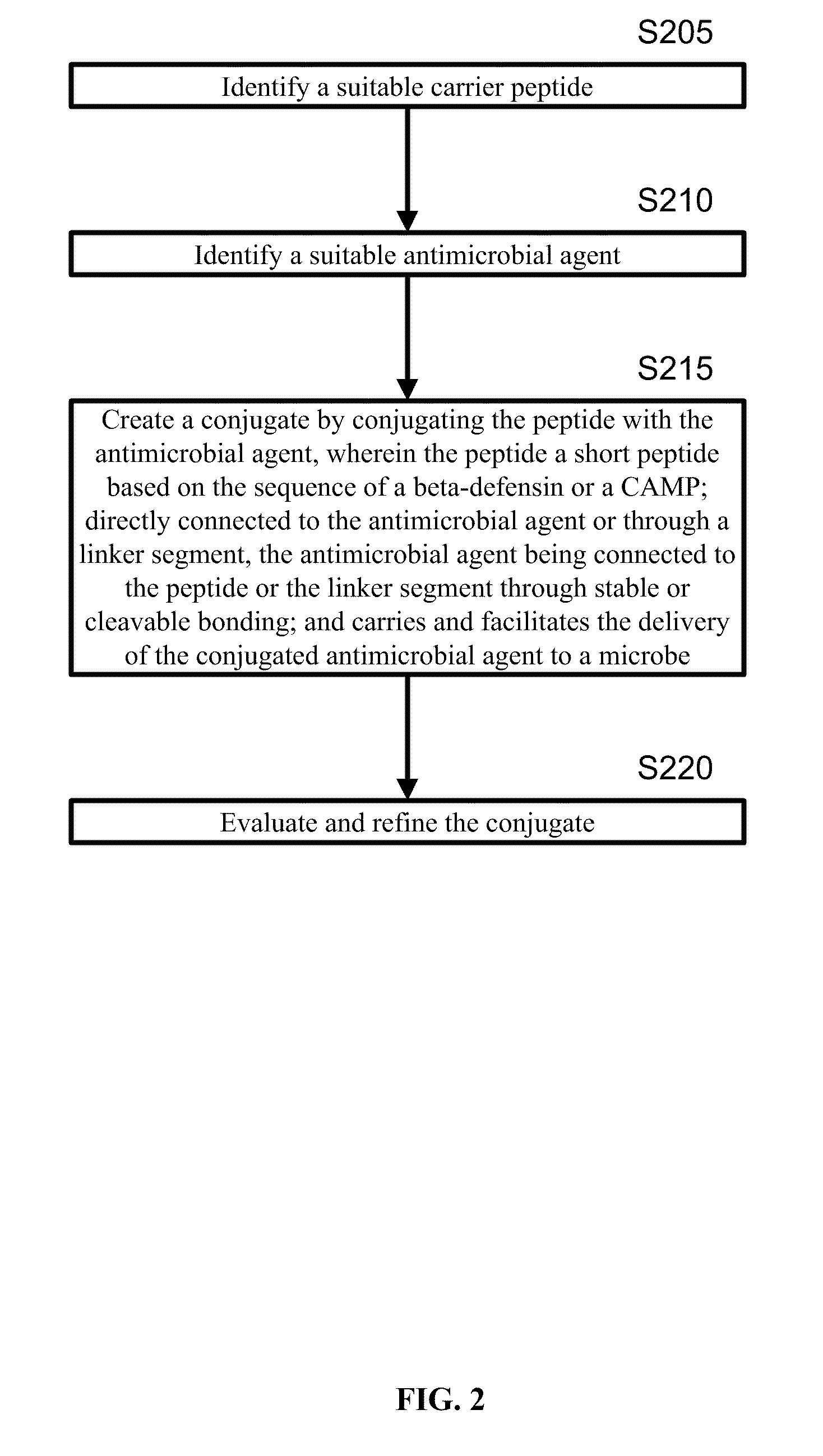
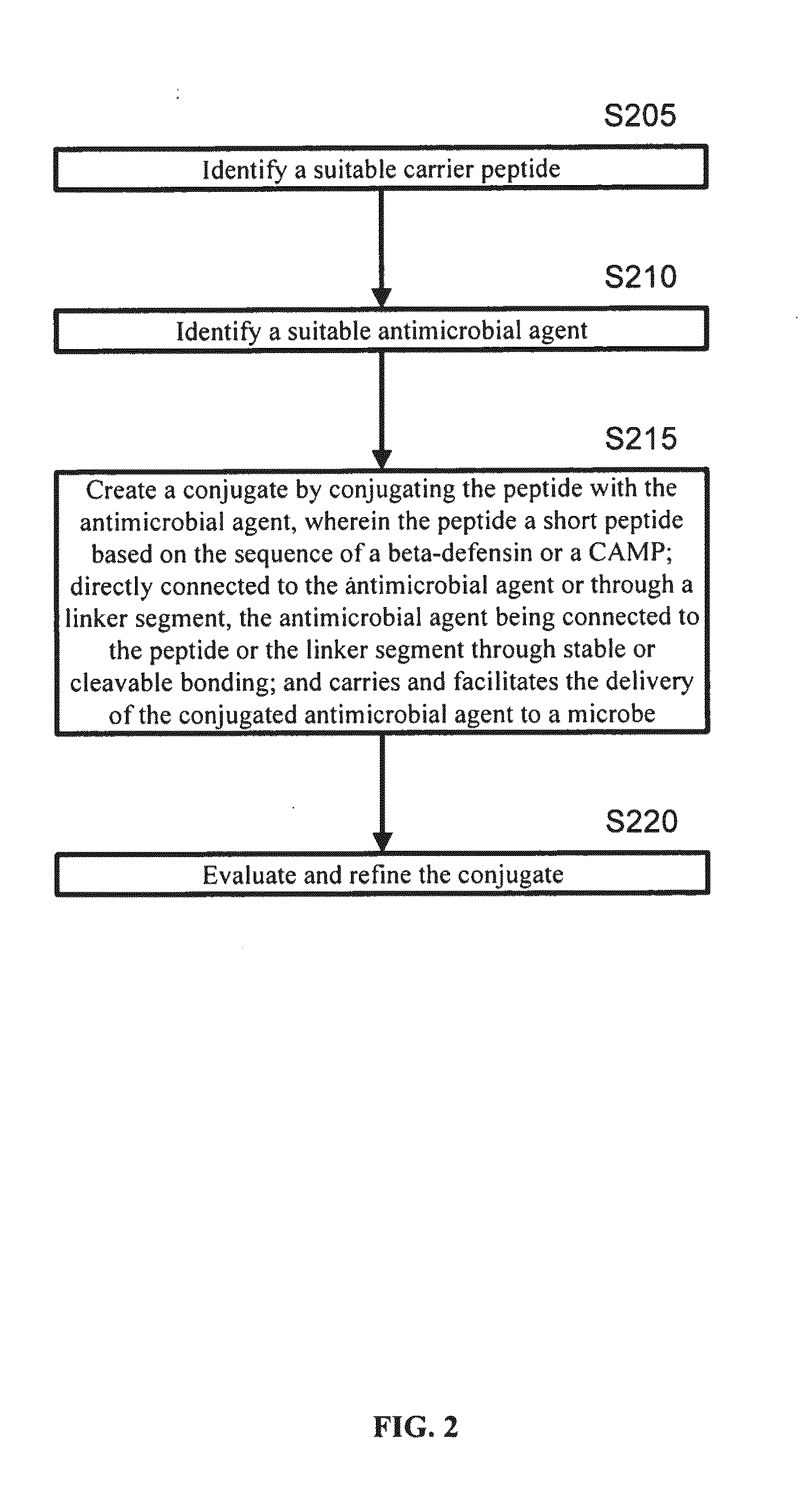
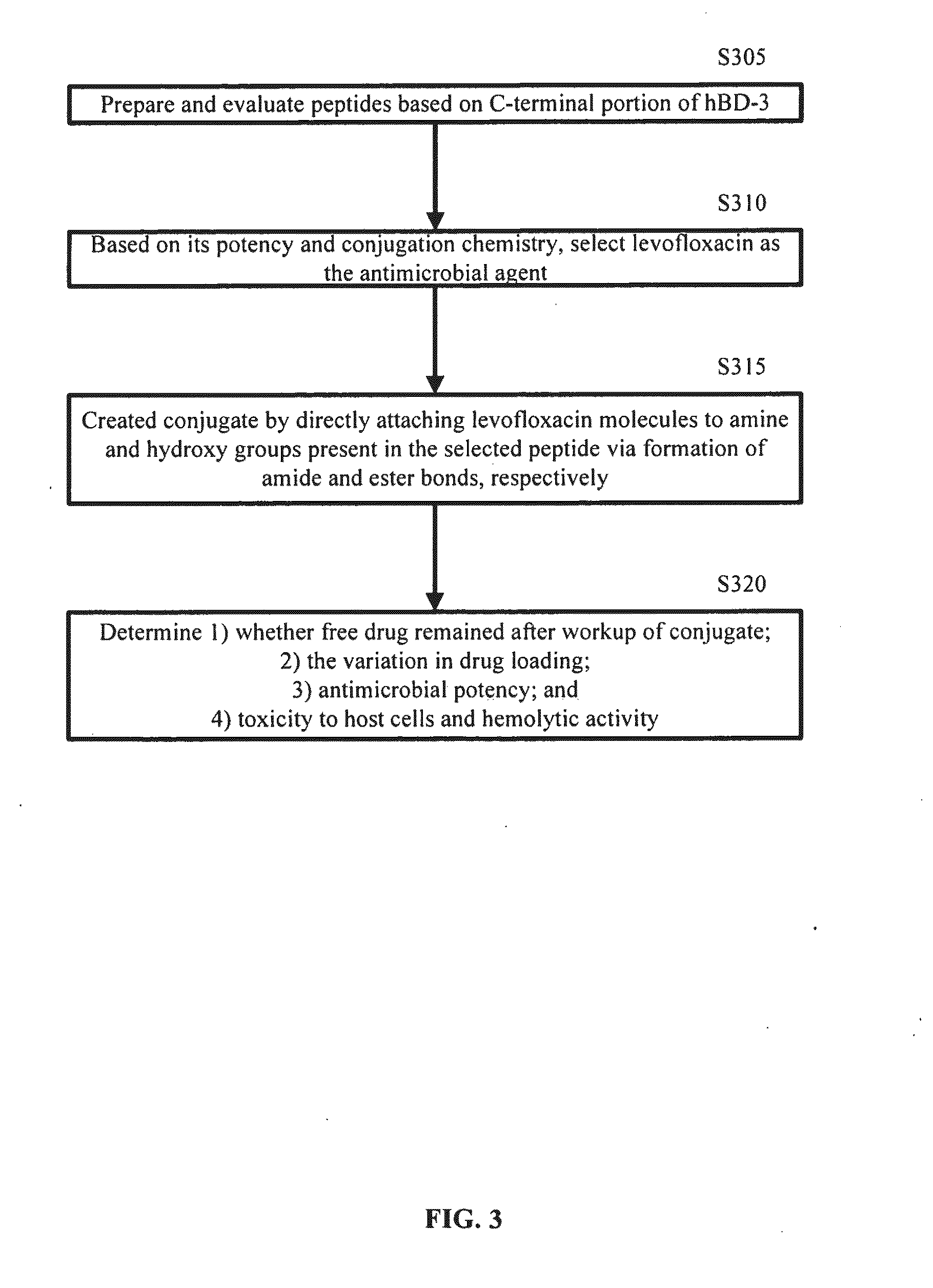
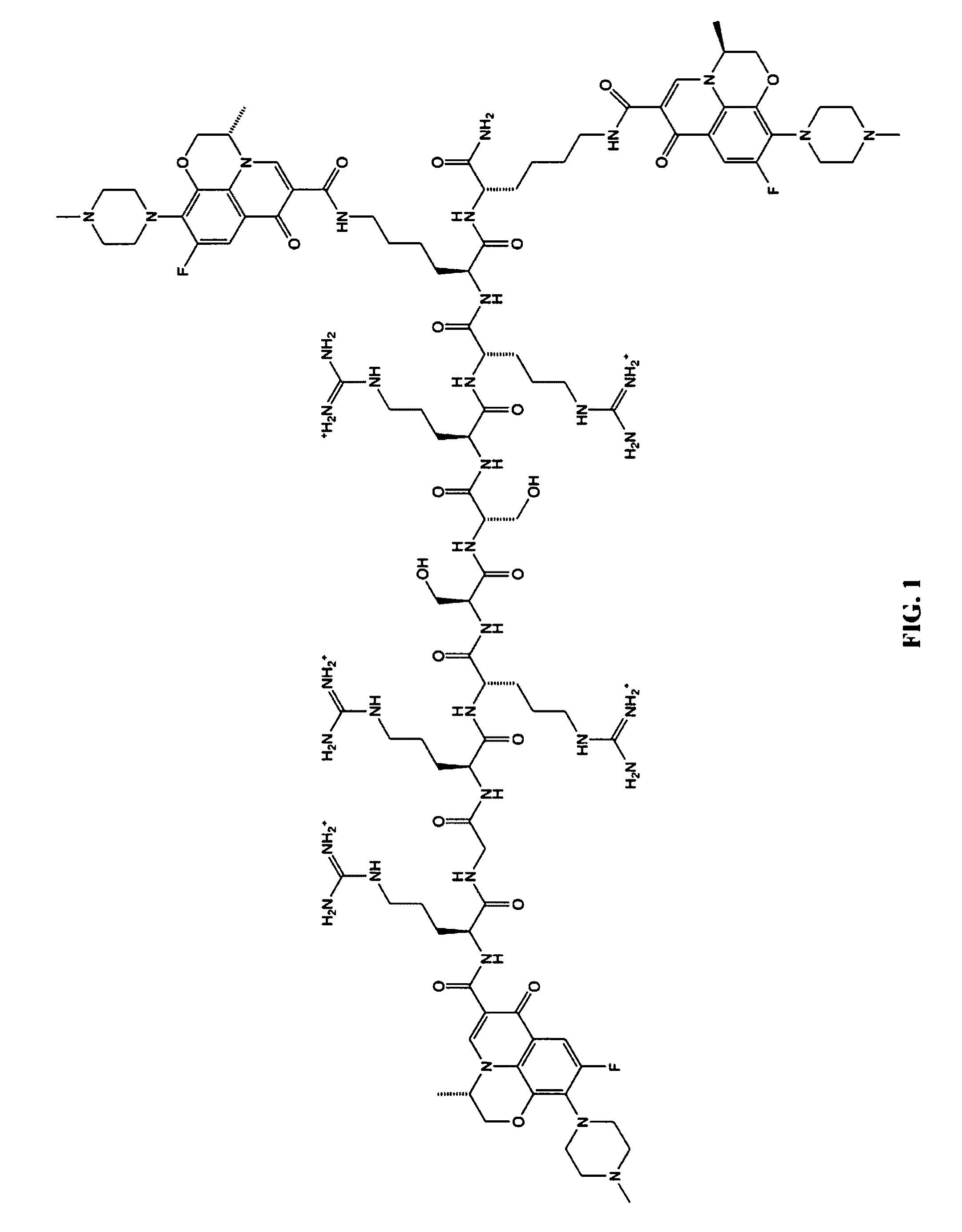
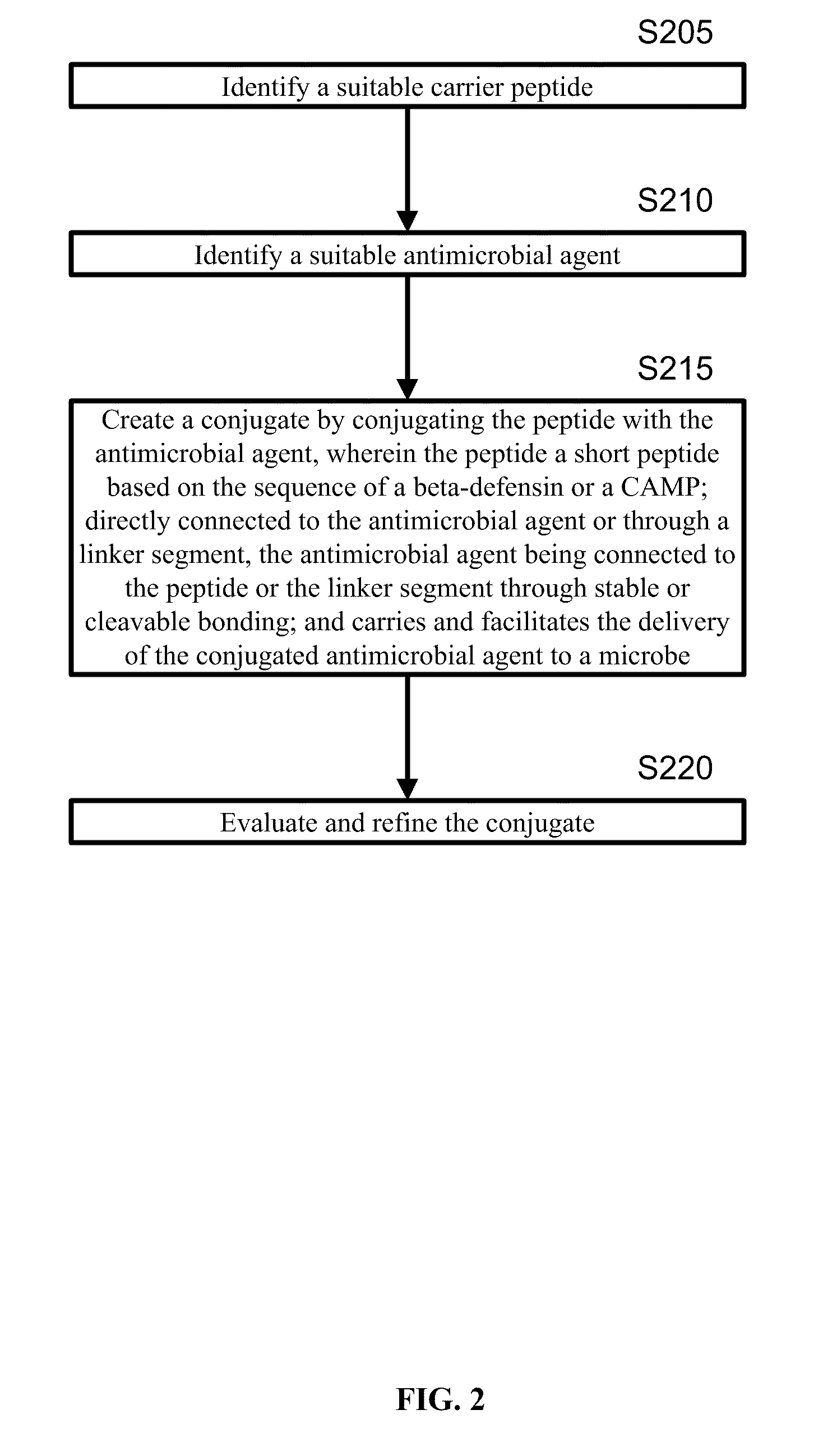
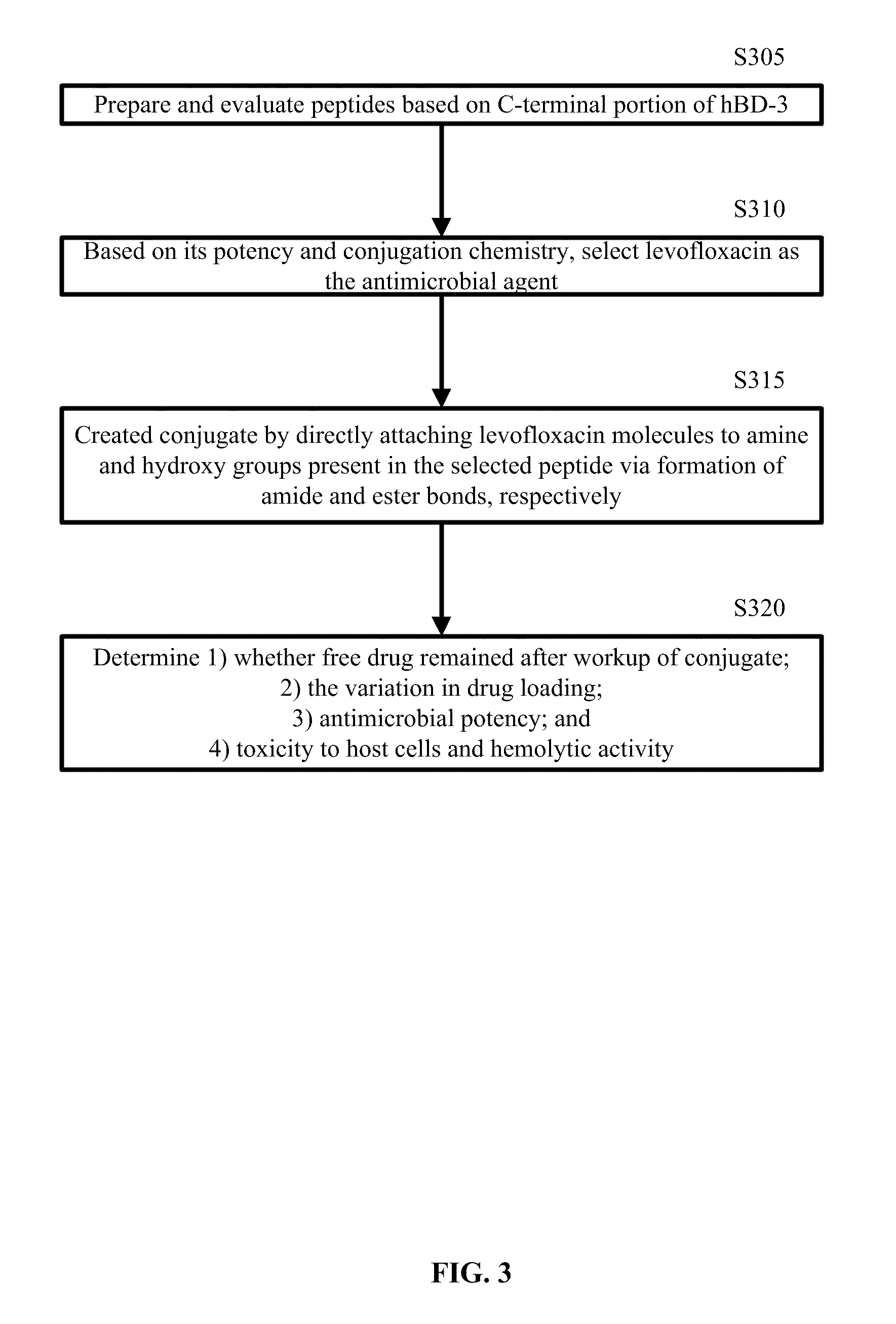
A cationic antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) conjugate is disclosed. The CAMP conjugate may be made by identifying a suitable carrier peptide; identifying a suitable antimicrobial agent; creating a conjugate by conjugating the peptide with the antimicrobial agent; and evaluating and refining the conjugate. The peptide may be short peptide based on the sequence of a CAMP, such as human β-defensin-3. The peptide can be directly connected to the antimicrobial agent or through a linker segment. The antimicrobial agent may be connected to the peptide or the linker segment through stable or cleavable bonding. The peptide may carry and facilitate the delivery of the conjugated antimicrobial agent to a microbe.
Owner:GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
Method for obtaining and fermenting prokaryotic genetic-engineered hybrid cationic antimicrobial peptide CC
The invention discloses a method for obtaining escherichia coli genetic-engineered bacteria of recombinant hybrid cationic antimicrobial peptide CC. The principle of the method disclosed by the invention is as follows: bioinformatics technology and molecular biological technology are combined to select natural antimicrobial peptide with therapeutic potential, a molecular design of the antimicrobial peptide is carried out, the antimicrobial peptide is synthesized to a gene sequence after being translated, and the escherichia coli genetic-engineered bacteria of hybrid cationic antimicrobial peptide CC is constructed by such technical programs as cloning vector construction, expression vector construction, and the like. A DPP tripeptide sequence is arranged between a GST tag and the antimicrobial peptide, and the DPP tripeptide sequence is purified after being expressed. IPTG (Isopropyl beta-D-1-Thiogalactopyranoside) induction is replaced by lactose induction to reduce the cost and optimize the culture conditions and the culture medium composition, and the lactose induction is combined with fermentation. As shown in a biological activity identification result, the escherichia coli genetic-engineered bacteria has a broad application prospect in food, feed and aquaculture due to efficient antimicrobial activity, thermal stability and pH stability and very weak hemolytic activity.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Microdetermination method for measuring minimum inhibitory concentration and minimal bactericidal concentration of cationic antimicrobial peptide
ActiveCN103173517AMeet measurement needsEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMinimum inhibitory concentration
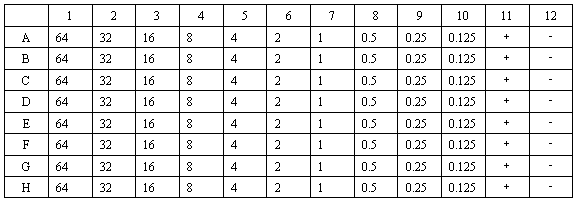
The invention discloses a microdetermination method for measuring minimum inhibitory concentration and minimal bactericidal concentration of cationic antimicrobial peptide. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a reagent, namely preparing an MHB culture medium; 2) preparing bacterial suspension, namely reviving the bacteria to logarithmic phase, and preparing bacterial suspension with a certain concentration; 3) counting the bacterial suspension, namely performing coubling dilution on the bacterial suspension in the step 2), dripping and counting; 4) diluting the agent, namely performing coubling dilution on the agent to different testing concentration gradient; 4) measuring the minimum inhibitory concentration, namely mixing and culturing the diluted agent in the step 4) with the bacterial suspension prepared in the step 2), and observing whether macroscopic bacterial precipitation exists; and 6) measuring the minimal bactericidal concentration, namely culturing the testing dripping plate with the antibacterial effect in the step 5), and observing whether colony growth exists. The method for measuring the minimum inhibitory concentration and minimal bactericidal concentration of cationic antimicrobial peptide has the characteristics of low interference, trace, convenience and rapidness.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Group of animal-derived cationic antibacterial peptides and its application
InactiveCN102391362AHigh bactericidal activityHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsLactoferricinStructural analysis
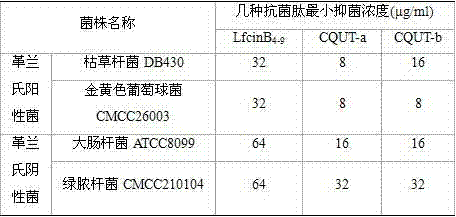
The invention provides a group of novel artificially designed animal-derived cationic antibacterial peptides, which is synthesized on the basis of a structural analysis of a natural lactoferricin antibacterial peptide sequence, the series of the antibacterial peptide sequence is shown as the following: CQUT-a: Phe Arg Trp Trp Trp Gln Arg; CQUT-b: Arg Arg Gln Trp Phe Trp. The antibacterial peptides are obtained by using a solid phase chemical method. The animal-derived cationic antibacterial peptides have the advantages that antibacterial spectrum is wide, no modification or connection is required, the structure is simple and artificial synthesis is convenient. Experiment proves that both G<+>bacteria (gram positive bacteria) and G<->bacteria (gram negative bacteria) possess the advantages of substantial bacteriostasis and bactericidal activity, long continuance and no hemolytic toxin; the animal-derived cationic antibacterial peptides have important value on aspects of exploitation and application of medicines for treating bacterial infection diseases.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Efficient methods for producing anti-microbial cationic peptides in host cells
Endogenously produced cationic antimicrobial peptides are ubiquitous components of host defenses in mammals, birds, amphibia, insects, and plants. Cationic peptides are also effective when administered as therapeutic agents. A practical drawback in cationic peptide therapy, however, is the cost of producing the agents. The methods described herein provide a means to efficiently produce cationic peptides from recombinant host cells. These recombinantly-produced cationic peptides can be rapidly purified from host cell proteins using anion exchange chromatography.
Owner:COMPHARE TRUST COMPANY
Antibacterial peptoid and vesicle and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106279635AReduce the chance of occurrenceHas broad-spectrum antibacterial propertiesLiposomal deliveryDrug releaseAntibacterial property
The invention provides an antibacterial peptoid and a vesicle and a preparation method and application thereof. A hydrophilic part of the antibacterial peptoid is a lysine residue, and a hydrophobic part of the antibacterial peptoid is a diisocyanate unit, and the lysine residue links with the diisocyanate unit by means of a covalent bond. The antibacterial drug-loading vesicle is formed by self-assembling of the antibacterial peptoid and a drug in a mixture of an organic solvent and water. The antibacterial peptoid of the invention has a similar structure to that of a natural cationic anti-microbial peptide, and thus has a similar antibacterial mechanism; the antibacterial peptoid has broad-spectrum antibacterial properties, and cause the bacteria to be hard to produce drug resistance thereto; the antibacterial drug-loading vesicle has both antibacterial effect and dug-loading function, and can achieve sustained drug release.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Induction of innate immunity by vitamin d3 and its analogs
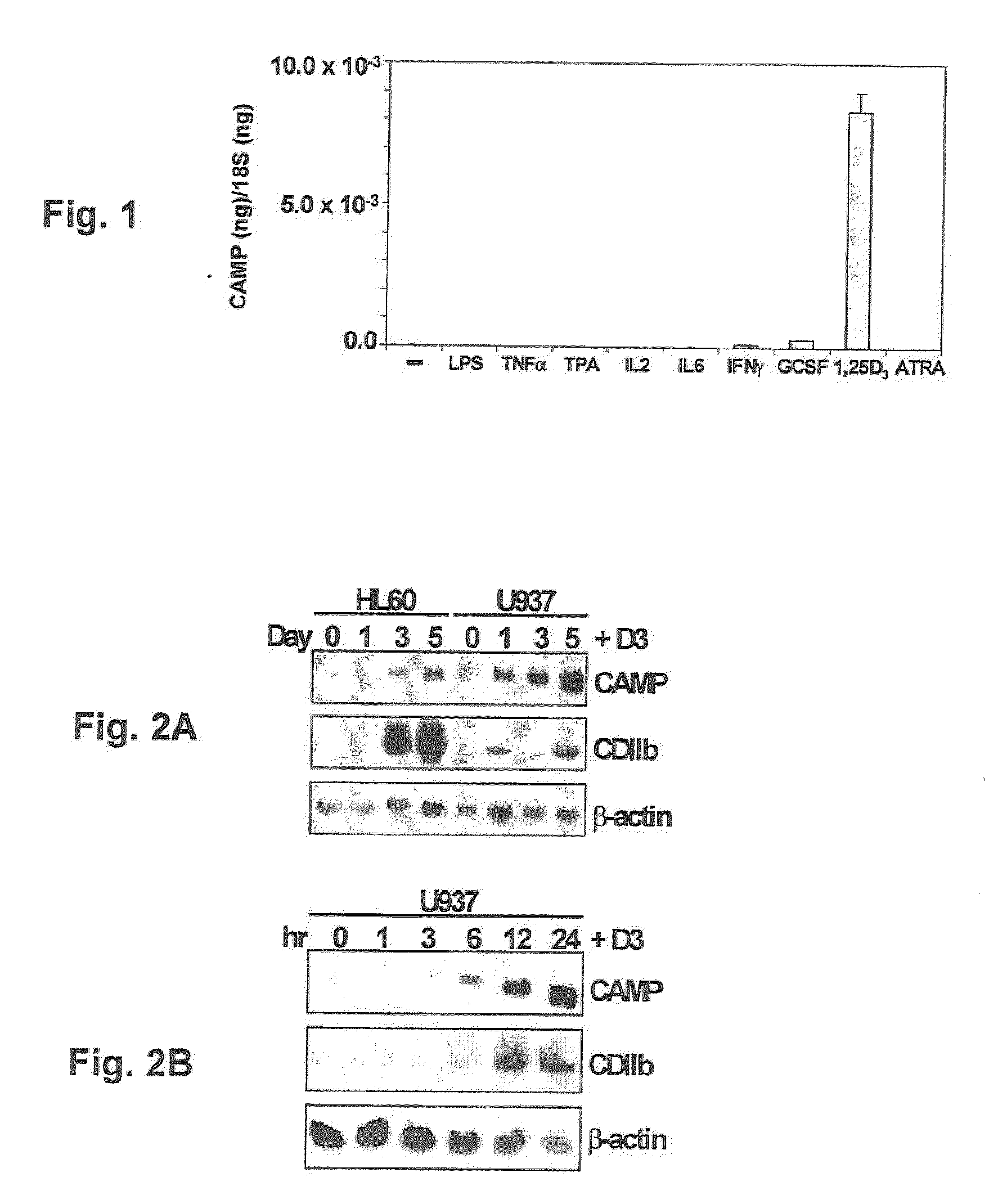
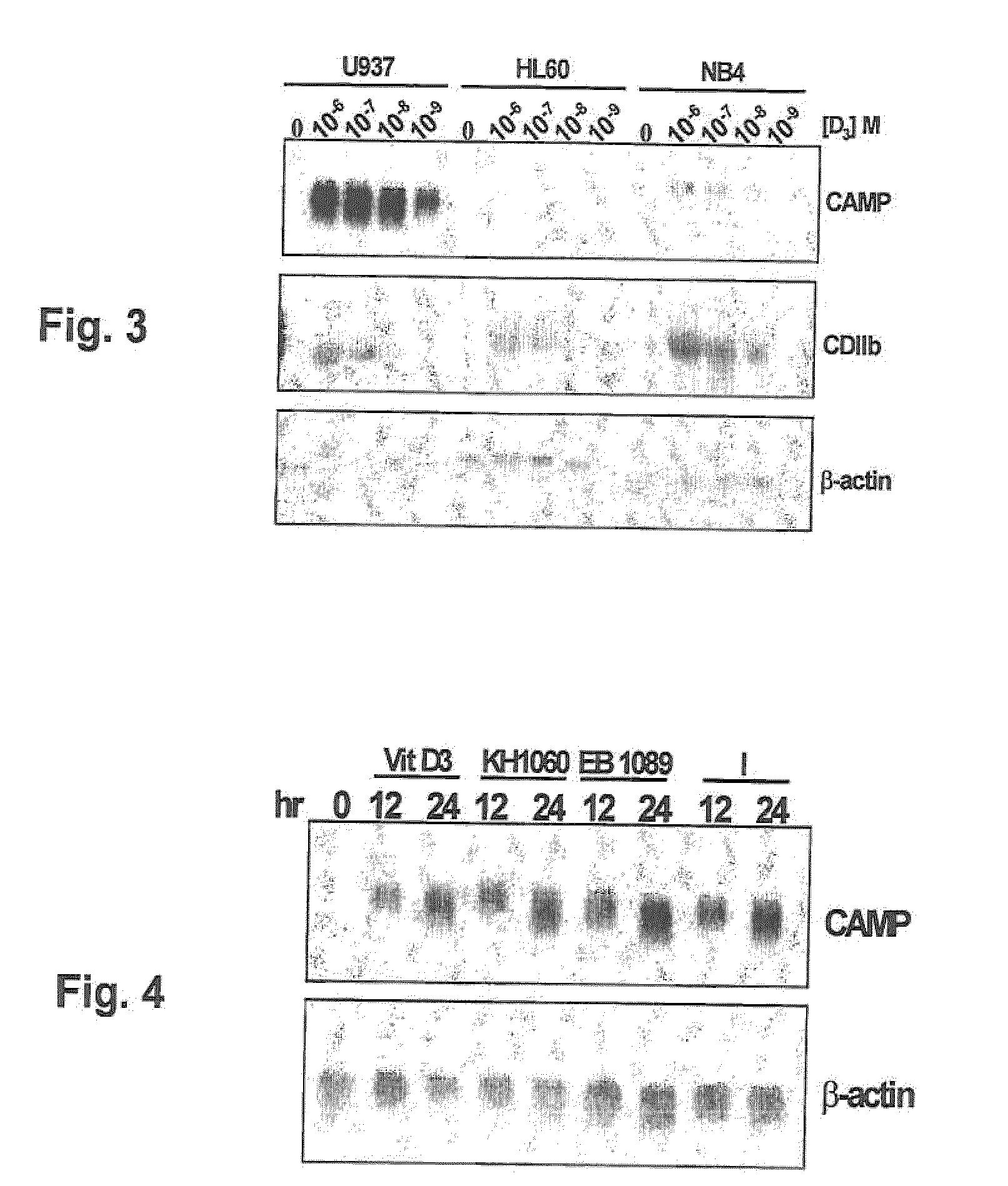
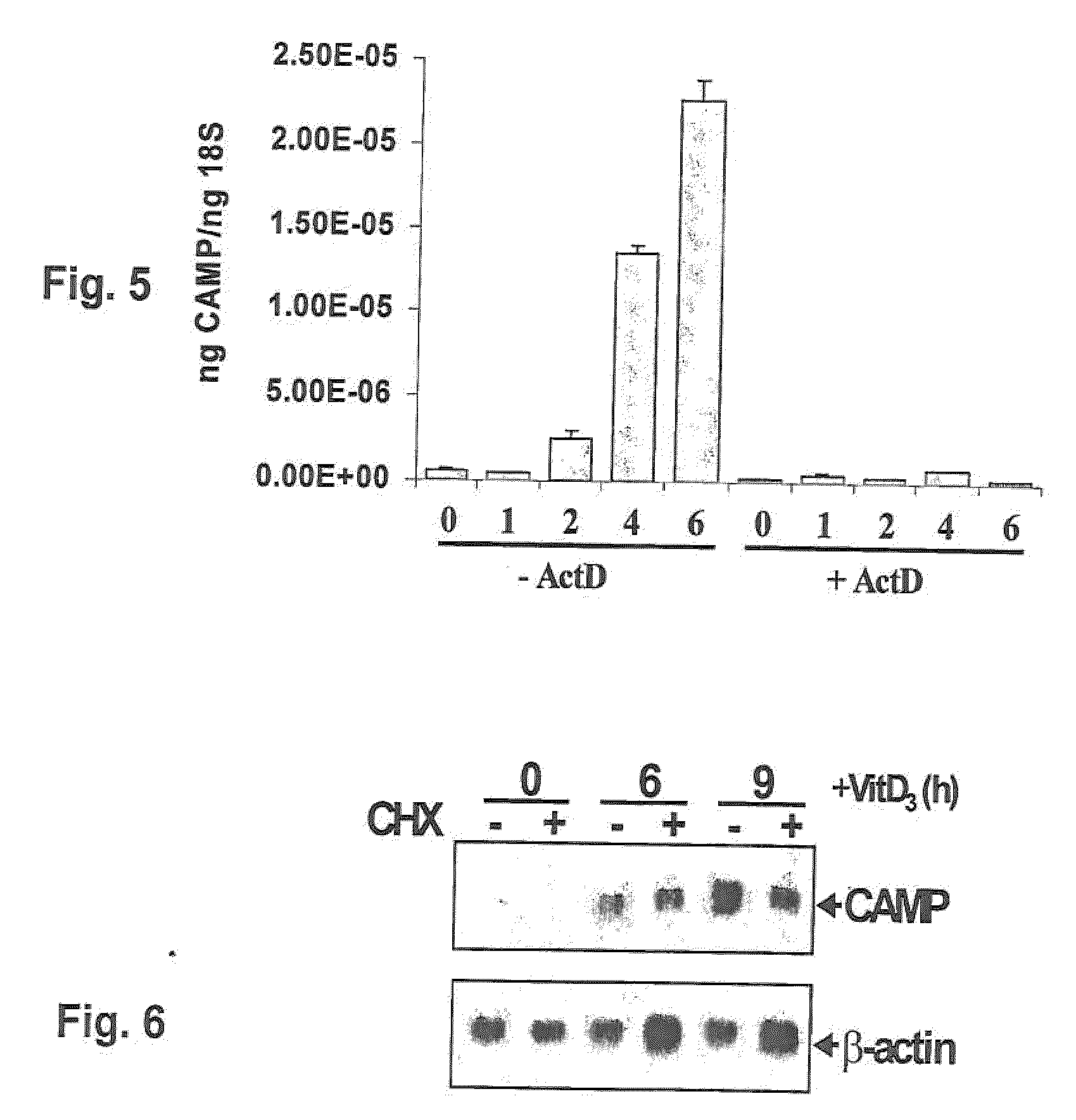
Cationic antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are an integral part of the innate immune system. Cathelicidin and defensin homologs from a variety of species exhibit broad-range bactericidal activity. The human cathelicidin analog, hCAP18, is encoded by the CAMP gene. Vitamin D3 and its analogs upregulate transcription of CAMP and defensin β2 (defB2) genes, leading to increased expression of hCAP18 mRNA and defB2. Induction of CAMP was observed in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), immortalized keratinocyte and colon cancer cell lines, as well as normal human bone marrow (BM)-derived macrophages and fresh BM cells. The present invention provides methods of inducing cathelicidin production by administering Vitamin D3 or Vitamin D3 analogs, as well as methods of treating skin infections and infections of the colon, sepsis and wound healing, preventing bacterial growth on skin grafts, promoting angiogenesis, and promoting chemoattraction by administering Vitamin D3 or Vitamin D3 analogs to upregulate cathelicidin and defensin expression.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
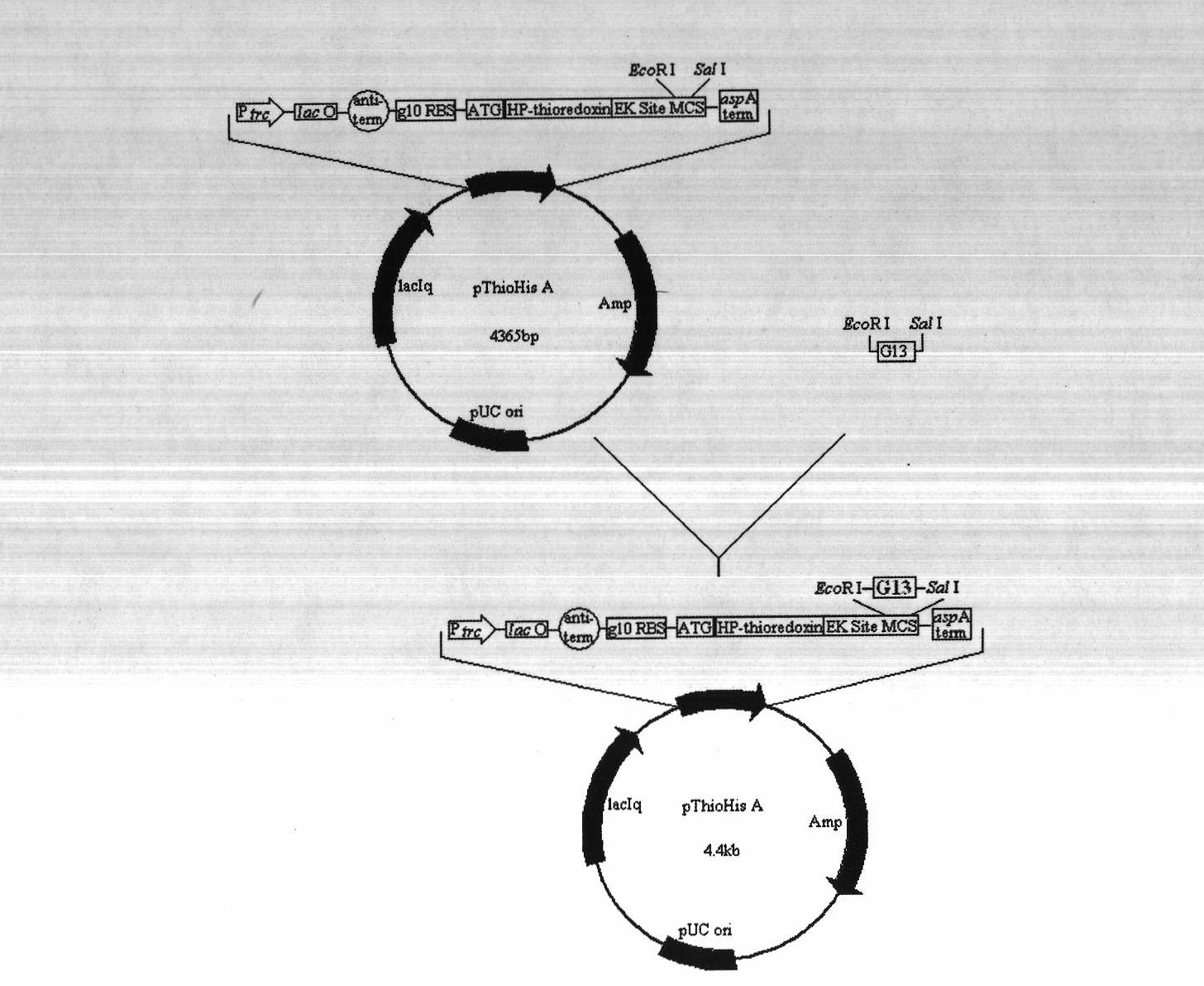
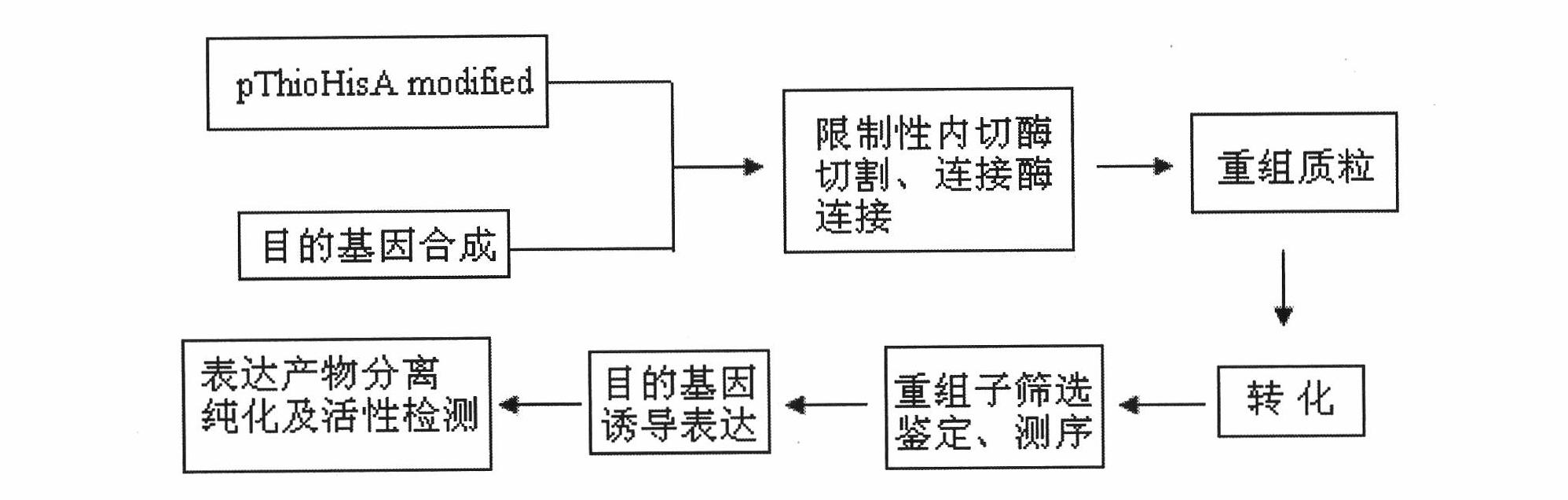
Construction of gene engineering bacteria for expressing recombinant cationic antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) G13 escherichia coli
ActiveCN102212541ALow toxicityIncreased toxicityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionAntimikrobielle peptideEscherichia coli
The invention discloses construction of gene engineering bacteria for expressing recombinant cationic antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) G13 escherichia coli, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and biology. A fusion head gene is connected with an AMPs gene to construct recombinant plasmid and convert escherichia coli BL21 competent cells, so that the expression yield is improved, and more effective treatment is obtained. The invention aims to design a shorter fusion head which has higher hydrophobic property, and the C final fragment of the fusion head has more negative charges, so that the fusion head can protect small molecular target AMPs; the toxicity of the AMPs to host cells is neutralized; and the cationic AMPs comprise alpha spiral amphipathic AMPs with net positivecharges and contain nucleotide sequences SEQ ID: NO 1 and SEQ ID: NO 2. According to the construction method, DNA recombination and gene engineering technology such as restriction endonuclease cutting, ligase connection and the like are used.
Owner:广东希普生物科技股份有限公司
New cationic antimicrobial peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN104478996ABroad-spectrum antimicrobial activityEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisAnimal testing
The invention relates to a new cationic antimicrobial peptide and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biochemical polypeptide medicines. The new cationic antimicrobial peptide is a small molecule polypeptide which is designed artificially and synthesized chemically by taking a natural antimicrobial peptide in skin secretions of rana temporaria chensinensis david as a template. The small molecule polypeptide comprises 13 amino acid residues, and the C terminal of the small molecule polypeptide is amidated. The small molecule polypeptide has the sequence of IKKILSKIKKLLK-NH2, the molecular weight of 1552.13Da and the isoelectric point of 10.70, and the small molecule polypeptide has 6 positive charges. Tests prove that the small molecule polypeptide has broad-spectrum inhibiting and killing effects on a variety of bacteria and human cancer cells in vitro and has no hemolytic activity and eukaryotic cell toxicity in an antimicrobial and anticancer concentration range, and drug resistance is not easy to produce. In addition, experiments on animals show that the small molecule polypeptide has the effect of resisting wound infection. The small molecule polypeptide has small molecular weight, is synthesized artificially and conveniently, has extremely high application value and can be used for preparing new antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer medicines.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
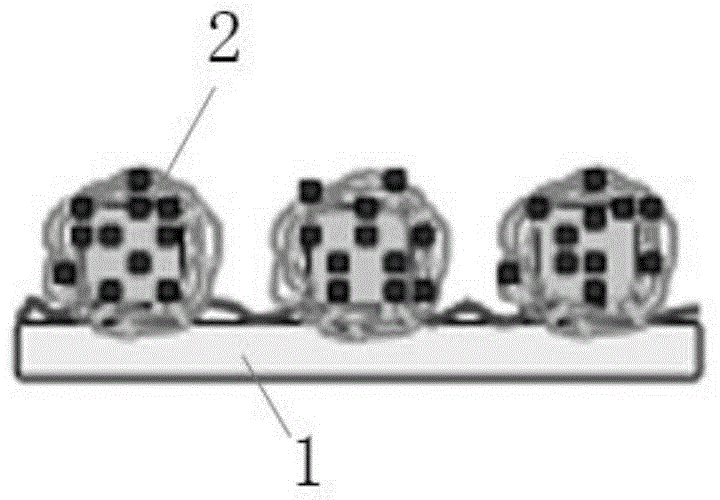
Intelligent antibacterial nano-hydrogel bone fracture plate with topological structure and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses an intelligent antibacterial nano-hydrogel bone fracture plate with a topological structure. The surface of a substrate is coated with composite micelles, wherein each composite micelle comprises a polyethylene glycol-co-acrylic acid microgel core which serves as inner core and an outer layer controlled release shell which is a pH sensitive polymethylacrylic acid microgel layer; the polyethylene glycol-co-acrylic acid microgel core and the pH sensitive polymethylacrylic acid microgel layer form intelligent charge gradient radial distribution; the composite micelle coating forms a topological antibacterial structure surface on stainless steel, titanium metal or titanium alloy bone fracture plate and is loaded with beta-defensin-1-3, lactoferrin 1-11, LL-37, histadine-rich protein analogues, endogenous antimicrobial peptide-1 and artificially synthesized cationic antimicrobial peptides. The intelligent antibacterial nano-hydrogel bone fracture plate with the topological structure is used as an intelligent simulation response mechanism of contact sterilization when the bacteria are generated on the surface of an orthopedic object and serve as a stimulation factor, so that osteoblasts can quickly grow on the surface of the orthopedic object; the bacterial adhesion is reduced; the bacteria are killed by antimicrobial peptide; target points used for controlling the formation of bacterial biofilms can be really restrained in the initial stage, thereby finally reducing the occurrence rate of orthopedic device related infections.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Dosage regime of fusion compounds
Owner:BIOVALENCE
Method for producing recombined cationic antibacterial peptide by adopting co-expression anionic ligand
ActiveCN101696417AAvoid it happening againImprove product qualityMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliPlasmid Vector
The invention discloses a method for producing a recombined cationic antibacterial peptide by adopting a co-expression anionic ligand, which is characterized in that an independent anionic ligand with net negative charges is co-expressed at the same time of expressing the cationic antibacterial peptide, namely, a cationic antibacterial peptide gene and an encoded DNA sequence of the anionic ligand are cloned to a plasmid vector and expressed in a colibacillus host cell in an independent non-fusing way, and the toxicity of the cationic antibacterial peptide to the host cell is restricted by the anionic ligand so as to improve the expression yield; and in the subsequent separation and purification processes, the step of cutting a fusing head, which consumes manpower, physical resources and financial resources, is avoided, therefore, the separation and purification efficiency and the yield ratio are improved. The invention can remarkably shorten the production cycle to one third or a half of the original production cycle and reduce the cost above 50 percent. The invention provides a high-efficiency and low-cost way for the large-scale production of the cationic antibacterial peptide.
Owner:安徽希普生物科技有限公司
Targeted delivery of antimicrobial agents
InactiveUS20130137851A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesCationic Antimicrobial PeptidesDefensin
A cationic antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) conjugate is disclosed. The CAMP conjugate may be made by identifying a suitable carrier peptide; identifying a suitable antimicrobial agent; creating a conjugate by conjugating the peptide with the antimicrobial agent; and evaluating and refining the conjugate. The peptide may be short peptide based on the sequence of a CAMP, such as human β-defensin-3. The peptide can be directly connected to the antimicrobial agent or through a linker segment. The antimicrobial agent may be connected to the peptide or the linker segment through stable or cleavable bonding. The peptide may carry and facilitate the delivery of the conjugated antimicrobial agent to a microbe.
Owner:GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
Cationic antibacterial peptide modified by dopamine or derivative thereof as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN110684078AImprove adhesionEfficient broad-spectrum killing effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological materialsAntibacterial property
The invention belongs to the field of antibacterial biological materials, and particularly relates to a cationic antibacterial peptide modified by dopamine or derivatives thereof as well as a preparation and an application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the antibacterial peptide from the N terminal to the C terminal is XX (AB) nXX, n is an integer from 3 to 8, X is a cationic amino acid, A isa hydrophobic amino acid, and B is an anionic amino acid. The antibacterial peptide containing a dopamine adhesion group shows a broad spectrum and excellent antibacterial performance. The antibacterial peptide containing the dopamine adhesion group provided by the invention has the property of forming hydrogel through ultraviolet irradiation. In addition, the antibacterial peptide containing thedopamine adhesion group, provided by the invention, can be used for tissue damage repair and antibacterial materials, and has good application prospect and value.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rapid specific pathogen free animal
InactiveUS20150173333A1Improve effectivenessAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEnzymesRibosome-inactivating proteinVirology
A method of producing at least one specific pathogen free (SPF) non-human animal and / or a method of producing at least one specific pathogen resistant (SPR) non-human animal, the method comprising administration of a fusion protein to the surviving animal wherein the fusion protein comprises at least one polypeptide B which is a Type 1 Ribosome Inactivating Protein (RIP) or fragment thereof; and (i) at least one polypeptide A which is an Antimicrobial peptide; and / or (ii) at least one polypeptide C which is a Cationic Antimicrobial Peptide (CAP) or fragment thereof.
Owner:BIOVALENCE
Bombesin-oriented anti-tumor polypeptide and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a bombesin-oriented anti-tumor polypeptide, which is a fusion peptide formed by connecting bombesin and cationic antibacterial peptide from bovine bone marrow cells, wherein the cationic antibacterial peptide has an active area of damaged mitochondria. The anti-tumor polypeptide has obvious targeted inhibiting effect on solid tumors and blood tumors, improves the safety of medicaments, provides a new path for clinical medicament application, and has good application prospect.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Antimicrobial fusion compounds and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130336955A1Improve effectivenessSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsCompound (substance)Ribosome-inactivating protein
A fusion protein comprising at least one Type 1 Ribosome Inactivating Protein, polypeptide B; and at least one polypeptide A capable of viral entry inhibition; and / or at least one Cationic AntiMicrobial Peptide, polypeptide C.
Owner:VALIANT BIOPHARMA
Targeted delivery of antimicrobial agents
A cationic antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) conjugate is disclosed. The CAMP conjugate may be made by identifying a suitable carrier peptide; identifying a suitable antimicrobial agent; creating a conjugate by conjugating the peptide with the antimicrobial agent; and evaluating and refining the conjugate. The peptide may be short peptide based on the sequence of a CAMP, such as human β-defensin-3. The peptide can be directly connected to the antimicrobial agent or through a linker segment. The antimicrobial agent may be connected to the peptide or the linker segment through stable or cleavable bonding. The peptide may carry and facilitate the delivery of the conjugated antimicrobial agent to a microbe.
Owner:GEORGE MASON UNIVERSITY
Group of antimicrobial peptides and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of medicine, and relates to a group of antimicrobial peptides and a preparation method thereof, particularly a group of cationic antimicrobial peptides, peptide derivatives and cyclic peptides with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activities, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The antimicrobial peptides have obvious bactericidal effects on Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Candida albicans, drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii and drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and have the characteristics of broad spectrum and high efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND +1
Preparation method and application of animal-derived cationic antimicrobial peptides
ActiveCN102229666AConvenient purification workOmit refoldingAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial drugAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of animal-derived cationic antimicrobial peptides. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cloning cationic antimicrobial peptide genes shown as SEQ ID NO.1 onto a carrier; transforming plasmids into genetic engineering strains; culturing for 12-16 hours on a culture medium; screening out bacterial colonies containing recombinant plasmids; selecting a single bacterial colony and placing in an LB (Load Balance) liquid culture medium; shaking and culturing till OD600 reaches 0.5-0.7; adding IPTG (Isopropyl Thiogalactoside), shaking and culturing for 3 hours and inducing protein expression; centrifuging for 10 minutes at 4 DEG C and collecting thallus; utilizing a lysis buffer solution to re-suspend the thallus, performing ice-bath, and ultrasonically breaking cells, thereby releasing protein; and utilizing a Chitin column to purify the protein. A test proves that the animal-derived cationic antimicrobial peptides have a broad spectrum antimicrobial function and an ultrahigh antimicrobial activity and can be used for replacing antibiotics for preventing and treating poultry and livestock bacterial infections. A new method for developing a novel clinic antimicrobial drug is demonstrated.
Owner:山东迅达康兽药有限公司
Cyclic peptide resistant to multi-drug resistant bacteria and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110066320AEasy to operateLow costAntibacterial agentsPeptide preparation methodsCyclic peptideOperability
The invention discloses a cyclic peptide resistant to multi-drug resistant bacteria. The cyclic peptide resistant to the multi-drug resistant bacteria is characterized in that the amino acid sequenceis any of CPeptide-A, CPeptide-B, CPeptide-C and CPeptide-D, and the antibacterial cyclic peptide is obtained through cyclization of amido bonds formed by amino groups and carboxy groups of head and tail amino acids of any of the amino acid sequence. The four novel artificially designed cationic antibacterial peptides can be synthesized by adopting an Fmoc solid-phase chemical method, the operability is strong, and the cost is low. The cationic antibacterial peptides have broad spectrum killing activity against multidrug-resistant acinetobacter baumannii, have stronger bactericidal activity than natural antimicrobial peptides, and have no toxic effect on animal and plant cells.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Antimicrobial fusion compounds and uses thereof
A fusion protein comprising at least one Type 1 Ribosome Inactivating Protein, polypeptide B; and at least one polypeptide A capable of viral entry inhibition; and / or at least one Cationic AntiMicrobial Peptide, polypeptide C.
Owner:VALIANT BIOPHARMA
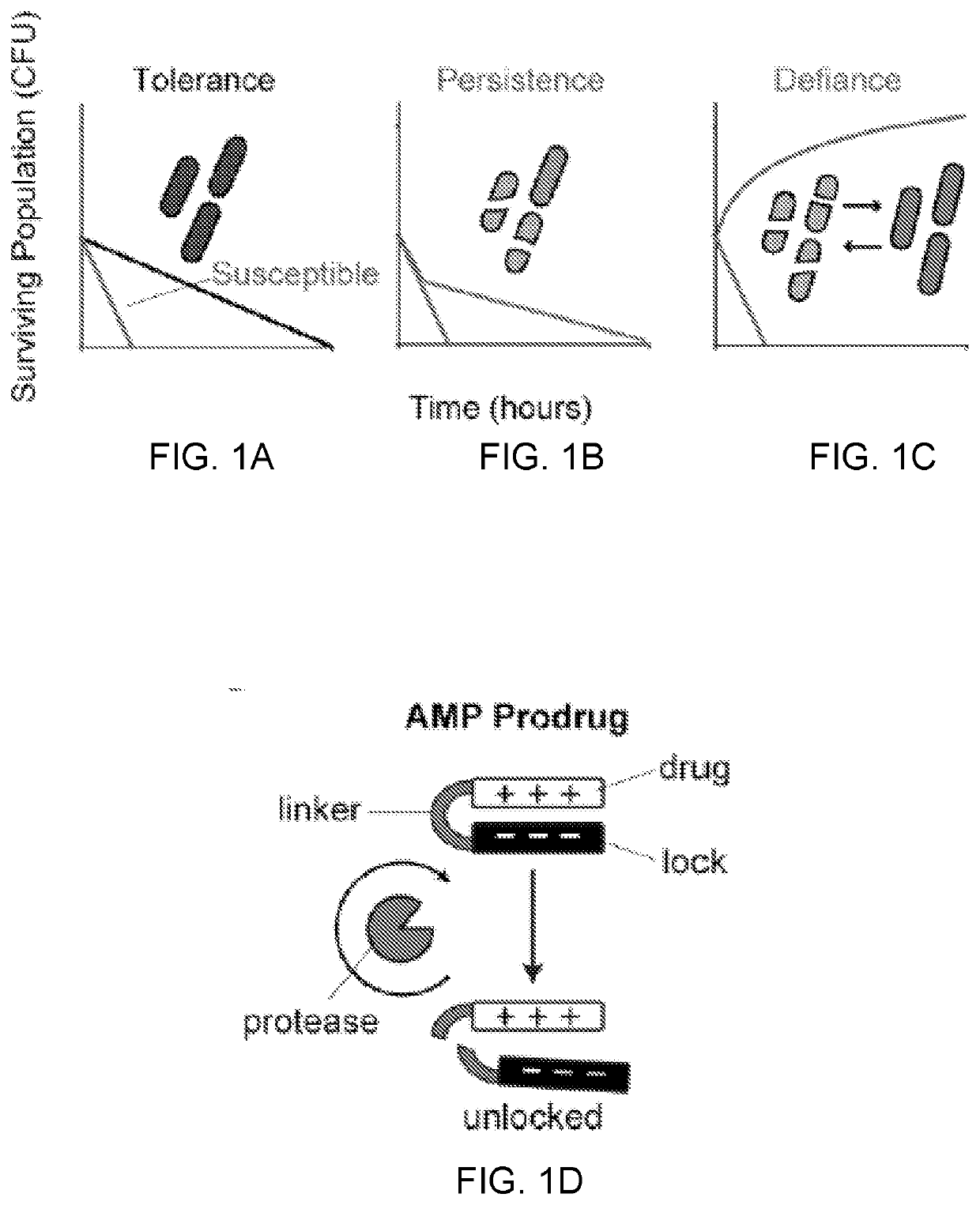
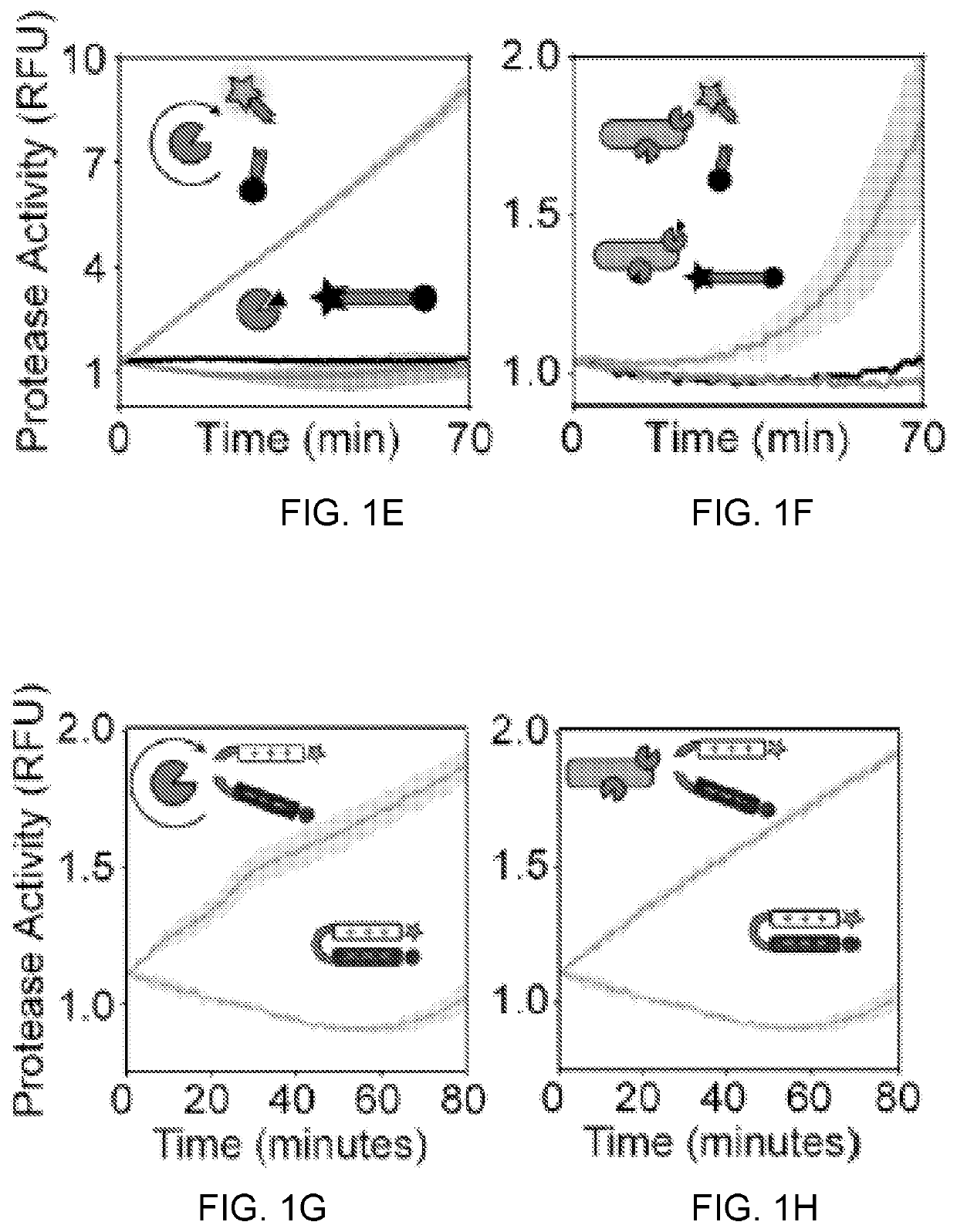
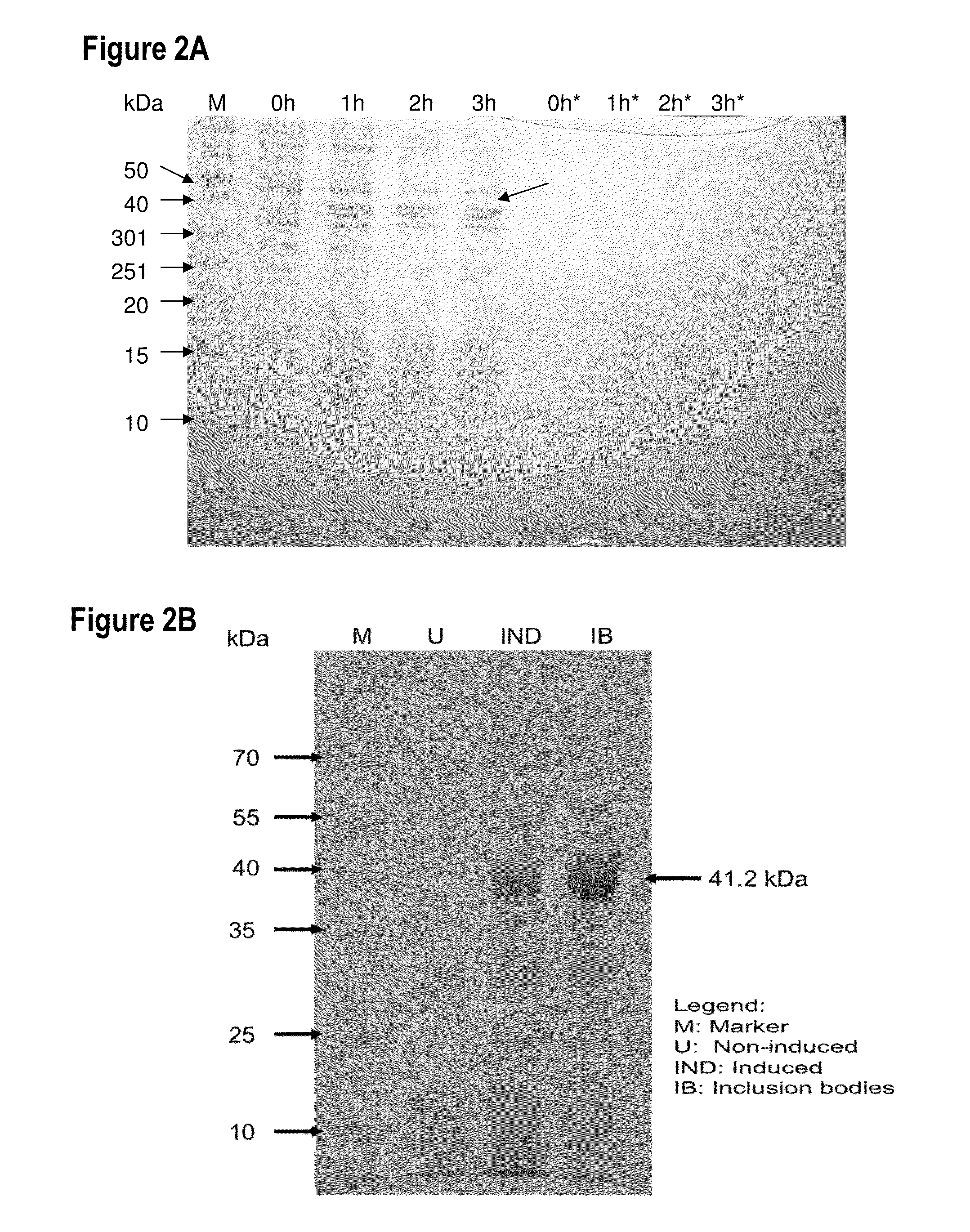
Self-titrating bacterial protease-activated prodrug
Disclosed herein are bacterial protease-activated prodrug compositions and methods of their use for the treatment and prevention of bacterial infection. Also disclosed are methods of reducing or eliminating defiant bacterial populations. An exemplary prodrug composition includes a cationic antimicrobial peptide conjugated to an anionic peptide with a protease cleavable linker substrate, wherein the antimicrobial peptide is inactive while it is in conjugation with the anionic peptide. Upon cleavage by the protease, the cationic AMP is released from the anionic peptide and can act upon bacteria. The protease is specific to the bacteria that are present in the sample or the subject, creating an auto-titrating mechanism wherein the AMP is released from the peptide only when there is bacteria present.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com