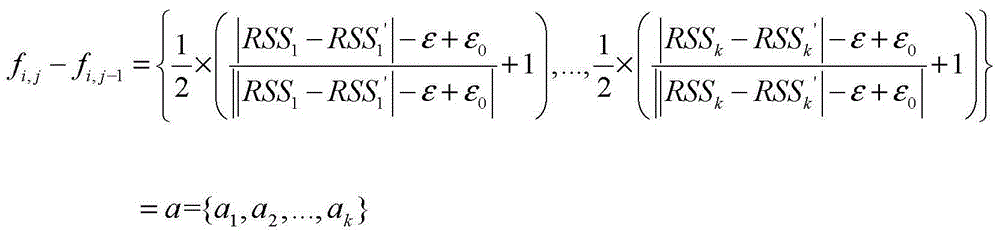AP (access point) selecting method based on clustering idea
An idea and resolution technology, applied in the field of AP selection based on the idea of clustering, which can solve the problems of prone to errors and large positioning variance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
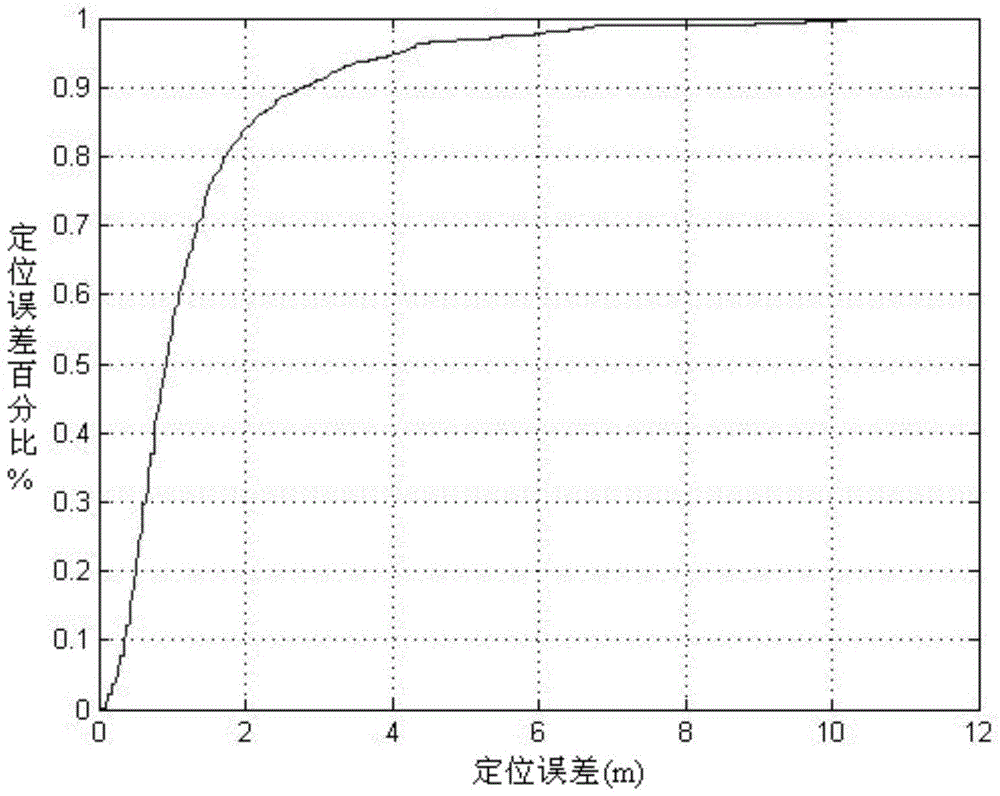
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
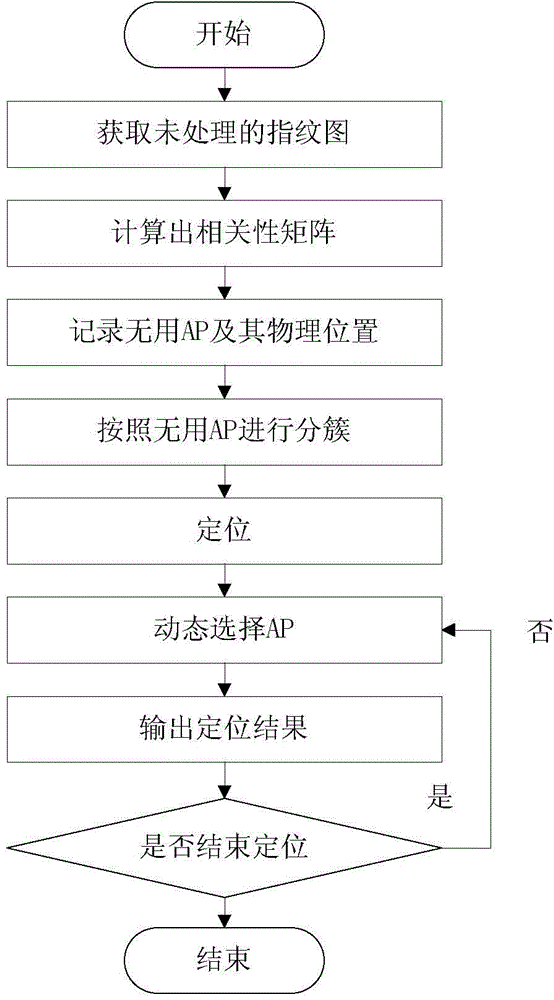
[0018] Specific embodiment one: a kind of AP selection method based on the idea of clustering in this embodiment is specifically prepared according to the following steps:
[0019] Step 1. Obtain the regular rectangular fingerprint of the unprocessed m×n reference points, then the signal part of the fingerprint is f i,j ={RSS 1 ,RSS 2 ,...,RSS k}; i=1,2,3...,m;j=1,2,3...,n;
[0020] Among them, f i,j Receive the signal strength RSS value corresponding to k APs corresponding to the reference point in row i, column j in the fingerprint graph, and the serial number k of the AP in the fingerprint graph = 1, 2, 3...k; the fingerprint graph is composed of a signal part and a position part, There is a one-to-one relationship between the signal part and the position part; the signal part is the signal strength of the positioning AP collected at each reference point; the distance between adjacent points of the reference point is 0.5-1.5m; the number of reference points in the fin...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0030] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: use f in step two i,j Find the correlation of each reference point in the fingerprint map as follows:
[0031] The correlation matrix is the degree of similarity between each reference point and its adjacent reference points, calculating f i,j The correlation of each reference point in , specifying f i,j Adjacent reference points in receive AP signals with the same serial number. If the RSS difference between two identical signals is less than the threshold ε, it is a useless AP for positioning, and the correlation of this useless AP is 0. If the RSS difference between two identical signals is greater than or equal to the gate The limit value ε is used to locate the useful AP, and the useful AP correlation is set as 1. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0032] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is: in step three, f i,j Add up the correlation of each reference point in i, j and the total correlation matrix of four adjacent points The specific process is:
[0033] (1), order Represents the total correlation matrix between reference point i, j and four adjacent points in row i, column j in the fingerprint graph;
[0034](2) Based on the topology of the fingerprint map, it is assumed that each reference point has four adjacent points, namely i, j-1 reference point, i, j+1 point, i-1, j reference point and i+ 1, j reference point; let f i,j ={RSS 1 ,RSS 2 ,...,RSS k}, f i,j-1 ={RSS 1 ',RSS 2 ',...,RSS k '}; f i,j+1 ={RSS″ 1 ,RSS″ 2 ,...,RSS″ k}; f i-1, j={RSS"' 1 , RSS"' 2 ,...,RSS"' k}; f i+1,j ={RSS"" 1 , RSS "" 2 ,...,RSS″″ k};
[0035] f ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com