Dynamic diagnosis support information generation system
A technology for information generation and diagnostic assistance, applied in the direction of diagnosis, informatics, medical informatics, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming, increased processing time, increased data capacity, etc., and achieve the effect of shortening the processing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
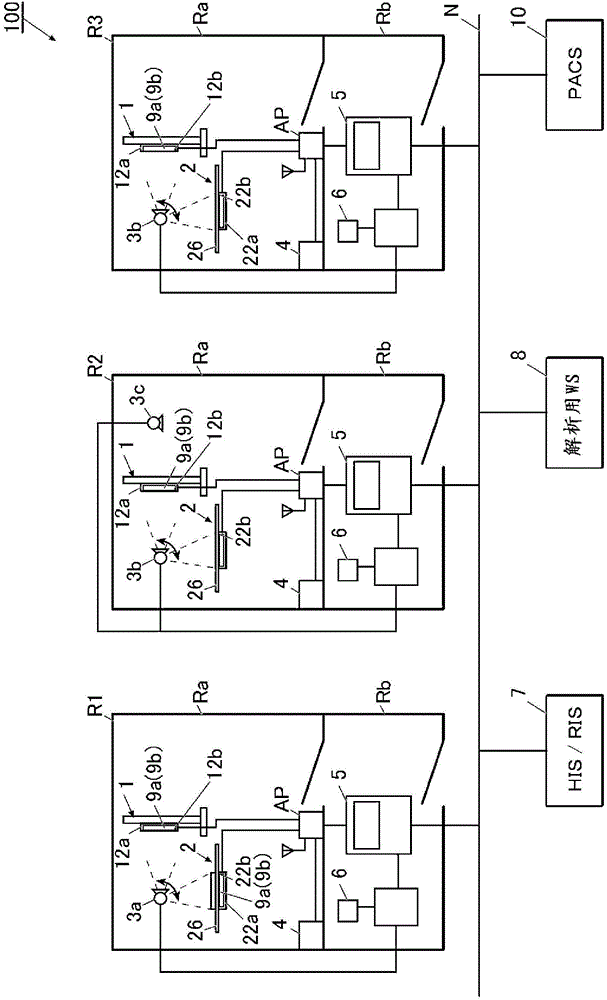
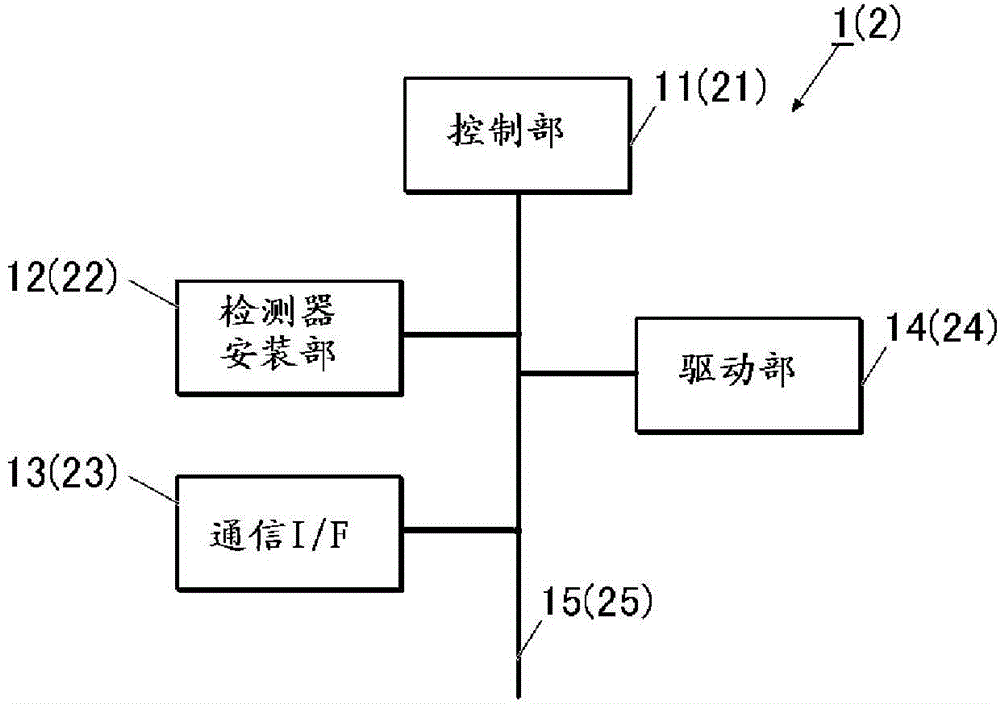
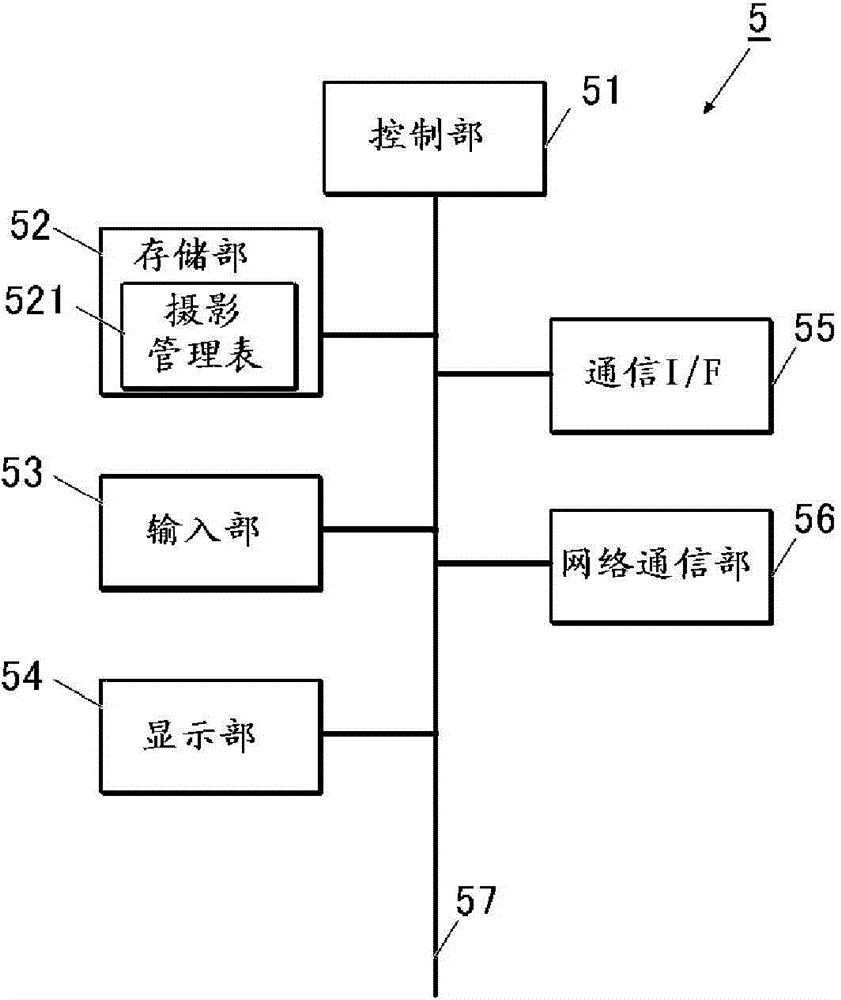
[0060] figure 1 It is a diagram showing the overall configuration of the auxiliary diagnostic information generating system 100 according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0061] figure 1 The illustrated imaging rooms R1 to R3 are rooms for performing dynamic imaging or still image imaging of the subject by irradiating radiation to the subject which is a part of the patient's body (ie, the imaging site of the patient).
[0062] Dynamic imaging refers to imaging in which a plurality of images are obtained by continuously irradiating a subject with radiation such as X-rays in a pulsed manner (that is, continuous imaging). Motion photography captures the movement of a subject that has periodicity, such as morphological changes such as expansion and contraction of the lungs accompanying respiratory movement, and heartbeats. A series of images obtained by this continuous shooting is called a moving image. In addition, a plurality of images constituting a moving...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0270] Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0271] First, the structure will be described.
[0272] Figure 17 The overall configuration of the auxiliary diagnostic information generating system 300 in the second embodiment is shown. The auxiliary diagnosis information generation system 300 is a system that uses the analysis server 30 of the analysis center to analyze moving images captured in small-scale facilities such as private hospitals and clinics, and provides the analysis results to the small-scale facilities. As described in the first embodiment, when the warping process can be omitted, it is not necessary to consider the pixel size of the FPD, the dynamic range of each pixel, and the like on the side of performing the analysis process. Therefore, irrespective of the type of FPD used in each facility, analysis processing can be provided in an open system as described below.
[0273] Such as Figure 17 As shown, the reception devi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com