Method and apparatus for supporting low-code-rate encoding
A low bit rate, coding technology, applied in coding, coding components, error detection coding using multi-bit parity bits, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in making full use of coding gain, poor performance of coding and decoding systems, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
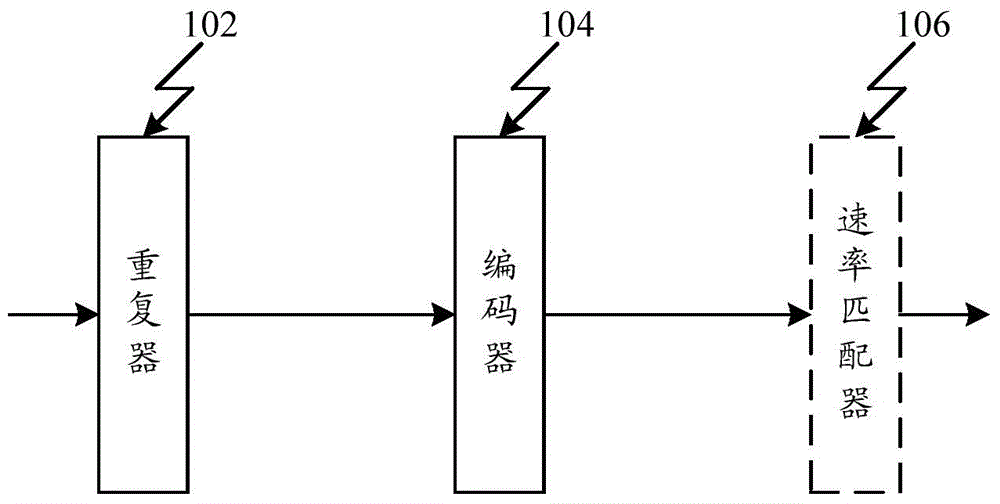
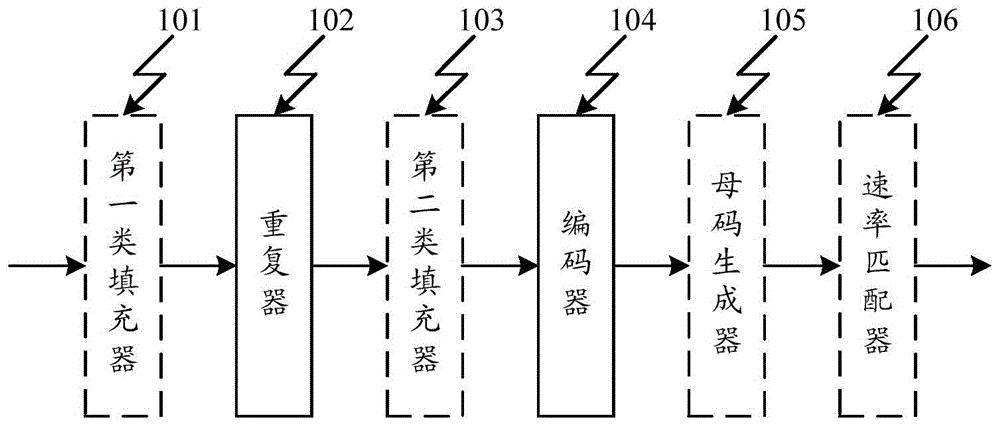
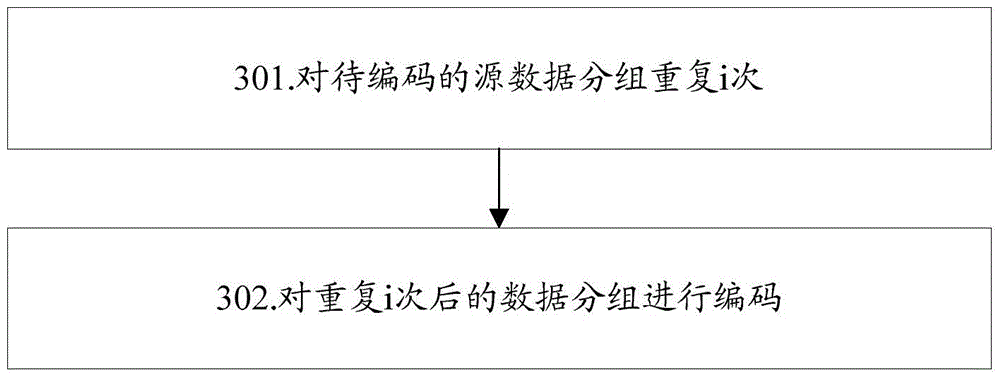
[0155] The embodiment of the present invention implements a device supporting low bit rate encoding, such as figure 1 As shown, the device at least includes: a repeater 102, an encoder 104, wherein,
[0156] The repeater 102 is configured to repeat i times the source data packet x to be coded k bits, where i is a positive integer;
[0157] The encoder 104 is configured to encode the data packets after the repeater 102, the encoding is LDPC encoding, Turbo encoding or convolutional encoding;
[0158] The repeater 102 is specifically used to directly repeat the source data packet x to be encoded i times; or, the source data packet x includes j sub-data packets, and repeat i times for the j sub-data packets respectively, and j is a positive integer, The value of i can generally be 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 or 6;
[0159] Specifically, the encoder 104 is an (nb×z, kb×z) LDPC encoder, which encodes a mother code data packet C′, where nb is the number of columns of the basic parity ch...
example 1
[0163] Set the basic parity check matrix Hb 8×16 as follows:
[0164]
[0165] The underlying parity-check matrix Hb shown 8×16 The corresponding code rate is 1 / 2, the expansion factor z=42, the number of matrix rows is 8 rows, and the number of matrix columns is 16 columns. The number shown on the left is the row index, and the number on the top is the column index, and the letter "A" Indicates the systematic bit part matrix, and the letter "B" means the check bit part matrix. The encoder 104 is a (16×42, 8×42) LDPC encoder, and the source data packet to be encoded is a k=80-bit signaling sequence a=[a 0 ,a 1 ,a 2 ,...,a 79 ], when using 1 / 2 code rate LDPC code basic parity check matrix to carry out LDPC encoding to signaling sequence a, when obtaining n=672 bits of coded data packet e, said repeater 102 first repeats signaling sequence a by 1 Times, and extended to get 336-bit data packets d=[d 0 , d 1 ,...,d 335 ], the value of d is as follows:
[0166]
[0...
example 2
[0171] Set the basic parity check matrix Hb 8×16 as follows:
[0172]
[0173] The underlying parity-check matrix Hb shown 8×16 The corresponding code rate is 1 / 2, the expansion factor z=42, the number of matrix rows is 8 rows, and the number of matrix columns is 16 columns. The number shown on the left is the row index, and the number on the top is the column index, and the letter "A" Indicates the systematic bit part matrix, and the letter "B" means the check bit part matrix. The encoder 104 is a (16×42, 8×42) LDPC encoder, the basic parity check matrix is an 8×16 matrix, the expansion factor z=42, and the source data to be encoded is grouped into k=40-bit signaling sequence f=[f 0 , f 1 ,..., f 39 ], when the 1 / 2 code rate LDPC code basic parity check matrix is used to perform LDPC encoding on the signaling sequence f to obtain an encoded data packet h of n=672 bits, the repeater 102 first repeats the signaling sequence f by Device 102 repeats 1 time, and expan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com