Improved algorithm for reducing power consumption of wireless sensor network node of farmland soil moisture content monitoring system based on RPL
A wireless sensor network, moisture monitoring technology, applied in wireless communication, power management, network topology and other directions, can solve the problems of long-term use of disadvantageous nodes, chaotic relationship between parent and child nodes, loss of related nodes, etc. Power consumption, the effect of reducing the transmission interval
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
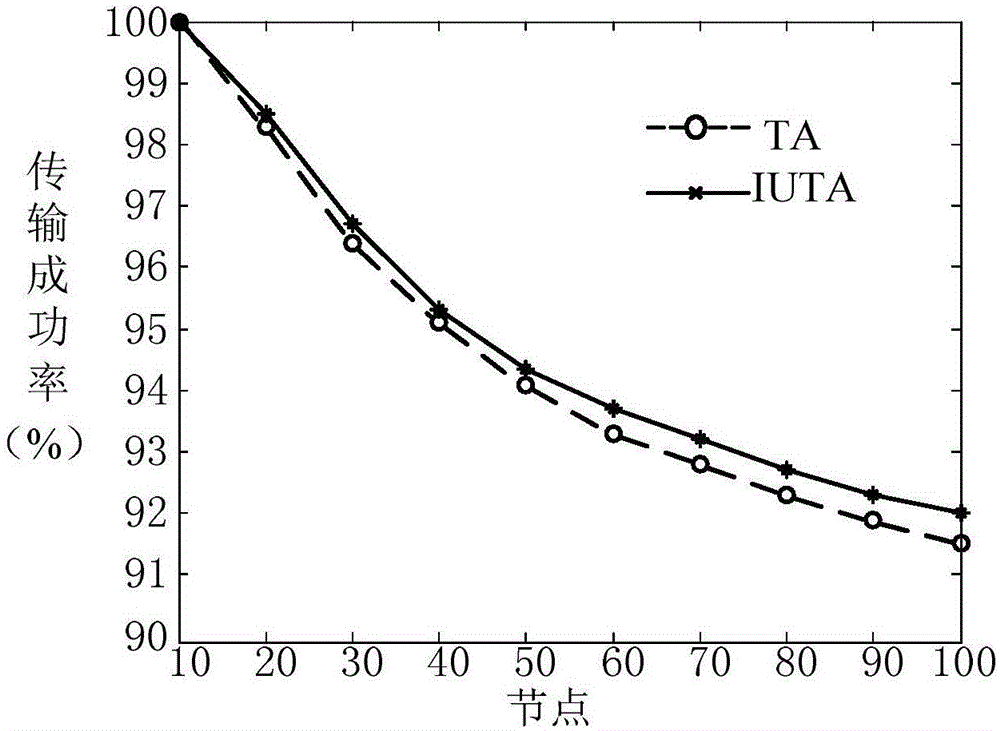
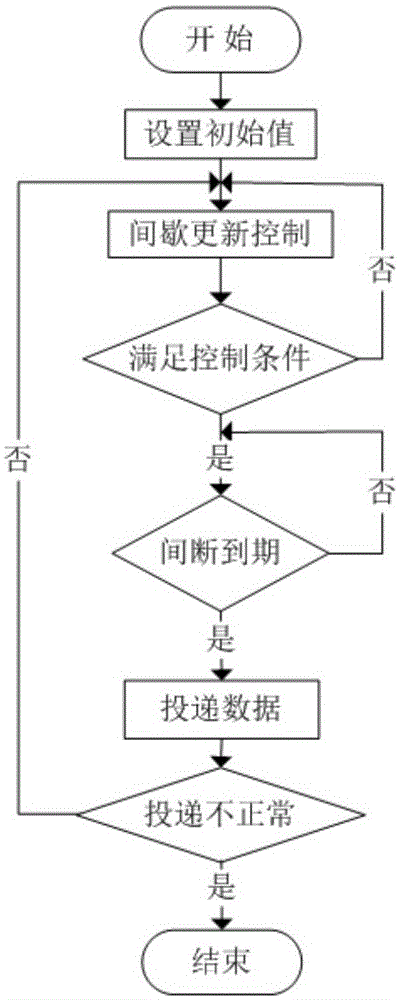
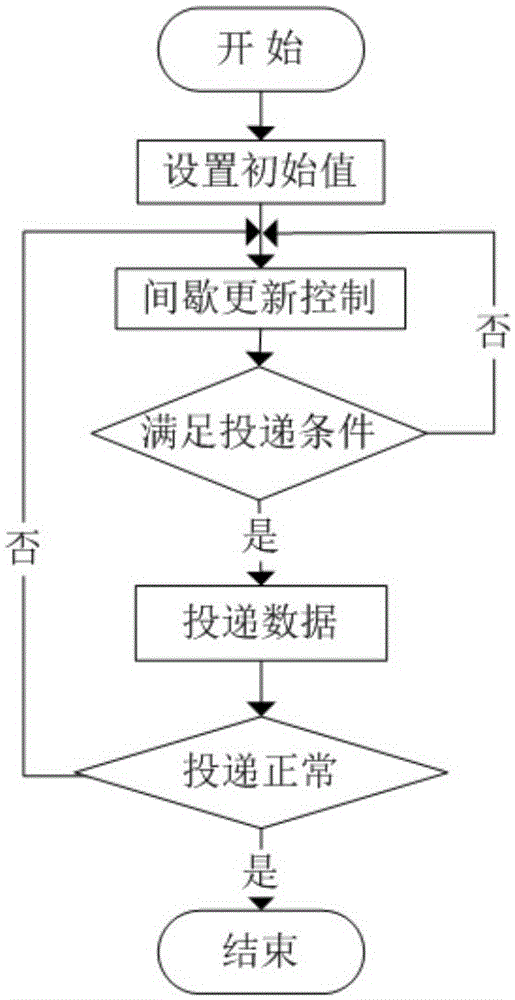
[0027] The improved algorithm for the interval update of the existing Trickle algorithm proposed by the present invention, when an abnormal situation occurs, the improved algorithm will allow the node to send messages intermittently, thereby saving power consumption, and when the node route is stable, the intermittent change The frequency at which a node sends DIO packets informs neighboring nodes of the quality of the relevant links, so as to maintain the routing stability of DODAG.
[0028] The improved interval update algorithm improves the transmission interval of the existing trickle algorithm when the node transmission in the network is in normal or abnormal state. When a node in the network is abnormal, the Trickle algorithm (TA for short) will uninterruptedly multicast messages to find a suitable parent node to break the reconstructed network, but in many cases this will lead to an increase in node power consumption and cause the node to use Reduced efficiency. The im...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com