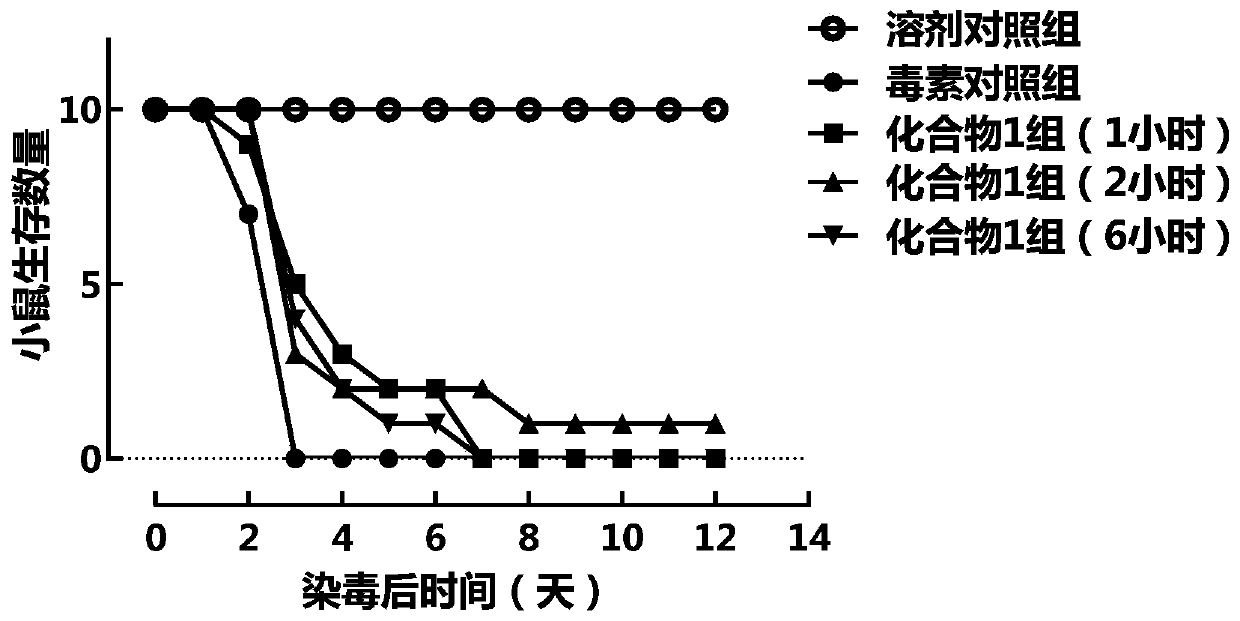
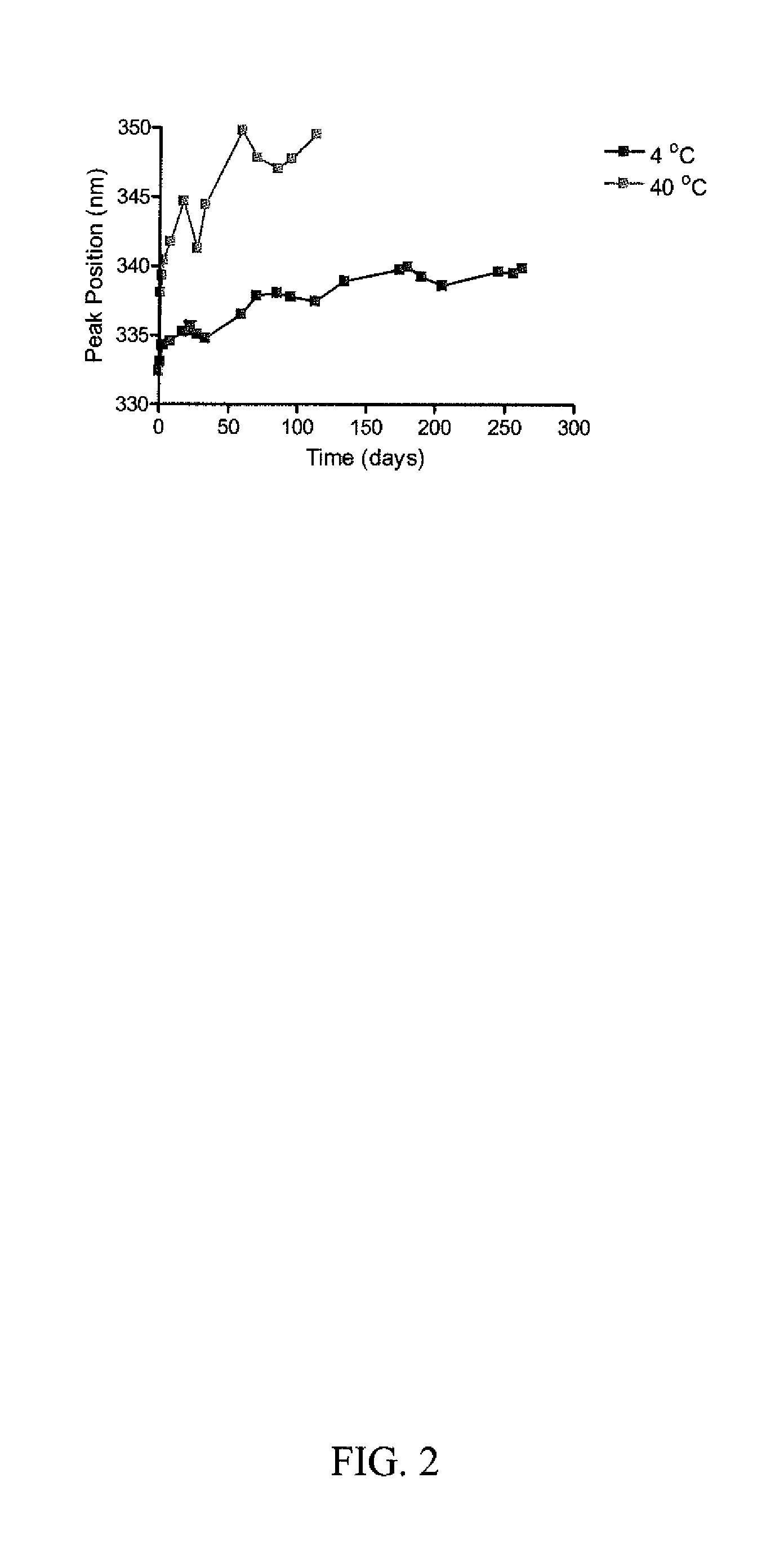Patents
Literature
60 results about "Ribosome-inactivating protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A ribosome-inactivating protein (RIP) is a protein synthesis inhibitor that acts at the ribosome. A number of bacterial and plant toxins act by inhibiting protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells. The toxins of the Shiga and ricin family inactivate 60S ribosomal subunits by an N-glycosidic cleavage, which releases a specific adenine base from the sugar-phosphate backbone of 28S rRNA. Members of the family include shiga and shiga-like toxins, and type I (e.g. trichosanthin and luffin) and type II (e.g. ricin, agglutinin, and abrin) ribosome inactivating proteins (RIPs). All these toxins are structurally related. RIPs have been of considerable interest because of their potential use, conjugated with monoclonal antibodies, as immunotoxins to treat cancers. Further, trichosanthin has been shown to have potent activity against HIV-1-infected T cells and macrophages. Elucidation of the structure-function relationships of RIPs has therefore become a major research effort. It is now known that RIPs are structurally related. A conserved glutamic residue has been implicated in the catalytic mechanism; this lies near a conserved arginine, which also plays a role in catalysis.
Balsm-pear-seed ribosome inactivated protein and its coding gene and use
InactiveCN101070342AImprove securityExpression conditions are simplePeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsRibosomal protein E-L30Ribosomal protein
This invention relates to a balsam pear seed ribosome inactivating protein(RIP) and its encode gene and application. This protein has one of the undermentioned amino acid residue sequence: (1) SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence table; (2) carry out substitution, deficiency or addition of protein that possess activity of inhibiting ribosomal protein synthesis to one to ten amino acid residue of SEQ ID NO: 1 amino acid residue sequence in sequence table. This protein possess hereinafter point: (1) notable effect of resisting tumour and virus infection; (2) high security; (3) simple protein expression condition, easy purification. low cost.
Owner:SHANXI KANGBAO BIOLOGICAL PROD +2
Anticancer treatment
InactiveUS20150202250A1Improve effectivenessPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRibosome-inactivating proteinCancer research
Use of fusion protein comprising at least one polypeptide B, comprising Type 1 Ribosome Inactivating Protein, and at least one C having anticancer properties in the manufacture of a medicament for treating cancer in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:BIOVALENCE
Pumpkin protein 2 and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101386644ASave manual and tedious operationsReduce cumbersome stepsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsPolyethylene glycolSingle crystal
The invention discloses a Cucurbita moschata protein 2 and a preparation method and application thereof, which relates to the field of biochemistry. The invention discloses a new ribosome inactivated protein extracted from flesh of Cucurbita moschata, namely the Cucurbita moschata protein 2 (type 2 Cucurbita moschata ribosome inactivated protein cucurmosin 2). The molecular weight of the Cucurbita moschata protein 2 is determined as 2, 7183Da by ESI-MS. The Cucurbita moschata protein 2 is put into phosphate buffer, citric acid buffer and Tris-HCl buffer in advance, and a single crystal for the diffraction of X-ray is produced taking carbowax as a precipitator. Through preliminary analysis, the crystal structure shows that the crystal is a type 1 ribosome inactivated protein with the functions of tumor and virus resistance, in particular human immunodeficiency virus resistance, thereby laying a material foundation for obtaining a protein for medicine use or preparing immunotoxin.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Immunotoxins comprising ribosome-inactivating proteins
InactiveUS7153932B2Reduced immunogenic responseNegative kinetic and steric effectBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDisulfide bondingAutoimmune disease
The present invention provides purified and isolated polynucleotides encoding Type I ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) and analogs of the RIPs having a cysteine available for disulfide bonding to targeting molecules. Vectors comprising the polynucleotides and host cells transformed with the vectors are also provided. The RIPs and RIP analogs are particularly suited for use as components of cytotoxic therapeutic agents of the invention which include gene fusion products and immunoconjugates. Cytotoxic therapeutic agents or immunotoxins according to the present invention may be used to selectively eliminate any cell type to which the RIP component is targeted by the specific binding capacity of the second component of the agent, and are suited for treatment of diseases where the elimination of a particular cell type is a goal, such as autoimmune disease, cancer and graft-versus-host disease.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Direct quantification of ribosome inactivating protein
A method for detecting ribosome inactivating protein (RIP) activity in a sample is provided that involves contacting a sample that contains an RIP with an inventive substrate that is depurinated to form product. The product is hybridized to a template and cleaved by an apurinic / apyrimidinic endonuclease such that releasing the blocked 3′ end only in a sample that contains RIP activity. The 5′ end of the product serves as a primer for extension by a polymerase reaction. The newly synthesized strand complementary to the template is detected by RT-PCR processes. A kit is provided suitable for field or laboratory use.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Fusion protein with function of selective killing endothelial cells in tumor neogenetic blood vessels and use thereof
InactiveCN101070349APeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsLysosomal membraneVascular endothelium
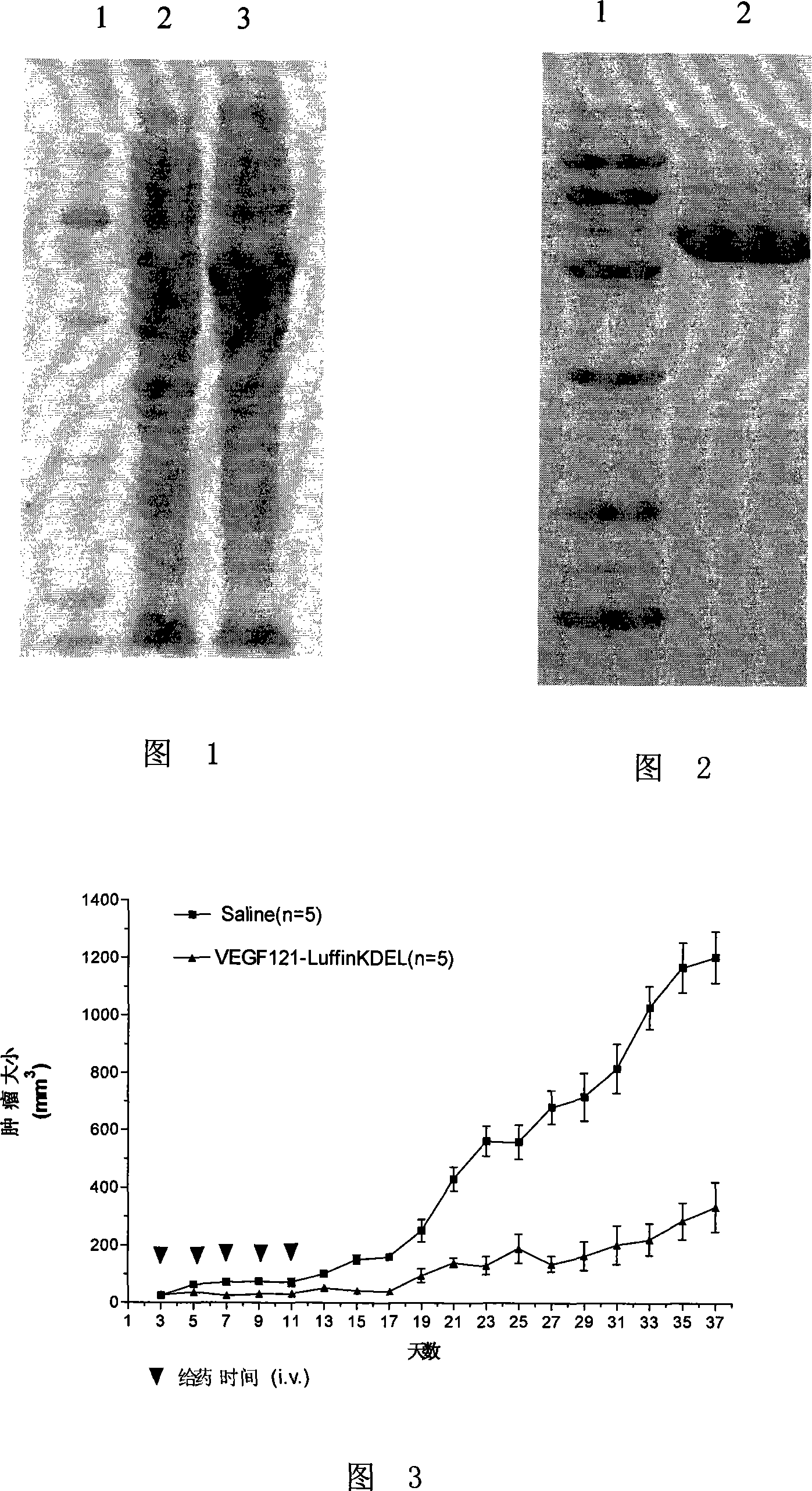
This invention relates to a fusion protein that possess action of selectively kill tumour rebirth blood vessel endotheliocyte, and its application. This fusion protein through connecting peptide connect VEGF121 with amido end of sponge gourd seed ribosome inactivating protein(RIP) Luffin Alpha. The vascular endothelial cell growth factor VEGF121 act as means of delivery, make this fusion toxin idiosyncratic incorporate with vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor F1k1 / KDR, thereby optionally ingress tumour rebirth vascular endothelial cell; the polypeptide possess amphipathic molecule character, by destroy lysosome membrane to promote the release of lysosome inside dissociate toxin molecule; the toxin carboxyl terminal endoplasmic reticulum loacting signal led toxin molecule( sponge gourd seed RIP Luffin Alpha) to target site to exert toxic effect, so to destroy rebirth blood vessel of tumour organization, cut off tumour blood supply, achieve the end of restraining tumor.
Owner:SHANXI KANGBAO BIOLOGICAL PROD +2
Dosage regime of fusion compounds
Owner:BIOVALENCE
Nanoparticle probes for detecting ribosome inactivating protein, manufacturing method thereof and use thereof
InactiveCN101738480AFast and portableSimplify operating proceduresBiological testingAntigenRibosome-inactivating protein
The invention provides nanoparticle probes for detecting ribosome inactivating protein, a manufacturing method thereof and use thereof. In the nanoparticle probes, nanoparticles with bioaffinity serving as a matrix can be combined with a target protein antibody after undergoing surface modification, and the interference of physical absorption is eliminated; and a monoclonal antibody of rat anti-human immunoglobulin IgG serving as a capture antibody is used to be coupled with a target ribosome inactivating protein through the specific interacting force between the antibody and the antigen. Thenanoparticle probes for detecting the ribosome inactivating protein of the invention combine the high concentrating capability of the nanoparticles with large specific surface area with the high antigen selectivity of the monoclonal antibody, so the sensitivity and specificity of the detection of the ribosome inactivating protein are improved. The nanoparticle probes of the invention comprehensively use nano technology and immunity technology and are applied to the detection of the target ribosome inactivating protein in the fields of food safety, anti-bioterrorism and the like. In addition, the nanoparticle probes have the advantages of quickness, convenient carrying, specific trace detection and the like.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Selective destruction of cells infected with human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS7018633B2Avoid problemsInhibition of replicationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWAS PROTEINViral protease
Compositions and methods for selectively killing a cell containing a viral protease are disclosed. The composition is a varient of a protein synthesis inactivating toxin wherein a viral protease cleavage site is interposed between the A and B chains. The variant of the type II ribosome-inactivating protein is activated by digestion of the viral protease cleavage site by the specific viral protease. The activated ribosome-inactivating protein then kills the cell by inactivating cellular ribosomes. A preferred embodiment of the invention is specific for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and uses ricin as the ribosome-inactivating protein. In another preferred embodiment of the invention, the variant of the ribosome-inactivating protein is modified by attachment of one or more hydrophobic agents. The hydrophobic agent facilitates entry of the variant of the ribosome-inactivating protein into cells and can lead to incorporation of the ribosome-inactivating protein into viral particles. Still another preferred embodiment of the invention includes a targeting moiety attached to the variants of the ribosome-inactivating protein to target the agent to HIV infectable cells.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Preparation and application of tumour vascular targeting agent VEGF*/RIP30fusion toxin
The invention discloses a fusion toxicant having the function of selectively killing new blood vessel endothelial cells of tumors and an application thereof. The fusion toxicant is a fusion protein which is prepared in the way that the amido ends of ribosome inactivating proteins RIP30 of balsam pear seeds are connected with VEGF121 through connecting peptides. As a carrier, VEGF121 can internalize and bond the fusion toxicant to blood vessel endothelial cell nutrilite receptors F1k1 / KDR in a specific way before the fusion toxicant enters blood vessel endothelial cells and plays a role as a toxicant to kill new blood vessel endothelial cells of tumors, to destroy the new blood vessels of tumor tissues and cut off the blood supply of tumors, thus inhibiting tumors. In addition, the expression conditions of the fusion toxicant are simple; the fusion toxicant is purified easily and can be produced in large scale. Accordingly, the fusion toxicant can be used as an active ingredient for preparing antineoplastic drugs. The fusion protein can play an important role in the medical and biological pharmacy field.
Owner:SHANXI KANGBAO BIOLOGICAL PROD +2
Method for determining ribosome inactivating protein activity
ActiveCN106434848AActive assayRapid responseMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative determinationRibosome-inactivating protein
The invention provides a method and a developing solution for determining ribosome inactivating protein activity and application of the developing solution. The method for determining the ribosome inactivating protein activity is simple to operate, low in cost and capable of completing a quantitative determination process only with a spectrophotometer, and can avoid interference of traditional RNA enzyme on reaction, thereby being promising in practical application prospect for the research and development field of ribosome inactivating protein.
Owner:CHENGDU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Rapid specific pathogen free animal
InactiveUS20150173333A1Improve effectivenessAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEnzymesRibosome-inactivating proteinVirology
A method of producing at least one specific pathogen free (SPF) non-human animal and / or a method of producing at least one specific pathogen resistant (SPR) non-human animal, the method comprising administration of a fusion protein to the surviving animal wherein the fusion protein comprises at least one polypeptide B which is a Type 1 Ribosome Inactivating Protein (RIP) or fragment thereof; and (i) at least one polypeptide A which is an Antimicrobial peptide; and / or (ii) at least one polypeptide C which is a Cationic Antimicrobial Peptide (CAP) or fragment thereof.
Owner:BIOVALENCE
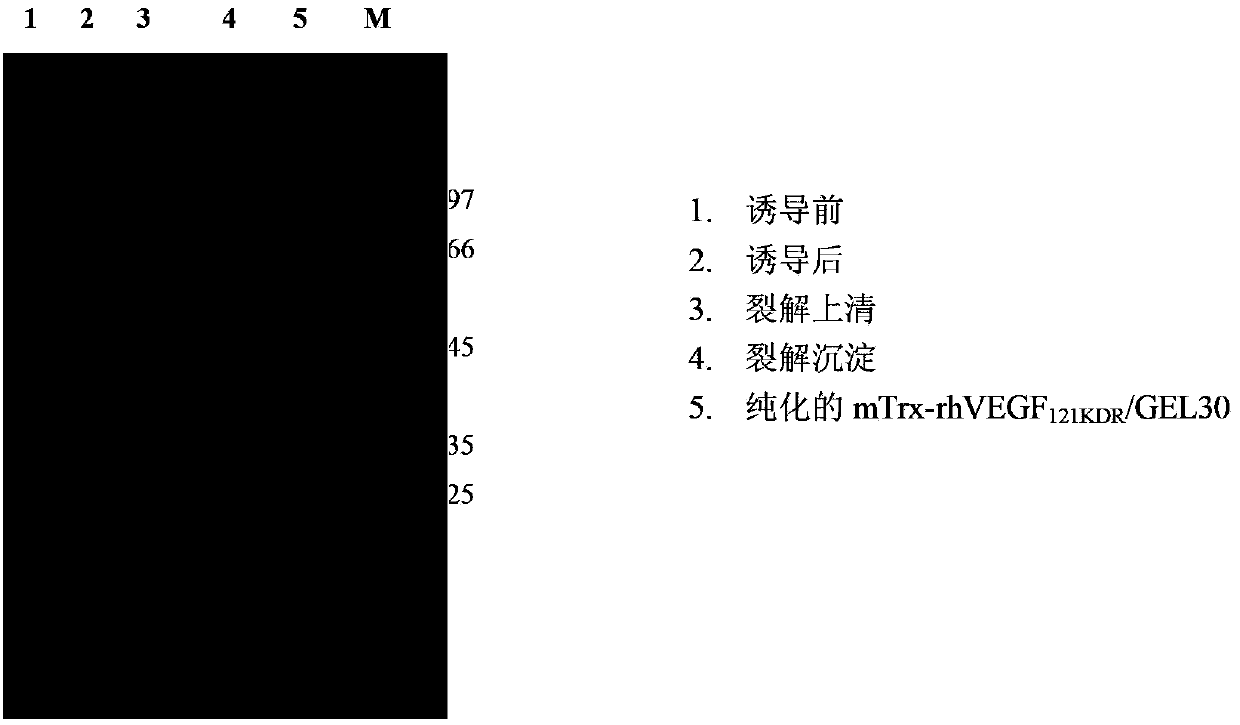
Fusion toxin with specificity of VEGFR2/KDR acceptor, and coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103865899AImprove anti-tumor effectExpression conditions are simpleFungiBacteriaVascular endotheliumReticulum cell
The invention discloses a fusion toxin (rhVEGF121KDR / Rgel30) with specificity of VEGFR2 / KDR acceptor, and coding gene thereof and application thereof to prepare antitumor medicines. The fusion toxin is obtained by connecting the amino terminal (N terminal) of gelonium multiflorum ribosome inactivating protein rGEL30 to recombinant human vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF121 mutant through a connecting peptide, and the carboxyl terminal (C terminal) of the fusion toxin possesses endoplasmic reticulum positioning sequence. VEGF121KDR taken as a carrying tool helps the fusion toxin to specifically combine with VEGFR2 / KDR through high affinity, to be internalized and to enter tumor newborn blood vessel endothelial cells, then ribosome inactivating protein rGEL30 gives a play to toxin effect and kills tumor newborn blood vessel endothelial cells and further destroys newborn blood vessels of tumor tissue for reaching the purpose of inhibiting tumor, and also an endoplasmic reticulum positioning signal at the C terminal of the fusion toxin is capable of promoting free rGEL30 toxin to be gathered on rough endoplasmic reticulum, so that the antitumor effect of the fusion toxin is further enhanced.
Owner:SHANXI KANGBAO BIOLOGICAL PROD +2
Amaranth seed ribosome inactivating protein
InactiveCN1491961AEnhanced inhibitory effectSynthetic inhibitory activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsIon exchangeAdemetionine
The present invention relates to amaranth seed ribosome inactivating protein, which is separated form the seed of Amaranthus mangostanus as one kind of vegetable, has molecular weight of 29 KDa and isoelectric point greater than 9. By means of mild extraction method, and through twice fast SP-agarose gel ion exchange chromatography, high purity of protein is obtained. The protein may be used as medicine material applied in preparing antitumor preparation, antiviral preparation and anti-HIV preparation, and may used as RNAN-glycoside for molecular biological and immulogical research and as toxin material for immunotoxin.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Antimicrobial fusion compounds and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130336955A1Improve effectivenessSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsCompound (substance)Ribosome-inactivating protein
A fusion protein comprising at least one Type 1 Ribosome Inactivating Protein, polypeptide B; and at least one polypeptide A capable of viral entry inhibition; and / or at least one Cationic AntiMicrobial Peptide, polypeptide C.
Owner:VALIANT BIOPHARMA
Dihydroquinozolinone antiport process blocking agent, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110372692AEffective preventionEffective therapeuticOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryChemical industryCures diseases
The invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical and chemical industry, and relates to dihydroquinozolinone antiport process blocking agent, and a preparation method and application thereof, in particular to a novel dihydroquinozolinone antiport process blocking agent compound, a medicinal salt, isomer, hydrate and solvate thereof, application of the compound and the medicinal salt, isomer, hydrate and solvate thereof to preparation of drugs for preventing and / or first aiding diseases caused by ribosome-inactivating proteins, and application of the compound and the medicinal salt, isomer,hydrate and solvate thereof to preparation of drugs for preventing and / or curing diseases caused by enterovirus, filoviridae or polyomavirus. The compound can effectively resist II-type ribosome-inactivating protein poisoning and / or the diseases caused by enterovirus, filoviridae or polyomavirus.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
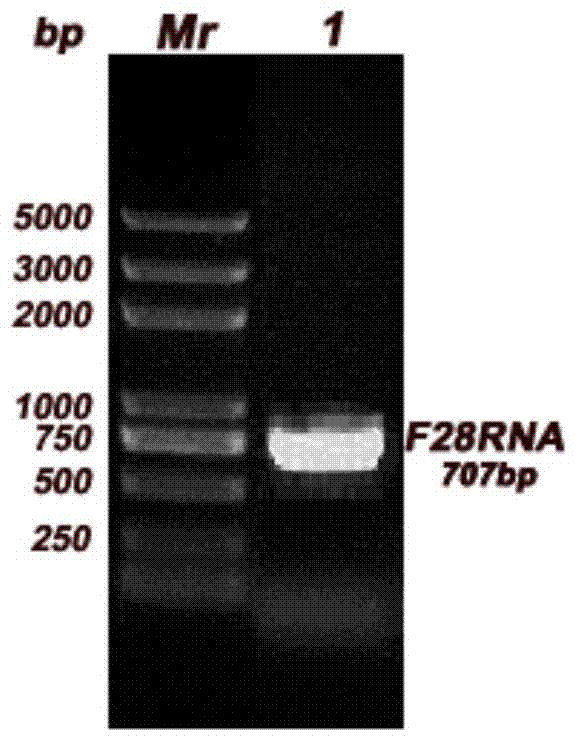
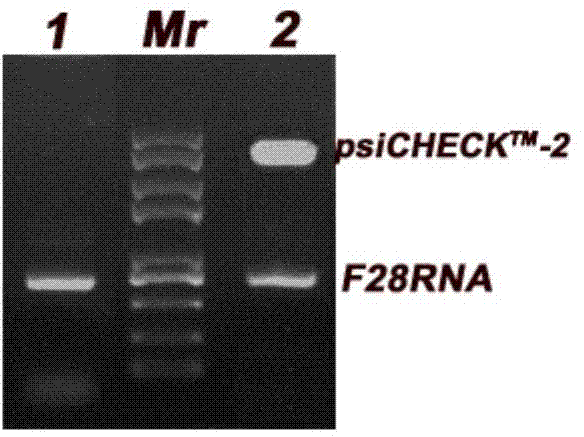
Plasmid for detecting activity of ribosome inactivating protein as well as construction method and application of plasmid
InactiveCN104498494AResolve SensitivitySimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRestriction enzyme digestionNucleotide
The invention provides a plasmid for detecting activity of ribosome inactivating protein as well as a construction method and application of the plasmid, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The plasmid comprises a gene fragment F28RNA with a recognition site of the ribosome inactivating protein, and the nucleotide sequence of the gene fragment is SEQ ID No.1. The plasmid is constructed by virtue of genetic engineering means including gene cloning, restriction enzyme digestion, connection, conversion and the like. The plasmid can be used for detecting the activity of the ribosome inactivating protein in vitro and in cells.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Method for constructing ribosome inactivating protein gene virus vector and expressing active proteins in tumor cell through ribosome inactivated protein gene virus vector
PendingCN110747231AHas RNAN-glycosidase activityInhibit synthesisPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic acid vectorPlant virusPlant cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and specifically discloses a method for constructing a ribosome inactivating protein gene virus vector and expressing active proteins intumor cells through the ribosome inactivated protein gene virus vector. The method comprises the following steps that first, suitable ribosome inactivated proteins are selected, and codon optimizationfor humanized expression is conducted on mature region genes of the ribosome inactivated proteins; second, an adenovirus carrier of wild type and optimized genes is constructed, and recombinant viruses are packaged; and third, recombinant adenoviruses infect the tumor cells, the recombinant adenoviruses express proteins in the tumor cells through detection, and the anti-tumor effect of the recombinant adenoviruses is detected. According to the method, an alpha-charantin gene is subjected to codon optimization, an expression vector system for the adenoviruses capable of infecting the tumor cells of mammals is constructed so as to be suitable for expressing the active proteins in the tumor cells, and the defects that in the prior art, a prokaryotic cell expression system can only be expressed in escherichia coli when being used, and a plant virus vector can only be expressed in plant cells but cannot be expressed in the tumor cells and kill tumors when being used are overcome.
Owner:成都富岱生物医药有限公司
Multivalent Stable Vaccine Composition and Methods of Making Same
ActiveUS20170007682A1Stable immunogenic compositionRobust and durable immune responseBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulinsSporeNeutralising antibody
Stable immunogenic composition capable of eliciting a robust and durable immune response yielding a measurable increase in neutralizing antibodies at least 200 days post-administration, comprising at least one antigen consisting of a ribosome inactivating protein and at least one antigen comprising a toxin derived from bacterial spores. Method making and using a stable immunogenic composition capable of eliciting a stable immune response yielding a measurable increase in neutralizing antibodies at least 200 days post-administration, comprising providing an immunogenic composition comprising at least one antigen comprising a ribosome inactivating protein and at least one antigen comprising a toxin derived from bacterial spores and administering the immunogenic composition to an individual.
Owner:SOLIGENIX INC
Jatropha curcas ribosome inactivating protein and its separation and purification method and application
ActiveCN107058261BStrong growth inhibitory effectObvious inhibitory effect on proliferation in vitroPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsRibosome-inactivating proteinNon-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
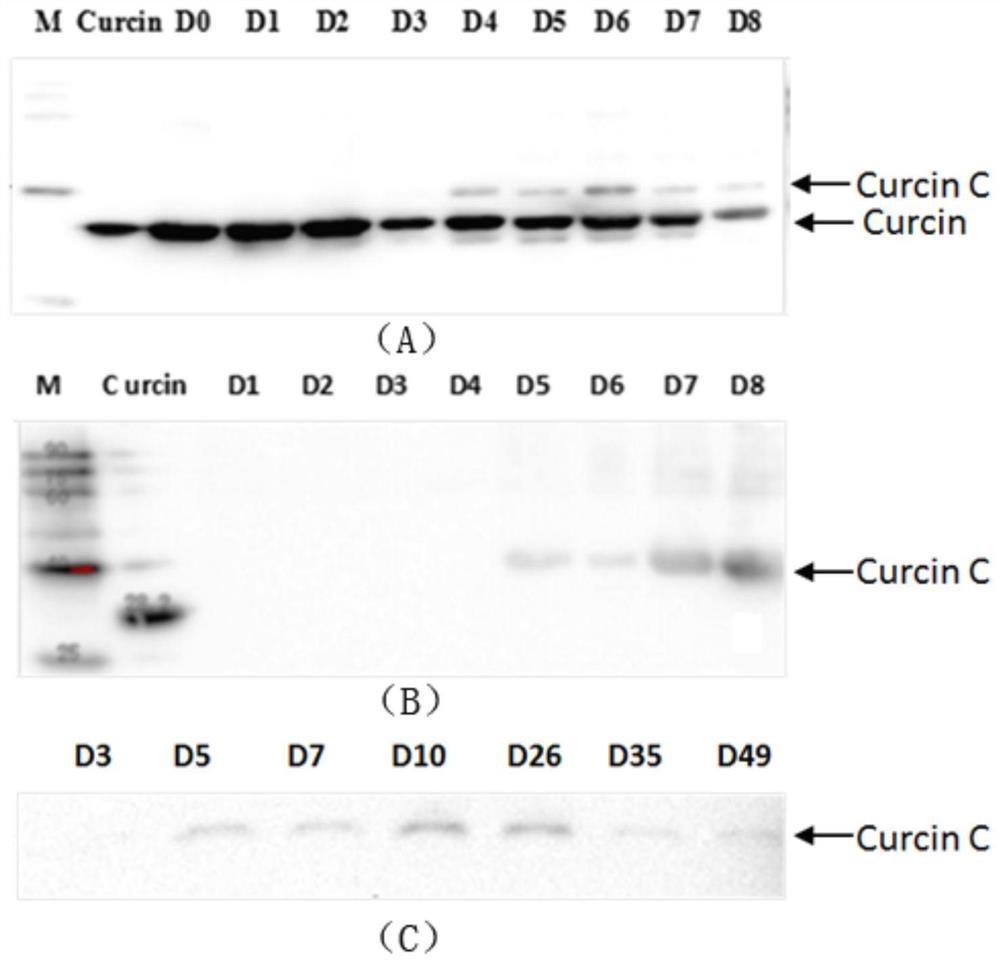
The invention provides jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein and a preparation method thereof. The jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein is separated and purified from cotyledon and / or endosperm of jatropha curcas L. seedlings which are generated by jatropha curcas L. seeds germinating for 4 to 49 days, relative molecular weight is 31.398kDa, an isoelectric point is 7.12, and a sequence of amino acid residue of an N-terminal of the ribosome-inactivating protein is shown as SEQ ID No: 1 in a sequence table. The invention further provides application of the jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein in preparing medicines for treating tumor. The jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein has an obvious anti-proliferative effect on human osteosarcoma U20S, human non-small cell lung cancer A549, human non-small cell lung cancer H1975 and human colon cancer HCT116; an in-vitro proliferation inhibition effect of the jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein on the human osteosarcoma U20S is superior to that of Curcin and taxol; furthermore, toxicity to human normal kidney cells is lower.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Methods and Systems for the Detection of Ricin and Other Ribosome Inactivating Proteins
ActiveUS20140065623A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceLyase
A device, method, and system for the detection of ribosome inactivating protein activity, including the ricin toxin, in a sample. According to one embodiment, the ribosome inactivating protein in the sample removes an adenine from a labeled DNA substrate to create an abasic site. An AP lyase can then cleave the DNA substrate at the abasic site, allowing the fluorophore located at or near one end of the DNA substrate and the quencher at or near the other end of the DNA substrate to spatially separate. Once the fluorophore and the quencher are sufficiently separated, the fluorophore will emit a fluorescence signal. Increasing fluorescence, indicating ribosome inactivating protein activity, will be monitored in real time using a detection system.
Owner:ACUMEN DETECTION INC
Fusion protein with function of selective killing endothelial cells in tumor neogenetic blood vessels and use thereof
InactiveCN101070349BPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsLysosomeVascular endothelium
Owner:SHANXI KANGBAO BIOLOGICAL PROD +2
Antimicrobial fusion compounds and uses thereof
A fusion protein comprising at least one Type 1 Ribosome Inactivating Protein, polypeptide B; and at least one polypeptide A capable of viral entry inhibition; and / or at least one Cationic AntiMicrobial Peptide, polypeptide C.
Owner:VALIANT BIOPHARMA
Multivalent Stable Vaccine Composition and Methods of Making Same
ActiveUS20170333544A9Robust and durable immune responseIncrease in neutralizing antibodiesBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaSporeNeutralising antibody
Stable immunogenic composition capable of eliciting a robust and durable immune response yielding a measurable increase in neutralizing antibodies at least 200 days post-administration, comprising at least one antigen consisting of a ribosome inactivating protein and at least one antigen comprising a toxin derived from bacterial spores. Method making and using a stable immunogenic composition capable of eliciting a stable immune response yielding a measurable increase in neutralizing antibodies at least 200 days post-administration, comprising providing an immunogenic composition comprising at least one antigen comprising a ribosome inactivating protein and at least one antigen comprising a toxin derived from bacterial spores and administering the immunogenic composition to an individual.
Owner:SOLIGENIX INC
Jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein and separation and purification method and application thereof
ActiveCN107058261AStrong growth inhibitory effectObvious inhibitory effect on proliferation in vitroPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsPurification methodsRibosome-inactivating protein
The invention provides jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein and a preparation method thereof. The jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein is separated and purified from cotyledon and / or endosperm of jatropha curcas L. seedlings which are generated by jatropha curcas L. seeds germinating for 4 to 49 days, relative molecular weight is 31.398kDa, an isoelectric point is 7.12, and a sequence of amino acid residue of an N-terminal of the ribosome-inactivating protein is shown as SEQ ID No: 1 in a sequence table. The invention further provides application of the jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein in preparing medicines for treating tumor. The jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein has an obvious anti-proliferative effect on human osteosarcoma U20S, human non-small cell lung cancer A549, human non-small cell lung cancer H1975 and human colon cancer HCT116; an in-vitro proliferation inhibition effect of the jatropha curcas L. ribosome-inactivating protein on the human osteosarcoma U20S is superior to that of Curcin and taxol; furthermore, toxicity to human normal kidney cells is lower.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Expression separation and purification method for Chinese Phytolacca acinosa cDNA mutant and TAT gene recombinant in prokaryon and application therefor
InactiveCN1952146AImprove biological activityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPokeweed antiviral proteinToxin protein
The invention concerns a Ribosome inactibating protein (RIPS) Chinese mainland protein separated from plants which plays a role in anti-AIDS through catalyzing rRNA depurination of prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosome with highly conserved stem-loop structure at the surface. The invention involves a Tat protein, the basic amino acid enrichment domain of which is protein transduction domain (PTD) and able to carry many exogenous protein directly into cells as protein orientation of cytokines or toxin. The invention involves a fusion protein of Tat and Chinese antiviral protein mutant. Performing deletion mutation to CAP using Quick-mutagenesis site-directed mutagenesis technology: 22 amino acid deletion in N-terminal, 29 amino acid deletion in C-terminal and site-specific mutagenesis: 151KI152 / 151AA152, 191FN192 / 191AA192. The recombinant protein of the invention has biological activity of anti-HIV-1 in vitro. It is found that CAP deletion and site-specific mutagenesis in fusion gene can significantly reduce its ability to combine with rRNA (cytotoxicity), however, without influence to its ability of combination of HIV RNA (anti-HIV activity), has more clinical application.
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Ricin a chain mutants lacking enzymatic activity as vaccines to protect against aerosolized ricin
The present invention provides methods to produce toxoid vaccines, such as ricin A chain vaccines, with reduced ability to promote vascular leak syndrome (VLS) and catalytic toxicity associated with various proteinaceous toxins, such as ribosome inactivating proteins. The invention also provides toxoids which have been mutated to lack amino acid sequences which induce VLS and toxic catalytic activity.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Application of cucurmosin in preparation of drug for treating breast cancer
InactiveCN102038934AGood anti-solid tumor effect in vivo and in vitroReduce inhibitionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsMelanomaApoptosis
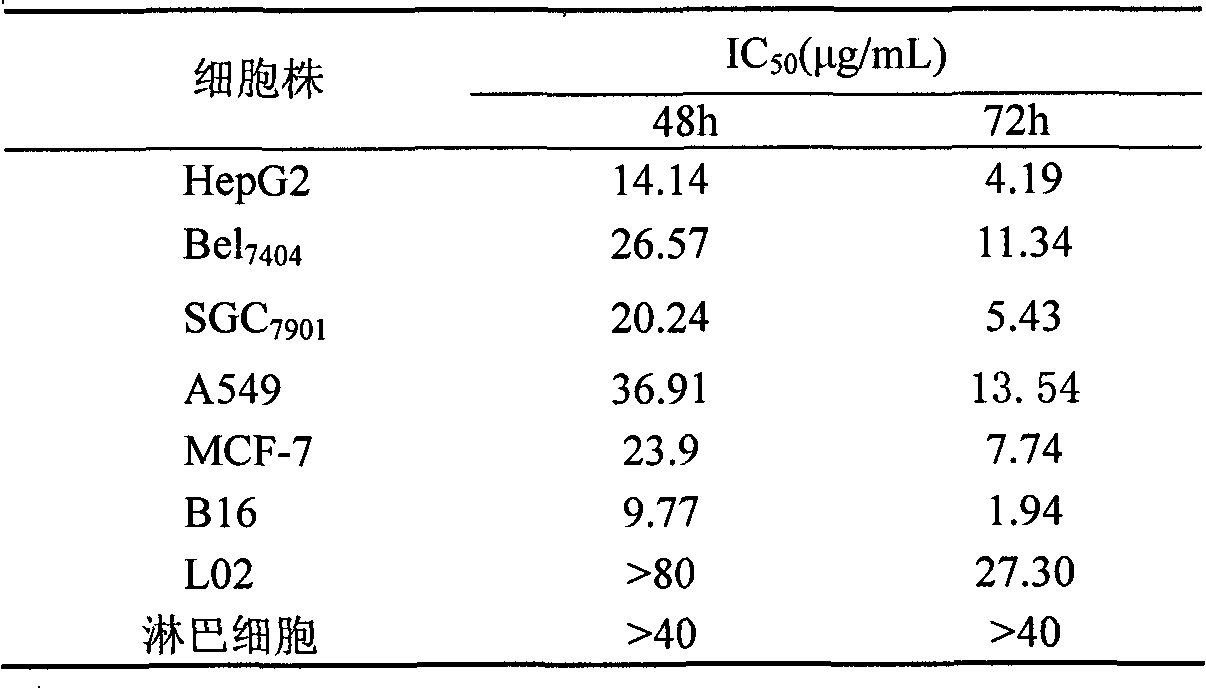
The invention provides application of cucurmosin in preparation of drugs. A ribosome-inactivating protein, namely the cucurmosin, can be separated from pumpkin flesh; and the protein well displays the good tumor resisting activity and can be used for preparing antineoplastic drugs. The cucurmosin can strikingly restrain gastric cancer cells SGC7901 and hepatoma cells HepG2 Bel7404, tiny lung cancer cells A549, breast cancer cells MCF-7 and melanoma cells B16 which are cultured in vitro, has little inhibitory action on normal liver cells and PBLC of a person and displays obvious selection, and can strikingly restrain animal transplanted tumors, such as cervical cancer U14, melanoma cells B16, lung cancer Lewis and the like. Furthermore, the application proves that the induction apoptosis and the induction differentiation of the cucurmosin on the tumor resisting activity serve as an important mechanism.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV +1
Novel cinnamomum hupehanum ribosome inactivated protein gene CcRIPII
InactiveCN103184226AReduce sizeImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOpen reading frameConserved sequence
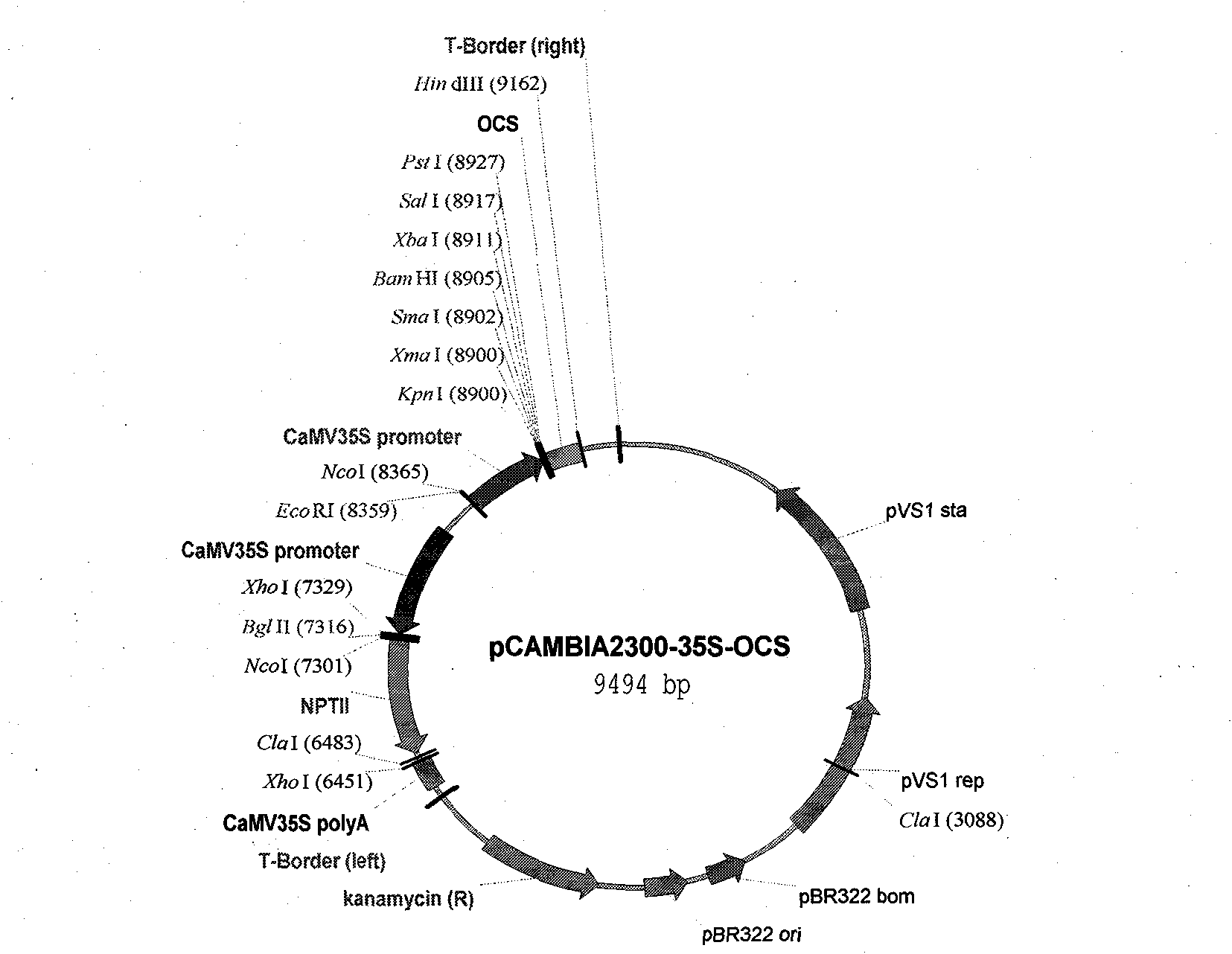
The invention designs a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primer according to a conserved sequence of a reported plant ribosome inactivated protein gene CcRIPII, and obtains a novel partial sequence of a novel cinnamomum hupehanum ribosome inactivated protein gene CcRIPII through homologous amplification; subsequently a full-length gene cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence is obtained through RACE (Rapid-Amplification of Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid Ends); the CcRIPII gene does not contain internal functors but contains a complete ORF (Open Reading Frame) area; and the ORF contains full-length 1758 nucleotides, coding 585 amino acids and one termination codon (TGA). A plant expression carrier pCAMBUA2300-CcRIPII of the CcRIPII gene is established, and a transgenetic seedling is obtained by using pCAMBIA2300-CcRIPII transformed Ningyang Chinese-date. The CcRIPII is the first woody plant ribosome inactivated protein gene which is cloned and subjected to wood genetic transformation on the international.
Owner:泰安市泰山林业科学研究院,翁曼丽 +1
Process for the separating gynostemma pentaphylla ribosome inactivation protein, product and encoding gene thereof
InactiveCN1482138APeptide preparation methodsPlant peptidesTobacco mosaic virusRibosome Inactivation
The present invention relates to the separation process, product and encoding gene of Gynostemma pentaphylla ribosome inactivating protein (RIP) and belongs to the field of biotechnology. A fast separation and purification system is established, which has the affinity chromatography with blue dye pseudoligand Cibacron Blue 3GA as main part, stepped ammonium sulfate precipitation and cation exchange chromatography. The RIP has molecular weight of 27 KDa and the 19 amino acid sequence of DINFSLAGADGQTYNTFIA. The RIP has homology of 10-37 % with the RIP of other plant and 37-73 % with the RIPof cucurbitaceous plant; tobacco mosaic virus resisting effect of 99 % and suppression to stomach cancer cell. The RIP has homology base level to RIP of cucurbitaceous plant 47-61 % and amino acid level 37-49 %, and has wide medicinal and agricultural application.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com